A Collaborative Deprescribing Intervention in a Subacute Medical Outpatient Clinic: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
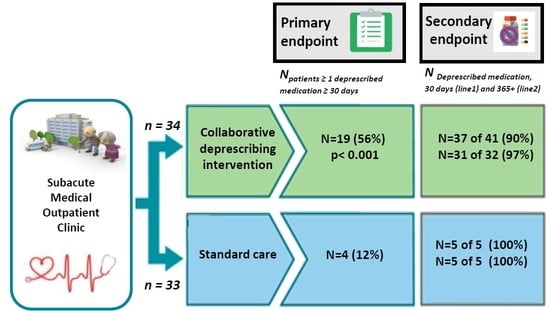
2. Results
2.1. Feasibility of Deprescribing
2.2. Deprescribed Medications and Number of Medications at 30 Days Post Inclusion
2.3. Deprescribed Medications Sustained at 365+ Days Post Inclusion
3. Discussion
3.1. Results in Context of Other Studies
3.2. Follow-Up, Shared Decision-Making, and Electronic Deprescribing Tools
3.3. Strengths and Limitations
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics Approval and Trial Registration
4.2. Setting
4.3. Trial Design and Participants
4.4. Baseline Data Collection
4.5. Best Possible Medication List and Medication Reconciliation
4.6. Intervention
4.6.1. Telephone Consultation Related to Described Medications Seven Days after Intervention
4.6.2. Telephone Data Collected 30 Days Post Inclusion
4.6.3. Telephone Data Collected 365+ Days Post Inclusion
4.6.4. Acute Admission after Inclusion
4.7. Outcomes
Assessment of the Primary Outcome
4.8. Sample Size
4.9. Randomization
4.10. Statistical Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Patient, Sex, Age | Deprescribed Medication (ATC Code) | Reason for Deprescribing | Discontinued or Reduced Dose | Sustained Deprescribing | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 Days | 365+ Days | ||||
| 1, M, 70 | ASA (B01AC06) Codeine (N02AJ01) Fusidic acid (D06AX01) Paracetamol (N02BE01) | C5: Risk of bleeding * L1: Opioids for mild pain * A2: Risk of bacterial resistance * A2: Lack of evidence >6 weeks and risk of MOH * | D D D R | + - + + | + N/A + + |
| 2, M, 83 | Bisacodyl (A06AB02) | A3: Any duplicate drug class and diarrhea * | D | + | † |
| 3, F, 79 | Ferric sodium citrate (B03AB01) Pantoprazole (A02BC01) | A1: No evidence-based clinical indication * F2: >8-week treatment dose reduction * | D R | + + | + + |
| 4, F, 61 | Potassium chloride (A12BA01) | No evidence-based clinical indication ** | D | + | † |
| 5, F, 82 | Metoprolol (C07AB02) | Side effect: Dizziness ** | D | + | + |
| 6, M, 69 | Amlodipine (C08CA01) Enalapril (C09AA02) Zopiclone (N05CF01) | Side effect: Edema ** Overdose according to eGFR ** K4: Hypnotic Z-drug * | R R D | - + + | N/A + + |
| 7, F, 79 | Diclofenac (M01AB05) Spironolactone (C03DA01) | H2: Heart failure * A3: Duplicate drug class * | D D | + + | † |
| 8, F, 65 | Ibuprofen (M01AE01) | H2: Severe hypertension * | D | + | + |
| 9, M, 78 | Bendroflumethiazide (C03AB01) Potassium chloride (A12BA01) Paracetamol (N02BE01) Bisacodyl (A06AB02) | A1: No evidence-based clinical indication * A1: No evidence-based clinical indication * A2: Lack of evidence >6 weeks and risk of MOH * A2: Prescribed beyond the recommended duration * | D D R D | + + + + | + + + + |
| 10, M, 88 | Nebivolol (C07AB12) | A3: Duplicate drug class * | D | + | + |
| 11, M, 61 | Paracetamol (N02BE01) | Lack of evidence >6 weeks and risk of MOH ** | D | + | + |
| 12, F, 85 | Gabapentin (N03AX12) | Side effect: Dizziness ** | R | + | + |
| 13, M, 41 | Gabapentin (N03AX12) Paracetamol (N02BE01) | Side effect: Tiredness and dizziness ** Lack of evidence >6 weeks and risk of MOH * | R D | + + | + + |
| 14, F, 95 | Metoprolol (C07AB02) | B4: Side effect: Bradycardia and hypotension * | D | + | + |
| 15, F, 80 | Pantoprazole (A02BC01) Zopiclone (N05CF01) | F2: >8-week treatment dose reduction * K4: Hypnotic Z-drug * | R D | + + | + - |
| 16, M, 51 | Atorvastatin (C10AA05) Chlorzoxazone (M03BB03) Desloratadine (R06AX27) Diclofenac (M02AA15) Glyceryl trinitrate (C01DA02) | Side effect: Headache and muscle pain ** No clinical indication ** No clinical indication ** No clinical indication ** No clinical indication ** | D D D D D | + + + + + | + + + + + |
| 17, M, 65 | Amitriptyline(N06AA09) Melatonin (N05CH01) Pantoprazole (A02BC01) Tramadol(N02AX02) | D2: Tricyclic antidepressants * Lack of effect ** F2: >8-week treatment dose reduction * Side effect: Dizziness ** | R D R R | + + + + | + + + + |
| 18, M, 69 | Alfuzosin (G04CA01) Cetirizine (R06AE07) | I2: Risk of symptomatic orthostatic hypotension * A1: No evidence-based clinical indication * | D D | + + | + + |
