Development of New Predictive Equations for the Resting Metabolic Rate (RMR) of Women with Lipedema
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Body Composition and Anthropometry
2.3. RMR Measurement
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.4.1. Machine Learning Model
2.4.2. Model Evaluation
3. Results
3.1. Soft Vector Regression (SVR)
3.2. Random Forest Regression (RFR)
3.3. k-Nearest Neighbor (kNN) Regression
3.4. Ridge Regression
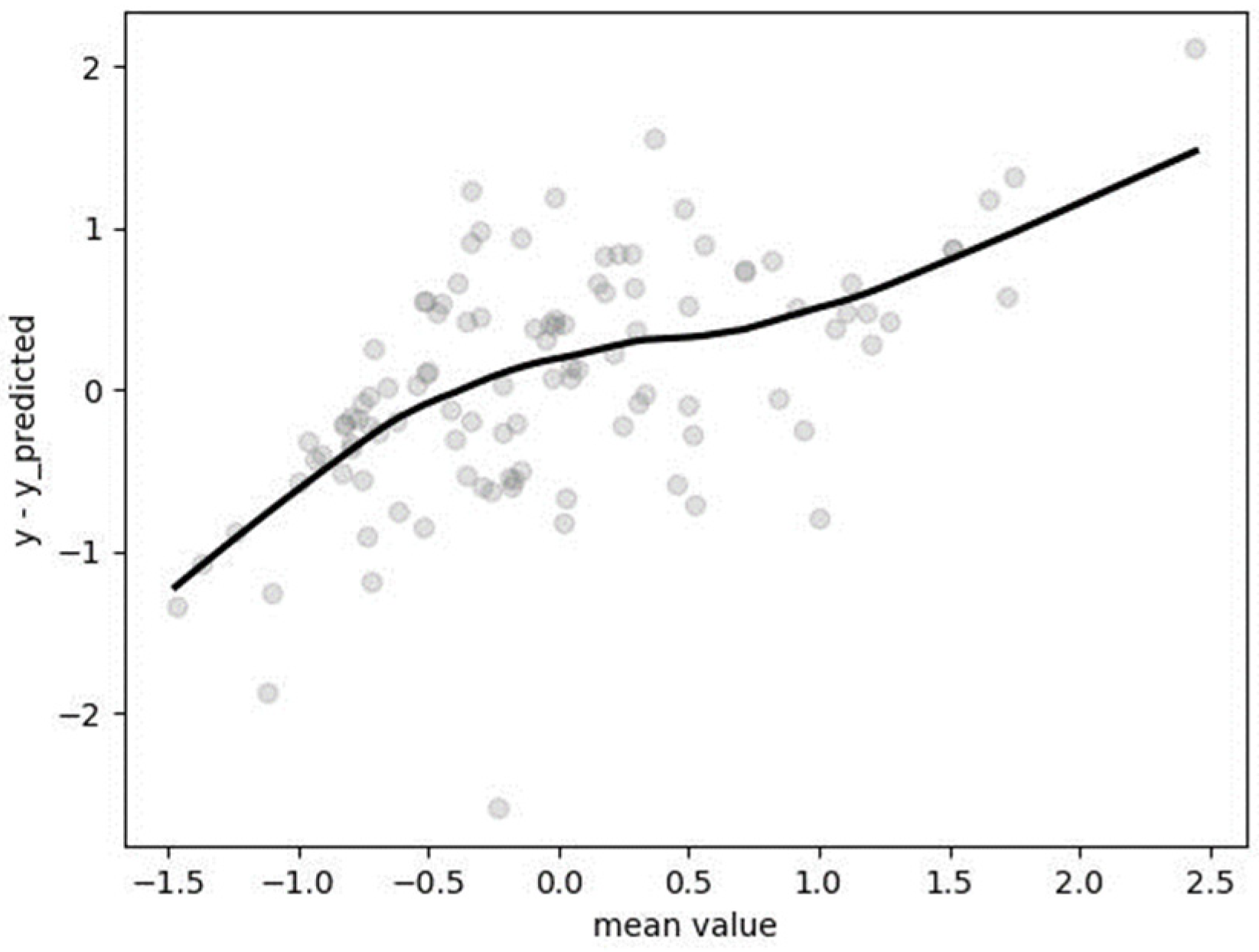
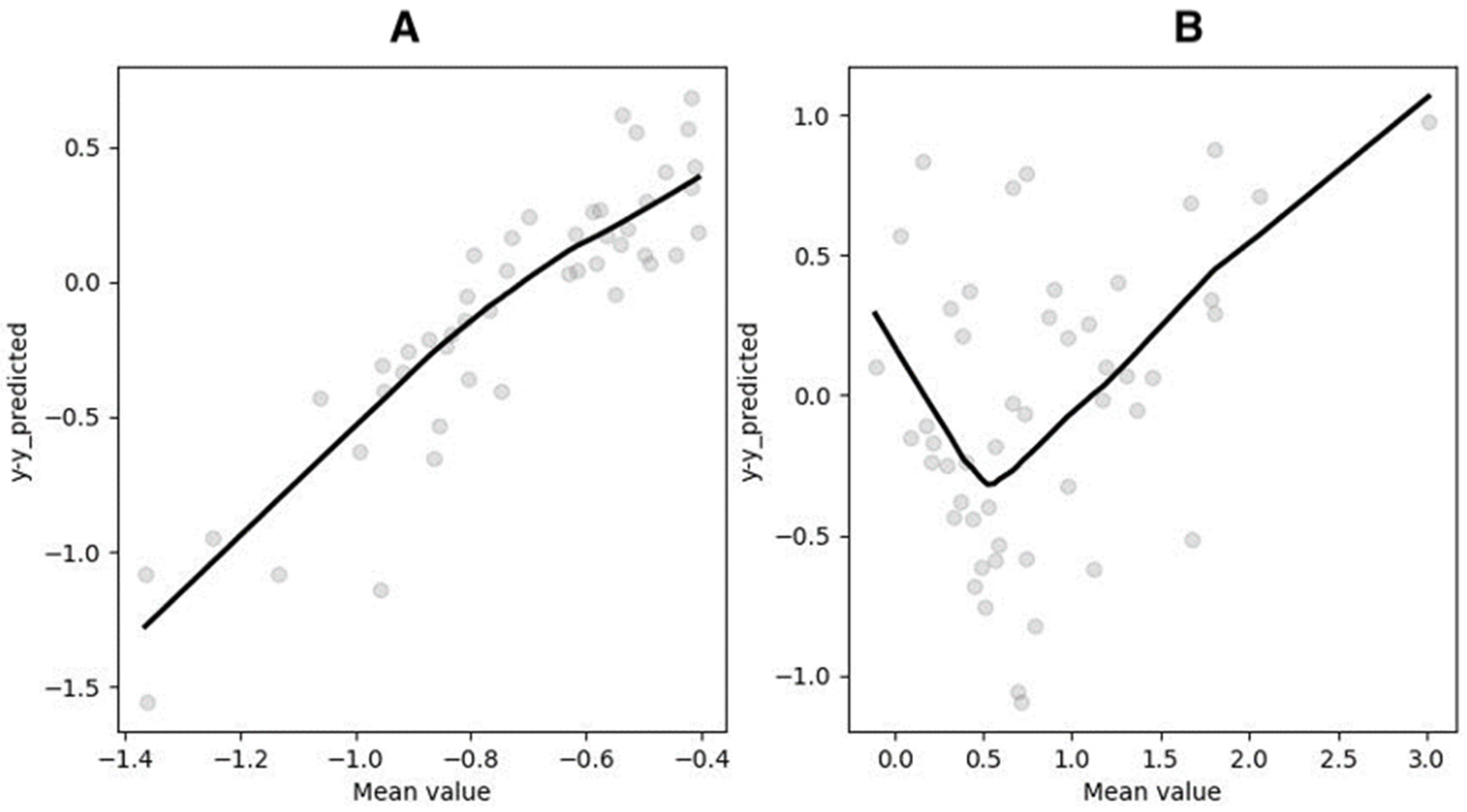
3.5. Segmented Regression (SR)
if
0.0482 × PC1st + 0.0452 × PC2st + 0.0509 × PC3st − 0.600 ≤ −0.0567
RMRst = 0.2160 × PC1st + 0.2184 × PC2st + 0.2116 × PC3st + 0.4945 otherwise
if
0.0482 × PC1st + 0.0452 × PC2st + 0.0509 × PC3st − 0.6000 ≤ −0.0567
RMR = (0.2160 × PC1st + 0.2184 × PC2st + 0.2116 × PC3st + 0.4945) × σRMR + xRMR otherwise
if
0.0482 × PC1st + 0.0452 × PC2st + 0.0509 × PC3st − 0.600 ≤ −0.0567
RMR = (0.2160 × PC1st + 0.2184 × PC2st + 0.2116 × PC3st + 0.4945) × 310.5558 + 1693.5234 otherwise
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Argyrakopoulou, G.; Fountouli, N.; Dalamaga, M.; Kokkinos, A. Revisiting Resting Metabolic Rate: What is the Relation to Weight Fluctuations? Curr. Obes. Rep. 2023, 12, 502–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wounds UK. Best Practice Guidelines: The Management of Lipoedema; Wounds UK: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ernst, A.M.; Bauer, H.; Bauer, H.C.; Steiner, M.; Malfertheiner, A.; Lipp, A.T. Lipedema Research—Quo Vadis? J. Pers. Med. 2022, 13, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbst, K.L.; Kahn, L.A.; Iker, E.; Ehrlich, C.; Wright, T.; McHutchison, L.; Schwartz, J.; Sleigh, M.; Donahue, P.M.; Lisson, K.H.; et al. Standard of Care for Lipedema in the United States. Phlebology 2021, 36, 