Identification of Medicinal Compounds of Fagopyri Dibotryis Rhizome from Different Origins and Its Varieties Using UPLC-MS/MS-Based Metabolomics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. Quantification of Epicatechin, Total Flavonoids and Total Tannins
2.3. Sample Preparation for Metabolomic Analysis
2.4. Multivariate Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Determination of Epicatechin, Total Flavonoids and Total Tannin in FDR from Different Producing Areas
3.2. Metabolic Profiling of FDR
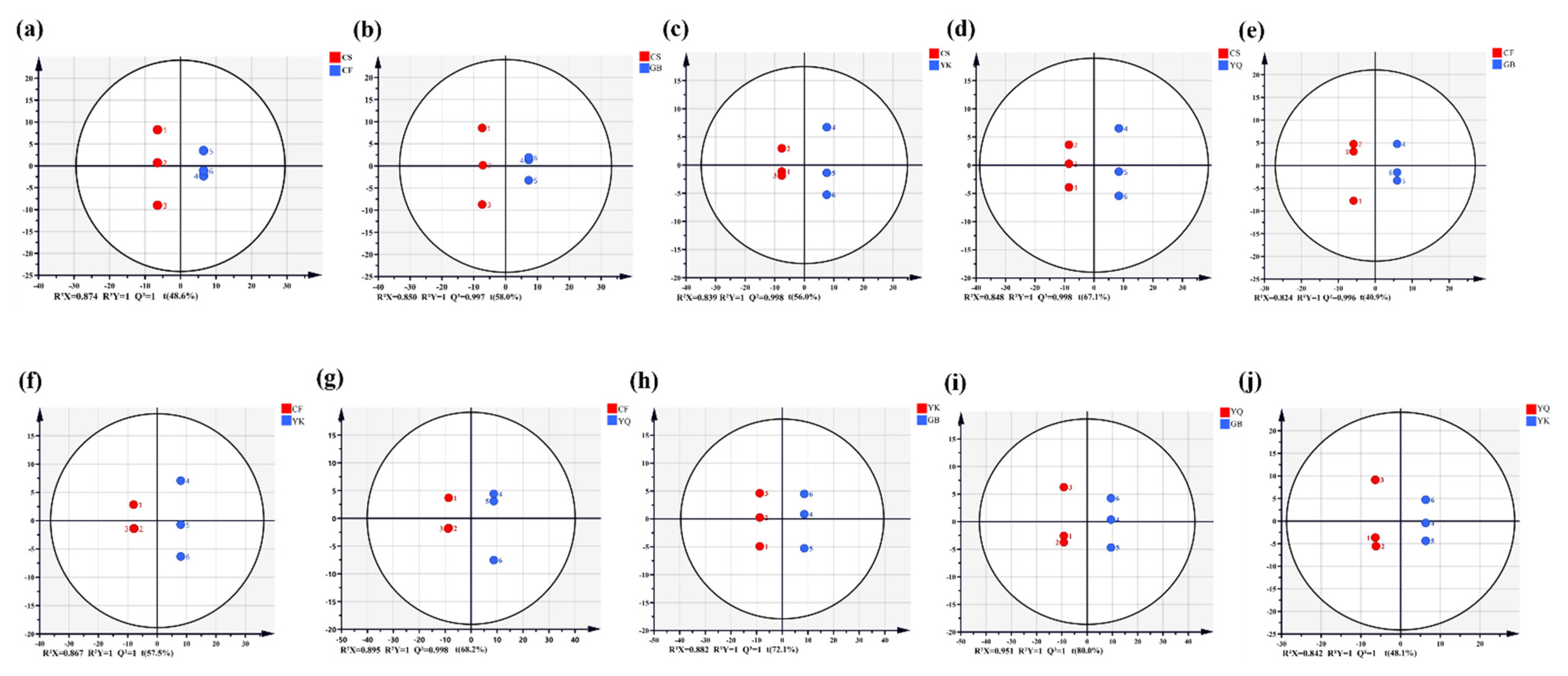
3.3. Differential Analysis of Phenolic Compounds Based on PCA
3.4. Differential Analysis of Phenolic Compounds Based on OPLS-DA
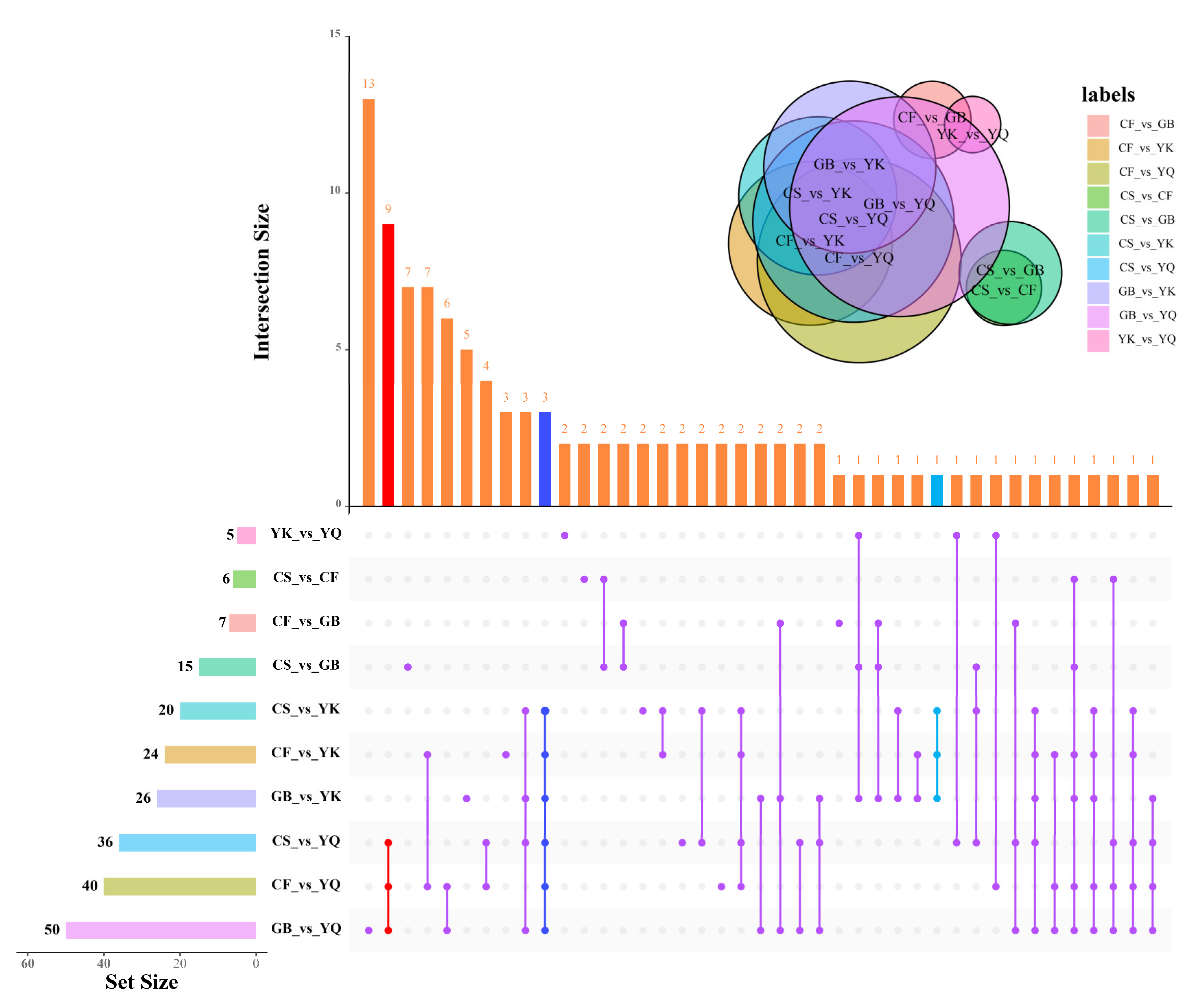
3.5. Differential Phenolic Analysis
3.6. Metabolite Differences among NYN Group and YN Group
4. Discussion
4.1. Metabolic Profiling of FDR from Different Origins
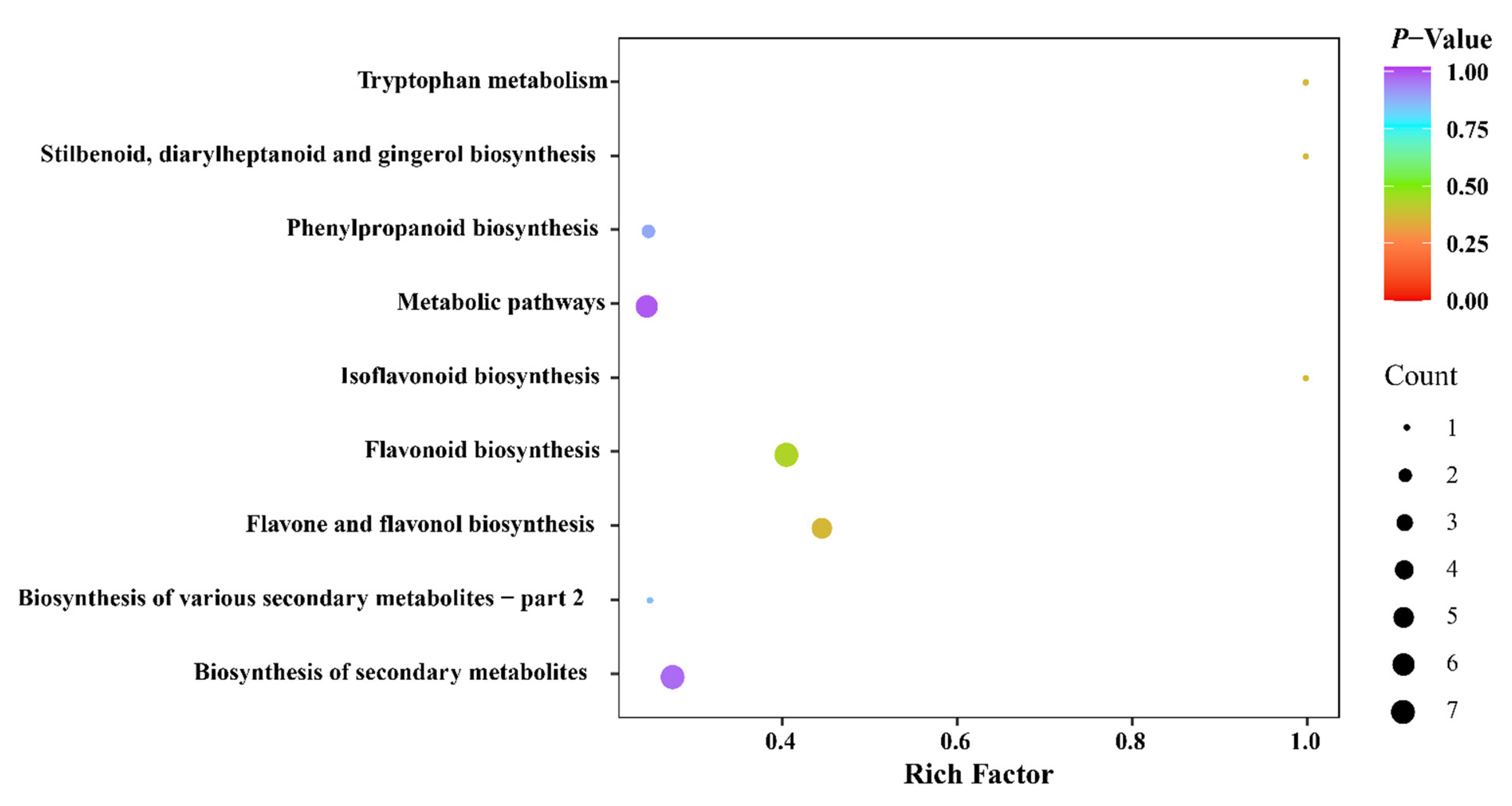
4.2. Differential Phenolic Metabolite Analysis of FDR from Different Origins
4.3. The Common DPMs of FDR from Different Origins
4.4. The ‘Good Traits’ of the High-Quality Fagopyri Dibotryis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, M.; He, Y.; Zhang, K.; Lu, X.; Zhang, X.; Gao, B.; Zhou, M. Comparison of buckwheat genomes reveals the genetic basis of metabolomic divergence and ecotype differentiation. New Phytol. 2022, 235, 1927–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Meng, F.H. Effect of Fagopyrum cymosum rootin on clonal formation of four human tumor cells. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 1993, 18, 498–500+511. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, H.; Ben, C. Editorial Committee of Chinese Materia Medica; Shanghai Science and Technology Press: Shanghai, China, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, P.K. Inhibition of tumor growth in vitro by the extract of Fagopyrum cymosum (fago-c). Life Sci. 2003, 72, 1851–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.J.; Zhang, Y.J.; Yang, C.R. Antioxidant phenolic constituents from Fagopyrum dibotrys. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 99, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, M.; Yang, Y.H.; Gao, H.Y.; Wu, B.; Wang, L.B.; Wu, L.J. Studies on the chemical constituents of Fagopyrum dibotrys. J. Shenyang Pharm. Univ. 2005, 22, 100–102. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Wang, L.; Tang, B.; Ren, R.; Shi, T.; Zhu, L.; Chen, Q. Integrated Transcriptomics and Wide Targeted Metabolomics Analyses Provide Insights into Flavonoid Biosynthesis in the Rhizomes of Golden Buckwheat (Fagopyrum Cymosum). Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 803472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hossain, M.S.; Ma, H.; Yang, Q.; Gong, X.; Yang, P.; Feng, B. Comparativ metabolomics reveals differences in flavonoid metabolites among different coloured buckwheat flowers. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2020, 85, 103335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vombergar, B.; Luthar, Z. The concentration of flavonoids, tannins and crude proteins in grain fractions of common buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum Moench) and Tartary buckwheat (Fagopyrum tataricum Gaertn.). Folia Biol. Geol. 2018, 59, 101–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luthar, Z.; Kreft, I. Influence of temperature on tannin content in different ripening phases of buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum Moench) seeds. Fagopyrum 1999, 16, 61–65. [Google Scholar]
- National Pharmacopoeia Committee. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China; China Pharmaceutical Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2020; p. 228. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Deng, B.; Tian, S.; Guo, M.; Liu, H.; Zhao, X. Metabolic and transcriptomic analyses reveal different metabolite biosynthesis profiles between leaf buds and mature leaves in Ziziphus jujuba mill. Food Chem. 2021, 347, 129005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisa, M.; Oliver, J.; Schmitz. Metabolome Studies of Herbal Medicine: Using High Performance Liquid Chromatography Ion-Mobility Mass Spectrometry. Gale Acad. OneFile 2020, 16, 2–8. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, R.; Hesser, L.A.; He, Z.; Zhou, X.; Nadeau, K.C.; Nagler, C.R. Fecal microbiome and metabolome differ in healthy and food-allergic twins. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e141935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinu, F.R.; Villas-Boas, S.G. Extracellular microbial metabolomics: The state of the art. Metabolites 2017, 7, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liang, X.; Li, Y.; Fan, Y.; Yan, L.; Cao, Y.; An, W.; Shi, Z.; Zhao, J.; Guo, S. Changes in Metabolome and Nutritional Quality of Lycium barbarum Fruits from Three Typical Growing Areas of China as Revealed by Widely Targeted Metabolomics. Metabolites 2020, 10, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Yang, P.; Yang, Q.; Gong, X.; Ma, H.; Dang, K.; Chen, G.; Gao, X.; Feng, B. Analysis of Flavonoid Metabolites in Buckwheat Leaves Using UPLC-ESI-MS/MS. Molecules 2019, 24, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.; Huang, D.