LC-MS/MS Insight into Vitamin C Restoration to Metabolic Disorder Evoked by Amyloid β in Caenorhabditis elegans CL2006
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. C. elegans Maintenance
2.3. Paralysis Bioassay on C. elegans CL2006
2.4. Collection and Preparation of Metabolic Analysis Samples
2.5. UPLC-ESI-MS/MS Analysis
2.6. Metabolomics Data Analysis
3. Results
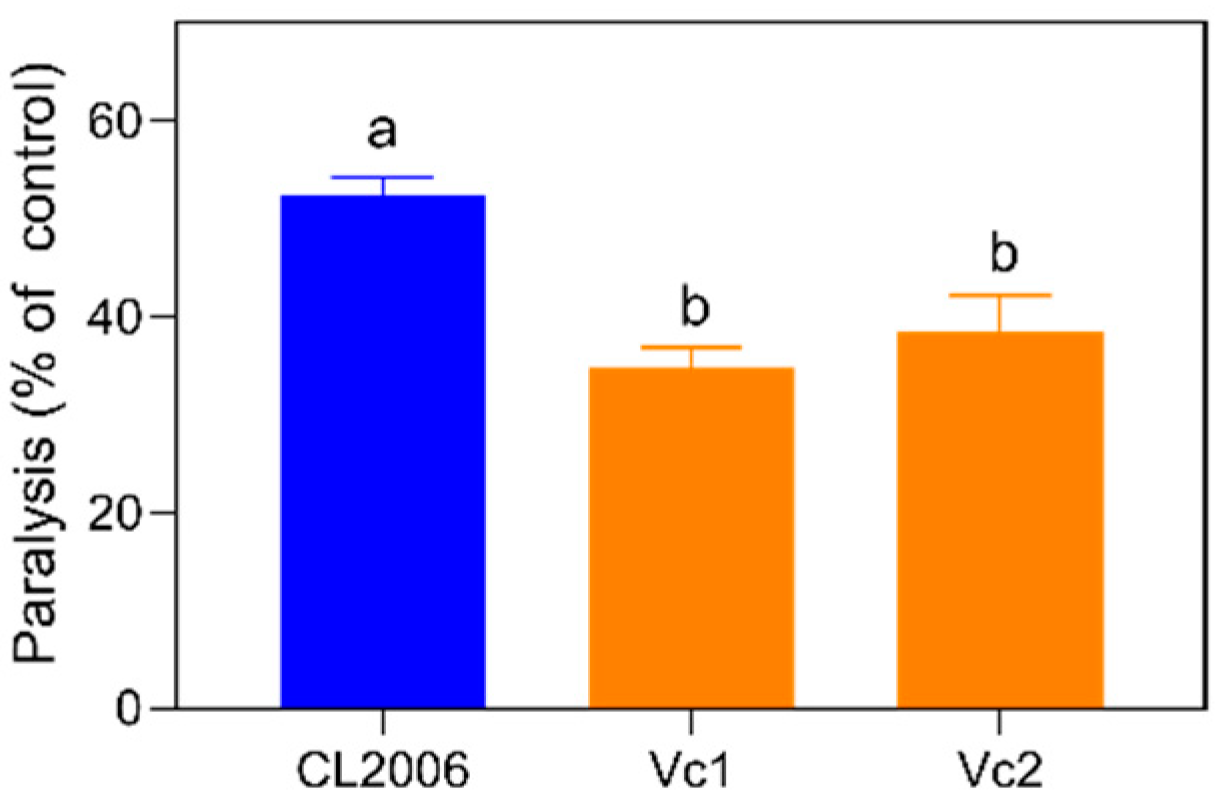
3.1. Inspection of Vc Effects against AD Paralysis
3.2. Principal Component Analysis (PCA) of Metabolic Profiles
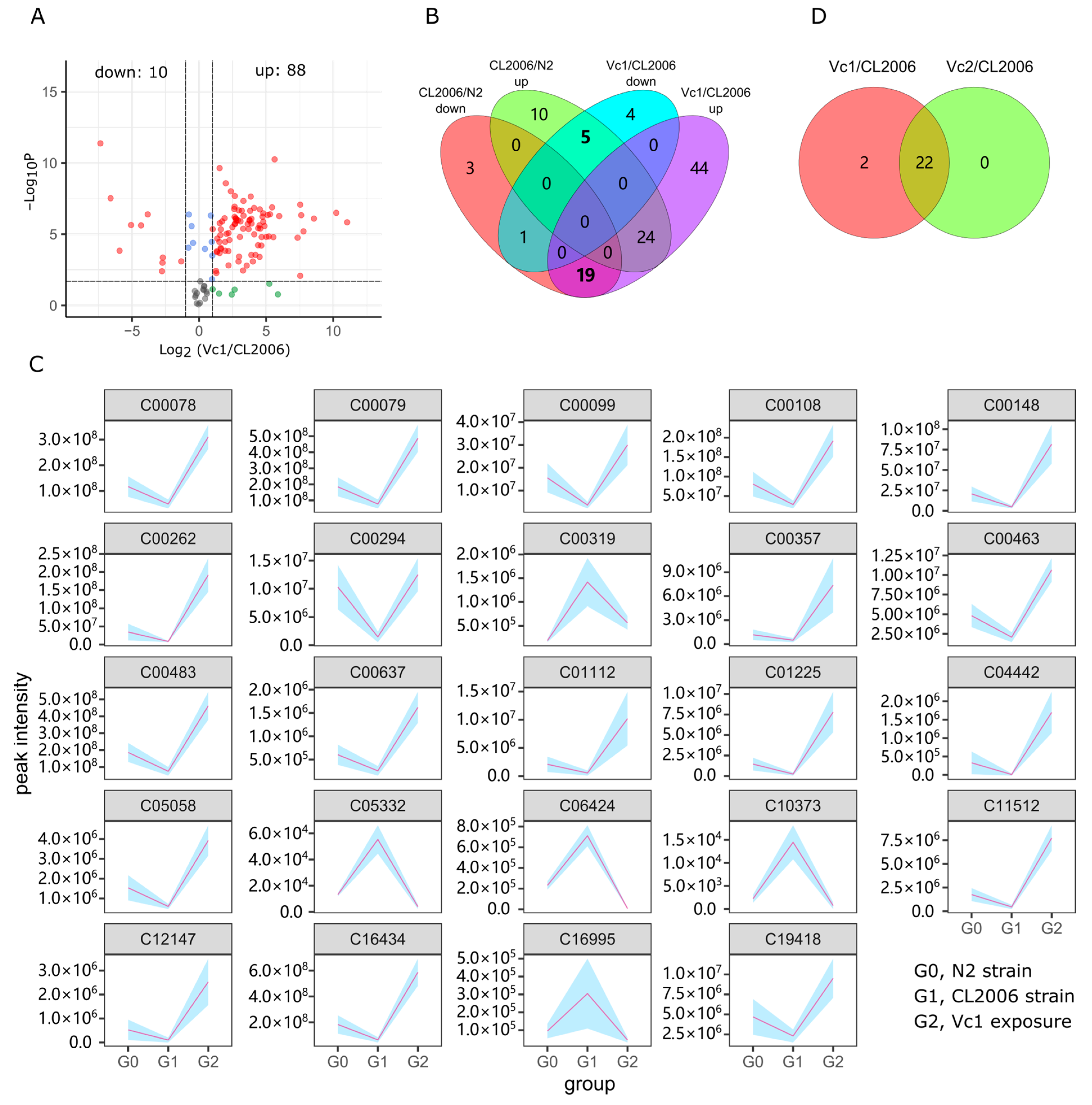
3.3. Metabolome Response to Aβ Overexpression and Aggregation
3.4. Vc Repair of Aβ Metabolic Disorder
4. Discussion
4.1. Abnormal Aβ and Vc Exposure Led to Significant Variation in Metabolome in CL2006
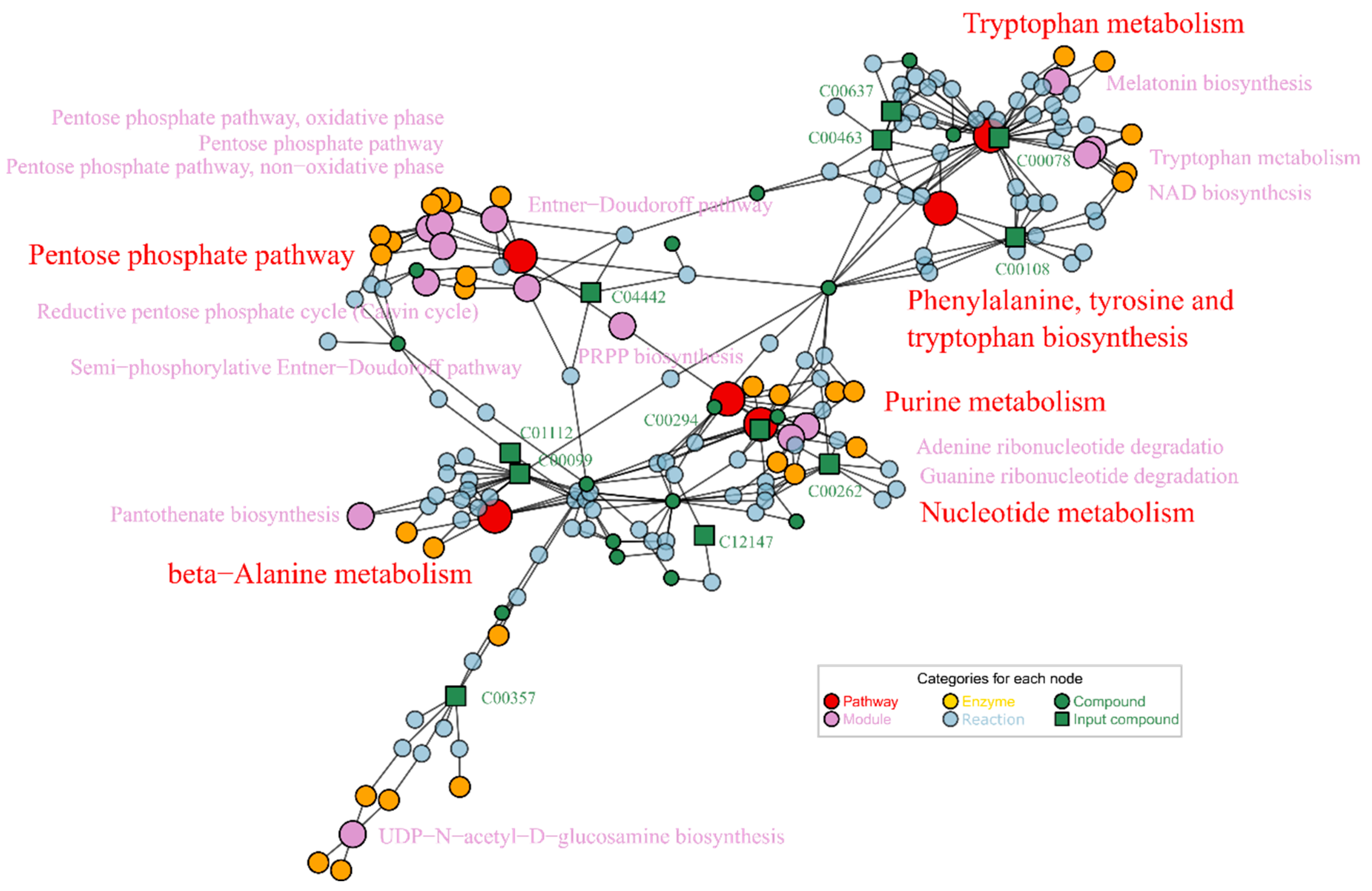
4.2. Abnormal Aβ Affected Metabolism of Essential Substances Related to Nervous System
4.3. Vc Restored Mainly Phenylalanine, Tyrosine and Tryptophan Metabolism
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Querfurth, H.W.; LaFerla, F.M. Alzheimer’s Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 329–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, J.M.; Henriques, A.G.; Martins, F.; Rebelo, S.; da Cruz e Silva, O.A.B. Amyloid-β Modulates Both AβPP and Tau Phosphorylation. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2015, 45, 495–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, W.S.; Di, J.; Cao, Q.; Li, B.; Seidler, P.M.; Murray, K.A.; Bitan, G.; Jiang, L. Amyloid β-Protein Oligomers Promote the Uptake of Tau Fibril Seeds Potentiating Intracellular Tau Aggregation. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2019, 11, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emmons, S.W. The Beginning of Connectomics: A Commentary on White et al. (1986) ‘The Structure of the Nervous System of the Nematode Caenorhabditis Elegans’. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 370, 20140309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaletta, T.; Hengartner, M.O. Finding Function in Novel Targets: C. Elegans as a Model Organism. