Modulation of the Primary Astrocyte-Enriched Cultures’ Oxylipin Profiles Reduces Neurotoxicity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
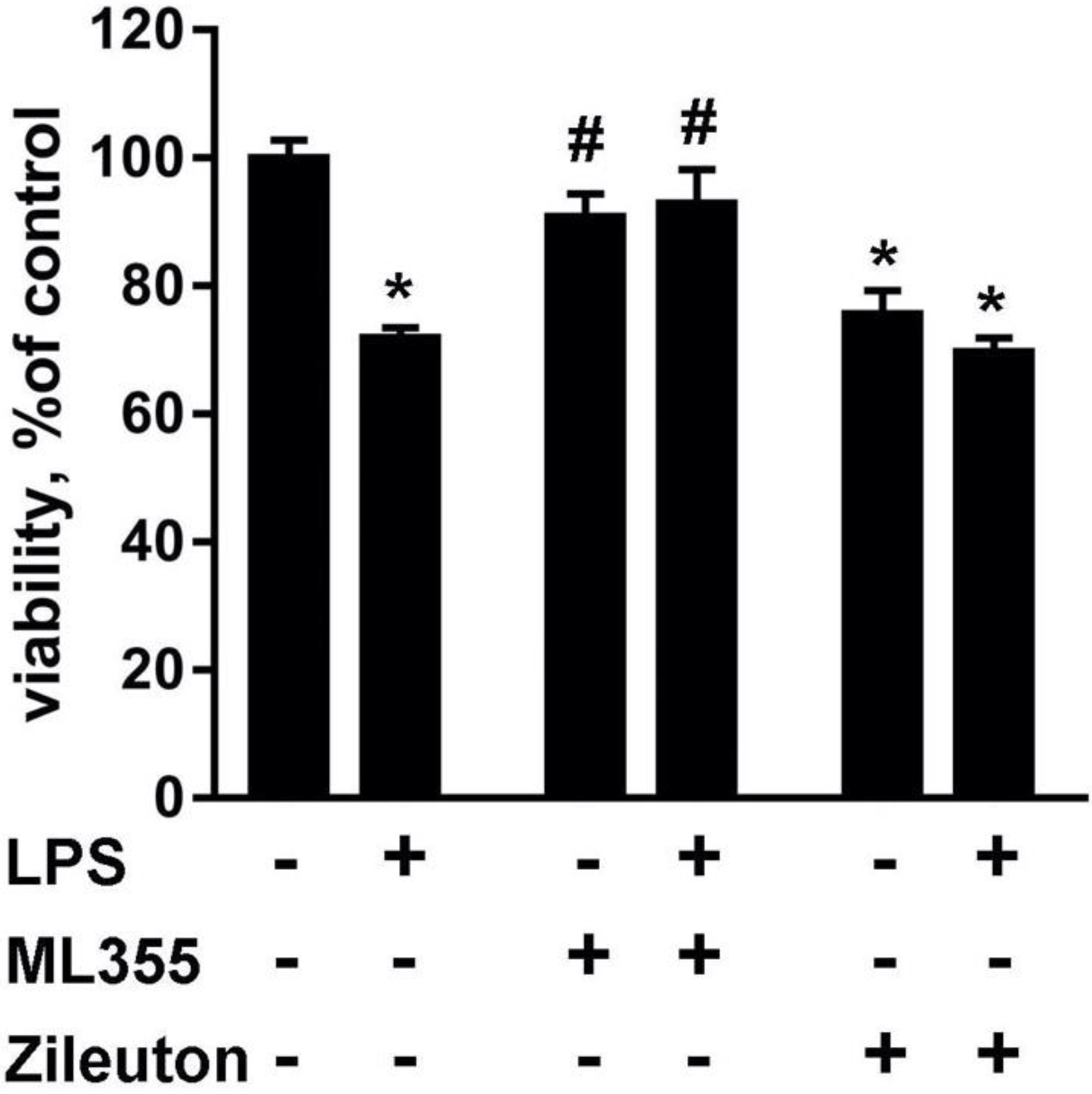
2.1. Lipid Fractions from LPS-Modulated Astrocytes Exerted Neurotoxicity That Can Be Modulated via Astrocytes’ Drug Treatments
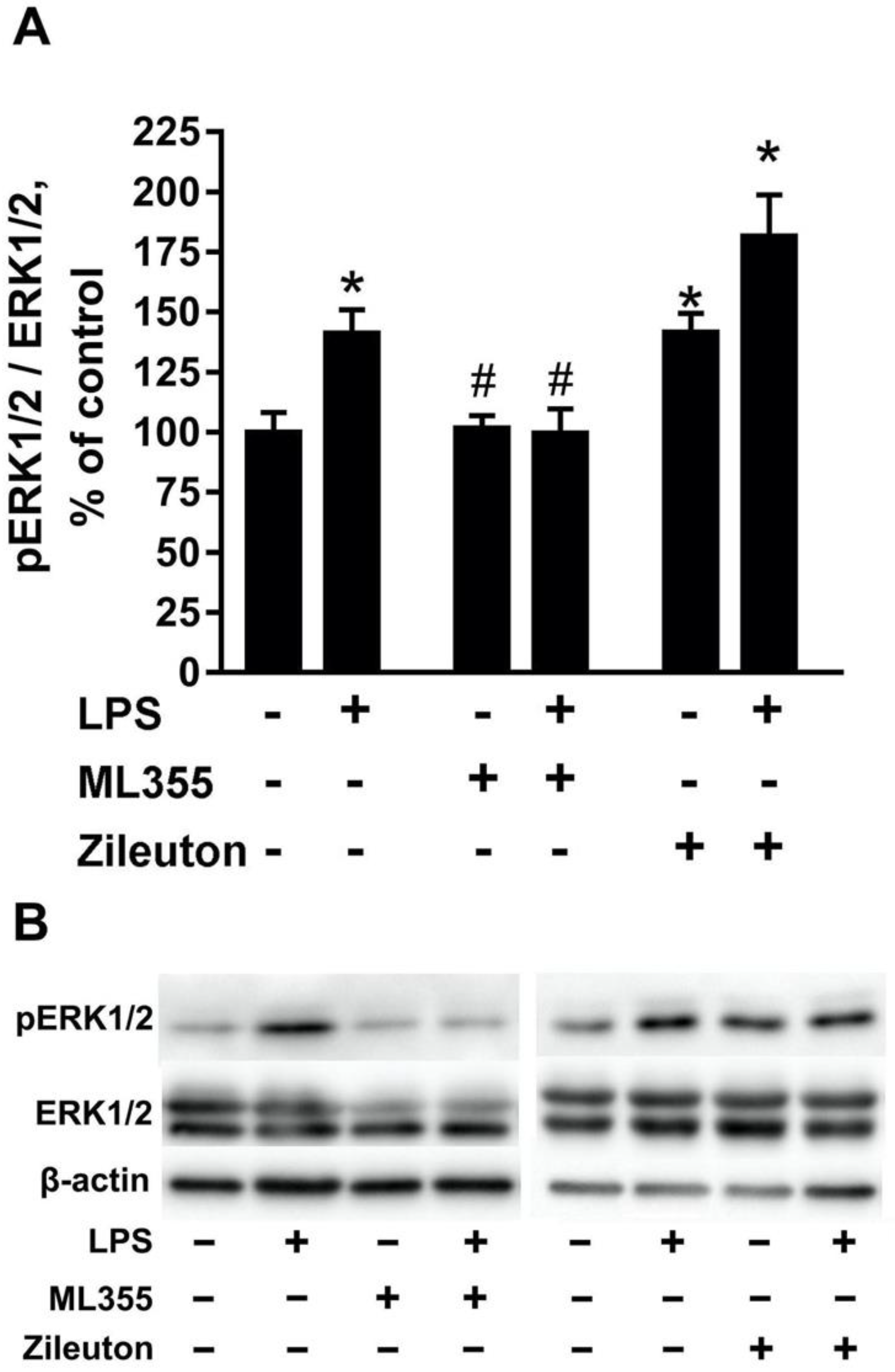
2.2. The Toxic Effect Is Accompanied by the Activation of ERK1/2 in Neurons
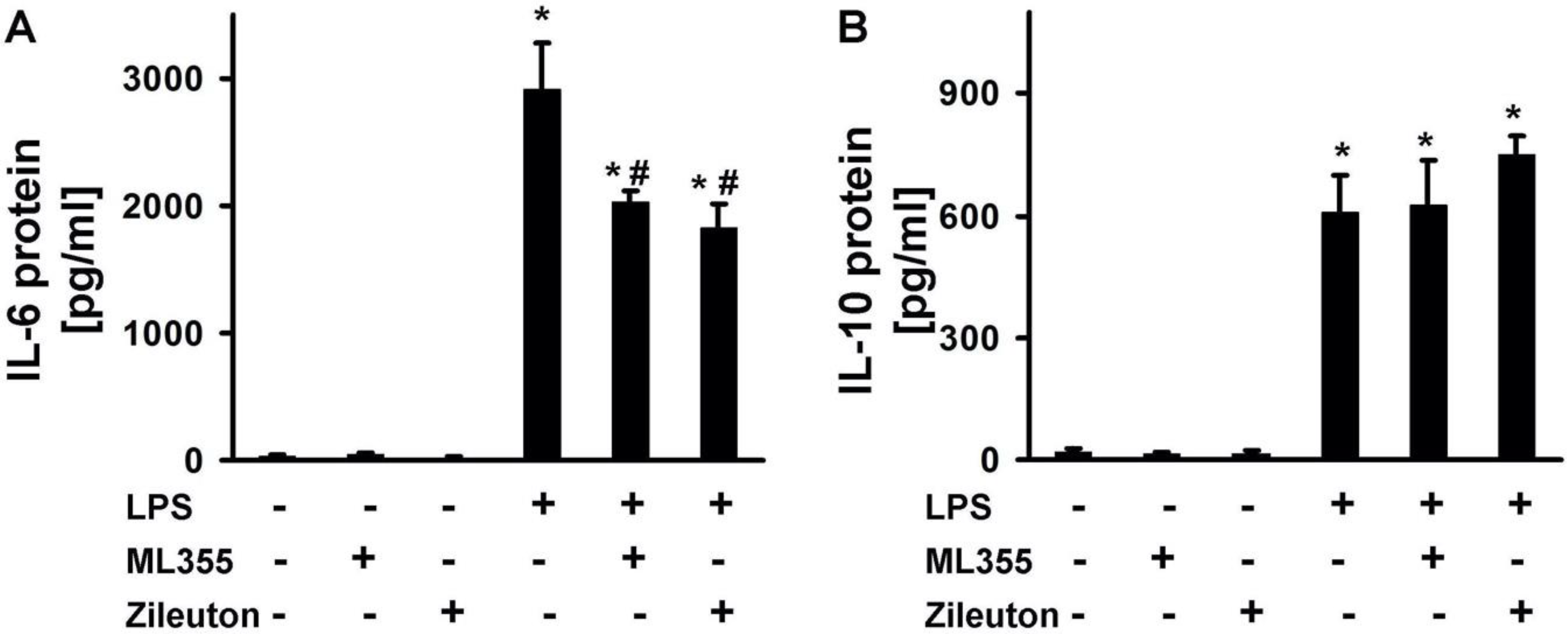
2.3. LPS-Induced Release of Cytokines Is Modulated by Zileuton and ML355
2.4. The Difference in the Neurotoxicity of Lipid Fractions Is Reflected in Their Oxylipin Profiles
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Primary Rat Astroglial-Enriched Cell Culture
4.3. Primary Cultures of Rat Neuron Cortical Cells
4.4. MTT Assay
4.5. UPLC-MS/MS Conditions and Sample Preparation
4.6. Western Blotting
4.7. Data Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Escartin, C.; Galea, E.; Lakatos, A.; O’Callaghan, J.P.; Petzold, G.C.; Serrano-Pozo, A.; Steinhäuser, C.; Volterra, A.; Carmignoto, G.; Agarwal, A.; et al. Reactive astrocyte nomenclature, definitions, and future directions. Nat. Neurosci. 2021, 24, 312–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liddelow, S.A.; Guttenplan, K.A.; Clarke, L.E.; Bennett, F.C.; Bohlen, C.J.; Schirmer, L.; Bennett, M.L.; Münch, A.E.; Chung, W.S.; Peterson, T.C.; et al. Neurotoxic reactive astrocytes are induced by activated microglia. Nature 2017, 541, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofroniew, M.V. Astrocyte barriers to neurotoxic inflammation. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2015, 16, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zamanian, J.L.; Xu, L.; Foo, L.C.; Nouri, N.; Zhou, L.; Giffard, R.G.; Barres, B.A. Genomic analysis of reactive astrogliosis. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 6391–6410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sergeeva, M.; Strokin, M.; Wang, H.; Ubl, J.J.; Reiser, G. Arachidonic acid in astrocytes blocks Ca2+ oscillations by inhibiting store-operated Ca2+ entry, and causes delayed Ca2+ influx. Cell Calcium 2003, 33, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moinfar, Z.; Dambach, H.; Faustmann, P.M. Influence of drugs on gap junctions in glioma cell lines and primary astrocytes in vitro. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matejuk, A.; Ransohoff, R.M. Crosstalk Between Astrocytes and Microglia: An Overview. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, F.; Qian, Z.M.; Zhu, L.; Wu, X.M.; Qian, C.; Chan, R.; Ke, Y. Purity, cell viability, expression of GFAP and bystin in astrocytes cultured by different procedures. J. Cell. Biochem. 2010, 109, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, L.C.; Allen, N.J.; Bushong, E.A.; Ventura, P.B.; Chung, W.-S.; Zhou, L.; Cahoy, J.D.; Daneman, R.; Zong, H.; Ellisman, M.H.; et al. Development of a method for the purification and culture of rodent astrocytes. Neuron 2011, 71, 799–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chistyakov, D.V.; Astakhova, A.A.; Azbukina, N.V.; Goriainov, S.V.; Chistyakov, V.V.; Sergeeva, M.G. High and Low Molecular Weight Hyaluronic Acid Differentially Influences Oxylipins Synthesis in Course of Neuroinflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chistyakov, D.V.; Azbukina, N.V.; Astakhova, A.A.; Polozhintsev, A.I.; Sergeeva, M.G.; Reiser, G. Toll-like receptors control p38 and JNK MAPK signaling pathways in rat astrocytes differently, when cultured in normal or high glucose concentrations. Neurochem. Int. 2019, 131, 104513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quincozes-Santos, A.; Bobermin, L.D.; de Assis, A.M.; Gonçalves, C.A.; Souza, D.O. Fluctuations in glucose levels induce glial toxicity with glutamatergic, oxidative and inflammatory implications. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2017, 1863, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, H.L.; Chi, P.L.; Lin, C.C.; Yang, C.C.; Yang, C.M. Up-regulation of ROS-Dependent Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 from High-Glucose-Challenged Astrocytes Contributes to the Neuronal Apoptosis. Mol. Neurobiol. 