Comparison of Osteosarcoma Aggregated Tumour Models with Human Tissue by Multimodal Mass Spectrometry Imaging
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
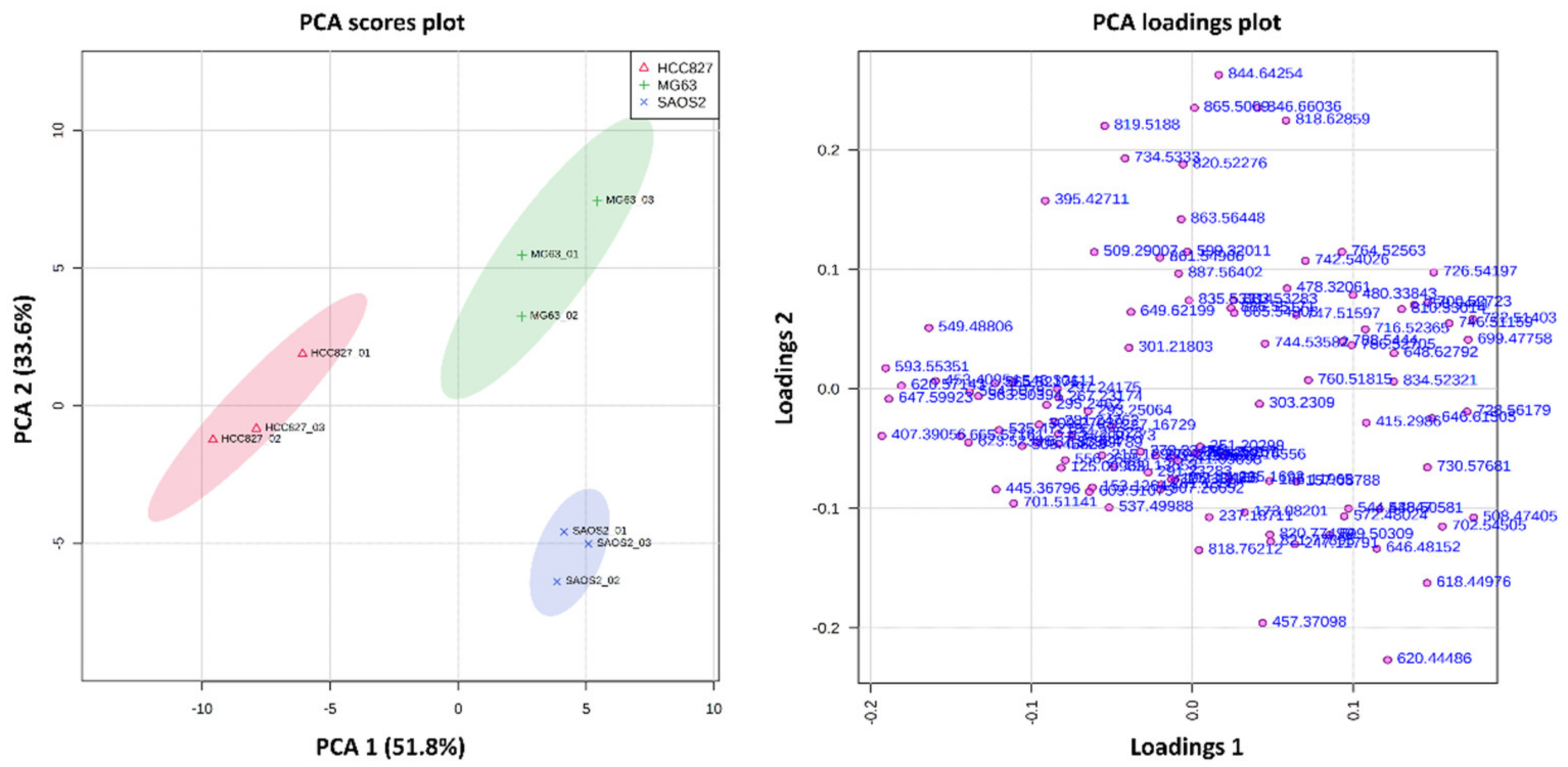
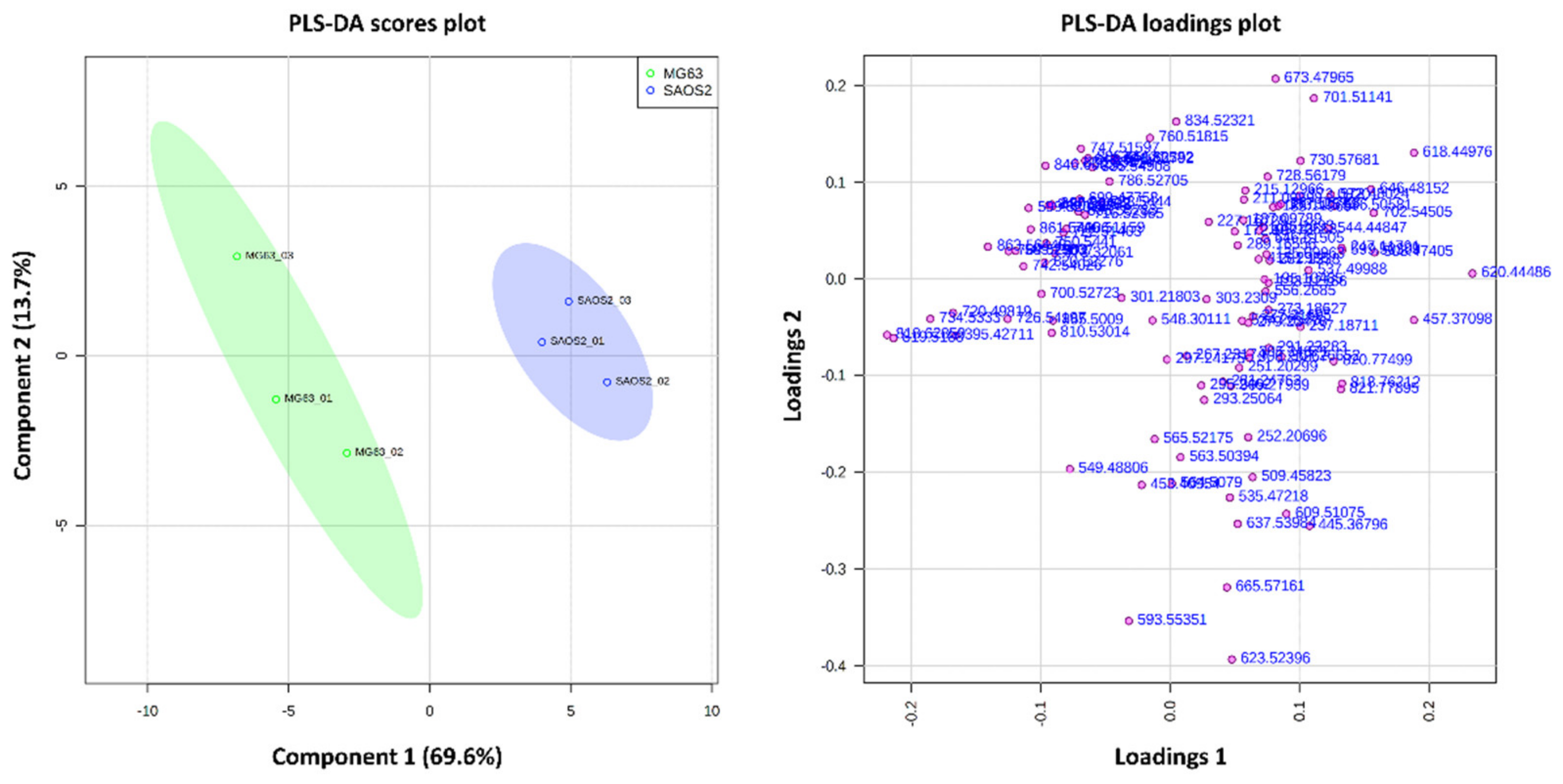
2.1. Metabolite Imaging
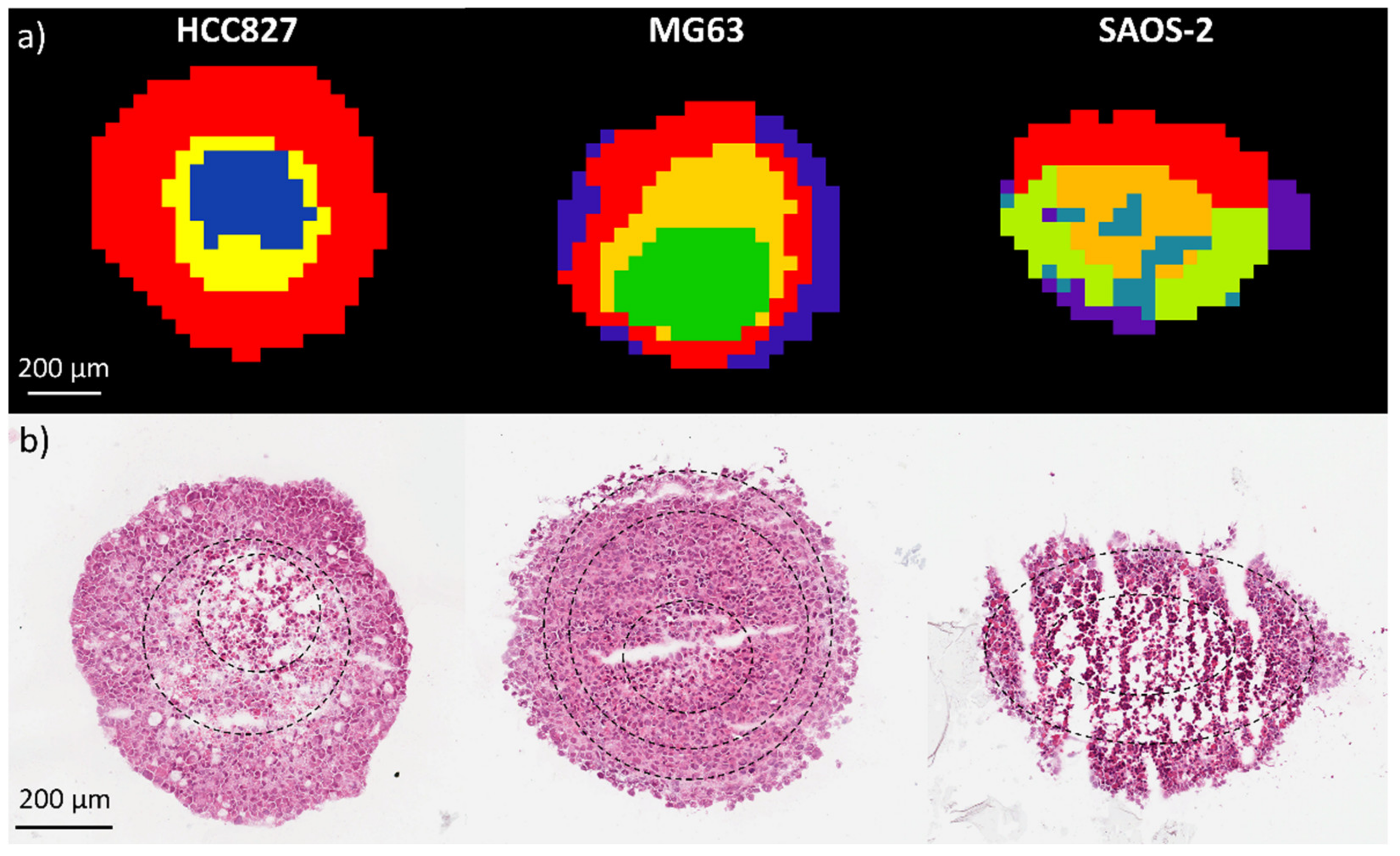
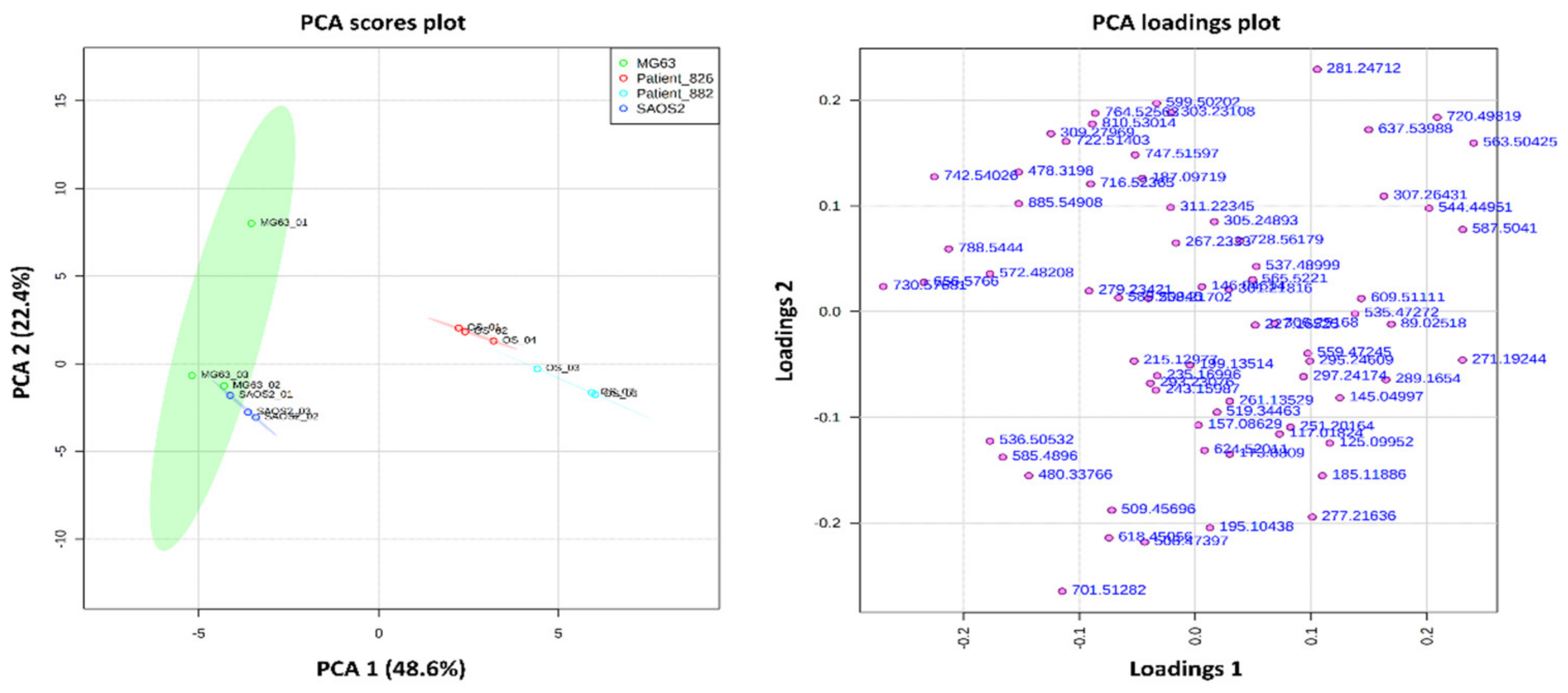
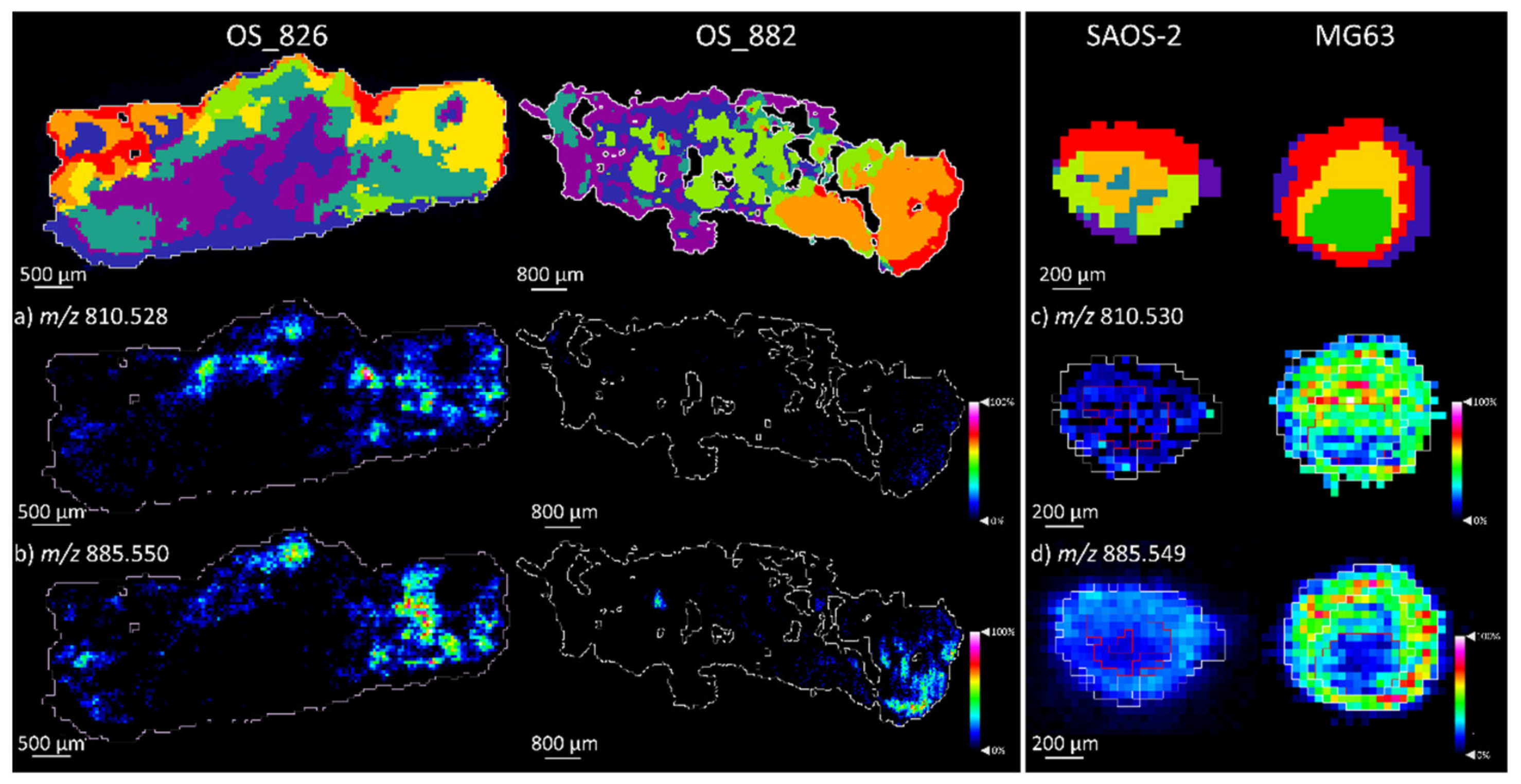
2.1.1. Aggregoid Phenotyping
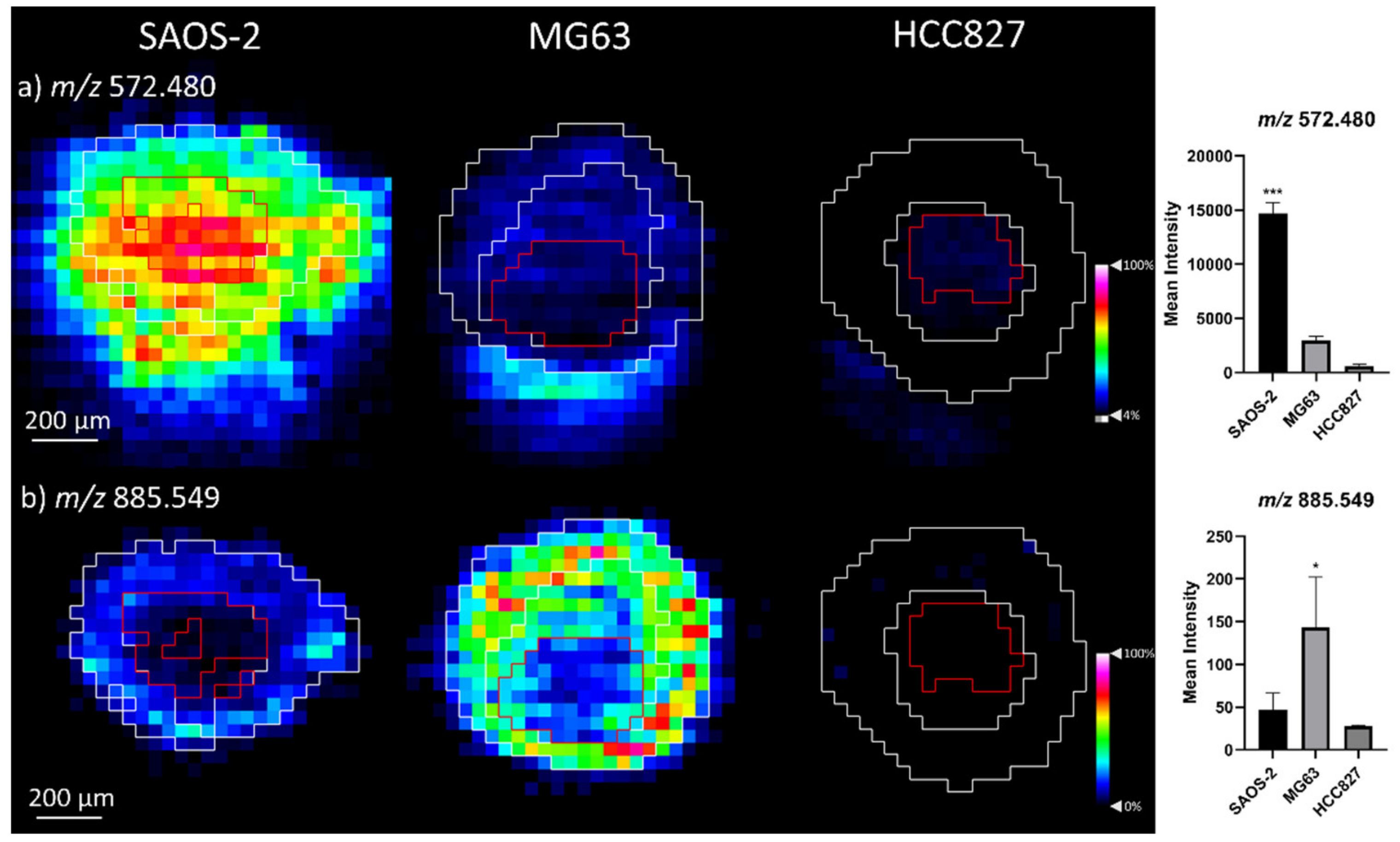
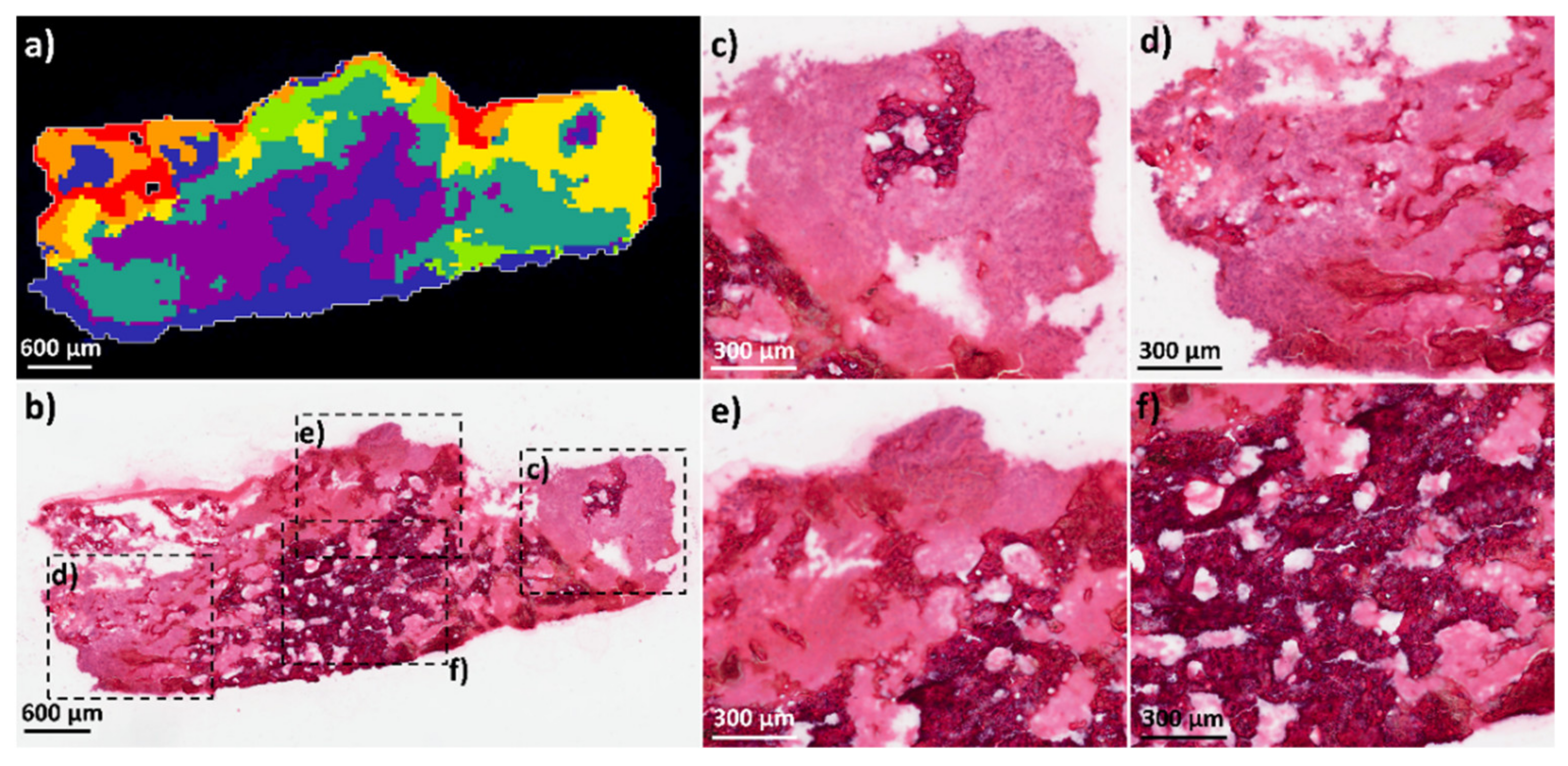
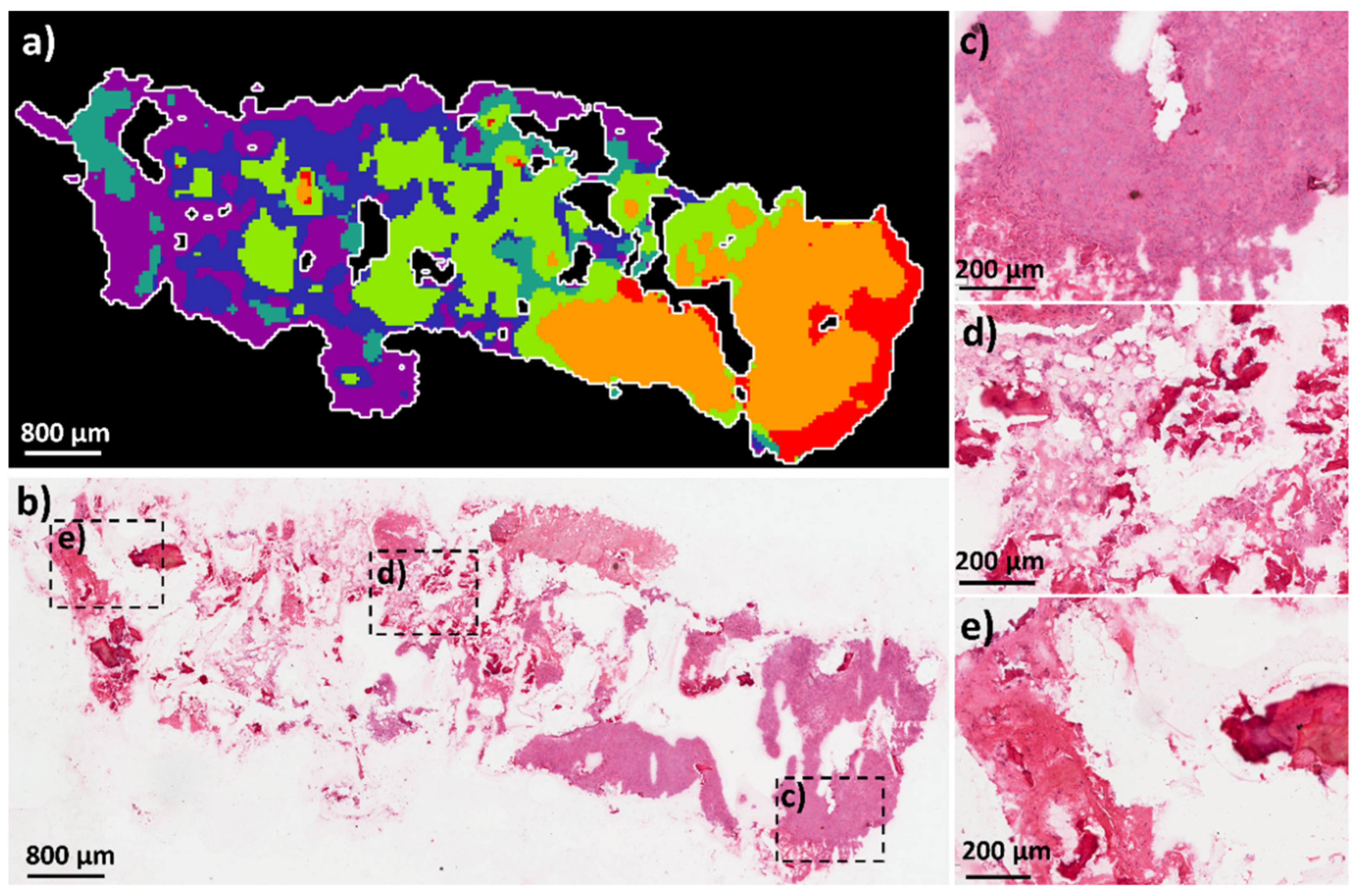
2.1.2. Comparison of OS Aggregoid Models with OS Human Tissue
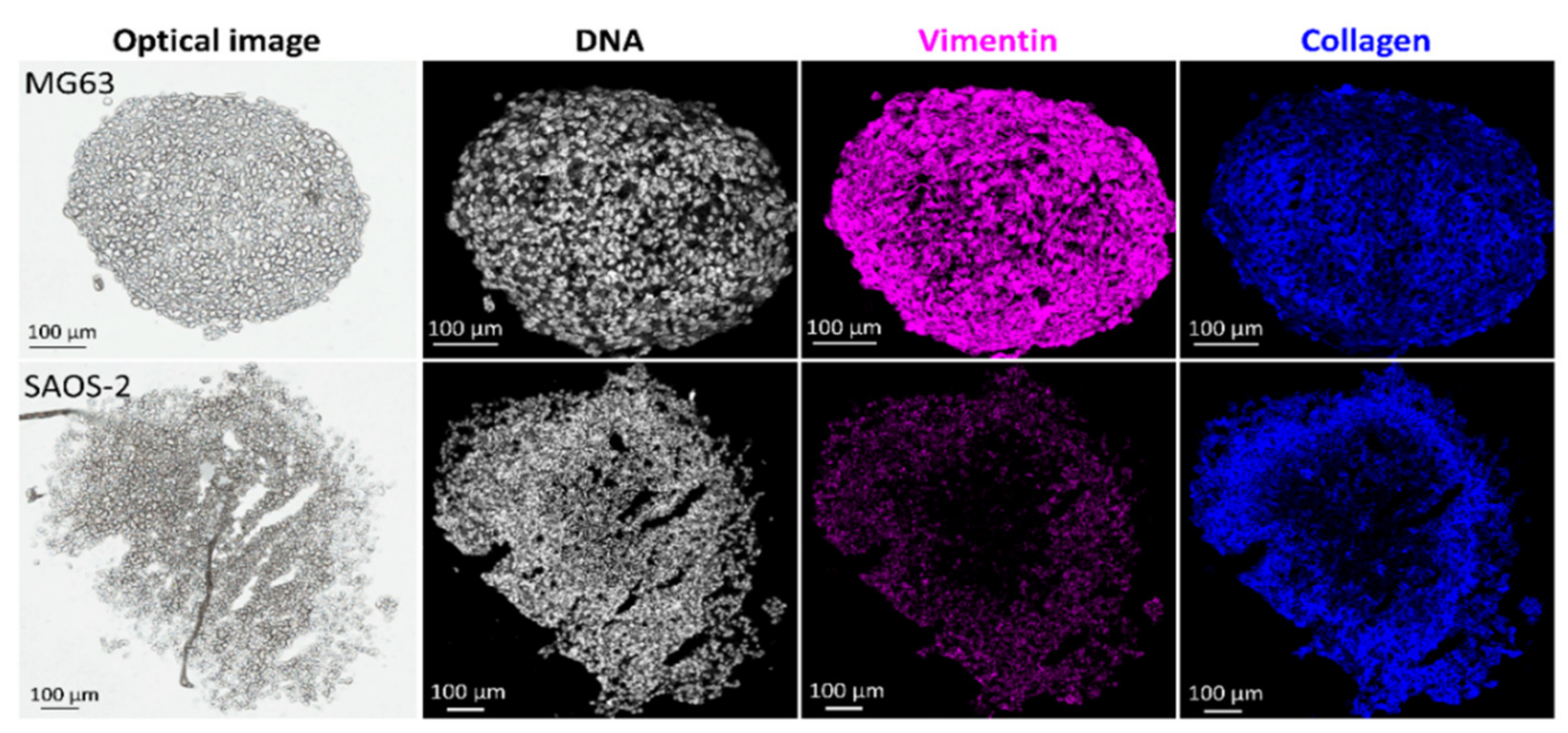
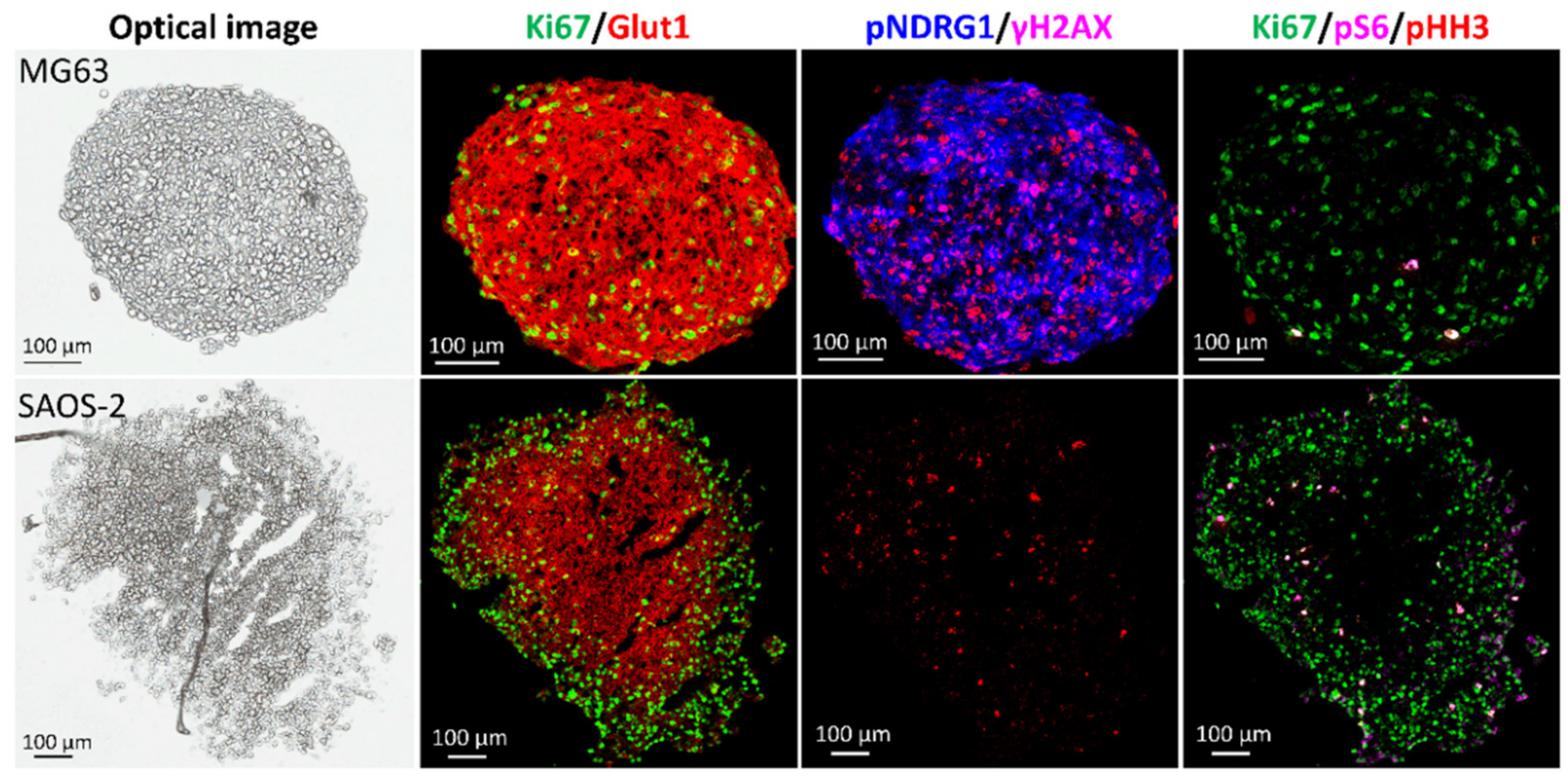
2.2. Protein Localisations
2.3. Elemental Compositions
3. Discussion
3.1. OS Metabolite Phenotyping
3.2. Protein Localisations Differ between OS Aggregoid Models
3.3. Elemental Compositions Complement Protein Expression
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.1.1. 3D Cell Culture Growth
4.1.2. Aggregoid Preparation
4.1.3. Tissue Sample Collection and Handling
4.1.4. Small Molecule Analysis
4.1.5. IMC Analysis
4.1.6. Elemental Analysis
4.1.7. Histology Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferguson, J.L.; Turner, S.P. Bone Cancer: Diagnosis and Treatment Principles. Am. Fam. Physician 2018, 98, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stiller, C.A.; Botta, L.; Brewster, D.H.; Ho, V.K.Y.; Frezza, A.M.; Whelan, J.; Casali, P.G.; Trama, A.; Gatta, G. Survival of adults with cancers of bone or soft tissue in Europe—Report from the EUROCARE-5 study. Cancer Epidemiol. 2018, 56, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Mendoza, A.; Zhu, J.; Briggs, J.W.; Halsey, C.; Hong, E.S.; Burkett, S.S.; Morrow, J.; Lizardo, M.M.; Osborne, T.; et al. Characterization of the metastatic phenotype of a panel of established osteosarcoma cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 29469–29481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murray, E.; Provvedini, D.; Curran, D.; Catherwood, B.; Sussman, H.; Manolagas, S. Characterization of a human osteoblastic osteosarcoma cell line (SAOS-2) with high bone alkaline phosphatase activity. J. Bone Miner. Res. 1987, 2, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheven, B.A.A.; Marshall, D.; Aspden, R.M. In vitro behaviour of human osteoblasts on dentin and bone. Cell. Biol. Int. 2002, 26, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paukte, C.; Schieker, M.; Tischer, T.; Kolk, A.; Neth, P.; Mutschler, W.; Milz, S. Characterization of Osteosarcoma Cell Lines MG-63, Saos-2 and U-2 OS in Comparison to Human Osteoblasts. Anticancer Res. 2004, 24, 3743–3748. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, L.; Hong, E.S.; Mendoza, A.; Issaq, S.; Tran Hoang, C.; Lizardo, M.; LeBlanc, A.; Khanna, C. Metabolomics uncovers a link between inositol metabolism and osteosarcoma metastasis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 38541–38553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wright Muelas, M.; Roberts, I.; Mughal, F.; O’Hagan, S.; Day, P.J.; Kell, D.B. An untargeted metabolomics strategy to measure differences in metabolite uptake and excretion by mammalian cell lines. Metabolomics 2020, 16, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santini, M.T.; Rainaldi, G.; Romano, R.; Ferrante, A.; Clemente, S.; Motta, A.; Indovina, P.L. MG-63 human osteosarcoma cells grown in monolayer and as three-dimensional tumor spheroids present a different metabolic profile: A 1H NMR study. FEBS Lett. 2004, 557, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gebhard, C.; Gabriel, C.; Walter, I. Morphological and Immunohistochemical Characterizationof Canine Osteosarcoma Spheroid Cell Cultures. Anat. Histol. Embryol. 2015, 45, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Park, P.; Lin, C. Characterization of stem cell attributes in human osteosarcoma cell lines. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2009, 8, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bassi, G.; Panseri, S.; Dozio, S.M.; Sandri, M.; Campodoni, E.; Dapporto, M.; Sprio, S.; Tampieri, A.; Montesi, M. Scaffold-based 3D cellular models mimicking the heterogeneity of osteosarcoma stem cell niche. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 22294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palubeckaite, I. Analysis of Three Dimensional Cell Cultures Using Mass Spectrometry Imaging. Ph.D. Thesis, Sheffield Hallam University, Sheffield, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Flint, L.E.; Hamm, G.; Ready, J.D.; Ling, S.; Duckett, C.J.; Cross, N.A.; Cole, L.M.; Smith, D.P.; Goodwin, R.J.A.; Clench, M.R. Characterization of an Aggregated Three-Dimensional Cell Culture Model by Multimodal Mass Spectrometry Imaging. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 12538–12547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, Q.; Sun, C.; Chu, X.; Li, L.; Gan, W.; Zhao, Z.; Song, Y.; He, J.; Zhang, R.; Abliz, Z. Spatially resolved metabolomics combined with multicellular tumor spheroids to discover cancer tissue relevant metabolic signatures. Anal. Chim Acta 2021, 1155, 338342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rimann, M.; Laternser, S.; Gvozdenovic, A.; Muff, R.; Fuchs, B.; Kelm, J.M.; Graf-Hausner, U. An in vitro osteosarcoma 3D microtissue model for drug development. J. Biotechnol. 2014, 189, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galadari, S.; Rahman, A.; Pallichankandy, S.; Thayyullathil, F. Tumor suppressive functions of ceramide: Evidence and mechanisms. Apoptosis 2015, 20, 689–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haimovitz-Friedman, A.; Kolesnick, R.N.; Fuks, Z. Ceramide signaling in apoptosis. Br. Med. Bull. 1997, 53, 539–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhang, N. Ceramide: Therapeutic Potential in Combination Therapy for Cancer Treatment. Curr. Drug Metab. 2016, 17, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, P.A.; Tumber, A. Ceramide-induced cell death/survival in murine osteoblasts. J. Endocrinol. 2010, 206, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beloribi-Djefaflia, S.; Vasseur, S.; Guillaumond, F. Lipid metabolic reprogramming in cancer cells. Oncogenesis 2016, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Cheng, C.; Tan, Z.; Li, N.; Tang, M.; Yang, L.; Cao, Y. Emerging roles of lipid metabolism in cancer metastasis. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.; Lee, K.; Kim, S.; Kwon, Y.; Chun, Y.; Choi, H. Comparative metabolic and lipidomic profiling of human breast cancer cells with different metastatic potentials. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 67111–67128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ding, X.Z.; Tong, W.G.; Adrian, T.E. Blockade of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in human pancreatic cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 2000, 20, 2625. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Borin, T.F.; Angara, K.; Rashid, M.H.; Achyut, B.R.; Arbab, A.S. Arachidonic Acid Metabolite as a Novel Therapeutic Target in Breast Cancer Metastasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nie, D.; Nemeth, J.; Qiao, Y.; Zacharek, A.; Li, L.; Hanna, K.; Tang, K.; Hillman, G.; Cher, M.; Grignon, D.; et al. Increased metastatic potential in human prostate carcinoma cells by overexpression of arachidonate 12-lipoxygenase. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2003, 20, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toné, S.; Sugimoto, K.; Tanda, K.; Suda, T.; Uehira, K.; Kanouchi, H.; Samejima, K.; Minatogawa, Y.; Earnshaw, W.C. Three distinct stages of apoptotic nuclear condensation revealed by time-lapse imaging, biochemical and electron microscopy analysis of cell-free apoptosis. Exp. Cell Res. 2007, 313, 3635–3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Qu, P.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, T.; Cao, N. COX-2 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and migration in osteosarcoma MG-63 cells via PI3K/AKT/NF-κB signaling. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 20, 3811–3819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, S.; Hennet, T. Collagen accumulation in osteosarcoma cells lacking GLT25D1 collagen galactosyltransferase. J. Biol. Chem. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Collin, P.; Nefussi, J.R.; Wetterwald, A.; Nicolas, V.; Boy-Lefevre, M.L.; Fleisch, H.; Forest, N. Expression of collagen, osteocalcin, and bone alkaline phosphatase in a mineralizing rat osteoblastic cell culture. Calcif. Tissue Int. 1992, 50, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jukkola, A.; Risteli, L.; Melkko, J.; Risteli, J. Procollagen synthesis and extracellular matrix deposition in MG-63 osteosarcoma cells. J. Bone Miner. Res. 1993, 8, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Airley, R.; Loncaster, J.; Davidson, S.; Bromley, M.; Roberts, S.; Patterson, A.; Hunter, R.; Stratford, I.; West, C. Glucose Transporter Glut-1 Expression Correlates with Tumor Hypoxia and Predicts Metastasis-free Survival in Advanced Carcinoma of the Cervix. Clin. Cancer Res. 2001, 7, 928–934. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Zeng, B.; Dong, Y.; Shi, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Huang, J. Overexpression of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α in Human Osteosarcoma: Correlation with Clinicopathological Parameters and Survival Outcome. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 37, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cifuentes, M.; García, M.A.; Arrabal, P.M.; Martínez, F.; Yañez, M.J.; Jara, N.; Weil, B.; Domínguez, D.; Medina, R.A.; Nualart, F. Insulin regulates GLUT1-mediated glucose transport in MG-63 human osteosarcoma cells. J. Cell. Physiol 2011, 226, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jian, F.; Yuan, F.; Jiong, M.; Zhu, X.; Yu, G.; Lu, D. Silencing of Glucose Transporter Protein-1 by RNA Interference Inhibits Human Osteosarcoma Mg63 Cells Growth in vivo. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2015, 14, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taketomi, Y.; Sugiki, T.; Saito, T.; Ishii, S.; Hisada, M.; Suzuki-Nishimura, T.; Uchida, M.K.; Moon, T.; Chang, H.; Natori, Y.; et al. Identification of NDRG1 as an early inducible gene during in vitro maturation of cultured mast cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 306, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, D.; Bae, D.; Sahni, S.; Jansson, P.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Yue, F.; Zheng, M.; Kovacevic, Z.; et al. Metastasis suppressor, NDRG1, mediates its activity through signaling pathways and molecular motors. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 1943–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Li, L.; Gao, G.; Wang, G.; Qu, L.; Li, J.; Wang, C. HIF-1α up-regulates NDRG1 expression through binding to NDRG1 promoter, leading to proliferation of lung cancer A549 cells. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2013, 40, 3723–3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cangul, H. Hypoxia upregulates the expression of the NDRG1 gene leading to its overexpression in various human cancers. BMC Genet. 2004, 5, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsugaki, T.; Zenmyo, M.; Hiraoka, K.; Fukushima, N.; Shoda, T.; Komiya, S.; Ono, M.; Kuwano, M.; Nagata, K. N-myc downstream-regulated gene 1/Cap43 expression promotes cell differentiation of human osteosarcoma cells. Oncol. Rep. 2010, 24, 721–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schneider, A.; Younis, R.H.; Gutkind, J.S. Hypoxia-Induced Energy Stress Inhibits the mTOR Pathway by Activating an AMPK/REDD1 Signaling Axis in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Neoplasia 2008, 10, 1295–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.; Jeong, H.S.; Chung, T.; Kim, M.; Lee, J.H.; Jung, W.H.; Koo, J.S. The value of phosphohistone H3 as a proliferation marker for evaluating invasive breast cancers: A comparative study with Ki67. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 65064–65076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wolf, F.I.; Trapani, V. Cell (patho)physiology of magnesium. Clin. Sci. 2008, 114, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Onder, S.; Calikoglu-Koyuncu, A.C.; Kazmanli, K.; Urgen, M.; Kok, F.N.; Torun-Kose, G. Magnesium doping on TiN coatings affects mesenchymal stem cell differentiation and proliferation positively in a dose-dependent manner. BioMed. Mater. Eng. 2018, 29, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, T.; Weng, J.; Yu, F.; Zhang, W.; Li, G.; Qin, H.; Tan, Z.; Zeng, H. Insights into the Role of Magnesium Ions in Affecting Osteogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2021, 199, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nardinocchi, L.; Pantisano, V.; Puca, R.; Porru, M.; Aiello, A.; Grasselli, A.; Leonetti, C.; Safran, M.; Rechavi, G.; Givol, D.; et al. Zinc Downregulates HIF-1α and Inhibits Its Activity in Tumor Cells In Vitro and In Vivo. PLoS ONE 2010, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monico, A.; Guzman-Caldentey, J.; Pajares, M.A.; Martin-Santamaria, S.; Perez-Sala, D. Elucidating vimentin interaction with zinc ions and its interplay with oxidative modifications through crosslinking assays and molecular dynamics simulations. bioRxiv. [CrossRef]
- Zimnicka, A.M.; Tang, H.; Guo, Q.; Kuhr, F.K.; Oh, M.; Wan, J.; Chen, J.; Smith, K.A.; Fraidenburg, D.R.; Choudhury, M.S.R.; et al. Upregulated Copper Transporters in Hypoxia-Induced Pulmonary Hypertension. PLoS ONE 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dannhorn, A.; Kazanc, E.; Ling, S.; Nikula, C.; Karali, E.; Serra, M.P.; Vorng, J.; Inglese, P.; Maglennon, G.; Hamm, G.; et al. Universal Sample Preparation Unlocking Multimodal Molecular Tissue Imaging. Anal. Chem. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swales, J.G.; Dexter, A.; Hamm, G.; Nilsson, A.; Strittmatter, N.; Michopoulos, F.; Hardy, C.; Morentin-Gutierrez, P.; Mellor, M.; Andren, P.E.; et al. Quantitation of Endogenous Metabolites in Mouse Tumors Using Mass-Spectrometry Imaging. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 6051–6058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, J.; Psychogios, N.; Young, N.; Wishart, D.S. MetaboAnalyst: A web server for metabolomic data analysis and interpretation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, W652–W660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

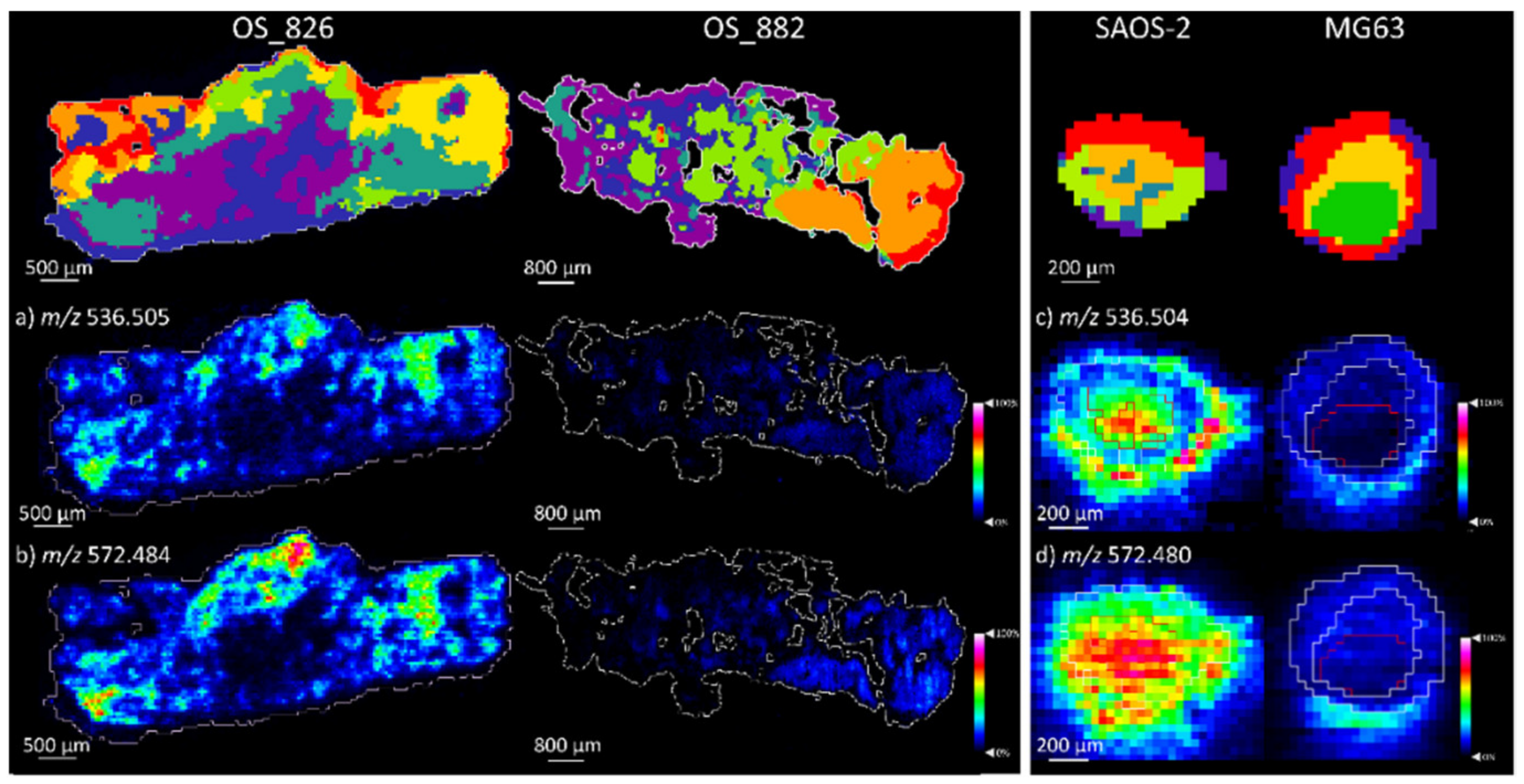

| Metabolite | m/z (Measured) | Accuracy (ppm Error) | Aggregoid |
|---|---|---|---|
| FA 8:1; O2 | 173.082 | 0.0 | OS: SAOS-2 * |
| FA 9:1; O2 | 187.098 | 0.0 | All |
| FA 11:1; O | 199.136 | 0.0 | All |
| FA 17:1 | 267.232 | 0.0 | All: HCC827 * |
