Novel Insights into Mice Multi-Organ Metabolism upon Exposure to a Potential Anticancer Pd(II)-Agent
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. 1H NMR Spectra of Aqueous and Lipophilic Metabolomes of Mouse Kidney, Liver, and Breast Tissue
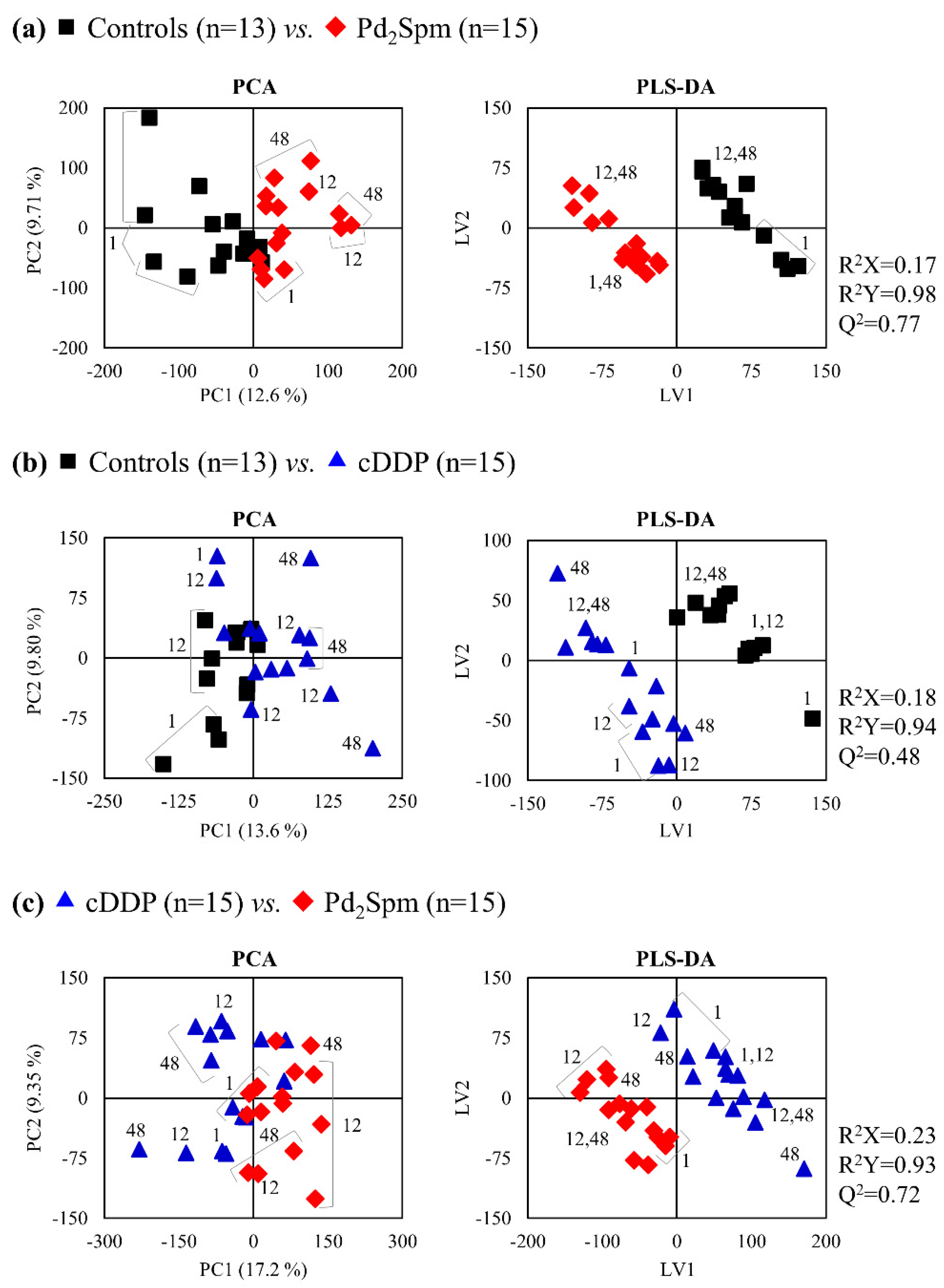
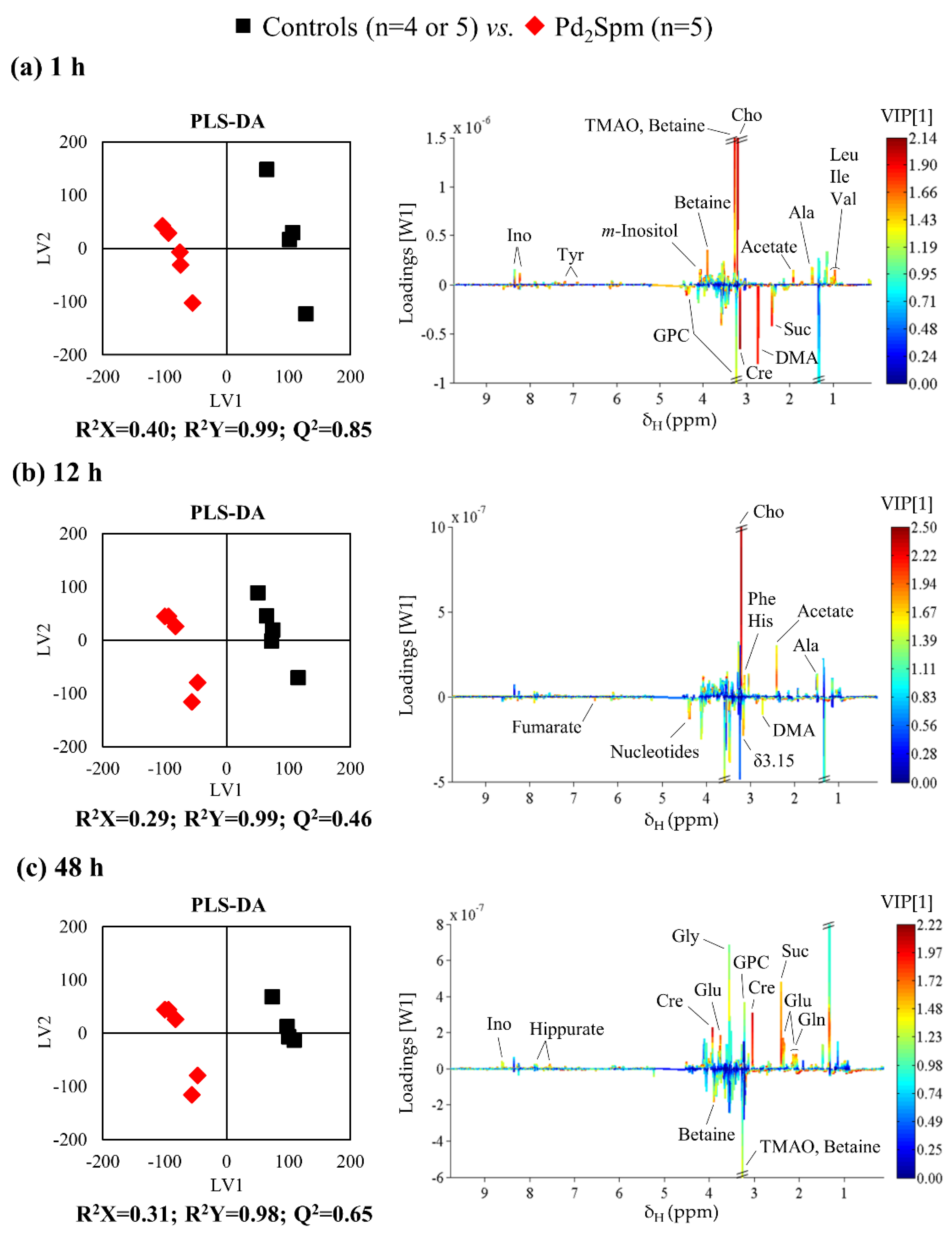
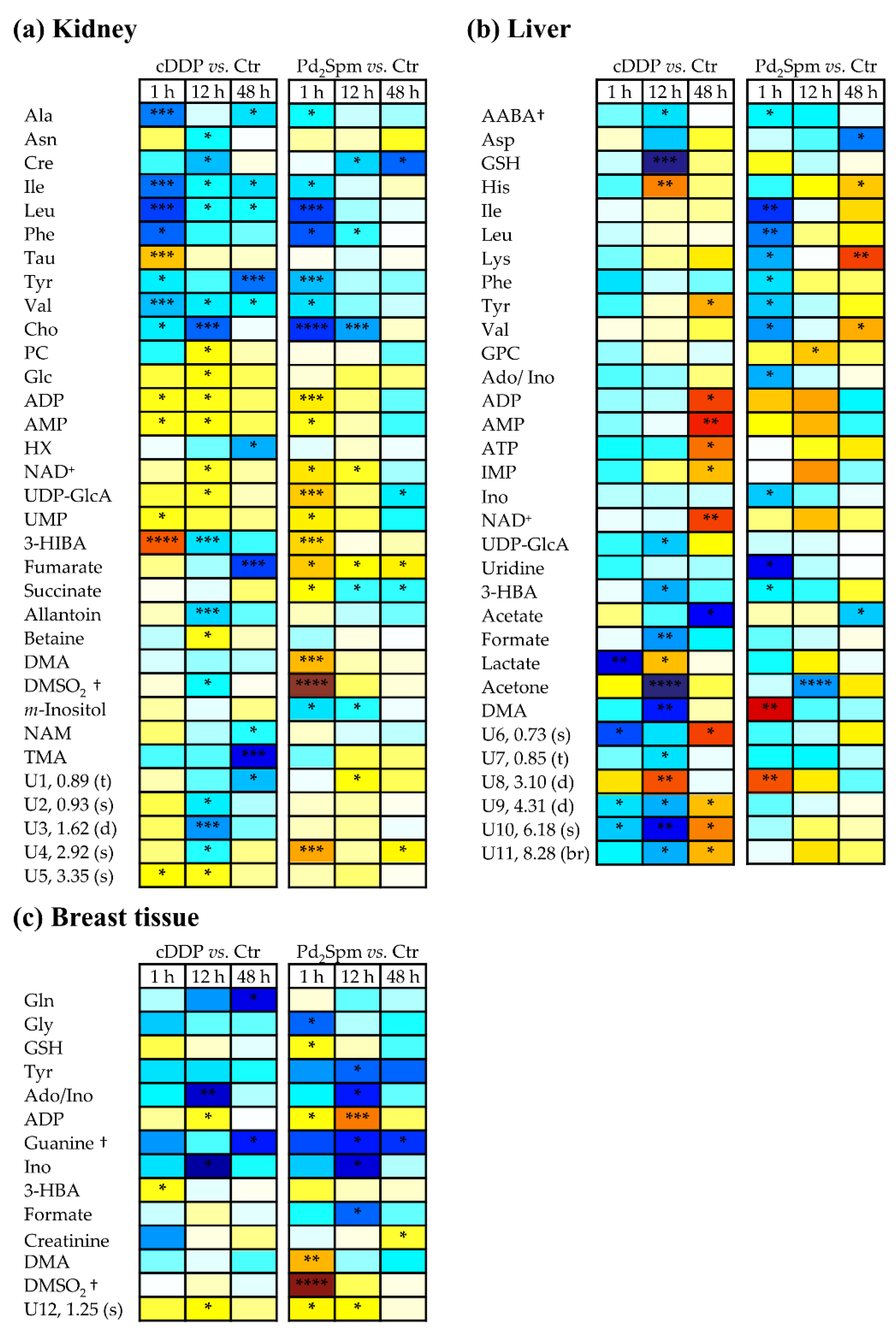
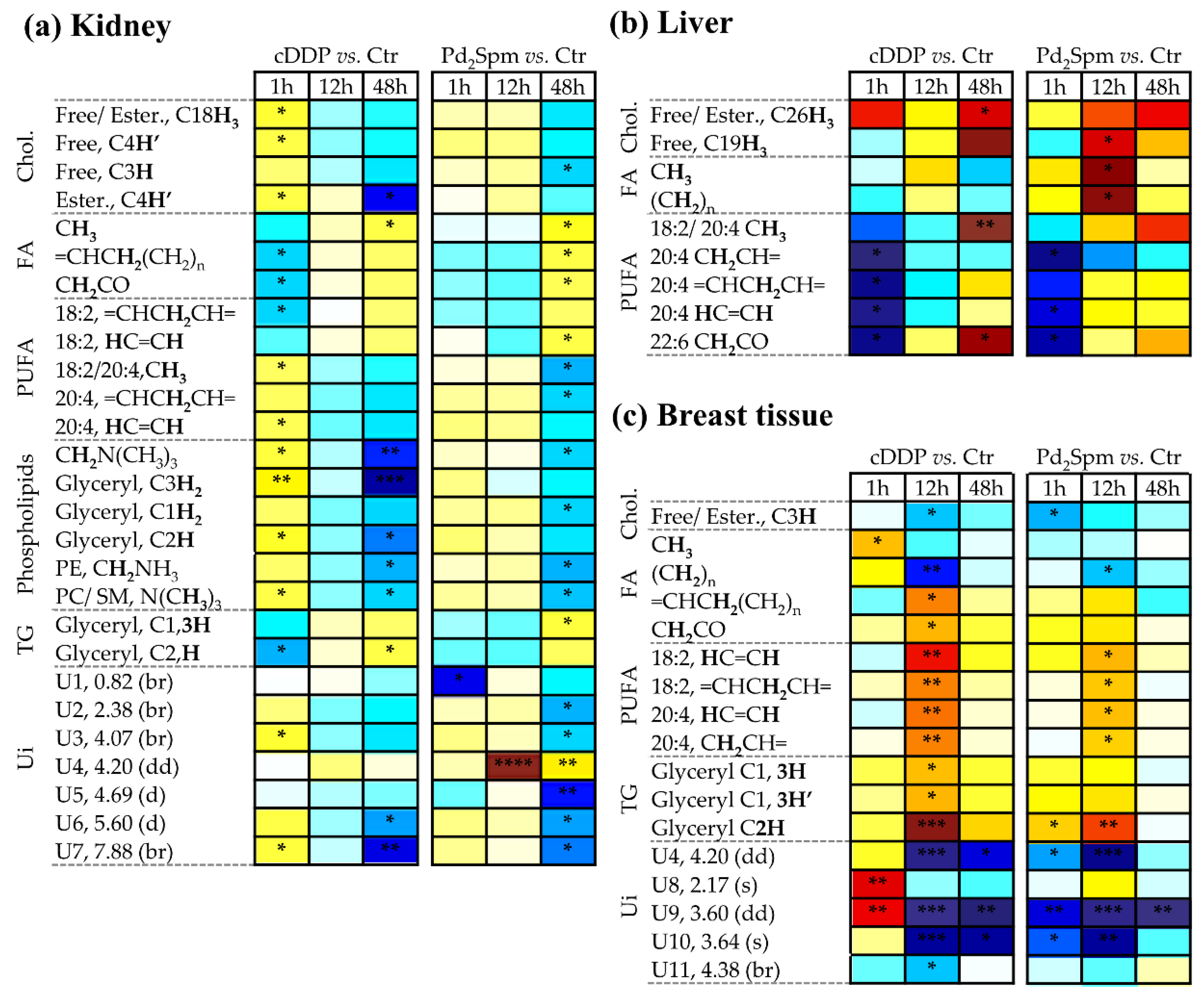
2.2. Impact of Pd2Spm on Kidney Metabolome
2.3. Impact of Pd2Spm on Liver Metabolome
2.4. Impact of Pd2Spm on Breast Tissue Metabolome
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Ethical Considerations
4.3. Animals
4.4. In vivo Experimental Procedures
4.5. Sample Preparation for NMR Analysis
4.6. NMR Spectroscopy
4.7. Data Processing and Statistics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Ethics Committee Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosenberg, B.; Van Camp, L.; Krigas, T. Inhibition of cell division in Escherichia coli by electrolysis products from a platinum electrode. Nature 1965, 205, 698–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, B.H.; Vancamp, L.; Trosko, J.E.; Mansour, V.H. Platinum compounds: A new class of potent antitumour agents. Nature 1969, 222, 385–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasari, S.; Tchounwou, P.B. Cisplatin in cancer therapy: Molecular mechanisms of action. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 740, 364–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raudenska, M.; Balvan, J.; Fojtu, M.; Gumulec, J.; Masarik, M. Unexpected therapeutic effects of cisplatin. Metallomics 2019, 11, 1182–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florea, A.-M.; Büsselberg, D. Cisplatin as an anti-tumor drug: Cellular mechanisms of activity, drug resistance and induced side effects. Cancers 2011, 3, 1351–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makovec, T. Cisplatin and beyond: Molecular mechanisms of action and drug resistance development in cancer chemotherapy. Radiol. Oncol. 2019, 53, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, C.S.; De Carvalho, A.L.M.B.; Lopes, R.P.; Marques, M.P.M. New strategies against prostate cancer—Pt(II)-based chemotherapy. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 4678–4687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcquity, R.J. Metal-based drugs. Sci. Prog. 2014, 97, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manohar, S.; Leung, N. Cisplatin nephrotoxicity: A review of the literature. J. Nephrol. 