Value Addition Employing Waste Bio-Materials in Environmental Remedies and Food Sector
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Food Squander/Waste (FW): An Overview
2.1. Types of Food Waste
2.1.1. Agricultural Residues
2.1.2. Industrial Waste
3. Food Waste Management
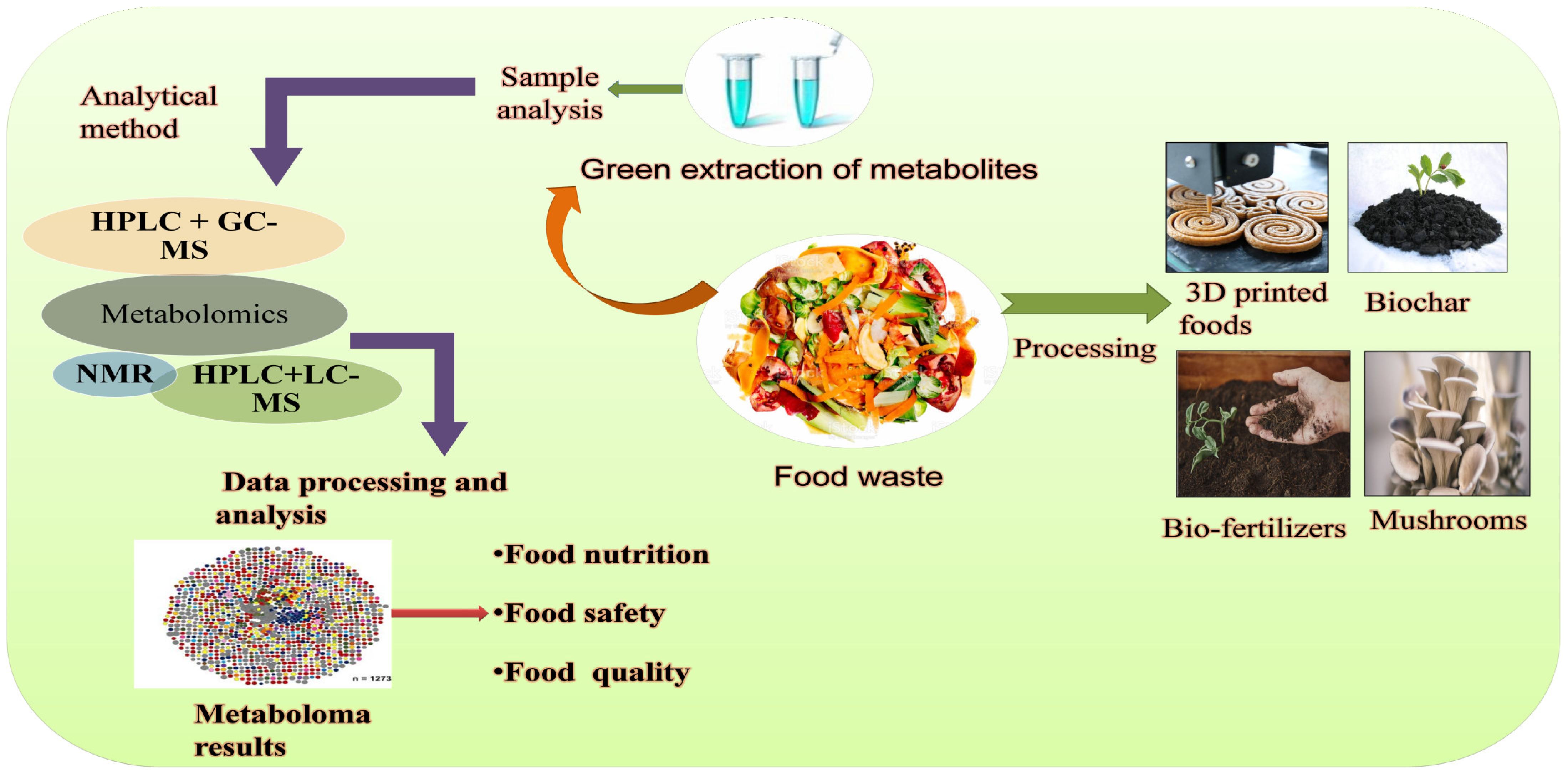
3.1. Metabolomics
3.2. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
4. Significant Wastage in Various Food Processing Segments and Their Valorisation
5. Reutilisation of FW
5.1. Bio Processes-Solid State Fermentation (SFF)
5.2. Mushroom Production
5.3. Anaerobic Co-Digestion (AcoD)
5.4. 3D/4D Food Printing: Extrusion Technology
5.5. Thermal Conversion and Composting of FW
6. Products Recovered from Industrial Wastes
6.1. Bioplastics and Biopolymers
6.2. Biofilms and Probiotics
6.3. Single-Cell Protein (SCP)
6.4. Bio Fertilisers, Biochar, and Biofuels
6.5. Organic Acids and Enzymes
6.6. Antibiotics and Biocontrol Agents (BCAs)
6.7. Food Additives and Antioxidants
7. Challenges Faced during Reutilisation of FW
8. Future Perspectives and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Strotmann, C.; Baur, V.; Börnert, N.; Gerwin, P. Generation and prevention of food waste in the German food service sector in the COVID-19 pandemic—Digital approaches to encounter the pandemic related crisis. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2022, 82, 101104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filimonau, V. The prospects of waste management in the hospitality sector post COVID-19. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 168, 105272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galanakis, C.M. The Food Systems in the Era of the Coronavirus (COVID-19) Pandemic Crisis. Foods 2020, 9, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arya, R.K.K.; Bisht, D.; Dhondiyal, K.; Kausar, M.; Lalhlenmawia, H.; Bhutia, P.L.; Kumar, D. Role of 3D Printing in Pharmaceutical Industry. In New Horizons for Industry 4.0 in Modern Business; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; Volume 102, pp. 273–294. [Google Scholar]
- Rudra, S.; Nishad, J.; Jakhar, N.; Kaur, C. Food industry waste: Mine of nutraceuticals. Int. J. Sci. Environ. Technol. 2015, 4, 205–229. [Google Scholar]
- Galali, Y.; Omar, Z.A.; Sajadi, S.M. Biologically active components in by-products of food processing. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 3004–3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melikoglu, M. Reutilisation of food wastes for generating fuels and value added products: A global review. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 19, 101040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phelan, A.; Meissner, K.; Humphrey, J.; Ross, H. Plastic pollution and packaging: Corporate commitments and actions from the food and beverage sector. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 331, 129827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Yu, X.; Wang, K.; Shen, D. Acidogenic fermentation of the main substrates of food waste to produce volatile fatty acids. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 21713–21720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannah, R.Y.; Merrylin, J.; Devi, T.P.; Kavitha, S.; Sivashanmugam, P.; Kumar, G.; Banu, J.R. Food waste valorization: Biofuels and value added product recovery. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2020, 11, 100524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishangulyyev, R.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.H. Understanding Food Loss and Waste—Why Are We Losing and Wasting Food? Foods 2019, 8, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginni, G.; Kavitha, S.; Kannah, Y.; Bhatia, S.K.; Kumar, A.; Rajkumar, M.; Kumar, G.; Pugazhendhi, A.; Chi, N.T.L.; Banu, R. Valorization of agricultural residues: Different biorefinery routes. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105435. [Google Scholar]
- El-Tayeb, T.; Abdelhafez, A.; Ali, S.; Ramadan, E. Effect of acid hydrolysis and fungal biotreatment on agro-industrial wastes for obtainment of free sugars for bioethanol production. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2012, 43, 1523–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motte, J.-C.; Trably, E.; Escudié, R.; Hamelin, J.; Steyer, J.-P.; Bernet, N.; Delgenes, J.-P.; Dumas, C. Total solids content: A key parameter of metabolic pathways in dry anaerobic digestion. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2013, 6, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scapinello, J.; Magro, J.D.; Block, J.M.; Di Luccio, M.; Tres, M.V.; Oliveira, J.V. Fatty acid profile of pecan nut oils obtained from pressurized n-butane and cold pressing compared with commercial oils. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 3366–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morsi, S.M.; Pakzad, A.; Amin, A.; Yassar, R.S.; Heiden, P.A. Chemical and nanomechanical analysis of rice husk modified by ATRP-grafted oligomer. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 360, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, D.; Giacobe, K.; Silva, C.M.; Saldanha, L.F.; Martins, A.F.; Flores, E.M.M.; Bizzi, C.A. Ultrasound-Assisted Demineralization Process of Sugarcane Straw and Its Influence on the Further Biomass Conversion. Sustainability 2022, 14, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida, L.G.F.; Parrella, R.A.D.C.; Simeone, M.L.F.; Ribeiro, P.C.D.O.; dos Santos, A.S.; Costa, A.; Guimarães, A.G.; Schaffert, R.E. Composition and growth of sorghum biomass genotypes for ethanol production. Biomass Bioenergy 2019, 122, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-León, B.; Corbino, G.; Dufresne, A.; Errea, M.I.; D’accorso, N.; Garcia, N.L. Arapey sweet potato peel waste as renewable source of antioxidant: Extraction, nanoencapsulation and nanoadditive potential in films. J. Polym. Res. 2021, 28, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, B.; Torrado, A.; Torre, P.; Converti, A.; Domínguez, J.M. Submerged Citric Acid Fermentation on Orange Peel Autohydrolysate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 2380–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesteros, L.F.; Teixeira, J.A.; Mussatto, S.I. Chemical, Functional, and Structural Properties of Spent Coffee Grounds and Coffee Silverskin. Food Bioproc. Technol. 