779–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruppa, P.; Georgiou, I.; Biermann, N.; Prantl, L.; Klein-Weigel, P.; Ghods, M. Lipedema—Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Dtsch. Ärzteblatt Int. 2020, 117, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Child, A.H.; Gordon, K.D.; Sharpe, P.; Brice, G.; Ostergaard, P.; Jeffery, S.; Mortimer, P.S. Lipedema: An inherited condition. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2010, 152A, 970–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertsch, T.; Erbacher, G.; Corda, D.; Damstra, R.J.; van Duinen, K.; Elwell, R.; van Esch-Smeenge, J.; Faerber, G.; Fetzer, S.; Fink, J.; et al. Lipoedema—Myths and facts, Part 5: European Best Practice of Lipoedema—Summary of the European Lipoedema Forum consensus. Phlebologie 2020, 49, 31–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halk, A.B.; Damstra, R.J. First Dutch guidelines on lipedema using the international classification of functioning, disability and health. Phlebology 2017, 32, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertsch, T.; Erbacher, G.; Elwell, R. Lipoedema: A paradigm shift and consensus. J. Wound Care 2020, 29, 1–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlidou, E.; Papadopoulou, S.K.; Seroglou, K.; Giaginis, C. Revised Harris–Benedict Equation: New Human Resting Metabolic Rate Equation. Metabolites 2023, 13, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siedler, M.R.; De Souza, M.J.; Albracht-Schulte, K.; Sekiguchi, Y.; Tinsley, G.M. The Influence of Energy Balance and Availability on Resting Metabolic Rate: Implications for Assessment and Future Research Directions. Sports Med. 2023, 53, 1507–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almajwal, A.M.; Abulmeaty, M.M.A. New Predictive Equations for Resting Energy Expenditure in Normal to Overweight and Obese Population. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2019, 2019, 5727496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeziorek, M.; Szuba, A.; Kujawa, K.; Regulska-Ilow, B. Comparison of Actual and Predicted Resting Metabolic Rate in Women with Lipedema. Lymphat. Res. Biol. 2023, 21, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porter, J.; Ward, L.C.; Nguo, K.; Davidson, Z.; Gibson, S.; Prentice, R.; Neuhouser, M.L.; Truby, H. Development and validation of new predictive equations for the resting metabolic rate of older adults aged ≥65 y. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2023, 117, 1164–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayan, E.; Kim, J.N.; Smith, M.L.; Seo, C.A.; Damstra, R.J.; Schmeller, W.; Frambach, Y.; Carmody, M.A.; Földi, E.; Rockson, S.G. Lipedema—The Disease They Call Fat; The Lipedema Project at The Friedman Center for Lymphedema Research and Treatment in collaboration with Lymphatic Education & Research Network (LE&RN): Boston, MA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Delsoglio, M.; Achamrah, N.; Berger, M.M.; Pichard, C. Indirect Calorimetry in Clinical Practice. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horner, N.K.; Lampe, J.W.; Patterson, R.E.; Neuhouser, M.L.; Beresford, S.A.; Prentice, R.L. Indirect Calorimetry Protocol Development for Measuring Resting Metabolic Rate as a Component of Total Energy Expenditure in Free-Living Postmenopausal Women. J. Nutr. 2001, 131, 2215–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Blasco Redondo, R. Gasto energético en reposo; métodos de evaluación y aplicaciones. Nutr. Hosp. 2015, 31 (Suppl. 3), 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdi, H.; Williams, L.J. Principal component analysis. WIREs Comput. Stats. 2010, 2, 433–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, M.; Jackson, S.; Cimentada, J. corrr: Correlations in R. 2022. Available online: https://github.com/tidymodels/corrr (accessed on 1 December 2023).