2014, 50, 520–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saura, J. Microglial cells in astroglial cultures: A cautionary note. J. Neuroinflamm. 2007, 4, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chistyakov, D.V.; Gavrish, G.E.; Goriainov, S.V.; Chistyakov, V.V.; Astakhova, A.A.; Azbukina, N.V.; Sergeeva, M.G. Oxylipin profiles as functional characteristics of acute inflammatory responses in astrocytes pre-treated with IL-4, IL-10, or LPS. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chistyakov, D.V.; Astakhova, A.A.; Sergeeva, M.G. Resolution of inflammation and mood disorders. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2018, 105, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabbs, M.; Leng, S.; Devassy, J.G.; Monirujjaman, M.; Aukema, H.M. Advances in Our Understanding of Oxylipins Derived from Dietary PUFAs. Adv. Nutr. 2015, 6, 513–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Serhan, C.N. Pro-resolving lipid mediators are leads for resolution physiology. Nature 2014, 510, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takadera, T.; Shiraishi, Y.; Ohyashiki, T. Prostaglandin E2 induced caspase-dependent apoptosis possibly through activation of EP2 receptors in cultured hippocampal neurons. Neurochem. Int. 2004, 45, 713–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.H.; Sung, Y.F.; Oyarzabal, E.A.; Tan, Y.M.; Leonard, J.; Guo, M.; Li, S.; Wang, Q.; Chu, C.H.; Chen, S.L.; et al. Physiological Concentration of Prostaglandin E2 Exerts Anti-inflammatory Effects by Inhibiting Microglial Production of Superoxide Through a Novel Pathway. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 8001–8013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Wu, L.; Hand, T.; Andreasson, K. Prostaglandin D2 mediates neuronal protection via the DP1 receptor. J. Neurochem. 2005, 92, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, K.J.; Jung, Y.S.; Lee, S.H.; Moon, C.H.; Baik, E.J. Arachidonic acid induces neuronal death through lipoxygenase and cytochrome P450 rather than cyclooxygenase. J. Neurosci. Res. 2005, 81, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.J.