In Vitro Assessment of Antistaphylococci, Antitumor, Immunological and Structural Characterization of Acidic Bioactive Exopolysaccharides from Marine Bacillus cereus Isolated from Saudi Arabia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Isolation and Identification of the EPS Producing Bacteria
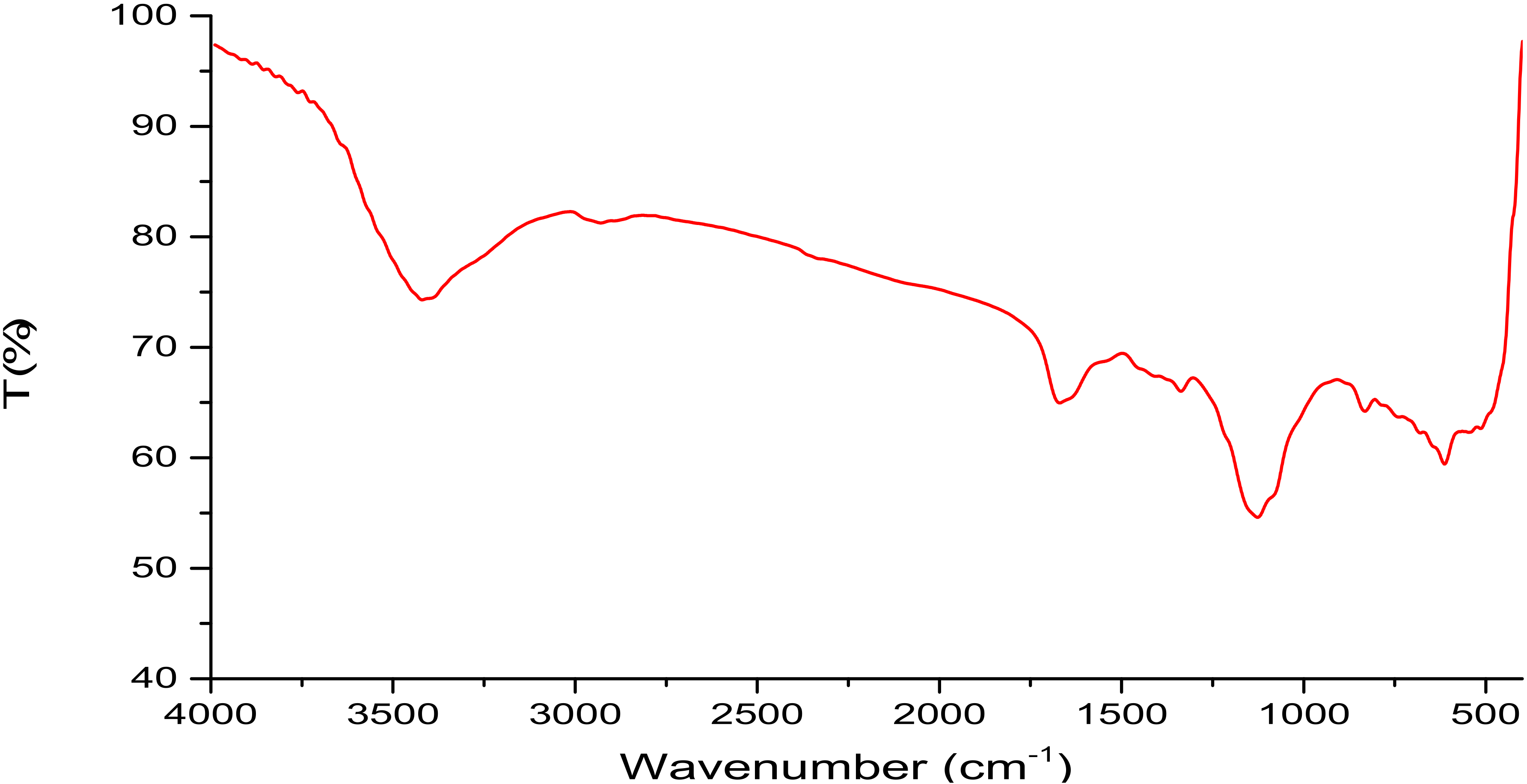
2.2. Isolation, Partial Purification and Composition of EPSR3
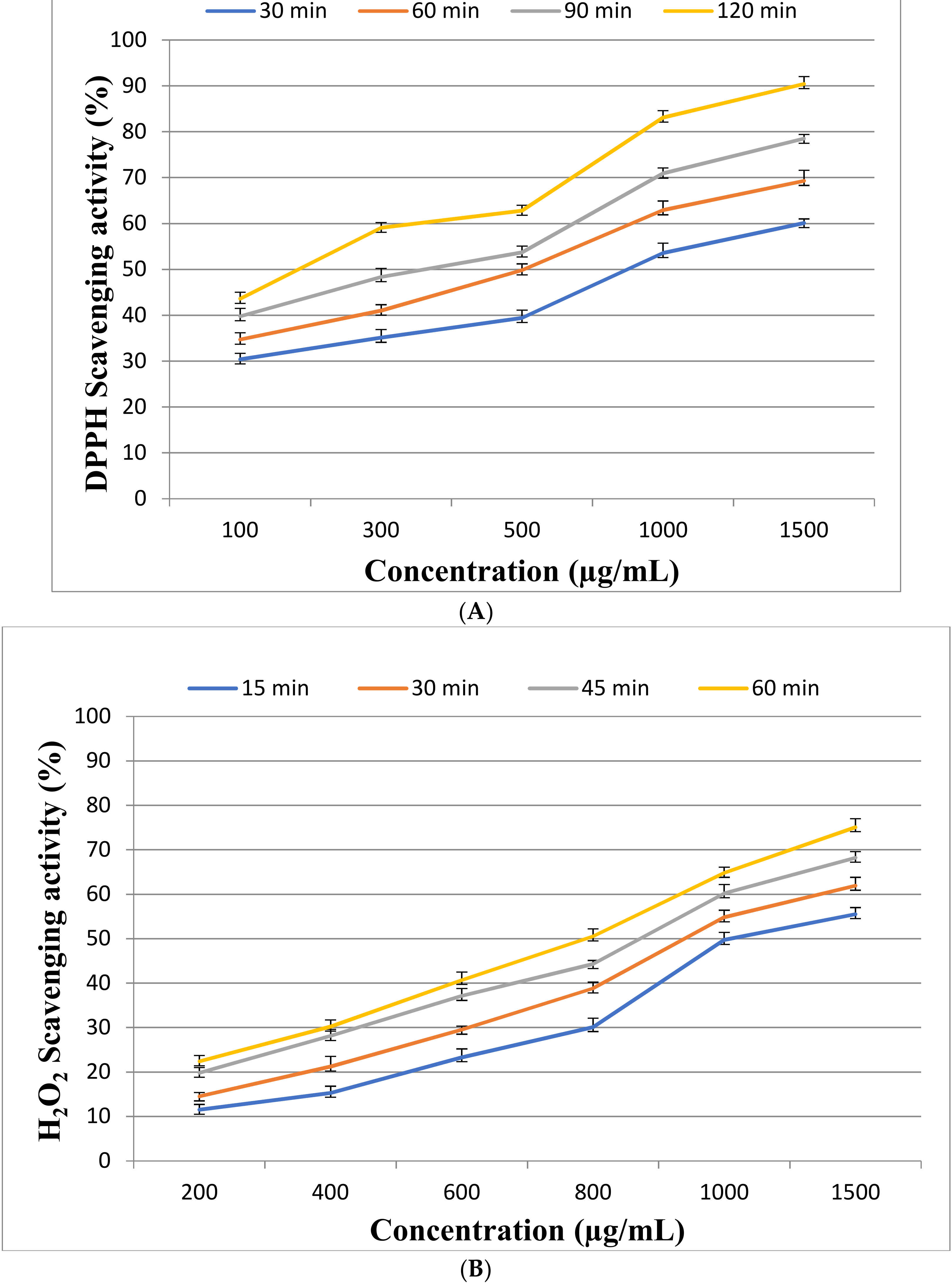
2.3. Antioxidant Activity of EPSR3
2.4. Antitumor Activity against Different Cell Lines
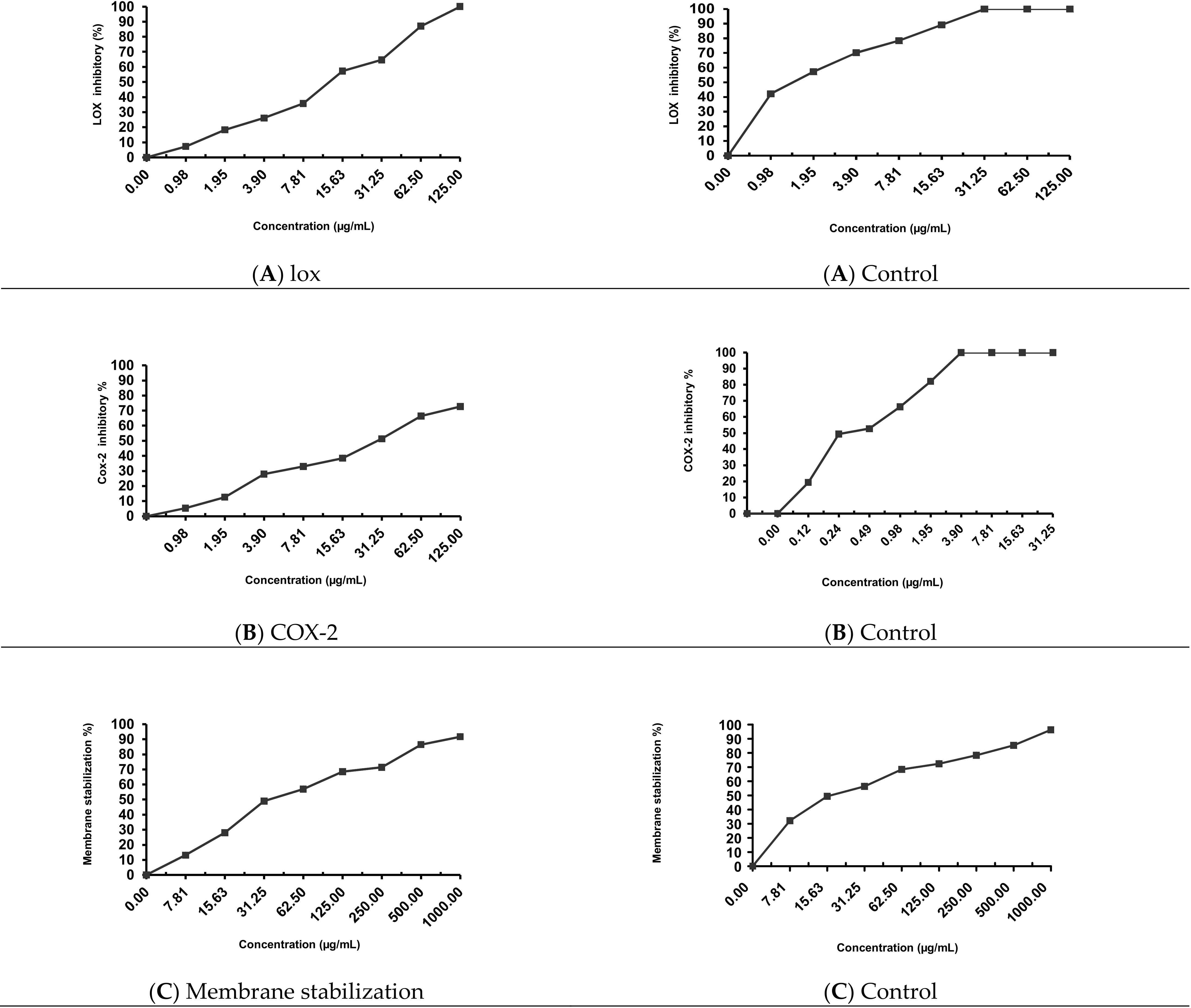
2.5. Anti-Inflammatory Activity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sampling and Isolation of Bacteria
4.2. Identification of Bacterial Isolates
4.3. Production and Fractionation of EPS
4.4. Analysis of EPSR3
4.5. Assessment of Antioxidant Activity
4.5.1. DPPH Assay
4.5.2. Hydrogen Peroxide Scavenging (H2O2) Assay
4.6. Evaluation of Cytotoxic Effects Using Different Cell Line
4.7. Evaluation of Anti-Inflammatory Activity
4.7.1. In Vitro Lipoxygenase (LOX) Inhibition
4.7.2. In Vitro Cyclooxygenase (COX-2) Inhibition
4.7.3. Membrane Stabilization
4.8. Antimicrobial Tests
4.8.1. Microbial Strains
4.8.2. Disc-Diffusion Assay
4.8.3. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Angelin, J.; Kavitha, M. Exopolysaccharides from Probiotic Bacteria and Their Health Potential. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 162, 853–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flemming, H.-C.; Neu, T.; Wingender, J. The Perfect Slime: Microbial Extracellular Polymeric Substances (EPS). Water Intell. Online 2016, 15, 9781780407425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuntiya, A.; Hanmoungjai, P.; Techapun, C.; Sasaki, K.; Seesuriyachan, P. Influence of PH, Sucrose Concentration and Agitation Speed on Exopolysaccharide Production by Lactobacillus Confusus TISTR 1498 Using Coconut Water as a Raw Material Substitute. Maejo Int. J. Sci. 2010, 4, 318–330. [Google Scholar]
- Prete, R.; Alam, M.K.; Perpetuini, G.; Perla, C.; Pittia, P.; Corsetti, A. Lactic Acid Bacteria Exopolysaccharides Producers: A Sustainable Tool for Functional Foods. Foods 2021, 10, 1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, T.; Chenjian, L.; Qin, X.; Li, X.; Luo, Y.; Yang, E. Optimization of Biosynthesis Conditions for the Production of Exopolysaccharides by Lactobacillus Plantarum YM-2. Food Sci. 2017, 38, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Nadzir, M.; Nurhayati, R.W.; Idris, F.N.; Nguyen, M.H. Biomedical Applications of Bacterial Exopolysaccharides: A Review. Polymers 2021, 13, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza de Azevedo, P.O.; Mendonça, C.M.N.; Moreno, A.C.R.; Bueno, A.V.I.; de Almeida, S.R.Y.; Seibert, L.; Converti, A.; Watanabe, I.