Clay Attenuates Diarrhea Induced by Fat in a Mouse Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Preparation of Solutions
2.3. Diarrhea and Anti-Diarrhea by MMT
2.4. Fecal Total Bile Acid Measurement
2.5. Histological Study
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
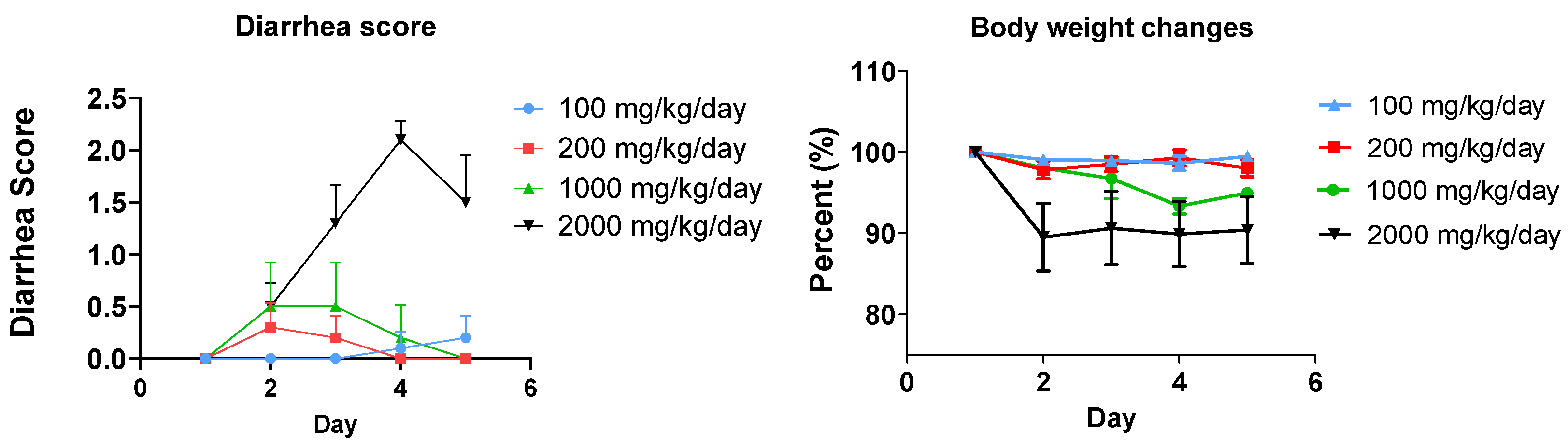
3.1. Fat-Induced Diarrhea Model in Mice
3.2. Anti-Diarrhea Efficacy of Clay (MMT)
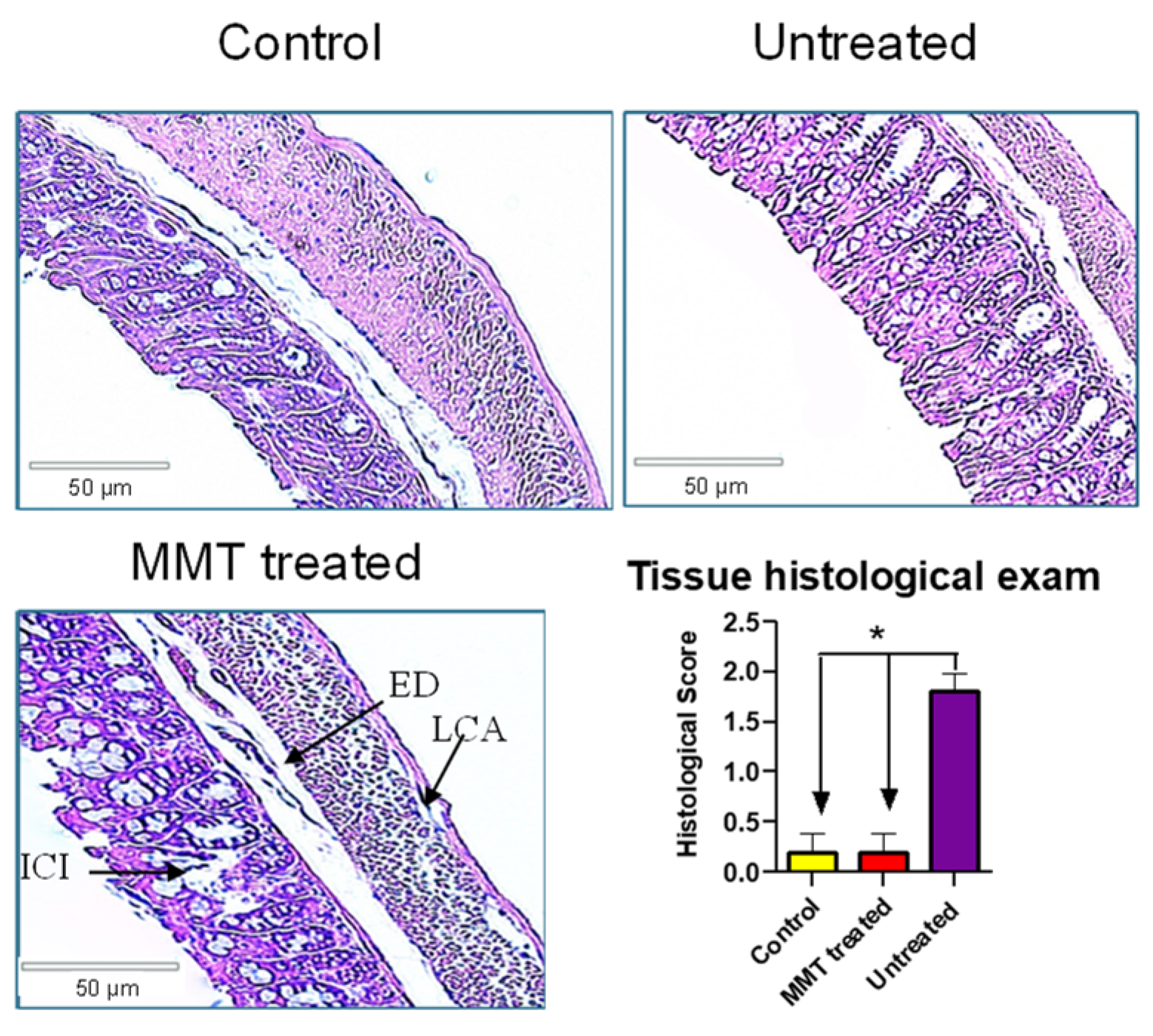
3.3. Tissue Histological Exam
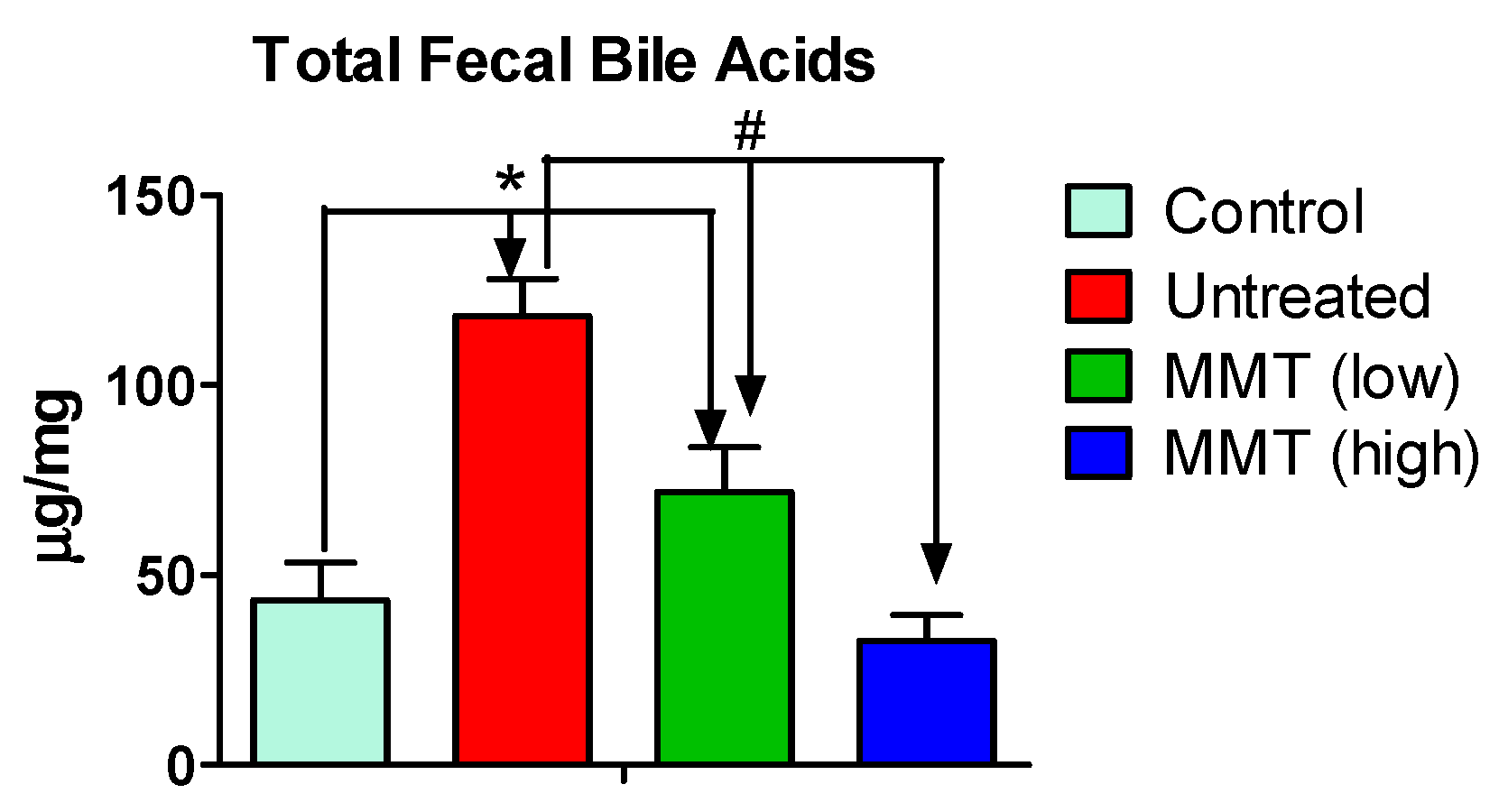
3.4. Fecal Bile Acids Level
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Duan, Y.; Zeng, L.; Zheng, C.; Song, B.; Li, F.; Kong, X.; Xu, K. Inflammatory Links Between High Fat Diets and Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owczarek, D.; Rodacki, T.; Domagala-Rodacka, R.; Cibor, D.; Mach, T. Diet and nutritional factors in inflammatory bowel diseases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 895–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardo, A.; Churruca, I.; Lasa, A.; Navarro, V.; Vazquez-Polo, M.; Perez-Junkera, G.; Larretxi, I. Nutritional Imbalances in Adult Celiac Patients Following a Gluten-Free Diet. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karunanithi, S.; Levi, L. High-fat diet and colorectal cancer: Myths and facts. Future Oncol. 2018, 14, 493–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjostrom, L.; Rissanen, A.; Andersen, T.; Boldrin, M.; Golay, A.; Koppeschaar, H.P.; Krempf, M. Randomised placebo-controlled trial of orlistat for weight loss and prevention of weight regain in obese patients. Eur. Multicentre Orlistat Study Group. Lancet. 