Liraglutide Therapy in Obese Patients Alters Macrophage Phenotype and Decreases Their Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha Release and Oxidative Stress Markers—A Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
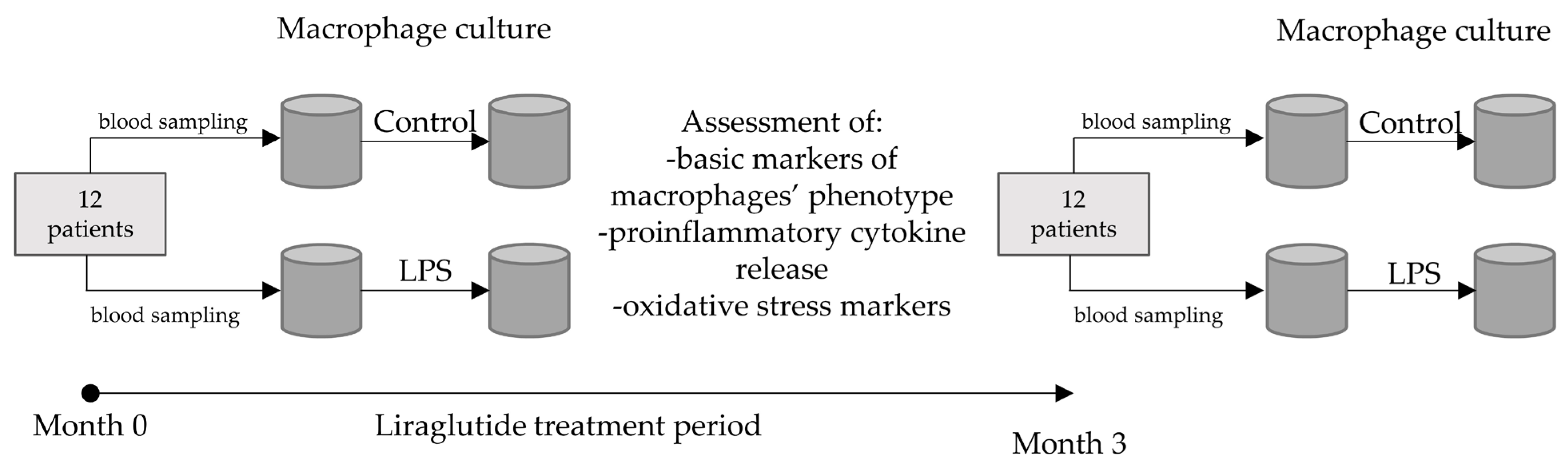
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Procedures (Monocyte Culture, Transition to Macrophages, Challenge with LPS)
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.3.1. RT-qPCR
2.3.2. Western Blotting
2.3.3. Immunofluorescence Microscopic Imaging
2.3.4. ELISAs
2.3.5. ROS and Malondialdehyde Assays
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
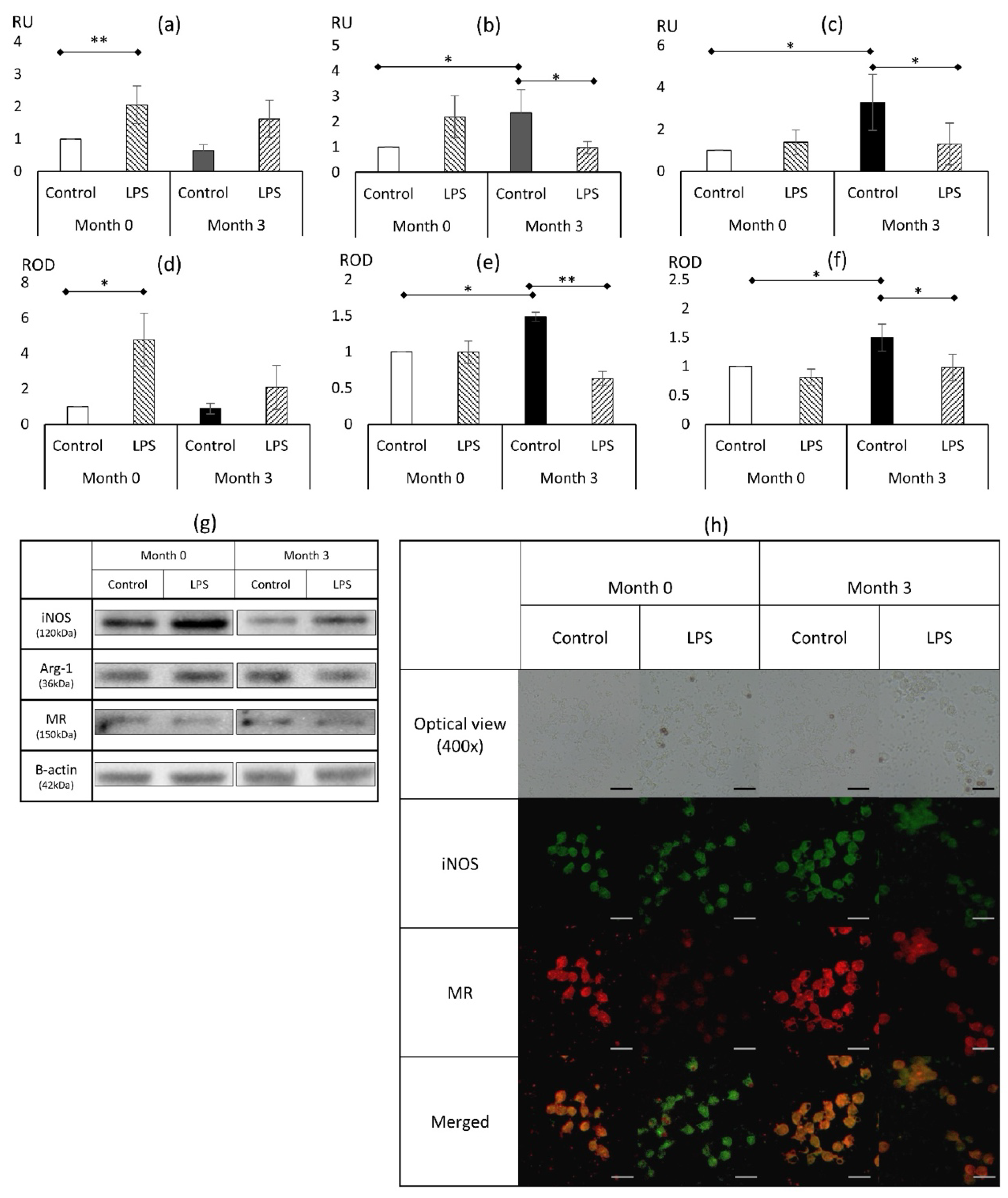
3.1. Basic Phenotypical Features of Macrophages During the Course of In Vivo Treatment with Liraglutide and In Vitro Challenge with LPS
3.1.1. Marker of Classical Activation (M1): Inducible Nitric Oxide
3.1.2. Markers of Alternative Activation (M2): Arginase 1, Mannose Receptor
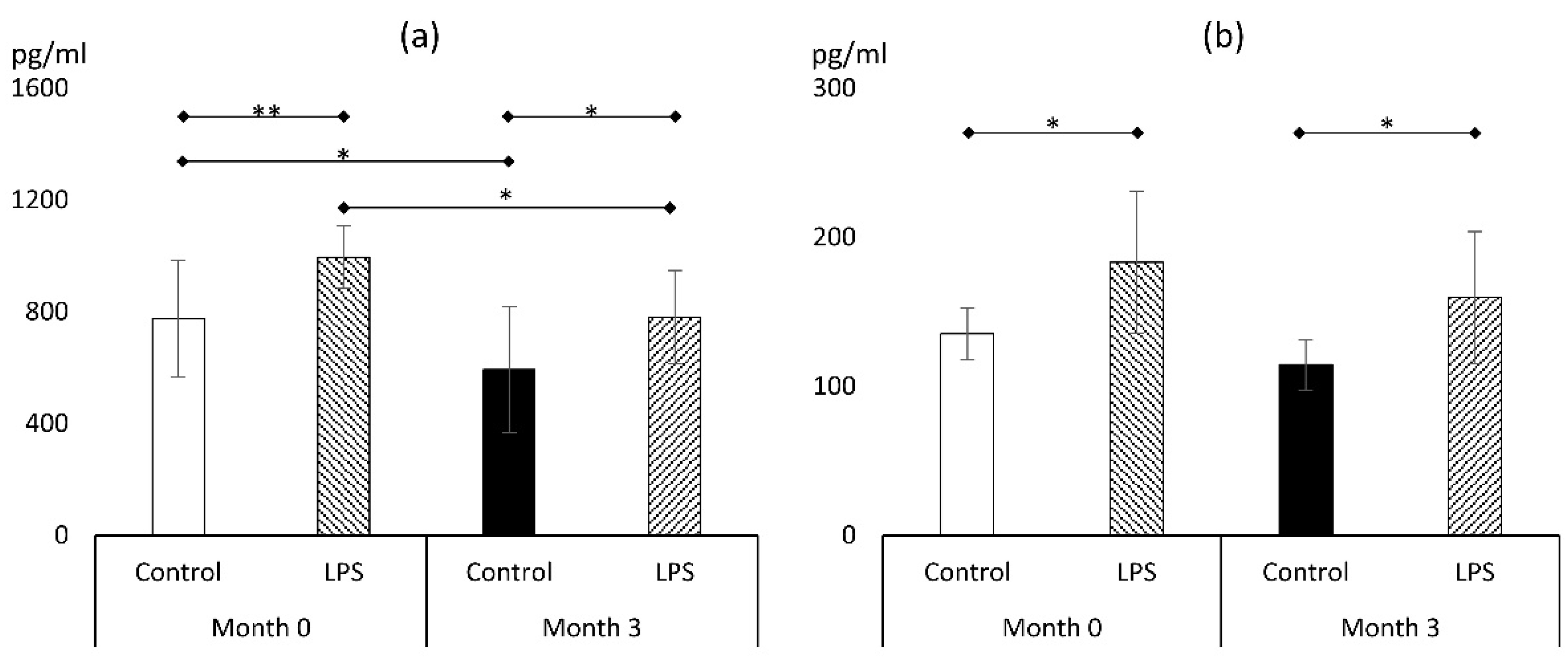
3.2. Markers of Proinflammatory Response
3.2.1. TNFα
3.2.2. IL-1β
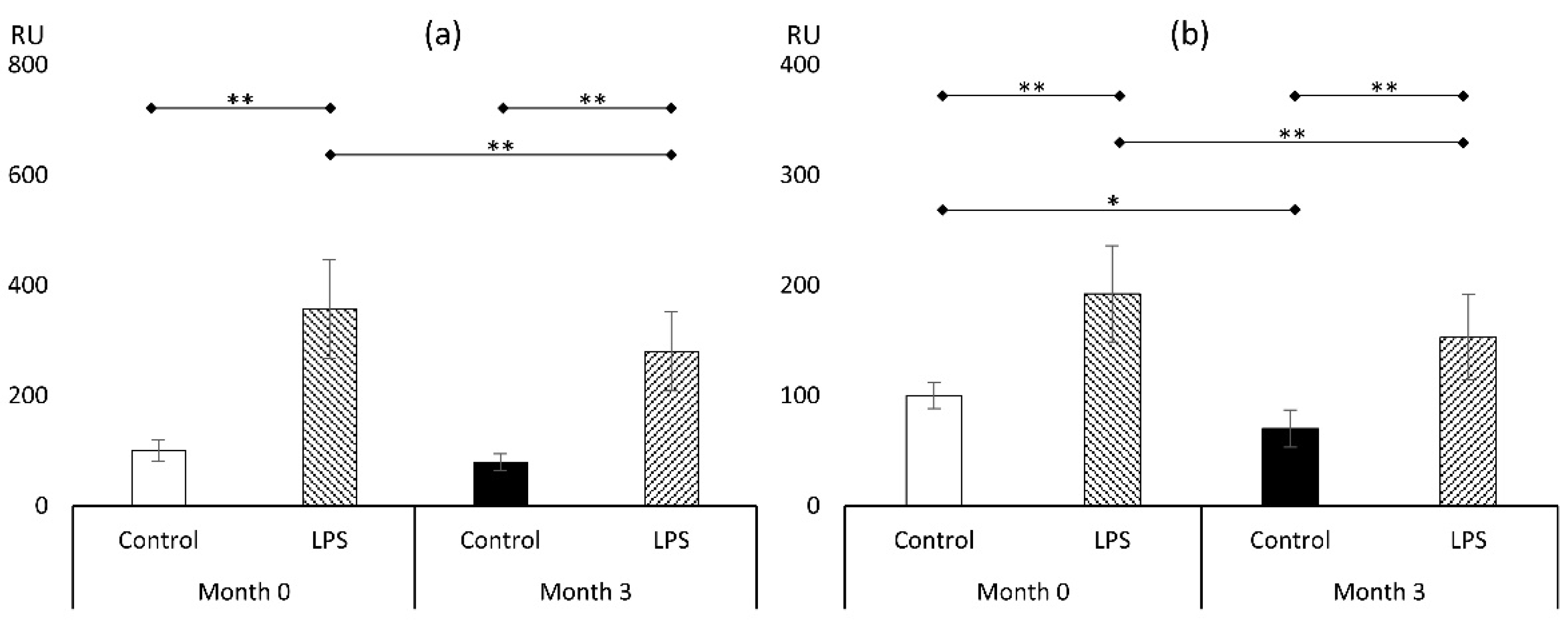
3.3. Markers of Oxidative Stress
3.3.1. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)
3.3.2. Malondialdehyde (MDA)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. One in Eight People Are Now Living with Obesity. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/01-03-2024-one-in-eight-people-are-now-living-with-obesity (accessed on 2 May 2024).
- Marso, S.P.; Bain, S.C.; Consoli, A.; Eliaschewitz, F.G.; Jódar, E.; Leiter, L.A.; Lingvay, I.; Rosenstock, J.; Seufert, J.; Warren, M.L.; et al. Semaglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1834–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisberg, S.P.; McCann, D.; Desai, M.; Rosenbaum, M.; Leibel, R.L.; Ferrante, A.W. Obesity Is Associated with Macrophage Accumulation in Adipose Tissue. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1796–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammarstedt, A.; Gogg, S.; Hedjazifar, S.; Nerstedt, A.; Smith, U. Impaired Adipogenesis and Dysfunctional Adipose Tissue in Human Hypertrophic Obesity. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 1911–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ren, Y.; Chang, K.; Wu, W.; Griffiths, H.R.; Lu, S.; Gao, D. Adipose Tissue Macrophages as Potential Targets for Obesity and Metabolic Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1153915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, S.; Fujita, T.; Shimabukuro, M.; Iwaki, M.; Yamada, Y.; Nakajima, Y.; Nakayama, O.; Makishima, M.; Matsuda, M.; Shimomura, I. Increased Oxidative Stress in Obesity and Its Impact on Metabolic Syndrome. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 114, 1752–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bołdys, A.; Bułdak, Ł.; Maligłówka, M.; Surma, S.; Okopień, B. Potential Therapeutic Strategies in the Treatment of Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease. Medicina 2023, 59, 1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lincoff, A.M.; Brown-Frandsen, K.; Colhoun, H.M.; Deanfield, J.; Emerson, S.S.; Esbjerg, S.; Hardt-Lindberg, S.; Hovingh, G.K.; Kahn, S.E.; Kushner, R.F.; et al. Semaglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Obesity without Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 2221–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bołdys, A.; Bułdak, Ł.; Skudrzyk, E.; Machnik, G.; Okopień, B. The Impact of Glucagon and Exenatide on Oxidative Stress Levels and Antioxidative Enzyme Expression in in Vitro Induced Steatosis in HepG2 Cell Culture. Endokrynol. Pol. 2024, 75, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izaguirre, M.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J.; Rodríguez, A.; Ramírez, B.; Becerril, S.; Valentí, V.; Moncada, R.; Unamuno, X.; Silva, C.; de la Higuera, M.; et al. GLP-1 Limits Adipocyte Inflammation and Its Low Circulating Pre-Operative Concentrations Predict Worse Type 2 Diabetes Remission after Bariatric Surgery in Obese Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bułdak, Ł.; Machnik, G.; Bułdak, R.J.; Łabuzek, K.; Bołdys, A.; Okopień, B. Exenatide