Abstract
Digital holography represents a novel media which promises to revolutionize the way the users interacts with content. This paper presents an in-depth review of the state-of-the-art algorithms for advanced processing and rendering of computer-generated holography. Open-access holographic data are selected and characterized as references for the experimental analysis. The design of a tool for digital hologram rendering and quality evaluation is presented and implemented as an open-source reference software, with the aim to encourage the approach to the holography research area, and simplify the rendering and quality evaluation tasks. Exploration studies focused on the reproducibility of the results are reported, showing a practical application of the proposed architecture for standardization activities. A final discussion on the results obtained is reported, also highlighting the future developments of the reconstruction software that is made publicly available with this work.
1. Introduction
Computer-generated holography is a novel digital media promising to revolutionize the interaction between users and digital content [1]. A holographic signal is a complex wavefield which brings all the characteristics needed to the observer for having a three-dimensional perception of the scene exactly as in reality. The interest in holographic imaging is growing both in academic and industrial areas. The ISO/IEC SC29 WG1 JPEG committee is currently developing a standard for coding different light-field modalities (JPEG Pleno) which comprise the definition of a framework to facilitate the representation of holographicdata [2]. High resolution and wide viewing angles, necessary for realizing high-quality and immersive holographic applications, make holographic imaging very data intensive. This aspect raises a set of open issues related to the areas of data coding, transmission, storage, rendering, and quality evaluation [3].
Digital holography applies not only in display applications, but also in a broad range of scientific fields such as microscopy and interferometry. Microscopy applications are heterogeneous, ranging from refractive index measurements and surface topography [4] to 3D mapping of biological cells for stimulation purposes and acquisition of the fluorescence distribution in a single recording step [5]. In the interferometric field, holography is applied as an extension of the classic techniques, enabling a non-contact, non-invasive analysis of test samples. Also in this case several application can be found, such as cortical bone compression and load tests [6], in which the digital hologram interferometric acquisitions of different bone groups have been exploited for comparison purpose, or the study of wood deformation and strain distribution caused by humidity variations [7].
Typically, holography employs coherent light sources, such as lasers, for the acquisition and reproduction processes. However, to reduce the inherent problem of speckle noise, incoherent techniques have also been developed. There are two main techniques to obtain incoherent holograms [8]. The first is the Optical Scanning Holography (OSH) that employs a laser light source during the acquisition process. Despite the light source being coherent, the acquired hologram can be incoherent: this feature depends on the acquisition geometry [8,9]. The other technique is called Fresnel Incoherent Correlation Holography (FICH), and in this case the light source can be incoherent (such as the sunlight) [8,10].
The acquisition of holograms with optical setups requires particular equipment (such as lasers, beam splitters, waveplates, and acquisition plates) and properly prepared environments. In contrast, digital holography, and in particular the computer-generated holography, allows the simulation of the entire acquisition process with numerical calculations [11]. Also, the reconstruction process of digital holograms can be simulated with numerical algorithms. Recent works have greatly improved digital hologram generation techniques, especially in the context of the tridimensionality, allowing the reproduction of the complete scene depth at one time [12].
However, holographic data digitization raises the challenge of data compression: although there exist advanced coding methods for image and video contents, they cannot reach the same performance on holographic contents, because of the different nature of the data. So far, different coding solutions have been proposed. Data quantization followed by different lossless compression techniques have been analyzed in [13,14], while the performance of different quantization techniques have been compared in [15]. The transform coding with well-known transforms has also been investigated, using the DWT (Discrete Wavelet Transform) [16] and the DCT (Discrete Cosine Transform) [17,18] transforms. To increase the holographic content-awareness during the transform stage, other types of transforms have also been proposed, such as Fresnelets and Gabor wavelets [19,20]. Furthermore, variation of standard still-image and video codecs have been proposed and investigated to improve compression performance on holographic data.Some examples include the JPEG 2000 variation proposed in [21] and the HEVC extension proposed in [22]. Despite the various proposals, no effective solution has been established on digital holographic data coding at the time of writing, and thus research in this field is still very active.
