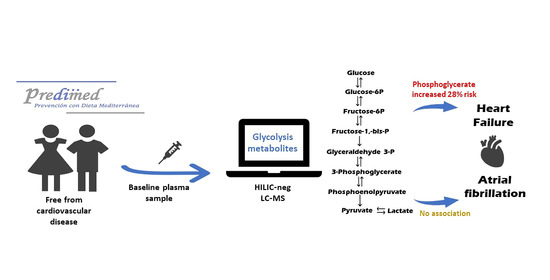
Glycolysis Metabolites and Risk of Atrial Fibrillation and Heart Failure in the PREDIMED Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Baseline Glycolysis Intermediate Metabolites, Other Related Metabolites, and Risk of AF
2.2. Baseline Glycolysis Intermediate Metabolites, Other Related Metabolites, and Risk of HF
2.3. Baseline Glycolysis Intermediate Metabolites, Other Related Metabolites, and Risk of AF and HF by Diabetes Status
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design and Participants
4.2. Sample Collection and Metabolomic Analysis
4.3. Outcome Assessment
4.4. Covariates Assessment
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Braunwald, E. Cardiovascular Medicine at the Turn of the Millennium: Triumphs, Concerns, and Opportunities. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997, 1360–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farmakis, D.; Chrysohoou, C.; Giamouzis, G.; Giannakoulas, G.; Hamilos, M.; Naka, K.; Tzeis, S.; Xydonas, S.; Karavidas, A.; Parissis, J. The management of atrial fibrillation in heart failure: An expert panel consensus. Heart Fail. Rev. 2020, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anter, E.; Jessup, M.; Callans, D.J. Atrial fibrillation and heart failure: Treatment considerations for a dual epidemic. Circulation 2009, 119, 2516–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zannad, F. Rising incidence of heart failure demands action. Lancet 2018, 391, 518–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rienstra, M.; McManus, D.D.; Benjamin, E.J. Novel risk factors for atrial fibrillation: Useful for risk prediction and clinical decision making? Circulation 2012, 125, e941–e946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diakos, N.A.; Navankasattusas, S.; Abel, E.D.; Rutter, J.; McCreath, L.; Ferrin, P.; McKellar, S.H.; Miller, D.V.; Park, S.Y.; Richardson, R.S.; et al. Evidence of Glycolysis Up-Regulation and Pyruvate Mitochondrial Oxidation Mismatch During Mechanical Unloading of the Failing Human Heart: Implications for Cardiac Reloading and Conditioning. JACC Basic Transl. Sci. 2016, 1, 432–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourliouros, A.; Yin, X.; Didangelos, A.; Hosseini, M.T.; Valencia, O.; Mayr, M.; Jahangiri, M. Substrate modifications precede the development of atrial fibrillation after cardiac surgery: A proteomic study. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2011, 92, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Hu, H.; Zhou, S.; Liu, Q. Alteration of myocardium glucose metabolism in atrial fibrillation: Cause or effect? Int. J. Cardiol. 2016, 203, 722–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, D.; Riles, E.M.; Marcos, E.G.; Magnani, J.W.; Lubitz, S.A.; Lin, H.; Long, M.T.; Schnabel, R.B.; McManus, D.D.; Ellinor, P.T.; et al. Metabolomic Profiling in Relation to New-Onset Atrial Fibrillation (from the Framingham Heart Study). Am. J. Cardiol. 