Stability of Wheat Floret Metabolites during Untargeted Metabolomics Studies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Extract Stability at Room Temperature (25 °C)
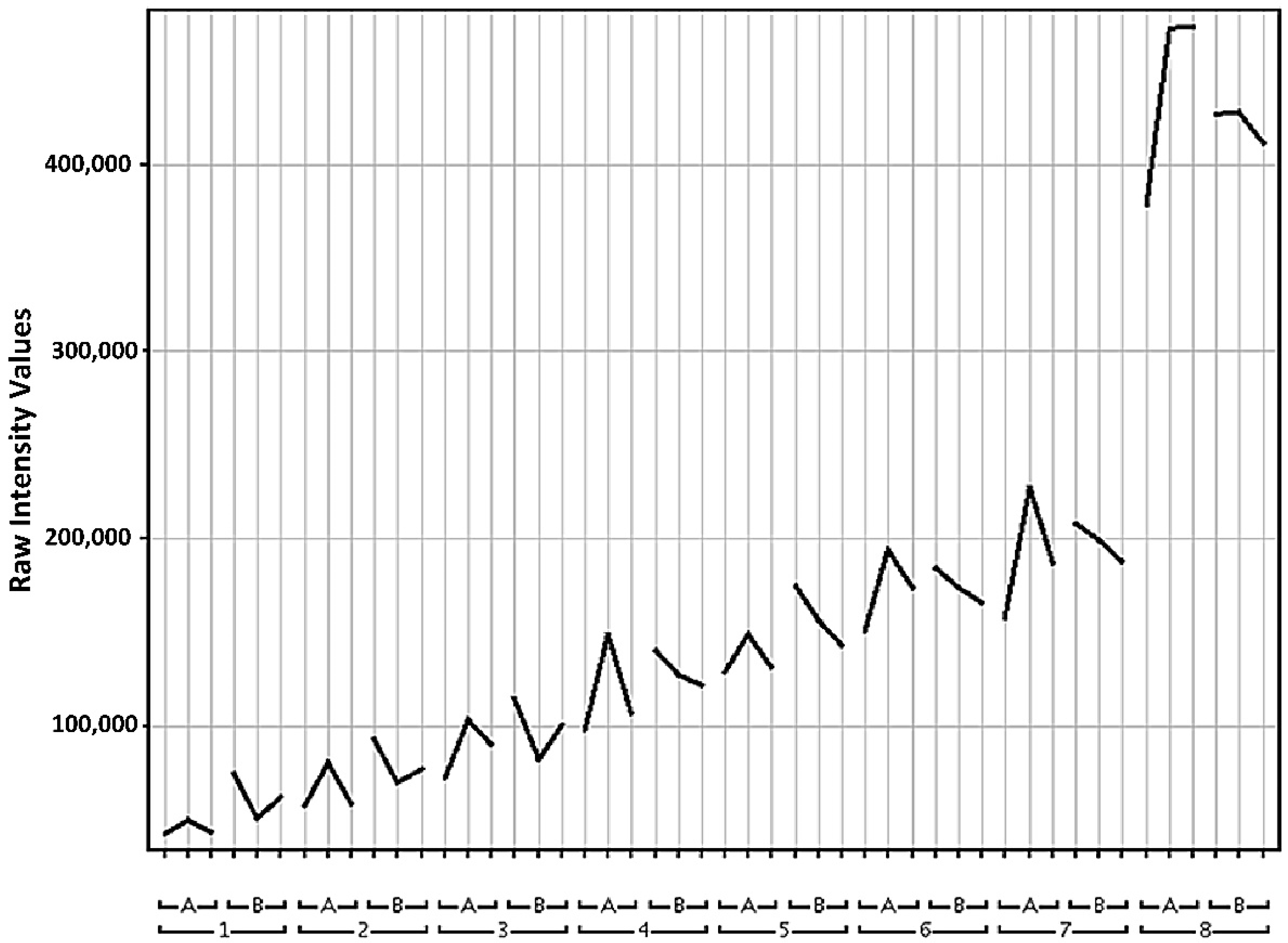
2.1.1. Sample Reproducibility
2.1.2. Data Pre-Processing
2.2. Analytical Window Determination
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Wheat Planting, Inoculation, and Sampling
3.2. Sample Extraction
3.3. Sample Analysis
3.4. Data Pre-Processing
3.4.1. Mass and Time Alignments
3.4.2. Recursion Analysis
3.5. Statistical Analyses
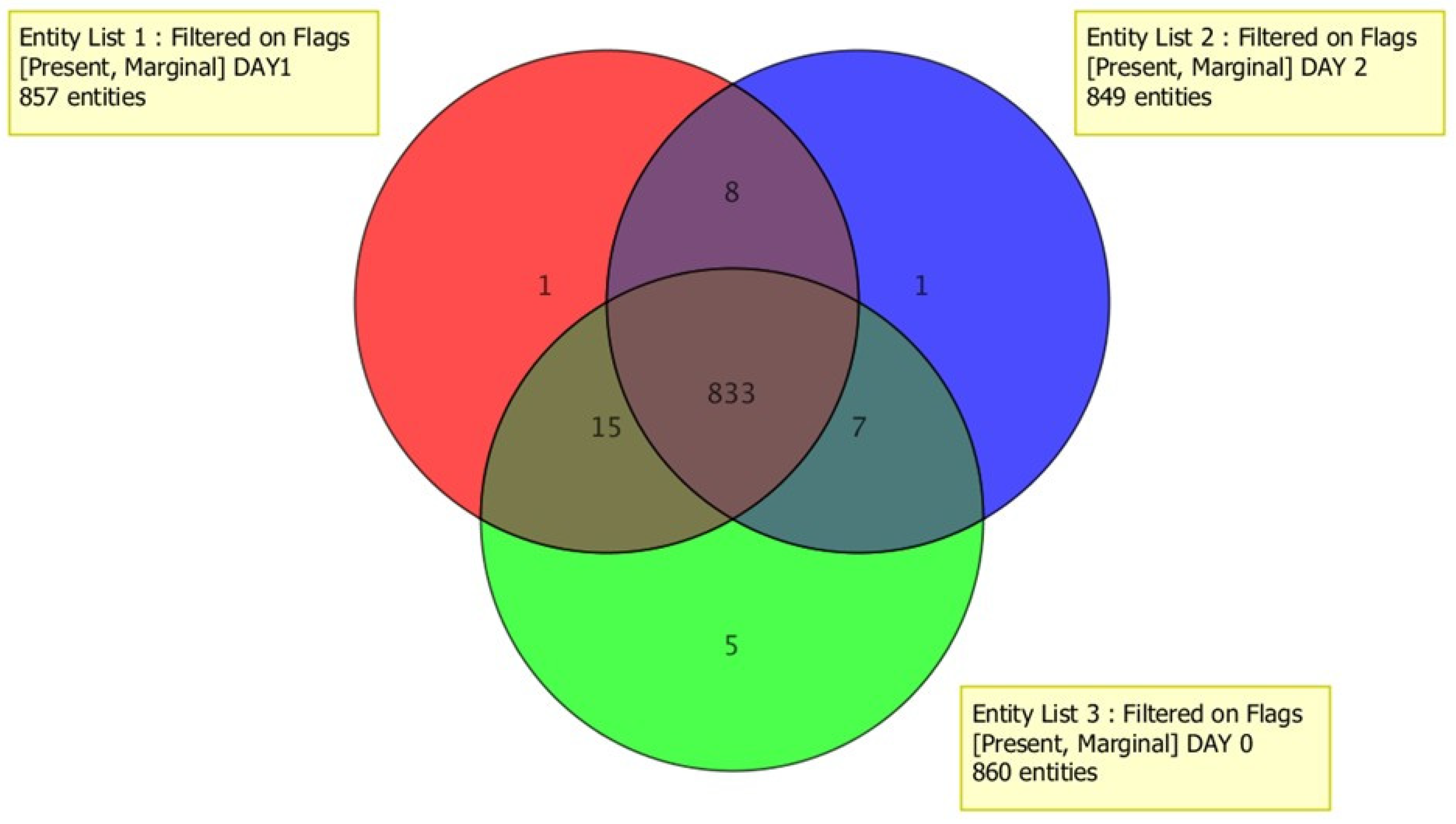
3.5.1. Blank Subtraction and Venn Diagrams
3.5.2. Interpretations
3.5.3. Principal Component Analysis
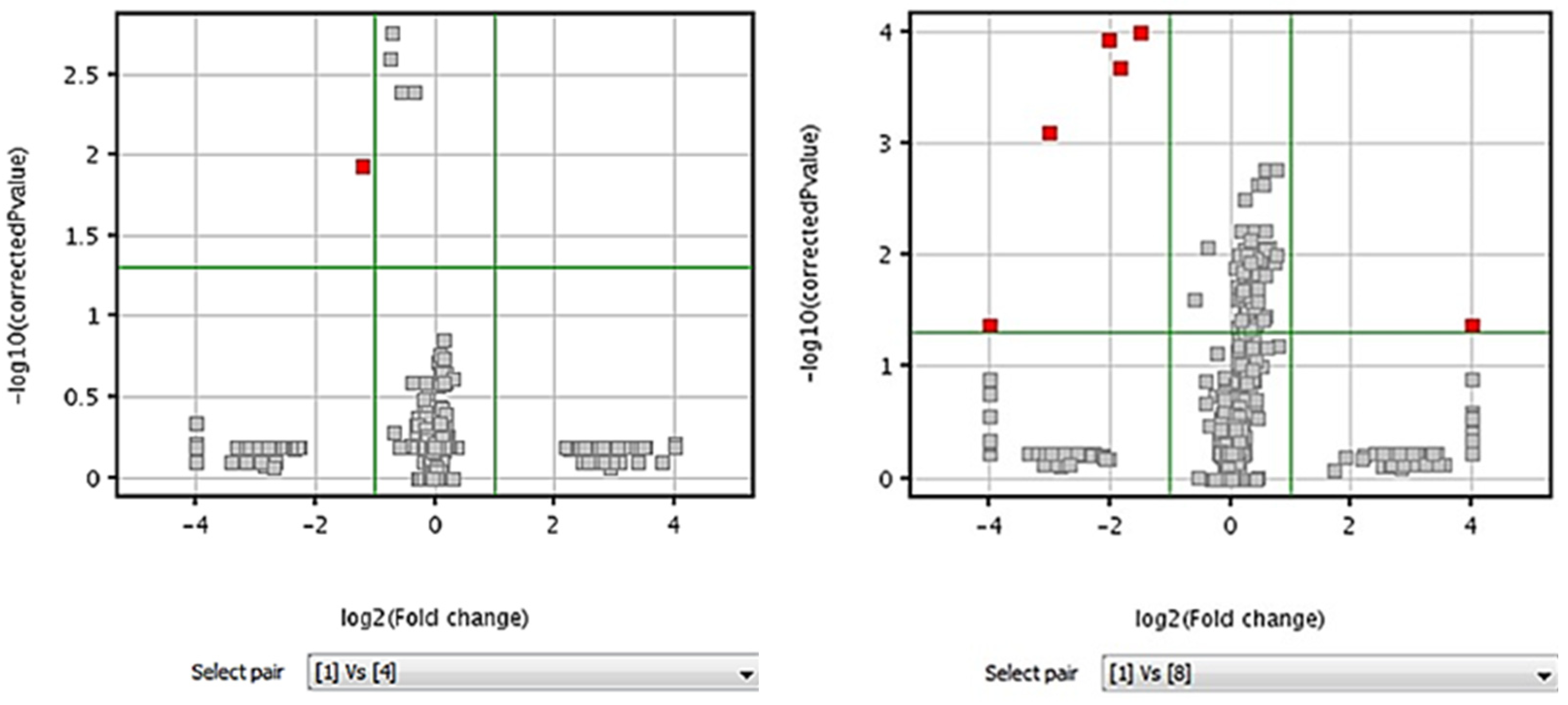
3.5.4. Volcano Plots
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lacalle-Bergeron, L.; Izquierdo-Sandoval, D.; Sancho, J.V.; López, F.J.; Hernández, F.; Portolés, T. Chromatography hyphenated to high resolution mass spectrometry in untargeted metabolomics for investigation of food (BIO) markers. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 135, 116161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, M.; Park, S.; Kim, H.; Choi, G.J.; Kim, S.H. Application of UPLC-QTOF-MS Based Untargeted Metabolomics in Identification of Metabolites Induced in Pathogen-Infected Rice. Plants 2021, 10, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khakimov, B.; Bak, S.; Engelsen, S.B. High-throughput cereal metabolomics: Current analytical technologies, challenges and perspectives. J. Cereal Sci. 2014, 59, 393–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodra, D.; Pousinis, P.; Vorkas, P.A.; Kademoglou, K.; Liapikos, T.; Pechlivanis, A.; Virgiliou, C.; Wilson, I.D.; Gika, H.; Theodoridis, G. Is Current Practice Adhering to Guidelines Proposed for Metabolite Identification in LC-MS Untargeted Metabolomics? A Meta-Analysis of the Literature. J. Proteome Res. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampler, E.; Hermann, G.; Grabmann, G.; El Abiead, Y.; Schoeny, H.; Baumgartinger, C.; Köcher, T.; Koellensperger, G. Benchmarking Non-Targeted Metabolomics Using Yeast-Derived Libraries. Metabolites 2021, 11, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vos, R.C.; Moco, S.; Lommen, A.; Keurentjes, J.J.; Bino, R.J.; Hall, R.D. Untargeted large-scale plant metabolomics using liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 778–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsagkaris, A.S.; Prusova, N.; Dzuman, Z.; Pulkrabova, J.; Hajslova, J. Regulated and Non-Regulated Mycotoxin Detection in Cereal Matrices Using an Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry (UHPLC-HRMS) Method. Toxins 2021, 13, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.C.B.; Barouh, N.; Durand, E.; Baréa, B.; Robert, M.; Micard, V.; Lullien-Pellerin, V.; Villeneuve, P.; Cameron, L.C.; Ryan, E.P.; et al. Metabolomics of Pigmented Rice Coproducts Applying Conventional or Deep Eutectic Extraction Solvents Reveal a Potential Antioxidant Source for Human Nutrition. Metabolites 2021, 11, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamany Djande, C.Y.; Piater, L.A.; Steenkamp, P.A.; Tugizimana, F.; Dubery, I.A. A Metabolomics Approach and Chemometric Tools for Differentiation of Barley Cultivars and Biomarker Discovery. Metabolites 2021, 11, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, P.; Zhao, L.; Li, W.; Zhao, J.; Yan, J.; Ma, X.; Li, A.; Wang, H.; Kong, L. Integrated metabolo-transcriptomics and functional characterization reveals that the wheat auxin receptor TIR1 negatively regulates defense against Fusarium graminearum. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2021, 63, 340–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, F.; Jiang, Q.; Sun, X.; Hu, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhang, H. Metabolic profiling of DREB-overexpressing transgenic wheat seeds by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Crop J. 2020, 8, 1025–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, T.Y.; Muttucumaru, N.; Shewry, P.R.; Parry, M.A.; Powers, S.J.; Elmore, J.S.; Mottram, D.S.; Hook, S.; Halford, N.G. Effects of genotype and environment on free amino acid levels in wheat grain: Implications for acrylamide formation during processing. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 1013–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beleggia, R.; Platani, C.; Nigro, F.; De Vita, P.; Cattivelli, L.; Papa, R. Effect of genotype, environment and genotype-by-environment interaction on metabolite profiling in durum wheat (Triticum durum Desf.) grain. J. Cereal Sci. 2013, 57, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, S.; Amigues, E.; Migaud, M.; Browne, R. Application of NMR based metabolomics for mapping metabolite variation in European wheat. Metabolomics 2009, 5, 302–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, S.B.; Santra, M.; Mensack, M.M.; Wolfe, P.; Byrne, P.F.; Thompson, H.J. Metabolite profiling of a diverse collection of wheat lines using ultraperformance liquid chromatography coupled with time-of-flight mass spectrometry. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ciasca, B.; Lanubile, A.; Marocco, A.; Pascale, M.; Logrieco, A.F.; Lattanzio, V.M. Application of an Integrated and Open Source Workflow for LC-HRMS Plant Metabolomics Studies. Case-Control Study: Metabolic Changes of Maize in Response to Fusarium verticillioides Infection. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, D.; Robards, K. Analytical chemistry considerations in plant metabolomics. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2006, 35, 319–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodoridis, G.A.; Gika, H.G.; Want, E.J.; Wilson, I.D. Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry based global metabolite profiling: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 711, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Sánchez, B.; Priego-Capote, F.; De Castro, M.L. Metabolomics analysis I. Selection of biological samples and practical aspects preceding sample preparation. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2010, 29, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villas-Boas, S.G.; Nielsen, J.; Smedsgaard, J.; Hansen, M.A.; Roessner-Tunali, U. Metabolome Analysis: An Introduction; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; Volume 24. [Google Scholar]
- Sumner, L.W.; Amberg, A.; Barrett, D.; Beale, M.H.; Beger, R.; Daykin, C.A.; Fan, T.W.-M.; Fiehn, O.; Goodacre, R.; Griffin, J.L. Proposed minimum reporting standards for chemical analysis. Metabolomics 2007, 3, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fiehn, O.; Wohlgemuth, G.; Scholz, M.; Kind, T.; Lee, D.Y.; Lu, Y.; Moon, S.; Nikolau, B. Quality control for plant metabolomics: Reporting MSI-compliant studies. Plant J. 2008, 53, 691–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauridsen, M.; Hansen, S.H.; Jaroszewski, J.W.; Cornett, C. Human urine as test material in 1H NMR-based metabonomics: Recommendations for sample preparation and storage. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 1181–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, W.B.; Broadhurst, D.; Ellis, D.I.; Brown, M.; Halsall, A.; O’Hagan, S.; Spasic, I.; Tseng, A.; Kell, D.B. A GC-TOF-MS study of the stability of serum and urine metabolomes during the UK Biobank sample collection and preparation protocols. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2008, 37, i23–i30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Teahan, O.; Gamble, S.; Holmes, E.; Waxman, J.; Nicholson, J.K.; Bevan, C.; Keun, H.C. Impact of analytical bias in metabonomic studies of human blood serum and plasma. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 4307–4318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.M.A.; Pawling, J.; Ryczko, M.; Caudy, A.A.; Dennis, J.W. Targeted metabolomics in cultured cells and tissues by mass spectrometry: Method development and validation. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 845, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- t’Kindt, R.; Morreel, K.; Deforce, D.; Boerjan, W.; Van Bocxlaer, J. Joint GC–MS and LC–MS platforms for comprehensive plant metabolomics: Repeatability and sample pre-treatment. J. Chromatogr. B 2009, 877, 3572–3580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moco, S.; Bino, R.J.; Vorst, O.; Verhoeven, H.A.; de Groot, J.; van Beek, T.A.; Vervoort, J.; De Vos, C.R. A liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry-based metabolome database for tomato. Plant Physiol. 2006, 141, 1205–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martins, M.C.; Caldana, C.; Wolf, L.D.; de Abreu, L.G.F. The importance of experimental design, quality assurance, and control in plant metabolomics experiments. In Plant Metabolomics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 3–17. [Google Scholar]
- Debegnach, F.; Brera, C.; Mazzilli, G.; Sonego, E.; Buiarelli, F.; Ferri, F.; Rossi, P.G.; Collini, G.; De Santis, B. Optimization and validation of a LC-HRMS method for aflatoxins determination in urine samples. Mycotoxin Res. 2020, 36, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vos, R.C.; Schipper, B.; Hall, R.D. High-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis of plant metabolites in Brassicaceae. In Plant Metabolomics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 111–128. [Google Scholar]
- Sobolev, A.P.; Brosio, E.; Gianferri, R.; Segre, A.L. Metabolic profile of lettuce leaves by high-field NMR spectra. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2005, 43, 625–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salminen, J.