2014, 7, 3493–3503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarry, S.E. Batch Equilibrium and Kinetic Studies of Simultaneous Adsorption and Biodegradation of Phenol by Pineapple Peels Immobilized Pseudomonas aeruginosa NCIB 950. Br. Biotechnol. J. 2012, 2, 26–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onipe, O.O.; Jideani, A.I.O.; Beswa, D. Composition and functionality of wheat bran and its application in some cereal food products. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 50, 2509–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalpanadevi, C.; Singh, V.; Subramanian, R. Influence of milling on the nutritional composition of bran from different rice varieties. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 2259–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pointner, M.; Kuttner, P.; Obrlik, T.; Jäger, A.; Kahr, H. Composition of corncobs as a substrate for fermentation of biofuels. Agron. Res. 2014, 12, 391–396. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; van der Heide, E.; Wang, H.; Li, B.; Yu, G.; Mu, X. Alkaline twin-screw extrusion pretreatment for fermentable sugar production. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2013, 6, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wadhwa, M.; Bakshi, M.P.S.; Makkar, H.P.S. Wastes to worth: Value added products from fruit and vegetable wastes. CAB Rev. 2015, 2015, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Kumari, S.; Dindhoria, K.; Manyapu, V.; Kumar, R. Efficient Utilization and Bioprocessing of Agro-Industrial Waste. Sustain. Agric. Rev. 2021, 56, 1–37. [Google Scholar]
- Gowman, A.C.; Picard, M.; Lim, L.-T.; Misra, M.; Mohanty, A.K. Fruit waste valorization for biodegradable biocomposite applications: A review. Bioresources 2019, 14, 10047–10092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van, J.C.F.; Tham, P.E.; Lim, H.R.; Khoo, K.S.; Chang, J.-S.; Show, P.L. Integration of Internet-of-Things as sustainable smart farming technology for the rearing of black soldier fly to mitigate food waste. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2022, 137, 104235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnemans, K.; Jones, P.T.; Blanpain, B.; Van Gerven, T.; Yang, Y.; Walton, A.; Buchert, M. Recycling of rare earths: A critical review. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 51, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badgett, A.; Milbrandt, A. Food waste disposal and utilization in the United States: A spatial cost benefit analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 314, 128057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar, N.; Laibach, N. Sustainability check for bio-based technologies: A review of process-based and life cycle approaches. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 135, 110213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makanjuola, O.; Arowosola, T.; Du, C. The Utilization of Food Waste: Challenges and Opportunities. J. Food Chem. Nanotechnol. 2020, 6, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Vimal, A.; Vishvakarma, R.; Kumar, P.; Vandenberghe, L.P.D.S.; Gaur, V.K.; Varjani, S. Deciphering the blackbox of omics approaches and artificial intelligence in food waste transformation and mitigation. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2022, 372, 109691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Hou, L.; Gao, J.; Li, D.; Tian, Z.; Fan, B.; Wang, F.; Li, S. Metabolomics Approaches for the Comprehensive Evaluation of Fermented Foods: A Review. Foods 2021, 10, 2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibarra-Estrada, E.; Soto-Hernández, R.M.; Palma-Tenango, M. Metabolomics as a Tool in Agriculture. Metab. Fundam. Appl. 2016, 28, 148–168. [Google Scholar]
- Alseekh, S.; Aharoni, A.; Brotman, Y.; Contrepois, K.; D’auria, J.; Ewald, J.; Ewald, J.C.; Fraser, P.D.; Giavalisco, P.; Hall, R.D.; et al. Mass spectrometry-based metabolomics: A guide for annotation, quantification and best reporting practices. Nat. Methods 2021, 18, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, M.A.; de Souza, L.P.; Serag, A.; Fernie, A.R.; Farag, M.A.; Ezzat, S.M.; Alseekh, S. Metabolomics in the Context of Plant Natural Products Research: From Sample Preparation to Metabolite Analysis. Metabolites 2020, 10, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, L.P.; Alseekh, S.; Scossa, F.; Fernie, A.R. Ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography high-resolution mass spectrometry variants for metabolomics research. Nat. Methods 2021, 18, 733–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano-Elena, F.; Fàbregas, N.; Coleto-Alcudia, V.; Caño-Delgado, A.I. Analysis of metabolic dynamics during drought stress in Arabidopsis plants. Sci. Data 2022, 9, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, R.; Peng, C.; Zhang, X.; Qiu, D.; Mao, G.; Lu, Y.; Zeng, J. A comparative UPLC-Q-Orbitrap-MS untargeted metabolomics investigation of different parts of Clausena lansium (Lour.) Skeels. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 5811–5822. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Hu, L.P.; Liu, G.M.; Zhang, D.S.; He, H.J. Evaluation of the nutritional quality of Chinese kale (Brassica alboglabra Bailey) using UHPLC-Quadrupole-Orbitrap MS/MS-based metabolomics. Molecules 2017, 22, 1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younis, I.Y.; Mohsen, E.; Ibrahim, R.M.; Fernie, A.R.; Alseekh, S.; Salem, M.A. Non-targeted metabolomics and chemometrics for saffron (Crocus sativus L.) authentication and adulteration detection in relation to its anticholinesterase activity. Food Chem. Adv. 2023, 2, 100217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciampa, A.; Danesi, F.; Picone, G. NMR-Based Metabolomics for a More Holistic and Sustainable Research in Food Quality Assessment: A Narrative Review. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roda, A.; Lucini, L.; Torchio, F.; Dordoni, R.; De Faveri, D.M.; Lambri, M. Metabolite profiling and volatiles of pineapple wine and vinegar obtained from pineapple waste. Food Chem. 2017, 229, 734–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, K.S.; Almalki, W.H.; Makeen, H.A.; Albratty, M.; Meraya, A.M.; Nagraik, R.; Sharma, A.; Kumar, D.; Chellappan, D.K.; Singh, S.K.; et al. Role of Medicinal plant-derived Nutraceuticals as a potential target for the treatment of breast cancer. J. Food Biochem. 2022, 19, e14387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truzzi, E.; Chaouch, M.A.; Rossi, G.; Tagliazucchi, L.; Bertelli, D.; Benvenuti, S. Characterization and Valorization of the Agricultural Waste Obtained from Lavandula Steam Distillation for Its Reuse in the Food and Pharmaceutical Fields. Molecules 2022, 27, 1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Reidah, I.M.; Arráez-Román, D.; Warad, I.; Fernández-Gutiérrez, A.; Segura-Carretero, A. UHPLC/MS2-based approach for the comprehensive metabolite profiling of bean (Vicia faba L.) by-products: A promising source of bioactive constituents. Food Res. Int. 2017, 93, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Lu, F.; Jia, Y.; Yang, B. Metabolomic analyses of banana during postharvest senescence by 1H-high resolution-NMR. Food Chem. 2017, 218, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Dong, T.; Huang, W.; Du, M.; Chen, D.; Fernie, A.R.; Yi, G.; Yan, S. Spatially resolved metabolomics reveals variety-specific metabolic changes in banana pulp during postharvest senescence. Food Chem. X 2022, 15, 100371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, D.M.; van den Berg, M.A.; Hall, R.D. Towards superior plant-based foods using metabolomics. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2021, 70, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durazzo, A.; Carocho, M.; Lucarini, M. Bioactive Molecules in Food: From Food Composition and Dedicated Databases to Metabolomic Pathways. J. Food Qual. 2022, 2022, 9897582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-Y.; Zhu, Z.-J.; Ren, S.-P.; Deng, Y.-C.; Xu, J.-Y.; Zhang, S.-M.; Gao, J.-M.; Zhang, Q. Metabolomic navigated Citrus waste repurposing to restore amino acids disorder in neural lesion. Food Chem. 2022, 387, 132933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Ma, Z.; Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Jiang, H.; Qu, T.; Zhang, W.; Li, C.; Liu, S. Characterization of the flavor and nutritional value of coconut water vinegar based on metabolomics. Food Chem. 2022, 369, 130872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Görgüç, A.; Özer, P.; Yılmaz, F.M. Microwave-assisted enzymatic extraction of plant protein with antioxidant compounds from the food waste sesame bran: Comparative optimization study and identification of metabolomics using LC/Q-TOF/MS. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2019, 44, e14304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Ruiz, R.; Costa-Font, M.; Gil, J.M. Moving ahead from food-related behaviours: An alternative approach to understand household food waste generation. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 1140–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, Y. Food Waste Management with Technological Platforms: Evidence from Indian Food Supply Chains. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolidis, C.; Brown, D.; Wijetunga, D.; Kathriarachchi, E. Sustainable value co-creation at the Bottom of the Pyramid: Using mobile applications to reduce food waste and improve food security. J. Mark. Manag. 2021, 37, 856–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farr-Wharton, G.; Choi, J.H.-J.; Foth, M. Food talks back. In Proceedings of the 26th Australian Computer-Human Interaction Conference on Designing Futures: The Future of Design, Sydney, Australia, 2–5 December 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Liegeard, J.; Manning, L. Use of intelligent applications to reduce household food waste. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 1048–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slanina, J. Food Waste Management System. U.S. Patent US 20120261320A1, 15 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Abdallah, M.; Abu Talib, M.; Feroz, S.; Nasir, Q.; Abdalla, H.; Mahfood, B. Artificial intelligence applications in solid waste management: A systematic research review. Waste Manag. 2020, 109, 231–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winnow Solutions Limited. System and Method for Monitoring Food Waste; Winnow Solutions Limited: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Feerer, A.; Hasbulatovich, M.; Zagorsky, D. Method and System for Wasteless Processing and Complete Utilization of Municipal and Domestic Wastes. U.S. Patent US8419902B2, 16 April 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Shakman, A.; Rogers, S.; Leppo, W. Systemis and Methods for Food Waste Monitoring. U.S. Patent US7415375B2, 19 August 2008. [Google Scholar]
- The 77-lab. 2022. Available online: https://meche.mit.edu/lab/77-lab (accessed on 5 April 2023).