- Lê, S.; Josse, J.; Husson, F. FactoMineR: An R Package for Multivariate Analysis. J. Stat. Soft. 2008, 25, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassambara, A.; Mundt, F. Factoextra: Extract and Visualize the Results of Multivariate Data Analyses. R Package Version 1.0.7. 2020. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=factoextra (accessed on 1 December 2023).
- Harris, C.R.; Millman, K.J.; van der Walt, S.J.; Gommers, R.; Virtanen, P.; Cournapeau, D.; Wieser, E.; Taylor, J.; Berg, S.; Smith, N.J.; et al. Array programming with NumPy. Nature 2020, 585, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinney, W. Data structures for statistical computing in python. In Proceedings of the 9th Python in Science Conference (SciPy 2010), Austin, TX, USA, 28 June–3 July 2010; Volume 445, pp. 51–56. [Google Scholar]
- Hunter, J.D. Matplotlib: A 2D Graphics Environment. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2007, 9, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waskom, M. seaborn: Statistical data visualization. JOSS 2021, 6, 3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine Learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Jeziorek, M.; Szuba, A.; Kujawa, K.; Regulska-Ilow, B. The Effect of a Low-Carbohydrate, High-Fat Diet versus Moderate-Carbohydrate and Fat Diet on Body Composition in Patients with Lipedema. DMSO 2022, 15, 2545–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mifflin, M.D.; St Jeor, S.T.; Hill, L.A.; Scott, B.J.; Daugherty, S.A.; Koh, Y.O. A new predictive equation for resting energy expenditure in healthy individuals. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1990, 51, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, J.A.; Benedict, F.G. A biometric study of human basal metabolism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1918, 4, 370–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira De Godoy, L.M.; Pereira De Godoy, H.J.; Pereira De Godoy Capeletto, P.; Guerreiro Godoy, M.D.F.; Pereira De Godoy, J.M. Lipedema and the Evolution to Lymphedema With the Progression of Obesity. Cureus 2020, 12, e11854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kfir, A.; Lahav, Y.; Gepner, Y. Cross-Validation of a New General Population Resting Metabolic Rate Prediction Equation Based on Body Composition. Nutrients 2023, 15, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, B.A.P.; Nicoletti, C.F.; De Oliveira, C.C.; de Souza Pinhel, M.A.; Quinhoneiro, D.C.G.; Noronha, N.Y.; Marchini, J.S.; Nonino, C.B. A new resting metabolic rate equation for women with class III