| FA 18:5 | 273.186 | 1.0 | All |
| FA 18:3 | 277.217 | −0.4 | OS |
| FA 18:2 | 279.235 | 6.3 | All: OS |
| FA 18:1 | 281.248 | −0.4 | All: HCC827 * |
| FA 18:2; O | 295.229 | 3.4 | All: HCC827 * |
| FA 20:5 | 301.218 | 0.0 | All: MG63 * |
| FA 20:4 | 303.231 | −0.2 | All: MG63 * |
| FOH 27:0 | 395.427 | 3.3 | MG63 * |
| FA 20:4 | 457.371 | 5.0 | SAOS-2 ** |
| Cer 32:1; O2 | 508.474 | 1.1 | SAOS-2 *** |
| FAHFA 34:2; O | 535.472 | −0.9 | All: HCC827 * |
| Cer 34:1; O2 | 536.506 | 1.9 | SAOS-2 *** |
| Cer 32:1; O2 [M + Cl]− | 544.449 | −3.2 | OS: SAOS-2 *** |
| FAHFA 36:2; O | 563.504 | −1.0 | All: HCC827 *** |
| Cer 34:1; O2 [M + Cl]− | 572.480 | −2.2 | OS: SAOS-2 *** |
| PI 18:0 | 599.320 | −0.2 | MG63 * |
| PE O-28:1 | 618.450 | −1.0 | SAOS-2 ** |
| PE O-30:1 | 646.482 | −0.3 | SAOS-2 *** |
| PE O-34:2 | 700.527 | −2.1 | OS: MG63 *** |
| PE 34:1 | 716.524 | 0.1 | OS: MG63 * |
| PE O-36:6 | 720.498 | 1.1 | MG63 ** |
| PE O-36:2 | 728.562 | 2.5 | OS *** |
| PC O-33:1 | 730.577 | 1.7 | OS: SAOS-2 * |
| PS O-33:0 | 734.533 | −1.2 | MG63 |
| PC 33:2 | 742.540 | 1.4 | MG63 ** |
| PG 34:1 | 747.516 | −3.0 | OS: MG63 * |
| PE O-38:5 | 750.544 | −0.3 | MG63 * |
| PS 34:1 | 760.518 | 7.0 | OS * |
| PE O-38:6; O | 764.526 | 2.7 | MG63 ** |
| PS 36:1 | 788.544 | −0.4 | OS: MG63 ** |
| PS 38:4 | 810.530 | 1.3 | MG63 ** |
| PG 40:7 | 819.519 | 0.7 | MG63 ** |
| PS 40:6 | 834.523 | −6.3 | OS * |
| PI 38:4 | 885.549 | −0.9 | OS: MG63 * |
| Metabolite | Osteosarcoma Tissue | Aggrecoid | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m/z (Measured) | Accuracy (ppm Error) | Patient Sample | m/z (Measured) | Accuracy (ppm Error) | Aggregoid Model | |
| FA 18:2 | 279.234 | 2.4 | Both | 279.235 | 6.3 | Both |
| FA 18:1 | 281.247 | −0.4 | Both | 281.248 | – 0.4 | Both |
| FA 18:2;O | 295.229 | 2.9 | OS_882 * | 295.229 | 3.4 | MG63 * |
| FA 18:1;O | 297.242 | −6.0 | Both | 297.242 | – 5.9 | MG63 * |
| FA 20:4 | 303.231 | 0.2 | OS_826 *** | 303.231 | – 0.2 | Both |
| FA 18:2;O2 | 311.224 | 3.5 | OS_882 * | 311.223 | 0.7 | Both |
| Cer 32:1;O2 | 508.474 | 0.7 | OS_826 ** | 508.474 | 1.1 | SAOS-2 *** |
| FAHFA 34:2;O | 535.473 | 1.1 | Both | 535.472 | –0.9 | Both |
| Cer 34:1;O2 | 536.505 | 0.0 | OS_826 *** | 536.506 | 1.9 | SAOS-2 *** |
| Cer 32:1;O2 [M+Cl]- | 544.451 | 0.6 | OS_826 ** | 544.448 | –3.2 | SAOS-2 *** |
| FAHFA 36:2;O | 563.505 | 0.1 | Both | 563.504 | –1.0 | Both |
| FAHFA 36:1;O | 565.522 | 4.2 | Both | 565.522 | 2.9 | Both |