2016, 118, 1493–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, A.; Yu, B.; Sun, Y.V.; Chen, L.Y.; Loehr, L.R.; O’Neal, W.T.; Soliman, E.Z.; Boerwinkle, E. Serum Metabolomics and Incidence of Atrial Fibrillation (from the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study). Am. J. Cardiol. 2019, 123, 1955–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, K.; Williams, E.K.; Mongraw-Chaffin, M.L.; Coresh, J.; Schmidt, M.I.; Brancati, F.L.; Hoogeveen, R.C.; Ballantyne, C.M.; Young, J.H. The association of plasma lactate with incident cardiovascular outcomes. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 178, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenori, L.; Hu, X.; Pantaleo, P.; Alterini, B.; Castelli, G.; Olivotto, I.; Bertini, I.; Luchinat, C.; Gensini, G.F. Metabolomic fingerprint of heart failure in humans: A nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy analysis. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 168, e113–e115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhao, H.; Luo, L.; Chen, C.; Xu, X.; Zhang, W.; Gao, K.; Li, B.; et al. Metabolomic identification of diagnostic plasma biomarkers in humans with chronic heart failure. Mol. Biosyst. 2013, 9, 2618–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, D.; Lombardi, R.; Rodriguez, G.; Mitchell, M.M.; Marian, A.J. Metabolomic distinction and insights into the pathogenesis of human primary dilated cardiomyopathy. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 41, 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Bilsen, M.; Van Nieuwenhoven, F.A.; Van Der Vusse, G.J. Metabolic remodelling of the failing heart: Beneficial or detrimental? Cardiovasc. Res. 2009, 81, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, W.G.; Martins-Santos, M.E.S.; Chaves, V.E. Uric acid as a modulator of glucose and lipid metabolism. Biochimie 2015, 116, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muiesan, M.L.; Salvetti, M.; Virdis, A.; Masi, S.; Casiglia, E.; Tikhonoff, V.; Barbagallo, C.M.; Bombelli, M.; Cicero, A.F.G.; Cirillo, M.; et al. Serum uric acid predicts heart failure in a large Italian cohort: Search for a cut-off value the URic acid Right for heArt Health study. J. Hypertens. 2021, 39, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ussher, J.R.; Elmariah, S.; Gerszten, R.E.; Dyck, J.R.B. The Emerging Role of Metabolomics in the Diagnosis and Prognosis of Cardiovascular Disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 68, 2850–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guasch-Ferré, M.; Santos, J.L.; Martínez-González, M.A.; Clish, C.B.; Razquin, C.; Wang, D.; Liang, L.; Li, J.; Dennis, C.; Corella, D.; et al. Glycolysis/gluconeogenesis- and tricarboxylic acid cycle-related metabolites, Mediterranean diet, and type 2 diabetes. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 111, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-González, M.Á.; Corella, D.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Ros, E.; Covas, M.I.; Fiol, M.; Wärnberg, J.; Arós, F.; Ruíz-Gutiérrez, V.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.M.; et al. Cohort profile: Design and methods of the PREDIMED study. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2012, 41, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubin, J.H.; Gail, M.H. Biased Selection of Controls for Case-Control Analyses of Cohort Studies. Biometrics 1984, 40, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.H.; Shugart, Y.Y.; Cole, S.R.; Platz, E.A. A simulation study of control sampling methods for nested case-control studies of genetic and molecular biomarkers and prostate cancer progression. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2009, 18, 706–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paynter, N.P.; Balasubramanian, R.; Giulianini, F.; Wang, D.D.; Tinker, L.F.; Gopal, S.; Deik, A.A.; Bullock, K.; Pierce, K.A.; Scott, J.; et al. Metabolic predictors of incident coronary heart disease in women. Circulation 2018, 137, 841–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.J.; Ngo, D.; Psychogios, N.; Dejam, A.; Larson, M.G.; Vasan, R.S.; Ghorbani, A.; O’Sullivan, J.; Cheng, S.; Rhee, E.P.; et al. 2-Aminoadipic acid is a biomarker for diabetes risk. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 4309–4317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayers, J.R.; Wu, C.; Clish, C.B.; Kraft, P.; Torrence, M.E.; Fiske, B.P.; Yuan, C.; Bao, Y.; Townsend, M.K.; Tworoger, S.S.; et al. Elevation of circulating branched-chain amino acids is an early event in human pancreatic adenocarcinoma development. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 1193–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swedberg, K.; Cleland, J.; Dargie, H.; Drexler, H.; Follath, F.; Komajda, M.; Tavazzi, L.; Smiseth, O.A.; Gavazzi, A.; Haverich, A.; et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of chronic heart failure: Executive summary (update 2005). Eur. Heart J. 2005, 1115–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elosua, R.; Marrugat, J.; Molina, L.; Pons, S.; Pujol, E. Validation of the Minnesota Leisure Time Physical Activity Questionnaire in Spanish men. The MARATHOM Investigators. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1994, 139, 1197–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blom, G. Statistical Estimates and Transformed Beta-Variables; John Wiley & Sons A/S: New York, NY, USA, 1958. [Google Scholar]
| Atrial Fibrillation | Heart Failure | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | Controls (n = 545) | Cases (n = 512) | p-Value | Controls (n = 408) | Cases (n = 334) | p-Value |
| Age (years) | 68.39 (6.21) | 68.28 (6.07) | 0.772 | 70.12 (5.92) | 70.34 (5.90) | 0.615 |
| Women (%) | 271 (49.7) | 255 (49.8) | 1 | 224 (54.9) | 196 (58.7) | 0.337 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 29.71 (3.7) | 30.67 (3.8) | <0.001 | 29.24 (3.6) | 31.07 (3.8) | <0.001 |
| LTFA (METs-min/d) | 231.2 (223.0) | 228.1 (216.6) | 0.823 | 212.9 (218.6) | 216.1 (203.1) | 0.837 |
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 146 (19) | 149 (22) | 0.239 | 145 (20) | 151 (20) | 0.009 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 82 (10) | 82 (12) | 0.765 | 80 (10) | 81 (11) | 0.812 |