obesity. Nutrition 2018, 49, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thom, G.; Gerasimidis, K.; Rizou, E.; Alfheeaid, H.; Barwell, N.; Manthou, E.; Fatima, S.; Gill, J.M.; Lean, M.E.; Malkova, D. Validity of predictive equations to estimate RMR in females with varying BMI. J. Nutr. Sci. 2020, 9, e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flack, K.D.; Siders, W.A.; Johnson, L.; Roemmich, J.N. Cross-Validation of Resting Metabolic Rate Prediction Equations. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2016, 116, 1413–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

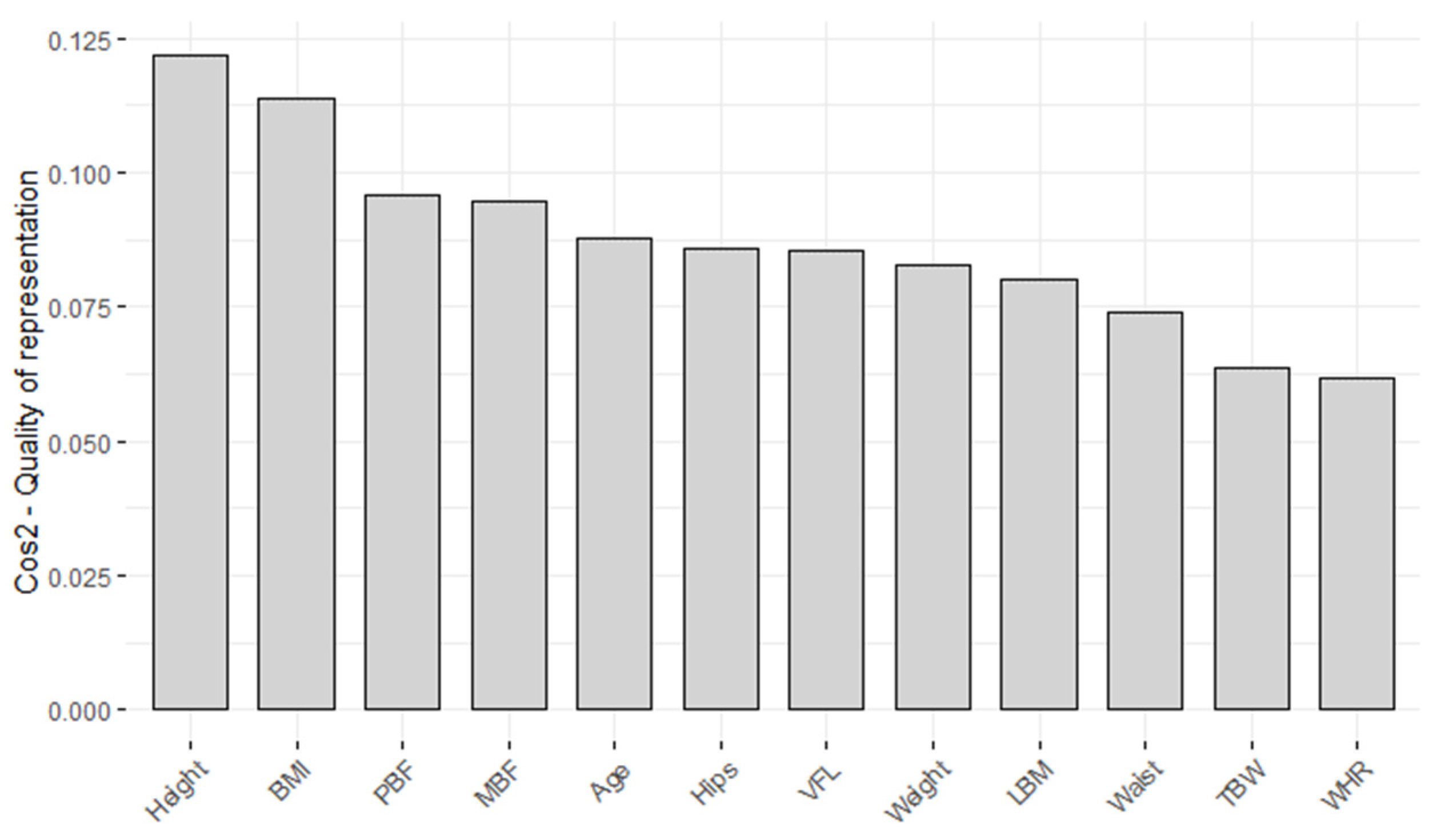

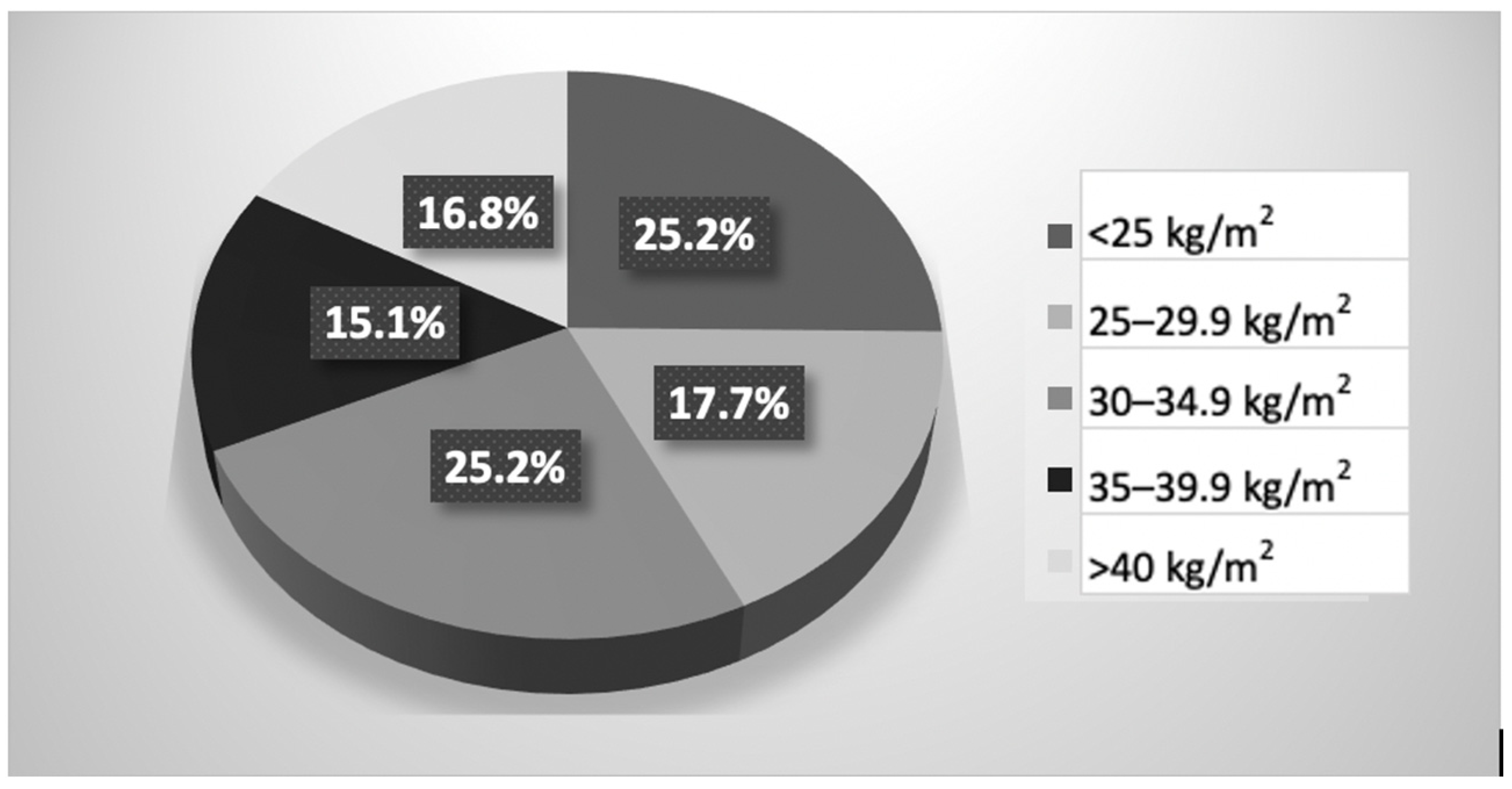
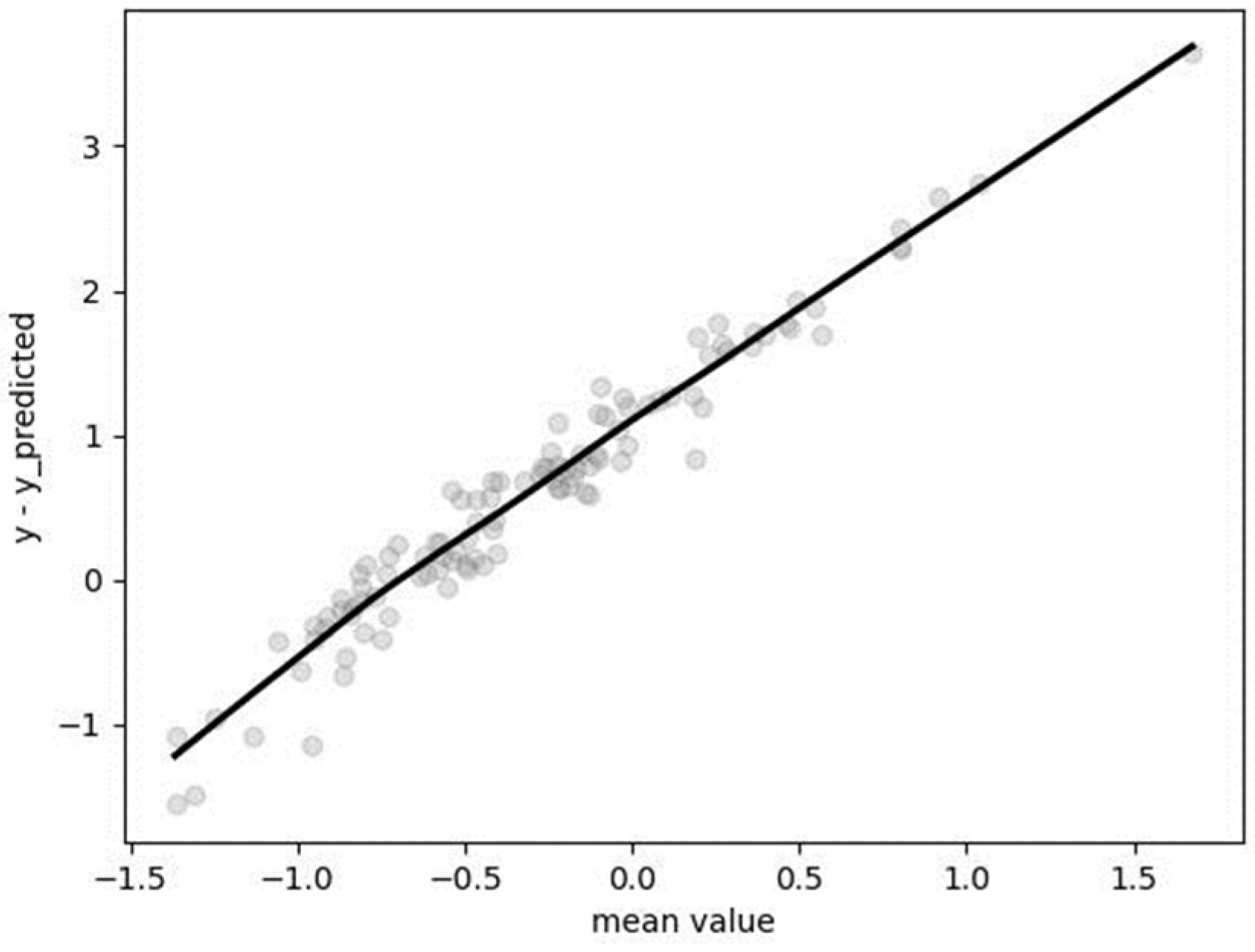
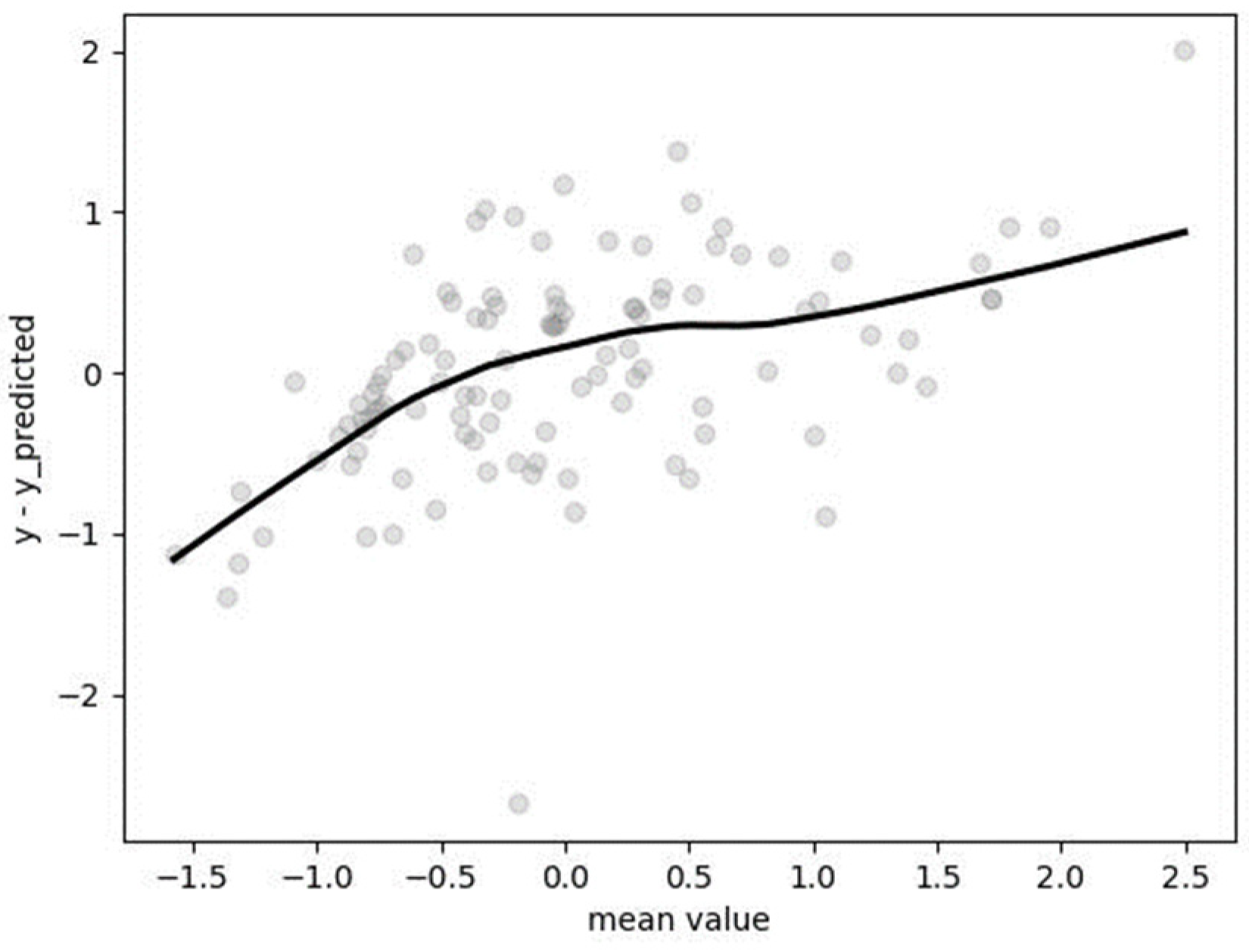

| Characteristic | Lipedema | Lymphedema |
|---|---|---|
| Gender | Female | Female and male |
| Onset | Puberty, pregnancy, menopause | Childhood to elderly |
| Family history | Common | In some cases of primary lymphedema |
| Areas affected | Buttock, hips, legs, sometimes arms | Legs and feet, arms and hands |
| Symmetry | Often | Possible |
| Pain in the legs/arms | Often | Rare |
| Tenderness of legs/arms | Often | Rare |
| Easy bruising | Often | Absent |
| Pitting edema | Absent | Present |
| Affected feet | Absent | Present |
