A Cohort Study of Gastric Fluid and Urine Metabolomics for the Prediction of Survival in Severe Prematurity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.1.1. Sampling
2.1.2. Outcomes
2.2. Analytical Techniques
2.2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2.2. Sample Preparation
Gastric Fluid Samples
Urine Samples
2.2.3. GC-MS Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
3.2. Metabolomic Analysis Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Clinical Prediction of Survival in Preterm Neonates
4.2. Use of Metabolomics to Prognosticate Survival of Preterm Neonates
4.3. Interpretation of the Metabolic Alternations
4.4. Advantages and Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blencowe, H.; Cousens, S.; Oestergaard, M.Z.; Chou, D.; Moller, A.-B.; Narwal, R.; Adler, A.; Vera Garcia, C.; Rohde, S.; Say, L.; et al. National, Regional, and Worldwide Estimates of Preterm Birth Rates in the Year 2010 with Time Trends since 1990 for Selected Countries: A Systematic Analysis and Implications. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2012, 379, 2162–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walani, S.R. Global Burden of Preterm Birth. Int. J. Gynaecol. Obstet. Off. Organ Int. Fed. Gynaecol. Obstet. 2020, 150, 31–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoll, B.J.; Hansen, N.I.; Bell, E.F.; Walsh, M.C.; Carlo, W.A.; Shankaran, S.; Laptook, A.R.; Sánchez, P.J.; Van Meurs, K.P.; Wyckoff, M.; et al. Trends in Care Practices, Morbidity, and Mortality of Extremely Preterm Neonates, 1993–2012. JAMA 2015, 314, 1039–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barfield, W.D. Public Health Implications of Very Preterm Birth. Clin. Perinatol. 2018, 45, 565–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, D.K.; Corcoran, J.D.; Escobar, G.J.; Lee, S.K. SNAP-II and SNAPPE-II: Simplified Newborn Illness Severity and Mortality Risk Scores. J. Pediatr. 2001, 138, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parry, G.; Tucker, J.; Tarnow-Mordi, W. UK Neonatal Staffing Study Collaborative Group CRIB II: An Update of the Clinical Risk Index for Babies Score. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2003, 361, 1789–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyson, J.E.; Parikh, N.A.; Langer, J.; Green, C.; Higgins, R.D. National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Neonatal Research Network Intensive Care for Extreme Prematurity—Moving beyond Gestational Age. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 1672–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agakidou, E.; Agakidis, C.; Gika, H.; Sarafidis, K. Emerging Biomarkers for Prediction and Early Diagnosis of Necrotizing Enterocolitis in the Era of Metabolomics and Proteomics. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 602255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarafidis, K.; Chatziioannou, A.C.; Thomaidou, A.; Gika, H.; Mikros, E.; Benaki, D.; Diamanti, E.; Agakidis, C.; Raikos, N.; Drossou, V.; et al. Urine Metabolomics in Neonates with Late-Onset Sepsis in a Case-Control Study. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomaidou, A.; Chatziioannou, A.C.; Deda, O.; Benaki, D.; Gika, H.; Mikros, E.; Agakidis, C.; Raikos, N.; Theodoridis, G.; Sarafidis, K. A Pilot Case-Control Study of Urine Metabolomics in Preterm Neonates with Necrotizing Enterocolitis. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life. Sci. 2019, 1117, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanos, V.; Pintus, M.C.; Lussu, M.; Atzori, L.; Noto, A.; Stronati, M.; Guimaraes, H.; Marcialis, M.A.; Rocha, G.; Moretti, C.; et al. Urinary Metabolomics of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia (BPD): Preliminary Data at Birth Suggest It Is a Congenital Disease. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. Off. J. Eur. Assoc. Perinat. Med. Fed. Asia Ocean. Perinat. Soc. Int. Soc. Perinat. Obstet. 2014, 27 (Suppl. S2), 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piñeiro-Ramos, J.D.; Núñez-Ramiro, A.; Llorens-Salvador, R.; Parra-Llorca, A.; Sánchez-Illana, Á.; Quintás, G.; Boronat-González, N.; Martínez-Rodilla, J.; Kuligowski, J.; Vento, M.; et al. Metabolic Phenotypes of Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy with Normal vs. Pathologic Magnetic Resonance Imaging Outcomes. Metabolites 2020, 10, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oltman, S.P.; Rogers, E.E.; Baer, R.J.; Anderson, J.G.; Steurer, M.A.; Pantell, M.S.; Partridge, J.C.; Rand, L.; Ryckman, K.K.; Jelliffe-Pawlowski, L.L. Initial Metabolic Profiles Are Associated with 7-Day Survival among Infants Born at 22–25 Weeks of Gestation. J. Pediatr. 2018, 198, 194–200.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashwood, E.R. Standards of Laboratory Practice: Evaluation of Fetal Lung Maturity. National Academy of Clinical Biochemistry. Clin. Chem. 1997, 43, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baraldi, E.; Giordano, G.; Stocchero, M.; Moschino, L.; Zaramella, P.; Tran, M.R.; Carraro, S.; Romero, R.; Gervasi, M.T. Untargeted Metabolomic Analysis of Amniotic Fluid in the Prediction of Preterm Delivery and Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widström, A.M.; Christensson, K.; Ransjö-Arvidson, A.B.; Matthiesen, A.S.; Winberg, J.; Uvnäs-Moberg, K. Gastric Aspirates of Newborn Infants: PH, Volume and Levels of Gastrin- and Somatostatin-like Immunoreactivity. Acta Paediatr. Scand. 1988, 77, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.D.; Kim, S.C.; Choi, K.U.; Jun, E.S. The Relationship between Amniotic and Newborn Gastric Fluid Inflammatory Mediators. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. Off. J. Eur. Assoc. Perinat. Med. Fed. Asia Ocean. Perinat. Soc. Int. Soc. Perinat. Obstet. 2013, 26, 1069–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bry, K.J.K.; Jacobsson, B.; Nilsson, S.; Bry, K. Gastric Fluid Cytokines Are Associated with Chorioamnionitis and White Blood Cell Counts in Preterm Infants. Acta Paediatr. Oslo Nor. 1992 2015, 104, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Qian, Y.; Wang, Q.; Ling, Y.; Hu, Q. Evaluation of the Diagnostic Value of Gastric Juice Aspirate Culture for Early-Onset Sepsis in Newborns 28–35 weeks’ Gestation. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 98, 115115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Methodol. 