and Metformin Express Their Anti-Inflammatory Effects on Human Monocytes/Macrophages by the Attenuation of MAPKs and NFκB Signaling. Naunyn Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2016, 389, 1103–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bułdak, Ł.; Łabuzek, K.; Bułdak, R.J.; Machnik, G.; Bołdys, A.; Okopień, B. Exenatide (a GLP-1 Agonist) Improves the Antioxidative Potential of in Vitro Cultured Human Monocytes/Macrophages. Naunyn Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2015, 388, 905–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carey, T.S.; Sanders, G.D.; Viswanathan, M.; Trikalinos, T.A.; Kato, E.; Chang, S. Framework for Considering Study Designs for Future Research Needs; AHRQ Methods Future Research Needs Series; Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US): Rockville, MD, USA, 2012.
- Spandidos, A.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Seed, B. PrimerBank: A Resource of Human and Mouse PCR Primer Pairs for Gene Expression Detection and Quantification. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, D792–D799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An Open-Source Platform for Biological-Image Analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bułdak, Ł.; Machnik, G.; Bułdak, R.J.; Łabuzek, K.; Bołdys, A.; Belowski, D.; Basiak, M.; Okopień, B. Exenatide (a GLP-1 Agonist) Expresses Anti-Inflammatory Properties in Cultured Human Monocytes/Macrophages in a Protein Kinase A and B/Akt Manner. Pharmacol. Rep. 2016, 68, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, J.; Jiang, S.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, L.; Hu, B.; Shi, H.; Li, Z.; Ran, G.; et al. Targeted Reprogramming of Tumor-Associated Macrophages for Overcoming Glioblastoma Resistance to Chemotherapy and Immunotherapy. Biomaterials 2024, 311, 122708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Chen, L.; Li, D.; Xu, H.; Chen, J.; Min, X.; He, M.; Wu, T.; Zhong, J.; Yang, H.; et al. Effect of GLP-1/GLP-1R on the Polarization of Macrophages in the Occurrence and Development of Atherosclerosis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2021, 2021, 5568159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiraishi, D.; Fujiwara, Y.; Komohara, Y.; Mizuta, H.; Takeya, M. Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) Induces M2 Polarization of Human Macrophages via STAT3 Activation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 425, 304–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Feng, P.-P.; Zhao, Z.-B.; Zhu, W.; Gong, J.-P.; Du, H.-M. Liraglutide Protects against Inflammatory Stress in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver by Modulating Kupffer Cells M2 Polarization via cAMP-PKA-STAT3 Signaling Pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 510, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.-H.; Zheng, X.-L.; Tang, C.-K. Nuclear Factor-κB Activation as a Pathological Mechanism of Lipid Metabolism and Atherosclerosis. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2015, 70, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Jiang, J.; Xu, J.; Chen, J.; Gu, Y.; Wu, G. Liraglutide, a Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist, Ameliorates Inflammation and Apoptosis via Inhibition of Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Products Signaling in AGEs Induced Chondrocytes. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2024, 25, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sherbiny, M.; El-Shafey, M.; Said, E.; Shaker, G.A.; El-Dosoky, M.; Ebrahim, H.A.; Abed, S.Y.; Ibraheem, K.M.; Faheem, A.M.; AlMutawa, M.; et al. Dapagliflozin, Liraglutide, and Their Combination Attenuate Diabetes Mellitus-Associated Hepato-Renal Injury—Insight into Oxidative Injury/Inflammation/Apoptosis Modulation. Life 2022, 12, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.Y.; Poudel, A.; Welchko, R.; Mekala, N.; Chandramani-Shivalingappa, P.; Rosca, M.G.; Li, L. Liraglutide Improves Insulin Sensitivity in High Fat Diet Induced Diabetic Mice through Multiple Pathways. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 861, 172594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.; Xu, M.; Sun, X.; Rao, X. Effects of Liraglutide on Extraglycemic Inflammatory Markers and Renal Hemodynamic Parameters in Diabetic Kidney Disease (DKD). Medicine 2023, 102, e35046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parichatikanond, W.; Pandey, S.; Mangmool, S. Exendin-4 Exhibits Cardioprotective Effects against High Glucose-Induced Mitochondrial Abnormalities: Potential Role of GLP-1 Receptor and mTOR Signaling. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2024, 229, 116552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z. Efficacy of Metformin Combined with Liraglutide on the Glucose and Lipid Metabolism, Vascular Endothelial Function, and Oxidative Stress of Patients with T2DM and Metabolic Syndrome. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2024, 40, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambadiari, V.; Thymis, J.; Kouretas, D.; Skaperda, Z.; Tekos, F.; Kousathana, F.; Kountouri, A.; Balampanis, K.; Parissis, J.; Andreadou, I.; et al. Effects of a 12-Month Treatment with Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists, Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors, and Their Combination on Oxidant and Antioxidant Biomarkers in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Cheng, Z.; Zhang, H.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, C.; Ye, P.; Zhang, K.; Ma, X.; Wu, Q. Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Inhibits the Progression of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm in Mice: The Earlier, the Better. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2023, 38, 873–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruen, R.; Curley, S.; Kajani, S.; Crean, D.; O’Reilly, M.E.; Lucitt, M.B.; Godson, C.G.; McGillicuddy, F.C.; Belton, O. Liraglutide Dictates Macrophage Phenotype in Apolipoprotein E Null Mice during Early Atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2017, 16, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Zhao, F.; Cheng, H.; Su, M.; Wang, Y. Macrophage Polarization: An Important Role in Inflammatory Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1352946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexiadou, K.; Hartley, A.; Tan, T.M.-M.; Khamis, R. The Cardiovascular Effects of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists beyond Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes: An Anti-Atherosclerotic Action. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2024, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bułdak, Ł.; Bołdys, A.; Skudrzyk, E.; Machnik, G.; Okopień, B. Liraglutide Therapy in Obese Patients Alters Macrophage Phenotype and Decreases Their Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha Release and Oxidative Stress Markers—A Pilot Study. Metabolites 2024, 14, 554. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14100554
Bułdak Ł, Bołdys A, Skudrzyk E, Machnik G, Okopień B. Liraglutide Therapy in Obese Patients Alters Macrophage Phenotype and Decreases Their Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha Release and Oxidative Stress Markers—A Pilot Study. Metabolites. 2024; 14(10):554. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14100554
Chicago/Turabian StyleBułdak, Łukasz, Aleksandra Bołdys, Estera Skudrzyk, Grzegorz Machnik, and Bogusław Okopień. 2024. "Liraglutide Therapy in Obese Patients Alters Macrophage Phenotype and Decreases Their Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha Release and Oxidative Stress Markers—A Pilot Study" Metabolites 14, no. 10: 554. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14100554
APA StyleBułdak, Ł., Bołdys, A., Skudrzyk, E., Machnik, G., & Okopień, B. (2024). Liraglutide Therapy in Obese Patients Alters Macrophage Phenotype and Decreases Their Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha Release and Oxidative Stress Markers—A Pilot Study. Metabolites, 14(10), 554. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14100554