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Zhang, F.; Li, W. Nematodes Feel a Craving—Using Caenorhabditis Elegans as a Model to Study Alcohol Addiction. Neurosci. Bull. 2014, 30, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lublin, A.L.; Link, C.D. Alzheimer’s Disease Drug Discovery: In Vivo Screening Using Caenorhabditis Elegans as a Model for β-Amyloid Peptide-Induced Toxicity. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2013, 10, e115–e119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowen, J.A.; Garcia-Segura, L.M. Microglia, Neurodegeneration and Loss of Neuroendocrine Control. Prog. Neurobiol. 2020, 184, 101720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonda, D.J.; Stone, J.G.; Torres, S.L.; Siedlak, S.L.; Perry, G.; Kryscio, R.; Jicha, G.; Casadesus, G.; Smith, M.A.; Zhu, X.; et al. Dysregulation of Leptin Signaling in Alzheimer Disease: Evidence for Neuronal Leptin Resistance. J. Neurochem. 2014, 128, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, T.H.; Nithiyanandam, S.; Lee, D.Y.; Kwon, D.H.; Hwang, J.S.; Kim, S.G.; Jang, Y.E.; Basith, S.; Park, S.; Mo, J.-S.; et al. Analysis of Nanotoxicity with Integrated Omics and Mechanobiology. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bizzarri, D.; Reinders, M.J.T.; Beekman, M.; Slagboom, P.E.; BBMRI-NL; van den Akker, E.B. 1H-NMR Metabolomics-Based Surrogates to Impute Common Clinical Risk Factors and Endpoints. eBioMedicine 2022, 75, 103764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Procaccini, C.; Santopaolo, M.; Faicchia, D.; Colamatteo, A.; Formisano, L.; de Candia, P.; Galgani, M.; De Rosa, V.; Matarese, G. Role of Metabolism in Neurodegenerative Disorders. Metabolism 2016, 65, 1376–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lahousse, L.; Nivard, M.G.; Bot, M.; Chen, L.; van Klinken, J.B.; Thesing, C.S.; Beekman, M.; van den Akker, E.B.; Slieker, R.C.; et al. Integration of Epidemiologic, Pharmacologic, Genetic and Gut Microbiome Data in a Drug–Metabolite Atlas. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, F.; Cappai, R.; Ciccotosto, G.D.; Svensson, G.; Multhaup, G.; Fransson, L.-Å.; Mani, K. Suppression of Amyloid β A11 Antibody Immunoreactivity by Vitamin C: Possible role of heparan sulfate oligosaccharides derived from glypican-1 by ascorbate-induced, nitric oxide (no)-catalyzed degradation*. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 27559–27572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monacelli, F.; Acquarone, E.; Giannotti, C.; Borghi, R.; Nencioni, A. Vitamin C, Aging and Alzheimer’s Disease. Nutrients 2017, 9, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathya, S.; Shanmuganathan, B.; Balasubramaniam, B.; Balamurugan, K.; Devi, K.P. Phytol Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles Regulate the Expression of Alzheimer’s Related Genes and Neuronal Apoptosis against Amyloid-β Induced Toxicity in Neuro-2a Cells and Transgenic Caenorhabditis Elegans. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 136, 110962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leiteritz, A.; Baumanns, S.; Wenzel, U. Amyloid-Beta (Aβ1–42)-Induced Paralysis in Caenorhabditis Elegans Is Reduced through NHR-49/PPARalpha. Neurosci. Lett. 2020, 730, 135042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huang, X.-B.; Wan, Q.-L.; Ding, A.-J.; Yang, Z.-L.; Qiu, M.-H.; Sun, H.-Y.; Qi, S.-H.; Luo, H.-R. Otophylloside B Protects Against Aβ Toxicity in Caenorhabditis Elegans Models of Alzheimer’s Disease. Nat. Prod. Bioprospecting 2017, 7, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.-Y.; Zhu, Z.-J.; Ren, S.-P.; Deng, Y.-C.; Xu, J.-Y.; Zhang, S.-M.; Gao, J.-M.; Zhang, Q. Metabolomic Navigated Citrus Waste Repurposing to Restore Amino Acids Disorder in Neural Lesion. Food Chem. 2022, 387, 132933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, A.; Zhu, Z.; Ren, S.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Q. Metabolomics Mechanism and Lignin Response to Laxogenin C, a Natural Regulator of Plants Growth. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsugawa, H.; Cajka, T.; Kind, T.; Ma, Y.; Higgins, B.; Ikeda, K.; Kanazawa, M.; VanderGheynst, J.; Fiehn, O.; Arita, M. MS-DIAL: Data-Independent MS/MS Deconvolution for Comprehensive Metabolome Analysis. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wishart, D.S.; Guo, A.; Oler, E.; Wang, F.; Anjum, A.; Peters, H.; Dizon, R.; Sayeeda, Z.; Tian, S.; Lee, B.L.; et al. HMDB 5.0: The Human Metabolome Database for 2022. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D622–D631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Liigand, J.; Tian, S.; Arndt, D.; Greiner, R.; Wishart, D.S. CFM-ID 4.0: More Accurate ESI-MS/MS Spectral Prediction and Compound Identification. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 11692–11700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djoumbou-Feunang, Y.; Pon, A.; Karu, N.; Zheng, J.; Li, C.; Arndt, D.; Gautam, M.; Allen, F.; Wishart, D.S. CFM-ID 3.0: Significantly Improved ESI-MS/MS Prediction and Compound Identification. Metabolites 2019, 9, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohart, F.; Gautier, B.; Singh, A.; Cao, K.-A.L. MixOmics: An R Package for ‘omics Feature Selection and Multiple Data Integration. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picart-Armada, S.; Fernández-Albert, F.; Vinaixa, M.; Yanes, O.; Perera-Lluna, A. FELLA: An R Package to Enrich Metabolomics Data. BMC Bioinform. 2018, 19, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalmankar, N.V.; Hari, H.; Sowdhamini, R.; Venkatesan, R. Disulfide-Rich Cyclic Peptides from Clitoria Ternatea Protect against β-Amyloid Toxicity and Oxidative Stress in Transgenic Caenorhabditis Elegans. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 7422–7433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhry, F.; Howlett, D.R.; Richardson, J.C.; Francis, P.T.; Williams, R.J. Pro-Oxidant Diet Enhances β/γ Secretase-Mediated APP Processing in APP/PS1 Transgenic Mice. Neurobiol. Aging 2012, 33, 960–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayub, M.; Jin, H.-K.; Bae, J. Novelty of Sphingolipids in the Central Nervous System Physiology and Disease: Focusing on the Sphingolipid Hypothesis of Neuroinflammation and Neurodegeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Lv, X.; Liu, Y.; Cui, D.; Wu, Y. Metabonomics Study in Mice With Learning and Memory Impairment on the Intervention of Essential Oil Extracted From Cinnamomum Camphora Chvar. Borneol. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 770411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.; Liu, M.; Liu, B.; Li, N.; Dong, X.; Hong, Z.; Chai, Y. UHPLC-QTOF/MS-Based Metabolomics Investigation for the Protective Mechanism of Danshen in Alzheimer’s Disease Cell Model Induced by Aβ1–42. Metabolomics 2019, 15, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, J.; Byun, M.S.; Yi, D.; Lee, J.H.; Jeon, S.Y.; Shin, S.A.; Kim, Y.K.; Kang, K.M.; Sohn, C.