- Sadh, P.K.; Chawla, P.; Duhan, J.S. Fermentation approach on phenolic, antioxidants and functional properties of peanut press cake. Food Biosci. 2018, 22, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pap, N.; Pongrácz, E.; Myllykoski, L.; Keiski, R.L. Waste minimization and utilization in the food industry: Valorization of food industry wastes and byproducts. In Introduction to Advanced Food Process Engineering; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; pp. 609–644. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Chen, Q.; Lü, X. Pectin extracted from apple pomace and citrus peel by subcritical water. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 38, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, A.; Ponnuchamy, M.; Kapoor, A.; Prabhakar, S. Valorization of food waste as adsorbents for toxic dye removal from contaminated waters: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiago, R.D.S.M.; Pedro, P.M.D.M.; Eliana, F.C.S. Solid wastes in brewing process: A review. J. Brew. Distill. 2014, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachwał, K.; Waśko, A.; Gustaw, K.; Polak-Berecka, M. Utilization of brewery wastes in food industry. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saraiva, A.; Carrascosa, C.; Raheem, D.; Ramos, F.; Raposo, A. Natural Sweeteners: The Relevance of Food Naturalness for Consumers, Food Security Aspects, Sustainability and Health Impacts. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belović, M.; Torbica, A.; Pajić-Lijaković, I.; Mastilović, J. Development of low calorie jams with increased content of natural dietary fibre made from tomato pomace. Food Chem. 2017, 237, 1226–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grassino, A.; Halambek, J.; Djaković, S.; Rimac Brnčić, S.; Dent, M.; Grabarić, Z. Utilization of tomato peel waste from canning factory as a potential source for pectin production and application as tin corrosion inhibitor. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 52, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čanadanović-Brunet, J.M.; Savatović, S.S.; Ćetković, G.S.; Vulić, J.J.; Djilas, S.M.; Markov, S.L.; Cvetković, D.D. Antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of beet root pomace extracts. Czech J. Food Sci. 2011, 29, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhang, C.; Li, W. Ultrasound-assisted enzyme catalyzed hydrolysis of olive waste and recovery of antioxidant phenolic compounds. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2017, 44, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayğılı, H.; Güzel, F.; Önal, Y. Conversion of grape industrial processing waste to activated carbon sorbent and its performance in cationic and anionic dyes adsorption. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 93, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giampieri, F.; Cianciosi, D.; Forbes-Hernández, T. Myrtle (Myrtus communis L.) berries, seeds, leaves, and essential oils: New undiscovered sources of natural compounds with promising health benefits. Food Front. 2020, 1, 276–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, A.; Schulz, P.; Rizvi, S.S. Valorization of bioactive compounds in fruit pomace from agro-fruit industries: Present Insights and future challenges. Food Biosci. 2021, 44, 101384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abebaw, G. Review on: Its Potentials and Application of Potato Peel (Waste). J. Aquac. Livest. Prod. 2020, 1, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Panesar, P.S.; Nanda, V. Utilization of carrot pomace for the preparation of a value added product. World J. Dairy Food Sci. 2006, 1, 22–27. [Google Scholar]
- Mousa, M.M.H.; El-Magd, M.A.; Ghamry, H.I.; Alshahrani, M.Y.; El-Wakeil, N.H.M.; Hammad, E.M.; Asker, G.A.H. Pea peels as a value-added food ingredient for snack crackers and dry soup. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 22747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šeregelj, V.; Pezo, L.; Šovljanski, O.; Lević, S.; Nedović, V.; Markov, S.; Tomić, A.; Čanadanović-Brunet, J.; Vulić, J.; Šaponjac, V.T.; et al. New concept of fortified yogurt formulation with encapsulated carrot waste extract. LWT 2021, 138, 110732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, O.; Pereira, R.; Rodrigues, R.M.; Texiera, J.A.; Vicente, A.A.; Malcata, F.X. Whey and whey powders: Production and uses. In The Encyclopedia of Food and Health; Caballero, B., Toldra, F., Eds.; Oxford Academic: Oxford, UK, 2016; pp. 498–505. [Google Scholar]
- Prazeres, A.; Carvalho, F.; Rivas, J. Cheese whey management: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 110, 48–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurilmalaa, M.; Suryamarevita, H.; Hizbullah, H.H.; Jacoeb, A.M.; Ochiai, Y. Fish skin as a biomaterial for halal collagen and gelatin. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 29, 1100–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnedy, P.A.; FitzGerald, R.J. Bioactive peptides from marine processing waste and shellfish: A review. J. Funct. Foods 2012, 4, 6–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Ghosh, R.; Cui, Z. High-resolution plasma protein fractionation using ultrafiltration. Desalination 2002, 144, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjakul, S.; Oungbho, K.; Visessanguan, W.; Thiansilakul, Y.; Roytrakul, S. Characteristics of gelatin from the skins of bigeye snapper, Priacanthus tayenus and Priacanthus macracanthus. Food Chem. 2009, 116, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayathilakan, K.; Sultana, K.; Radhakrishna, K.; Bawa, A.S. Utilization of byproducts and waste materials from meat, poultry and fish processing industries: A review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 49, 278–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.; Munir, D.; Santos, R.M. Beneficial use of animal hides for abattoir and tannery waste management: A review of unconventional, innovative, and sustainable approaches. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 1807–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kizilkaya, B.; Tekınay, A.A. Utilization to Remove Pb (II) Ions from Aqueous Environments Using Waste Fish Bones by Ion Exchange. J. Chem. 2014, 2014, 739273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebayo, F.; Obiekezie, S. Microorganisms in Waste Management. Res. J. Sci. Technol. 