-P. Effects of sample drying and storage, and choice of extraction solvent and analysis method on the yield of birch leaf hydrolyzable tannins. J. Chem. Ecol. 2003, 29, 1289–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gika, H.G.; Theodoridis, G.A.; Wilson, I.D. Liquid chromatography and ultra-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry fingerprinting of human urine: Sample stability under different handling and storage conditions for metabonomics studies. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1189, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollina, V.; Kumaraswamy, G.K.; Kushalappa, A.C.; Choo, T.M.; Dion, Y.; Rioux, S.; Faubert, D.; Hamzehzarghani, H. Mass spectrometry-based metabolomics application to identify quantitative resistance-related metabolites in barley against Fusarium head blight. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2010, 11, 769–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mergoum, M.; Frohberg, R.; Miller, J.; Stack, R. Registration of ‘Steele-ND’ wheat. Crop Sci. 2005, 45, 1163–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ransom, J.; Mergoum, M.; Simsek, S.; Acevedo, M.; Friesen, T.; McMullen, M.; Zhong, S.; Eriksmoen, E.; Halvorson, M.; Hansen, B.; et al. North Dakota Hard Red Spring Wheat Variety Trial Results for 2011 and Selection Guide. Available online: https://mnwheat.org/wp-content/uploads/formidable/46/2011NDHRSWGuide.pdf (accessed on 29 September 2021).
- Gracia-Gonzalez, G. Metabolite Profiling of Hard Red Spring Wheat (Triticum aestivum) Inoculated with Fusarium Graminearum Utilizing Ultra High Pressure Liquid Chromatography-Quadrupole Time of Flight/Mass Spectrometry PhD Dissertation. Ph.D. Thesis, North Dakota State University, Fargo, ND, USA, 2015. Available online: https://library.ndsu.edu/ir/bitstream/handle/10365/24874/Metabolite%20Profiling%20of%20Hard%20Red%20Spring%20Wheat%20%28Triticum%20Aestivum%29%20Inoculated%20with%20Fusarium%20Graminearum%20Utilizing%20Ultra%20High%20Pressure%20Liquid%20Chromatography-Quadrupo.pdf?sequence=2&isAllowed=y (accessed on 8 January 2022).