-H.; Jung, G.; et al. Genetic Associations of in Vivo Pathology Influence Alzheimer’s Disease Susceptibility. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2020, 12, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso-Andrés, P.; Albasanz, J.L.; Ferrer, I.; Martín, M. Purine-Related Metabolites and Their Converting Enzymes Are Altered in Frontal, Parietal and Temporal Cortex at Early Stages of Alzheimer’s Disease Pathology. Brain Pathol. Zurich Switz. 2018, 28, 933–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| KEGG ID 1 | Formula | Rt 2 (min) | Adduct | m/z | Peak Intensity (106, Mean ± SD) 3 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2 | CL2006 | Vc Treated | |||||
| C00078 | C11H12N2O2 | 5.24 | [M+H]+ | 205.0966 | 117.04 ± 39.79 | 49.13 ± 17.24 | 310.96 ± 47.16 |
| C00079 | C9H11NO2 | 2.45 | [M+H]+ | 166.0858 | 184.9 ± 59.04 | 77.65 ± 27.81 | 486.3 ± 85.1 |
| C00099 | C3H7NO2 | 1.04 | [M+H]+ | 90.0551 | 15.59 ± 6.36 | 3.64 ± 1.49 | 30.02 ± 8.87 |
| C00108 | C7H7NO2 | 5.63 | [M+H−H2O]+ | 120.0443 | 80.85 ± 31.67 | 28.18 ± 9.91 | 192.18 ± 41.24 |
| C00148 | C5H9NO2 | 1.03 | [M+H]+ | 116.0705 | 20.74 ± 9.09 | 4.74 ± 1.90 | 81.74 ± 23.89 |
| C00262 | C5H4N4O | 1.39 | [M+H]+ | 137.0455 | 34.54 ± 23.03 | 8.46 ± 1.95 | 191.87 ± 46.69 |
| C00294 | C10H12N4O5 | 1.89 | [M−H]− | 267.0731 | 10.31 ± 3.94 | 1.47 ± 0.94 | 12.49 ± 2.96 |
| C00319 | C18H37NO2 | 16.89 | [M+H−H2O]+ | 282.2789 | 0.19 ± 0.03 | 1.42 ± 0.51 | 0.56 ± 0.14 |
| C00357 | C8H16NO9P | 0.92 | [M−H]− | 300.0486 | 1.17 ± 0.67 | 0.49 ± 0.25 | 7.38 ± 3.39 |
| C00463 | C8H7N | 5.24 | [M+H]+ | 118.0650 | 4.82 ± 1.48 | 2.06 ± 0.64 | 10.65 ± 1.52 |
| C00483 | C8H11NO | 2.45 | [M+H−H2O]+ | 120.0806 | 186.1 ± 56.29 | 74.88 ± 25.63 | 462.15 ± 82.78 |
| C00637 | C10H9NO | 5.24 | [M+H−H2O]+ | 142.0647 | 0.60 ± 0.22 | 0.26 ± 0.10 | 1.62 ± 0.33 |
| C01112 | C5H11O8P | 0.91 | [M−H]− | 229.0115 | 2.09 ± 1.37 | 0.55 ± 0.46 | 10.20 ± 4.76 |
| C01225 | C9H19O11P | 0.90 | [M−H]− | 333.0595 | 1.45 ± 0.78 | 0.24 ± 0.20 | 7.80 ± 2.48 |