2018, 10, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadj Saadoun, J.; Bertani, G.; Levante, A.; Vezzosi, F.; Ricci, A.; Bernini, V.; Lazzi, C. Fermentation of Agri-Food Waste: A Promising Route for the Production of Aroma Compounds. Foods 2021, 10, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggelopoulos, T.; Katsieris, K.; Bekatorou, A.; Pandey, A.; Banat, I.M.; Koutinas, A.A. Solid state fermentation of food waste mixtures for single cell protein, aroma volatiles and fat production. Food Chem. 2014, 145, 710–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, O.; Sánchez, A.; Font, X.; Barrena, R. Enhancing the bioproduction of value-added aroma compounds via solid-state fermentation of sugarcane bagasse and sugar beet molasses: Operational strategies and scaling-up of the process. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 263, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, B.; Favini, F.; Scaglia, B.; Sciarria, T.P.; D’imporzano, G.; Pognani, M.; Alekseeva, A.; Eisele, G.; Cosentino, C.; Adani, F. Enhanced polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) production from the organic fraction of municipal solid waste by using mixed microbial culture. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2017, 10, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cudjoe, D.; Zhu, B.; Wang, H. Towards the realization of sustainable development goals: Benefits of hydrogen from biogas using food waste in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 360, 132161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, C.C.J.; Cheung, A.S.Y.; Zhang, A.Y.-Z.; Lam, K.F.; Lin, C.S.K. Utilisation of waste bread for fermentative succinic acid production. Biochem. Eng. J. 2012, 65, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkan, H.; Baysal, Z.; Uyar, F.; Dogru, M. Production of lipase by a newly isolated Bacillus coagulans under solid-state fermentation using melon wastes. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2007, 136, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, R.; Paul, T.; Soren, J.P.; Halder, S.K.; Mondal, K.C.; Pati, B.R.; Das Mohapatra, P.K. Acidophilic α-Amylase Production from Aspergillus niger RBP7 Using Potato Peel as Substrate: A Waste to Value Added Approach. Waste Biomass Valorization 2017, 10, 851–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Loh, K.-C. Enhanced food waste anaerobic digestion: An encapsulated metal additive for shear stress-based controlled release. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 235, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peinemann, J.C.; Rhee, C.; Shin, S.G.; Pleissner, D. Non-sterile fermentation of food waste with indigenous consortium and yeast—Effects on microbial community and product spectrum. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 306, 123175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, J.; Saxena, J.; Sanwal, P. Biochar: A sustainable approach for improving plant growth and soil properties. In Biochar—An Imperative Amendment for Soil and the Environment; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Lopes, F.C.; Ligabue-Braun, R. Agro-Industrial Residues: Eco-Friendly and Inexpensive Substrates for Microbial Pigments Production. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2021, 5, 589414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siqueira, F.; Martos, E.; Silva, R.; Dias, E. Cultivation of Pleurotus sajor-caju on banana stalk and Bahia grass based substrates. Hortic. Bras. 2011, 29, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushpa, S.M.; Manonmani, H.K. Bioconversion of coffee industry wastes with white rot fungus Pleurotus florida. Res. J. Environ. Sci. 2008, 2, 145–150. [Google Scholar]
- Babu, P.D.; Subhasree, R.S. Valuing the suitable agro-industrial wastes for cultivation of P. platypus and P. eous. Adv. Biol. Res. 2010, 4, 207–210. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, F.; Okopi, S.I.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Meng, L.; Li, Y.; Sun, W.; Li, C. Multi-criteria assessment of food waste and waste paper anaerobic co-digestion: Effects of inoculation ratio, total solids content, and feedstock composition. Renew. Energy 2022, 194, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Chang, N.; Li, Y.-Y.; Liu, J. Anaerobic co-digestion of food waste with municipal solid waste leachate: A review and prospective application with more benefits. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 174, 105832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fermoso, F.G.; Serrano, A.; Alonso-Fariñas, B.; Fernandez-Bolaños, J.; Borja, R.; Rodríguez-Gutiérrez, G. Valuable Compound Extraction, Anaerobic Digestion, and Composting: A Leading Biorefinery Approach for Agricultural Wastes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 8451–8468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anjum, M.; Khalid, A.; Qadeer, S.; Miandad, R. Synergistic effect of co-digestion to enhance anaerobic degradation of catering waste and orange peel for biogas production. Waste Manag. Res. J. Sustain. Circ. Econ. 2017, 35, 967–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koszel, M.; Lorencowicz, E. Agricultural Use of Biogas Digestate as a Replacement Fertilizers. Agric. Agric. Sci. Procedia 2015, 7, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andriamanohiarisoamanana, F.J.; Yasui, S.; Yamashiro, T.; Ramanoelina, V.; Ihara, I.; Umetsu, K. Anaerobic co-digestion: A sustainable approach to food processing organic waste management. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2020, 22, 1501–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Wang, Y.; Lin, H.; van Lierop, L.; Hu, B. Facilitating solid-state anaerobic digestion of food waste via bio-electrochemical treatment. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 166, 112637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taneja, A.; Sharma, R.; Ayush, K.; Sharma, A.; Khaneghah, A.M.; Regenstein, J.M.; Barba, F.J.; Phimolsiripol, Y.; Sharma, S. Innovations and applications of 3-D printing in food sector. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 3326–3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagadiswaran, B.; Alagarasan, V.; Palanivelu, P.; Theagarajan, R.; Moses, J.; Anandharamakrishnan, C. Valorization of food industry waste and by-products using 3D printing: A study on the development of value-added functional cookies. Futur. Foods 2021, 4, 100036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthurajan, M.; Veeramani, A.; Rahul, T.; Gupta, R.K.; Anukiruthika, T.; Moses, J.A.; Anandharamakrishnan, C. Valorization of Food Industry Waste Streams Using 3D Food Printing: A Study on Noodles Prepared from Potato Peel Waste. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2021, 14, 1817–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Rocha-Mendoza, D.; Shan, S.; Smith, Z.; García-Cano, I.; Prost, J.; Jimenez-Flores, R.; Campanella, O. Characterization and Cellular Uptake of Peptides Derived from In Vitro Digestion of Meat Analogues Produced by a Sustainable Extrusion Process. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 8124–8133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agapios, A.; Andreas, V.; Marinos, S.; Katerina, M.; Antonis, Z.A. Waste aroma profile in the framework of food waste management through household composting. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 257, 120340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobaharan, K.; Novair, S.B.; Lajayer, B.A.; van Hullebusch, E.D. Phosphorus Removal from Wastewater: The Potential Use of Biochar and the Key Controlling Factors. Water 2021, 13, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galanakis, C.M. (Ed.) Sustainable Food Processing and Engineering Challenges; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Q.; Liu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, J.; Wang, Y.; Ma, X. Active edible films with plant extracts: A updated review of their types, preparations, reinforcing properties, and applications in muscle foods packaging and preservation. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, Y.F.; Kumar, V.; Samadar, P.; Yang, Y.; Lee, J.; Ok, Y.S.; Song, H.; Kim, K.-H.; Kwon, E.E.; Jeon, Y.J. Production of bioplastic through food waste valorization. Environ. Int. 2019, 127, 625–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Vazquez, S.A.; Hailes, H.; Evans, J.R.G. Hydrophobic Polymers from Food Waste: Resources and Synthesis. Polym. Rev. 2013, 53, 627–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleissner, D.; Lam, W.C.; Sun, Z.; Lin, C.S.K. Food waste as nutrient source in heterotrophic microalgae cultivation. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 137, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prameela, K.; Mohan, C.M.; Ramakrishna, C. Biopolymers for food design: Consumer-friendly natural ingredients. In Biopolymers for Food Design; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Cecchini, C. Bioplastics made from upcycled food waste. Prospects for their use in the field of design. Des. J. 2017, 20 (Suppl. S1), S1596–S1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratap Singh, D.; Packirisamy, G. Biopolymer based edible coating for enhancing the shelf life of Horticulture Products. Food Chem. Mol. Sci. 2022, 4, 100085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Luo, X.; Liu, S.; Wan, W.; Huang, Q.; Chen, W. A novel eco-friendly recycling of food waste for preparing biofilm-attached biochar to remove Cd and Pb in wastewater. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 311, 127514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zan, F.; Liang, Z.; Jiang, F.; Dai, J.; Chen, G. Effects of food waste addition on biofilm formation and sulfide production in a gravity sewer. Water Res. 2019, 157, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, B.; Mei, S.; Su, X.; Chen, H.; Zhu, J.; Zheng, Z.; Lin, H.; Dai, C.; Luque, R.; Yang, D.-P. Integrating waste fish scale-derived gelatin and chitosan into edible nanocomposite film for perishable fruits. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 191, 1164–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinika, I.; Verma, D.K.; Balia, R.; Utama, G.L.; Patel, A.R. Potential of cheese whey bioactive proteins and peptides in the development of antimicrobial edible film composite: A review of recent trends. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 103, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.-H.; Dong, X.; Lv, L.; Wang, Z.-G.; Xu, Q.-Q.; Liu, X.-L.; Yan, H. Economic production of probiotics from kitchen waste. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2013, 22, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paredes-López, O.; Medoza-Madrid, J.E.; Camargo, E. Production of single-cell protein from waste paper by a mixed culture. Experientia 1974, 30, 205–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, A.K.; Sengupta, S.; Bhowal, J.; Bhattacharya, D.K. Utilization of fruit wastes producing single cell protein. Int. J. Sci. Environ. Technol. 2012, 1, 430–438. [Google Scholar]
- Anupama; Ravindra, P. Value-added food: Single cell protein. Biotechnol. Adv. 2000, 18, 459–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makan, A.; Fadili, A.; Oubenali, M. Interaction of physicochemical parameters during pressurized in-vessel composting of food waste. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2020, 10, 100350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.I.; Chen, Y. Effects of bulking agents on food waste composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 5917–5924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, B.; Laibach, N. Extraction of valuable components from waste biomass. In Waste to Food; Wageningen Academic Publishers: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 147–168. [Google Scholar]
- Alghashm, S.; Qian, S.; Hua, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W.; Shen, G. Properties of Biochar from Anaerobically Digested Food Waste and Its Potential Use in Phosphorus Recovery and Soil Amendment. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutherford, D.W.; Wershaw, R.L.; Rostad, C.E.; Kelly, C.N. Effect of formation conditions on biochars: Compositional and structural properties of cellulose, lignin, and pine biochars. Biomass Bioenergy 2012, 46, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashiq, W.; Nadeem, M.; Ali, W.; Zaeem, M.; Wu, J.; Galagedara, L.; Thomas, R.; Kavanagh, V.; Cheema, M. Biochar amendment mitigates greenhouse gases emission and global warming potential in dairy manure based silage corn in boreal climate. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Schreiter, I.J.; Wefer-Roehl, A.; Tsechansky, L.; Schüth, C.; Graber, E.R. Production and utilization of biochar from organic wastes for pollutant control on contaminated sites. In Environmental Materials and Waste; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 91–116. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Rahman, M.A.; Hassan, S.E.-D.; Roushdy, M.M.; Azab, M.S.; Gaber, M.A. Free-nutrient supply and thermo-alkaline conditions for direct lactic acid production from mixed lignocellulosic and food waste materials. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2019, 7, 100256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogaki, M.; Sonomoto, K.; Nakajima, H.; Tanaka, A. Continuous production of oxytetracycline by immobilized growing Streptomyces rimosus cells. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1986, 24, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saurabh Jyoti, R.K. Can production of biocontrol agent from waste biomass maximize waste utilization? J. Biofertil. Biopestic. 2013, 4, e113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuek, M.; McLean, S.K.; Palombo, E.A. Application of bacteriophages in food production and their potential as biocontrol agents in the organic farming industry. Biol. Control 2022, 165, 104817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidhyalakshmi, R.; Vallinachiyar, C.; Radhika, R. Production of xanthan from agro-industrial waste. J. Adv. Sci. Res. 2012, 3, 56–59. [Google Scholar]