- Puri, K.D.; Zhong, S. The 3ADON population of Fusarium graminearum found in North Dakota is more aggressive and produces a higher level of DON than the prevalent 15ADON population in spring wheat. Phytopathology 2010, 100, 1007–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zadoks, J.C.; Chang, T.T.; Konzak, C.F. A decimal code for the growth stages of cereals. Weed Res. 1974, 14, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamzehzarghani, H.; Kushalappa, A.; Dion, Y.; Rioux, S.; Comeau, A.; Yaylayan, V.; Marshall, W.; Mather, D. Metabolic profiling and factor analysis to discriminate quantitative resistance in wheat cultivars against fusarium head blight. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2005, 66, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


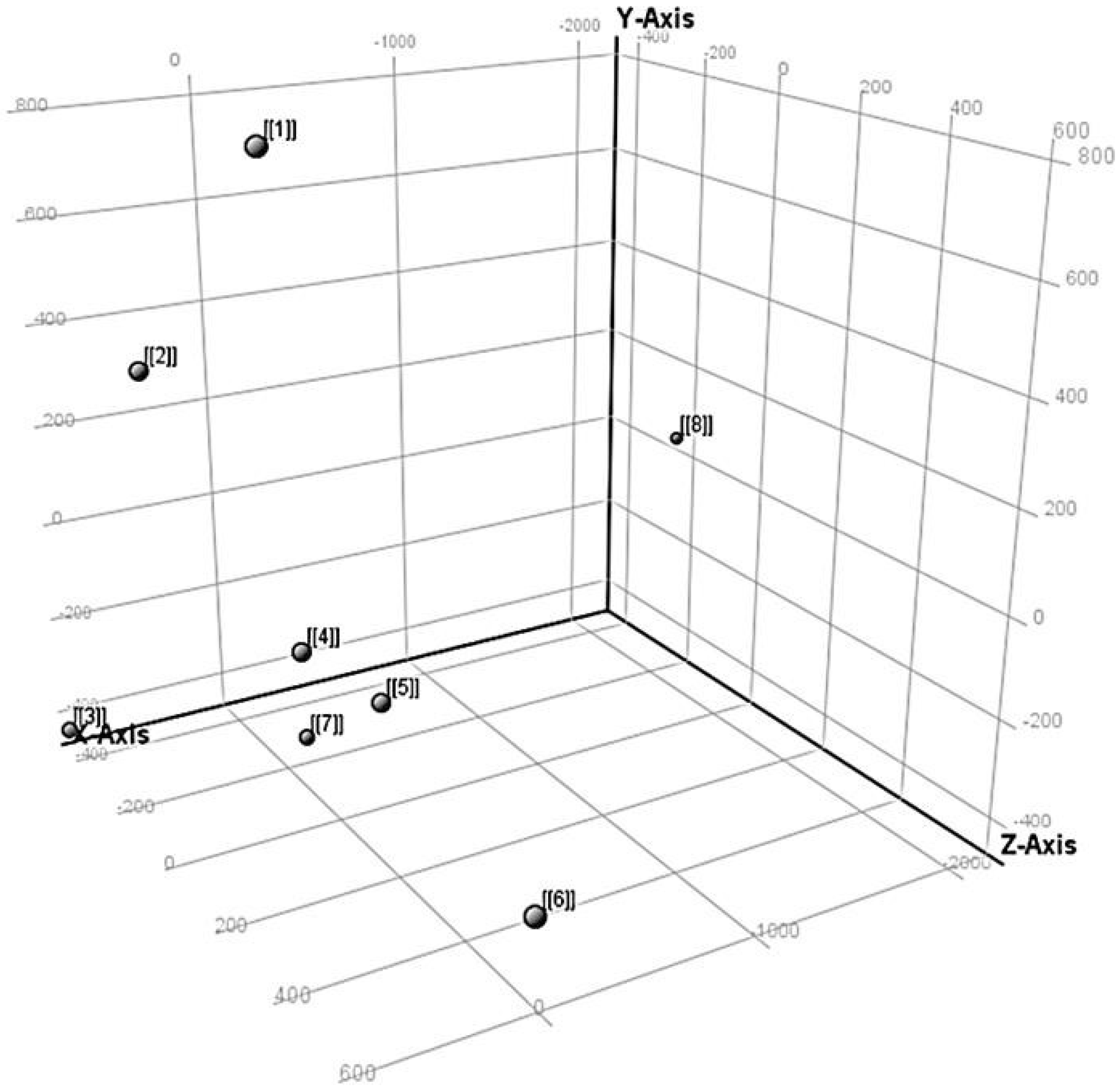
| Time Point | Injection Time (h:min) a |
|---|---|
| 1 | 5:15 |
| 2 | 6:30 |
| 3 | 7:45 |
| 4 | 9:00 |
| 5 | 10:15 |
| 6 | 11:30 |
| 7 | 12:45 |
| 8 | 27:15 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Whitney, K.; Gracia-Gonzalez, G.; Simsek, S. Stability of Wheat Floret Metabolites during Untargeted Metabolomics Studies. Metabolites 2022, 12, 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12010062
Whitney K, Gracia-Gonzalez G, Simsek S. Stability of Wheat Floret Metabolites during Untargeted Metabolomics Studies. Metabolites. 2022; 12(1):62. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12010062
Chicago/Turabian StyleWhitney, Kristin, Gerardo Gracia-Gonzalez, and Senay Simsek. 2022. "Stability of Wheat Floret Metabolites during Untargeted Metabolomics Studies" Metabolites 12, no. 1: 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12010062
APA StyleWhitney, K., Gracia-Gonzalez, G., & Simsek, S. (2022). Stability of Wheat Floret Metabolites during Untargeted Metabolomics Studies. Metabolites, 12(1), 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12010062