| Fasting glucose (mg/dL) | 120.5 (39.0) | 121.8 (44.3) | 0.631 | 121 (40) | 130 (52) | 0.011 |
| LDL cholesterol (mg/dL) | 130.5 (31.5) | 128.1 (34.4) | 0.255 | 128.6 (34.4) | 127.2 (34.8) | 0.591 |
| Hypertension (%) | 447 (82.0) | 452 (88.3) | 0.006 | 335 (82.1) | 293 (87.7) | 0.045 |
| Dyslipidemia (%) | 382 (70.1) | 332 (64.8) | 0.079 | 281 (68.9) | 214 (64.1) | 0.193 |
| T2D (%) | 278 (51.0) | 245 (47.9) | 0.335 | 212 (52.0) | 197 (59.0) | 0.066 |
| Family history of premature CHD (%) | 110 (20.2) | 98 (19.1) | 0.727 | 0.46 (1.54) | 0.52 (1.69) | 0.645 |
| Oral hypoglycemic agents (%) | 117 (32.5) | 156 (30.5) | 0.525 | 134 (32.8) | 134 (40.1) | 0.048 |
| Lipid-lowering agents (%) | 225 (41.3) | 207 (40.4) | 0.826 | 166 (40.7) | 133 (39.8) | 0.870 |
| Antihypertensive agents (%) | 110 (20.2) | 143 (27.9) | 0.004 | 96 (23.5) | 85 (25.4) | 0.603 |
| Other medication use (%) | 137 (25.1) | 152 (29.7) | 0.112 | 109 (26.7) | 136 (40.7) | <0.001 |
| Smoking (%) | 0.893 | |||||
| Current smoker | 76 (13.9) | 73 (14.3) | 46 (11.3) | 48 (14.4) | 0.442 | |
| Former smoker | 154 (28.3) | 138 (27.0) | 109 (26.7) | 84 (25.1) | ||
| Never smoker | 315 (57.8) | 301 (58.8) | 253 (62.0) | 202 (60.5) | ||
| Intervention group (%) | 0.224 | 0.059 | ||||
| Control | 188 (34.5) | 189 (36.9) | 148 (36.3) | 122 (36.5) | ||
| MedDiet plus EVOO | 201 (36.9) | 163 (31.8) | 156 (38.2) | 104 (31.1) | ||
| MedDiet plus nuts | 156 (28.6) | 160 (31.2) | 104 (25.5) | 108 (32.3) | ||
| Metabolite | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | P-Trend | Per 1-SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phosphoglycerate 1 | 122/188 | 141/182 | 132/179 | 117/185 | 512/734 | |
| Crude model | 1 (Ref) | 1.21 (0.86, 1.71) | 1.06 (0.74, 1.52) | 0.89 (0.62, 1.3) | 0.4212 | 0.98 (0.86, 1.11) |
| Multivariate model | 1 (Ref) | 1.21 (0.85, 1.73) | 1.05 (0.72, 1.52) | 0.87 (0.59, 1.28) | 0.3796 | 0.96 (0.84, 1.1) |
| Hexose monophosphate 1 | 135/177 | 120/177 | 122/191 | 131/182 | 508/727 | |
| Crude model | 1 (Ref) | 0.88 (0.62, 1.24) | 0.8 (0.57, 1.14) | 0.92 (0.65, 1.3) | 0.6319 | 0.95 (0.84, 1.07) |
| Multivariate model | 1 (Ref) | 0.87 (0.61, 1.24) | 0.79 (0.55, 1.15) | 0.94 (0.65, 1.36) | 0.7371 | 0.94 (0.82, 1.07) |
| Fructose/glucose/galactose 1 | 144/188 | 122/184 | 117/180 | 129/182 | 512/734 | |
| Crude model | 1 (Ref) | 0.84 (0.61, 1.17) | 0.79 (0.57, 1.11) | 0.9 (0.65, 1.25) | 0.4974 | 1.00 (0.89, 1.13) |
| Model 2 | 1 (Ref) | 0.83 (0.59, 1.18) | 0.75 (0.51, 1.09) | 0.94 (0.63, 1.42) | 0.6463 | 1.03 (0.89, 1.19) |
| Lactate 1 | 113/184 | 135/181 | 120/188 | 144/181 | 512/734 | |
| Crude model | 1 (Ref) | 1.2 (0.85, 1.69) | 1.13 (0.8, 1.60) | 1.4 (0.98, 2.01) | 0.0848 | 1.09 (0.97, 1.24) |
| Multivariate model | 1 (Ref) | 1.21 (0.85, 1.74) | 1.1 (0.77, 1.59) | 1.28 (0.88, 1.86) | 0.2571 | 1.05 (0.92, 1.20) |
| Sucrose 1 | 125/185 | 118/182 | 132/190 | 137/177 | 512/734 | |
| Crude model | 1 (Ref) | 0.93 (0.67, 1.29) | 1.04 (0.75, 1.46) | 1.09 (0.78, 1.53) | 0.5279 | 1.04 (0.92, 1.18) |
