Instrumental Drift in Untargeted Metabolomics: Optimizing Data Quality with Intrastudy QC Samples
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Intrastudy QC-Samples in Metabolomics
3. Methods to Correct Metabolomics Data for Batch Effects
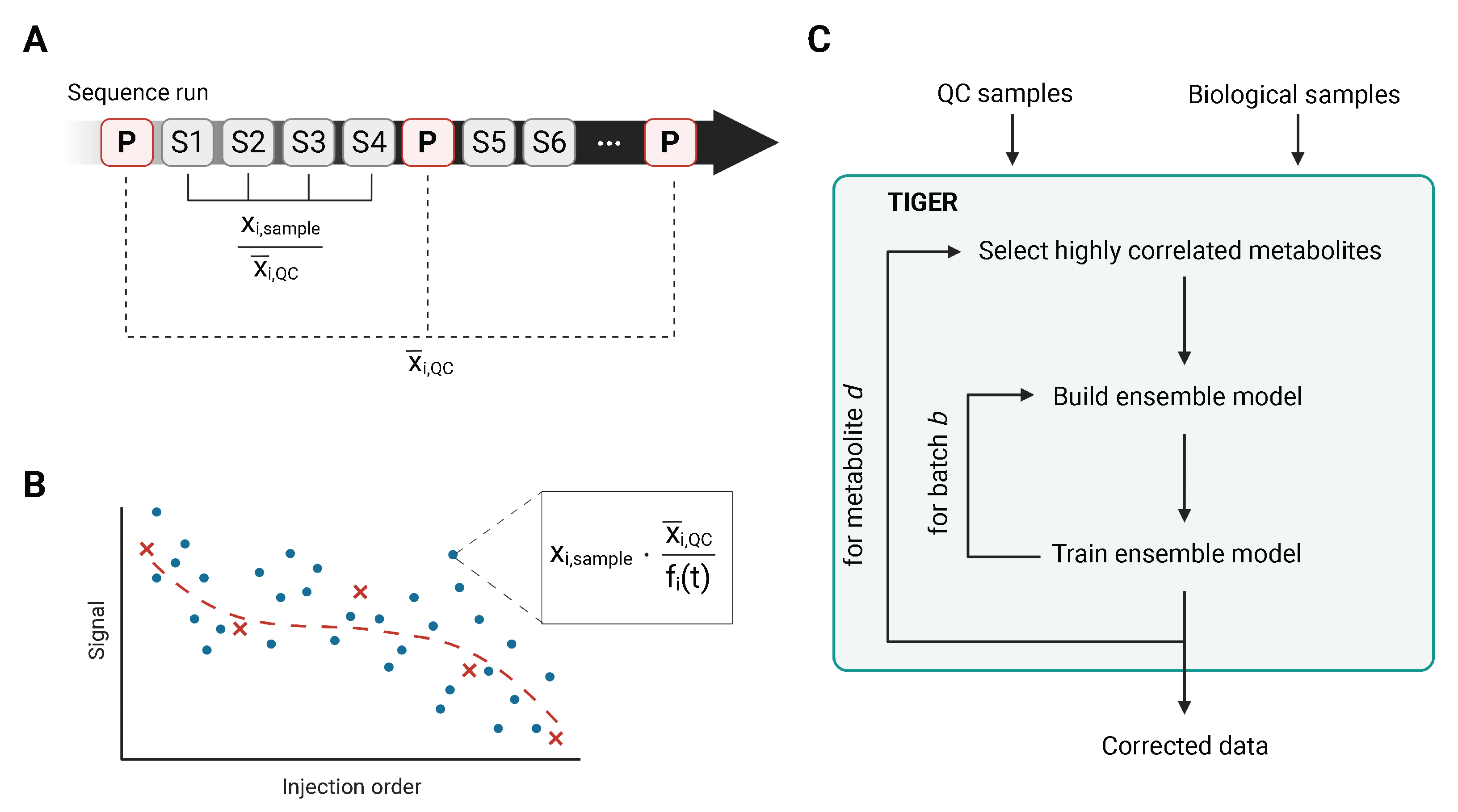
3.1. Median Normalization
3.2. Quality Control-Robust Spline Correction
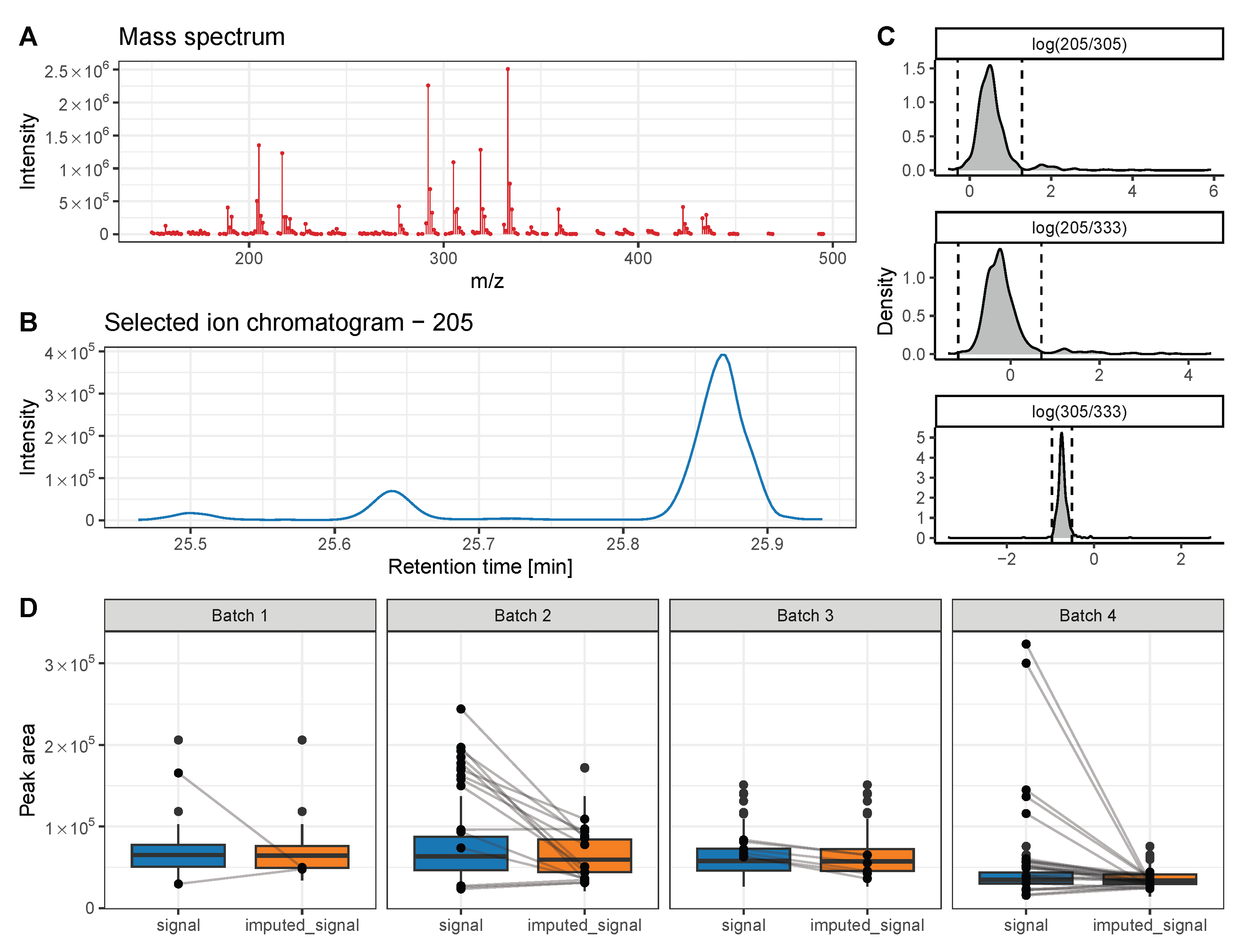
3.3. Technical Variation Elimination with Ensemble Learning Architecture
4. Evaluation of Batch-Effect Correction Methods
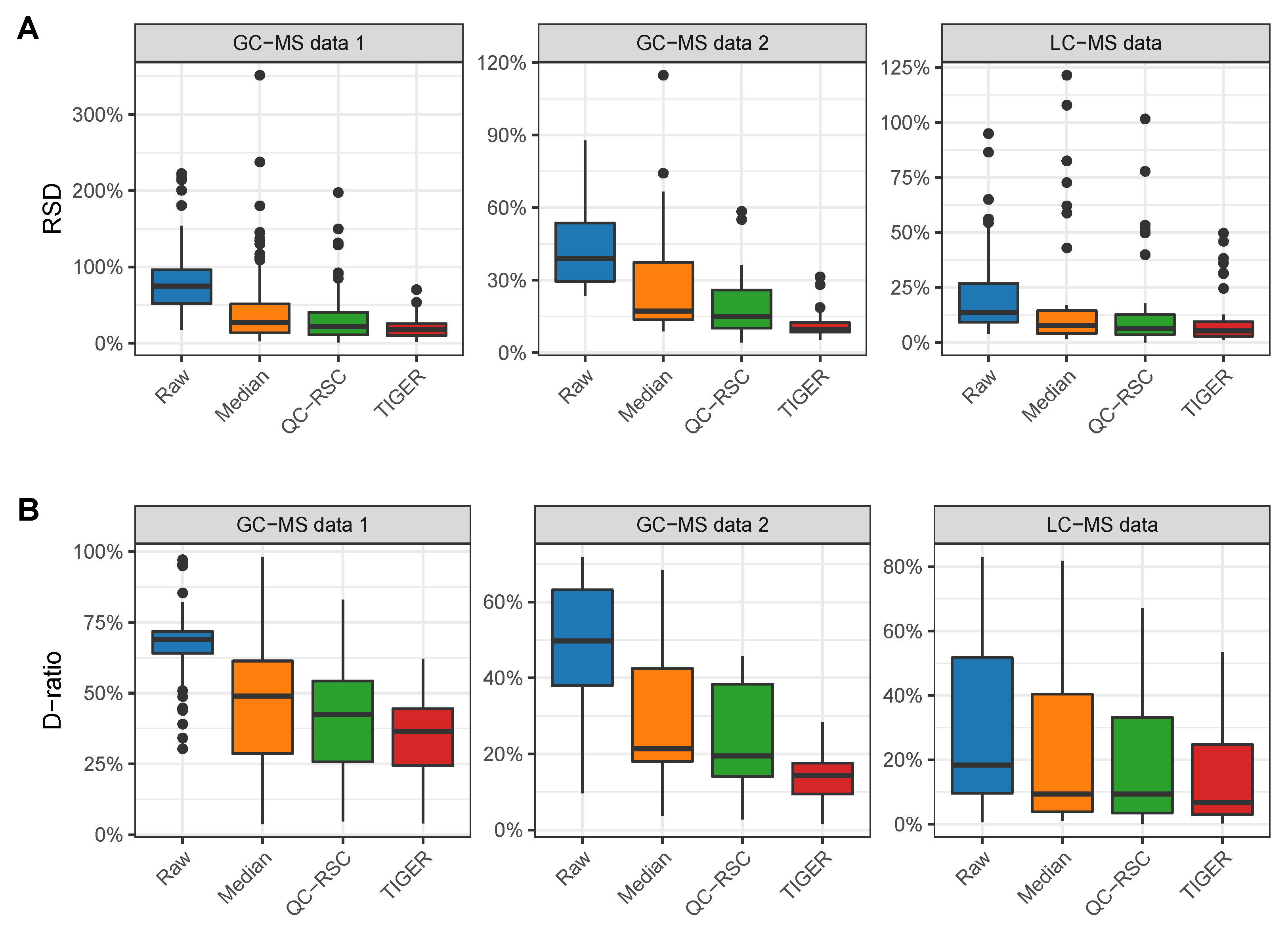
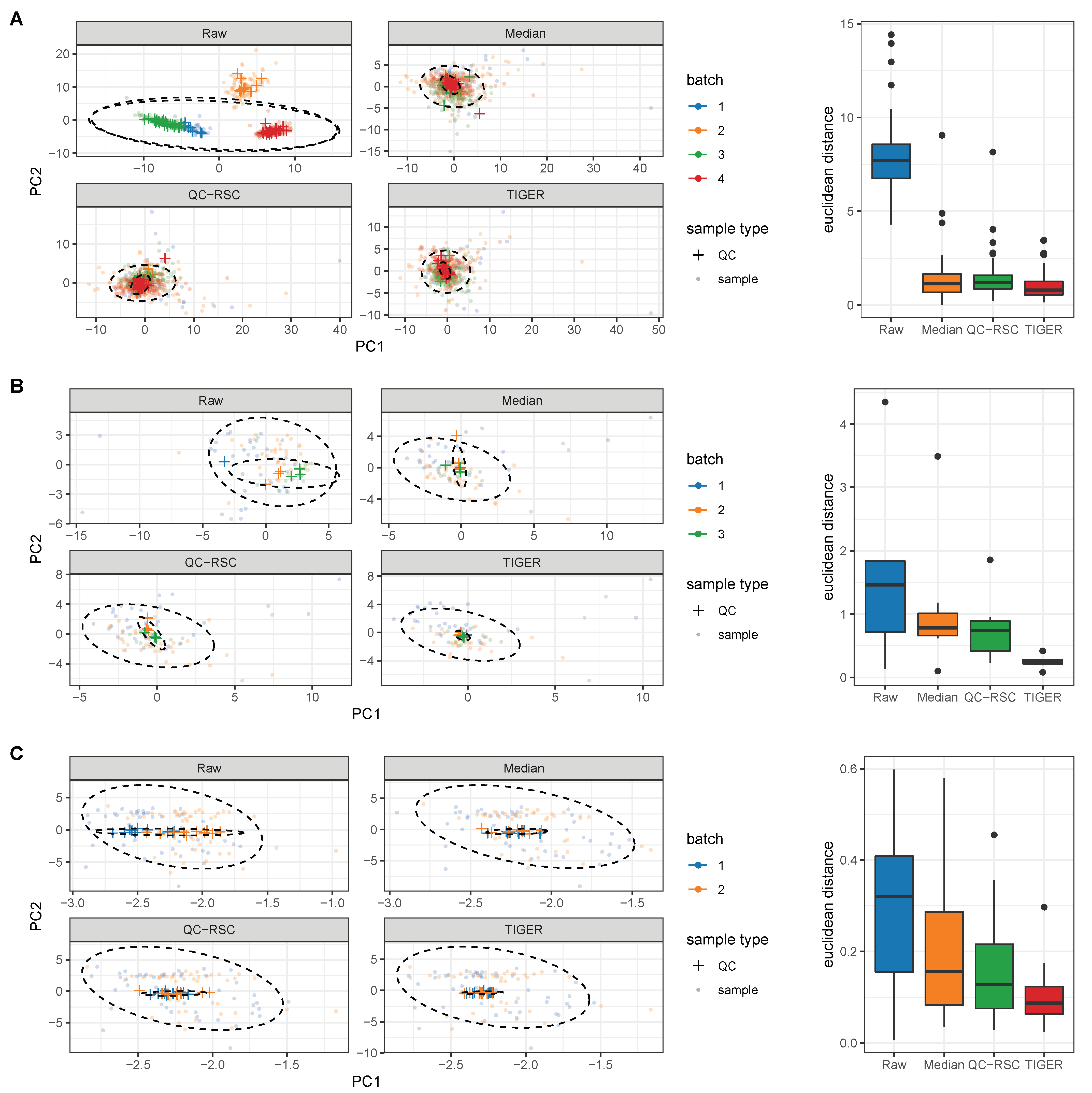
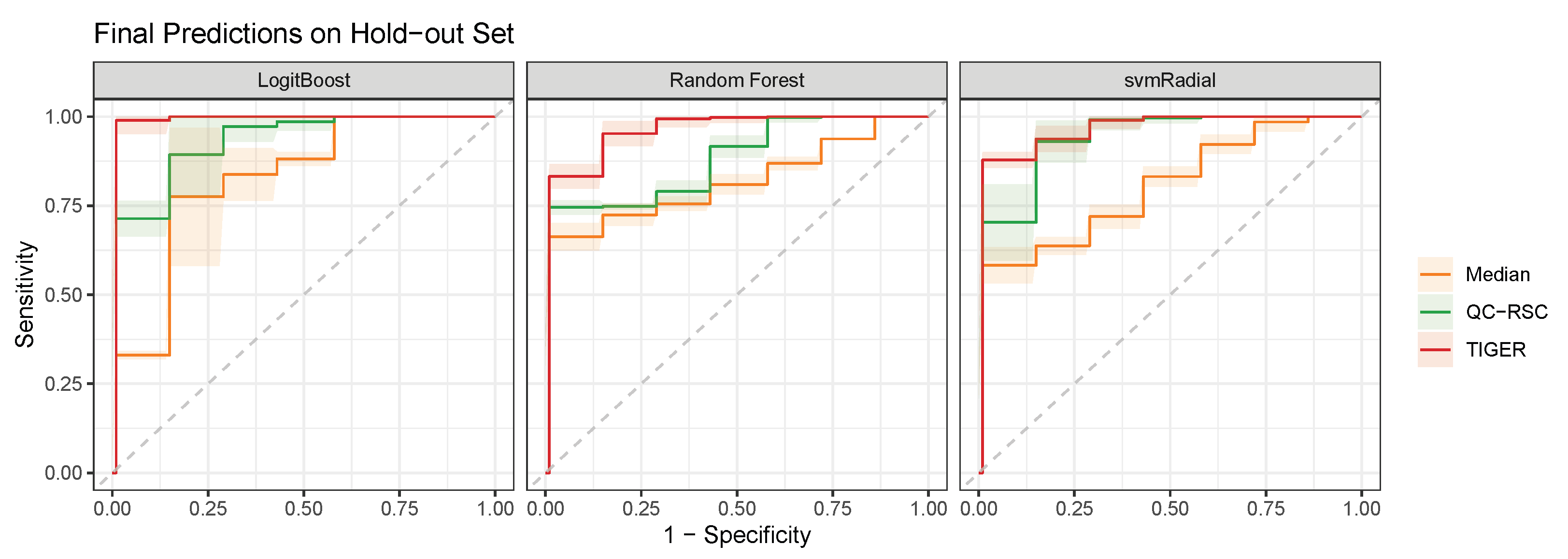
4.1. Evaluation Metrics
4.2. Comparison of Batch-Effect Correction Methods
5. Advanced Strategies to Further Improve Metabolite Quantification and Chromatogram Alignment
6. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AUROC | Area under the Receiver Operating Characteristic |
| CSF | Cerebrospinal fluid |
| CV | Cross validation |
| D-ratio | Dispersion-ratio |
| GC | Gas chromatography |
| LC | Liquid chromatography |
| LogitBoost | Boosted Logistic Regression |
| MS | Mass spectrometry |
| PCA | Principal component analysis |
| QC | Quality control |
| QC-RSC | Quality Control-Robust Spline Correction |
| RF | Random Forest |
| RFE | Recursive feature elimination |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristic |
| RSD | Relative standard deviation |
| RT | Retention time |
| svmRadial | Radial Kernel Support Vector Machine |
| TIGER | Technical variation elImination with ensemble learninG architEctuRe |
References
- Xia, J.; Broadhurst, D.I.; Wilson, M.; Wishart, D.S. Translational biomarker discovery in clinical metabolomics: An introductory tutorial. Metabolomics 2013, 9, 280–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wishart, D.S. Emerging applications of metabolomics in drug discovery and precision medicine. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2016, 15, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mapstone, M.; Cheema, A.K.; Fiandaca, M.S.; Zhong, X.; Mhyre, T.R.; MacArthur, L.H.; Hall, W.J.; Fisher, S.G.; Peterson, D.R.; Haley, J.M.; et al. Plasma phospholipids identify antecedent memory impairment in older adults. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 415–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siskos, A.P.; Jain, P.; Römisch-Margl, W.; Bennett, M.; Achaintre, D.; Asad, Y.; Marney, L.; Richardson, L.; Koulman, A.; Griffin, J.L.; et al. Interlaboratory Reproducibility of a Targeted Metabolomics Platform for Analysis of Human Serum and Plasma. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barri, T.; Dragsted, L.O. UPLC-ESI-QTOF/MS and multivariate data analysis for blood plasma and serum metabolomics: Effect of experimental artefacts and anticoagulant. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 768, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Han, W.; Su, X.; Li, L.; Li, L. Overcoming Sample Matrix Effect in Quantitative Blood Metabolomics Using Chemical Isotope Labeling Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 9424–9431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Yuen, P.; Pisitkun, T.; Gonzales, P.; Yasuda, H.; Dear, J.; Gross, P.; Knepper, M.; Star, R. Collection, storage, preservation, and normalization of human urinary exosomes for biomarker discovery. Kidney Int. 2006, 69, 1471–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammerlaan, W.; Trezzi, J.P.; Lescuyer, P.; Mathay, C.; Hiller, K.; Betsou, F. Method Validation for Preparing Serum and Plasma Samples from Human Blood for Downstream Proteomic, Metabolomic, and Circulating Nucleic Acid-Based Applications. Biopreservation Biobanking 2014, 12, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trezzi, J.P.; Bulla, A.; Bellora, C.; Rose, M.; Lescuyer, P.; Kiehntopf, M.; Hiller, K.; Betsou, F. LacaScore: A novel plasma sample quality control tool based on ascorbic acid and lactic acid levels. Metabolomics 2016, 12, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmquist, G.; Danielsson, R. Alignment of chromatographic profiles for principal component analysis: A prerequisite for fingerprinting methods. J. Chromatogr. A 1994, 687, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran, A.L.; Yang, J.; Wang, L.; Sumner, L.W. Metabolomics spectral formatting, alignment and conversion tools (MSFACTs). Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 2283–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.J.; Wright, B.W.; Jarman, K.H.; Synovec, R.E. High-speed peak matching algorithm for retention time alignment of gas chromatographic data for chemometric analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 2003, 996, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katajamaa, M.; Orešič, M. Processing methods for differential analysis of LC/MS profile data. BMC Bioinform. 