Image-quality evaluation, with objective and subjective experiments, is another crucial aspect in holographic field, often closely linked with data compression. Holographic displays have been improved, focusing on the image quality [23] and on the compactness and portability [24], nevertheless they are not actually ready for consumer production. Due to the lack of high-performance holographic displays, other types of displays are used in these experiments, such as autostereoscopic [25], and light field [26]. Moreover, conventional 2D displays are often adopted for experimenting image reproduction schemes for analyzing the scene from different perspectives and reconstruction distances [27,28,29]. In these cases, the rendering and the image-quality evaluation processes are often carried out with computerized simulations. However, the absence of universally recognized standard methodologies and tools represent an obstacle that hampers the progress in this field and fragments the efforts of the research community.
The main contribution of this work to the state of the art is to provide a reference reconstruction software for digital holograms that can be employed in different experimentation and/or standardization activities on holography. These activities include, but are not limited to: data compression; design and/or evaluation of objective and subjective metrics for holographic image-quality assessment; and design and/or evaluation of image enhancement techniques applicable to holographic images. This tool supports the reconstruction of most holograms belonging to the JPEG Pleno Database [30], i.e., to the best of the authors’ knowledge, one of the biggest and most heterogeneous datasets actually publicly available. Moreover, the proposed software has been embedded in a compression architecture to test several standard codecs (JPEG XT, JPEG XS, JPEG 2000, JPEG LS, PNG, and HEVC) for digital hologram data compression.
The paper is structured as follows. In Section 2 a brief description of the different computer-generated hologram techniques is provided, reporting also some hardware and software tools recently proposed for digital hologram generation and rendering. Section 3 provides a description of the different hologram datasets included in the publicly available JPEG Pleno Database. In Section 4 the reconstruction software proposed in this work is presented and its features are described, while in Section 5 a compression testbed with standard codecs, whose architecture includes the rendering software, is employed to benchmark different standard codecs on holographic data. Finally, in Section 6 the conclusions are drawn, and future work is described.
2. Algorithms for Advanced Processing and Rendering of Computer-Generated Holography
In this section, the main techniques of computerized hologram generation and rendering tools will be described and analyzed, including also examples of publicly available software implementations that are currently developed and maintained. The generation and rendering processes, especially for high-quality holograms, can be very complex and burdensome also for modern hardware architectures. Research in this area is very active not only for improving the final image quality, but also for reducing the computational complexity of the existing techniques.
2.1. Computer-Generated Hologram Generation
The increasing processing power of Central Process Units (CPUs) and Graphics Processing Units (GPUs) has led to the development of several different computer-generated hologram (CGH) techniques. In the following, some of the most common generation methods will be illustrated.
2.1.1. Point-Cloud Approach
In point-cloud approaches, the scene of interest is discretized through a set of points, properly distributed in the tridimensional space. On first approximation, to acquire the hologram of the scene, each point is considered a light-emitting primitive: the hologram is obtained by summing the contribution of all points in the scene on the acquisition plane (the hologram plane). The main advantage of this method is the relatively simple calculations involved during the acquisition process. Another advantage is the possibility of recording not only synthetic scenes, but also real scenes, previously acquired as point clouds. However, when the scene consists of a huge amount of points and occlusion or reflection effects need to be taken into account, the computational cost of the algorithm is typically unacceptable for modern hardware. To speed up the generation process, several techniques have been proposed in the literature [31], such as the Look-Up-Tables (LUTs), originally proposed in [32] that consist of pre-calculated, store-and-reuse parts of the computations performed during the recording process. Another acceleration method is the wavefront-recording plane (WRP) [33], which consists of the interposition of an intermediate plane (the WRP) between the point cloud and the hologram plane. The contributions of the points are first evaluated in the WRP, and then the content of the WRP is propagated through the hologram plane. The original WRP method has also been extended using multiple WRPs [34]. Other recent speed-up proposals rely on wavelet transforms [35] that allow representation of the emitted light with a reduced number of coefficients. This method, called WASABI, has also been combined with the WRP concept to further increase computational speeds [36].
2.1.2. Layer-Based Approach
The layer-based method consists of slicing the scene of interest in different layers. These layers are typically parallel to the hologram plane, crossing the scene along his depth. Each layer is considered a light-emitting primitive and is propagated towards the hologram plane. The hologram of the scene is obtained summing all contributions of all layers involved [37,38]. If compared to other methods, such as the point-cloud approach, the layer-based synthesis turns out to be faster, because the number of layers could be lower than the number of points that describe the scene. Despite this fact, to ensure that the depth of the scene is acquired without visual-perceptible discontinuities, the number of layers required may be high [37], then different acceleration techniques have been proposed to improve the generation process, such as those proposed in [39] and in [40]. Recently, an acceleration method based on LUTs has been proposed [41], enabling the generation of CGH video sequences, minimizing the memory required and the overall hologram generation process complexity.