-S.; Gierus, M.; de Souza Oliveira, R.P. Antibacterial and Antifungal Activity of Crude and Freeze-Dried Bacteriocin-like Inhibitory Substance Produced by Pediococcus Pentosaceus. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escárcega-González, C.E.; Garza-Cervantes, J.A.; Vázquez-Rodríguez, A.; Morones-Ramírez, J.R. Bacterial Exopolysaccharides as Reducing and/or Stabilizing Agents during Synthesis of Metal Nanoparticles with Biomedical Applications. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2018, 2018, 7045852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sungur, T.; Aslim, B.; Karaaslan, C.; Aktas, B. Impact of Exopolysaccharides (EPSs) of Lactobacillus Gasseri Strains Isolated from Human Vagina on Cervical Tumor Cells (HeLa). Anaerobe 2017, 47, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adesulu-Dahunsi, A.T.; Jeyaram, K.; Sanni, A.I.; Banwo, K. Production of Exopolysaccharide by Strains of Lactobacillus Plantarum YO175 and OF101 Isolated from Traditional Fermented Cereal Beverage. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adrio, J.L.; Demain, A.L. Microbial Enzymes: Tools for Biotechnological Processes. Biomolecules 2014, 4, 117–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coker, J.A. Extremophiles and Biotechnology: Current Uses and Prospects. F1000Research 2016, 5, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, O.Y.A.; Raaijmakers, J.M.; Kuramae, E.E. Microbial Extracellular Polymeric Substances: Ecological Function and Impact on Soil Aggregation. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vijayabaskar, P.; Babinastarlin, S.; Shankar, T.; Sivakumar, T.; Anandapandian, K.T.K. Quantification and Characterization of Exopolysaccharides from Bacillus Subtilis (MTCC 121). Adv. Biol. Res. 2011, 5, 71–76. [Google Scholar]
- Kodali, V.P.; Perali, R.S.; Sen, R. Purification and Partial Elucidation of the Structure of an Antioxidant Carbohydrate Biopolymer from the Probiotic Bacterium Bacillus Coagulans RK-02. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 1692–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casillo, A.; Lanzetta, R.; Parrilli, M.; Corsaro, M.M. Exopolysaccharides from Marine and Marine Extremophilic Bacteria: Structures, Properties, Ecological Roles and Applications. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xie, J.-H.; Xie, M.-Y.; Nie, S.-P.; Shen, M.-Y.; Wang, Y.