Fibroblast Activation Protein Compared with Other Markers of Activated Smooth Muscle Cells, Extracellular Matrix Turnover and Inflammation in a Mouse Model of Atherosclerosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Model
2.2. Tissue Preparation
2.3. mRNA Isolation
2.4. PCR Analysis
2.5. Immunohistochemistry
2.6. Correlation Between Immunochemistry and Gene Expression
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Fap Expression in Atherosclerotic Lesions
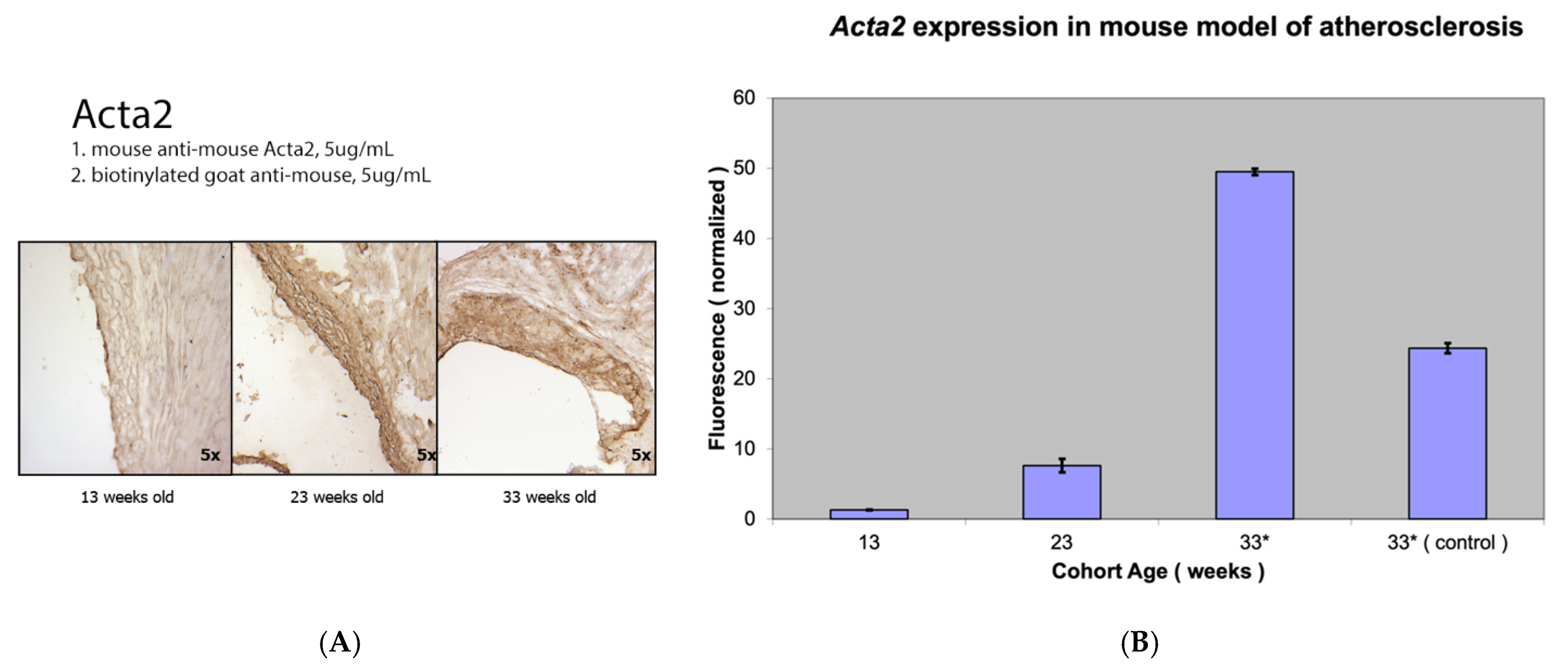
3.2. Comparison of Fap Expression with Other Markers of Activated Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells
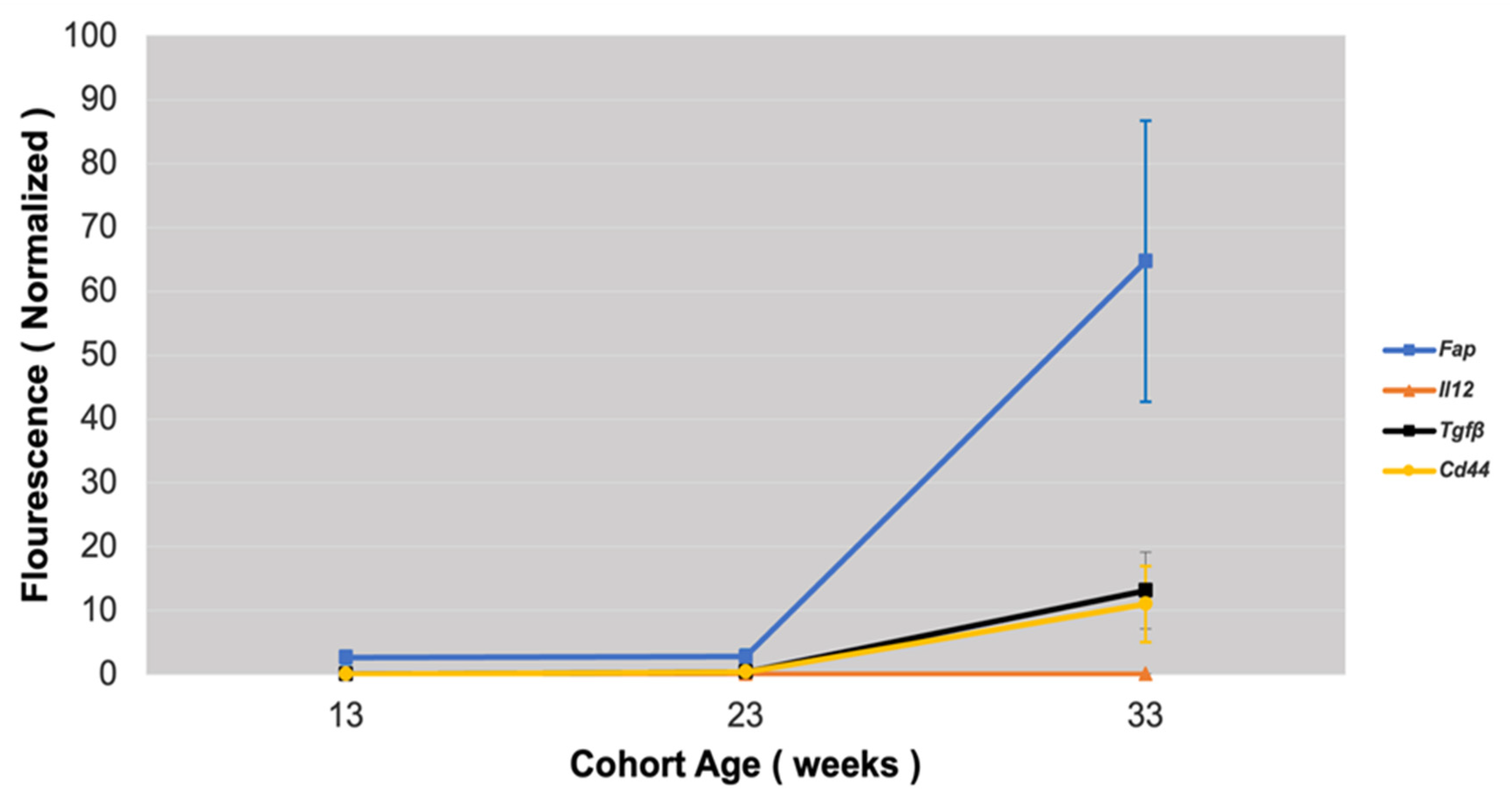
3.3. Fap Expression Versus Expression of Markers of ECM Turnover
3.4. Fap Expression Against Inflammation Markers in Atherosclerotic Lesions
4. Discussion
Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bentzon, J.F.; Otsuka, F.; Virmani, R.; Falk, E. Mechanisms of plaque formation and rupture. Circ. Res. 2014, 114, 1852–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bäck, M.; Weber, C.; Lutgens, E. Regulation of atherosclerotic plaque inflammation. J. Intern. Med. 2015, 278, 462–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badimon, L.; Vilahur, G. Thrombosis formation on atherosclerotic lesions and plaque rupture. J. Intern. Med. 2014, 276, 618–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansson, G.K.; Libby, P.; Tabas, I. Inflammation and plaque vulnerability. J. Intern. Med. 2015, 278, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanadis, C.; Antoniou, C.; Tsiachris, D.; Pietri, P. Coronary Atherosclerotic Vulnerable Plaque: Current Perspectives. J. Am. Hear. Assoc. 2017, 6, e005543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Monte-Nieto, G.; Fischer, J.W.; Gorski, D.J.; Harvey, R.P.; Kovacic, J.C. Basic Biology of Extracellular Matrix in the Cardiovascular System, Part 1/4: JACC Focus Seminar. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 75, 2169–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frangogiannis, N.G.; Kovacic, J.C. Extracellular Matrix in Ischemic Heart Disease, Part 4/4: JACC Focus Seminar. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 75, 2219–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shami, A.; Gonçalves, I.; Hultgårdh-Nilsson, A. Collagen and related extracellular matrix proteins in atherosclerotic plaque de-velopment. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2014, 25, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raines, E.W. The extracellular matrix can regulate vascular cell migration, proliferation, and survival: Relationships to vascular disease. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2000, 81, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekhter, M.D. Collagen synthesis in atherosclerosis: Too much and not enough. Cardiovasc. Res. 1999, 41, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avery, D.; Govindaraju, P.; Jacob, M.; Todd, L.; Monslow, J.; Puré, E. Extracellular matrix directs phenotypic heterogeneity of activated fibroblasts. Matrix Biol. 2018, 67, 90–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacLean, J.; Pasumarthi, K.B. Signaling mechanism regulating fibroblast activation, phenoconversion and fibrosis in the heart. Indian. J. Biochem. Biophys. 2014, 51, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Díaz-Araya, G.; Vivar, R.; Humeres, C.; Boza, P.; Bolivar, S.; Muñoz, C. Cardiac fibroblasts as sentinel cells in cardiac tissue: Receptors, signaling pathways and cellular functions. Pharmacol. Res. 2015, 101, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, C.; Law, J.P.; Reyat, J.S.; Cumberland, M.J.; Hang, S.; Vo, N.T.N.; Raniga, K.; Weston, C.J.; O’shea, C.; Townend, J.N.; et al. Chronic activation of human cardiac fibroblasts in vitro attenuates the reversibility of the myofibroblast phenotype. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiansen, V.J.; Jackson, K.W.; Lee, K.N.; KcKnee, P. Effect of fibroblast activation protein and alpha2-antiplasmin cleaving en-zyme on collagen types I, III and IV. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2007, 457, 177–186. [Google Scholar]
- Edosada, C.Y.; Quan, C.; Wiesmann, C.; Tran, T.; Sutherlin, D.; Reynolds, M.; Elliott, J.M.; Raab, H.; Fairbrother, W.; Wolf, B.B. Selective Inhibition of Fibroblast Activation Protein Protease Based on Dipeptide Substrate Specificity. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 7437–7444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.E.; Hamson, E.J.; Koczorowska, M.M.; Tholen, S.; Chowdhury, S.; Bailey, C.G.; Lay, A.J.; Twigg, S.M.; Lee, Q.; Roediger, B.; et al. Identification of Novel Natural Substrates of Fibroblast Activation Protein-alpha by Differential Degradomics and Proteomics. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2019, 18, 65–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.-Z.; Yu, X.; Tang, J.-J.; Ouyang, X.; Huang, X.