| 19, M, 78 | Metoprolol (C07AB02) | Side effect: Confusion and change in personality ** | D | + | + |
| 20, M, 58 | Eplerenone (C03DA04) | B12: Potassium sparing medication and adrenal gland disease ** | D | - | N/A |
| 21, M, 28 | Chlorzoxazone (M03BB03) | Side effect: Dizziness and tiredness ** | R | - | N/A |
| Patient, Sex, Age | Deprescribed Medication (ATC Code) | Reason for Deprescribing | Discontinued or Reduced Dose | Sustained Deprescribing | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 Days | 365 + Days | ||||
| 22, F, 69 | Venlafaxine (N06AX16) Folic acid (B03BB01) | Side effect ** Prescribed beyond the recommended duration | D D | + + | + + |
| 23, F, 84 | Alogliptin (A10BH04) | Duplicate drug class | D | + | † |
| 24, M, 82 | Colchicin (M04AC01) | Long-term use ** | D | + | + |
| 25, F, 61 | Insulin aspart (A10AB05) | Duplicate drug class | D | + | + |
References
- Simonson, W. Polypharmacy, MRPs, PIMs and deprescribing. Geriatr. Nurs. 2015, 36, 467–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, I.A.; Hilmer, S.N.; Reeve, E.; Potter, K.; Le Couteur, D.; Rigby, D.; Gnjidic, D.; Del Mar, C.B.; Roughead, E.E.; Page, A.; et al. Reducing Inappropriate Polypharmacy. JAMA Intern. Med. 2015, 175, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, C.; Weir, E. Deprescribing for older patients. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2014, 186, 1369–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willadsen, T.G.; Siersma, V.; Nicolaisdóttir, D.R.; Køster-Rasmussen, R.; Jarbøl, E.D.; Reventlow, S.; Mercer, S.W.; Olivarius, N.D.F. Multimorbidity and mortality. J. Comorbidity 2018, 8, 2235042–18804063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, L.D.; Andersen, O.; Hallin, M.; Petersen, J. Potentially inappropriate medication related to weakness in older acute medical patients. Int. J. Clin. Pharm. 2014, 36, 570–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ie, K.; Felton, M.; Springer, S.; Wilson, S.A.; Albert, S.M. Multimorbidity and Polypharmacy in Family Medicine Residency Practices. J. Pharm. Technol. 2017, 33, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, C. Deprescribing: A new word to guide medication review. Can. Med Assoc. J. 2014, 186, 407–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, W.; Lundby, C.; Graabaek, T.; Nielsen, D.S.; Ryg, J.; Søndergaard, J.; Pottegård, A. Tools for Deprescribing in Frail Older Persons and Those with Limited Life Expectancy: A Systematic Review. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2018, 67, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinewine, A.; Schmader, K.E.; Barber, N.; Hughes, C.; Lapane, K.L.; Swine, C.; Hanlon, J.T. Prescribing in Elderly People. Lancet 2007, 370, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Mannheimer, B.; Ulfvarson, J.; Eklöf, S.; Bergqvist, M.; Andersén-Karlsson, E.; Pettersson, H. Drug-Related Problems and Pharma-cotherapeutic Advisory Intervention at a Medicine Clinic. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2006, 7, 1075–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisby, M.; Thomsen, A.; Nielsen, L.P.; Lyhne, N.M.; Breum-Leer, C.; Fredberg, U.; Jã¸rgensen, H.; Brock, B.; Jørgensen, H. The Effect of Systematic Medication Review in Elderly Patients Admitted to an Acute Ward of Internal Medicine. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2009, 106, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graabæk, T.; Kjeldsen, L.J.; Graabaek, T. Medication Reviews by Clinical Pharmacists at Hospitals Lead to Improved Patient Outcomes: A Systematic Review. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2013, 112, 359–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, M.; Lundh, A. Medication review in hospitalised patients to reduce morbidity and mortality. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 2, CD008986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graabaek, T.; Hedegaard, U.; Christensen, M.B.; Clemmensen, M.H.; Knudsen, T.; Aagaard, L. Effect of a medicines management model on medication-related readmissions in older patients admitted to a medical acute admission unit-A randomized controlled trial. J. Eval. Clin. Pr. 2019, 25, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, T.R.H.; Honoré, P.H.; Rasmussen, M.; Andersen, S.E. Clinical Effects of a Pharmacist Intervention in Acute Wards-A Randomized Controlled Trial. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2017, 121, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houlind, M.B.; Andersen, A.L.; Treldal, C.; Jørgensen, L.M.; Kannegaard, P.N.; Castillo, L.S.; Christensen, L.D.; Tavenier, J.; Rasmussen, L.J.H.; Ankarfeldt, M.Z.; et al. A Collaborative Medication Review Including Deprescribing for Older Patients in an Emergency Department: A Longitudinal Feasibility Study. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bülow, C.; Flagstad Bech, C.; Ullitz Faerch, K.; Trærup Andersen, J.; Byg Armandi, H.; Treldal, C. Discrepancies Between the Med-ication List in Electronic Prescribing Systems and Patients’ Actual Use of Medicines. Sr. Care Pharm. 2019, 34, 317–324. [Google Scholar]
- Jansen, J.; Naganathan, V.; Carter, S.M.; McLachlan, A.J.; Nickel, B.; Irwig, L.; Bonner, C.; Doust, J.; Colvin, J.; Heaney, A.; et al. Too much medicine in older people? Deprescribing through shared decision making. BMJ 2016, 353, i2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huiskes, V.J.B.; Ende, C.H.M.; Kruijtbosch, M.; Ensing, H.T.; Meijs, M.; Meijs, V.M.M.; Burger, D.M.; Bemt, B.J.F. Effectiveness of medication review on the number of drug-related problems in patients visiting the outpatient cardiology clinic: A randomized controlled trial. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2020, 86, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergkvist, A.; Midlöv, P.; Höglund, P.; Larsson, L.; Eriksson, T. A multi-intervention approach on drug therapy can lead to a more appropriate drug use in the elderly. LIMM-Landskrona Integrated Medicines Management. J. Eval. Clin. Pr. 2009, 15, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinewine, A.; Swine, C.; Dhillon, S.; Lambert, P.; Nachega, J.B.; Wilmotte, L.; Tulkens, P.M. Effect of a Collaborative Approach on the Quality of Prescribing for Geriatric Inpatients: A Randomized, Controlled Trial. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2007, 55, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellström, L.M.; Bondesson, Å.; Höglund, P.; Midlöv, P.; Holmdahl, L.; Rickhag, E.; Eriksson, T. Impact of the Lund Integrated Medicines Management (LIMM) model on medication appropriateness and drug-related hospital revisits. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2011, 67, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakib, S.; Dundon, B.K.; Maddison, J.; Thomas, J.; Stanners, M.; Caughey, G.E.; Clark, R.A. Effect of a Multidisciplinary Outpatient Model of Care on Health Outcomes in Older Patients with Multimorbidity: A Retrospective Case Control Study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bondesson, Å.; Holmdahl, L.; Midlöv, P.; Höglund, P.; Andersson, E.; Eriksson, T. Acceptance and importance of clinical pharmacists’ LIMM-based recommendations. Int. J. Clin. Pharm. 2012, 34, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravn-Nielsen, L.V.; Duckert, M.-L.; Lund, M.L.; Henriksen, J.P.; Nielsen, M.L.; Eriksen, C.S.; Buck, T.C.; Pottegård, A.; Hansen, M.R.; Hallas, J. Effect of an In-Hospital Multifaceted Clinical Pharmacist Intervention on the Risk of Readmission. JAMA Intern. Med. 2018, 178, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dharmarajan, T.S.; Choi, H.; Hossain, N.; Munasinghe, U.; Lakhi, F.; Lourdusamy, D.; Onuoha, S.; Murakonda, P.; Skokowska-Lebelt, A.; Kanagala, M.; et al. Deprescribing as a Clinical Improvement Focus. J. Am. Med Dir. Assoc. 2020, 21, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marvin, V.; Ward, E.; Poots, A.J.; Heard, K.; Rajagopalan, A.; Jubraj, B. Deprescribing medicines in the acute setting to reduce the risk of falls. Eur. J. Hosp. Pharm. 