2.1.3. Polygon-Based Approach
In the polygon-based method, the scene to be acquired is composed of a set of 2D surfaces. Similar to the previous approaches, each surface is considered a light-emitter, and its contribution is propagated on the hologram plane. To generate the hologram of the whole scene, the contributions of all the surfaces are summed on the hologram plane. This method is typically less computationally expensive than the point-cloud synthesis, especially if the complexity of the scene is not high, because the number of polygons needed to approximate the scene is lower than the number of points that would occur in a point-cloud representation [42]. When the complexity of the scene is high (and therefore a large number of polygons are present) more advanced techniques are needed to speed up the calculations [43]; moreover, the hidden-surface removal process can be very computationally intensive, so the search in this field is still very active [44].
2.1.4. Ray-Based Approach
The ray-based approach exploits an intermediate plane between the scene and the hologram plane: the so-called light-ray sampling plane (RS). The light field forming the scene is sampled in the RS plane. This light field often is captured as a set of images showing the scene from different perspectives. These images are Fourier-transformed, and the wavefront obtained with this transform is propagated to the hologram plane, simulating the object wave. Along the path towards the hologram plane, the object wave interferes with a reference wave, and this interference is recorded in the hologram plane to acquire the hologram of the scene. An advantage of this method is that it can be applied to both synthetic and real scenes, acquired through camera arrays that record different views of the scene simultaneously. Furthermore, the reproduction of reflections by surfaces or occlusion effects can be easily taken into account [45]. The computational cost, similar to the other existing methods, can be high for the generation of high-resolution holograms. Examples of solutions proposed to speed up the generation processes involve the use of multiple GPUs [46] or the tile segmentation of the hologram [47].
2.2. CGHs Rendering
The phenomenon of light propagation is crucial in the process of generation and reconstruction of holograms. It can be expressed numerically by means of scalar diffraction theory. Let be the optical field at the hologram plane, placed at ; the reconstructed wavefield in the reconstruction plane, placed at distance z is given by [48]:
where j is the imaginary unit, is the wavelength and is the distance between a point in the hologram plane and a point in the reconstruction plane. From Equation (1) different approximations can be derived that are often implemented via software employing one or more bidimensional Discrete Fourier Transforms (2D DFT). Among these approximations, the Angular Spectrum Method (ASM) and the Fresnel transformation [49] are two widely used techniques for digital holograms reconstruction.
Starting from Equation (1), if z is much bigger than the other terms, the approximation can be performed, and Equation (1) can be rewritten as:
where . The approximation has not been performed in the exponent because in this case small variations in r can result in strong variations in . The integral in Equation (2) is a convolution:
where is the kernel:
To simplify the calculations, the well-known Fresnel approximation can be applied:
that holds if . In this case, the new kernel will be:
Using this approximation, the reconstructed wavefield at the reconstruction plane can be calculated with one 2D DFT as [50]:
where F indicates the Fourier Transform that can be implemented via software with a 2D DFT. The Equation (7) represents the Frensnel transformation (or Fresnel Method).
An alternative reconstruction method is the ASM. If is Fourier-transformed, its Angular Spectrum can be obtained:
and obviously with the Inverse Fourier Transform can be retrieved:
that can also be seen as a set of plane waves propagating in different directions , where , in which every component has amplitude . During the propagation at distance z, another phase factor needs to be taken into account. The reconstructed wavefield at the reconstruction plane will be:
that is the Inverse Fourier Transform of . In summary the reconstructed wavefield is [50]:
where indicates the Inverse Fourier Transform and it is assumed that . As it can be noted from Equation (11), the ASM needs two Fourier Transforms in order to be implemented (thus is more computational-intensive compared to the Fresnel Method), but it does not involve any approximation as in the Frensel Method.