-X.; Li, C. Isolation, Chemical Composition and Antioxidant Activities of a Water-Soluble Polysaccharide from Cyclocarya Paliurus (Batal.) Iljinskaja. Food Chem. 2010, 119, 1626–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanmani, P.; Kumar, R.S.; Yuvaraj, N.; Paari, K.A.; Pattukumar, V.; Arul, V. Production and Purification of a Novel Exopolysaccharide from Lactic Acid Bacterium Streptococcus Phocae PI80 and Its Functional Characteristics Activity in Vitro. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 4827–4833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, R.; Fang, J.; Goodwin, A.; Lawther, J.; Bolton, A.J. Fractionation and Characterization of Polysaccharides from Abaca Fibre. Carbohydr. Polym. 1998, 37, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, A.; Wan, F.; Jin, Z.; Wang, J.; Xu, X. Nitrite Oxide and Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase Were Regulated by Polysaccharides Isolated from Glycyrrhiza Uralensis Fisch. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 118, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.V.; Bathe, G.A.; Patil, A.V.; Patil, R.H.; Salunkea, B.K. Production of Bioflocculant Exopolysaccharide by Bacillus Subtilis. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 8, 14–21. [Google Scholar]
- Fusconi, R.; Godinho, M.J.L. Screening for Exopolysaccharide-Producing Bacteria from Sub-Tropical Polluted Groundwater. Braz. J. Biol. 2002, 62, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodali, V.P.; Sen, R. Antioxidant and Free Radical Scavenging Activities of an Exopolysaccharide from a Probiotic Bacterium. Biotechnol. J. 2008, 3, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Liu, F.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, M. Antioxidant Activities of an Exopolysaccharide Isolated and Purified from Marine Pseudomonas PF-6. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 764–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Newary, S.A.; Ibrahim, A.Y.; Asker, M.S.; Mahmoud, M.G.; El Awady, M.E. Production, Characterization and Biological Activities of Acidic Exopolysaccharide from Marine Bacillus Amyloliquefaciens 3MS 2017. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2017, 10, 652–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selim, M.S.; Amer, S.K.; Mohamed, S.S.; Mounier, M.M.; Rifaat, H.M. Production and Characterisation of Exopolysaccharide from Streptomyces Carpaticus Isolated from Marine Sediments in Egypt and Its Effect on Breast and Colon Cell Lines. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2018, 16, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Wang, J.-W.; Fang, L.; Gao, X.-D.; Tan, R.