-R.; Fingerle-Rowson, G.; Bacher, M.; Scher, L.A.; Bucala, R.; Lan, H.Y. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor induces MMP-9 expression: Implications for destabilization of human atherosclerotic plaques. Atherosclerosis 2005, 178, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brokopp, C.E.; Schoenauer, R.; Richards, P.; Bauer, S.; Lohmann, C.; Emmert, M.Y.; Weber, B.; Winnik, S.; Aikawa, E.; Graves, K.; et al. Fibroblast activation protein is induced by inflammation and de-grades type I collagen in thin cap fibroatheromata. Eur. Heart J. 2011, 32, 2713–2722. [Google Scholar]
- Meletta, R.; Herde, A.M.; Chiotellis, A.; Isa, M.; Rancic, Z.; Borel, N.; Ametamey, S.M.; Krämer, S.D.; Schibli, R. Evaluation of the Radiolabeled Boronic Acid-Based FAP Inhibitor MIP-1232 for Atherosclerotic Plaque Imaging. Molecules 2015, 20, 2081–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohmand-Borkowski, A.; Rozmyslowicz, T. Expression of fibroblast activation protein in human coronary vessels. Pol Merkur Lek. 2021, 49, 5–8. [Google Scholar]
- Mohmand-Borkowski, A.; Rozmyslowicz, T. Immunohistochemical Localization of Fibroblast Activation Protein in Coronary Arteries with Different Forms of Atherosclerosis. Metabolites 2024, 14, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, S.; Weber, J.; Nusser-Stein, S.; Pahla, J.; E Zhang, H.; A Mohammed, S.; Oppi, S.; Gaul, D.S.; Paneni, F.; Tailleux, A.; et al. Deletion of fibroblast activation protein provides atheroprotection. Cardiovasc. Res. 2020, 117, 1060–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monslow, J.; Todd, L.; Chojnowski, J.E.; Govindaraju, P.K.; Assoian, R.K.; Puré, E. Fibroblast Activation Protein Regulates Lesion Burden and the Fibroinflammatory Response in Apoe-Deficient Mice in a Sexually Dimorphic Manner. Am. J. Pathol. 2020, 190, 1118–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daugherty, A.; Whitman, S. Quantification of Atherosclerosis in Mice. Methods Mol. Biol. 2003, 209, 293–309. [Google Scholar]
- Venegas-Pino, D.E.; Banko, N.; Khan, M.I. Quantitative Analysis and Characterization of Atherosclerotic Lesions in the Murine Aortic Sinus. J. Vis. Exp 2013, 82, e50933. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Chen, X.; Yang, T.; Guo, F.; Wu, C.; Liang, Y.-K. The availability of the fibroblast activation protein receptor in early identification of vulnera-ble atherosclerotic plaques: A preclinical study using a 68Ga-FAPI PET. J. Nuc. Med. 2021, 62 (Suppl. S1), 1395. [Google Scholar]
