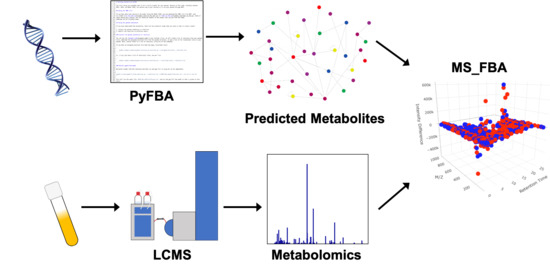
Towards Predicting Gut Microbial Metabolism: Integration of Flux Balance Analysis and Untargeted Metabolomics
Abstract
1. Introduction
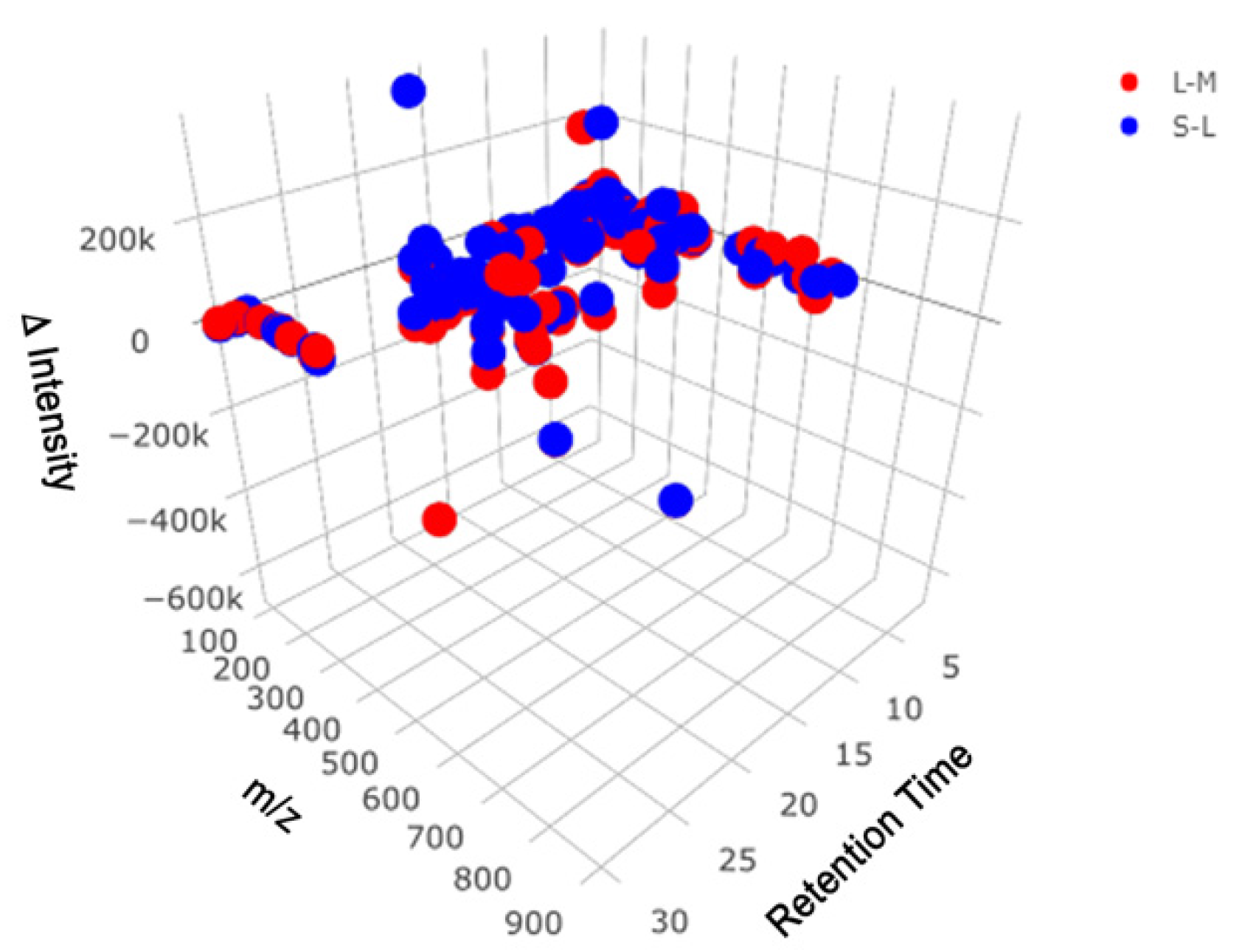
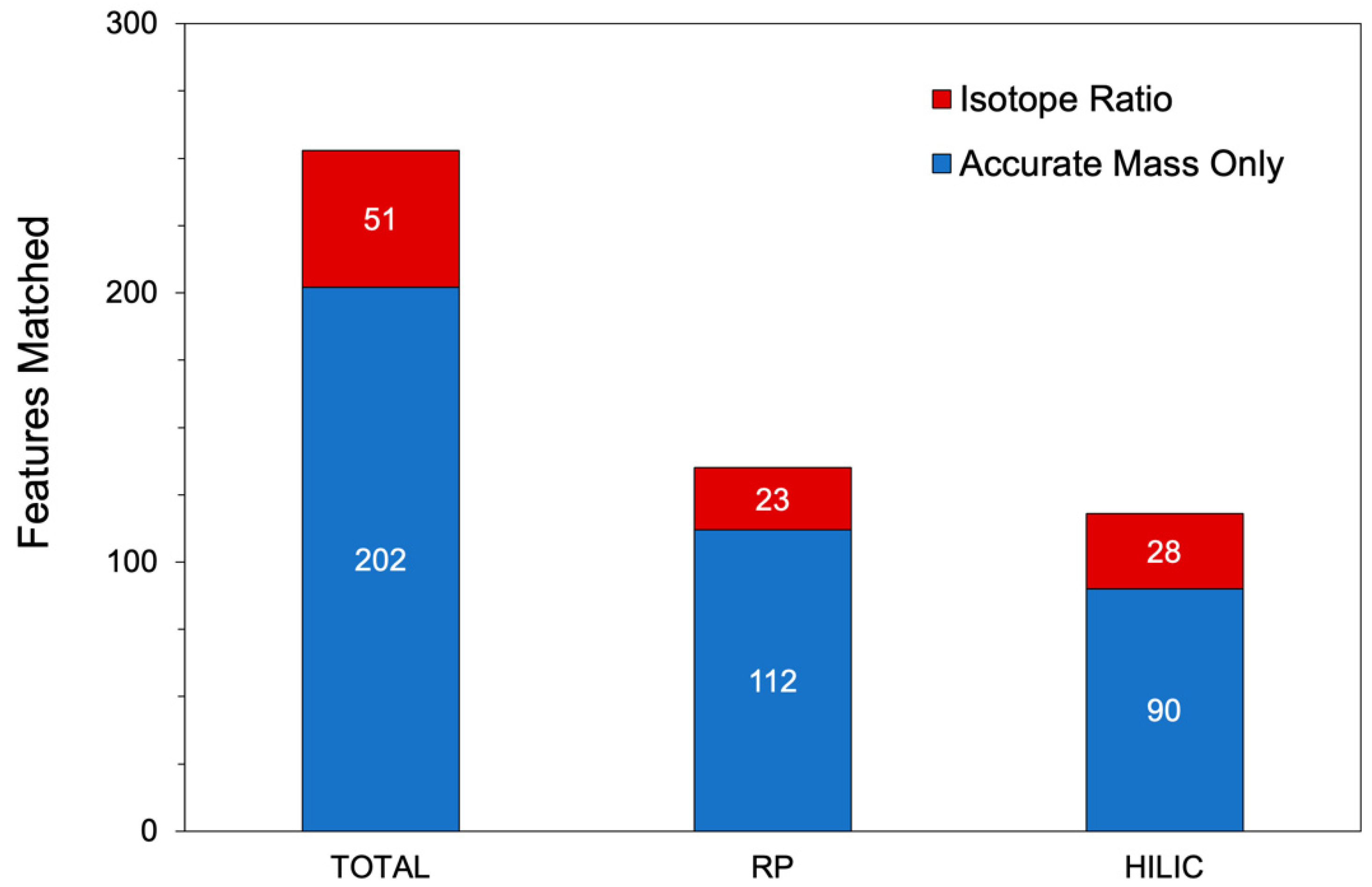
2. Results
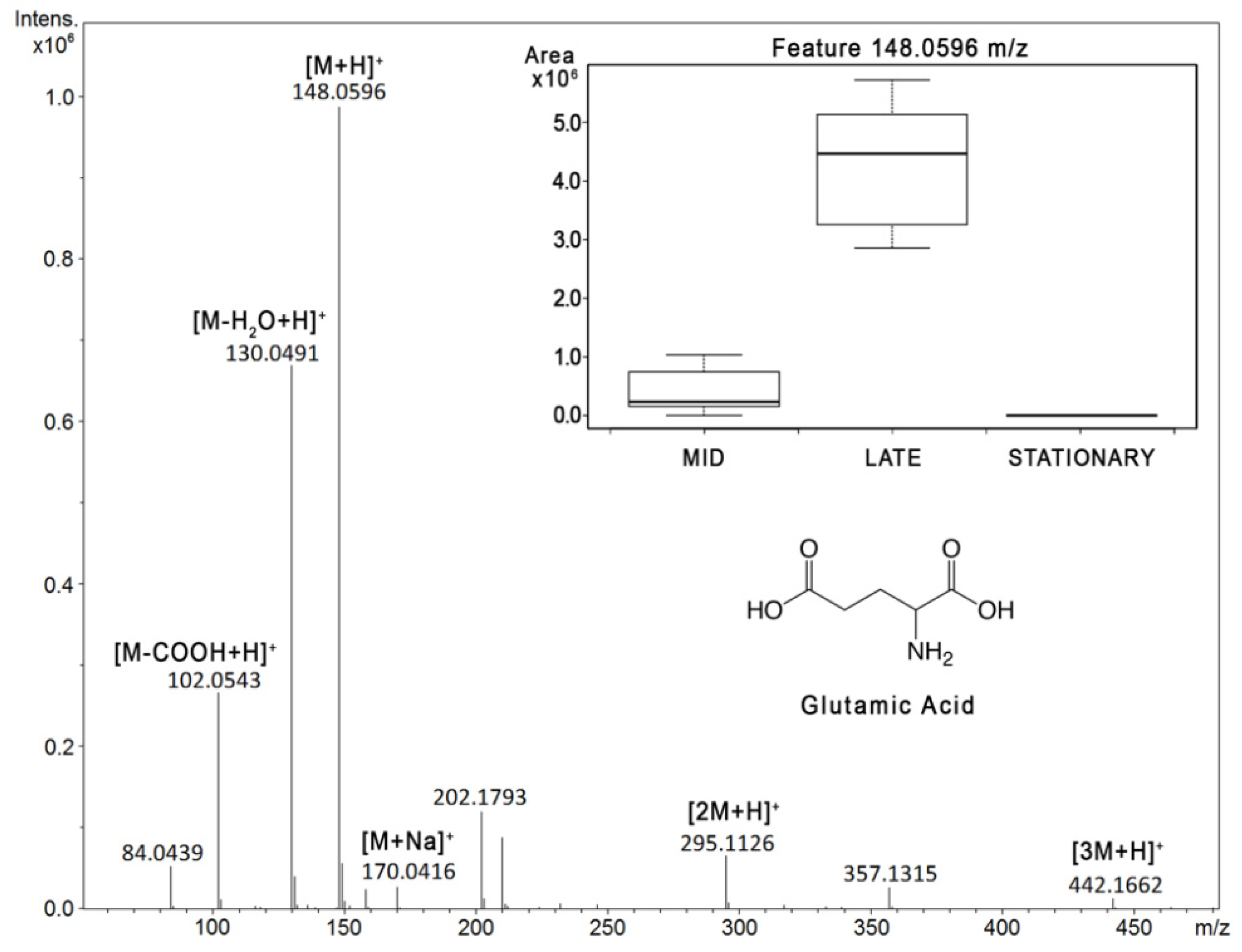
2.1. Reverse Phase Results
2.2. HILIC Results
3. Discussion
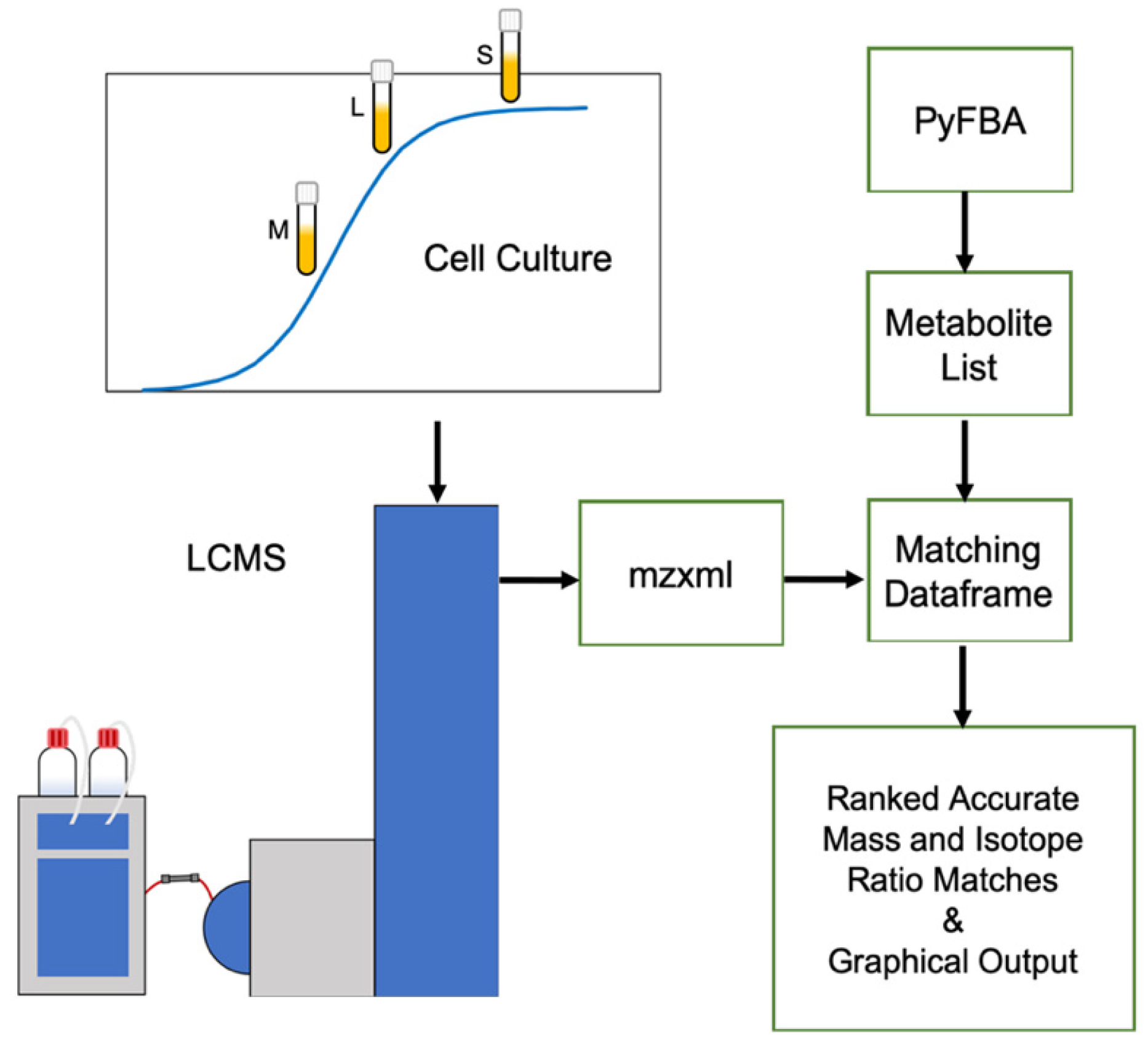
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Culturing and Sample Preparation
4.2. LCMS Conditions
4.3. XCMS Online Feature Detection
4.4. PyFBA Flux Balance Analysis
4.5. Metabolite Prediction for Metabolomics Integration
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Belkaid, Y.; Hand, T.W. Role of the microbiota in immunity and inflammation. Cell 2014, 157, 121–141. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Wang, P.; Wang, P.; Hu, X.; Chen, F. The gut microbiota: A treasure for human health. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 1210–1224. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Magnúsdóttir, S.; Thiele, I. Modeling metabolism of the human gut microbiome. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2018, 51, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ji, B.; Nielsen, J. From next-generation sequencing to systematic modeling of the gut microbiome. Front. Genet. 2015, 6, 219. [Google Scholar]
- Palsson, B.Ø.; Varma, A. Metabolic Flux Balancing: Basic Concepts, Scientific and Practical Use. Biotechnology 1994, 12, 994–998. [Google Scholar]