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, L.; Ming, R.; Zeng, W.; Yan, H. Identification of nutritional ingredients and medicinal components of Pueraria lobata and Its varieties using UPLC-MS/MS-based metabolomics. Molecules 2021, 26, 6587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Qiu, X.; Tan, Q.; Xiao, Q.; Mei, S. A comparative metabolomics study of flavonoids in radish with different skin and flesh colors (Raphanus sativus L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 14463–14470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, C.G.; Clowers, B.H.; Moore, R.J.; Zink, E.M. Signature-discovery approach for sample matching of a nerve-agent precursor using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry, XCMS, and chemometrics. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 4165–4173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, B.; Shi, Y.; Ntambiyukuri, A.; Li, X.; Zhan, J.; Wang, A.; He, L. Integration of Small RNA and Degradome Sequencing Reveals the Regulatory Network of Al-Induced Programmed Cell Death in Peanut. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 23, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penin, A.A.; Kasianov, A.S.; Klepikova, A.V.; Kirov, I.V.; Gerasimov, E.S.; Fesenko, A.N.; Logacheva, M.D. High-Resolution Transcriptome Atlas and Improved Genome Assembly of Common Buckwheat, Fagopyrum esculentum. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 612382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nóra, M.D.; Andrew, J.; Cal, J.D. Progress and prospects for interspecific hybridization in buckwheat and the genus Fagopyrum. Biotechnol. Adv. 2013, 31, 1768–1775. [Google Scholar]
- Yasuo, Y.; Hideki, H.; Mariko, U.; Katsuhiro, M.; Tomoyuki, K.T.; Yang, S.; Jotaro, A.; Shingo, S. Masashi Mori. Assembly of the draft genome of buckwheat and its applications in identifying agronomically useful genes. DNA Res. 2016, 23, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohsako, T.; Li, C.; Tian, B. Evolutionary relationship between a wild ancestor of common buckwheat Fagopyrum esculentum subsp. ancestrale and a self-compatible relative F. homotropicum based on microsatellite variability. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2017, 64, 1595–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; He, Y.; Sheng, F.; Hu, Y.; Song, Y.; Li, W.; Zou, L. Towards a better understanding of Fagopyrum dibotrys: A systematic review. Chin. Med. 2021, 16, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Li, L.; Pei, J.; Liu, C.; Huang, L. Metabolome and transcriptome profiling reveals quality variation and underlying regulation of three ecotypes for Cistanche deserticola. Plant Mol. Biol. 2021, 102, 253–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Zhao, W.; Han, L.; Ding, J.; Chang, Y. Metabolomics analysis of sea cucumber (Apostichopus japonicus) in different geographical origins using UPLC–Q-TOF/MS. Food Chem. 2020, 333, 127453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehal, I.; Ashaimaa, Y.M. Comparative metabolite profiling of Callistemon macropunctatus and Callistemon subulatus volatiles from different geographical origins. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 147, 112222. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.; Yi, Z.; Zhang, Y. Natural phenolic compounds from medicinal herbs and dietary plants: Potential use for cancer prevention. Nutr. Cancer 2009, 62, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, M.; Pinto, D.; Silva, A. Plant flavonoids: Chemical characteristics and biological activity. Molecules 2021, 26, 5377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Cao, H.; Huang, Q.; Xiao, J.; Teng, H. Absorption, metabolism and bioavailability of flavonoids: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Amit, S.; Abha, M. Gallic acid: Molecular rival of cancer. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2013, 35, 473–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, B.R.; Kim, S.Z.; Kim, S.H.; Park, W.H. Gallic acid-induced lung cancer cell death is accompanied by ROS increase and glutathione depletion. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2011, 357, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Liu, K.; Ruan, M.; Yang, J.; Gao, Z. Gallic acid inhibits fibroblast growth and migration in keloids through the AKT/ERK signaling pathway. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2018, 50, 1114–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Chu, J.; Zhou, X. Anti-carious effects of Galla chinensis: A systematic review. Phytother. Res. 2015, 12, 1837–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Li, P.; Wang, W.; Cai, X.; Xue, H. Separation of gallic acid from Cornus officinalis and its interactions with corn starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 208, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Wu, S.; Tian, L. Effective genome editing and identification of a regiospecific gallic acid 4-O-glycosyltransferase in pomegranate (Punica granatum L.). Hortic. Res. 2019, 6, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Hei, X.; Li, Y.; Gao, J.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, H. Accumulation profile of nine constituents in different years old stage and parts of Rheum palmatum L. by HPLC analysis. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 2019, 31, 923–931. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.Q.; Shen, J.; Li, P.; Liu, S.; Yi, F.; Liu, H.B.; Xiao, P. Research on quality markers of Moutan Cortex: Quality evaluation and quality standards of Moutan Cortex. Chin. Herb. Med. 2017, 9, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashiwada, Y.; Nonaka, G.; Nishioka, I. Tannins and related compounds. XXIII. Rhubarb (4): Isolation and structures of new classes of gallotannins. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1984, 32, 3461–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Huang, Y.; Yang, K.; Wang, Y.; He, R.; Li, D. Isolation and Identification of Polyphenols from the Leaves of Castanopsis fordii Hance. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 2017, 29, 67–73. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Hsu, F.; Tsai, J.; Chan, P.; Liu, J.; Thomas, G.; Lin, J. Antihypertensive effects of tannins isolated from traditional Chinese herbs as non-specific inhibitors of angiontensin converting enzyme. Life Sci. 2003, 73, 1543–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, M.; Yang, Y.; Gao, H.; Wu, B.; Wang, L.; Wu, L. Phenolic acid derivatives from the rhizome of Fagopyrum cymosum. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2005, 30, 1591–1593. [Google Scholar]
- Jin-Zhi, J.I.; Yu, L.; Hong-Sheng, R.; Ming-Chao, C.; Ke, D.; Ping, P.; Xiao, L. Study on improvement and mechanism of tableting properties of porous Fagopyri Dibotryis Rhizoma powders. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2020, 45, 5518–5524. [Google Scholar]
