New Markers for the Assessment of Microvascular Complications in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Definition
1.2. Epidemiology
1.3. Pathophysiology
1.4. Microvascular Complications
1.5. Biomarkers
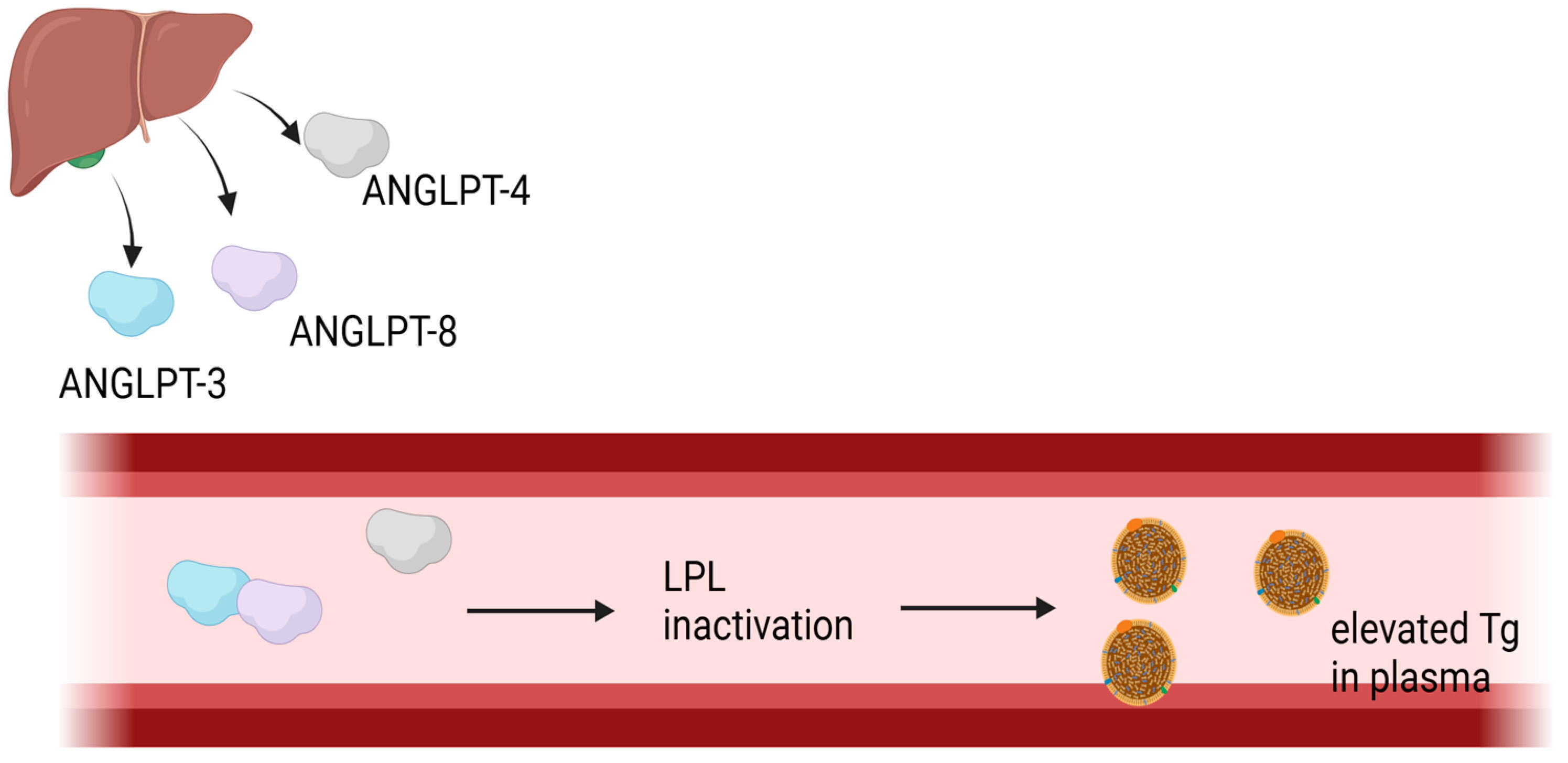
1.5.1. Angiopoetin-like Protein 4 and Angiopoetin-like Protein 8
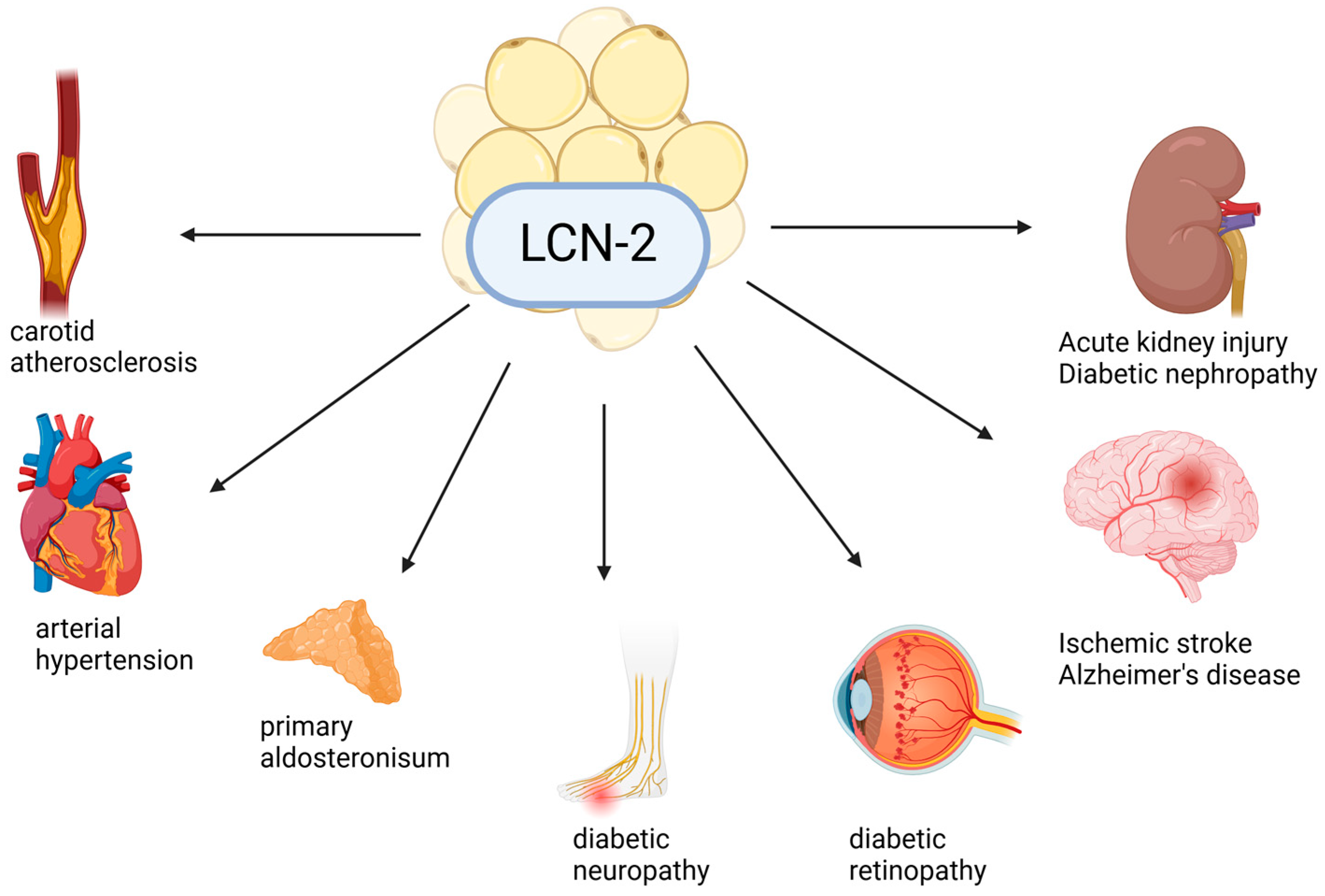
1.5.2. Lipocalin-2/NGAL
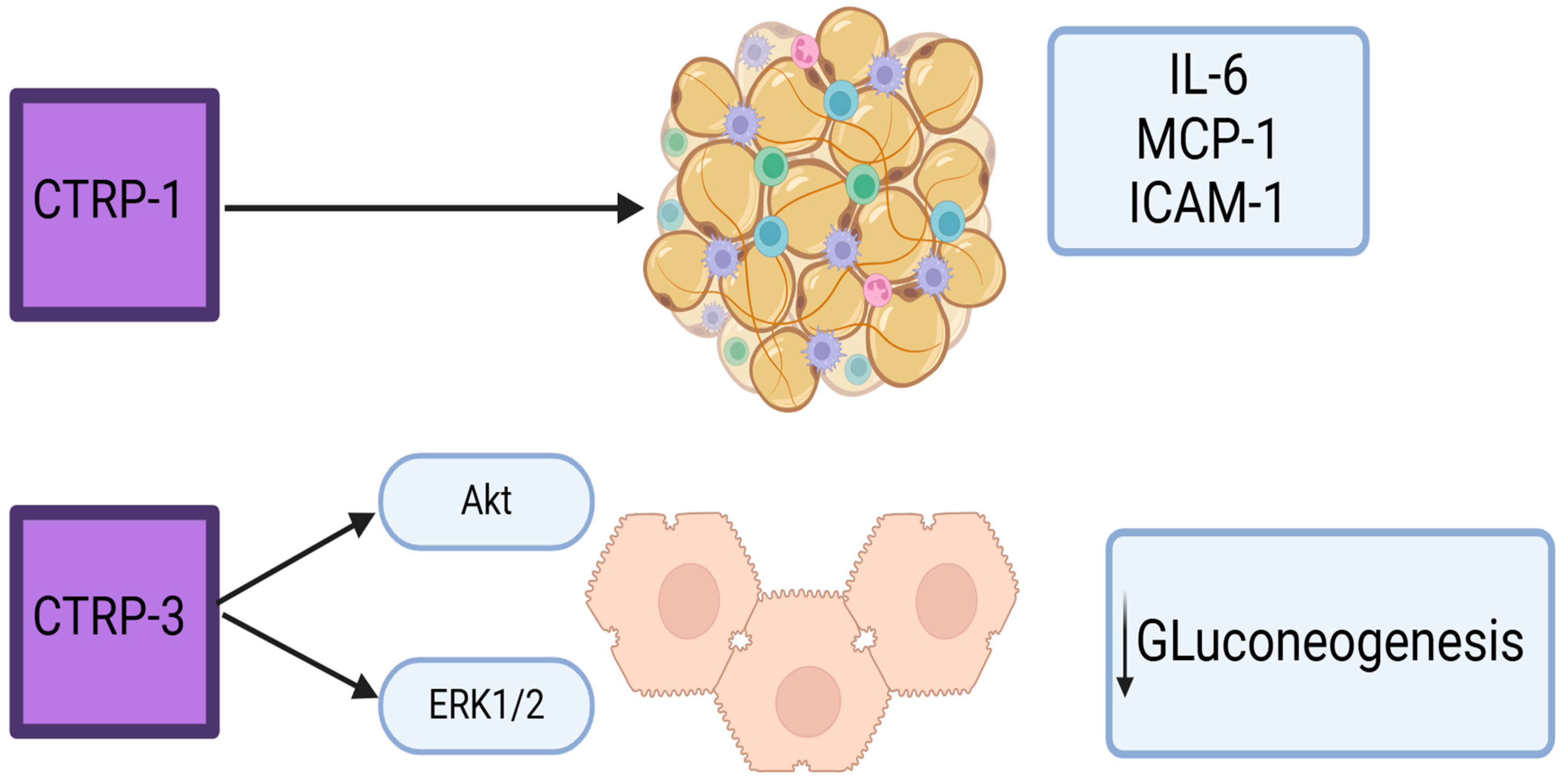
1.5.3. CTRP
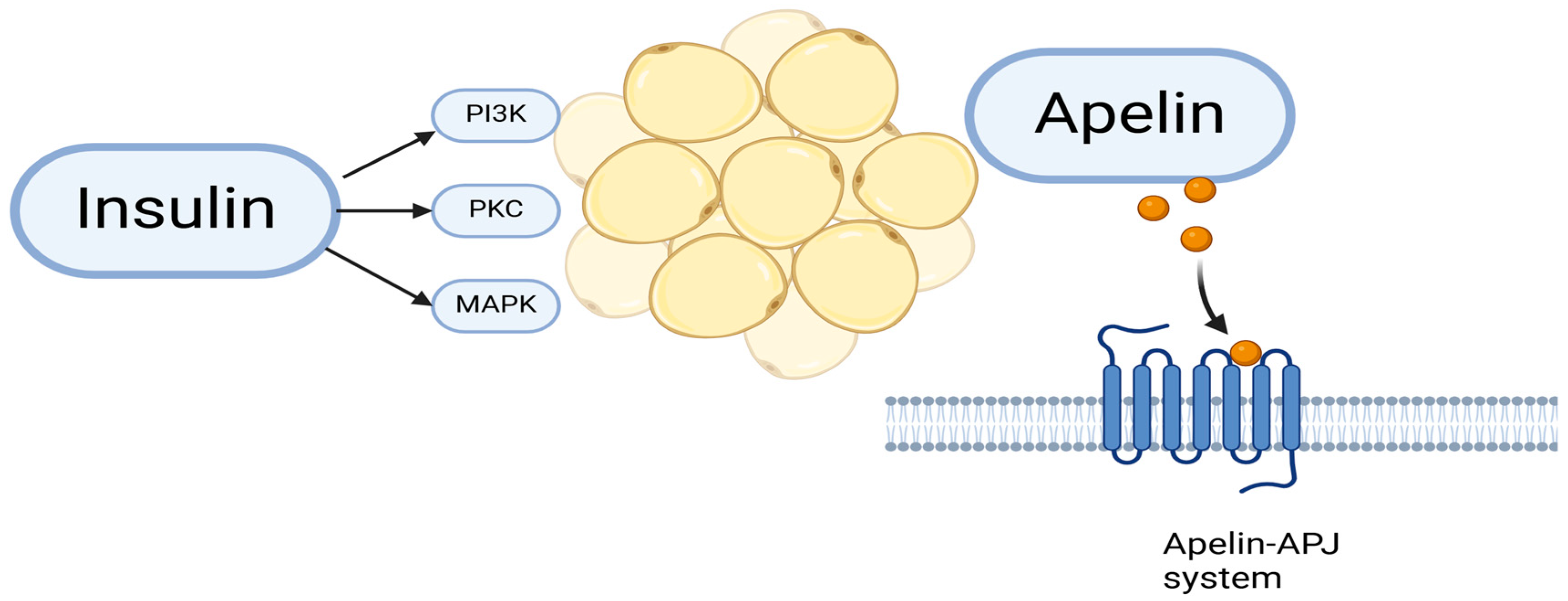
1.5.4. Apelin
1.5.5. Galectin-3
1.6. Recent Advances in Diabetes Treatment: Mechanisms of Action of Novel Drugs
2. Discussion
3. Conclusions
4. Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MetS | Metabolic syndrome |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| IR | Insulin resistance |
| NCEP | The 2001 US National Cholesterol Education Program Adult Treatment Panel III |
| TG | Triglycerides |
| HDL | High-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| BP | Blood pressure |
| IDF | International Diabetes Association |
| FPG | Fasting plasma glucose |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| ADA | American Diabetes Association |
| T2DM | Type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| FFA | Free fatty acid |
| PI3K | Phosphoinositide 3-kinase |
| MAP | Mitogen-activated protein |
| eNOS | Endothelial nitric oxide synthase |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| VLDL | Very low-density lipoproteins |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor alfa |
| TLRs | Toll-like receptors |
| RAS | Renin–angiotensinogen system |
| Ang II | Angiotensin II |
| LOX-1 | Low-density lipoprotein receptor-1 |
| DR | Diabetic retinopathy |
| NPDR | Nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy |
| PDR | Proliferative diabetic retinopathy |
| DPP | Diabetes Prevention Program |
| DN | Diabetic nephropathy |
| ESRD | End-stage renal disease |
| GFR | Glomerular filtration rate |
| DPN | Diabetic polyneuropathy |
| DAN | Diabetic autonomic neuropathy |
| CAN | Cardiac autonomic neuropathy |
| ANGPTL | Angiopoietin-like proteins |
| ANGPLT | Angiopoietin-like protein 3 |
| ANGPLT4 | Angiopoietin-like protein 4 |
| ANGLPT8 | Angiopoietin-like protein 8 |
| LCN2 | Lipocalin-2 |
| MMP-9 | Matrix metalloproteinase |
| NGAL | Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin |
| AGEs | Advanced Glycation End Products |
| CTRPs | C1q tumor necrosis factor-related protein |
| AMPK | AMP-activated protein kinase |
| MCP1 | Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 |
| ICAM1 | Intracellular adhesion molecule 1 |
| APJ | Apelin receptor |
| Gal-3 | Galectin-3 |
| ALEs | Advanced lipoxidation end-products |
| SGLT2 | Sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 |
| NAFLD | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease |
| GLP-1 | Glucagon-like peptide-1 |
| GLP-1 RAs | GLP-1 receptor agonists |
| GIP | Gastric inhibitory polypeptide |
References
- Al-Hamad, D.; Raman, V. Metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents. Transl. Pediatr. 2017, 6, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kassi, E.; Pervanidou, P.; Kaltsas, G.; Chrousos, G. Metabolic syndrome: Definitions and controversies. BMC Med. 2011, 9, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults. Executive Summary of The Third Report of The National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, And Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol In Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). JAMA 2001, 285, 2486–2497. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Definition, Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus and Its Complication; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Balkau, B.; Charles, M.A. Comment on the provisional report from the WHO consultation. European Group for the Study of Insulin Resistance (EGIR). Diabet. Med. 1999, 16, 442–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberti, K.G.; Zimmet, P.; Shaw, J. Metabolic syndrome—a new world-wide definition. A Consensus Statement from the International Diabetes Federation. Diabet. Med. 2006, 23, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grundy, S.M.; Cleeman, J.I.; Daniels, S.R.; Donato, K.A.; Eckel, R.H.; Franklin, B.A.; Gordon, D.J.; Krauss, R.M.; Savage, P.J.; Smith, S.C., Jr.; et al. Diagnosis and management of the metabolic syndrome: An American Heart Association/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Scientific Statement. Circulation 2005, 112, 2735–2752, Erratum in Circulation 2005, 112, e297–e298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regufe, V.M.G.; Pinto, C.M.C.B.; Perez, P.M.V.H.C. Metabolic syndrome in type 2 diabetic patients: A review of current evidence. Porto Biomed. J. 2020, 5, e101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ahmed, M.; Kumari, N.; Mirgani, Z.; Saeed, A.; Ramadan, A.; Ahmed, M.H.; Almobarak, A.O. Metabolic syndrome; Definition, Pathogenesis, Elements, and the Effects of medicinal plants on its elements. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2022, 21, 1011–1022, Erratum in J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2022, 21, 1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Vrdoljak, J.; Kumric, M.; Vilovic, M.; Martinovic, D.; Rogosic, V.; Borovac, J.A.; Ticinovic Kurir, T.; Bozic, J. Can Fasting Curb the Metabolic Syndrome Epidemic? Nutrients 2022, 14, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Li, R.; Li, W.; Lun, Z.; Zhang, H.; Sun, Z.; Kanu, J.S.; Qiu, S.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, Y. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome in Mainland China: A meta-analysis of published studies. BMC Public Health 2016, 16, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Qin, X.; Qiu, L.; Tang, G.; Tsoi, M.F.; Xu, T.; Zhang, L.; Qi, Z.; Zhu, G.; Cheung, B.M.Y. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome among ethnic groups in China. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dekker, J.M.; Girman, C.; Rhodes, T.; Nijpels, G.; Stehouwer, C.D.; Bouter, L.M.; Heine, R.J. Metabolic syndrome and 10-year cardiovascular disease risk in the Hoorn Study. Circulation 2005, 112, 666–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Yu, B.; Yu, W.; Dai, S.; Feng, C.; Shao, Y.; Zhao, X.; Li, X.; He, T.; Jia, P. Development and validation of an age-sex-ethnicity-specific metabolic syndrome score in the Chinese adults. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Asghar, S.; Asghar, S.; Shahid, S.; Fatima, M.; Bukhari, S.M.H.; Nadeem Siddiqui, S. Metabolic Syndrome in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients: Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Associated Microvascular Complications. Cureus 2023, 15, e39076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gupta, A.; Gupta, V. Metabolic syndrome: What are the risks for humans? Biosci. Trends 2010, 4, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sulistiyowati, N.; Sudikno, S.; Nainggolan, O.; Titaley, C.R.; Adyarani, W.P.; Hapsari, D. Risk factors for the metabolic syndrome in non-obese older Indonesians. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 31, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahed, G.; Aoun, L.; Bou Zerdan, M.; Allam, S.; Bou Zerdan, M.; Bouferraa, Y.; Assi, H.I. Metabolic Syndrome: Updates on Pathophysiology and Management in 2021. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rochlani, Y.; Pothineni, N.V.; Kovelamudi, S.; Mehta, J.L. Metabolic syndrome: Pathophysiology, management, and modulation by natural compounds. Ther. Adv. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2017, 11, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Xu, H.; Li, X.; Adams, H.; Kubena, K.; Guo, S. Etiology of Metabolic Syndrome and Dietary Intervention. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 20, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Boden, G.; Shulman, G.I. Free fatty acids in obesity and type 2 diabetes: Defining their role in the development of insulin resistance and beta-cell dysfunction. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 32 (Suppl. 3), 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.L. A comprehensive definition for metabolic syndrome. Dis. Model. Mech. 2009, 2, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tripathy, D.; Mohanty, P.; Dhindsa, S.; Syed, T.; Ghanim, H.; Aljada, A.; Dandona, P. Elevation of free fatty acids induces inflammation and impairs vascular reactivity in healthy subjects. Diabetes 2003, 52, 2882–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, T.; Michelagnoli, S.; Longhi, R.; Gianfranceschi, G.; Pazzucconi, F.; Calabresi, L.; Sirtori, C.R.; Franceschini, G. Triglycerides are major determinants of cholesterol esterification/transfer and HDL remodeling in human plasma. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1995, 15, 1819–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, K. Adipokines: Therapeutic targets for metabolic syndrome. Curr. Drug Targets 2005, 6, 525–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotamisligil, G.S.; Murray, D.L.; Choy, L.N.; Spiegelman, B.M. Tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibits signaling from the insulin receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 4854–4858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ridker, P.M.; Howard, C.P.; Walter, V.; Everett, B.; Libby, P.; Hensen, J.; Thuren, T.; CANTOS Pilot Investigative Group. Effects of interleukin-1β inhibition with canakinumab on hemoglobin A1c, lipids, C-reactive protein, interleukin-6, and fibrinogen: A phase IIb randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Circulation 2012, 126, 2739–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: Update on Toll-like receptors. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Kokoeva, M.V.; Inouye, K.; Tzameli, I.; Yin, H.; Flier, J.S. TLR4 links innate immunity and fatty acid-induced insulin resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 3015–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Saiki, A.; Ohira, M.; Endo, K.; Koide, N.; Oyama, T.; Murano, T.; Watanabe, H.; Miyashita, Y.; Shirai, K. Circulating angiotensin II is associated with body fat accumulation and insulin resistance in obese subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Metabolism 2009, 58, 708–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, R.M.M.; Chua, Z.J.Y.; Tan, J.C.; Yang, Y.; Liao, Z.; Zhao, Y. From Pre-Diabetes to Diabetes: Diagnosis, Treatments and Translational Research. Medicina 2019, 55, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Crasto, W.; Patel, V.; Davies, M.J.; Khunti, K. Prevention of Microvascular Complications of Diabetes. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 50, 431–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brannick, B.; Wynn, A.; Dagogo-Jack, S. Prediabetes as a toxic environment for the initiation of microvascular and macrovascular complications. Exp. Biol. Med. 2016, 241, 1323–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, C.; Shi, K.; Yin, X. Relationship between dyslipidemia and diabetic retinopathy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2018, 97, e12283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiello, L.M. Perspectives on diabetic retinopathy. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2003, 136, 122–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uppamma, P.; Bhattacharya, S. A multidomain bio-inspired feature extraction and selection model for diabetic retinopathy severity classification: An ensemble learning approach. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 18572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wang, W.; Lo, A.C.Y. Diabetic Retinopathy: Pathophysiology and Treatments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lin, K.Y.; Hsih, W.H.; Lin, Y.B.; Wen, C.Y.; Chang, T.J. Update in the epidemiology, risk factors, screening, and treatment of diabetic retinopathy. J. Diabetes Investig. 2021, 12, 1322–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Diabetes Prevention Program Research Group. The prevalence of retinopathy in impaired glucose tolerance and recent-onset diabetes in the Diabetes Prevention Program. Diabet. Med. 2007, 24, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Peng, X.Y.; Wang, F.H.; Liang, Y.B.; Wang, J.J.; Sun, L.P.; Peng, Y.; Friedman, D.S.; Liew, G.; Wang, N.L.; Wong, T.Y. Retinopathy in persons without diabetes: The Handan Eye Study. Ophthalmology 2010, 117, 531–537.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Yue, S.; Wu, J.; Zhang, J.; Lian, J.; Teng, W.; Huang, D.; Chen, L. Prevalence and risk factors of retinopathy in patients with or without metabolic syndrome: A population-based study in Shenyang. BMJ Open 2015, 5, e008855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mbata, O.; Abo El-Magd, N.F.; El-Remessy, A.B. Obesity, metabolic syndrome and diabetic retinopathy: Beyond hyperglycemia. World J. Diabetes 2017, 8, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- de Boer, I.H.; Rue, T.C.; Hall, Y.N.; Heagerty, P.J.; Weiss, N.S.; Himmelfarb, J. Temporal trends in the prevalence of diabetic kidney disease in the United States. JAMA 2011, 305, 2532–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Maric, C.; Hall, J.E. Obesity, metabolic syndrome and diabetic nephropathy. Contrib. Nephrol. 2011, 170, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Szostak, J.; Gorący, A.; Durys, D.; Dec, P.; Modrzejewski, A.; Pawlik, A. The Role of MicroRNA in the Pathogenesis of Diabetic Nephropathy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Thipsawat, S. Early detection of diabetic nephropathy in a patient with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A review of the literature. Diabetes Vasc. Dis. Res. 2021, 18, 14791641211058856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Samsu, N. Diabetic Nephropathy: Challenges in Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 1497449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pop-Busui, R.; Boulton, A.J.M.; Feldman, E.L.; Bril, V.; Freeman, R.; Malik, R.A.; Sosenko, J.M.; Ziegler, D. Diabetic Neuropathy: A Position Statement by the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 136–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faselis, C.; Katsimardou, A.; Imprialos, K.; Deligkaris, P.; Kallistratos, M.; Dimitriadis, K. Microvascular Complications of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2020, 18, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stino, A.M.; Smith, A.G. Peripheral neuropathy in prediabetes and the metabolic syndrome. J. Diabetes Investig. 2017, 8, 646–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Verrotti, A.; Prezioso, G.; Scattoni, R.; Chiarelli, F. Autonomic Neuropathy in Diabetes Mellitus. Front. Endocrinol. 