1998, 352, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Lin, Y.; Zhuo, S.; Dong, Z.; Shao, C.; Ye, J.; Zhong, B. Treatment of obesity and metabolic-associated fatty liver disease with a diet or orlistat: A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2023, 117, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gad, S.C.; Spainhour, C.B.; Shoemake, C.; Pallman, D.R.; Stricker-Krongrad, A.; Downing, P.A.; Seals, R.E.; Eagle, L.A.; Polhamus, K.; Daly, J. Tolerable Levels of Nonclinical Vehicles and Formulations Used in Studies by Multiple Routes in Multiple Species With Notes on Methods to Improve Utility. Int. J. Toxicol. 2016, 35, 95–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geboes, K.; Riddell, R.; Ost, A.; Jensfelt, B.; Persson, T.; Lofberg, R. A reproducible grading scale for histological assessment of inflammation in ulcerative colitis. Gut 2000, 47, 404–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vespa, E.; D’Amico, F.; Sollai, M.; Allocca, M.; Furfaro, F.; Zilli, A.; Dal Buono, A.; Gabbiadini, R.; Danese, S.; Fiorino, G. Histological Scores in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: The State of the Art. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabian, O.; Bajer, L. Histopathological assessment of the microscopic activity in inflammatory bowel diseases: What are we looking for? World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 5300–5312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dadu, R.; Hu, M.I.; Cleeland, C.; Busaidy, N.L.; Habra, M.; Waguespack, S.G.; Sherman, S.I.; Ying, A.; Fox, P.; Cabanillas, M.E. Efficacy of the Natural Clay, Calcium Aluminosilicate Anti-Diarrheal, in Reducing Medullary Thyroid Cancer-Related Diarrhea and Its Effects on Quality of Life: A Pilot Study. Thyroid 2015, 25, 1085–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guarino, A.; Lo Vecchio, A.; Pirozzi, M.R. Clinical role of diosmectite in the management of diarrhea. Expert. Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2009, 5, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Gaxiola, G.; Cuello-Garcia, C.A.; Florez, I.D.; Perez-Pico, V.M. Smectite for acute infectious diarrhoea in children. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 4, CD011526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madkour, A.A.; Madina, E.M.; el-Azzouni, O.E.; Amer, M.A.; el-Walili, T.M.; Abbass, T. Smectite in acute diarrhea in children: A double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 1993, 17, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Garcia, F.A.; Cristiani-Urbina, E.; Morales-Barrera, L.; Rodriguez-Pena, O.N.; Hernandez-Portilla, L.B.; Flores-Ortiz, C.M. Spectroscopic and Microestructural Evidence for T-2 Toxin Adsorption Mechanism by Natural Bentonite Modified with Organic Cations. Toxins 2023, 15, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, P.; Dai, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, F.; Zhai, Y. Preventive obesity agent montmorillonite adsorbs dietary lipids and enhances lipid excretion from the digestive tract. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appleby, R.; Moghul, I.; Khan, S.; Yee, M.; Manousou, P.; Neal, T.D.; Waters, J.R.F. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with dysregulated bile acid synthesis and diarrhea: A prospective observational study. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0211348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reagan-Shaw, S.; Nihal, M.; Ahmad, N. Dose translation from animal to human studies revisited. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2008, 22, 659–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camilleri, M. Bile Acid diarrhea: Prevalence, pathogenesis, and therapy. Gut Liver 2015, 9, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ducrotte, P.; Dapoigny, M.; Bonaz, B.; Siproudhis, L. Symptomatic efficacy of beidellite montmorillonite in irritable bowel syndrome: A randomized, controlled trial. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2005, 21, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Wang, S.; Wang, L. Efficacy of montmorillonite and vitamin A combined with zinc preparation in children with diarrheal disease and its effect on inflammatory factors. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2021, 13, 5428–5435. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Emmanuel, S.; Siddiqui, N.; Du, T.; Asare, E.; Chen, Y.; Xie, H.; Liang, D.; Gao, S. Clay Attenuates Diarrhea Induced by Fat in a Mouse Model. Metabolites 2025, 15, 483. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15070483
Emmanuel S, Siddiqui N, Du T, Asare E, Chen Y, Xie H, Liang D, Gao S. Clay Attenuates Diarrhea Induced by Fat in a Mouse Model. Metabolites. 2025; 15(7):483. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15070483
Chicago/Turabian StyleEmmanuel, Shalom, Nyma Siddiqui, Ting Du, Eric Asare, Yuan Chen, Huan Xie, Dong Liang, and Song Gao. 2025. "Clay Attenuates Diarrhea Induced by Fat in a Mouse Model" Metabolites 15, no. 7: 483. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15070483
APA StyleEmmanuel, S., Siddiqui, N., Du, T., Asare, E., Chen, Y., Xie, H., Liang, D., & Gao, S. (2025). Clay Attenuates Diarrhea Induced by Fat in a Mouse Model. Metabolites, 15(7), 483. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15070483