The reconstruction process (but also the generation process) can be an operation that requires not-negligible computational resources, especially if the hologram has high resolution and is in color. Thus, some software implementations have been proposed to perform the reconstruction process (and in some cases also the generation process) of digital holograms in a computation-efficient way. An example of reconstruction software is proposed in [51]. This program is specialized in the reconstructions of holograms belonging to microscopy, Optical Coherent Tomography (OCT), vibrometry, angiography, and plethysmography. The author shows that and interferograms can be rendered in real time, exploiting the parallel computing power of modern GPUs. Another proposal is the Computational Wave Optics library for C++ (CWO++) [52], a C++ class library that implements different light-diffraction models for digital hologram reconstruction. The authors also show a CGH hologram generation from a point cloud. Other than exploiting the CPU power, this library allows the use of the GPU to hasten the calculations. Both the cited software implementations are currently maintained and publicly available.
Other than the software development, the research has also been headed towards special-purpose hardware modules. With typical computer hardware configurations, operations such as real-time generation or rendering are hard to achieve, if not impossible in some cases, depending on hardware specifications and CGH features. In [53], a GPU cluster composed of up to 12 GPUs has been shown to render holographic images at 30 frames-per-second in real time. Such solutions, based on general-purpose hardware, provide a high number of cores to speed up calculations through parallelism; moreover, the availability of efficient software libraries released directly from the hardware manufacturer simplifies the development operations. However, the necessary infrastructure to establish these systems and the total energy consumption might be limiting factors in determined use scenarios. Therefore, special-purpose solutions have also been proposed, which are typically smaller in size and require less energy compared to general-purpose hardware [44]. One of the main drawbacks is longer design and development times [44]. An example of a recently proposed solution of this type is the HORN-8 system [54,55], composed of 8 Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) mounted on a custom Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCI-E) board. In this system, the hologram generation method implemented is the point-cloud approach. The results obtained suggest that using dedicated hardware is a viable alternative to high-parallelized general-purpose hardware, and for hologram rendering in real time. In particular, in [56] the HORN-8 system has been used to calculate and display, at video rate, a CGH generated from a 3D model composed of 390,000 points, highlighting the advantage in terms of performance, compared to general-purpose CPU and GPU hardware. Another recent hardware prototype is showed in [57], which focuses on lightness and portability. The core processor is based on a single FPGA chip. This system exploits the layer-based approach for CGH generation and include a user eye-tracking mechanism.
3. Digital Hologram Reference Datasets
To advance the progress within the context of holography, it is essential to have as many samples as possible on which to carry out the experiments. Moreover, holography is a technique with several and different application fields, ranging from display purposes to microscopy or interferometry. As can be seen also from Section 2.1, there is no single method for CGH generation, and a similar situation can be seen in optical acquisition, in which different setups and methods exist [11]. These aspects make it necessary to also have a good degree of variety in samples types.
Despite the number of different techniques and proposed algorithms present in the literature for digital hologram generation, there are very few publicly available hologram datasets. In the last few years, some research groups have publicly released their own samples, to attempt to mitigate this problem. In [58], the dataset Interfere I has been proposed. The samples are both two-dimensional and three-dimensional and they have been generated with an algorithm created by the authors that supports the occlusion effect. The dataset consists of 5 CGHs. All the holograms are monochromatic and do not support parallax effects; they have pixel pitch equal to m and resolution equal to , except for the sample 3D Cat, whose pixel pitch is equal to m and it has resolution of . The wavelength used during the generation process is equal to 632.8 nm. The sources of 2D holograms are two-dimensional images, while the sources of three-dimensional samples are point clouds. The generation algorithm has been improved in [59], including, in addition to occlusion, the simulation of diffuse light reflection from surfaces: the light is spread over a wide angle, providing an extended view of the scene with full parallax support. This dataset is called Interfere II and includes 6 diffuse and 6 specular monochromatic samples, generated from point clouds. The resolution is , the pixel pitch is m and the generation wavelength 633 nm for all samples. Recently, also Interfere III has been released [60] consisting of 6 color CGH generated from point clouds with an algorithm which extends the Phong illumination model that allows ambient, diffuse, and specular reflection support. The samples have resolutions of and with pixel pitch equal to m, with the exception of Biplane 16k which has resolution of 16,384 × 16,384, pixel pitch of m and has also full parallax support. The wavelengths used during the generation are equal to 633 nm, 532 nm and 460 nm for the red, green, and blue channels, respectively.