| Response to diet and exercises | Absent | Possible |
| Age | Height | Weight | BMI | LBM | PBF | MBF | TBW | VFL | Waist | Hips | WHR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.74 | 40.64 | 864.54 | 375.52 | 106.58 | 26.57 | 240.12 | 37.01 | 12.00 | 197.63 | 96.05 | 88.62 |
| Parameter | PC 1 | PC 2 | PC 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agest | 0.2328 | 0.4479 | 0.3150 |
| Heightst | −0.2903 | 0.4934 | −0.1447 |
| Weightst | 0.2936 | −0.2250 | −0.0650 |
| BMIst | 0.3674 | −0.0695 | −0.0215 |
| LBMst | 0.2726 | −0.2927 | −0.1423 |
| PBFst | 0.3374 | 0.0497 | 0.1300 |
| MBFst | 0.3294 | −0.1349 | −0.0030 |
| TBWst | 0.2066 | −0.3635 | −0.2148 |
| VFLst | 0.3174 | 0.0776 | 0.3330 |
| Waistst | 0.2962 | 0.0535 | −0.3125 |
| Hipsst | 0.2795 | −0.3113 | 0.2579 |
| WHRst | 0.1853 | 0.3951 | −0.7189 |
| Parameter | Lipedema, n = 119 Mean ± SD |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | 43.4 ± 13.4 |
| Height (cm) | 165.5 ± 6.8 |
| Weight (kg) | 87.5 ± 21.8 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 32.1 ± 8.5 |
| LBM (kg) | 48.7 ± 19.8 |
| PBF (%) | 37.7 ± 7.3 |
| MBF (kg) | 34.4 ± 13.8 |
| TBW (kg) | 38.6 ± 6.5 |
| VFL | 12.7 ± 5.1 |
| Waist (cm) | 96.5 ± 17.5 |
| Hips (cm) | 115.6 ± 13.6 |
| WHR | 0.8 ± 0.1 |
| RMR (kcal/day) | 1685.8 ± 310.4 |