2005, 6, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.A.; Want, E.J.; O’Maille, G.; Abagyan, R.; Siuzdak, G. XCMS: Processing Mass Spectrometry Data for Metabolite Profiling Using Nonlinear Peak Alignment, Matching, and Identification. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Souza, D.P.; Saunders, E.C.; McConville, M.J.; Likić, V.A. Progressive peak clustering in GC-MS Metabolomic experiments applied to Leishmania parasites. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 1391–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Styczynski, M.P.; Moxley, J.F.; Tong, L.V.; Walther, J.L.; Jensen, K.L.; Stephanopoulos, G.N. Systematic Identification of Conserved Metabolites in GC/MS Data for Metabolomics and Biomarker Discovery. Anal. Chem. 2006, 79, 966–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, L.; Ivosev, G.; Tate, S.; Impey, G.; Wingate, J.; Bonner, R. Instrumental and experimental effects in LC–MS-based metabolomics. J. Chromatogr. B 2008, 871, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Y.; Kuo, C.H.; Tseng, Y.J. Batch Normalizer: A Fast Total Abundance Regression Calibration Method to Simultaneously Adjust Batch and Injection Order Effects in Liquid Chromatography/Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics Data and Comparison with Current Calibration Methods. Anal. Chem. 2012, 85, 1037–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tautenhahn, R.; Patti, G.J.; Rinehart, D.; Siuzdak, G. XCMS Online: A Web-Based Platform to Process Untargeted Metabolomic Data. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 5035–5039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Lei, Z.; Huhman, D.; Sumner, L.W.; and Zhao, P.X. MET-XAlign: A Metabolite Cross-Alignment Tool for LC/MS-Based Comparative Metabolomics. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 9114–9119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunius, C.; Shi, L.; Landberg, R. Large-scale untargeted LC-MS metabolomics data correction using between-batch feature alignment and cluster-based within-batch signal intensity drift correction. Metabolomics 2016, 12, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiller, K.; Hangebrauk, J.; Jäger, C.; Spura, J.; Schreiber, K.; Schomburg, D. MetaboliteDetector: Comprehensive Analysis Tool for Targeted and Nontargeted GC/MS Based Metabolome Analysis. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 3429–3439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huan, T.; Wu, Y.; Tang, C.; Lin, G.; Li, L. DnsID in MyCompoundID for Rapid Identification of Dansylated Amine- and Phenol-Containing Metabolites in LC–MS-Based Metabolomics. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 9838–9845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benton, H.P.; Wong, D.M.; Trauger, S.A.; Siuzdak, G. XCMS2: Processing Tandem Mass Spectrometry Data for Metabolite Identification and Structural Characterization. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 6382–6389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clasquin, M.F.; Melamud, E.; Rabinowitz, J.D. LC-MS Data Processing with MAVEN: A Metabolomic Analysis and Visualization Engine; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehrens, R.; Hageman, J.A.; van Eeuwijk, F.; Kooke, R.; Flood, P.J.; Wijnker, E.; Keurentjes, J.J.B.; Lommen, A.; van Eekelen, H.D.L.M.; Hall, R.D.; et al. Improved batch correction in untargeted MS-based metabolomics. Metabolomics 2016, 12, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinal, M.; Viallon, C.; Thonat, C.; Berdagué, J.L. Pyrolysis-mass spectrometry for rapid classification of oysters according to rearing area. Endocr. Disruptors 2000, 28, 825–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérès, C.; Viallon, C.; Berdagué, J.L. Solid-Phase Microextraction-Mass Spectrometry: A New Approach to the Rapid Characterization of Cheeses. Anal. Chem. 2001, 73, 1030–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Albert, F.; Llorach, R.; Garcia-Aloy, M.; Ziyatdinov, A.; Andres-Lacueva, C.; Perera, A. Intensity drift removal in LC/MS metabolomics by common variance compensation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2899–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Gong, X.; Cai, Y.; Guo, Y.; Tu, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, T.; Wang, J.; Xue, F.; Zhu, Z.J. Normalization and integration of large-scale metabolomics data using support vector