Low Inflammatory Stimulus Increases D2 Activity and Modulates Thyroid Hormone Metabolism during Myogenesis In Vitro
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
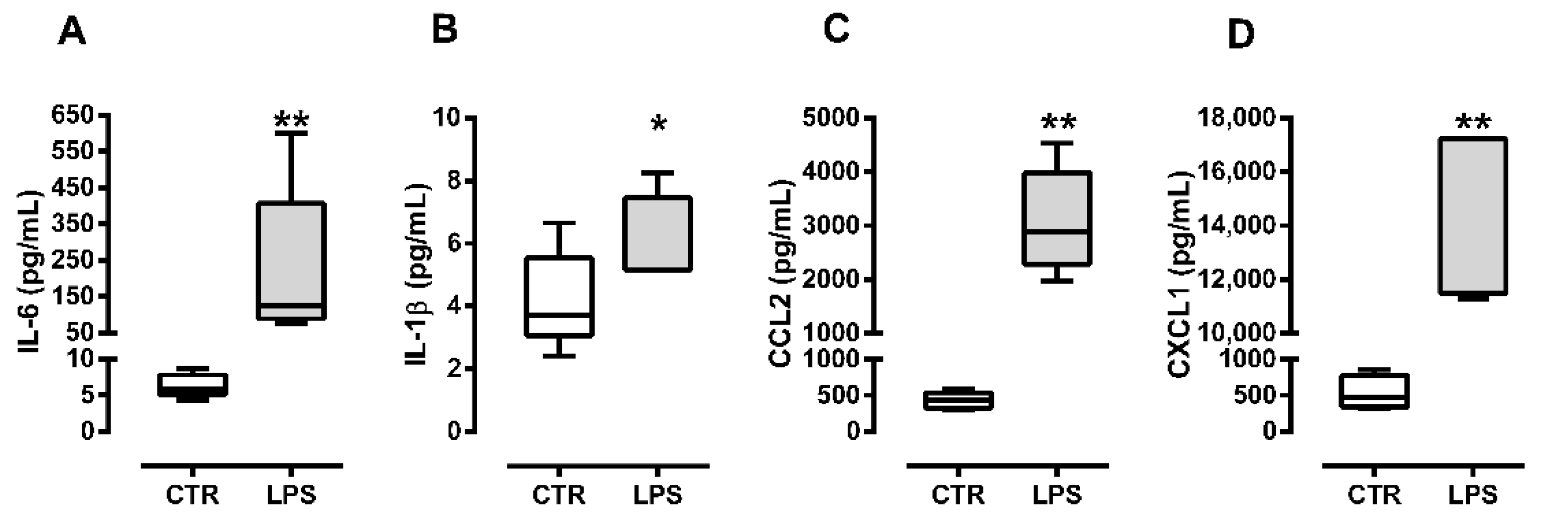
2.1. C2C12 Myoblasts Produce Cytokines and Chemokines in Response to Bacterial Lipopolysaccharide
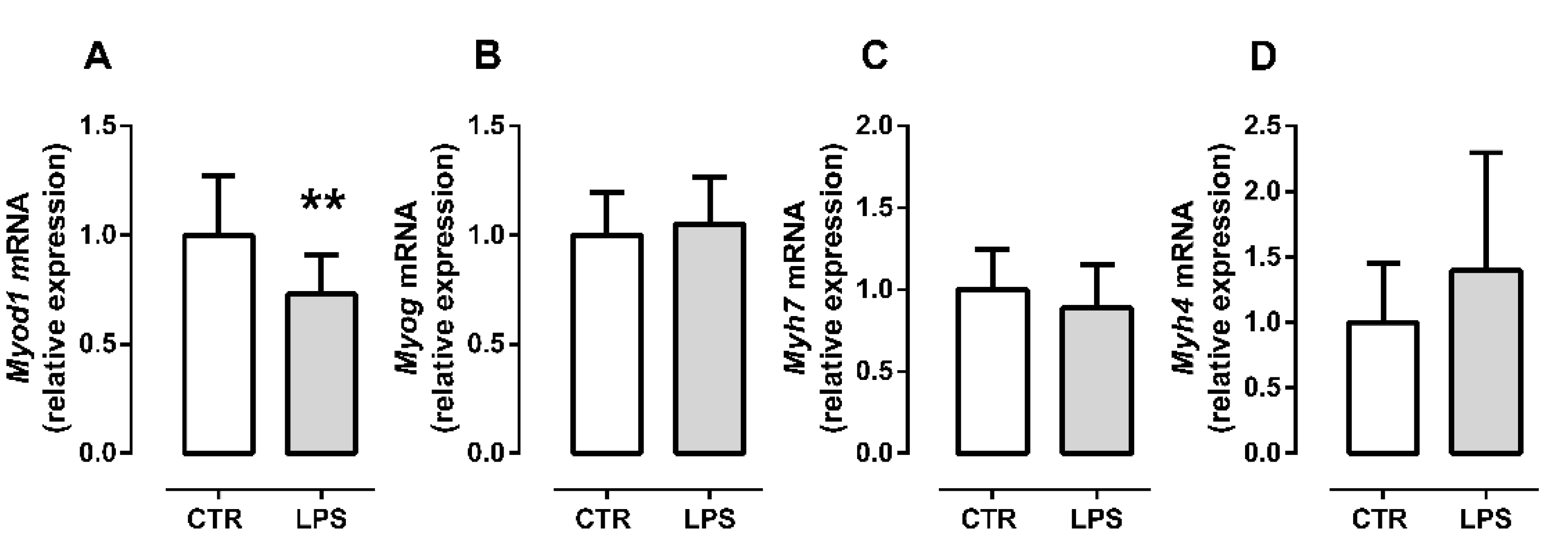
2.2. LPS Treatment Decreases the Initial Myogenic Stimulus but Does Not Affect Late Differentiation
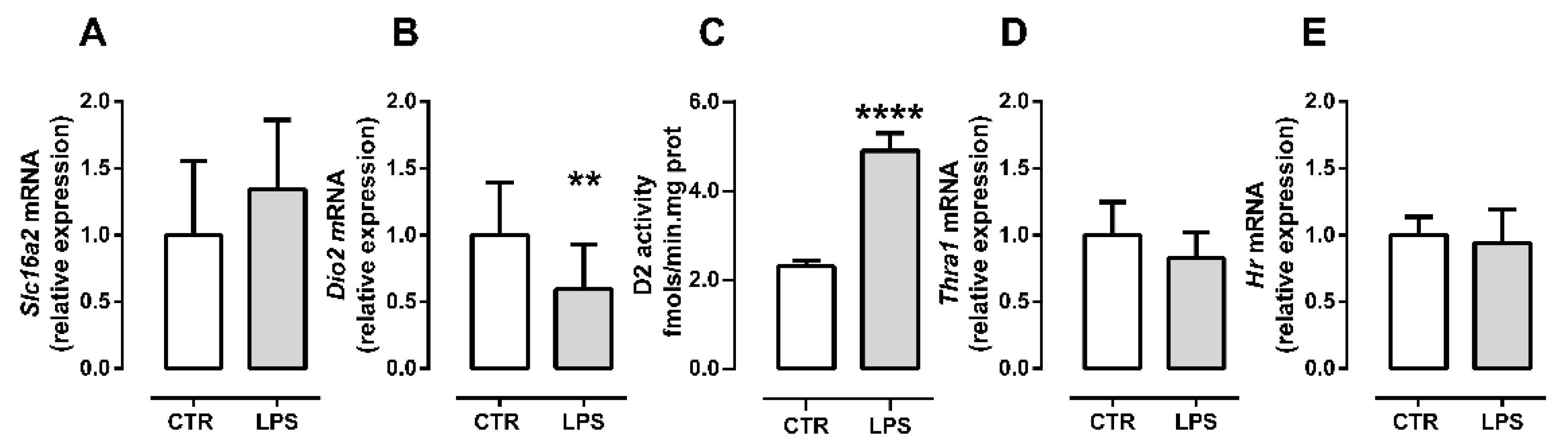
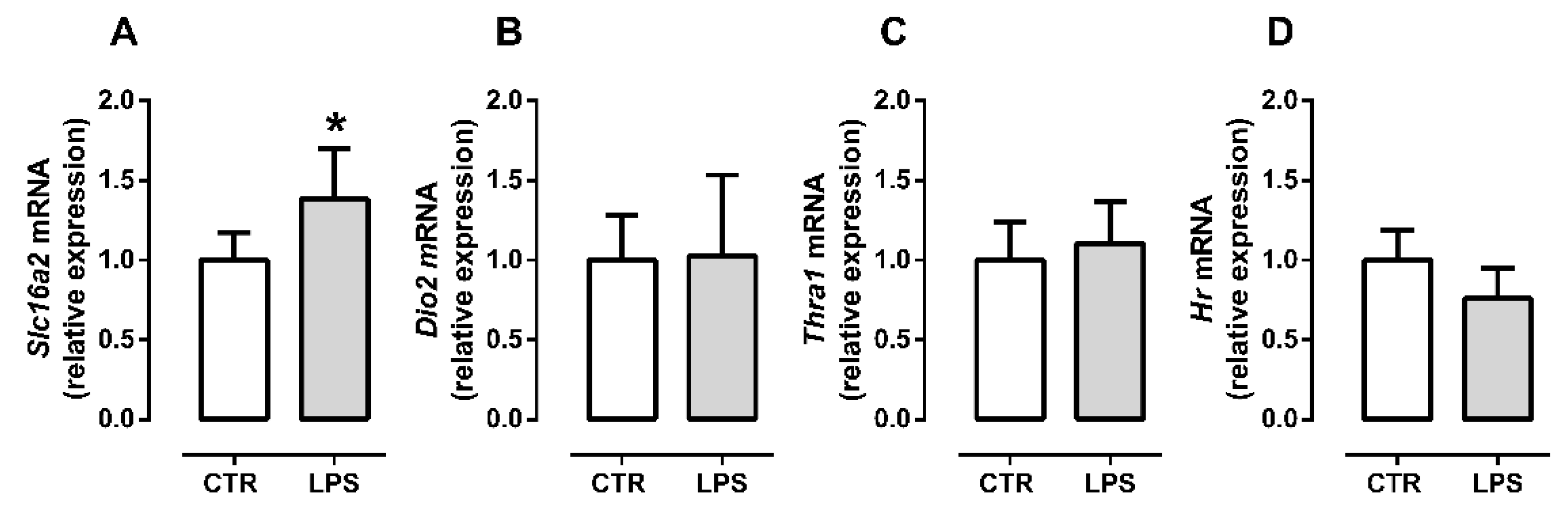
2.3. Inflammation Differently Affects TH Signaling during Initial and Late Myogenic Differentiation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. RNA Extraction and Gene Expression (qPCR)
4.3. Deiodinase Activity
4.4. Cytokines and Chemokines Measurement
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mauro, A. satellite cell of skeletal muscle fibers. J. Biophys. Biochem. Cytol. 1961, 9, 493–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chal, J.; Pourquié, O. Making muscle: Skeletal myogenesis in vivo and in vitro. Development 2017, 144, 2104–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dumont, N.A.; Wang, Y.X.; Rudnicki, M.A. Intrinsic and extrinsic mechanisms regulating satellite cell function. Development 2015, 142, 1572–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nappi, A.; Murolo, M.; Sagliocchi, S.; Miro, C.; Cicatiello, A.G.; Di Cicco, E.; Di Paola, R.; Raia, M.; D’esposito, L.; Stornaiuolo, M.; et al. Selective inhibition of genomic and non-genomic effects of thyroid hormone regulates muscle cell differentiation and metabolic behavior. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnac, G.; Albagli-Curiel, O.; Vandromme, M.; Pinset, C.; Montarras, D.; Laudet, V.; Bonnieu, A. 3,5,3’-Triiodothyronine positively regulates both MyoD1 gene transcription and terminal differentiation in C2 myoblasts. Mol. Endocrinol. 1992, 6, 1185–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downes, M.; Griggs, R.; Atkins, A.; Olson, E.N.; Muscat, G.E.O. Identification of a thyroid hormone response element in the mouse myogenin gene: Characterization of the thyroid hormone and retinoid X receptor heterodimeric binding site. Cell Growth Differ. 1993, 4, 901–910. [Google Scholar]
