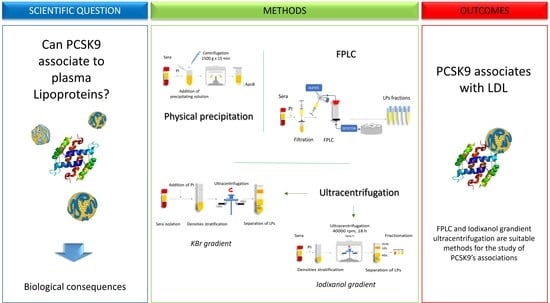
The Association of Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9 to Plasma Low-Density Lipoproteins: An Evaluation of Different Methods
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
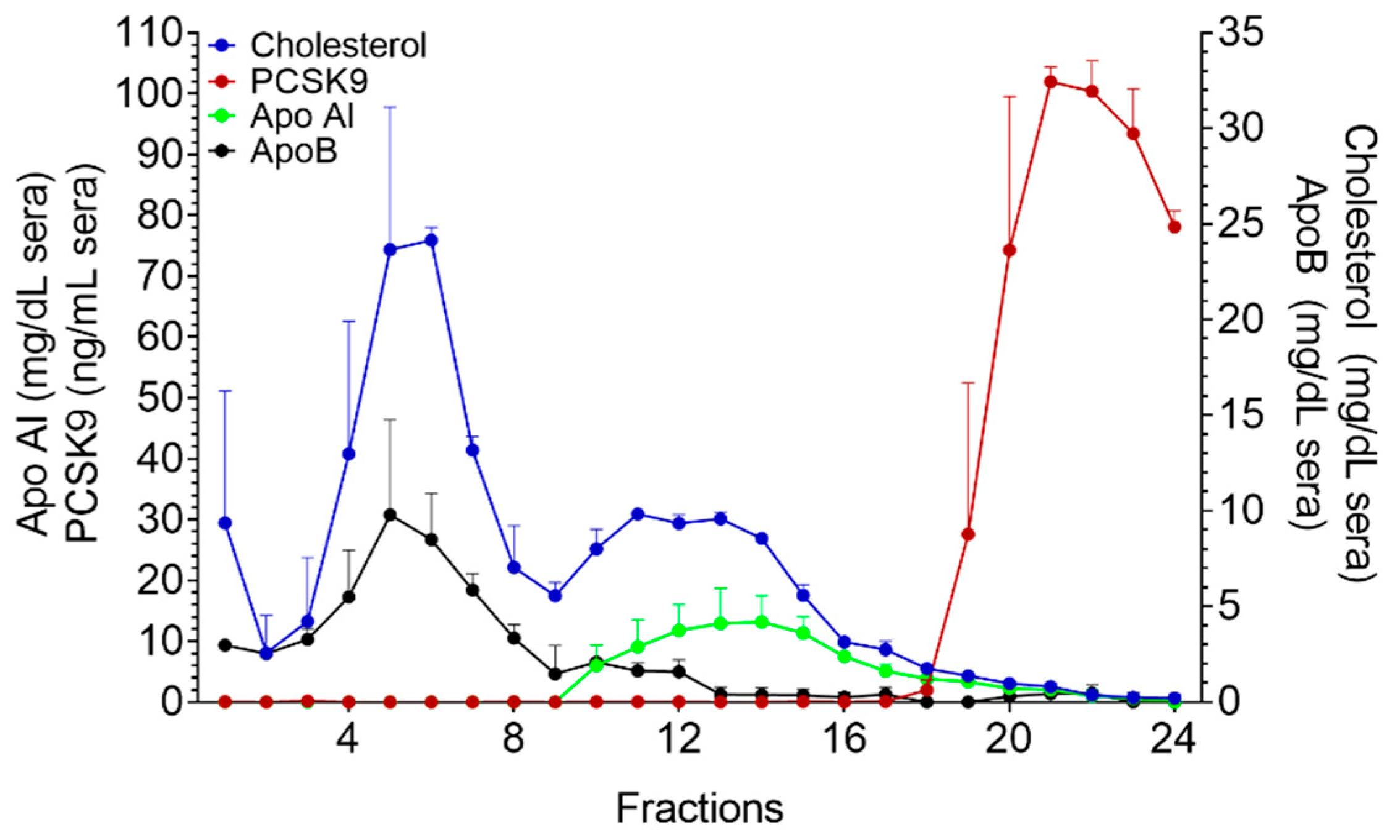
2.1. KBr-Based Methods
2.2. Precipitation of ApoB-LPs with Phosphotungstic Acid and MgCl2
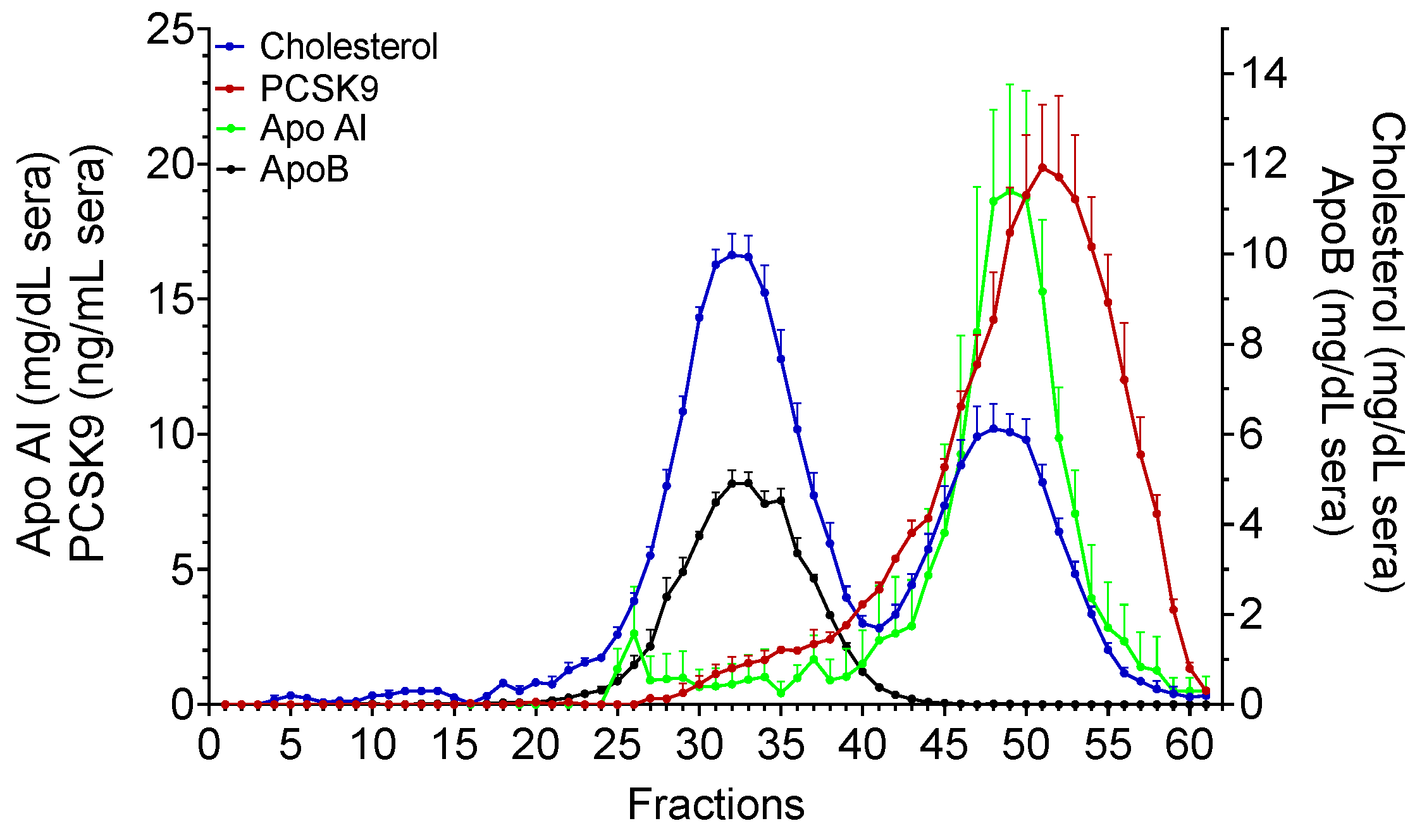
2.3. Fast Protein Liquid Chromatography
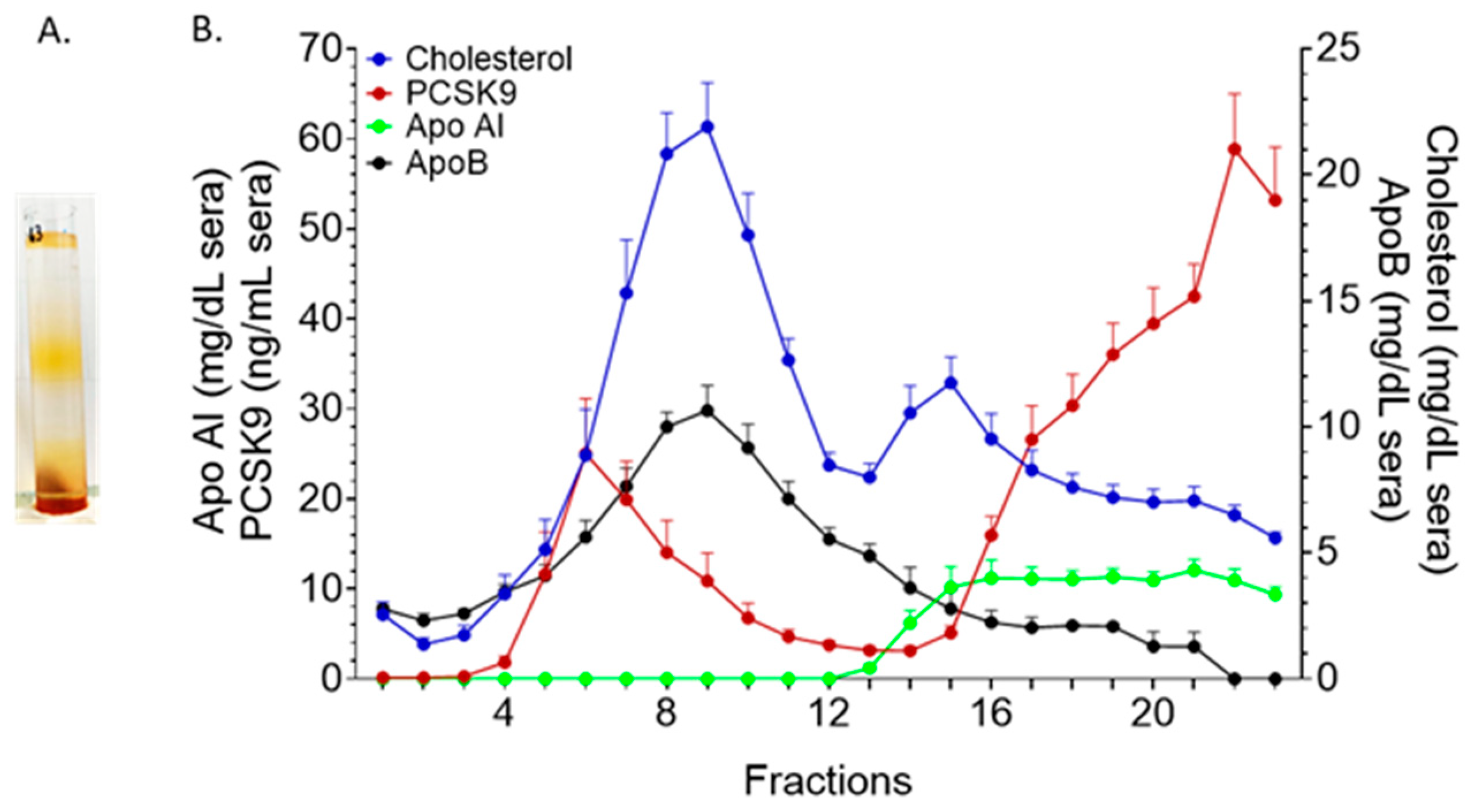
2.4. Iodixanol Gradient Ultracentrifugation (OptiPrep)
2.5. PCSK9 Associates with ApoB-LPs with Its Active Form
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Subjects and Samples
5.2. KBr Gradient Ultracentrifugation
5.3. Phosphotungstic Acid Precipitation of ApoB-LPs
5.4. Fast Protein Liquid Chromatography (FPLC)
5.5. Iodixanol Density Gradient Ultracentrifugation (OptiPrep)
5.6. Immunoblot of OptiPrep Fractions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Borén, J.; Chapman, M.J.; Krauss, R.M.; Packard, C.J.; Bentzon, J.F.; Binder, C.J.; Daemen, M.J.; Demer, L.L.; Hegele, R.A.; Nicholls, S.J.; et al. Low-density lipoproteins cause atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: Pathophysiological, genetic, and therapeutic insights: A consensus statement from the European Atherosclerosis Society Consensus Panel. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 2313–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cholesterol Treatment Trialists’ (CTT) Collaboration. Efficacy and safety of more intensive lowering of LDL cholesterol: A meta-analysis of data from 170 000 participants in 26 randomised trials. Lancet 2010, 376, 