Tissue-Based Metabolomic Profiling of Endometrial Cancer and Hyperplasia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Population and Study Design
2.2. Metabolite Extraction
2.3. Metabolite Analysis
2.4. Data Handling and Processing
2.5. Bioinformatic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Mass Ion Detection and Metabolite Identification
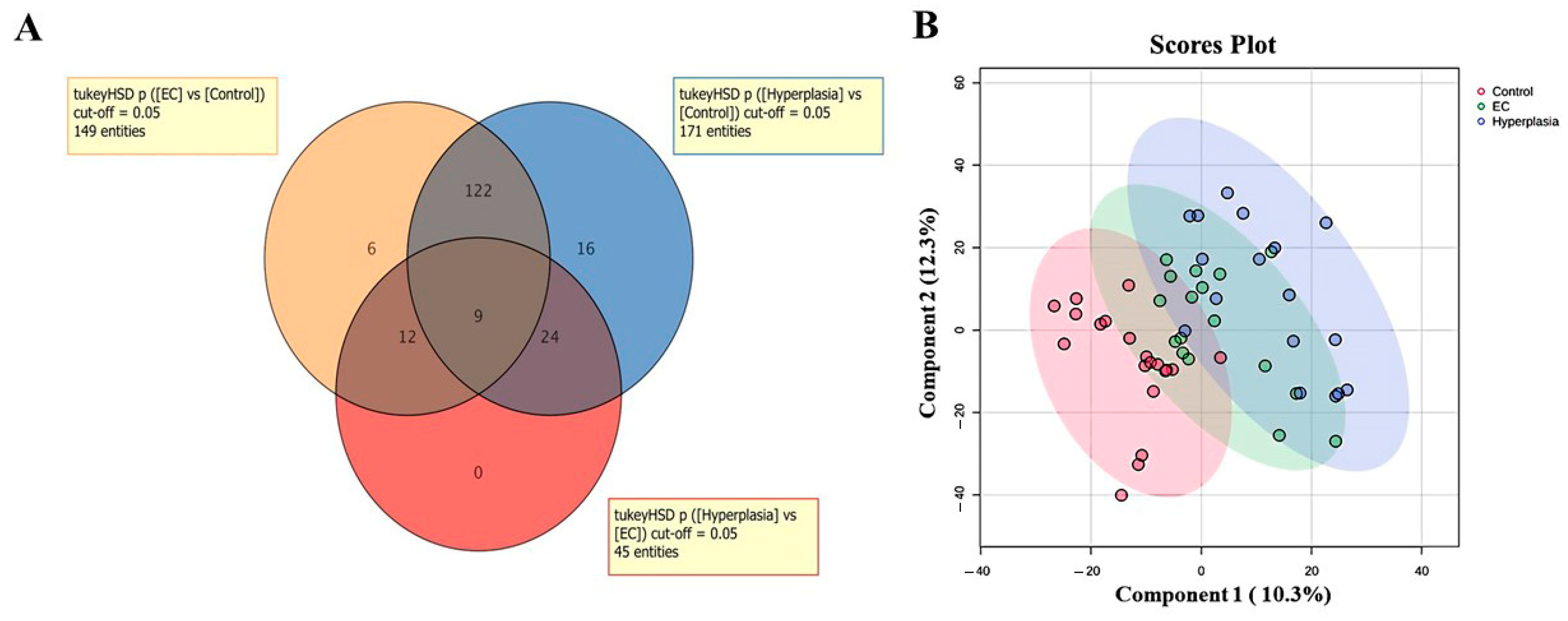
3.2. Overview of the Three Study Groups (CO, HY, and EC)
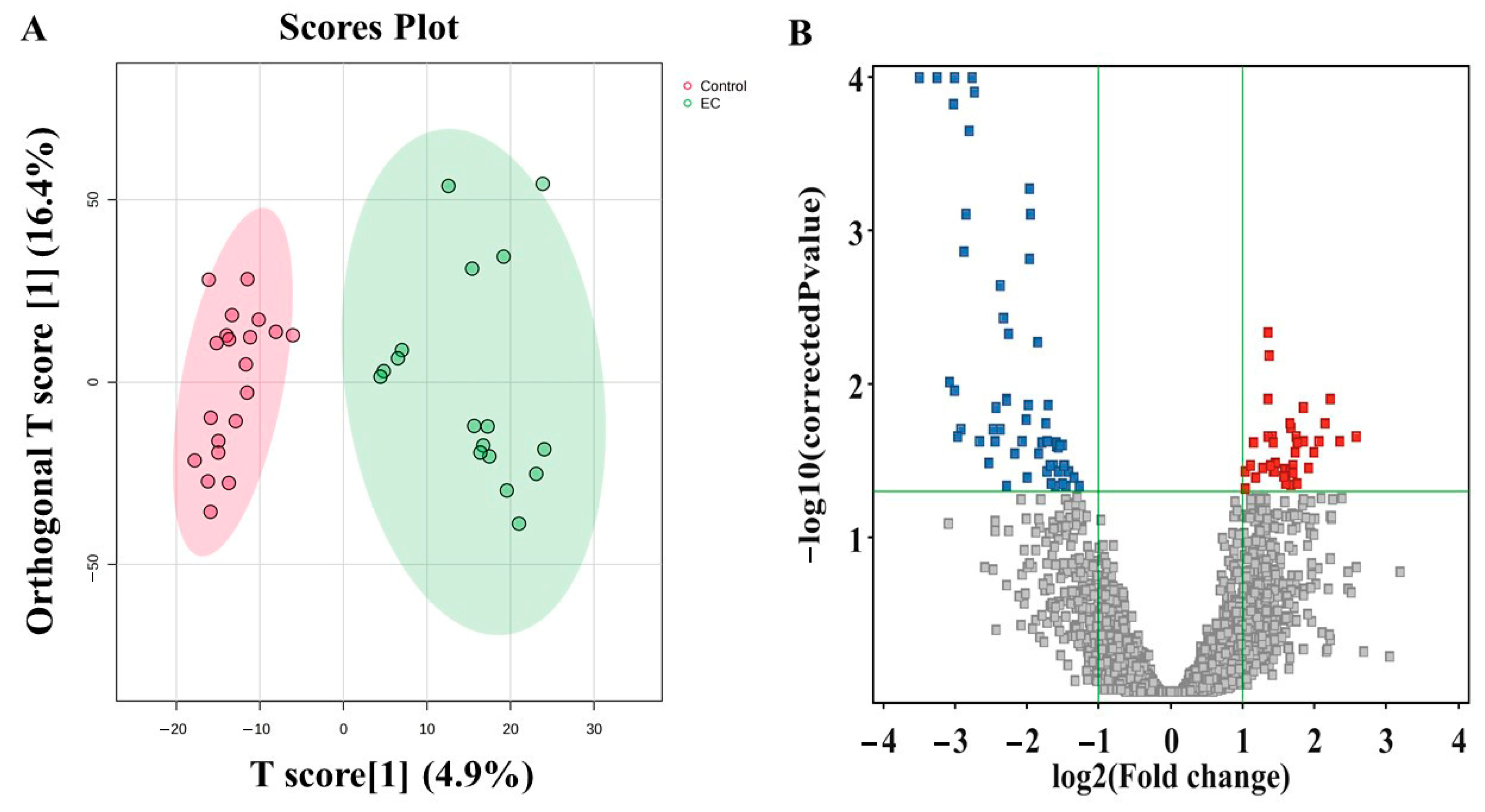
3.3. Metabolomic Profiling Between EC and CO
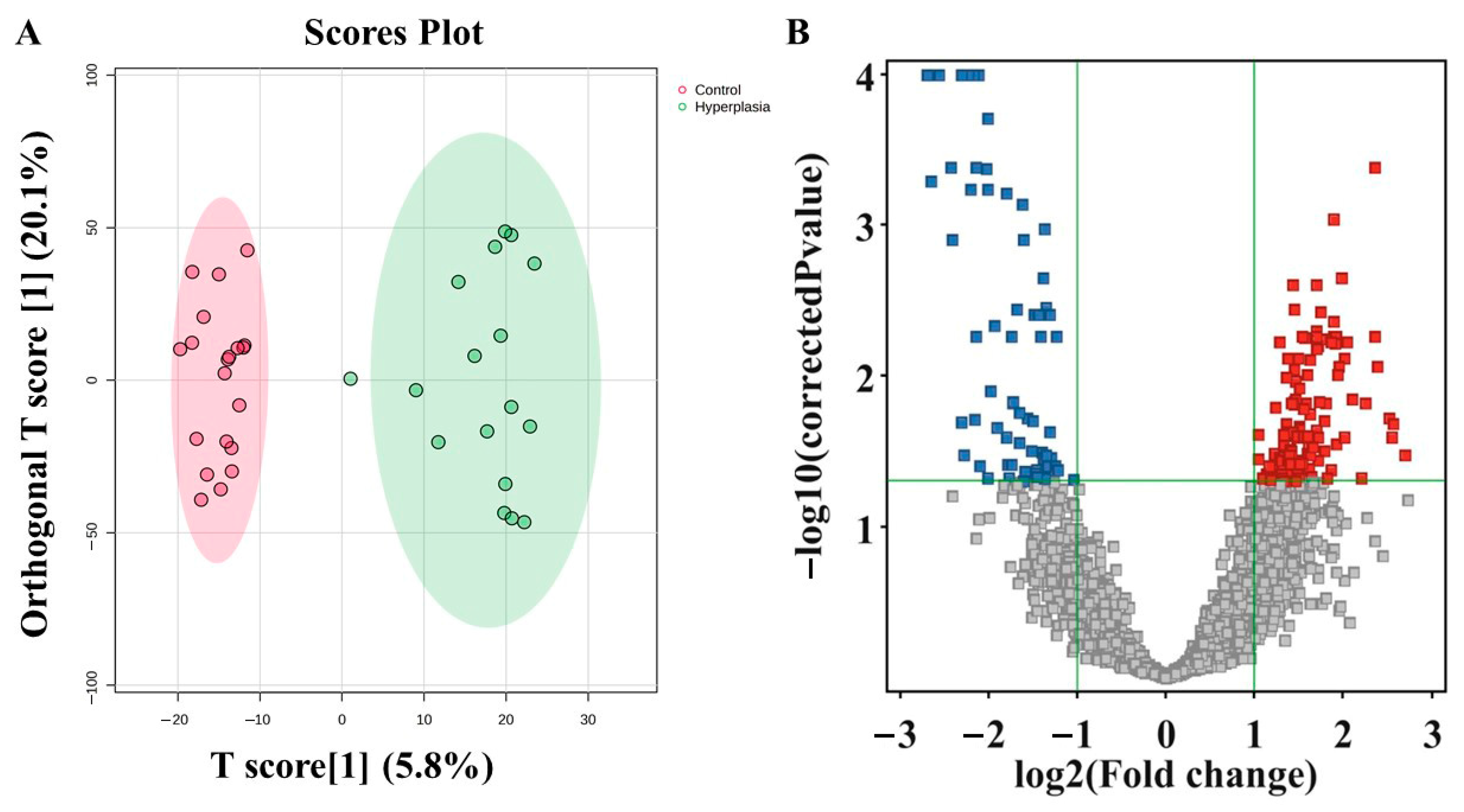
3.4. Metabolomic Profiling Between HY and CO
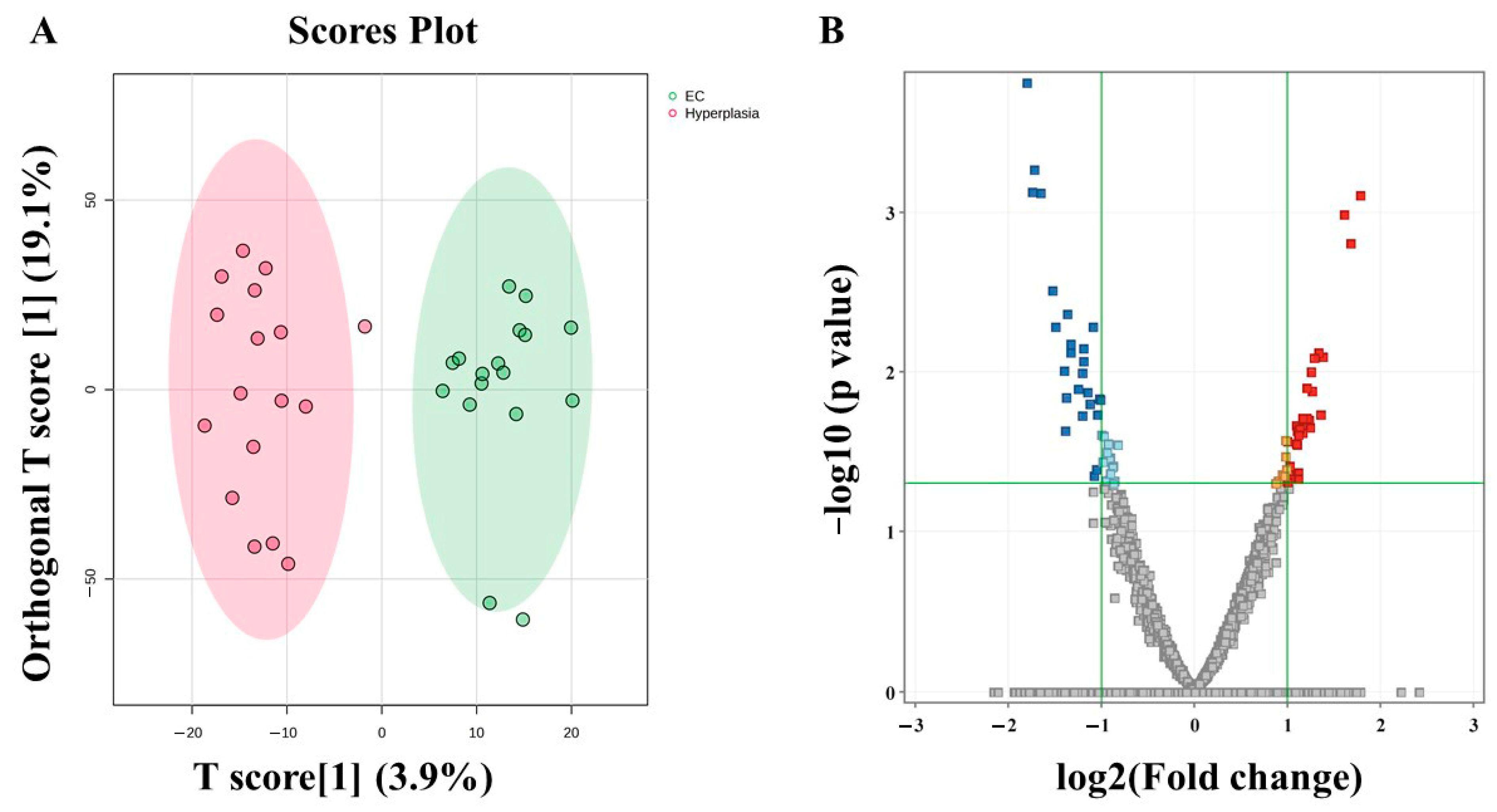
3.5. Metabolomic Profiling Between EC and HY
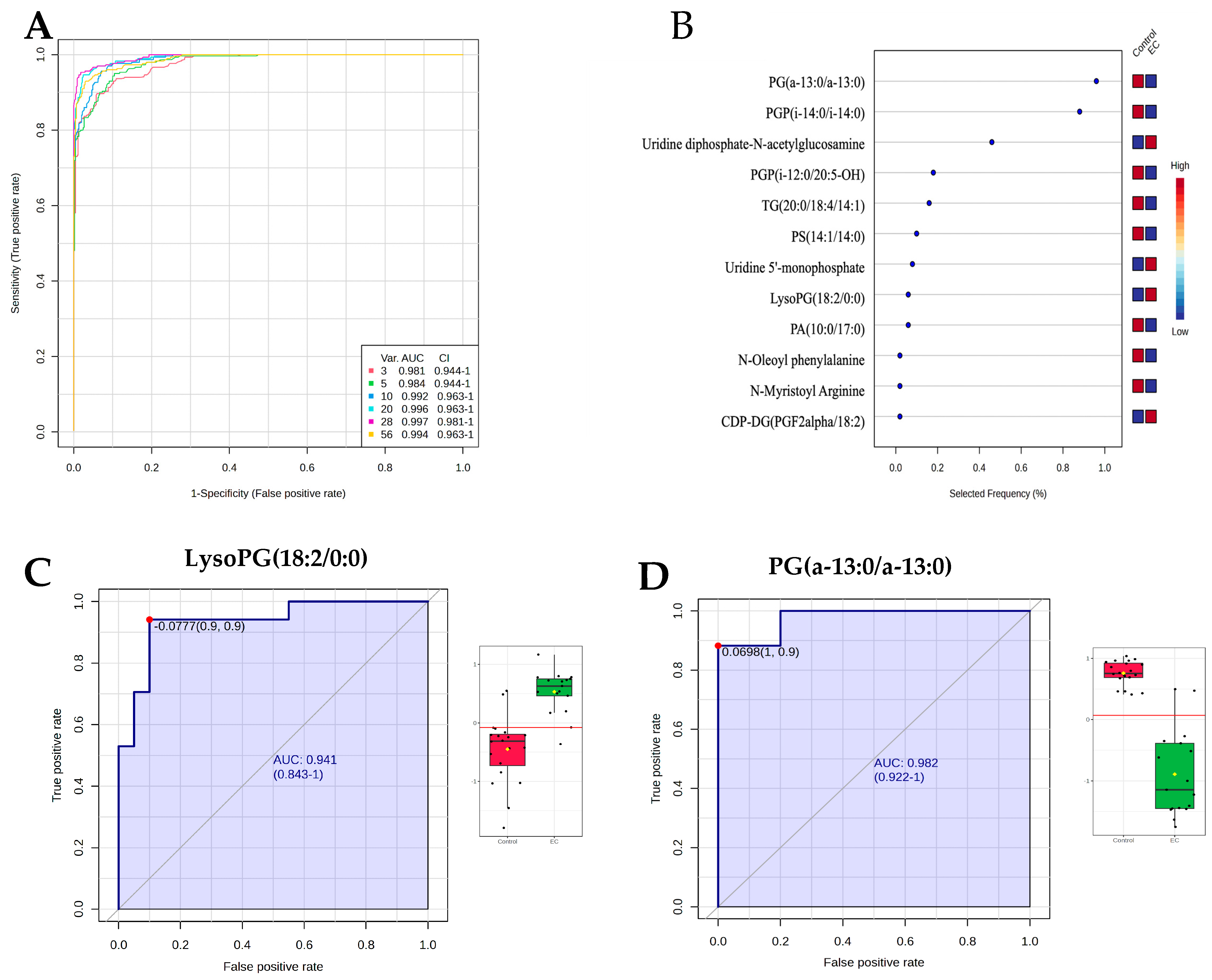
3.6. Evaluation of Metabolite Biomarkers Between EC and CO Groups and Network Pathway
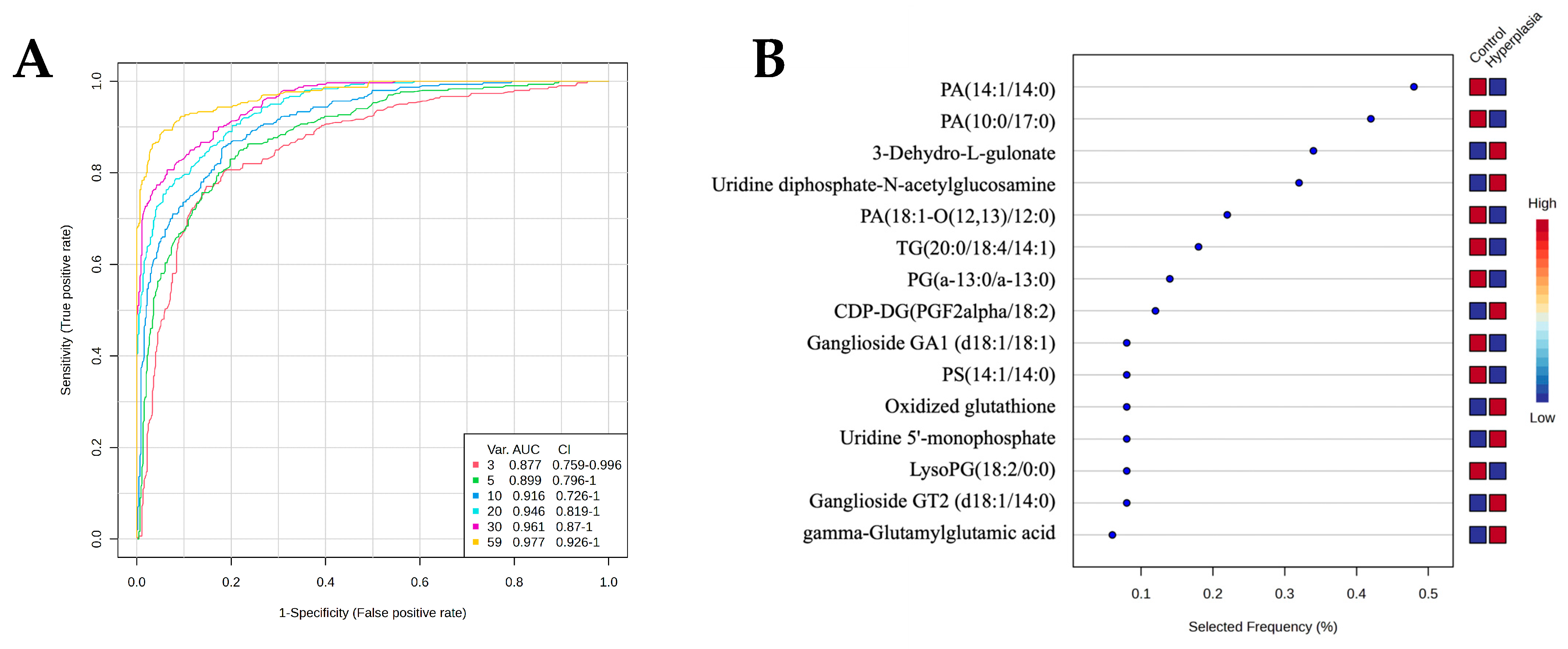
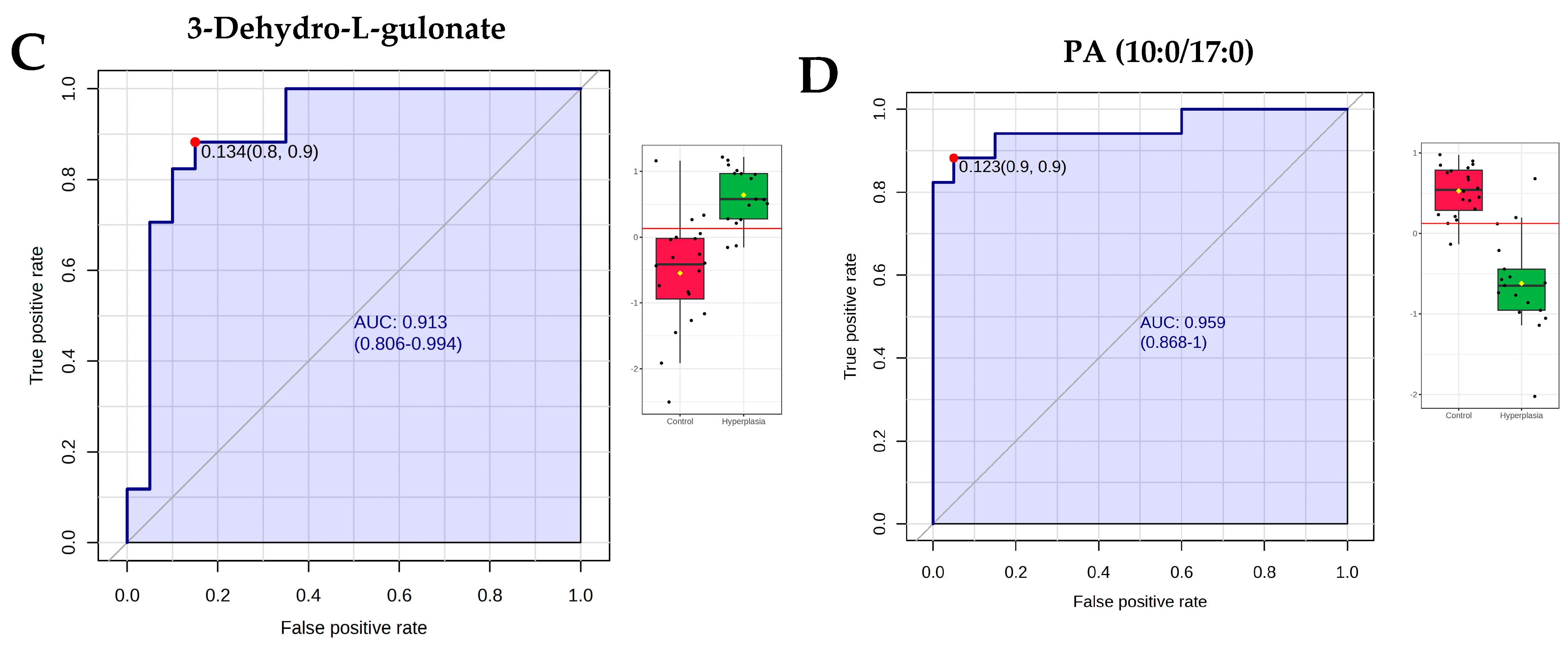
3.7. Evaluation of Metabolite Biomarkers Between HY and CO Groups and Network Pathway
3.8. Evaluation of Metabolite Biomarkers Between EC and HY Groups and Network Pathway
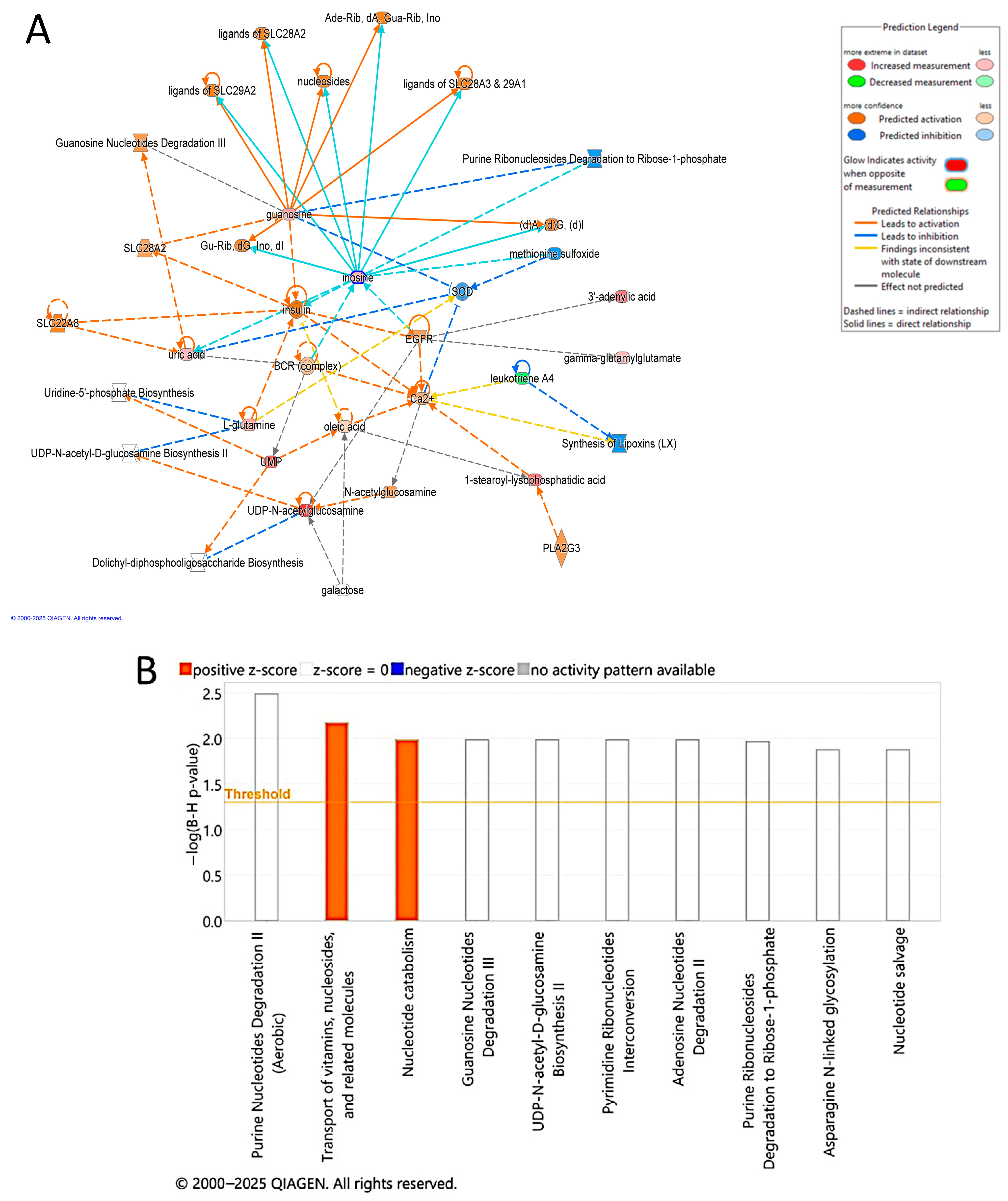
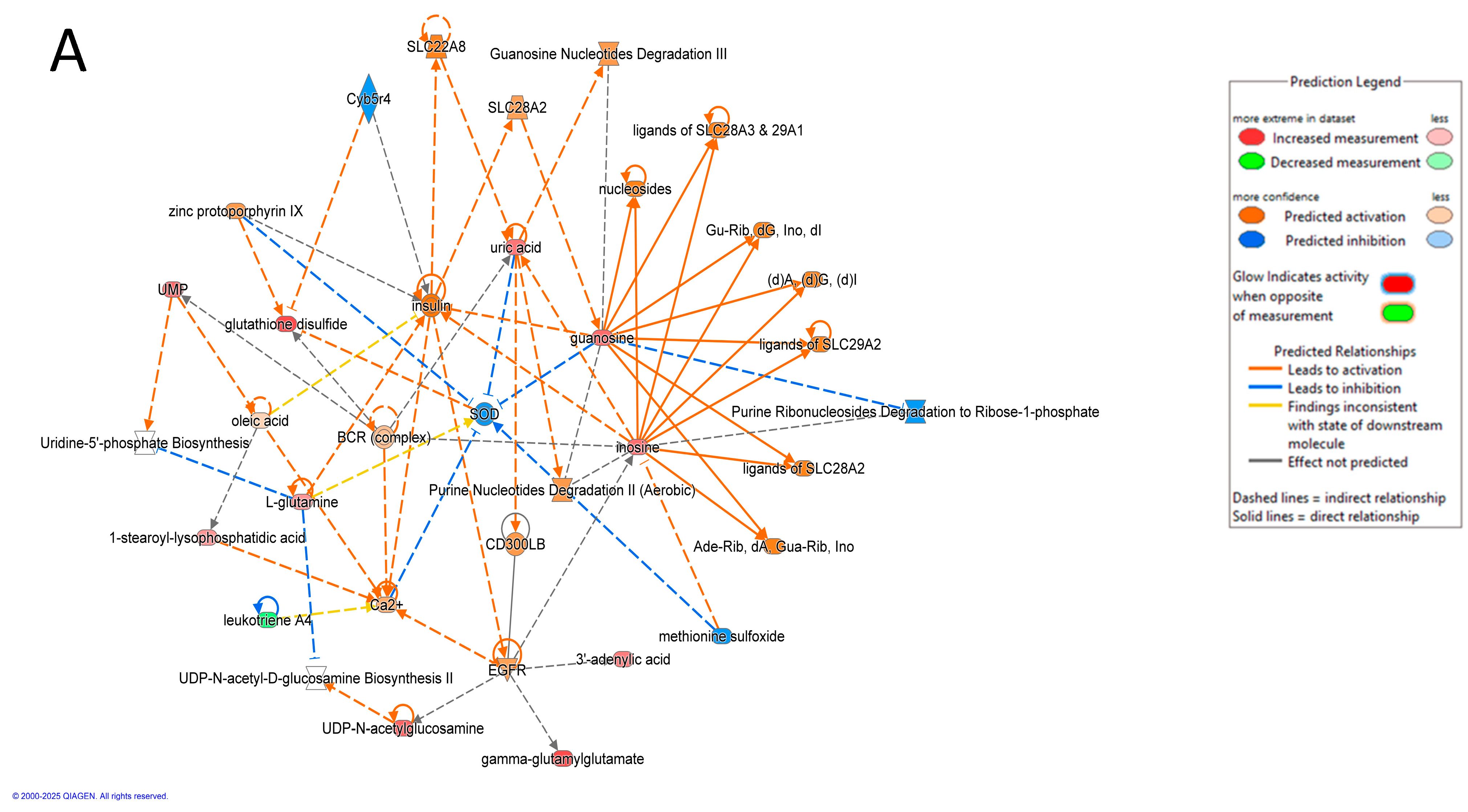
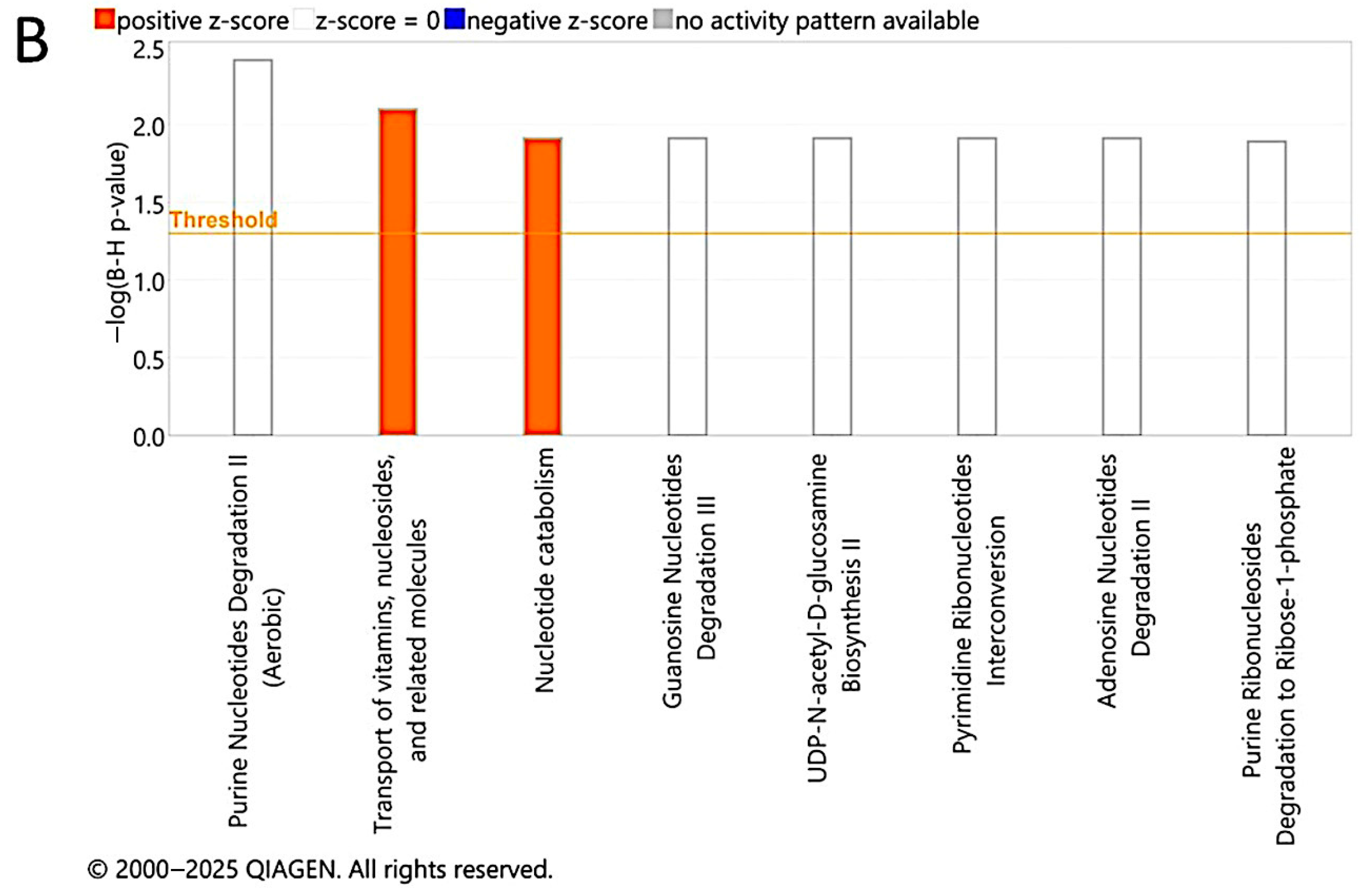
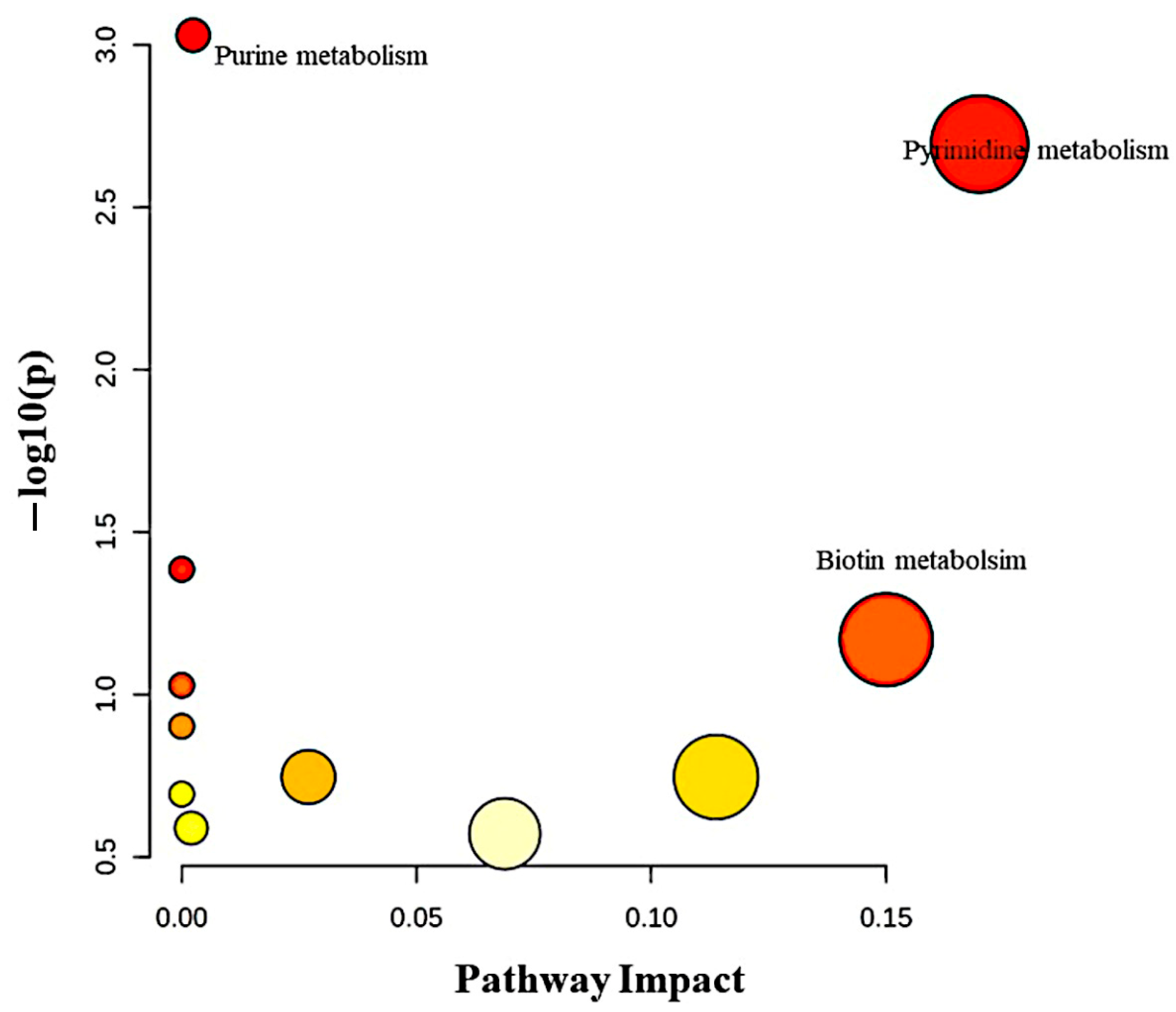
3.9. Pathway Analysis of Significantly Dysregulated Metabolites in EC Compared to HY and CO Groups
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bryant, B.H.; Doughty, E.; Kalof, A.N. Selective vs Complete Sampling in Hysterectomy Specimens Performed for Atypical Hyperplasia. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2019, 152, 666–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacey, J.V., Jr.; Sherman, M.E.; Rush, B.B.; Ronnett, B.M.; Ioffe, O.B.; Duggan, M.A.; Glass, A.G.; Richesson, D.A.; Chatterjee, N.; Langholz, B. Absolute risk of endometrial carcinoma during 20-year follow-up among women with endometrial hyperplasia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 788–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, M.T.; Sanni, O.B.; Coleman, H.G.; Cardwell, C.R.; McCluggage, W.G.; Quinn, D.; Wylie, J.; McMenamin, Ú.C. Concurrent and future risk of endometrial cancer in women with endometrial hyperplasia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannella, L.; Piva, F.; Delli Carpini, G.; Di Giuseppe, J.; Grelloni, C.; Giulietti, M.; Sopracordevole, F.; Giorda, G.; Del Fabro, A.; Clemente, N.; et al. Concurrent Endometrial Cancer in Women with Atypical Endometrial Hyperplasia: What Is the Predictive Value of Patient Characteristics? Cancers 2023, 16, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, S.D.; Newton, K.M.; Garcia, R.L.; Allison, K.H.; Voigt, L.F.; Jordan, C.D.; Epplein, M.; Swisher, E.; Upson, K.; Ehrlich, K.J.; et al. Complex hyperplasia with and without atypia: Clinical outcomes and implications of progestin therapy. Obstet. Gynecol. 2010, 116, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ring, K.L.; Mills, A.M.; Modesitt, S.C. Endometrial Hyperplasia. Obstet. Gynecol. 2022, 140, 1061–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulfatah, E.; Wakeling, E.; Sakr, S.; Al-Obaidy, K.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Morris, R.; Feldman, G.; Ali-Fehmi, R. Molecular classification of endometrial carcinoma applied to endometrial biopsy specimens: Towards early personalized patient management. Gynecol. Oncol. 