- Muscat, G.E.O.; Mynett-Johnson, L.; Dowhan, D.; Downes, M.; Griggs, R. Activation of myoD gene transcription by 3,5,3’-triiodo-L-thyronine: A direct role for the thyroid hormone and retinoid X receptors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Russo, S.C.; Salas-Lucia, F.; Bianco, A.C. Deiodinases and the Metabolic Code for Thyroid Hormone Action. Endocrinology 2021, 162, bqab059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luongo, C.; Dentice, M.; Salvatore, D. Deiodinases and their intricate role in thyroid hormone homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dentice, M.; Ambrosio, R.; Damiano, V.; Sibilio, A.; Luongo, C.; Guardiola, O.; Yennek, S.; Zordan, P.; Minchiotti, G.; Colao, A.; et al. Intracellular Inactivation of Thyroid Hormone Is a Survival Mechanism for Muscle Stem Cell Proliferation and Lineage Progression. Cell Metab. 2014, 20, 1038–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dentice, M.; Marsili, A.; Ambrosio, R.; Guardiola, O.; Sibilio, A.; Paik, J.-H.; Minchiotti, G.; DePinho, R.A.; Fenzi, G.; Larsen, P.R.; et al. The FoxO3/type 2 deiodinase pathway is required for normal mouse myogenesis and muscle regeneration. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 4021–4030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Stefano, M.A.; Ambrosio, R.; Porcelli, T.; Orlandino, G.; Salvatore, D.; Luongo, C. Thyroid hormone action in muscle atrophy. Metabolites 2021, 11, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayerl, S.; Schmidt, M.; Doycheva, D.; Darras, V.M.; Hüttner, S.S.; Boelen, A.; Visser, T.J.; Kaether, C.; Heuer, H.; von Maltzahn, J. Thyroid Hormone Transporters MCT8 and OATP1C1 Control Skeletal Muscle Regeneration. Stem Cell Rep. 2018, 10, 1959–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Milanesi, A.; Lee, J.-W.; Kim, N.-H.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Yang, A.; Sedrakyan, S.; Kahng, A.; Cervantes, V.; Tripuraneni, N.; Cheng, S.; et al. Thyroid Hormone Receptor α Plays an Essential Role in Male Skeletal Muscle Myoblast Proliferation, Differentiation, and Response to Injury. Endocrinology 2016, 157, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fliers, E.; Boelen, A. An update on non-thyroidal illness syndrome. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2021, 44, 1597–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloise, F.F.; Van Der Spek, A.H.; Surovtseva, O.V.; Ortiga-Carvalho, T.M.; Fliers, E.; Boelen, A. Differential Effects of Sepsis and Chronic Inflammation on Diaphragm Muscle Fiber Type, Thyroid Hormone Metabolism, and Mitochondrial Function. Thyroid 2016, 26, 600–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloise, F.F.; Santos, A.T.; de Brito, J.; de Andrade, C.B.V.; Oliveira, T.S.; de