| Parameter | Mean | SD |
|---|---|---|
| PC1 | 109.5763 | 34.5448 |
| PC2 | 109.9039 | 34.5661 |
| PC3 | 108.9802 | 34.5062 |
| RMR | 1693.5234 | 310.5558 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeziorek, M.; Wronowicz, J.; Janek, Ł.; Kujawa, K.; Szuba, A. Development of New Predictive Equations for the Resting Metabolic Rate (RMR) of Women with Lipedema. Metabolites 2024, 14, 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14040235
Jeziorek M, Wronowicz J, Janek Ł, Kujawa K, Szuba A. Development of New Predictive Equations for the Resting Metabolic Rate (RMR) of Women with Lipedema. Metabolites. 2024; 14(4):235. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14040235
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeziorek, Małgorzata, Jakub Wronowicz, Łucja Janek, Krzysztof Kujawa, and Andrzej Szuba. 2024. "Development of New Predictive Equations for the Resting Metabolic Rate (RMR) of Women with Lipedema" Metabolites 14, no. 4: 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14040235
APA StyleJeziorek, M., Wronowicz, J., Janek, Ł., Kujawa, K., & Szuba, A. (2024). Development of New Predictive Equations for the Resting Metabolic Rate (RMR) of Women with Lipedema. Metabolites, 14(4), 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14040235