- Barba, F.J.; Zhu, Z.; Koubaa, M.; Sant’Ana, A.S.; Orlien, V. Green alternative methods for the extraction of antioxidant bioactive compounds from winery wastes and by-products: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 49, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Kumar, R.; Ramajayam, R.; Lee, K.W.; Shin, D.S. Synthesis, antioxidant and molecular docking studies of (-)-catechin derivatives. J. Korean Chem. Soc. 2021, 65, 106–112. [Google Scholar]
- Alharbi, K.S.; Javed, S.M.A.; Imam, S.S.; Alshehri, S.; Ghoneim, M.M.; Almalki, W.H.; Singh, S.K.; Kumar, D.; Kumar, A.P.; Dua, K.; et al. Role of Flavonoids in Management of Various Biological Targets in Alzheimer’s Disease: Evidence from Preclinical to Clinical Studies. Curr. Med. Chem. 2023, 30, 2061–2074. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Amado, I.R.; Franco, D.; Sánchez, M.; Zapata, C.; Vázquez, J.A. Optimisation of antioxidant extraction from Solanum tuberosum potato peel waste by surface response methodology. Food Chem. 2014, 165, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinova, D.; Bogueva, D. Reducing Food Waste and Packaging. In Food in a Planetary Emergency; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 57–72. [Google Scholar]
| Agricultural Residues | Chemical Composition (%w/w) | References | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cellulose | Hemicellulose | Total Solids (%) | Moisture (%) | Lignin | Ash (%) | ||
| Barley straw | 33.8 | 21.9 | ND | ND | 13.8 | 11 | [6] |
| Wheat straw | 32.9 | 24.0 | 95.6 | 7 | 8.9 | 6.7 | [6] |
| Cotton stalks | 58.5 | 14.4 | ND | ND | 21.5 | 9.98 | [6] |
| Sugarcane Bagasse | 30.2 | 56.7 | 91.66 | 4.8 | 13.4 | 1.9 | [13] |
| Sugar beet waste | 26.3 | 18.5 | 87.5 | 12.4 | 2.5 | 4.8 | [13] |
| Rice straw | 39.2 | 23.5 | 98.62 | 6.58 | 36.1 | 12.4 | [13] |
| Corn stalks | 61.2 | 19.3 | 97.78 | 6.40 | 6.9 | 10.8 | [13] |
| Sawdust | 45.1 | 28.1 | 98.54 | 1.12 | 24.2 | 1.2 | [13] |
| Oat straw | 39.4 | 27.1 | ND | ND | 17.5 | 8 | [13] |
| Soya stalks | 34.5 | 24.8 | ND | 11.84 | 19.8 | 10.39 | [14] |
| Sunflower stalks | 42.1 | 29.7 | ND | ND | 13.4 | 11.7 | [14] |
| Nut shells | 25–30 | 25–30 | ND | 5.02–7.79 | 30–40 | ND | [15] |
| Rice husk | 21.5 | 33.1 | 89.41 | 10–15 | 14.6 | 20 | [16] |
| Sugarcane straw | 40.8 | 30.8 | ND | 35–50 | 25.5 | 5.3 | [17] |
| Sorghum bagasse | 40.4 | 35.5 | ND | 8.52 | 3.9 | 5 | [18] |
| Type of Food Waste | Chemical Composition/Elemental Composition (%w/w) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Waste | Carbon | Cellulose | Nitrogen | Hydrogen | Hemicellulose | Lignin | Ash | Moisture | References |
| Potato peel | 1.3 | 2.2 | 9.1 | ND | ND | 20 | 7.7 | 9.89 | [19] |
| Orange peel | 3.87 | 9.21 | ND | ND | 10.5 | 0.84 | 3.5 | 11.86 | [20] |
| Coffee skin | ND | 23.77 | ND | ND | 16.68 | 28.58 | 5.36 | ND | [21] |
| Pineapple peel | 40.8 | 18.11 | 0.99 | ND | 47.72 | 1.37 | ND | 91 | [22] |
| Wheat bran | 49.81 | 24 | 0.7 | 6.11 | ND | 6 | 5.5 | 5.5–9.25 | [23] |
| Rice bran | 48.39 | 35 | 0.89 | 5.43 | 25 | 20 | 17 | 5.4 | [24] |
| Corn cob | 53.61 | 15 | 1.91 | 8.97 | ND | 6.2 | ND | 24-28 | [25] |
| Corn stover | 44 | ND | 0.8 | 6.3 | 17 | ND | 6.6 | ND | [26] |
| Start-Up Name | Headquarters | Launching Year | Features | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Winnow | London, UK | 2019 |
| [64] |
| Wasteless | Tel Aviv, Israel | 2013 |
| [65] |
| Gamaya | Switzerland | 2008 |
| [66] |
| Greyparrot | London, UK | 2012 |
| [62] |
| The 77 Lab | MIT, Cambridge, USA | 2022 |
| [67] |
| By-Product | Food Waste | Operation/Extraction Parameters | Use/Benefits | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fruit juice processing | ||||
| Pectin | Orange peel; Apple pomace | Extraction of pectin with hot water acidification, filtrations, centrifugations, and then precipitation with alcohol | Fat/sugar replacer, reduce blood cholesterol levels, prevents gastrointestinal disorders | [70] |
| Natural sweeteners | Fruit pomace | Chicory processing: liquid has evaporated, and the sugars were crystallized and dried | Lowers blood pressure, prevents heart disease and risks of diabetes, acts as anti-inflammatory substance | [74] |
| Low-calorie jam | Tomato pomace | Basic jam formulation with TSS value of 48°Brix | Decreases blood pressure, constipation, and risk of heart attack | [75] |
| Pectin as Corrosion inhibitors | Tomato peel | Extraction of pectin with oxalic acid/ammonium oxalate under reflux | Decrease in waste disposal of canning factory 71% corrosion inhibition efficiency | [76] |
| Antioxidants | Fruit pomace (beet root) | Extraction using organic solvents (ethanol, acetone, hexane) followed by fractionation and purification | Reduce risk of cancer and other diseases | [77] |
| Antioxidants | Olive fruit waste | Time-40 min; Temperature-55 °C; pH-5.75. | Better economic enhancement of antioxidant properties in fatty food than synthetic additives | [78] |
| Activated carbon absorbent | Grape waste | Impregnation ratio—6:1; activation temperature—600 °C; and activation time—60 min | Effectively removes cationic and anionic dyes from aqueous solution | [79] |
| Essential oil | Fruit pomace; berry seeds | Supercritical fluid extraction, cold pressing, and distillation | Antiseptic and antibiotic properties, natural decongestant, anti-inflammatory properties | [80] |
| Fibers | Fruit pomace | Grinding and centrifugation or mechanical dewatering until 1% dry matter | Reduce cholesterol, maintain blood sugar level, slow down fat absorption | [81] |
| Vegetable processing | ||||
| Potato fiber | Potato peel | Washing and drying in an oven at 60 °C/ 12 h, milling to a particle size of 500µm, sieving, and storage under refrigeration | Prevention of diseases | [82] |
| Carrot-based condensed milk | Carrot pomace | Vacuum drying | Abundant source of carotenoids, fibers, and phenolic compounds | [83] |
| Green pea powder (snack crackers and dry soup) | Green pea peels | Drying in an oven at 60 °C/12 h; grinding and sieving (500–600 µm) | Rich source of cellulose | [84] |