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, H.Y.; Choi, Y.H.; Park, J.S.; Suh, Y.H.; Park, S.M.; Joe, E.; Jou, I. Astrocytes, but Not Microglia, Rapidly Sense H2O2 via STAT6 Phosphorylation, Resulting in Cyclooxygenase-2 Expression and Prostaglandin Release. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 5132–5141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chistyakov, D.V.; Grabeklis, S.; Goriainov, S.V.; Chistyakov, V.V.; Sergeeva, M.G.; Reiser, G. Astrocytes synthesize primary and cyclopentenone prostaglandins that are negative regulators of their proliferation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 500, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyen, K.V. Lipoxygenase: An Emerging Target for Stroke Therapy. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2013, 12, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Czapski, G.A.; Czubowicz, K.; Strosznajder, J.B.; Strosznajder, R.P. The lipoxygenases: Their regulation and implication in alzheimer’s disease. Neurochem. Res. 2016, 41, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karatas, H.; Cakir-Aktas, C. 12/15 Lipoxygenase as a Therapeutic Target in Brain Disorders. Noro Psikiyatr. Ars. 2019, 56, 288–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Leyen, K.; Arai, K.; Jin, G.; Kenyon, V.; Gerstner, B.; Rosenberg, P.A.; Holman, T.R.; Lo, E.H. Novel lipoxygenase inhibitors as neuroprotective reagents. J. Neurosci. Res. 2008, 86, 904–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arai, K.; Nishiyama, N.; Matsuki, N.; Ikegaya, Y. Neuroprotective effects of lipoxygenase inhibitors against ischemic injury in rat hippocampal slice cultures. Brain Res. 2001, 904, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahal, A.; Kumar, A.; Singh, V.; Yadav, B.; Tiwari, R.; Chakraborty, S.; Dhama, K. Oxidative stress, prooxidants, and antioxidants: The interplay. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silva, B.; de Miranda, A.; Rodrigues, F.; Malheiros Silveira, A.; de Souza Resende, G.; Dutra Moraes, M.; Pinheiro de Oliveira, A.; Parreiras, P.; Barcelos, L.; Teixeira, M.; et al. The 5-lipoxygenase (5-LOX) Inhibitor Zileuton Reduces Inflammation and Infarct Size with Improvement in Neurological Outcome Following Cerebral Ischemia. Curr. Neurovasc. Res. 2015, 12, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, X.K.; Yang, W.Z.; Wang, C.H.; Shi, S.S.; Zhang, Y.L.; Chen, C.M.; Yang, Y.K.; Jin, C.D.; Wen, S. Zileuton reduces inflammatory reaction and brain damage following permanent cerebral ischemia in rats. Inflammation 2010, 33, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramaniam, S.; Unsicker, K. ERK and cell death: ERK1/2 in neuronal death. FEBS J. 2010, 277, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pihlaja, R.; Haaparanta-Solin, M.; Rinne, J.O. The anti-inflammatory effects of lipoxygenase and cyclo-oxygenase inhibitors in inflammation-induced human fetal glia cells and the aβ degradation capacity of human fetal astrocytes in an ex vivo assay. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chistyakov, D.V.; Nikolskaya, A.I.; Goriainov, S.V.; Astakhova, A.A.; Sergeeva, M.G. Inhibitor of hyaluronic acid synthesis 4-methylumbelliferone as an anti-inflammatory modulator of lps-mediated astrocyte responses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chistyakov, D.V.; Astakhova, A.A.; Goriainov, S.V.; Sergeeva, M.G. Comparison of PPAR ligands as modulators of resolution of inflammation, via their influence on cytokines and oxylipins release in astrocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liddelow, S.A.; Barres, B.A. Reactive Astrocytes: Production, Function, and Therapeutic Potential. Immunity 2017, 46, 957–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adili, R.; Tourdot, B.E.; Mast, K.; Yeung, J.; Freedman, J.C.; Green, A.; Luci, D.K.; Jadhav, A.; Simeonov, A.; Maloney, D.J.; et al. First selective 12-LOX inhibitor, ML355, impairs thrombus formation and vessel occlusion in vivo with minimal effects on hemostasis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2017, 37, 1828–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rossi, A.; Pergola, C.; Koeberle, A.; Hoffmann, M.; Dehm, F.; Bramanti, P.