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohart, F.; Gautier, B.; Singh, A.; Cao, K.-A.L. MixOmics: An R Package for omics Feature Selection and Multiple Data Integration. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyamundanda, G.; Gormley, I.C.; Fan, Y.; Gallagher, W.M.; Brennan, L. MetSizeR: Selecting the Optimal Sample Size for Metabolomic Studies Using an Analysis Based Approach. BMC Bioinformat. 2013, 14, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, S.; Chow, R.; Popovic, M.; Lam, M.; Popovic, M.; Merrick, J.; Stashefsky Margalit, R.N.; Lam, H.; Milakovic, M.; Chow, E.; et al. A Selected Review of the Mortality Rates of Neonatal Intensive Care Units. Front. Public Health 2015, 3, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudzik, D.; Revello, R.; Barbas, C.; Bartha, J.L. LC-MS-Based Metabolomics Identification of Novel Biomarkers of Chorioamnionitis and Its Associated Perinatal Neurological Damage. J. Proteome Res. 2015, 14, 1432–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryckman, K.K.; Berberich, S.L.; Dagle, J.M. Predicting Gestational Age Using Neonatal Metabolic Markers. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2016, 214, 515.e1–515.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huck, J.H.J.; Verhoeven, N.M.; Struys, E.A.; Salomons, G.S.; Jakobs, C.; van der Knaap, M.S. Ribose-5-Phosphate Isomerase Deficiency: New Inborn Error in the Pentose Phosphate Pathway Associated with a Slowly Progressive Leukoencephalopathy. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2004, 74, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jauniaux, E.; Hempstock, J.; Teng, C.; Battaglia, F.C.; Burton, G.J. Polyol Concentrations in the Fluid Compartments of the Human Conceptus during the First Trimester of Pregnancy: Maintenance of Redox Potential in a Low Oxygen Environment. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 1171–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, C.C.; Tjoa, S.; Fennessey, P.V.; Wilkening, R.B.; Battaglia, F.C. Transplacental Carbohydrate and Sugar Alcohol Concentrations and Their Uptakes in Ovine Pregnancy. Exp. Biol. Med. Maywood NJ 2002, 227, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koy, A.; Waldhaus, A.; Hammen, H.-W.; Wendel, U.; Mayatepek, E.; Schadewaldt, P. Urinary Excretion of Pentose Phosphate Pathway-Associated Polyols in Early Postnatal Life. Neonatology 2009, 95, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanos, V.; Caboni, P.; Corsello, G.; Stronati, M.; Gazzolo, D.; Noto, A.; Lussu, M.; Dessì, A.; Giuffrè, M.; Lacerenza, S.; et al. Urinary (1)H-NMR and GC-MS Metabolomics Predicts Early and Late Onset Neonatal Sepsis. Early Hum. Dev. 2014, 90 (Suppl. S1), S78–S83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelke, U.F.H.; Zijlstra, F.S.M.; Mochel, F.; Valayannopoulos, V.; Rabier, D.; Kluijtmans, L.A.J.; Perl, A.; Verhoeven-Duif, N.M.; de Lonlay, P.; Wamelink, M.M.C.; et al. Mitochondrial Involvement and Erythronic Acid as a Novel Biomarker in Transaldolase Deficiency. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1802, 1028–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, I.; Dickens, A.M.; Posti, J.P.; Mohammadian, M.; Ledig, C.; Takala, R.S.K.; Hyötyläinen, T.; Tenovuo, O.; Orešič, M. Integrative Analysis of Circulating Metabolite Profiles and Magnetic Resonance Imaging Metrics in Patients with Traumatic Brain Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knafo, L.; Chessex, P.; Rouleau, T.; Lavoie, J.-C. Association between Hydrogen Peroxide-Dependent Byproducts of Ascorbic Acid and Increased Hepatic Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase Activity. Clin. Chem. 2005, 51, 1462–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Zhou, N.; Lu, M.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, C.; Wang, J.; Zhou, M.; Xu, Y. Effects of Electroacupuncture on Urinary Metabolome and Microbiota in Presenilin1/2 Conditional Double Knockout Mice. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1047121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahrner, R.; Beyoğlu, D.; Beldi, G.; Idle, J.R. Metabolomic Markers for Intestinal Ischemia in a Mouse Model. J. Surg. Res. 2012, 178, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shen, N.; Li, J.; Hu, R.; Mo, X.; Xu, L. Changes in Intestinal Flora and Metabolites in Neonates with Breast Milk Jaundice. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimer, N.W.; Schuck, P.F.; Streck, E.L.; Ferreira, G.C. D-Glyceric Aciduria. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 2015, 87, 1409–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locci, E.; Bazzano, G.; Demontis, R.; Chighine, A.; Fanos, V.; d’Aloja, E. Exploring Perinatal Asphyxia by Metabolomics. Metabolites 2020, 10, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouchani, E.T.; Pell, V.R.; Gaude, E.; Aksentijević, D.; Sundier, S.Y.; Robb, E.L.; Logan, A.; Nadtochiy, S.M.; Ord, E.N.J.; Smith, A.C.; et al. Ischaemic Accumulation of Succinate Controls Reperfusion Injury through Mitochondrial ROS. Nature 2014, 515, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, M.; Robbins, M.E.; Revhaug, C.; Saugstad, O.D. Oxygen Radical Disease in the Newborn, Revisited: Oxidative Stress and Disease in the Newborn Period. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 142, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiring, C.; Verder, H.; Schousboe, P.; Jessen, T.E.; Bender, L.; Ebbesen, F.; Dahl, M.; Eschen, C.; Fenger-Grøn, J.; Höskuldsson, A.; et al. Predicting Respiratory Distress Syndrome at Birth Using a Fast Test Based on Spectroscopy of Gastric Aspirates: 2. Clinical Part. Acta Paediatr. Oslo Nor. 1992 2020, 109, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toth, M.; Witkin, S.S.; Ledger, W.; Thaler, H. The Role of Infection in the Etiology of Preterm Birth. Obstet. Gynecol. 1988, 71, 723–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jobe, A.H.; Bancalari, E. Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 163, 1723–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballard, J.L.; Khoury, J.C.; Wedig, K.; Wang, L.; Eilers-Walsman, B.L.; Lipp, R. New Ballard Score, Expanded to Include Extremely Premature Infants. J. Pediatr. 1991, 119, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, M.C.; Kliegman, R.M. Necrotizing Enterocolitis: Treatment Based on Staging Criteria. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 1986, 33, 179–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweet, D.G.; Carnielli, V.P.; Greisen, G.; Hallman, M.; Klebermass-Schrehof, K.; Ozek, E.; Te Pas, A.; Plavka, R.; Roehr, C.C.; Saugstad, O.D.; et al. European Consensus Guidelines on the Management of Respiratory Distress Syndrome: 2022 Update. Neonatology 2023, 120, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Speer, C.P. Late-Onset Neonatal Sepsis: Recent Developments. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2015, 100, F257-263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortese, F.; Scicchitano, P.; Gesualdo, M.; Filaninno, A.; De Giorgi, E.; Schettini, F.; Laforgia, N.; Ciccone, M.M. Early and Late Infections in Newborns: Where Do We Stand? A Review. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2016, 57, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papile, L.A.; Burstein, J.; Burstein, R.; Koffler, H. Incidence and Evolution of Subependymal and Intraventricular Hemorrhage: A Study of Infants with Birth Weights Less than 1500 Gm. J. Pediatr. 1978, 92, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenton, T.R.; Kim, J.H. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis to Revise the Fenton Growth Chart for Preterm Infants. BMC Pediatr. 2013, 13, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Survivors D3 | Non-Survivors D3 | P1 | Survivors D15 | Non-Survivors D15 | P2 | Overall Survivors | Overall Non-Survivors | P3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Count | 90 | 6 | 78 | 18 | 75 | 21 | |||
| Gestational age (weeks) | 28.5 ± 2.1 | 25.1 ± 2.3 | <0.001 | 29 ± 1.6 | 25.2 ± 1.9 | <0.001 | 29 ± 1.6 | 25.7 ± 2.3 | <0.001 |
| Birth weight (g) | 1172 ± 342 | 770 ± 235 | <0.001 | 1237 ± 309 | 756 ± 230 | <0.001 | 1248 ± 305 | 783 ± 242 | <0.001 |
| SGA | 7 (7.8) | 1 (16.7) | 0.415 | 6 (7.7) | 2 (11.1) | 0.642 | 5 (6.7) | 3 (14.3) | 0.367 |
| Male sex | 36 (40) | 4 (66.7) | 0.231 | 32 (41) | 8 (44.4) | 0.797 | 31 (41.3) | 9 (42.9) | 1 |
| Multiple gestation | 29 (32.2) | 0 (0) | 0.173 | 27 (34.6) | 2 (11.1) | 0.085 | 27 (36) | 2 (9.5) | 0.029 |
| Hypertension/pregnancy-induced hypertension | 11 (12.2) | 1 (16.7) | 0.511 | 11 (14.1) | 1 (9.1) | 0.511 | 10 (13.3) | 2 (11.1) | 1 |
| Prenatal steroids | 87 (96.7) | 5 (83.3) | 0.231 | 75 (96.2) | 17 (94.4) | 0.571 | 72 (96) | 20 (95.2) | 1 |
| Maternal MgSO4 administration | 55 (61.8) | 3 (50) | 1 | 45 (57.6) | 13 (72.2) | 0.270 | 43 (58.1) | 15 (75) | 0.202 |
| Mode of delivery—CS | 80 (89.9) | 5 (83.3) | 0.497 | 71 (92.2) | 14 (77.8) | 0.091 | 68 (91.9) | 17 (81) | 0.220 |
| Chorioamnionitis (clinical or histological) | 46 (51.1) | 3 (50) | 1 | 37 (47.4) | 12 (66.7) | 0.192 | 37 (49.3) | 12 (57.1) | 0.624 |
| Intubation in the delivery room | 30 (33.3) | 6 (100) | 0.002 | 22 (28.2) | 14 (77.8) | <0.001 | 22 (29.3) | 14 (66.7) | 0.004 |
| Apgar score at 1 min | 6.3 ± 1.9 | 4.4 ± 2.4 | 0.038 | 6.4 ± 1.9 | 5.3 ± 2.2 | 0.063 | 6.4 ± 1.9 | 5.6 ± 2.1 | 0.197 |
| Apgar score at 5 min | 8.1 ± 0.9 | 7.2 ± 0.4 | 0.005 | 8.2 ± 0.9 | 7.4 ± 0.5 | <0.001 | 8.2 ± 0.9 | 7.6 ± 0.7 | 0.003 |