| Cer 34:1;O2 [M+CI]- | 572.484 | 4.2 | OS_826 *** | 572.480 | –2.2 | SAOS-2 *** |
| PE O-28:1 | 618.451 | 1.6 | OS_826 ** | 618.450 | –1.0 | SAOS-2 ** |
| PE O-30:1 | 646.613 | −2.1 | OS_826 *** | 646.615 | 1.0 | Both |
| Cer 40:1;O2 [M+CI]- | 656.578 | 3.5 | OS_826 ** | 656.576 | 0.2 | Both |
| PA 36:3 | 701.514 | 3.0 | Both | 701.511 | –1.0 | Both |
| PE 34:1 | 716.524 | 0.3 | OS_826 * | 716.524 | 0.1 | MG63 * |
| PE O-36:2 | 728.560 | −0.4 | OS_826 * | 728.562 | 2.5 | Both |
| PC O-33:1 | 730.575 | −0.8 | Both | 730.577 | 1.7 | SAOS-2 * |
| PC 33:2 | 742.539 | 0.1 | OS_826 * | 742.540 | 1.4 | MG63 * |
| PG 34:1 | 747.517 | −1.1 | OS_826 ** | 747.516 | –3.0 | MG63 * |
| PE O-38:5 | 750.542 | −2.6 | OS_826 * | 750.544 | –0.3 | MG63 * |
| PE O-38:6;O | 764.524 | 0.4 | OS_826 * | 764.526 | 2.7 | MG63 ** |
| PS 36:1 | 788.544 | −1.3 | OS_826 ** | 788.544 | –0.4 | MG63 ** |
| PS 38:4 | 810.528 | −1.5 | OS_826 ** | 810.530 | 1.3 | MG63 * |
| PS 40:4 | 838.559 | −1.3 | OS_826 ** | 838.562 | 2.2 | Both |
| PI 38:4 | 885.550 | 0.5 | OS_826 ** | 885.549 | –0.9 | MG63 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Flint, L.E.; Hamm, G.; Ready, J.D.; Ling, S.; Duckett, C.J.; Cross, N.A.; Cole, L.M.; Smith, D.P.; Goodwin, R.J.A.; Clench, M.R. Comparison of Osteosarcoma Aggregated Tumour Models with Human Tissue by Multimodal Mass Spectrometry Imaging. Metabolites 2021, 11, 506. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11080506
Flint LE, Hamm G, Ready JD, Ling S, Duckett CJ, Cross NA, Cole LM, Smith DP, Goodwin RJA, Clench MR. Comparison of Osteosarcoma Aggregated Tumour Models with Human Tissue by Multimodal Mass Spectrometry Imaging. Metabolites. 2021; 11(8):506. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11080506
Chicago/Turabian StyleFlint, Lucy E., Gregory Hamm, Joseph D. Ready, Stephanie Ling, Catherine J. Duckett, Neil A. Cross, Laura M. Cole, David P. Smith, Richard J. A. Goodwin, and Malcolm R. Clench. 2021. "Comparison of Osteosarcoma Aggregated Tumour Models with Human Tissue by Multimodal Mass Spectrometry Imaging" Metabolites 11, no. 8: 506. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11080506
APA StyleFlint, L. E., Hamm, G., Ready, J. D., Ling, S., Duckett, C. J., Cross, N. A., Cole, L. M., Smith, D. P., Goodwin, R. J. A., & Clench, M. R. (2021). Comparison of Osteosarcoma Aggregated Tumour Models with Human Tissue by Multimodal Mass Spectrometry Imaging. Metabolites, 11(8), 506. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11080506