1670–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anderson, R.G.; Goldstein, J.L.; Brown, M.S. Localization of low density lipoprotein receptors on plasma membrane of normal human fibroblasts and their absence in cells from a familial hypercholesterolemia homozygote. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1976, 73, 2434–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Malvandi, A.M.; Canclini, L.; Alliaj, A.; Magni, P.; Zambon, A.; Catapano, A.L. Progress and prospects of biological approaches targeting PCSK9 for cholesterol-lowering, from molecular mechanism to clinical efficacy. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2020, 20, 1477–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seidah, N.; Prat, A.; Pirillo, A.; Catapano, A.L.; Norata, G.D. Novel strategies to target proprotein convertase subtilisin kexin 9: Beyond monoclonal antibodies. Cardiovasc. Res. 2019, 115, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kosenko, T.; Golder, M.; Leblond, G.; Weng, W.; Lagace, T.A. Low Density Lipoprotein Binds to Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type-9 (PCSK9) in Human Plasma and Inhibits PCSK9-mediated Low Density Lipoprotein Receptor Degradation. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 8279–8288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tavori, H.; Giunzioni, I.; Linton, M.F.; Fazio, S. Loss of Plasma Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin 9 (PCSK9) After Lipoprotein Apheresis. Circ. Res. 2013, 113, 1290–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luo, Y.; Warren, L.; Xia, D.; Jensen, H.; Sand, T.; Petras, S.; Qin, W.; Miller, K.S.; Hawkins, J. Function and distribution of circulating human PCSK9 expressed extrahepatically in transgenic mice. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, 1581–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tavori, H.; Fan, D.; Blakemore, J.L.; Yancey, P.G.; Ding, L.; Linton, M.F.; Fazio, S. Serum Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9 and Cell Surface Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor. Circulation 2013, 127, 2403–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tavori, H.; Christian, D.; Minnier, J.; Plubell, D.; Shapiro, M.D.; Yeang, C.; Giunzioni, I.; Croyal, M.; Duell, P.B.; Lambert, G.; et al. PCSK9 Association With Lipoprotein(a). Circ. Res. 2016, 119, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruscica, M.; Simonelli, S.; Botta, M.; Ossoli, A.; Lupo, M.G.; Magni, P.; Corsini, A.; Arca, M.; Pisciotta, L.; Veglia, F.; et al. Plasma PCSK9 levels and lipoprotein distribution are preserved in carriers of genetic HDL disorders. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2018, 1863, 991–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, D.; Yancey, P.G.; Qiu, S.; Ding, L.; Weeber, E.J.; Linton, M.F.; Fazio, S. Self-Association of Human PCSK9 Correlates with Its LDLR-Degrading Activity. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 1631–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Havel, R.J.; Eder, H.A.; Bragdon, J.H. The Distribution and Chemical Composition of Ultracentrifugally Separated Lipoproteins in Human Serum. J. Clin. Investig. 1955, 34, 1345–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alborn, W.E.; Cao, G.; Careskey, H.E.; Qian, Y.