2014, 5, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinik, A.I.; Maser, R.E.; Mitchell, B.D.; Freeman, R. Diabetic autonomic neuropathy. Diabetes Care 2003, 26, 1553–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2017: Summary of Revisions. Diabetes Care 2017, 40 (Suppl. 1), S4–S5. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serhiyenko, V.A.; Serhiyenko, A.A. Cardiac autonomic neuropathy: Risk factors, diagnosis and treatment. World J. Diabetes 2018, 9, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Peng, Y.; Jin, J.; Chen, Y.; Chen, C.; Chen, Z.; Huang, H.; Xu, L. Insulin resistance is independently associated with cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy in type 2 diabetes. J. Diabetes Investig. 2021, 12, 1651–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, P.K.; Barzilay, J.I.; Domitrovich, P.P.; Chaves, P.M.; Gottdiener, J.S.; Heckbert, S.R.; Kronmal, R.A. The relationship of heart rate and heart rate variability to non-diabetic fasting glucose levels and the metabolic syndrome: The Cardiovascular Health Study. Diabet. Med. 2007, 24, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laitinen, T.; Lindström, J.; Eriksson, J.; Ilanne-Parikka, P.; Aunola, S.; Keinänen-Kiukaanniemi, S.; Tuomilehto, J.; Uusitupa, M. Cardiovascular autonomic dysfunction is associated with central obesity in persons with impaired glucose tolerance. Diabet. Med. 2011, 28, 699–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammedsaeed, W.; Ahmed, A.; Alharbi, N.; Aljohani, A.; Alruwaithi, R.; Alharbi, R.; Alahmadi, S. Evaluation of Adiponectin and ANGPTL8 in Women With Metabolic Syndrome in the Madinah Region of Saudi Arabia. Cureus 2023, 15, e44219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Morelli, M.B.; Chavez, C.; Santulli, G. Angiopoietin-like proteins as therapeutic targets for cardiovascular disease: Focus on lipid disorders. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2020, 24, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Aryal, B.; Singh, A.K.; Zhang, X.; Varela, L.; Rotllan, N.; Goedeke, L.; Chaube, B.; Camporez, J.P.; Vatner, D.F.; Horvath, T.L.; et al. Absence of ANGPTL4 in adipose tissue improves glucose tolerance and attenuates atherogenesis. JCI Insight. 2018, 3, e97918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jonker, J.T.; Smit, J.W.; Hammer, S.; Snel, M.; van der Meer, R.W.; Lamb, H.J.; Mattijssen, F.; Mudde, K.; Jazet, I.M.; Dekkers, O.M.; et al. Dietary modulation of plasma angiopoietin-like protein 4 concentrations in healthy volunteers and in patients with type 2 diabetes. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 97, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, S.; He, Y.; Tiheiran, M.; Liu, W.; Guo, H. The Angiopoietin-like protein 4: A promising biomarker to distinguish brucella spondylitis from tuberculous spondylitis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2021, 40, 4289–4294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Al Shawaf, E.; Abu-Farha, M.; Devarajan, S.; Alsairafi, Z.; Al-Khairi, I.; Cherian, P.; Ali, H.; Mathur, A.; Al-Mulla, F.; Al Attar, A.; et al. ANGPTL4: A Predictive Marker for Diabetic Nephropathy. J. Diabetes Res. 2019, 2019, 4943191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lu, Q.; Lu, P.; Chen, W.; Lu, L.; Zheng, Z. ANGPTL-4 induces diabetic retinal inflammation by activating Profilin-1. Exp. Eye Res. 2018, 166, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Linghu, M.; Hu, W.; Huang, X. Conbercept improves macular microcirculation and retinal blood supply in the treatment of nonischemic branch retinal vein occlusion macular edema. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2022, 36, e24774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Xin, X.; Rodrigues, M.; Umapathi, M.; Kashiwabuchi, F.; Ma, T.; Babapoor-Farrokhran, S.; Wang, S.; Hu, J.; Bhutto, I.; Welsbie, D.S.; et al. Hypoxic retinal Muller cells promote vascular permeability by HIF-1-dependent up-regulation of angiopoietin-like 4. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E3425–E3434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kovrov, O.; Kristensen, K.K.; Larsson, E.; Ploug, M.; Olivecrona, G. On the mechanism of angiopoietin-like protein 8 for control of lipoprotein lipase activity. J. Lipid Res. 2019, 60, 783–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bini, S.; D’Erasmo, L.; Di Costanzo, A.; Minicocci, I.; Pecce, V.; Arca, M. The Interplay between Angiopoietin-Like Proteins and Adipose Tissue: Another Piece of the Relationship between Adiposopathy and Cardiometabolic Diseases? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Nidhina Haridas, P.A.; Soronen, J.; Sädevirta, S.; Mysore, R.; Quagliarini, F.; Pasternack, A.; Metso, J.; Perttilä, J.; Leivonen, M.; Smas, C.M.; et al. Regulation of Angiopoietin-Like Proteins (ANGPTLs) 3 and 8 by Insulin. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, E1299–E1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.; Cao, S.; Wang, X. Betatrophin and Insulin Resistance. Metabolites 2022, 12, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Guo, C.; Wang, C.; Deng, X.; He, J.; Yang, L.; Yuan, G. ANGPTL8 in metabolic homeostasis: More friend than foe? Open Biol. 2021, 11, 210106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- AlMajed, H.T.; Abu-Farha, M.; Alshawaf, E.; Devarajan, S.; Alsairafi, Z.; Elhelaly, A.; Cherian, P.; Al-Khairi, I.; Ali, H.; Jose, R.M.; et al. Increased Levels of Circulating IGFBP4 and ANGPTL8 with a Prospective Role in Diabetic Nephropathy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bauer, C.; Sim, M.; Prince, R.L.; Zhu, K.; Lim, E.M.; Byrnes, E.; Pavlos, N.; Lim, W.H.; Wong, G.; Lewis, J.R.; et al. Circulating lipocalin-2 and features of metabolic syndrome in community-dwelling older women: A cross-sectional study. Bone 2023, 176, 116861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaberi, S.A.; Cohen, A.; D’Souza, C.; Abdulrazzaq, Y.M.; Ojha, S.; Bastaki, S.; Adeghate, E.A. Lipocalin-2: Structure, function, distribution and role in metabolic disorders. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 142, 112002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romejko, K.; Markowska, M.; Niemczyk, S. The Review of Current Knowledge on Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin (NGAL). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wu, G.; Li, H.; Zhou, M.; Fang, Q.; Bao, Y.; Xu, A.; Jia, W. Mechanism and clinical evidence of lipocalin-2 and adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein linking obesity and atherosclerosis. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2014, 30, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosialou, I.; Shikhel, S.; Liu, J.-M.; Maurizi, A.; Luo, N.; He, Z.; Huang, Y.; Zong, H.; Friedman, R.A.; Barasch, J.; et al. MC4R-dependent suppression of appetite by bone-derived lipocalin 2. Nature 2017, 543, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malyszko, J.; Bachorzewska-Gajewska, H.; Malyszko, J.S.; Pawlak, K.; Dobrzycki, S. Serum neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a marker of renal function in hypertensive and normotensive patients with coronary artery disease. Nephrology 2008, 13, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araos, P.; Amador, C.A. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as an immunomodulator in endocrine hypertension. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1006790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wang, H.; Lou, H.; Li, Y.; Ji, F.; Chen, W.; Lu, Q.; Xu, G. Elevated vitreous Lipocalin-2 levels of patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy. BMC Ophthalmol. 2020, 20, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, L.; Keshtkar Rajabi, S.; Pirsaheb, S.; Keyvani, H.; Khajavi, A.; Shati, M.; Hadavand, F.; Amouzegar, A. Assessment of Serum and Urine Neurophil Gelatinase- Associated Lipocalin (s-NGAL and u-NGAL) Level as a Predictive Factor of Disease Progression in Diabetic Nephropathy in Type 2 DM. Iran J. Kidney Dis. 2021, 15, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gan, J.; Zheng, Y.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, W.; Shi, Y.; Yu, N.; Yan, Y.; Lin, Z.; Yang, H. Serum Lipocalin-2 Levels Are Increased and Independently Associated With Early-Stage Renal Damage and Carotid Atherosclerotic Plaque in Patients With T2DM. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 855616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhusal, A.; Lee, W.H.; Suk, K. Lipocalin-2 in Diabetic Complications of the Nervous System: Physiology, Pathology, and Beyond. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 638112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Albert, C.; Zapf, A.; Haase, M.; Röver, C.; Pickering, J.W.; Albert, A.; Bellomo, R.; Breidthardt, T.; Camou, F.; Chen, Z.; et al. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin measured on clinical laboratory platforms for the prediction of acute kidney injury and the associated need for dialysis therapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2020, 76, 826–841.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Şen, S.; Özalp Kızılay, D.; Taneli, F.; Özen, Ç.; Ertan, P.; Özunan, İ.; Yıldız, R.; Ersoy, B. Urinary NGAL is a Potential Biomarker for Early Renal Injury in Insulin Resistant Obese Non-diabetic Children. J. Clin. Res. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2021, 13, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Peterson, J.M.; Aja, S.; Wei, Z.; Wong, G.W. CTRP1 protein enhances fatty acid oxidation via AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activation and acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) inhibition. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 1576–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Si, Y.; Fan, W.; Sun, L. A Review of the Relationship Between CTRP Family and Coronary Artery Disease. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2020, 22, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Schanbacher, C.; Hermanns, H.M.; Lorenz, K.; Wajant, H.; Lang, I. Complement 1q/Tumor Necrosis Factor-Related Proteins (CTRPs): Structure, Receptors and Signaling. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rodriguez, S.; Lei, X.; Petersen, P.S.; Tan, S.Y.; Little, H.C.; Wong, G.W. Loss of CTRP1 disrupts glucose and lipid homeostasis. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 311, E678–E697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yagmur, E.; Buergerhausen, D.; Koek, G.H.; Weiskirchen, R.; Trautwein, C.; Koch, A.; Tacke, F. Elevated CTRP1 Plasma Concentration Is Associated with Sepsis and Pre-Existing Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Critically Ill Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Weigert, J.; Neumeier, M.; Schäffler, A.; Fleck, M.; Schölmerich, J.; Schütz, C.; Buechler, C. The adiponectin paralog CORS-26 has anti-inflammatory properties and is produced by human monocytic cells. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 5565–5570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, K.M.; Hwang, S.Y.; Hong, H.C.; Choi, H.Y.; Yoo, H.J.; Youn, B.S.; Baik, S.H.; Seo, H.S. Implications of C1q/TNF-related protein-3 (CTRP-3) and progranulin in patients with acute coronary syndrome and stable angina pectoris. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2014, 13, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Peterson, J.M.; Wei, Z.; Wong, G.W. C1q/TNF-related protein-3 (CTRP3), a novel adipokine that regulates hepatic glucose output. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 39691–39701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Choi, K.M.; Hwang, S.Y.; Hong, H.C.; Yang, S.J.; Choi, H.Y.; Yoo, H.J.; Lee, K.W.; Nam, M.S.; Park, Y.S.; Woo, J.T.; et al. C1q/TNF-related protein-3 (CTRP-3) and pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) concentrations in patients with type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome. Diabetes 2012, 61, 2932–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lin, K.; Yang, L.; Xiong, Y.; Feng, K.; Zeng, W.; Deng, B. Plasma C1q/tumor necrosis factor-related protein-3 concentrations are associated with diabetic peripheral neuropathy. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2022, 10, e002746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wong, G.W.; Krawczyk, S.A.; Kitidis-Mitrokostas, C.; Ge, G.; Spooner, E.; Hug, C.; Gimeno, R.; Lodish, H.F. Identification and characterization of CTRP9, a novel secreted glycoprotein, from adipose tissue that reduces serum glucose in mice and forms heterotrimers with adiponectin. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 241–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yang, J.; Zhao, D.; Chen, Y.; Ma, Y.; Shi, X.; Wang, X.; Lv, Y.; Yuan, H. Association of serum CTRP9 levels with cardiac autonomic neuropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Diabetes Investig. 2021, 12, 1442–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Li, W.; Ma, N.; Liu, M.X.; Ye, B.J.; Li, Y.J.; Hu, H.Y.; Tang, Y.H. C1q/TNF-related protein-9 attenuates retinal inflammation and protects blood-retinal barrier in db/db mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 853, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Li, W.; Liu, M.; Xiong, J.; Li, Y.; Wei, Y.; Huang, C.; Tang, Y. C1q/Tumor Necrosis Factor-Related Protein-9 Attenuates Diabetic Nephropathy and Kidney Fibrosis in db/db Mice. DNA Cell Biol. 2020, 39, 938–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, R.M.; Steele, K.E.; Peterson, L.A.; Zeng, X.; Jaffe, A.E.; Schweitzer, M.A.; Magnuson, T.H.; Wong, G.W. C1q/TNF-Related Protein-9 (CTRP9) Levels Are Associated With Obesity and Decrease Following Weight Loss Surgery. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 2211–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Li, C.; Cheng, H.; Adhikari, B.K.; Wang, S.; Yang, N.; Liu, W.; Sun, J.; Wang, Y. The Role of Apelin-APJ System in Diabetes and Obesity. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 820002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Estienne, A.; Bongrani, A.; Reverchon, M.; Ramé, C.; Ducluzeau, P.H.; Froment, P.; Dupont, J. Involvement of Novel Adipokines, Chemerin, Visfatin, Resistin and Apelin in Reproductive Functions in Normal and Pathological Conditions in Humans and Animal Models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhang, M.; Peng, F.; Lin, L.; Yu, M.; Huang, C.; Hu, D.; Guo, Q.; Xu, C.; Lin, J. Association study of apelin-APJ system genetic polymorphisms with incident metabolic syndrome in a Chinese population: A case-control study. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 3807–3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mund, C.; Kellellu, C.K.; Rattan, R.; Mahapatra, S.; Lamare, A.A.; Jena, S. Study of Serum Apelin and Insulin Resistance in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients With or Without Obesity. Cureus 2023, 15, e43401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Boucher, J.; Masri, B.; Daviaud, D.; Gesta, S.; Guigné, C.; Mazzucotelli, A.; Castan-Laurell, I.; Tack, I.; Knibiehler, B.; Carpéné, C.; et al. Apelin, a newly identified adipokine up-regulated by insulin and obesity. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 1764–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaki, M.; Kamal, S.; Ezzat, W.; Hassan, N.; Yousef, W.; Ryad, H.; Mohamed, R.; Youness, E.; Basha, W.; Elhosary, Y. Serum apelin levels and metabolic risk markers in obese women. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2017, 15, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Soriguer, F.; Garrido-Sanchez, L.; Garcia-Serrano, S.; Garcia-Almeida, J.M.; Garcia-Arnes, J.; Tinahones, F.J.; Garcia-Fuentes, E. Apelin levels are increased in morbidly obese subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Obes. Surg. 2009, 19, 1574–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelova, P.; Kamenov, Z.; Tsakova, A. Apelin and testosterone levels in men with metabolic syndrome. Open J. Endocr. Metab. Dis. 2014, 4, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Karbek, B.; Bozkurt, N.C.; Topaloglu, O.; Aslan, M.S.; Gungunes, A.; Cakal, E.; Delibasi, T. Relationship of vaspin and apelin levels with insulin resistance and atherosclerosis in metabolic syndrome. Minerva Endocrinol. 2014, 39, 99–105. [Google Scholar]
- Onalan, E.; Yakar, B.; Barım, A.O.; Gursu, M.F. Serum apelin and resistin levels in patients with impaired fasting glucose, impaired glucose tolerance, type 2 diabetes, and metabolic syndrome. Endokrynol. Pol. 2020, 71, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, J.H. Interleukin-1β induces pericyte apoptosis via the NF-κB pathway in diabetic retinopathy. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 546, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Yang, W.; Luan, F.; Ma, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, L.; Hu, X.; Tao, Y. The Protective Role of Apelin in the Early Stages of Diabetic Retinopathy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Che, X.Q.; Liu, X.; Zhao, S.; Wang, S. Clinical significance of apelin in the treatment of type 2 diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Medicine 2021, 100, e25710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ionin, V.A.; Baranova, E.I.; Zaslavskaya, E.L.; Petrishcheva, E.Y.; Morozov, A.N.; Shlyakhto, E.V. Galectin-3, N-terminal Propeptides of Type I and III Procollagen in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation and Metabolic Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kumar, S.; Ranawat, C.S.; Bhandiwad, C.; Arya, H.; Mali, M.; Singh, C.P.; Sharma, N.; Lathwal, N.; Wasim, S. Galectin-3 as a Potential Biomarker of Microvascular Complications in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 26, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Li, M.; Tian, M.; Wang, Y.; Ma, H.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, X.; Liu, Y. Association of plasma galectin-3 and fetuin-A levels with diabetic retinopathy in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Endokrynol. Pol. 2023, 74, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodeib, H.; Hagras, M.M.; Abdelhai, D.; Watany, M.M.; Selim, A.; Tawfik, M.A.; Elsebaey, M.A.; Elshweikh, S.A. Galectin-3 as a prognostic biomarker for diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2019, 12, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Li, P.; Liu, S.; Lu, M.; Bandyopadhyay, G.; Oh, D.; Imamura, T.; Johnson, A.M.F.; Sears, D.; Shen, Z.; Cui, B.; et al. Hematopoietic-Derived Galectin-3 Causes Cellular and Systemic Insulin Resistance. Cell 2016, 167, 973–984.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hara, A.; Niwa, M.; Noguchi, K.; Kanayama, T.; Niwa, A.; Matsuo, M.; Hatano, Y.; Tomita, H. Galectin-3 as a Next-Generation Biomarker for Detecting Early Stage of Various Diseases. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Aderinto, N.; Abdulbasit, M.O.; Olatunji, D.; Edun, M. Unveiling the potential of galectin-3 as a diagnostic biomarker for pancreatic cancer: A review. Ann. Med. Surg. 2023, 85, 5557–5567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Menini, S.; Iacobini, C.; Blasetti Fantauzzi, C.; Pesce, C.M.; Pugliese, G. Role of Galectin-3 in Obesity and Impaired Glucose Homeostasis. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 9618092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yilmaz, H.; Cakmak, M.; Inan, O.; Darcin, T.; Akcay, A. Increased levels of galectin-3 were associated with prediabetes and diabetes: New risk factor? J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2015, 38, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pugliese, G.; Iacobini, C.; Pesce, C.M.; Menini, S. Galectin-3: An emerging all-out player in metabolic disorders and their complications. Glycobiology 2015, 25, 136–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Q.H.; Lou, Y.F.; Li, T.L.; Chen, H.H.; Liu, Q.; He, X.J. Serum galectin-3: A risk factor for vascular complications in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Chin. Med. J. 2013, 126, 2109–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivian, E.M. Sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors: A growing class of antidiabetic agents. Drugs Context 2014, 3, 212264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dai, Z.C.; Chen, J.X.; Zou, R.; Liang, X.B.; Tang, J.X.; Yao, C.W. Role and mechanisms of SGLT-2 inhibitors in the treatment of diabetic kidney disease. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1213473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Młynarska, E.; Czarnik, W.; Dzieża, N.; Jędraszak, W.; Majchrowicz, G.; Prusinowski, F.; Stabrawa, M.; Rysz, J.; Franczyk, B. Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: New Pathogenetic Mechanisms, Treatment and the Most Important Complications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Joumaa, J.P.; Raffoul, A.; Sarkis, C.; Chatrieh, E.; Zaidan, S.; Attieh, P.; Harb, F.; Azar, S.; Ghadieh, H.E. Mechanisms, Biomarkers, and Treatment Approaches for Diabetic Kidney Disease: Current Insights and Future Perspectives. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Scardini, P.G.; Shih Katsuyama, E.; Armani Prata, A.; Marques Fernandes, J.; Ken Fukunaga, C.; Falco Neto, W.; Covre Coan, A.C.; Machado de Andrade, N.; Santana Silva, A.; Petri Pinheiro, R.; et al. Impact of sodium–glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors in patients with recent versus previous myocardial infarction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2025, 24, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Li, H.; Hou, Y.; Xin, W.; Ding, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, W.; Wang, Z.; Ding, W. The efficacy of sodium-glucose transporter 2 inhibitors in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Pharmacol. Res. 2025, 213, 107647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madsbad, S. Review of head-to-head comparisons of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2016, 18, 317–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Moiz, A.; Filion, K.B.; Tsoukas, M.A.; Yu, O.H.; Peters, T.M.; Eisenberg, M.J. Mechanisms of GLP-1 receptor agonist-induced weight loss: A review of central and peripheral pathways in appetite and energy regulation. Am. J. Med. 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alharbi, S.H. Anti-inflammatory role of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists and its clinical implications. Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 15, 20420188231222367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, H.; Ye, H.; Wang, R.; Ma, C.; Duo, T.; Wang, J.; Yang, X.; Yu, M.; et al. SGLT2 inhibitor downregulates ANGPTL4 to mitigate pathological aging of cardiomyocytes induced by type 2 diabetes. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2024, 23, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Darawshi, S.; Yaseen, H.; Gorelik, Y.; Faor, C.; Szalat, A.; Abassi, Z.; Heyman, S.N.; Khamaisi, M. Biomarker evidence for distal tubular damage but cortical sparing in hospitalized diabetic patients with acute kidney injury (AKI) while on SGLT2 inhibitors. Ren. Fail. 2020, 42, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Garbuzova Striukova, E.V.; Shramko, V.S.; Kashtanova, E.V.; Polonskaya, Y.V.; Stakhneva, E.M.; Kurguzov, A.V.; Murashov, I.S.; Chernyavsky, A.M.; Ragino, Y.I. Adipokine-Cytokine Profile in Patients with Unstable Atherosclerotic Plaques and Abdominal Obesity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Berezin, A.A.; Fushtey, I.M.; Berezin, A.E. The Effect of SGLT2 Inhibitor Dapagliflozin on Serum Levels of Apelin in T2DM Patients with Heart Failure. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nikolova, D.; Kamenov, Z. New Markers for the Assessment of Microvascular Complications in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome. Metabolites 2025, 15, 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15030184
Nikolova D, Kamenov Z. New Markers for the Assessment of Microvascular Complications in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome. Metabolites. 2025; 15(3):184. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15030184
Chicago/Turabian StyleNikolova, Diana, and Zdravko Kamenov. 2025. "New Markers for the Assessment of Microvascular Complications in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome" Metabolites 15, no. 3: 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15030184
APA StyleNikolova, D., & Kamenov, Z. (2025). New Markers for the Assessment of Microvascular Complications in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome. Metabolites, 15(3), 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15030184