| SNAPPE-II score | 22.1 ± 22.6 | 77.5 ± 22 | 0.003 | 17.9 ± 17.1 | 58.7 ± 30.2 | <0.001 | 17.4 ± 17 | 54.3 ± 30.5 | <0.001 |
| RDS | 60 (66.6) | 6 (100) | 0.173 | 51 (65.4) | 15 (83.3) | 0.083 | 48 (64) | 18 (85.7) | 0.029 |
| Surfactant treatment | 53 (58.9) | 6 (100) | 0.079 | 43 (55.1) | 16 (88.9) | 0.008 | 40 (46.7) | 19 (90.5) | 0.002 |
| IMV in first 3 DOL IMV first 14 DOL IMV during NICU stay | 42 (46.7) N/A N/A | 6 (100) N/A N/A | 0.026 | N/A 19 (24.4) N/A | N/A 10 (55.6) N/A | 0.020 | N/A N/A 31 (41.3) | N/A N/A 21 (100) | <0.001 |
| Air-leak syndromes | 7 (7.8) | 4 (66.7) | <0.001 | 3 (3.8) | 8 (44.4) | <0.001 | 3 (4) | 8 (38.1) | <0.001 |
| IVH 3-4 | 16 (17.8) | 2 (33.3) | 0.313 | 7 (9) | 11 (61.1) | <0.001 | 6 (89) | 12 (51.7) | <0.001 |
| Confirmed EOS | 1 (1.1) | 1 (16.7) | 0.112 | 0 (0) | 2 (11.1) | 0.034 | 0 (0) | 2 (9.5) | 0.046 |
| Confirmed LOS | N/A | N/A | 27 (34.6) | 5 (27.8) | 0.782 | 25 (33.3) | 7 (33.3) | 1 | |
| Inotropes in first 3 DOL Inotropes in first 14 DOL Inotropes during NICU stay | 22 (24.4) N/A N/A | 6 (100) N/A N/A | <0.001 | N/A 13 (16.7) N/A | N/A 16 (88.9) N/A | <0.001 | N/A N/A 11 (14.7) | N/A N/A 18 (87.5) | <0.001 |
| Drug treatment for PDA | 25 (27.8) | 0 (0) | 0.334 | 18 (23.1) | 7 (38.9) | 0.232 | 15 (20) | 10 (47.6) | 0.022 |
| NEC (all stages) | N/A | N/A | 17 (21.8) | 2 (11.1) | 0.512 | 15 (20) | 4 (19) | 1 | |
| Surgical NEC | N/A | N/A | 2 (2.6) | 1 (5.6) | 0.468 | 1 (1.3) | 2 (9.5) | 0.120 | |
| BPD | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 38 (50.7) | 1 (4.8) | <0.001 |
| Survival | DOL 3 | DOL 15 | Overall | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC | p-Value | AUC | p-Value | AUC | p-Value | |
| Gestational age | 0.853 | 0.004 | 0.919 | 0.000 | 0.869 | 0.003 |
| Birth weight | 0.833 | 0.006 | 0.895 | 0.000 | 0.882 | 0.000 |
| SGA | 0.544 | 0.716 | 0.517 | 0.822 | 0.544 | 0.716 |
| Sex | 0.633 | 0.276 | 0.517 | 0.822 | 0.508 | 0.915 |
| Multiple gestation | 0.661 | 0.188 | 0.618 | 0.121 | 0.632 | 0.065 |
| Hypertension/pregnancy induced hypertension | 0.537 | 0.783 | 0.502 | 0.983 | 0.512 | 0.875 |
| Prenatal steroids | 0.567 | 0.586 | 0.509 | 0.910 | 0.504 | 0.958 |
| Maternal MgSO4 administration | 0.509 | 0.946 | 0.590 | 0.246 | 0.584 | 0.248 |
| Mode of delivery-CS | 0.567 | 0.586 | 0.509 | 0.910 | 0.504 | 0.958 |
| Chorioamnionitis (clinical or histological) | 0.506 | 0.122 | 0.596 | 0.205 | 0.539 | 0.586 |
| Intubation in the delivery room | 0.833 | 0.006 | 0.748 | 0.001 | 0.689 | 0.001 |
| Apgar at 1 min | 0.771 | 0.042 | 0.660 | 0.004 | 0.597 | 0.186 |
| Apgar at 5 min | 0.837 | 0.012 | 0.811 | 0.000 | 0.754 | 0.001 |
| SNAPPE-II score | 0.951 | 0.000 | 0.889 | 0.000 | 0.867 | 0.000 |
| RDS | 0.888 | 0.002 | 0.704 | 0.009 | 0.744 | 0.001 |
| Surfactant treatment | 0.746 | 0.044 | 0.701 | 0.008 | 0.736 | 0.001 |
| IMV in first 3 DOL IMV in first 14 DOL IMV during NICU stay | 0.767 N/A N/A | 0.029 | N/A 0.656 N/A | 0.04 | N/A N/A 0.759 | 0.000 |
| Air-leak syndromes | 0.794 | 0.016 | 0.703 | 0.007 | 0.670 | 0.017 |
| IVH 3-4 | 0.578 | 0.525 | 0.761 | 0.010 | 0.746 | 0.001 |
| Confirmed EOS | 0.490 | 0.934 | N/A | N/A | ||
| Confirmed LOS | N/A | N/A | 0.562 | 0.417 | 0.510 | 0.887 |