regression. Metabolomics 2016, 12, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccard, J.; Tonoli, D.; Strajhar, P.; Jeanneret, F.; Odermatt, A.; Rudaz, S. Removal of batch effects using stratified subsampling of metabolomic data for in vitro endocrine disruptors screening. Talanta 2019, 195, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, K.; Zhang, F.; Tan, Q.; Huang, Y.; Song, W.; Rong, Z.; Zhu, Z.J.; Li, K.; Li, Z. WaveICA: A novel algorithm to remove batch effects for large-scale untargeted metabolomics data based on wavelet analysis. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1061, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Hao, Z.; Zhao, C.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Huang, X.; Lin, X.; Zeng, Z.; et al. A Novel Strategy for Large-Scale Metabolomics Study by Calibrating Gross and Systematic Errors in Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 2234–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forshed, J. Experimental Design in Clinical ‘Omics Biomarker Discovery. J. Proteome Res. 2016, 16, 3954–3960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Tang, J.; Yang, Q.; Li, S.; Cui, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xue, W.; Li, X.; Zhu, F. NOREVA: Normalization and evaluation of MS-based metabolomics data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W162–W170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trezzi, J.P.; Galozzi, S.; Jaeger, C.; Barkovits, K.; Brockmann, K.; Maetzler, W.; Berg, D.; Marcus, K.; Betsou, F.; Hiller, K.; et al. Distinct metabolomic signature in cerebrospinal fluid in early parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2017, 32, 1401–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirwan, J.A.; Broadhurst, D.I.; Davidson, R.L.; Viant, M.R. Characterising and correcting batch variation in an automated direct infusion mass spectrometry (DIMS) metabolomics workflow. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 5147–5157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Huang, J.; Foppiano, F.; Prehn, C.; Adamski, J.; Suhre, K.; Li, Y.; Matullo, G.; Schliess, F.; Gieger, C.; et al. TIGER: Technical variation elimination for metabolomics data using ensemble learning architecture. Brief. Bioinform. 