Souza, A.F.P.; Fontes, K.N.; Silva, J.D.; Blanco, N.; Silva, P.L.; et al. Sepsis Impairs Thyroid Hormone Signaling and Mitochondrial Function in the Mouse Diaphragm. Thyroid 2020, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boelen, A.; van der Spek, A.H.; Bloise, F.; de Vries, E.M.; Surovtseva, O.V.; van Beeren, M.; Ackermans, M.T.; Kwakkel, J.; Fliers, E. Tissue thyroid hormone metabolism is differentially regulated during illness in mice. J. Endocrinol. 2017, 233, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schefold, J.C.; Wollersheim, T.; Grunow, J.J.; Luedi, M.M.; Z’Graggen, W.J.; Weber-Carstens, S. Muscular weakness and muscle wasting in the critically ill. J. Cachexia. Sarcopenia Muscle 2020, 11, 1399–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costamagna, D.; Costelli, P.; Sampaolesi, M.; Penna, F. Role of Inflammation in Muscle Homeostasis and Myogenesis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 805172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ono, Y.; Sakamoto, K. Lipopolysaccharide inhibits myogenic differentiation of C2C12 myoblasts through the Toll-like receptor 4-nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway and myoblast-derived tumor necrosis factor-α. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hindi, S.M.; Kumar, A. Toll-like receptor signalling in regenerative myogenesis: Friend and foe. J. Pathol. 2016, 239, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Juban, G.; Chazaud, B. Efferocytosis during skeletal muscle regeneration. Cells 2021, 10, 3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frost, R.A.; Nystrom, G.J.; Lang, C.H. Lipopolysaccharide regulates proinflammatory cytokine expression in mouse myoblasts and skeletal muscle. Am. J. Physiol. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2002, 283, R698–R709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyd, J.H.; Divangahi, M.; Yahiaoui, L.; Gvozdic, D.; Qureshi, S.; Petrof, B.J. Toll-Like Receptors Differentially Regulate CC and CXC Chemokines in Skeletal Muscle via NF-κB and Calcineurin. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 6829–6838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dumont, N.A.; Bentzinger, C.F.; Sincennes, M.-C.C.; Rudnicki, M.A. Satellite cells and skeletal muscle regeneration. Compr. Physiol. 2015, 5, 1027–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferri, P.; Barbieri, E.; Burattini, S.; Guescini, M.; D’Emilio, A.; Biagiotti, L.; Del Grande, P.; De Luca, A.; Stocchi, V.; Falcieri, E. Expression and subcellular localization of myogenic regulatory factors during the differentiation of skeletal muscle C2C12 myoblasts. J. Cell. Biochem. 