- Cuevas, D.A.; Edwards, R.A. PMAnalyzer: A new web interface for bacterial growth curve analysis. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 1905–1906. [Google Scholar]
- More, T.; RoyChoudhury, S.; Gollapalli, K.; Patel, S.K.; Gowda, H.; Chaudhury, K.; Rapole, S. Metabolomics and its integration with systems biology: PSI 2014 conference panel discussion report. J. Proteom. 2015, 127, 73–79. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, S.; Michalski, A.; Raether, O.; Lubeck, M.; Kaspar, S.; Goedecke, N.; Baessmann, C.; Hornburg, D.; Meier, F.; Paron, I.; et al. The impact II, a very high-resolution quadrupole time-of-flight instrument (QTOF) for deep shotgun proteomics. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2015, 14, 2014–2029. [Google Scholar]
- Tsugawa, H.; Cajka, T.; Kind, T.; Ma, Y.; Higgins, B.; Ikeda, K.; Kanazawa, M.; Vandergheynst, J.; Fiehn, O.; Arita, M. MS-DIAL: Data-independent MS/MS deconvolution for comprehensive metabolome analysis. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 523–526. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, Z.; Tsugawa, H.; Wohlgemuth, G.; Mehta, S.; Mueller, M.; Zheng, Y.; Ogiwara, A.; Meissen, J.; Showalter, M.; Takeuchi, K.; et al. Identifying metabolites by integrating metabolome databases with mass spectrometry cheminformatics. Nat. Methods 2018, 15, 53–56. [Google Scholar]
- Chong, J.; Wishart, D.S.; Xia, J. Using MetaboAnalyst 4.0 for Comprehensive and Integrative Metabolomics Data Analysis. Curr. Protoc. Bioinforma. 2019, 68, e86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pluskal, T.; Castillo, S.; Villar-Briones, A.; Orešič, M. MZmine 2: Modular framework for processing, visualizing, and analyzing mass spectrometry-based molecular profile data. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Carver, J.J.; Phelan, V.V.; Sanchez, L.M.; Garg, N.; Peng, Y.; Nguyen, D.D.; Watrous, J.; Kapono, C.A.; Luzzatto-Knaan, T.; et al. Sharing and community curation of mass spectrometry data with Global Natural Products Social Molecular Networking. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 828–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forsberg, E.M.; Huan, T.; Rinehart, D.; Benton, H.P.; Warth, B.; Hilmers, B.; Siuzdak, G. Data processing, multi-omic pathway mapping, and metabolite activity analysis using XCMS Online. Nat. Protoc. 2018, 13, 633–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordbar, A.; Yurkovich, J.T.; Paglia, G.; Rolfsson, O.; Sigurjónsson, Ó.E.; Palsson, B.O. Elucidating dynamic metabolic physiology through network integration of quantitative time-course metabolomics. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, V.; Hadadi, N.; Hatzimanikatis, V. Enhanced flux prediction by integrating relative expression and relative metabolite abundance into thermodynamically consistent metabolic models. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2019, 15, 481499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampieri, M.; Hörl, M.; Hotz, F.; Müller, N.F.; Sauer, U. Regulatory mechanisms underlying coordination of amino acid and glucose catabolism in Escherichia coli. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, N.A.; Lau, R.; Swenson, T.L.; Klitgord, N.; Garcia-Pichel, F.; Bowen, B.P.; Baran, R.; Northen, T.R. Flux balance modeling to predict bacterial survival during pulsed-activity events. Biogeosciences 2018, 15, 2219–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkel, G.W.; Ghosh, A.; Kumar, V.S.; Weaver, D.; Ando, D.; Backman, T.W.H.; Arkin, A.P.; Keasling, J.D.; Martín, H.G. The JBEI quantitative metabolic modeling library (jQMM): A python library for modeling microbial metabolism. BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18, 205. [Google Scholar]
- Henry, C.S.; DeJongh, M.; Best, A.A.; Frybarger, P.M.; Linsay, B.; Stevens, R.L. High-throughput generation, optimization and analysis of genome-scale metabolic models. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 977–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas, D.A.; Edirisinghe, J.; Henry, C.S.; Overbeek, R.; O’Connell, T.G.; Edwards, R.A. From DNA to FBA: How to Build Your Own Genome-Scale Metabolic Model. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tautenhahn, R.; Patti, G.J.; Rinehart, D.; Siuzdak, G. XCMS online: A web-based platform to process untargeted metabolomic data. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 5035–5039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuevas, D.A.; Garza, D.; Sanchez, S.E.; Rostron, J.; Henry, C.S.; Vonstein, V.; Overbeek, R.A.; Segall, A.; Rohwer, F.; Dinsdale, E.A.; et al. Elucidating genomic gaps using phenotypic profiles. F1000Research 2016, 3, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowda, H.; Ivanisevic, J.; Johnson, C.H.; Kurczy, M.E.; Benton, H.P.; Rinehart, D.; Nguyen, T.; Ray, J.; Kuehl, J.; Arevalo, B.; et al. Interactive XCMS Online: Simplifying Advanced Metabolomic Data Processing and Subsequent Statistical Analyses. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 6931–6939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortmayr, K.; Causon, T.J.; Hann, S.; Koellensperger, G. Increasing selectivity and coverage in LC-MS based metabolome analysis. TrAC—Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 82, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiele, I.; Palsson, B. A protocol for generating a high-quality genome-scale metabolic reconstruction. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 93–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanisevic, J.; Zhu, Z.J.; Plate, L.; Tautenhahn, R.; Chen, S.; O’Brien, P.J.; Johnson, C.H.; Marletta, M.A.; Patti, G.J.; Siuzdak, G. Toward ’Omic scale metabolite profiling: A dual separation-mass spectrometry approach for coverage of lipid and central carbon metabolism. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 6876–6884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huan, T.; Forsberg, E.M.; Rinehart, D.; Johnson, C.H.; Ivanisevic, J.; Benton, H.P.; Fang, M.; Aisporna, A.; Hilmers, B.; Poole, F.L.; et al. Systems biology guided by XCMS Online metabolomics. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 461–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo-Almenara, X.; Siuzdak, G. Metabolomics Data Processing Using XCMS. In Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana Press Inc.: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2020; Volume 2104, pp. 11–24. [Google Scholar]
| Features Matched | RP | HILIC |
|---|---|---|
| XCMS features (pre-MS_FBA) | 1210 | 1560 |
| Matched to PyFBA | 135 | 118 |
| PyFBA isotope matches | 23 | 28 |
| Matched to Model SEED | 846 | 621 |
| Model SEED isotope matches | 107 | 90 |
| Unique annotated metabolites to PyFBA | 218 | |
| PyFBA compounds in search list | 699 | |
| Model SEED compounds in search list | 27,693 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuang, E.; Marney, M.; Cuevas, D.; Edwards, R.A.; Forsberg, E.M. Towards Predicting Gut Microbial Metabolism: Integration of Flux Balance Analysis and Untargeted Metabolomics. Metabolites 2020, 10, 156. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10040156
Kuang E, Marney M, Cuevas D, Edwards RA, Forsberg EM. Towards Predicting Gut Microbial Metabolism: Integration of Flux Balance Analysis and Untargeted Metabolomics. Metabolites. 2020; 10(4):156. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10040156
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuang, Ellen, Matthew Marney, Daniel Cuevas, Robert A. Edwards, and Erica M. Forsberg. 2020. "Towards Predicting Gut Microbial Metabolism: Integration of Flux Balance Analysis and Untargeted Metabolomics" Metabolites 10, no. 4: 156. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10040156
APA StyleKuang, E., Marney, M., Cuevas, D., Edwards, R. A., & Forsberg, E. M. (2020). Towards Predicting Gut Microbial Metabolism: Integration of Flux Balance Analysis and Untargeted Metabolomics. Metabolites, 10(4), 156. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10040156