2018, 31, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana-Davila, R.; Szabo, A.; Arce-Lara, C.; Williams, C.D.; Kelley, M.J.; Whittle, J. Cisplatin versus carboplatin-based regimens for the treatment of patients with metastatic lung cancer. An analysis of Veterans Health Administration data. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2014, 9, 702–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokich, J. What Is the “Best” Platinum: Cisplatin, Carboplatin, or Oxaliplatin? Cancer Investig. 2001, 19, 756–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griesinger, F.; Korol, E.E.; Kayaniyil, S.; Varol, N.; Ebner, T.; Goring, S.M. Efficacy and safety of first-line carboplatin-versus cisplatin-based chemotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis. Lung Cancer 2019, 135, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, L.J.; Seabra, M.; Reis, E.; Girão da Cruz, M.T.; Pedroso de Lima, M.C.; Pereira, E.; Miranda, M.A.; Marques, M.P.M. Cytotoxic activity of metal complexes of biogenic polyamines: Polynuclear platinum(II) chelates. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 2917–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, M.P.M. Platinum and palladium polyamine complexes as anticancer agents: The structural factor. Hindawi 2013, 2013, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, T.J.; Araújo, R.; Vojtek, M.; Gonçalves-Monteiro, S.; Diniz, C.; De Carvalho, A.L.M.B.; Marques, M.P.M.; Gil, A.M. Multi-organ NMR metabolomics to assess in vivo overall metabolic impact of cisplatin in mice. Metabolites 2019, 9, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Castro, F.; Benedetti, M.; Del Coco, L.; Fanizzi, F.P. NMR-based metabolomics in metal-based drug research. Molecules 2019, 24, 2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndagi, U.; Mhlongo, N.; Soliman, M.E. Metal complexes in cancer therapy—an update from drug design perspective. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2017, 11, 599–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, P.V.; Desai, N.M.; Casari, I.; Massi, M.; Falasca, M. Metal-based antitumor compounds: Beyond cisplatin. Futur. Med. Chem. 2019, 11, 119–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiuza, S.M.; Holy, J.; De Carvalho, L.A.E.B.; Marques, M.P.M. Biologic activity of a dinuclear pd(II)-spermine complex toward human breast cancer. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2011, 77, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, T.M.; Fiuza, S.M.; Marques, M.P.M.; Persson, L.; Oredsson, S. Increased breast cancer cell toxicity by palladination of the polyamine analogue N1,N11-bis(ethyl)norspermine. Amino Acids 2013, 46, 339–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista de Carvalho, A.L.M.; Pilling, M.; Gardner, P.; Doherty, J.; Cinque, G.; Wehbe, K.; Kelley, C.; Batista de Carvalho, L.A.E.; Marques, M.P.M. Chemotherapeutic response to cisplatin-like drugs in human breast cancer cells probed by vibrational mi-crospectroscopy. Faraday Discuss. 2016, 187, 273–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Carvalho, A.L.M.B.; Medeiros, P.S.C.; Costa, F.M.; Ribeiro, V.P.; Sousa, J.B.; Diniz, C.; Marques, M.P.M. Anti-invasive and anti-proliferative synergism between docetaxel and a polynuclear pd-spermine agent. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vojtek, M.; Marques, M.P.M.; Ferreira, I.M.P.L.V.O.; Mota-Filipe, H.; Diniz, C. Anticancer activity of palladium-based com-plexes against triple negative breast cancer. Drug Discov. Today 2019, 24, 1044–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulukaya, E.; Ari, F.; Dimas, K.; Sarimahmut, M.; Guney, E.; Sakellaridis, N.; Guney, E.; Sakellaridis, N.; Yilmaz, V.T. Cell death-inducing effect of novel palladium(II) and platinum(II) complexes on non-small cell lung cancer cells in vitro. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 137, 1425–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunc, D.; Dere, E.; Karakas, D.; Cevatemre, B.; Yilmaz, V.T.; Ulukaya, E. Cytotoxic and apoptotic effects of the combination of palladium (II) 5,5-diethylbarbiturate complex with bis(2-pyridylmethyl)amine and curcumin on non small lung cancer cell lines. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 1717–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhangian, H.; Moghadam, E.M.; Divsalar, A.; Rahiminezhad, A. Anticancer activity of novel amino acid derivative of pal-ladium complex with phendione ligand against of human colon cancer cell line. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 22, 1055–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kacar, O.; Cevatemre, B.; Hatipoglu, I.; Arda, N.; Ulukaya, E.; Yilmaz, V.T.; Acilan, C. The role of cell cycle progression for the apoptosis of cancer cells induced by palladium(II)-saccharinate complexes of terpyridine. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 1770–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Icsel, C.; Yilmaz, V.T.; Aygun, M.; Cevatemre, B.; Alperd, P.; Ulukayad, E. Palladium(II) and platinum(II) saccharinate com-plexes with bis(diphenylphosphino)methane/ ethane: Synthesis, S-phase arrest and ROS mediated apoptosis in human colon cancer cells. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 11397–11410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, S.; Chowdhury, S.; Chattapadhyay, A.P.; Bhattacharya, A. Spectroscopic, cytotoxic and DFT studies of a luminescent palladium(II) complex of a hydrazone ligand that induces apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2011, 373, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentini, A.; Conforti, F.; Crispini, A.; De Martino, A.; Condello, R.; Stellitano, C.; Rotilio, G.; Ghedini, M.; Federici, G.; Ber-nardini, S.; et al. Synthesis, oxidant properties, and antitumoral effects of a heteroleptic palladium (II) complex of curcumin on human prostate cancer cells. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Megharbel, S.M.; Hegab, M.S.; Manaaa, E.-S.A.; Al-Humaidi, J.Y.; Refatag, M.S. Synthesis and physicochemical characterizations of coordination between palladium(II) metal ions with floroquinolone drugs as medicinal model against cancer cells: Novel metallopharmaceuticals. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 9709–9719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Kataoka, H.; Yano, S.; Ohi, H.; Kawamoto, K.; Shibahara, T.; Mizoshita, T.; Mori, Y.; Tanida, S.; Kamiya, T.; et al. Anti-cancer effects of newly developed chemotherapeutic agent, glycoconjugated palladium (II) complex, against cisplatin-resistant gastric cancer cells. BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.-T.; Smith, C.E.; Kwok, K.S.; Chen, J.; Kong, H.; Yang, H. Functionalized ultrathin palladium nanosheets as patches for HepG2 cancer cells. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 14171–14174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Ranninger, C.; Zamora, F.; Masaguer, J.; Perez, J.; Gonzalez, V.M.; Alonso, C. Palladium(II) compounds of putrescine and spermine. Synthesis, characterization, and DNA-binding and antitumor properties. J. Inorg. Biochem. 1993, 52, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, A.; Fiuza, S.; Goncalves, M.; De Carvalho, L.A.E.B.; Marques, M.P.; Urbano, A. Effect of the metal center on the antitumor activity of the analogous dinuclear spermine chelates (PdCl2)2(spermine) and (PtCl2)2(spermine). Lett. Drug Des. Discov. 