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Werz, O.; Sautebin, L. The 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor, zileuton, suppresses prostaglandin biosynthesis by inhibition of arachidonic acid release in macrophages. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 161, 555–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luci, D.; Brian Jameson, J., II; Yasgar, A.; Diaz, G.; Joshi, N.; Kantz, A.; Markham, K.; Perry, S.; Kuhn, N.; Yeung, J.; et al. Discovery of ML355, a Potent and Selective Inhibitor of Human 12-Lipoxygenase. In Probe Reports from the NIH Molecular Libraries Program; National Center for Biotechnology Information (US): Bethesda, MD, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Archambault, A.S.; Turcotte, C.; Martin, C.; Provost, V.; Larose, M.C.; Laprise, C.; Chakir, J.; Bissonnette, É.; Laviolette, M.; Bossé, Y.; et al. Comparison of eight 15-lipoxygenase (LO) inhibitors on the biosynthesis of 15-LO metabolites by human neutrophils and eosinophils. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morgan, L.T.; Thomas, C.P.; Kühn, H.; O’Donnell, V.B. Thrombin-activated human platelets acutely generate oxidized docosahexaenoic-acid-containing phospholipids via 12-lipoxygenase. Biochem. J. 2010, 431, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Sims, H.F.; Jenkins, C.M.; Guan, S.; Dilthey, B.G.; Gross, R.W. 12-LOX catalyzes the oxidation of 2-arachidonoyl-lysolipids in platelets generating eicosanoid-lysolipids that are attenuated by iPLA2γ knockout. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 5307–5320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galano, J.M.; Roy, J.; Durand, T.; Lee, J.C.Y.; Le Guennec, J.Y.; Oger, C.; Demion, M. Biological activities of non-enzymatic oxygenated metabolites of polyunsaturated fatty acids (NEO-PUFAs) derived from EPA and DHA: New anti-arrhythmic compounds? Mol. Aspects Med. 2018, 64, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Trépanier, M.-O.; Eiden, M.; Morin-Rivron, D.; Bazinet, R.P.; Masoodi, M. High-resolution lipidomics coupled with rapid fixation reveals novel ischemia-induced signaling in the rat neurolipidome. J. Neurochem. 