The Institute of Research and Technology B-com has developed a color CGH dataset, generated with two different algorithms, described in [40,61]: the former is a hybrid technique that combines the point-cloud and the layer-based approach and includes occlusion effect support, while the latter is based on multiple 2D-with-depth images of the scene acquired from different viewpoints from which a point cloud is derived. The algorithm takes also into account specular reflections. The dataset comprises 21 holograms, some of them with full parallax support, generated from synthetic scenes. The resolutions range from to 16,384 × 16,384 with different pixel pitches, from m to m. Two video sequences at different resolutions of real scenes are also proposed.
Other than the CGHs dataset, there are also few examples of optically acquired hologram datasets. The EmergImg Holographic Database [62] is one of them, and it includes holograms of real objects acquired with the phase-shifting technique. Each hologram derives from the acquisition and combination of four interferograms. The database is composed of two sample sets. The first set (v1) includes three samples with m pixel pitch and a video sequence of 54 holograms at resolution. The second set (v2) comprises six samples with pixel pitch m. The samples are all monochromatic and do not support relevant parallax effects, also because there are actually strong limits in resolution and pixel pitch of currently available optical acquisition hardware, if compared to CGH acquisition techniques.
Microscopy and tomography are two other important fields in which holography has been demonstrated to provide important improvements over standard techniques [63,64], and currently different commercial hardware apparatus and related rendering software are available. Despite this, there is not a big availability of these types of hologram. One example of a publicly available dataset is the Tomocube [65], which comprises four monochrome samples with resolutions from to 24,478 × 16,641 and pixel pitch from m to m.
Although some holographic datasets are actually publicly available as reported above, it is necessary that their number and variety in type continue to grow: perhaps even more than other imaging techniques, research areas within holography such as data compression, image rendering, enhancement, and objective and subjective quality assessment require a high number of samples to provide results with an adequate generality.
4. Digital Hologram Rendering and Quality Evaluation
4.1. Rendering Algorithm
As described in the Section 2.2, currently there are some freely accessible software applications that allow the rendering of digital holograms. From the research point of view, having a wide variety of available data is crucial, as stated in Section 3, but, especially for those who approach the study of this imaging technique for the first time, it is also important to establish a clear correspondence between the operations that the software is able to do, and the samples on which these operations can be performed. Holography is an area in which standardization activities are in their initial stages [2], and a standard data representation format is not available yet. Moreover, holography has different application fields such as display, tomography, microscopy, and interferometry and often every application requires specific processing steps that are not necessary or useful for another application. It is, therefore, important to clearly specify on which type of data a reconstruction tool has been tested and therefore can be used.
This work proposes a tool for the reconstruction of digital holograms dedicated to display applications, designed to simplify, even for non-expert users, the reproduction of most of the currently accessible and downloadable holographic datasets. The architecture of the proposed tool is shown in Figure 1 and has been developed in MATLAB language.
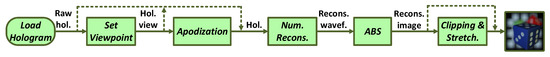
Figure 1.
Rendering architecture.
The first block, Load Hologram, allows the user to load the hologram in memory through a window dialog. The currently supported datasets are:
- B-com, 8-bit and 32-bit format, (the hologram sequences reconstruction is allowed frame-by-frame only);
- Interfere, I, II, and III;
- EmergImg, v1 and v2, (the hologram sequences reconstruction is allowed frame-by-frame only).
Once the complex matrix representing the hologram is loaded, the next step is to set the view on the scene to be reconstructed: this operation is performed by Set Viewpoint. A specific view on the scene is obtained selecting only a portion of the entire hologram, thus generating the so-called “synthetic aperture” (e.g., if the aperture is positioned on the top-right side of the hologram, the user obtains the top-right view of the scene). To facilitate the aperture positioning, this tool employs two angles, as shown in Figure 2a, in which is the reconstruction distance.
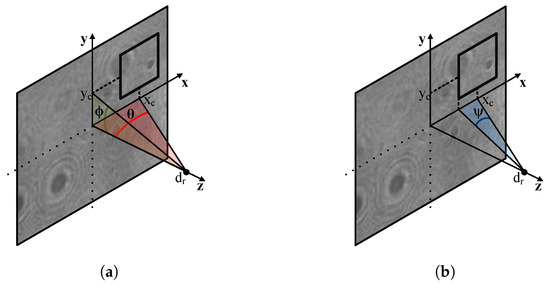
Figure 2.