2022, 23, bbab535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holle, J.; Bartolomaeus, H.; Löber, U.; Behrens, F.; Bartolomaeus, T.U.; Anandakumar, H.; Wimmer, M.I.; Vu, D.L.; Kuhring, M.; Brüning, U.; et al. Inflammation in Children with CKD Linked to Gut Dysbiosis and Metabolite Imbalance. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2022, 33, 2259–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, W.B.; Wilson, I.D.; Nicholls, A.W.; Broadhurst, D. The importance of experimental design and QC samples in large-scale and MS-driven untargeted metabolomic studies of humans. Bioanalysis 2012, 4, 2249–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zheng, P.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, C.; Li, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, J.; Xie, P.; Xu, G. Discovery and Validation of Plasma Biomarkers for Major Depressive Disorder Classification Based on Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry. J. Proteome Res. 2015, 14, 2322–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangster, T.; Major, H.; Plumb, R.; Wilson, A.J.; Wilson, I.D. A pragmatic and readily implemented quality control strategy for HPLC-MS and GC-MS-based metabonomic analysis. Analyst 2006, 131, 1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barton, R.H.; Nicholson, J.K.; Elliott, P.; Holmes, E. High-throughput 1H NMR-based metabolic analysis of human serum and urine for large-scale epidemiological studies: Validation study. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2008, 37, i31–i40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, W.B.; Broadhurst, D.; Begley, P.; Zelena, E.; Francis-McIntyre, S.; Anderson, N.; Brown, M.; Knowles, J.D.; Halsall, A. Procedures for large-scale metabolic profiling of serum and plasma using gas chromatography and liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry. Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 1060–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godzien, J.; Alonso-Herranz, V.; Barbas, C.; Armitage, E.G. Controlling the quality of metabolomics data: New strategies to get the best out of the QC sample. Metabolomics 2014, 11, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadhurst, D.; Goodacre, R.; Reinke, S.N.; Kuligowski, J.; Wilson, I.D.; Lewis, M.R.; Dunn, W.B. Guidelines and considerations for the use of system