| Multivariate model | 1 (Ref) | 0.86 (0.61, 1.21) | 1 (0.7, 1.42) | 1.02 (0.71, 1.46) | 0.7782 | 1.01 (0.89, 1.15) |
| α-glycerophosphate 1 | 125/179 | 114/184 | 146/186 | 127/184 | 512/733 | |
| Crude model | 1 (Ref) | 0.91 (0.64, 1.28) | 1.25 (0.88, 1.77) | 1.11 (0.77, 1.59) | 0.3700 | 1.08 (0.95, 1.24) |
| Multivariate model | 1 (Ref) | 0.94 (0.66, 1.35) | 1.27 (0.88, 1.83) | 1.14 (0.78, 1.68) | 0.3189 | 1.10 (0.96, 1.27) |
| PEP 1 | 99/162 | 111/160 | 98/155 | 125/154 | 433/631 | |
| Crude model | 1 (Ref) | 1.3 (0.88, 1.91) | 1.13 (0.75, 1.68) | 1.41 (0.94, 2.13) | 0.1560 | 1.13 (0.98, 1.3) |
| Multivariate model | 1 (Ref) | 1.36 (0.89, 2.06) | 1.15 (0.75, 1.75) | 1.42 (0.91, 2.22) | 0.1892 | 1.12 (0.96, 1.31) |
| Ratio PEP:lactate 1 | 98/158 | 94/157 | 122/162 | 119/154 | 433/631 | |
| Crude model | 1 (Ref) | 0.93 (0.63, 1.37) | 1.25 (0.85, 1.83) | 1.21 (0.81, 1.82) | 0.2311 | 1.08 (0.94, 1.24) |
| Multivariate model | 1 (Ref) | 0.82 (0.54, 1.24) | 1.27 (0.84, 1.92) | 1.21 (0.78, 1.88) | 0.2125 | 1.09 (0.94, 1.27) |
| Metabolite | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | P-Trend | Per 1-SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phosphoglycerate 1 | 72/122 | 82/130 | 84/119 | 95/136 | 333/507 | |
| Crude model | 1 (Ref) | 1.08 (0.72, 1.63) | 1.30 (0.83, 2.03) | 1.25 (0.81, 1.93) | 0.2808 | 1.17 (1.00, 1.38) |
| Multivariate model | 1 (Ref) | 1.30 (0.81, 2.1) | 1.43 (0.86, 2.38) | 1.54 (0.94, 2.54) | 0.0975 | 1.28 (1.06, 1.53) |
| Hexose monophosphate 1 | 88/133 | 73/126 | 72/123 | 96/122 | 329/504 | |
| Crude model | 1 (Ref) | 0.87 (0.57, 1.35) | 0.89 (0.58, 1.36) | 1.24 (0.8, 1.9) | 0.3519 | 1.08 (0.92, 1.27) |
| Multivariate model | 1 (Ref) | 0.93 (0.57, 1.53) | 0.86 (0.54, 1.39) | 1.16 (0.71, 1.88) | 0.6258 | 1.05 (0.87, 1.25) |
| Fructose/glucose/galactose 1 | 73/133 | 77/119 | 90/134 | 94/122 | 334/508 | |
| Crude model | 1 (Ref) | 1.21 (0.8, 1.82) | 1.26 (0.83, 1.9) | 1.42 (0.96, 2.11) | 0.0827 | 1.17 (1.01, 1.35) |
| Multivariate model | 1 (Ref) | 1.09 (0.68, 1.74) | 0.88 (0.52, 1.49) | 0.93 (0.53, 1.63) | 0.7498 | 1.04 (0.85, 1.27) |
| Lactate 1 | 79/136 | 88/126 | 70/123 | 97/123 | 334/508 | |
| Crude model | 1 (Ref) | 1.12 (0.75, 1.67) | 0.94 (0.59, 1.48) | 1.39 (0.89, 2.18) | 0.2012 | 1.08 (0.92, 1.27) |
| Multivariate model | 1 (Ref) | 1.00 (0.64, 1.56) | 0.91 (0.55, 1.51) | 1.13 (0.68, 1.86) | 0.6855 | 1.00 (0.83, 1.20) |
| Sucrose 1 | 68/125 | 78/136 | 68/124 | 120/123 | 334/508 | |
| Crude model | 1 (Ref) | 1.09 (0.72, 1.66) | 1.16 (0.73, 1.83) | 1.92 (1.26, 2.94) | 0.0014 | 1.26 (1.08, 1.47) |
| Multivariate model | 1 (Ref) | 1.01 (0.64, 1.61) | 0.94 (0.56, 1.57) | 1.57 (0.98, 2.52) | 0.0461 | 1.18 (0.99, 1.40) |
| α-glycerophosphate 1 | 82/129 | 85/130 | 85/125 | 82/123 | 334/507 | |
| Crude model | 1 (Ref) | 1.15 (0.75, 1.77) | 1.15 (0.74, 1.78) | 1.19 (0.75, 1.88) | 0.4946 | 1.02 (0.87, 1.2) |
| Multivariate model | 1 (Ref) | 0.98 (0.6, 1.62) | 0.99 (0.6, 1.62) | 1.23 (0.73, 2.08) | 0.4054 | 1.04 (0.87, 1.25) |
| PEP 1 | 63/108 | 74/115 | 50/116 | 94/122 | 281/461 | |