-W.; Subramaniam, D.R.; Davies, J.; Conner, E.M.; Konrad, R.J. Serum Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin Kexin Type 9 Is Correlated Directly with Serum LDL Cholesterol. Clin. Chem. 2007, 53, 1814–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yuana, Y.; Levels, J.; Grootemaat, A.; Sturk, A.; Nieuwland, R. Co-isolation of extracellular vesicles and high-density lipoproteins using density gradient ultracentrifugation. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2014, 3, 23262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burstein, M.; Scholnick, H.; Morfin, R. Rapid method for the isolation of lipoproteins from human serum by precipitation with polyanions. J. Lipid Res. 1970, 11, 583–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murdoch, S.; Breckenridge, W. Development of a Density Gradient Ultracentrifugation Technique for the Resolution of Plasma Lipoproteins which Avoids Apo E Dissociation. Anal. Biochem. 1994, 222, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norata, G.D.; Tibolla, G.; Catapano, A.L. Targeting PCSK9 for Hypercholesterolemia. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2014, 54, 273–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Parameter | Men (n = 6) | Women (n = 13) |
|---|---|---|
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 182 ± 15 | 168 ± 5 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 96 ± 29 | 74 ± 7 |
| LDL-cholesterol (mg/dL) | 105 ± 11 | 103 ± 5 |
| HDL-cholesterol (mg/dL) | 58 ± 2 | 56 ± 3 |
| PCSK9 (ng/mL) | 380 ± 40 | 300 ± 13 |
| Material | 14% OptiPrep-Serum Density | 10% OptiPrep Density | 8% OptiPrep Density |
|---|---|---|---|