suitability and quality control samples in mass spectrometry assays applied in untargeted clinical metabolomic studies. Metabolomics 2018, 14, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelena, E.; Dunn, W.B.; Broadhurst, D.; Francis-McIntyre, S.; Carroll, K.M.; Begley, P.; O’Hagan, S.; Knowles, J.D.; Halsall, A.; Wilson, I.D.; et al. Development of a Robust and Repeatable UPLC-MS Method for the Long-Term Metabolomic Study of Human Serum. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 1357–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begley, P.; Francis-McIntyre, S.; Dunn, W.B.; Broadhurst, D.I.; Halsall, A.; Tseng, A.; Knowles, J.; Goodacre, R.; and, D.B.K. Development and Performance of a Gas Chromatography-Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry Analysis for Large-Scale Nontargeted Metabolomic Studies of Human Serum. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 7038–7046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michopoulos, F.; Lai, L.; Gika, H.; Theodoridis, G.; Wilson, I. UPLC-MS-Based Analysis of Human Plasma for Metabonomics Using Solvent Precipitation or Solid Phase Extraction. J. Proteome Res. 2009, 8, 2114–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gika, H.G.; Theodoridis, G.A.; Wingate, J.E.; Wilson, I.D. Within-Day Reproducibility of an HPLC-MS-Based Method for Metabonomic Analysis: Application to Human Urine. J. Proteome Res. 2007, 6, 3291–3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, Z.; Tan, Q.; Cao, L.; Zhang, L.; Deng, K.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, Z.J.; Li, Z.; Li, K. NormAE: Deep Adversarial Learning Model to Remove Batch Effects in Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics Data. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 5082–5090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuligowski, J.; Sánchez-Illana, Á.; Sanjuán-Herráez, D.; Vento, M.; Quintás, G. Intra-batch effect correction in liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry using quality control samples and support vector regression (QC-SVRC). Anal. Chem. 2015, 140, 7810–7817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamleh, M.A.; Ebbels, T.M.D.; Spagou, K.; Masson, P.; Want, E.J. Optimizing the Use of Quality Control Samples for Signal Drift Correction in Large-Scale Urine Metabolic Profiling Studies. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 2670–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, M.R.; Pearce, J.T.M.; Spagou, K.; Green, M.; Dona, A.C.; Yuen, A.H.Y.; David, M.; Berry, D.J.; Chappell, K.; van der Sluis, V.H.; et al. Development and Application of Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography-TOF MS for Precision Large Scale Urinary Metabolic Phenotyping. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 9004–9013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinke, S.N.; Gallart-Ayala, H.; Gómez, C.; Checa, A.; Fauland, A.; Naz, S.; Kamleh, M.A.; Djukanović, R.; Hinks, T.S.; Wheelock, C.E. Metabolomics analysis identifies different metabotypes of asthma severity. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 49, 1601740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stekhoven, D.J.; Buhlmann, P. MissForest–non-parametric missing value imputation for mixed-type data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, R.; Wang, J.; Su, M.; Jia, E.; Chen, S.; Chen, T.; Ni, Y. Missing Value Imputation Approach for Mass Spectrometry-based Metabolomics Data. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Märtens, A.; Holle, J.; Mollenhauer, B.; Wegner, A.; Kirwan, J.; Hiller, K. Instrumental Drift in Untargeted Metabolomics: Optimizing Data Quality with Intrastudy QC Samples. Metabolites 2023, 13, 665. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13050665
Märtens A, Holle J, Mollenhauer B, Wegner A, Kirwan J, Hiller K. Instrumental Drift in Untargeted Metabolomics: Optimizing Data Quality with Intrastudy QC Samples. Metabolites. 2023; 13(5):665. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13050665
Chicago/Turabian StyleMärtens, Andre, Johannes Holle, Brit Mollenhauer, Andre Wegner, Jennifer Kirwan, and Karsten Hiller. 2023. "Instrumental Drift in Untargeted Metabolomics: Optimizing Data Quality with Intrastudy QC Samples" Metabolites 13, no. 5: 665. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13050665
APA StyleMärtens, A., Holle, J., Mollenhauer, B., Wegner, A., Kirwan, J., & Hiller, K. (2023). Instrumental Drift in Untargeted Metabolomics: Optimizing Data Quality with Intrastudy QC Samples. Metabolites, 13(5), 665. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13050665