2007, 4, 460–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tummala, R.; Diegelman, P.; Fiuza, S.M.; Batista de Carvalho, L.A.; Marques, M.P.; Kramer, D.L.; Clark, K.; Vujcic, S.; Porter, C.W.; Pendyala, L. Characterization of Pt-, Pd-spermine complexes for their effect on polyamine pathway and cisplatin re-sistance in A2780 ovarian carcinoma cells. Oncol. Rep. 2010, 24, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, P.; Majumder, P.; Halder, S.; Drew, M.G.B.; Bhattacharya, S.; Mazumder, S. Comparative anti-proliferative activity of some new 2-(arylazo)phenolate–palladium (II) complexes and cisplatin against some human cancer cell lines. Free Radic. Res. 2015, 49, 253–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agostinelli, E.; Marques, M.P.M.; Calheiros, R.; Gil, F.P.S.C.; Tempera, G.; Viceconte, N.; Battaglia, V.; Grancara, S.; Toninello, A. Polyamines: Fundamental characters in chemistry and biology. Amino Acids 2010, 38, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corduneanu, O.; Chiorcea-Paquim, A.-M.; Diculescu, V.; Fiuza, S.M.; Marques, M.P.M.; Oliveira-Brett, A.M. DNA Interaction with palladium chelates of biogenic polyamines using atomic force microscopy and voltammetric characterization. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 1245–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corduneanu, O.; Chiorcea-Paquim, A.-M.; Fiuza, S.M.; Marques, M.P.M.; Oliveira-Brett, A.M. Polynuclear palladium com-plexes with biogenic polyamines: AFM and voltammetric characterization. Bioelectrochemistry 2010, 78, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, M.P.M.; De Carvalho, A.L.M.B.; Mamede, A.P.; Dopplapudi, A.; Rudić, S.; Tyagi, M.; Sakai, V.G.; De Carvalho, L.A.E.B. A new look into the mode of action of metal-based anticancer drugs. Molecules 2020, 25, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiuza, S.M.; Amado, A.M.; Parker, S.F.; Marques, M.P.M.; De Carvalho, L.A.E.B. Conformational insights and vibrational study of a promising anticancer agent: The role of the ligand in Pd(II)–amine complexes. New J. Chem. 2015, 39, 6274–6283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, M.P.M.; Batista de Carvalho, A.L.M.; Mamede, A.P.; Santos, I.P.; Garcia Sakai, V.; Dopplapudi, A.; Cinque, G.; Wolna, M.; Gardner, P.; Batista de Carvalho, L.A.E. Chemotherapeutic targets in osteosarcoma—Insights from synchrotron-microFTIR and quasi-elastic neutron scattering. J. Phys. Chem. B 2019, 123, 6968–6979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, A.S.; De Carvalho, A.L.M.B.; Lamego, I.; Marques, M.P.M.; Gil, A.M. Cytotoxicity of platinum and palladium chelates against osteosarcoma. ChemistrySelect 2020, 5, 5993–6000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, T.J.; Martins, A.S.; Marques, M.P.M.; Gil, A.M. Metabolic aspects of palladium(II) potential anti-cancer drugs. Front. Oncol. Cancer Metab. 