2017, 140, 766–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Colas, R.A.; Shinohara, M.; Dalli, J.; Chiang, N.; Serhan, C.N. Identification and signature profiles for pro-resolving and inflammatory lipid mediators in human tissue. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2014, 307, C39–C54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jouvène, C.; Fourmaux, B.; Géloën, A.; Balas, L.; Durand, T.; Lagarde, M.; Létisse, M.; Guichardant, M. Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Analysis of Free and Esterified Oxygenated Derivatives from Docosahexaenoic Acid in Rat Brain. Lipids 2018, 53, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francos-Quijorna, I.; Santos-Nogueira, E.; Gronert, K.; Sullivan, A.B.; Kopp, M.A.; Brommer, B.; David, S.; Schwab, J.M.; López-Vales, R. Maresin 1 promotes inflammatory resolution, neuroprotection, and functional neurological recovery after spinal cord injury. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 11731–11743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fredman, G.; Hellmann, J.; Proto, J.D.; Kuriakose, G.; Colas, R.A.; Dorweiler, B.; Connolly, E.S.; Solomon, R.; Jones, D.M.; Heyer, E.J.; et al. An imbalance between specialized pro-resolving lipid mediators and pro-inflammatory leukotrienes promotes instability of atherosclerotic plaques. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serhan, C.N.; de la Rosa, X.; Jouvene, C. Novel mediators and mechanisms in the resolution of infectious inflammation: Evidence for vagus regulation. J. Intern. Med. 2019, 286, 240–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Strokin, M.; Sergeeva, M.; Reiser, G. Docosahexaenoic acid and arachidonic acid release in rat brain astrocytes is mediated by two separate isoforms of phospholipase A 2 and is differently regulated by cyclic AMP and Ca2+. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 139, 1014–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chistyakov, D.V.; Azbukina, N.V.; Lopachev, A.V.; Kulichenkova, K.N.; Astakhova, A.A.; Sergeeva, M.G. Rosiglitazone as a Modulator of TLR4 and TLR3 Signaling Pathways in Rat Primary Neurons and Astrocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rohart, F.; Gautier, B.; Singh, A.; Lê Cao, K.A. mixOmics: An R package for ‘omics feature selection and multiple data integration. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