| Yogurt | Carrot pomace | Extraction of carotenoids by electrostatic extrusion; carrot waste beads concentrations of 2.5 and 5 g/100 g were added to yogurt. | Fortified yogurt with enhanced antioxidant properties | [85] |
| Dairy industry | ||||
| Whey powder | Whey | Spray drying | Animal feed, ethanol production | [86] |
| Lactic ferments | Skimmed milk, whey | ND | Fermentation process | [86] |
| Demineralised whey powder | Whey | Ion-exchange, elect-dialysis | Food products for lactose-intolerant people | [86] |
| Lactose | Whey | Crystallization of concentrated whey | Syrups | [86] |
| Whey protein concentrate | Whey | ND | Food and pharmaceutical ingredients | [86] |
| Whey cheese | Whey | Condensation | Ricotta cheese or messoer | [87] |
| Marine industry | ||||
| Edible gelatin | Fish and rejected parts | Extraction in hot water and air-drying | Stabilizers, Clarifiers, texturing agents, and preservatives used in medication formulation and dietary supplements | [88] |
| Industrial gelatin | Fish and rejected parts | Extraction in hot water and air-drying | Dyes micro-encapsulation | [89] |
| Collagen | Fish skins and bones | Cold-water extraction | ND | [90] |
| Bioactive | Fish rejected parts | Enzymatic hydrolysis of crustacean and mollusk marine waste | Anti-microbial, anticoagulant, antidiabetic, antihypertensive, hypo-cholesteraemic, and anticancer agents as promising nutraceuticals | [91] |
| Fish protein concentrate (FPC) | Fish and rejected parts | Solvent extraction | Limited applications due to legislative issues | [90] |
| Photographic | Fish and rejected parts | Extraction with hot water and air-drying | Electronics industry coating that is light-sensitive | [91] |
| Glue | Fish and rejected parts | Extraction with hot water and air-drying | Adhesive applications | [91] |
| Meat industry | ||||
| Blood | Animal carcass | Blood is approved for food use when it has been removed by bleeding an animal that has been inspected | Non-food substances viz fertilizer, feedstuffs, and binders; high levels of protein and heme iron as a result used in making blood sausages, blood pudding, biscuits, and bread; pharmacological use | [92] |
| Hides and skin | Animal carcass | ND | Shelters, clothing, finished products obtained from hides of pigs and cattle and sheep pelts includes leather bags and shoes, rawhide, cosmetic products, edible gelatine, sausage skins, and glue | [93] |
| Bone | Animal skeleton | ND | Marrow inside some of the bones can also be used as food, making soup and gelatine. | [94] |
| Glands and organs | Animal body | ND | Human foods comprise heart, brain, liver, lungs, kidneys, etc; stomach and uterus of pigs, the rumen, reticulum, absomasum and omasum of cattle and sheep, and thymus and testes of sheep and pigs | [94] |
| Brewery industry | ||||
| Animal feed | Brewers spent gain (BSG), hot trub | Formed during mashing process and removed before the boiling step of the brewing process. | Showed positive influence on the production efficiency in cattle, without affecting fertility; improvement in the milk yield and composition | [74] |
| Essential oil (myrcene, α-humulene, and β-caryophyllene) | Spent hops | Hydro distillation. | More affordable and environmentally friendly alternative to chemical insecticides; can be utilized for prevention of stored food-stuff | [74] |
| Food additives | BSG | ND | Enhancement of aroma binding properties and positive effect on gelling and emulsifying potential | [74] |
| Antioxidants | Brewers spent yeast (BSY) | Recovered by sedimentation before full maturation of beer at the final stage of the second fermentation and maturation | Lower the risk of development of certain diseases-cancer, cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases | [74] |
| Value Added Product | Food Waste | Operation | Experimental Conditions | Product Yield | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bio plastic-Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) | Organic fraction of municipal solid waste (OFMSW) | Fermentation in sequencing batch reactor | Volume—100 L; Temperature—25–28 °C; Cycle Length—0.25 days | 76 g PHA/kg | [99] |
| Hydrogen gas- an alternative to fossil fuel | Food waste in China | Steam reforming process’s stoichiometric chemical equations with water–gas shift reaction | ND | 221.13 × 109 kg | [100] |
| Succinic acid | Bread waste | Solid-state fermentation in bioreactor | Volume—2.5 L; Substrate to inoculum Temperature—37 °C; pH—6.6–6.8; Time—48 h | 47.3 g/L | [101] |
| Lipase enzyme | Melon waste | Solid-state fermentation in Erlenmeyer flask | Volume—250 mL; Temperature—37 °C; Time—24 h; pH—7.0 | 148 U/g | [102] |
| α-amylase enzyme | Potato peel | Solid-state fermentation in Erlenmeyer flask | Volume—500 mL; Time—24 h; pH—7.5; Temperature—35 °C | 676 U/mL | [103] |
| Butanol and hydrogen | Food waste-moisture with known carbohydrate, protein, total fat ash content | Fermentation without enzymatic pre-treatment using amylolytic Clostridium sp. strain BOH3. | ND | ND | [104] |
| Ethanol and lactic acid | Meat, noodle, potato, and vegetable waste | Fermentation of food waste using indigenous consortium with Saccharomyces cerevisiae | ND | ND | [105] |
| Biochar | Food waste | Pyrolysis in Muffle furnace | Time—45–60 min; Heating rate—10 °C/min; Temperature—500 °C | 71% | [106] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Taneja, A.; Sharma, R.; Khetrapal, S.; Sharma, A.; Nagraik, R.; Venkidasamy, B.; Ghate, M.N.; Azizov, S.; Sharma, S.; Kumar, D. Value Addition Employing Waste Bio-Materials in Environmental Remedies and Food Sector. Metabolites 2023, 13, 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13050624
Taneja A, Sharma R, Khetrapal S, Sharma A, Nagraik R, Venkidasamy B, Ghate MN, Azizov S, Sharma S, Kumar D. Value Addition Employing Waste Bio-Materials in Environmental Remedies and Food Sector. Metabolites. 2023; 13(5):624. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13050624
Chicago/Turabian StyleTaneja, Akriti, Ruchi Sharma, Shreya Khetrapal, Avinash Sharma, Rupak Nagraik, Baskar Venkidasamy, Manju Nath Ghate, Shavkatjon Azizov, Somesh Sharma, and Deepak Kumar. 2023. "Value Addition Employing Waste Bio-Materials in Environmental Remedies and Food Sector" Metabolites 13, no. 5: 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13050624
APA StyleTaneja, A., Sharma, R., Khetrapal, S., Sharma, A., Nagraik, R., Venkidasamy, B., Ghate, M. N., Azizov, S., Sharma, S., & Kumar, D. (2023). Value Addition Employing Waste Bio-Materials in Environmental Remedies and Food Sector. Metabolites, 13(5), 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13050624