2016, 24, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curtin, D.; Gallagher, P.; O’Mahony, D. Deprescribing in older people approaching end-of-life: Development and validation of STOPPFrail version 2. Age Ageing 2021, 50, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitman, A.; DeGregory, K.; Morris, A.; Mohile, S.; Ramsdale, E. Pharmacist-led medication assessment and deprescribing intervention for older adults with cancer and polypharmacy: A pilot study. Support. Care Cancer 2018, 26, 4105–4113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundby, C.; Graabæk, T.; Ryg, J.; Søndergaard, J.; Pottegård, A.; Nielsen, D.S. Above All, It’s a Matter of This Person’s Quality of Life: Health Care Professionals’ Perspectives on Deprescribing in Older Patients With Limited Life Expectancy. Gerontol. 2019, 60, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kua, C.-H.; Mak, V.S.; Lee, S.W.H. Health Outcomes of Deprescribing Interventions Among Older Residents in Nursing Homes: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2019, 20, 362–372.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, M.D.; Rosholm, J.U.; Hallas, J. The influence of comprehensive geriatric assessment on drug therapy in elderly patients. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 70, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strehlau, A.G.; Larsen, M.D.; Søndergaard, J.; Almarsdóttir, A.B.; Rosholm, J.-U. General practitioners’ continuation and acceptance of medication changes at sectorial transitions of geriatric patients-a qualitative interview study. BMC Fam. Pr. 2018, 19, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeve, E.; Shakib, S.; Hendrix, I.; Roberts, M.S.; Wiese, M.D. Review of deprescribing processes and development of an evidence-based, patient-centred deprescribing process. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2014, 78, 738–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Bosquet, K.; Barnett, N.; Minshull, J. Deprescribing: Practical Ways to Support Person-Centred, Evidence-Based Deprescribing. Pharmacy 2019, 7, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtin, D.; Jennings, E.; Daunt, R.; Curtin, S.; Randles, M.; Gallagher, P.; O’Mahony, D. Deprescribing in Older People Approaching End of Life: A Randomized Controlled Trial Using STOPPFrail Criteria. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2020, 68, 762–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barry, M.J.; Edgman-Levitan, S. Shared Decision Making—The Pinnacle of Patient-Centered Care. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 780–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, L.J.H.; Ladelund, S.; Haupt, T.H.; Ellekilde, G.; Poulsen, J.H.; Iversen, K.; Eugen-Olsen, J.; Andersen, O. Soluble urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (suPAR) in acute care: A strong marker of disease presence and severity, readmission and mortality. A retrospective cohort study. Emerg. Med. J. 2016, 33, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, L.J.H.; Ladelund, S.; Haupt, T.H.; Ellekilde, G.E.; Eugen-Olsen, J.; Andersen, O. Combining National Early Warning Score With Soluble Urokinase Plasminogen Activator Receptor (suPAR) Improves Risk Prediction in Acute Medical Patients. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 46, 1961–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, M.; Östling, G.; Smith, G.; Hamrefors, V.; Melander, O.; Hedblad, B.; Engström, G. Soluble Urokinase Plasminogen Activator Receptor. Stroke 2014, 45, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edsfeldt, A.; Nitulescu, M.; Grufman, H.; Grönberg, C.; Persson, A.; Nilsson, M.; Persson, M.; Björkbacka, H.; Gonçalves, I. Soluble Urokinase Plasminogen Activator Receptor is Associated With Inflammation in the Vulnerable Human Atherosclerotic Plaque. Stroke 2012, 43, 3305–3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iversen, E.; Houlind, M.B.; Kallemose, T.; Rasmussen, L.J.H.; Hornum, M.; Feldt-Rasmussen, B.; Hayek, S.S.; Andersen, O.; Eugen-Olsen, J. Elevated suPAR Is an Independent Risk Marker for Incident Kidney Disease in Acute Medical Patients. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shared Medicine Card. Available online: Https://Www.Danishhealthdata.Com/Find-Health-Data/,-w- (accessed on 26 November 2020).