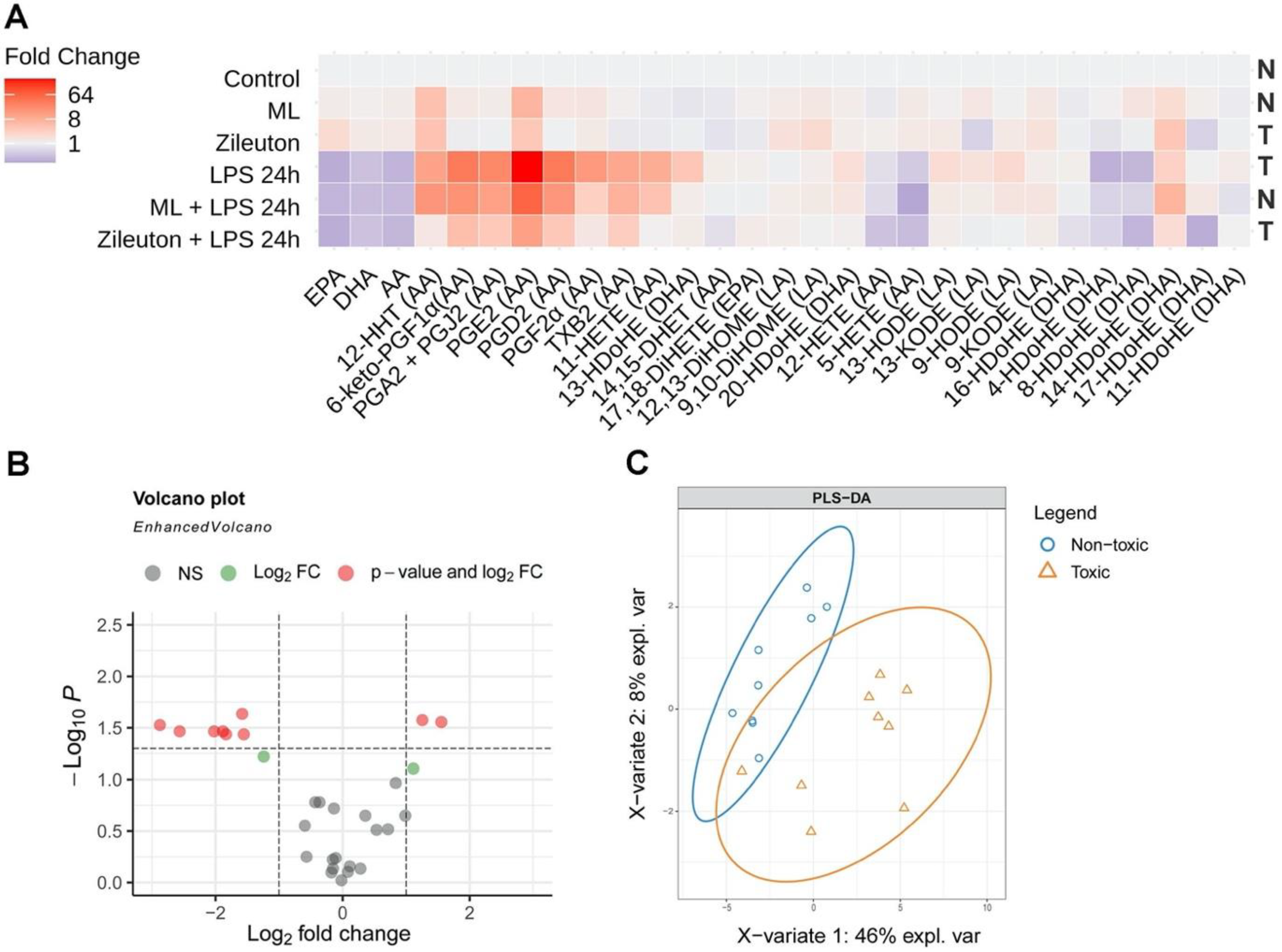
| Name | 13-HDoHE | 4-HDoHE | 8-HDoHE | PGE2 | PGA2 + PGJ2 | PGD2 | PGF2a | 11-HETE | 6-keto-PGF1a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| log2FC | −1.58 | 1.25 | 1.56 | −2.87 | −1.88 | −2.02 | −2.56 | −1.55 | −1.84 |
| Name | 13-HDoHE * | 4-HDoHE * | 17-HDoHE |
|---|---|---|---|
| VIP-scores | 1.6235235 | 1.5420719 | 1.588623 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guryleva, M.V.; Chistyakov, D.V.; Lopachev, A.V.; Goriainov, S.V.; Astakhova, A.A.; Timoshina, Y.A.; Khutorova, A.V.; Fedorova, T.N.; Sergeeva, M.G. Modulation of the Primary Astrocyte-Enriched Cultures’ Oxylipin Profiles Reduces Neurotoxicity. Metabolites 2021, 11, 498. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11080498
Guryleva MV, Chistyakov DV, Lopachev AV, Goriainov SV, Astakhova AA, Timoshina YA, Khutorova AV, Fedorova TN, Sergeeva MG. Modulation of the Primary Astrocyte-Enriched Cultures’ Oxylipin Profiles Reduces Neurotoxicity. Metabolites. 2021; 11(8):498. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11080498
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuryleva, Mariia V., Dmitry V. Chistyakov, Alexander V. Lopachev, Sergei V. Goriainov, Alina A. Astakhova, Yulia A. Timoshina, Anastasiya V. Khutorova, Tatiana N. Fedorova, and Marina G. Sergeeva. 2021. "Modulation of the Primary Astrocyte-Enriched Cultures’ Oxylipin Profiles Reduces Neurotoxicity" Metabolites 11, no. 8: 498. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11080498
APA StyleGuryleva, M. V., Chistyakov, D. V., Lopachev, A. V., Goriainov, S. V., Astakhova, A. A., Timoshina, Y. A., Khutorova, A. V., Fedorova, T. N., & Sergeeva, M. G. (2021). Modulation of the Primary Astrocyte-Enriched Cultures’ Oxylipin Profiles Reduces Neurotoxicity. Metabolites, 11(8), 498. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11080498