2020, 10, 590970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Čuperlović-Culf, M.; Barnett, D.A.; Culf, A.S.; Chute, I. Cell culture metabolomics: Applications and future directions. Drug Discov. Today 2010, 15, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattner, J.; Bathe, O.F. Monitoring for response to antineoplastic drugs: The potential of a metabolomic approach. Metabolites 2017, 7, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irie, M.; Hayakawa, E.; Fujimura, Y.; Honda, Y.; Setoyama, D.; Wariishi, H.; Hyodo, F.; Miura, D. Analysis of spatiotemporal metabolomic dynamics for sensitively monitoring biological alterations in cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 496, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boudonck, K.J.; Mitchell, M.W.; Német, L.; Keresztes, L.; Nyska, A.; Shinar, D.; Rosenstock, M. Discovery of metabolomics biomarkers for early detection of nephrotoxicity. Toxicol. Pathol. 2009, 37, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezaki, T.; Nishiumi, S.; Azuma, T.; Yoshida, M. Metabolomics for the early detection of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. Toxicol. Res. 2017, 6, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamego, I.; Marques, M.P.M.; Duarte, I.F.; Martins, A.S.; Oliveira, H.; Gil, A.M. Impact of the Pd2Spermine chelate on osteosarcoma metabolism: An NMR metabolomics study. J. Proteome Res. 2017, 16, 1773–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezeshki, Z.; Khosravi, A.; Nekuei, M.; Khoshnood, S.; Zandi, E.; Eslamian, M.; Talebi, A.; Emami, S.N.; Nematbakhsh, M. Time course of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity and hepatotoxicity. J. Nephropathol. 2017, 6, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckonert, O.; Monnerjahn, J.; Bonk, U.; Leibfritz, D. Visualizing metabolic changes in breast-cancer tissue using1H-NMR spectroscopy and self-organizing maps. NMR Biomed. 2003, 16, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.-C.; Dai, Y.-Q.; Hui, R.-R.; Hua, J.; Chen, H.-J.; Luo, Q.-Y.; Li, J.-X. NMR-based metabonomic approach on the toxicological effects of a Cimicifuga triterpenoid. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2012, 32, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Y.S.; Liang, H.