-X. Free Radical Scavenging and Antioxidant Activities of EPS2, an Exopolysaccharide Produced by a Marine Filamentous Fungus Keissleriella Sp. YS 4108. Life Sci. 2004, 75, 1063–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asker, M.M.S.; Ahmed, Y.M.; Ramadan, M.F. Chemical Characteristics and Antioxidant Activity of Exopolysaccharide Fractions from Microbacterium Terregens. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 3, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, W.; Zhang, L.; Yi, H.; Han, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xin, L. Exopolysaccharides Produced by Lactobacillus Strains Suppress HT-29 Cell Growth via Induction of G0/G1 Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 3577–3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, L.; Wang, C. The Anti-Cancer Effects and Mechanisms of Lactic Acid Bacteria Exopolysaccharides in Vitro: A Review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 253, 117308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.N.; Ipsen, R.; Janzen, T.; Qvist, K.B. Microstructure and Rheology of Yogurt Made with Cultures Differing Only in Their Ability to Produce Exopolysaccharides. Int. J. Dairy Sci. 2003, 86, 1632–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooi, V.E.; Liu, F. Immunomodulation and Anti-Cancer Activity of Polysaccharide-Protein Complexes. Curr. Med. Chem. 2000, 7, 715–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zeng, F.; Kennedy, J.F. Structure and Antitumor Activities of the Water-Soluble Polysaccharides from Ganoderma Tsugae Mycelium. Carbohydr. Polym. 2005, 3, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasser, S.P. Medicinal Mushrooms as a Source of Antitumor and Immunomodulating Polysaccharides. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2002, 60, 258–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Xiong, Q.; Lai, X.; Li, X.; Wan, M.; Zhang, J.; Yan, Y.; Cao, M.; Lu, L.; Guan, J.; et al. Molecular Modification of Polysaccharides and Resulting Bioactivities. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. 2016, 15, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, S.; Shah, N.P. Characterization, Anti-Inflammatory and Antiproliferative Activities of Natural and Sulfonated Exo-Polysaccharides from Streptococcus Thermophilus ASCC 1275. J. Food Sci. 2016, 81, M1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Li, W.; Rui, X.; Chen, X.; Jiang, M.; Dong, M. Structural Characterization and Bioactivity of Released Exopolysaccharides from Lactobacillus Plantarum 70810. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 67, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Liu, H.; Liu, S.; Zhang, X.; Chen, P.; Li, W.; Xu, X.; Tian, W. Purification, Preliminary Structure and Antitumor Activity of Exopolysaccharide Produced by Streptococcus Thermophilus CH9. Molecules 2018, 23, E2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Tang, W.; Ji, J.; Xia, X.; Rui, X.; Chen, X.; Jiang, M.; Zhou, J.; Dong, M. Characterization of a Novel Polysaccharide with Anti-Colon Cancer Activity from Lactobacillus Helveticus MB2-1. Carbohydr. Res. 2015, 411, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, A.; Yang, Z. Characterization and Bioactivities of an Exopolysaccharide Produced by Lactobacillus Plantarum YW32. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 74, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarghi, A.; Arfaei, S. Selective COX-2 Inhibitors: A Review of Their Structure-Activity Relationships. Iran J. Pharm. Res. 2011, 10, 655–683. [Google Scholar]
- Attiq, A.; Jalil, J.; Husain, K.; Ahmad, W. Raging the War Against Inflammation With Natural Products. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenab, A.; Roghanian, R.; Emtiazi, G. Bacterial Natural Compounds with Anti-Inflammatory and Immunomodulatory Properties (Mini Review). Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2020, 14, 3787–3801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, M.; Nonomura, H. Humic Acid-Vitamin Agar, A New Medium for the Selective Isolation of Soil Actinomycetes. J. Ferment. Technol. 1987, 65, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-W.; Ahn, S.-G.; Seo, W.-T.; Kwon, G.-S.; Park, Y.-H. Rheological Properties of a Novel High Viscosity Polysaccharide, A49-Pol, Produced by Bacillus Polymyxa. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1998, 8, 178–181. [Google Scholar]
- Bergey, D.H.; Holt, J.G. Bergey’s Manual of Determinative Bacteriology, 9th ed.; Hensyl, W.R., Ed.; Williams & Wilkins: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1994; ISBN 978-0-683-00603-2. [Google Scholar]
- Tamura, K.; Peterson, D.; Peterson, N.; Stecher, G.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. MEGA5: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Using Maximum Likelihood, Evolutionary Distance, and Maximum Parsimony Methods. Mol. Biol. 2011, 28, 2731–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gardes, M.; Bruns, T.D. ITS Primers with Enhanced Specificity for Basidiomycetes--Application to the Identification of Mycorrhizae and Rusts. Mol. Ecol. 1993, 2, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Lu, J.; Lu, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, F.; Xiao, M. Isolation, Structural Characterization and Immunological Activity of an Exopolysaccharide Produced by Bacillus Licheniformis 8-37-0-1. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 5528–5533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Jiang, X.; Mu, H.; Liang, X.; Guan, H. Structure and Protective Effect of Exopolysaccharide from P. Agglomerans Strain KFS-9 against UV Radiation. Microbiol. Res. 2007, 162, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicely, W.B. Infrared Spectra of Carbohydrates. In Advances in Carbohydrate Chemistry and Biochemistry; Wolfrom, M.L., Tipson, R.S., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1957; Volume 12, pp. 13–33. [Google Scholar]
- Filisetti-Cozzi, T.M.; Carpita, N.C. Measurement of Uronic Acids without Interference from Neutral Sugars. Anal. Biochem. 1991, 197, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodgson, K.S.; Price, R.G. A Note on the Determination of the Ester Sulphate Content of Sulphated Polysaccharides. Biochem. J. 1962, 84, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Randall, R.C.; Phillips, G.O.; Williams, P.A. The Role of the Proteinaceous Component on the Emulsifying Properties of Gum Arabic. Food Hydrocoll. 1988, 2, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, J.; Dou, L.; Yoshimura, K.; Kato, T.; Ohya, K.; Moriarty, T.; Emery, K.; Chen, C.-C.; Gao, J.; Li, G.; et al. A Polymer Tandem Solar Cell with 10.6% Power Conversion Efficiency. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brand-Williams, W.; Cuvelier, M.E.; Berset, C. Use of a Free Radical Method to Evaluate Antioxidant Activity. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 1995, 28, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruch, R.J.; Crist, K.A.; Klaunig, J.E. Effects of Culture Duration on Hydrogen Peroxide-Induced Hepatocyte Toxicity. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 1989, 100, 451–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid Colorimetric Assay for Cellular Growth and Survival: Application to Proliferation and Cytotoxicity Assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granica, S.; Czerwińska, M.E.; Piwowarski, J.P.; Ziaja, M.; Kiss, A.K. Chemical Composition, Antioxidative and Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Extracts Prepared from Aerial Parts of Oenothera Biennis L. and Oenothera Paradoxa Hudziok Obtained after Seeds Cultivation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amessis-Ouchemoukh, N.; Madani, K.; Falé, P.L.V.; Serralheiro, M.L.; Araújo, M.E.M. Antioxidant Capacity and Phenolic Contents of Some Mediterranean Medicinal Plants and Their Potential Role in the Inhibition of Cyclooxygenase-1 and Acetylcholinesterase Activities. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2014, 53, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovic, N.; Murray, M. Using N,N,N’,N’-Tetramethyl-p-Phenylenediamine (TMPD) to Assay Cyclooxygenase Activity in Vitro. Methods Mol. Biol. 2010, 594, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, U.A.; Phadke, A.S.; Nair, A.M.; Mungantiwar, A.A.; Dikshit, V.J.; Saraf, M.N. Membrane Stabilizing Activity—A Possible Mechanism of Action for the Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Cedrus Deodara Wood Oil. Fitoterapia 1999, 70, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manual of Clinical Microbiology. In Mycopathologia, 7th ed.; Lehmann, P.F.; Murray, P.R.; Baron, E.J.; Pfaller, M.A.; Tenover, F.C.; Yolken, R.H. (Eds.) 1999; Volume 146, pp. 107–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Selim, S.; Almuhayawi, M.S.; Alharbi, M.T.; Nagshabandi, M.K.; Alanazi, A.; Warrad, M.; Hagagy, N.; Ghareeb, A.; Ali, A.S. In Vitro Assessment of Antistaphylococci, Antitumor, Immunological and Structural Characterization of Acidic Bioactive Exopolysaccharides from Marine Bacillus cereus Isolated from Saudi Arabia. Metabolites 2022, 12, 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12020132
Selim S, Almuhayawi MS, Alharbi MT, Nagshabandi MK, Alanazi A, Warrad M, Hagagy N, Ghareeb A, Ali AS. In Vitro Assessment of Antistaphylococci, Antitumor, Immunological and Structural Characterization of Acidic Bioactive Exopolysaccharides from Marine Bacillus cereus Isolated from Saudi Arabia. Metabolites. 2022; 12(2):132. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12020132
Chicago/Turabian StyleSelim, Samy, Mohammed S. Almuhayawi, Mohanned Talal Alharbi, Mohammed K. Nagshabandi, Awadh Alanazi, Mona Warrad, Nashwa Hagagy, Ahmed Ghareeb, and Abdallah S. Ali. 2022. "In Vitro Assessment of Antistaphylococci, Antitumor, Immunological and Structural Characterization of Acidic Bioactive Exopolysaccharides from Marine Bacillus cereus Isolated from Saudi Arabia" Metabolites 12, no. 2: 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12020132
APA StyleSelim, S., Almuhayawi, M. S., Alharbi, M. T., Nagshabandi, M. K., Alanazi, A., Warrad, M., Hagagy, N., Ghareeb, A., & Ali, A. S. (2022). In Vitro Assessment of Antistaphylococci, Antitumor, Immunological and Structural Characterization of Acidic Bioactive Exopolysaccharides from Marine Bacillus cereus Isolated from Saudi Arabia. Metabolites, 12(2), 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12020132