- Moustapha, B.; Marina, G.; Raúl, F.; Raquel, C.; Mahinda, M. Chemical constituents of the Mexican mistletoe (Psittacanthus calyculatus). Molecules 2011, 16, 9397–9403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Chu, S.; Gui, S.; Qin, Y.; Xu, R.; Shan, T.; Peng, H. Tissue-specific metabolite profiling of Fallopia multiflora (Heshouwu) and Fallopia multiflora var. angulata by mass spectrometry imaging and laser microdissection combined with UPLC-Q/TOF-MS. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 200, 114070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Zhang, M.; Wen, C.; Xie, X.; Tian, W.; Wen, S.; Lu, R.; Liu, L. Integrated metabolomic and transcriptomic analysis of the anthocyanin regulatory networks in Salvia miltiorrhiza Bge. Flowers. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yang, Z.; Zeng, Q.; Wang, S.; Luo, Y.; Huang, Y.; Xin, Y.; He, N. Abnormal expression of bHLH3 disrupts a flavonoid homeostasis network, causing differences inpigment composition among mulberry fruits. Hortic. Res. 2020, 7, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, G.; Liu, P.; Liu, M. Transcriptome and metabolome profiling unveil the mechanisms of Ziziphus jujuba Mill. peel coloration. Food Chem. 2020, 312, 125903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, C.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, C.; Shi, L.; Li, J.; Zeng, Y.; Guo, L.; Wang, S. Identification of Medicinal Compounds of Fagopyri Dibotryis Rhizome from Different Origins and Its Varieties Using UPLC-MS/MS-Based Metabolomics. Metabolites 2022, 12, 790. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12090790
Zhang C, Jiang Y, Liu C, Shi L, Li J, Zeng Y, Guo L, Wang S. Identification of Medicinal Compounds of Fagopyri Dibotryis Rhizome from Different Origins and Its Varieties Using UPLC-MS/MS-Based Metabolomics. Metabolites. 2022; 12(9):790. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12090790
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Chengcai, Yang Jiang, Changzheng Liu, Linyuan Shi, Jintong Li, Yan Zeng, Lanping Guo, and Sheng Wang. 2022. "Identification of Medicinal Compounds of Fagopyri Dibotryis Rhizome from Different Origins and Its Varieties Using UPLC-MS/MS-Based Metabolomics" Metabolites 12, no. 9: 790. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12090790
APA StyleZhang, C., Jiang, Y., Liu, C., Shi, L., Li, J., Zeng, Y., Guo, L., & Wang, S. (2022). Identification of Medicinal Compounds of Fagopyri Dibotryis Rhizome from Different Origins and Its Varieties Using UPLC-MS/MS-Based Metabolomics. Metabolites, 12(9), 790. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12090790