2009, 108, 1302–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagliocchi, S.; Cicatiello, A.G.; Di Cicco, E.; Ambrosio, R.; Miro, C.; Di Girolamo, D.; Nappi, A.; Mancino, G.; De Stefano, M.A.; Luongo, C.; et al. The thyroid hormone activating enzyme, type 2 deiodinase, induces myogenic differentiation by regulating mitochondrial metabolism and reducing oxidative stress. Redox Biol. 2019, 24, 101228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeöld, A.; Doleschall, M.; Haffner, M.C.; Capelo, L.P.; Menyhért, J.; Liposits, Z.; da Silva, W.S.; Bianco, A.C.; Kacskovics, I.; Fekete, C.; et al. Characterization of the Nuclear Factor-κB Responsiveness of the Human dio2 Gene. Endocrinology 2006, 147, 4419–4429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, A.C.; Dumitrescu, A.; Gereben, B.; Ribeiro, M.O.; Fonseca, T.L.; Fernandes, G.W.; Bocco, B.M.L.C.L.C. Paradigms of Dynamic Control of Thyroid Hormone Signaling. Endocr. Rev. 2019, 40, 1000–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, T.; Autieri, M.V.; Scalia, R. Adipose tissue inflammation and metabolic dysfunction in obesity. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2021, 320, C375–C391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franceschi, C.; Garagnani, P.; Parini, P.; Giuliani, C.; Santoro, A. Inflammaging: A new immune–metabolic viewpoint for age-related diseases. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 576–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloise, F.F.; Oliveira, T.S.; Cordeiro, A.; Ortiga-Carvalho, T.M. Thyroid hormones play role in sarcopenia and myopathies. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kalinkovich, A.; Livshits, G. Sarcopenic obesity or obese sarcopenia: A cross talk between age-associated adipose tissue and skeletal muscle inflammation as a main mechanism of the pathogenesis. Ageing Res. Rev. 2017, 35, 200–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanyal, D.; Raychaudhuri, M. Hypothyroidism and obesity: An intriguing link. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 20, 554–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosio, R.; De Stefano, M.A.; Di Girolamo, D.; Salvatore, D. Thyroid hormone signaling and deiodinase actions in muscle stem/progenitor cells. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2017, 459, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Hu, P. Skeletal muscle regeneration is modulated by inflammation. J. Orthop. Transl. 2018, 13, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, C.C. Thyroid Hormone-Responsive Genes in Developing Cerebellum Include a Novel Synaptotagmin and a hairless Homolog. J. Neurosci. 1996, 16, 7832–7840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Cosmo, C.; Liao, X.H.; Ye, H.; Ferrara, A.M.; Weiss, R.E.; Refetoff, S.; Dumitrescu, A.M. Mct8-deficient mice have increased energy expenditure and reduced fat mass that is abrogated by normalization of serum T3 levels. Endocrinology 2013, 154, 4885–4895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wajner, S.M.; Goemann, I.M.; Bueno, A.L.; Larsen, P.R.; Maia, A.L. IL-6 promotes nonthyroidal illness syndrome by blocking thyroxine activation while promoting thyroid hormone inactivation in human cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 1834–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oliveira, T.S.d.; Shimabukuro, M.K.; Monteiro, V.R.S.; Andrade, C.B.V.; Boelen, A.; Wajner, S.M.; Maia, A.L.; Ortiga-Carvalho, T.M.; Bloise, F.F. Low Inflammatory Stimulus Increases D2 Activity and Modulates Thyroid Hormone Metabolism during Myogenesis In Vitro. Metabolites 2022, 12, 416. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12050416
Oliveira TSd, Shimabukuro MK, Monteiro VRS, Andrade CBV, Boelen A, Wajner SM, Maia AL, Ortiga-Carvalho TM, Bloise FF. Low Inflammatory Stimulus Increases D2 Activity and Modulates Thyroid Hormone Metabolism during Myogenesis In Vitro. Metabolites. 2022; 12(5):416. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12050416
Chicago/Turabian StyleOliveira, Thamires Siqueira de, Marilia Kimie Shimabukuro, Victoria Regina Siqueira Monteiro, Cherley Borba Vieira Andrade, Anita Boelen, Simone Magagnin Wajner, Ana Luiza Maia, Tania Maria Ortiga-Carvalho, and Flavia Fonseca Bloise. 2022. "Low Inflammatory Stimulus Increases D2 Activity and Modulates Thyroid Hormone Metabolism during Myogenesis In Vitro" Metabolites 12, no. 5: 416. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12050416
APA StyleOliveira, T. S. d., Shimabukuro, M. K., Monteiro, V. R. S., Andrade, C. B. V., Boelen, A., Wajner, S. M., Maia, A. L., Ortiga-Carvalho, T. M., & Bloise, F. F. (2022). Low Inflammatory Stimulus Increases D2 Activity and Modulates Thyroid Hormone Metabolism during Myogenesis In Vitro. Metabolites, 12(5), 416. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12050416