2019, 154, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benabdelkamel, H.; Jaber, M.A.; Akkour, K.; AlMalki, R.H.; Alfadda, A.A.; Masood, A.; Joy, S.S.; Alhala, l.H.; Alwehaibi, M.A.; Arafah, M.; et al. Metabolomic Profiling of Blood Plasma in Females with Hyperplasia and Endometrial Cancer. Metabolites 2024, 14, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkour, K.; Alanazi, I.O.; Alfadda, A.A.; Alhalal, H.; Masood, A.; Musambil, M.; Rahman, A.M.; Alwehaibi, M.A.; Arafah, M.; Bassi, A.; et al. Tissue-Based Proteomic Profiling in Patients with Hyperplasia and Endometrial Cancer. Cells 2022, 11, 2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkour, K.; Alanazi, I.O.; Alfadda, A.A.; Masood, A.; Alhalal, H.; Joy, S.S.; Bassi, A.; Alshehri, E.; Alwehaibi, M.A.; Arafah, M.; et al. Plasma-based proteomic profiling identifies the distinct regulation of proteins in hyperplasia and endometrial cancer. BMC Cancer 2024, 24, 752. [Google Scholar]
- Mujammami, M.; Rafiullah, M.; Akkour, K.; Alfadda, A.A.; Masood, A.; Joy, S.S.; Alhalal, H.; Arafah, M.; Alshehri, E.; Alanazi, I.O.; et al. Plasma Proteomic Signature of Endometrial Cancer in Patients with Diabetes. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 4721–4732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ren, B.; Ren, J.; Gu, M.; You, L.; Zhao, Y. The significant role of amino acid metabolic reprogramming in cancer. Cell Commun. Signal 2024, 22, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fomenko, M.V.; Yanshole, L.V.; Tsentalovich, Y.P. Stability of metabolomic content during sample preparation: Blood and brain tissues. Metabolites 2022, 12, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlMalki, R.H.; Sebaa, R.; Al-Ansari, M.M.; Al-Alwan, M.; Alwehaibi, M.A.; Rahman, A.M.A. E. coli Secretome Metabolically Modulates MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells’ Energy Metabolism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worley, B.; Powers, R. Multivariate analysis in metabolomics. Curr. Metab. 2013, 1, 92–107. [Google Scholar]