Synthetic aperture position expressed with the angles and (a) and size expressed with the angle (b).
The horizontal position of the aperture is declared through the angle , defined as , while the vertical position is set through the angle , defined as . A third angle, , is used to set the aperture’s dimension as shown in Figure 2b and proposed in [66]. The reconstruction distance and the three angles for aperture position and size definition are declared by the user before launching the tool. The synthetic aperture can be apodized with a bidimensional Hanning window as proposed in [26] to reduce strong diffraction effects at the aperture’s borders that may occurs in the reconstruction process. The synthetic aperture setting and its apodization are optional steps that the user can decide whether or not to perform. The hologram reconstruction is performed in the Numerical Reconstruction (Num. Recons.) block: the additional reconstruction parameters such as wavelength(s), pixel pitch and reconstruction method can be set by the user by means of external configuration files, in order to avoid re-declaration of these parameters during subsequent reconstructions that share equal parameters. Currently, the tool implements two reconstructions methods, namely the ASM and the Fresnel Method. Subsequently, the Absolute (ABS) block extracts the complex magnitude of the reconstructed wavefield. At this stage, the reconstructed image can be enhanced with a linear histogram stretching after a percentile clip to remove extreme values, as suggested in [26]. This optional process is performed on the Clipping & Stretch. block, and the user can select the percentile value at which the clipping is executed. Finally, the reconstructed image is generated as standard PNG image.
In Figure 3, two reconstructed images are reported. Figure 3a shows Dices 8K of the B-com dataset, reconstructed with the ASM at a distance m with a synthetic aperture of size positioned at , . Figure 3b shows Skull of the EmergImg v2 dataset, reconstructed with the Fresnel Method at a distance m with synthetic aperture size equal to the hologram size.

Figure 3.
Numerical reconstructions examples: (a) B-com Dices 8K reconstructed with ASM, and (b) EmergImg Skull reconstructed with the Fresnel Method.
4.2. Quality Evaluation
Digital holograms, whether they are optically acquired or computer-generated, typically include much more data if compared with standard image or video contents. Data compression is therefore an important milestone for the evolution of this imaging technology, as much as the development of high-quality holographic displays and the improvement of generation techniques. Without an efficient coding technique, it is impossible to process and transmit holographic data in a similar way as other contents, such as images and videos. As already pointed out in Section 1, standard image or video codecs are not optimal solutions, since they are designed for completely different data types. Nevertheless, during the design, development and test of new coding solutions, dedicated for holographic data, it is also important to compare the obtained results with current state-of-the-art codecs, to have a common reference. In this work, a comparative evaluation of different standard coding solution has been carried out with the architecture reported in Figure 4 that will be described in the following, and that includes the rendering algorithm described in Section 4.1.
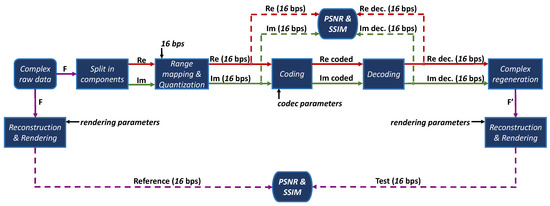
Figure 4.
Compression architecture.
The compression architecture (Figure 4) requires that the input raw hologram is represented in the complex-valued form, since the majority of dataset currently publicly available are expressed in this form. However, it is easily adaptable to other representation forms as phase-only or double-phase. Moreover, in this work only the algebraic form is considered, because it is known from previous state-of-the-art works that it shows better compression performance than polar form [22,62,67].
From the raw complex hologram, represented by the Complex raw data block, the real and imaginary components are extracted in the Split in components block. The two components are two distinct real-valued matrices. In the Range mapping & Quantization block these two matrices are quantized with 16 bits per sample (bps), since most of current standard codecs support integer data only. Subsequently, the two quantized components are coded (Coding block) and then decoded (Decoding block) with a standard codec. At this stage, the first quality evaluation is carried out, in the so-called hologram domain. The hologram’s real and imaginary components are compared before and after the compression with the peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) and structural similarity index (SSIM) objective metrics, taking the component before the coding stage as reference. After the decoding process, the Complex regeneration block takes the two components as inputs and merge them again in a single complex matrix. The reconstruction process is then performed from the decoded data (F’), on the right, but also from the original raw data (F), on the left. The Reconstruction & Rendering block is essentially the algorithm described in Section 4.1, with a custom Load Hologram block, in order to load the input data automatically, without user intervention. The two reconstructed images are finally compared with the PSNR and SSIM metrics in the so-called reconstructed domain, taking the image originating from the raw data as reference.