- Diekmann, J.; Bengel, F.M. Cardiac Applications of Fibroblast Activation Protein Imaging. PET Clin. 2023, 18, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Du, B.; Li, X.; Li, Y. Highlighting Fibroblasts Activation in Fibrosis: The State-of-The-Art Fibroblast Activation Protein Inhibitor PET Imaging in Cardiovascular Diseases. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmala, A.; Serfling, S.E.; Michalski, K.; Lindner, T.; Schirbel, A.; Higuchi, T.; Hartrampf, P.E.; Derlin, T.; Buck, A.K.; Weich, A.; et al. Molecular imaging of arterial fibroblast activation protein: Association with calcified plaque burden and cardiovascular risk factors. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 2023, 50, 3011–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillmanns, J.; Weiglein, J.; Neuser, J.; Fraccarollo, D.; Galuppo, P.; König, T.; Diekmann, J.; Ross, T.; Bengel, F.; Bauersachs, J.; et al. Circulating soluble fibroblast activation protein (FAP) levels are independent of cardiac and extra-cardiac FAP expression determined by targeted molecular imaging in patients with myocardial FAP activation. Int. J. Cardiol. 2024, 406, 132044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillmanns, J.; Widera, C.; Habbaba, Y.; Galuppo, P.; Kempf, T.; Wollert, K.C.; Bauersachs, J. Circulating concentrations of fibroblast activation protein α in apparently healthy individuals and patients with acute coronary syndrome as assessed by sandwich ELISA. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 168, 3926–3931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillmanns, J.; Fraccarollo, D.; Galuppo, P.; Wollert, K.C.; Bauersachs, J. Changes in concentrations of circulating fibroblast activation protein alpha are associated with myocardial damage in patients with acute ST-elevation MI. Int. J. Cardiol. 2017, 232, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Willige, S.U.; Malfliet, J.J.; Deckers, J.W.; Dippel, D.W.; Leebeek, F.W.; Rijken, D.C. Plasma levels of soluble fibroblast activation protein in arterial thrombosis; determinants and cleavage of its substrate alpha-2-antiplasmin. Int. J. Cardiol. 