| Inotropes in first 3 DOL Inotropes in first 14 DOL Inotrope during NICU stay | 0.878 N/A N/A | 0.002 | N/A 0.861 N/A | 0.000 | N/A N/A 0.855 | 0.000 |
| Drug treatment for PDA | 0.639 | 0.256 | 0.579 | 0.297 | 0.638 | 0.054 |
| NEC (all stages) | N/A | 0.543 | 0.567 | 0.509 | 0.905 | |
| Surgical NEC | N/A | 0.485 | 0.844 | 0.459 | 0.568 | |
| BPD | N/A | N/A | 0.733 | 0.001 | ||
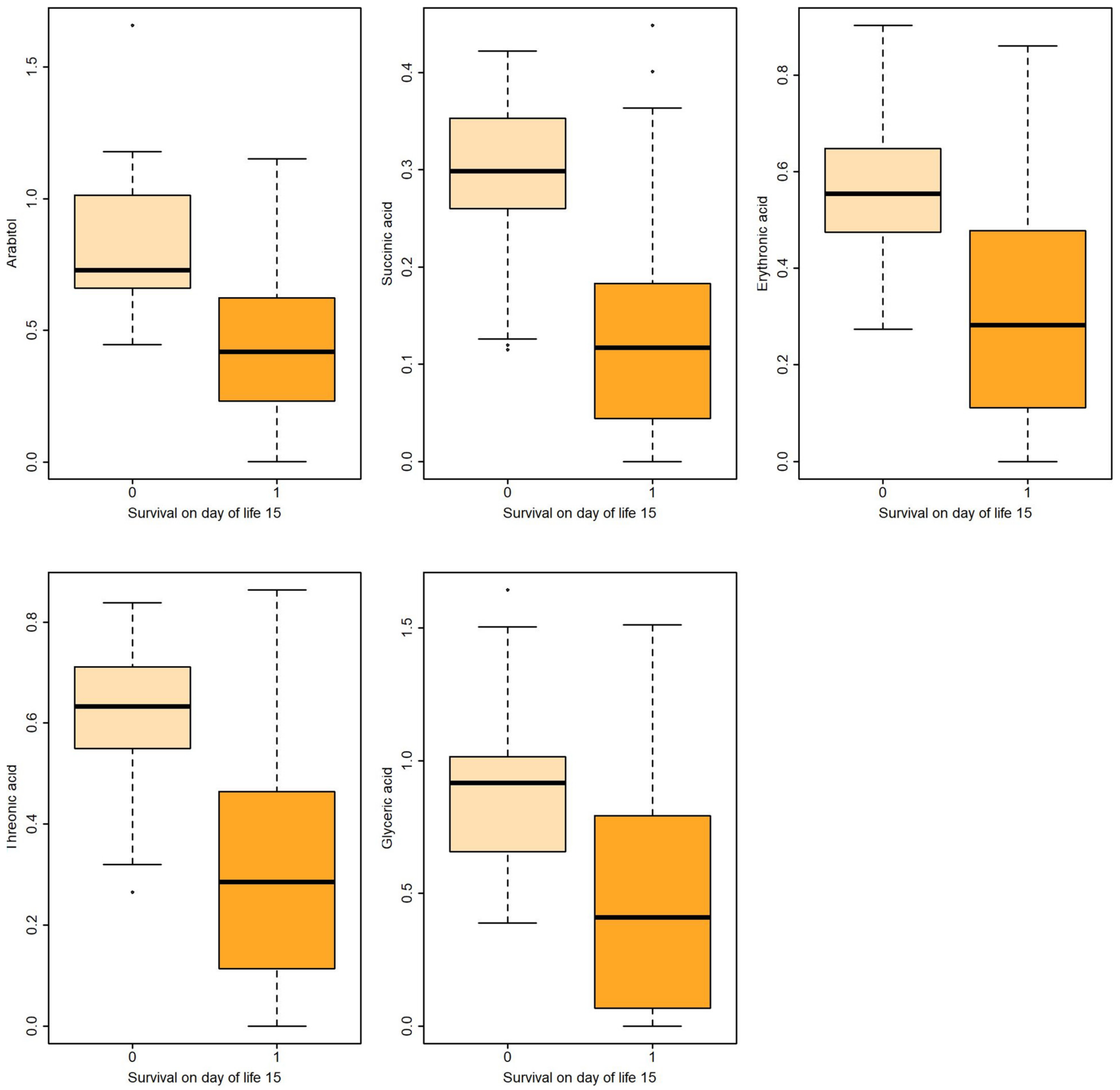
| Metabolite | Outcome | N | Mean | SD | SE | Q0.25 | Q0.5 | Q0.75 | AUC | AUC 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Survival on Day of Life 15 | ||||||||||
| Arabitol (HMDB0000568) | Non-survival | 13 | 0.842 | 0.323 | 0.089 | 0.661 | 0.729 | 1.012 | 0.863 | [0.769,0.956] |
| Survival | 60 | 0.425 | 0.261 | 0.034 | 0.236 | 0.419 | 0.6216 | |||
| Succinic acid (HMDB0000254) | Non-survival | 13 | 0.285 | 0.105 | 0.029 | 0.259 | 0.298 | 0.352 | 0.824 | [0.708,0.940] |
| Survival | 60 | 0.129 | 0.112 | 0.014 | 0.044 | 0.117 | 0.182 | |||
| Erythronic acid (HMDB0000613) | Non-survival | 13 | 0.580 | 0.192 | 0.053 | 0.474 | 0.554 | 0.647 | 0.841 | [0.734,0.948] |
| Survivors | 60 | 0.288 | 0.215 | 0.027 | 0.124 | 0.282 | 0.477 | |||
| Threonic (HMDB0000943) | Non-survival | 13 | 0.605 | 0.173 | 0.048 | 0.551 | 0.633 | 0.711 | 0.845 | [0.737,0.953] |
| Survival | 60 | 0.304 | 0.234 | 0.031 | 0.129 | 0.285 | 0.461 | |||
| Glyceric acid (HMDB0000139) | Non-survival | 13 | 0.910 | 0.369 | 0.102 | 0.656 | 0.916 | 1.014 | 0.786 | [0.668,0.904] |
| Survival | 60 | 0.483 | 0.416 | 0.053 | 0.081 | 0.408 | 0.780 | |||
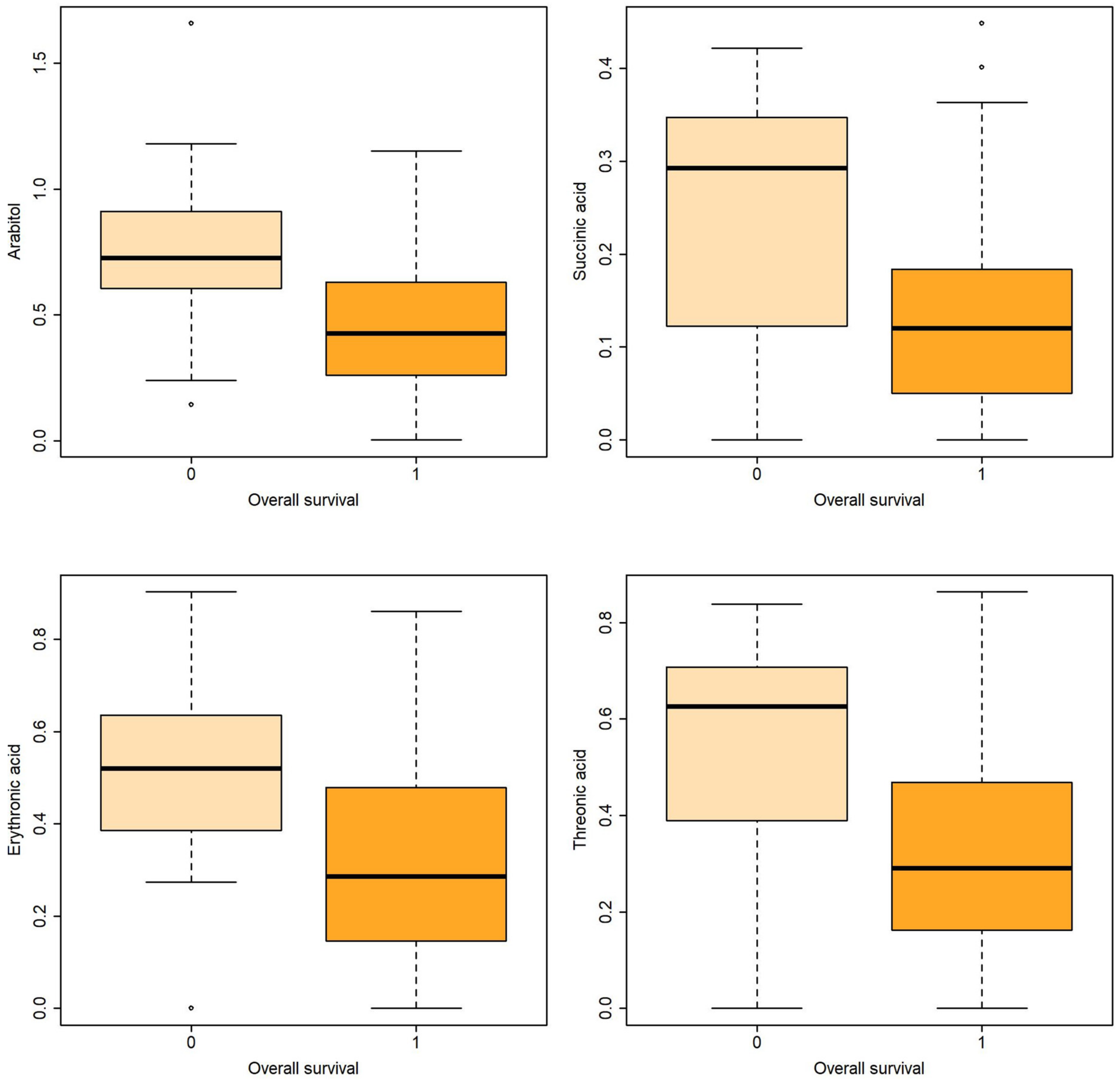
| Overall survival | ||||||||||
| Arabitol | Non-survival | 15 | 0.755 | 0.376 | 0.097 | 0.604 | 0.725 | 0.911 | 0.771 | [0.626,0.916] |
| Survival | 58 | 0.433 | 0.262 | 0.034 | 0.265 | 0.426 | 0.626 | |||
| Succinic acid | Non-survival | 15 | 0.247 | 0.139 | 0.036 | 0.122 | 0.292 | 0.347 | 0.737 | [0.575,0.900] |
| Survival | 58 | 0.133 | 0.112 | 0.014 | 0.051 | 0.120 | 0.183 | |||
| Erythronic acid | Non-survival | 15 | 0.502 | 0.271 | 0.069 | 0.385 | 0.519 | 0.635 | 0.737 | [0.575,0.900] |
| Survival | 58 | 0.297 | 0.212 | 0.027 | 0.147 | 0.285 | 0.478 | |||
| Threonic acid | Non-survival | 15 | 0.524 | 0.266 | 0.068 | 0.388 | 0.626 | 0.707 | 0.741 | [0.577,0.905] |
| Survival | 58 | 0.315 | 0.231 | 0.031 | 0.164 | 0.291 | 0.466 | |||
| Univariate Analysis | Multivariable Analysis | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | OR | 95% CI | p-Value | OR | 95% CI | p-Value |
| Survival on Day of Life 15 | ||||||
| Arabitol | 0.175 | [0.051,0.425] | <0.01 | 0.043 | [0.0007,0.311] | 0.032 |
| Succinic acid | 0.259 | [0.112,0.517] | <0.01 | 0.004 | [0.0013,0.242] | 0.011 |
| Erythronic acid | 0.194 | [0.060,0.453] | <0.01 | 0.076 | [0,0.012] | 0.011 |
| Threonic acid | 0.212 | [0.076,0.474] | <0.01 | 0.0000002 | [0,0.003] | 0.024 |
| Glyceric Acid | 0.476 | [0.244,0.839] | 0.017 | 0.197 | [0.043,0.787] | 0.020 |
| Overall survival | ||||||
| Arabitol | 0.004 | [0.0001,0.066] | <0.01 | 0.005 | [0.00005,0.123] | <0.01 |
| Succinic Acid | 0.004 | [0,0.005] | <0.01 | 0.000025 | [0.000000003,0.026] | <0.01 |
| Threonic acid | 0.001 | [0,0.036] | <0.01 | 0.005324 | [0.00006,0.202] | <0.01 |