- Wishart, D.S.; Guo, A.; Oler, E.; Wang, F.; Anjum, A.; Peters, H.; Dizon, R.; Sayeeda, Z.; Tian, S.; Lee, B.L.; et al. HMDB 5.0: The human metabolome database for 2022. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D622–D631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nees, L.K.; Heublein, S.; Steinmacher, S.; Juhasz-Böss, I.; Brucker, S.; Tempfer, C.B.; Wallwiener, M. Endometrial hyperplasia as a risk factor of endometrial cancer. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2022, 306, 407–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snaebjornsson, M.T.; Janaki-Raman, S.; Schulze, A. Greasing the Wheels of the Cancer Machine: The Role of Lipid Metabolism in Cancer. Cell Metab. 2020, 31, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koundouros, N.; Poulogiannis, G. Reprogramming of fatty acid metabolism in cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 122, 4–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandu, R.; Mok, H.J.; Kim, K.P. Phospholipids as cancer biomarkers: Mass spectrometry-based analysis. Mass. Spectrom. Rev. 2018, 37, 107–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, D.Y.; Ahn, S.J.; Lee, R.A.; Park, I.A.; Kim, J.H.; Suh, P.G.; Ryu, S.H.; Lee, K.H.; Han, J.S. Overexpression of phospholipase D1 in human breast cancer tissues. Cancer Lett. 2000, 161, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Ehara, H.; Akao, Y.; Shamoto, M.; Nakagawa, Y.; Banno, Y.; Deguchi, T.; Ohishi, N.; Yagi, K.; Nozawa, Y. Increased activity and intranuclear expression of phospholipase D2 in human renal cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 278, 140–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchida, N.; Okamura, S.; Kuwano, H. Phospholipase D activity in human gastric carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 1999, 19, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Blunsom, N.J.; Cockcroft, S. CDP-Diacylglycerol Synthases (CDS): Gateway to Phosphatidylinositol and Cardiolipin Synthesis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pakiet, A.; Sikora, K.; Kobiela, J.; Rostkowska, O.; Mika, A.; Sledzinski, T. Alterations in complex lipids in tumor tissue of patients with colorectal cancer. Lipids Health Dis. 2021, 20, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mika, A.; Pakiet, A.; Czumaj, A.; Kaczynski, Z.; Liakh, I.; Kobiela, J.; Perdyan, A.; Adrych, K.; Makarewicz, W.; Sledzinski, T. Decreased Triacylglycerol Content and Elevated Contents of Cell Membrane Lipids in Colorectal Cancer Tissue: A Lipidomic Study. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crimi, M.; Esposti, M.D. Apoptosis-induced changes in mitochondrial lipids. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1813, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birge, R.B.; Boeltz, S.; Kumar, S.; Carlson, J.; Wanderley, J.; Calianese, D.; Barcinski, M.; Brekken, R.A.; Huang, X.; Hutchins, J.T.; et al. Phosphatidylserine is a global immunosuppressive signal in efferocytosis, infectious disease, and cancer. Cell Death Differ. 2016, 23, 962–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadfield, L.A.; Pane, A.A.; Talebi, A.; Swinnen, J.V.; Fendt, S.M. Lipid metabolism in cancer: New perspectives and emerging mechanisms. Dev. Cell 2021, 56, 