| OptiPrepTM | 1.28 mL | 0.42 mL | 0.33 mL |
| Trizma base 10 mM pH 7.4 | 1.42 mL | 2.08 mL | 2.17 mL |
| Serum | 2.8 mL | - | - |
| Total Volume | 5.5 mL | 2.5 mL | 2.5 mL |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Canclini, L.; Malvandi, A.M.; Uboldi, P.; Jabnati, N.; Grigore, L.; Zambon, A.; Baragetti, A.; Catapano, A.L. The Association of Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9 to Plasma Low-Density Lipoproteins: An Evaluation of Different Methods. Metabolites 2021, 11, 861. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11120861
Canclini L, Malvandi AM, Uboldi P, Jabnati N, Grigore L, Zambon A, Baragetti A, Catapano AL. The Association of Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9 to Plasma Low-Density Lipoproteins: An Evaluation of Different Methods. Metabolites. 2021; 11(12):861. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11120861
Chicago/Turabian StyleCanclini, Laura, Amir Mohammad Malvandi, Patrizia Uboldi, Najoua Jabnati, Liliana Grigore, Alberto Zambon, Andrea Baragetti, and Alberico Luigi Catapano. 2021. "The Association of Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9 to Plasma Low-Density Lipoproteins: An Evaluation of Different Methods" Metabolites 11, no. 12: 861. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11120861
APA StyleCanclini, L., Malvandi, A. M., Uboldi, P., Jabnati, N., Grigore, L., Zambon, A., Baragetti, A., & Catapano, A. L. (2021). The Association of Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9 to Plasma Low-Density Lipoproteins: An Evaluation of Different Methods. Metabolites, 11(12), 861. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11120861