-J.; Chung, M.-H.; Lin, M.-H.; Lin, C.-Y. NMR- and MS-based metabolomics: Various organ responses following naphthalene intervention. Mol. BioSyst. 2014, 10, 1918–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Chen, J.-Q.; Huang, W.-Q.; Li, W.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Z.-J.; Xu, F.-G. Renal medulla is more sensitive to cisplatin than cortex revealed by untargeted mass spectrometry-based metabolomics in rats. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, srep44804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janeiro, M.H.; Ramírez, M.J.; Milagro, F.I.; Martínez, J.A.; Solas, M. Implication of Trimethylamine N-Oxide (TMAO) in disease: Potential biomarker or new therapeutic target. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Slupsky, C.M. Metabolic fingerprint of dimethyl sulfone (DMSO2) in microbial–mammalian Co-metabolism. J. Proteome Res. 2014, 13, 5281–5292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Codina, G.; Caubet, A.; López, C.; Moreno, V.; Molins, E. Palladium(II) and platinum(II) polyamine complexes: X-ray crystal structures of (SP-4-2) chloro{N-[(3-amino-κN)propyl]propane-1,3-diamine-κN,κN′}palladium(1+) tetrachloropalladate (2–) (2:1) and (R,S)-tetrachloro[μ-(spermine)]dipalladium(II) (={μ {N,N′-Bis[(3-amino-κN)propyl]butane-1,4-diamine-κN:κN′}}tetrachlorodipalladium). Helv. Chim. Acta 1999, 82, 1025–1037. [Google Scholar]
- Kilkenny, C.; Browne, W.J.; Cuthill, I.C.; Emerson, M.; Altman, D.G. Improving bioscience research reporting: The ARRIVE guidelines for reporting animal research. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckonert, O.; Keun, H.C.; Ebbels, T.M.D.; Bundy, J.G.; Holmes, E.; Lindon, J.C.; Nicholson, J.K. Metabolic profiling, metabolomic and metabonomic procedures for NMR spectroscopy of urine, plasma, serum and tissue extracts. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 2692–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.Y.; Wu, H.; Tjeerdema, R.S.; Viant, M.R. Evaluation of metabolite extraction strategies from tissue samples using NMR metabolomics. Metabolomics 2007, 3, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Belle, J.E.; Harris, N.G.; Williams, S.R.; Bhakoo, K.K. A comparison of cell and tissue extraction techniques using high-resolution1H-NMR spectroscopy. NMR Biomed. 2002, 15, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Southam, A.D.; Hines, A.; Viant, M.R. High-throughput tissue extraction protocol for NMR- and MS-based metabolomics. Anal. Biochem. 