1363–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korbecki, J.; Bosiacki, M.; Pilarczyk, M.; Gąssowska-Dobrowolska, M.; Jarmużek, P.; Szućko-Kociuba, I.; Kulik-Sajewicz, J.; Chlubek, D.; Baranowska-Bosiacka, I. Phospholipid Acyltransferases: Characterization and Involvement of the Enzymes in Metabolic and Cancer Diseases. Cancers 2024, 16, 2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omi, J.; Kano, K.; Aoki, J. Current Knowledge on the Biology of Lysophosphatidylserine as an Emerging Bioactive Lipid. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2021, 79, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falasca, M.; Ferro, R. Role of the lysophosphatidylinositol/GPR55 axis in cancer. Adv. Biol. Regul. 2016, 60, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitamura, C.; Sonoda, H.; Nozawa, H.; Kano, K.; Emoto, S.; Murono, K.; Kaneko, M.; Hiyoshi, M.; Sasaki, K.; Nishikawa, T.; et al. The component changes of lysophospholipid mediators in colorectal cancer. Tumour Biol. 2019, 41, 1010428319848616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Fang, X.J.; Casey, G.; Mills, G.B. Lysophospholipids activate ovarian and breast cancer cells. Biochem. J. 1995, 309, 933–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamphorst, J.J.; Cross, J.R.; Fan, J.; De Stanchina, E.; Mathew, R.; White EPThompson, C.B.; Rabinowitz, J.D. Hypoxic and Ras-transformed cells support growth by scavenging unsaturated fatty acids from lysophospholipids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 8882–8887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emoto, S.; Kurano, M.; Kano, K.; Matsusaki, K.; Yamashita, H.; Nishikawa MIgarashi, K.; Ikeda, H.; Aoki, J.; Kitayama, J.; Yatomi, Y. Analysis of glycero-lysophospholipids in gastric cancerous ascites. J. Lipid Res. 2017, 58, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, S.; Gupta, S.C.; Pandey, M.K.; Tyagi, A.K.; Deb, L. Oxidative Stress and Cancer: Advances and Challenges. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2016, 2016, 5010423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, J.D.; Dinkova-Kostova, A.T.; Tew, K.D. Oxidative Stress in Cancer. Cancer Cell 2020, 38, 167–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, R.; Zhu, W.; Chu, H.; Yu, H.; Wei, P.; Wu, X.; Zhu, H.; Gao, H.; Liang, J.; et al. UDP-glucose accelerates SNAI1 mRNA decay and impairs lung cancer metastasis. Nature 2019, 571, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucena, M.C.; Carvalho-Cruz, P.; Donadio, J.L.; Oliveira, I.A.; de Queiroz, R.M.; Marinho-Carvalho, M.M.; Sola-Penna, M.; de Paula, I.F.; Gondim, K.C.; McComb, M.E.; et al. Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition Induces Aberrant Glycosylation through Hexosamine Biosynthetic Pathway Activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 12917–12929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akella, N.M.; Ciraku, L.; Reginato, M.J. Fueling the fire: Emerging role of the hexosamine biosynthetic pathway in cancer. BMC Biol. 2019, 17, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, J.; Ichu, T.A.; Zanca, C.; Yang, H.; Zhang, W.; Gu, Y.; Chowdhry, S.; Reed, A.; Ikegami, S.; Turner, K.M.; et al. Oncogene Amplification in Growth Factor Signaling Pathways Renders Cancers Dependent on Membrane Lipid Remodeling. Cell Metab. 2019, 30, 525–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saarelainen, S.K.; Peltonen, N.; Lehtimäki, T.; Perheentupa, A.; Vuento, M.H.; Mäenpää, J.U. Predictive value of serum human epididymis protein 4 and cancer antigen 125 concentrations in endometrial carcinoma. Am. J. Obstet Gynecol. 