5. Exploration Studies
In this work, the compression architecture described in Section 4.2 has been applied to two different holograms, Dices 8K of the B-com dataset and Skull of the EmergImg v2 dataset. The former is a full-parallax color hologram, numerically computed from a synthetic scene, while the latter is grayscale and it has been physically acquired through an optical setup. This choice allows observation and comparison of the performance of the codecs on two relatively different types of data. More details about the samples are available in Section 3. The experimentation involves the use of 5 still-image codecs, namely JPEG XT (Libjpeg implementation [68]), JPEG XS [69], JPEG 2000 (Kakadu Software implementation [70]), tested in lossy mode, in addition to JPEG LS (Libjpeg implementation [71]) and PNG (FFmpeg implementation [72]), which are lossless codecs. These are among the most recent and used codecs for standard images. Moreover, the HEVC (HM 16.19 [73]) video codec is employed for lossy coding, in Intra mode. This is useful for verifying whether the performance of HEVC that in previous works was demonstrated to be higher than some standard codecs on grayscale CGH [22,67] is also confirmed with color CGH samples and with respect to the JPEG XT and JPEG XS codecs. The exploration studies have been performed on a Windows 10 Pro machine, equipped with a dual Intel Xeon E5-2640-v4 CPU, 64 GB of RAM and a Nvidia Quadro P5000 GPU.
Table 1 shows the numerical results obtained after the coding process. For each codec, the compressed total bitrate (the sum of real and imaginary bitrates) and the corresponding compressed file size are reported.

Table 1.
Lossy compression results.
Figure 5a,b show the rate-distortion curves in terms of mean PSNR, calculated in the hologram domain, for Dices 8K and Skull respectively.
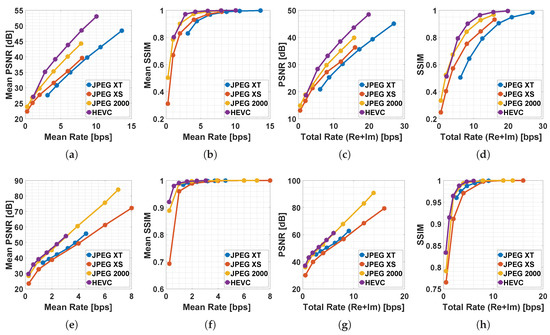
Figure 5.
Dices 8K (a–d) and Skull (e–h) compression results: mean PSNR (a,e) and mean SSIM (b,f) in the hologram domain vs. bps (bits per sample); PSNR (c,g) and SSIM (d,h) in the reconstructed domain vs. bps.
Since for both samples the results obtained for the real and imaginary parts are almost identical, the means of these results are shown for each sample. Analyzing the graph in Figure 5a, related to Dices 8K, it can be noted that the HEVC has better performance than the other codecs. Among the still-image codecs, the best is JPEG 2000, followed by the most recent JPEG XS, and by the JPEG XT. The results for Skull in terms of mean PSNR are shown in Figure 5e: it can be noted that with this sample there is not a significant difference between HEVC and JPEG 2000. Moreover, the JPEG XS is the worst codec, perhaps even penalized by the fact that there is not a specific profile for grayscale inputs (dev profile has been used). The mean SSIM results obtained in the hologram domain are shown in Figure 5b (Dices 8K) and in Figure 5f (Skull): the SSIM metric confirms the results obtained in terms of PSNR, even if after nearly 8 bps for Dices 8K and 2 bps for Skull there is no significant distinction between codec performance with this metric. The analysis performed in the hologram domain provides information on how much the data have been altered by the encoding process. However, another fundamental aspect is to establish how much this data alteration, i.e., the coding process, affects the holographic image quality. Therefore, analysis in the reconstructed domain has been performed.