| Crude model | 1 (Ref) | 0.93 (0.57, 1.51) | 0.77 (0.47, 1.27) | 1.12 (0.68, 1.82) | 0.7114 | 1.07 (0.90, 1.28) |
| Multivariate model | 1 (Ref) | 0.62 (0.35, 1.10) | 0.8 (0.46, 1.41) | 0.89 (0.51, 1.56) | 0.9817 | 1.03 (0.84, 1.25) |
| Ratio PEP:lactate 1 | 65/111 | 68/111 | 77/113 | 71/126 | 281/461 | |
| Crude model | 1 (Ref) | 1.05 (0.65, 1.68) | 1.11 (0.7, 1.77) | 0.91 (0.56, 1.5) | 0.7976 | 1.02 (0.85, 1.21) |
| Multivariate model | 1 (Ref) | 0.91 (0.52, 1.61) | 0.98 (0.58, 1.68) | 0.89 (0.51, 1.57) | 0.7650 | 1.03 (0.85, 1.26) |
| Atrial Fibrillation | Heart failure | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metabolite | Without Diabetes | With Diabetes | Without Diabetes | With Diabetes |
| Phosphoglycerate | 0.89 (0.73, 1.07) | 1.03 (0.87, 1.23) | 0.95 (0.72, 1.25) | 1.57 (1.24, 1.98) |
| Hexose monophosphate | 0.90 (0.75, 1.09) | 0.97 (0.81, 1.16) | 0.83 (0.63, 1.1) | 1.19 (0.95, 1.48) |
| Fructose/glucose/galactose | 1.12 (0.88, 1.43) | 0.99 (0.82, 1.19) | 1.04 (0.73, 1.47) | 1.01 (0.79, 1.28 |
| Lactate | 1.01 (0.85, 1.21) | 1.10 (0.92, 1.31) | 1.01 (0.77, 1.32) | 1.01 (0.8, 1.27) |
| Sucrose | 1.05 (0.88, 1.25) | 0.97 (0.81, 1.17) | 1.11 (0.87, 1.41) | 1.18 (0.94, 1.48) |
| α-glycerophosphate | 1.18 (0.97, 1.43) | 1.04 (0.86, 1.26) | 1.15 (0.87, 1.52) | 0.95 (0.76, 1.18) |
| PEP | 1.13 (0.93, 1.37) | 1.11 (0.89, 1.38) | 1.00 (0.76, 1.31) | 1.10 (0.86, 1.4) |
| Ratio PEP:lactate | 1.12 (0.92, 1.37) | 1.05 (0.85, 1.29) | 1.01 (0.76, 1.34) | 1.09 (0.85, 1.39) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Becerra-Tomás, N.; Ruiz-Canela, M.; Hernández-Alonso, P.; Bulló, M.; Li, J.; Guasch-Ferré, M.; Toledo, E.; Clish, C.B.; Estruch, R.; Ros, E.; et al. Glycolysis Metabolites and Risk of Atrial Fibrillation and Heart Failure in the PREDIMED Trial. Metabolites 2021, 11, 306. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11050306
Becerra-Tomás N, Ruiz-Canela M, Hernández-Alonso P, Bulló M, Li J, Guasch-Ferré M, Toledo E, Clish CB, Estruch R, Ros E, et al. Glycolysis Metabolites and Risk of Atrial Fibrillation and Heart Failure in the PREDIMED Trial. Metabolites. 2021; 11(5):306. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11050306
Chicago/Turabian StyleBecerra-Tomás, Nerea, Miguel Ruiz-Canela, Pablo Hernández-Alonso, Mònica Bulló, Jun Li, Marta Guasch-Ferré, Estefanía Toledo, Clary B. Clish, Ramon Estruch, Emilio Ros, and et al. 2021. "Glycolysis Metabolites and Risk of Atrial Fibrillation and Heart Failure in the PREDIMED Trial" Metabolites 11, no. 5: 306. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11050306
APA StyleBecerra-Tomás, N., Ruiz-Canela, M., Hernández-Alonso, P., Bulló, M., Li, J., Guasch-Ferré, M., Toledo, E., Clish, C. B., Estruch, R., Ros, E., Fitó, M., Lee, C.-H., Pierce, K., Arós, F., Serra-Majem, L., Liang, L., Razquin, C., Gómez-Gracia, E., Martínez-González, M. A., ... Salas-Salvadó, J. (2021). Glycolysis Metabolites and Risk of Atrial Fibrillation and Heart Failure in the PREDIMED Trial. Metabolites, 11(5), 306. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11050306