2013, 209, 142.e1–142.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbink, K.; Zusterzeel, P.L.; Geurts-Moespot, A.J.; Herwaarden, A.E.V.; Pijnenborg, J.M.; Sweep, F.C.; Massuger, L.F. HE4 is superior to CA125 in the detection of recurrent disease in high-risk endometrial cancer patients. Tumour Biol. 2018, 40, 1010428318757103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akkour, K.; Masood, A.; Al Mogren, M.; AlMalki, R.H.; Alfadda, A.A.; Joy, S.S.; Bassi, A.; Alhalal, H.; Arafah, M.; Othman, O.M.; et al. Tissue-Based Metabolomic Profiling of Endometrial Cancer and Hyperplasia. Metabolites 2025, 15, 458. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15070458
Akkour K, Masood A, Al Mogren M, AlMalki RH, Alfadda AA, Joy SS, Bassi A, Alhalal H, Arafah M, Othman OM, et al. Tissue-Based Metabolomic Profiling of Endometrial Cancer and Hyperplasia. Metabolites. 2025; 15(7):458. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15070458
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkkour, Khalid, Afshan Masood, Maha Al Mogren, Reem H. AlMalki, Assim A. Alfadda, Salini Scaria Joy, Ali Bassi, Hani Alhalal, Maria Arafah, Othman Mahmoud Othman, and et al. 2025. "Tissue-Based Metabolomic Profiling of Endometrial Cancer and Hyperplasia" Metabolites 15, no. 7: 458. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15070458
APA StyleAkkour, K., Masood, A., Al Mogren, M., AlMalki, R. H., Alfadda, A. A., Joy, S. S., Bassi, A., Alhalal, H., Arafah, M., Othman, O. M., Awwad, H. M., Rahman, A. M. A., & Benabdelkamel, H. (2025). Tissue-Based Metabolomic Profiling of Endometrial Cancer and Hyperplasia. Metabolites, 15(7), 458. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15070458