2008, 372, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wishart, D.S.; Feunang, Y.D.; Marcu, A.; Guo, A.C.; Liang, K.; Vázquez-Fresno, R.; Sajed, T.; Johnson, D.; Li, C.; Karu, N.; et al. HMDB 4.0—The human metabolome database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D608–D617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berben, L.; Sereika, S.M.; Engberg, S. Effect size estimation: Methods and examples. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2012, 49, 1039–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Methodol. 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Tissue | Aqueous Extracts | Lipophilic Extracts | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cDDP | Pd2Spm | cDDP | Pd2Spm | |||||||||
| 1 h | 12 h | 48 h | 1 h | 12 h | 48 h | 1 h | 12 h | 48 h | 1 h | 12 h | 48 h | |
| Kidney | 0.81 | 0.73 | 0.54 | 0.85 | 0.46 | 0.65 | 0.55 | 0.37 | 0.96 | 0.45 | 0.66 | 0.76 |
| Liver | 0.42 | 0.70 | 0.52 | 0.68 | 0.74 | 0.33 | 0.79 | <0 | 0.65 | 0.14 | 0.44 | 0.30 |
| Breast tissue | <0 | 0.54 | 0.54 | 0.43 | 0.31 | 0.59 | 0.59 | 0.54 | 0.31 | 0.30 | 0.47 | ≈0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carneiro, T.J.; Araújo, R.; Vojtek, M.; Gonçalves-Monteiro, S.; Diniz, C.; Batista de Carvalho, A.L.M.; Marques, M.P.M.; Gil, A.M. Novel Insights into Mice Multi-Organ Metabolism upon Exposure to a Potential Anticancer Pd(II)-Agent. Metabolites 2021, 11, 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11020114
Carneiro TJ, Araújo R, Vojtek M, Gonçalves-Monteiro S, Diniz C, Batista de Carvalho ALM, Marques MPM, Gil AM. Novel Insights into Mice Multi-Organ Metabolism upon Exposure to a Potential Anticancer Pd(II)-Agent. Metabolites. 2021; 11(2):114. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11020114
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarneiro, Tatiana J., Rita Araújo, Martin Vojtek, Salomé Gonçalves-Monteiro, Carmen Diniz, Ana L. M. Batista de Carvalho, M. Paula M. Marques, and Ana M. Gil. 2021. "Novel Insights into Mice Multi-Organ Metabolism upon Exposure to a Potential Anticancer Pd(II)-Agent" Metabolites 11, no. 2: 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11020114
APA StyleCarneiro, T. J., Araújo, R., Vojtek, M., Gonçalves-Monteiro, S., Diniz, C., Batista de Carvalho, A. L. M., Marques, M. P. M., & Gil, A. M. (2021). Novel Insights into Mice Multi-Organ Metabolism upon Exposure to a Potential Anticancer Pd(II)-Agent. Metabolites, 11(2), 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11020114