- O’Mahony, D.; O’Sullivan, D.; Byrne, S.; O’Connor, M.N.; Ryan, C.; Gallagher, P. STOPP/START criteria for potentially inappropriate prescribing in older people: Version 2. Age Ageing 2014, 44, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministry of Health. Seponeringslisten 2020. Available online: Https://Www.Sst.Dk/-/Media/Udgivelser/2019/Seponeringslisten2020.Ashx?La=da&hash=3E27830D475F39794290E7E50BDFEA208F02644E (accessed on 29 November 2020). (In Danish)
| Parameter | Control Group (n = 33) | Intervention Group (n =34) | p Value | Total (n = 67) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (men), n (%) | 18 (55) | 20 (59) | 0.35 | 38 (57) |
| Age (years), mean (SD) | 73.3 (10.3) | 71.8 (14.2) | 0.91 | 72.5 (12.3) |
| Number of drugs, mean (SD) | 10.5 (4.0) | 9.3 (3.2) | 0.18 | 9.9 (3.7) |
| Regular drugs, mean (SD) | 8.8 (3.4) | 7.3 (3.1) | 0.063 | 8.0 (3.3) |
| Pro re nata drugs, mean (SD) | 1.9 (1.4) | 2.0 (1.5) | 0.78 | 1.9 (1.5) |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73m2), mean (SD) | 66.2 (18.5) | 68.9 (18.4) | 0.55 | 67.6 (18.4) |
| Comorbidities, mean (SD) | 4.5 (1.4) | 4.3 (1.4) | 0.56 | 4.4 (1.4) |
| Acute admission within 30 days, n (%) Acute admission within 90 days, n (%) Acute admission within 180 days, n (%) | 8 (23.2) 14 (42.4) 21 (63.6) | 3 (8.8) 9 (26.5) 13 (38.2) |
0.11 0.20 0.052 | 11 (16.4) 25 (34.3) 34 (50.7) |
| Control Group (n = 33) | Intervention Group (n =34) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of patients with ≥1 medication deprescribed, n (%) | 4 (12) | 19 (56) | <0.001 |
| Number of patients with ≥2 medication deprescribed, n (%) | 1 (3) | 9 (26) | 0.007 |
| Number of patients with ≥3 medication deprescribed, n (%) | 0 (0) | 4 (12) | 0.042 |
| Class and Medication | Frequency n (%) |
|---|---|
| Analgesics Paracetamol NSAID Gabapentin Cardiovascular Beta blockers Antihypertensives Statins Vasodilators Gastrointestinal Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) Stimulant laxatives Sedatives * Others Total | 14 (37.8) 5 (13.5) 4 (10.8) 2 (5.4) 9 (24.3) 4 (10.8) 2 (5.4) 1 (2.7) 1 (2.7) 5 (13.5) 3 (8.1) 2 (5.4) 3 (8.1) 6 (16.2) 37 (100) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aharaz, A.; Rasmussen, J.H.; McNulty, H.B.Ø.; Cyron, A.; Fabricius, P.K.; Bengaard, A.K.; Sejberg, H.R.C.; Simonsen, R.R.L.; Treldal, C.; Houlind, M.B. A Collaborative Deprescribing Intervention in a Subacute Medical Outpatient Clinic: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial. Metabolites 2021, 11, 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11040204
Aharaz A, Rasmussen JH, McNulty HBØ, Cyron A, Fabricius PK, Bengaard AK, Sejberg HRC, Simonsen RRL, Treldal C, Houlind MB. A Collaborative Deprescribing Intervention in a Subacute Medical Outpatient Clinic: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial. Metabolites. 2021; 11(4):204. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11040204
Chicago/Turabian StyleAharaz, Anissa, Jens Henning Rasmussen, Helle Bach Ølgaard McNulty, Arne Cyron, Pia Keinicke Fabricius, Anne Kathrine Bengaard, Hayley Rose Constance Sejberg, Rikke Rie Løvig Simonsen, Charlotte Treldal, and Morten Baltzer Houlind. 2021. "A Collaborative Deprescribing Intervention in a Subacute Medical Outpatient Clinic: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial" Metabolites 11, no. 4: 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11040204
APA StyleAharaz, A., Rasmussen, J. H., McNulty, H. B. Ø., Cyron, A., Fabricius, P. K., Bengaard, A. K., Sejberg, H. R. C., Simonsen, R. R. L., Treldal, C., & Houlind, M. B. (2021). A Collaborative Deprescribing Intervention in a Subacute Medical Outpatient Clinic: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial. Metabolites, 11(4), 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11040204