| Erythronic acid | 0.0021 | [0,0.051] | <0.01 | 0.005208 | [0.00005,0.197] | <0.01 |
| Metabolite | Outcome | N | Mean | SD | SE | Q0.25 | Q0.5 | Q0.75 | AUC | AUC 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Survival | 68 | 0.611 | 0.971 | 0.117 | 0.129 | 0.274 | 0.569 | |||
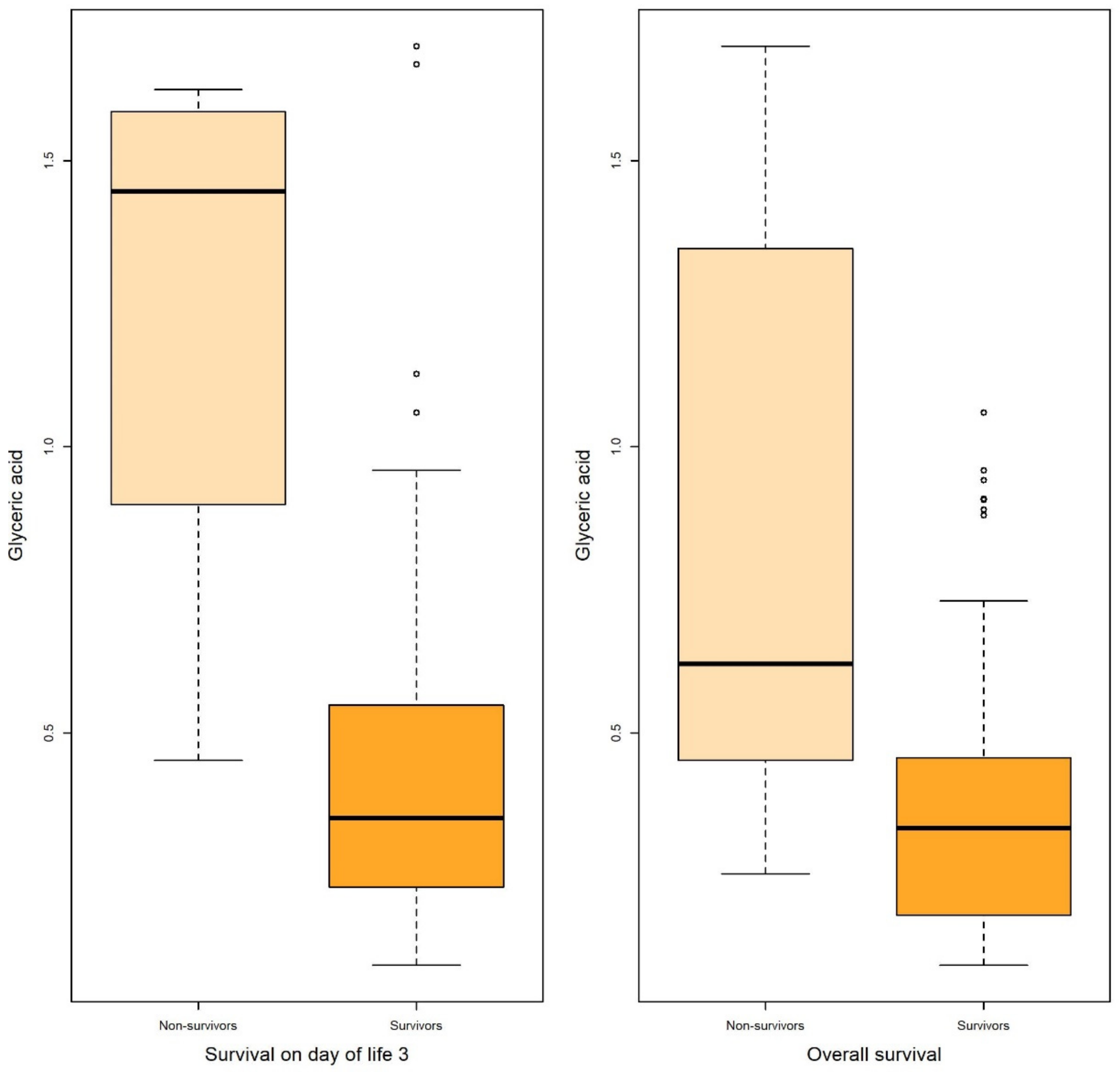
| Survival on Day of Life 3 | ||||||||||
| Glyceric acid | Non-survival | 4 | 1.242 | 0.540 | 0.270 | 1.122 | 1.446 | 1.566 | 0.896 | [0.736,1.000] |
| Survival | 82 | 0.437 | 0.318 | 0.035 | 0.231 | 0.351 | 0.543 | |||
| Survival on Day of Life 15 | ||||||||||
| Glyceric acid | Non-survival | 15 | 0.893 | 0.547 | 0.141 | 0.491 | 0.601 | 1.446 | 0.809 | [0.689,0.929] |
| Survival | 71 | 0.3867 | 0.244 | 0.028 | 0.190 | 0.341 | 0.466 | |||
| Proline | Non-survival | 15 | 2.287 | 2.781 | 0.718 | 0.139 | 1.126 | 3.4261 | 0.681 | [0.494–0.869] |
| Survival | 71 | 0.601 | 0.953 | 0.113 | 0.130 | 0.272 | 0.591 | |||
| Overall Survival | ||||||||||
| Glyceric acid | Non-survival | 18 | 0.837 | 0.517 | 0.122 | 0.471 | 0.620 | 1.291 | 0.805 | [0.696–0.914] |
| Survival | 68 | 0.379 | 0.244 | 0.029 | 0.182 | 0.333 | 0.454 | |||
| Proline HMDB0000162 | Non-survival | 18 | 1.965 | 2.632 | 0.621 | 0.166 | 0.841 | 3.008 | 0.648 | [0.481–0.815] |
| Survival | 68 | 0.611 | 0.971 | 0.117 | 0.129 | 0.274 | 0.569 | |||
| Univariate Analysis | Multivariable Analysis | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | OR | 95% CI | p-Value | OR | 95% CI | p-Value |
| Survival on Day of Life 3 | ||||||
| Glyceric acid | 0.287 | [0.136,0.518] | <0.01 | 0.267 | [0.110,0.521] | <0.01 |
| Survival on Day of Life 15 | ||||||
| Glyceric acid | 0.287 | [0.136,0.518] | <0.01 | 0.078 | [0.004,0.893] | 0.052 |
| Overall Survival | ||||||
| Glyceric acid | 0.297 | [0.144, 0.530] | <0.01 | 0.056 | [0.004,0.403] | <0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Besiri, K.; Begou, O.; Deda, O.; Bataka, E.; Nakas, C.; Gika, H.; Kontou, A.; Agakidou, E.; Sarafidis, K. A Cohort Study of Gastric Fluid and Urine Metabolomics for the Prediction of Survival in Severe Prematurity. Metabolites 2023, 13, 708. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13060708
Besiri K, Begou O, Deda O, Bataka E, Nakas C, Gika H, Kontou A, Agakidou E, Sarafidis K. A Cohort Study of Gastric Fluid and Urine Metabolomics for the Prediction of Survival in Severe Prematurity. Metabolites. 2023; 13(6):708. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13060708
Chicago/Turabian StyleBesiri, Konstantia, Olga Begou, Olga Deda, Evmorfia Bataka, Christos Nakas, Helen Gika, Angeliki Kontou, Eleni Agakidou, and Kosmas Sarafidis. 2023. "A Cohort Study of Gastric Fluid and Urine Metabolomics for the Prediction of Survival in Severe Prematurity" Metabolites 13, no. 6: 708. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13060708
APA StyleBesiri, K., Begou, O., Deda, O., Bataka, E., Nakas, C., Gika, H., Kontou, A., Agakidou, E., & Sarafidis, K. (2023). A Cohort Study of Gastric Fluid and Urine Metabolomics for the Prediction of Survival in Severe Prematurity. Metabolites, 13(6), 708. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13060708