2015, 178, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, J.; Rosas, E.A.; Juarez, E.I.C.; Ferro-Flores, G.; Cuevas, C.L.S.; Luna-Gutiérrez, M.; Ramírez, G.M.; Ahumada, J.V.; Sandoval, S.H.; León, N.C.; et al. Cardiac fibroblast activation after acute coronary syndrome detected by 99MTCIFAP spect, multimodality approach and follow up. J. Am. Coll. Card. 2024, 83, 4402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diekmann, J.; Koenig, T.; Thackeray, J.T.; Derlin, T.; Czerner, C.; Neuser, J.; Ross, T.L.; Schaefer, A.; Tillmanns, J.; Bauersachs, J.; et al. Cardiac Fibroblast Activation in Patients Early After Acute Myocardial Infarction: Integration with MR Tissue Characterization and Subsequent Functional Outcome. J. Nucl. Med. 2022, 63, 1415–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moyola, F.M.; Thackeray, J. The Potential of Fibroblast Activation Protein-Targeted Imaging as a Biomarker of Cardiac Remod-eling and Injury. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2023, 25, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diekmann, J.; Koenig, T.; Zwadlo, C.; Derlin, T.; Neuser, J.; Thackeray, J.T.; Schäfer, A.; Ross, T.L.; Bauersachs, J.; Bengel, F.M. Molecular Imaging Identifies Fibroblast Activation Beyond the Infarct Region After Acute Myocardial Infarction. J. Am. Coll. Card. 2021, 77, 1835–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohmand-Borkowski, A.; Conover, D.O.; Rozmyslowicz, T. Fibroblast Activation Protein Compared with Other Markers of Activated Smooth Muscle Cells, Extracellular Matrix Turnover and Inflammation in a Mouse Model of Atherosclerosis. Metabolites 2025, 15, 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15040243
Mohmand-Borkowski A, Conover DO, Rozmyslowicz T. Fibroblast Activation Protein Compared with Other Markers of Activated Smooth Muscle Cells, Extracellular Matrix Turnover and Inflammation in a Mouse Model of Atherosclerosis. Metabolites. 2025; 15(4):243. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15040243
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohmand-Borkowski, Adam, Dareus O. Conover, and Tomasz Rozmyslowicz. 2025. "Fibroblast Activation Protein Compared with Other Markers of Activated Smooth Muscle Cells, Extracellular Matrix Turnover and Inflammation in a Mouse Model of Atherosclerosis" Metabolites 15, no. 4: 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15040243
APA StyleMohmand-Borkowski, A., Conover, D. O., & Rozmyslowicz, T. (2025). Fibroblast Activation Protein Compared with Other Markers of Activated Smooth Muscle Cells, Extracellular Matrix Turnover and Inflammation in a Mouse Model of Atherosclerosis. Metabolites, 15(4), 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15040243