| C04442 | C6H11O9P | 0.91 | [M−H]− | 257.0061 | 0.33 ± 0.31 | 0.01 ± 0.03 | 1.70 ± 0.56 |
| C05058 | C6H7NO | 5.63 | [M+H−H2O]+ | 92.0496 | 1.54 ± 0.64 | 0.6 ± 0.13 | 3.93 ± 0.77 |
| C05332 | C8H11N | 5.39 | [M+H]+ | 122.0964 | 0.01 ± 0.00 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 0.00 ± 0.00 |
| C06424 | C14H28O2 | 16.22 | [M−H]− | 227.2006 | 0.23 ± 0.04 | 0.71 ± 0.10 | 0.01 ± 0.00 |
| C10373 | C18H28O4 | 11.63 | [M−H]− | 307.1909 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.01 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 |
| C11512 | C13H20O3 | 10.59 | [M−H]− | 223.1332 | 1.75 ± 0.69 | 0.45 ± 0.22 | 7.72 ± 1.36 |
| C12147 | C4H10NO6P | 0.91 | [M+AcO]− | 258.0381 | 0.52 ± 0.43 | 0.10 ± 0.10 | 2.53 ± 0.97 |
| C16434 | C6H13NO2 | 1.47 | [M+H]+ | 132.1015 | 183.22 ± 70.92 | 64.32 ± 20.31 | 587.5 ± 105.3 |
| C16995 | C17H34O2 | 17.53 | [M−H]− | 269.2479 | 0.10 ± 0.04 | 0.30 ± 0.20 | 0.04 ± 0.01 |
| C19418 | C18H34O3 | 12.31 | [M−H]− | 297.2432 | 4.69 ± 2.24 | 2.31 ± 0.81 | 9.52 ± 2.45 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, A.; Yan, L.; Zhang, Z.; Wei, J.; Zhang, Q. LC-MS/MS Insight into Vitamin C Restoration to Metabolic Disorder Evoked by Amyloid β in Caenorhabditis elegans CL2006. Metabolites 2022, 12, 841. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12090841
Zhang S, Deng Y, Zhang A, Yan L, Zhang Z, Wei J, Zhang Q. LC-MS/MS Insight into Vitamin C Restoration to Metabolic Disorder Evoked by Amyloid β in Caenorhabditis elegans CL2006. Metabolites. 2022; 12(9):841. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12090841
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Simeng, Yuchan Deng, Annan Zhang, Lili Yan, Zhichao Zhang, Jing Wei, and Qiang Zhang. 2022. "LC-MS/MS Insight into Vitamin C Restoration to Metabolic Disorder Evoked by Amyloid β in Caenorhabditis elegans CL2006" Metabolites 12, no. 9: 841. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12090841
APA StyleZhang, S., Deng, Y., Zhang, A., Yan, L., Zhang, Z., Wei, J., & Zhang, Q. (2022). LC-MS/MS Insight into Vitamin C Restoration to Metabolic Disorder Evoked by Amyloid β in Caenorhabditis elegans CL2006. Metabolites, 12(9), 841. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12090841