The results obtained in the reconstructed domain, in terms of PSNR, are shown in Figure 5c,g, for Dices 8K and Skull respectively. It can be noted that for both samples the results are very similar to those obtained in the hologram domain. Based on these results, the use of PSNR metric in the hologram domain can be effective in predicting the results that will be obtained on the holographic image, after the hologram reconstruction. The SSIM results (Figure 5d,h) are in accordance with PSNR results also in this domain. It can be also observed that at high bitrates (hence when the holographic image quality is also high), the SSIM discriminates the performance of the various codecs less than the PSNR.
From the inspection of the obtained results it can be observed that most of the time HEVC performs better than the other codecs. This is probably because HEVC employs very complex prediction tools that compare several different possible coding solutions based not only on block transform and quantization but also on a so-called intra-prediction aimed at finding redundancies between adjacent blocks. Moreover, the results show that the performance of JPEG2000 are similar to those of HEVC. These results suggest that the wavelet transform adopted by JPEG2000 can provide a compact representation of the information of the holographic signal. The lower performance of JPEG XS with respect to HEVC and JPEG2000 are mainly related to the low complexity design of the JPEG XS encoder. While for JPEG XT the main reason for the lower performance is that for providing backward compatibility with the legacy JPEG standard, it makes use of JPEG coding tools.
The results obtained using the lossless codecs are shown in Table 2 (PNG codec) and in Table 3 (JPEG LS codec). In these tables, also the Compression Ratio (CR) is reported, defined as

Table 2.
PNG compression results.

Table 3.
JPEG LS compression results.
The quantization process (carried out in the Range mapping & Quantization block, Figure 4) maps the raw real-value representation of the hologram to a positive fixed-point representation, allocating in this case 16 bits to store each real (or imaginary) sample of the output Re (or Im) matrix.
The data quantization process is not part of the codec itself, and it contributes in a non-negligible manner to reduce the data size. The PNG codec (Table 2) shows negligible differences in performance when the prediction mode changes. The CR varies between 1.04 and 1.08 for Dices 8K and between 1.37 and 1.44 for Skull. Especially with the first sample (color full-parallax CGH hologram), the PNG coding is thus ineffective, because the CR is very close to 1 (no compression). The JPEG LS shows slightly higher performance, with CR of 1.19 for Dices 8K and 1.60 for Skull. The real and imaginary components show, with both codecs, very similar results in terms of bps, as already seen during the lossy experiments. However, the overall lossless coding results are lower than the typical performance expected from these codecs (during standard image compression). Moreover, it can be noted that the color CGH is more difficult to compress than the optically acquired one.
6. Conclusions
In this work, after an initial introduction to digital holography and the challenges that it currently poses, different CGH generation techniques have been illustrated, together with some dedicated hardware solutions and software implementations that are currently publicly available. Subsequently, a reconstruction software implementation has been illustrated and made publicly available (http://digitalmedia.diee.unica.it/nrsh) along with a detailed user guide. This software, unlike other open-access implementations, aims to be a reference reconstruction software that can be used not only by those approaching digital holography for the first time, but also during the various exploration studies that will be conducted in the future, such as data compression and/or evaluation and enhancement, of rendered image quality. For these reasons, the proposed software focuses on the reconstruction of holograms belonging to the JPEG Pleno Database, which contains different types of publicly accessible holograms.
A practical application of the proposed software has been shown in the context of data compression, in which a benchmark of different standard codecs for images and videos has been performed on two holograms of different types. Although the performance on the grayscale optical-acquired sample are nearly identical to JPEG 2000, HEVC has been confirmed to be the standard lossy codec with the best performance, as already pointed out by the state of the art. Thus, HEVC could be used in subsequent exploration studies as codec anchor, to evaluate new compression techniques. The most recent lossless codecs have instead shown great difficulty in compressing digital hologram data, especially on the computer-generated sample under test, obtaining CRs often close to 1 and in any case lower than 2. Finally, it has emerged that real and imaginary components behave very similarly during compression, both on CGH and on optically acquired holograms.
Future developments of this work will include: updates to the set of the software-supported samples, as soon as new holograms are added to the JPEG Pleno Database; support of GPU hardware during the rendering process, to improve performance compared to the CPU-only rendering, as currently happens; and inclusion of additional options for image-quality enhancement, in particular aimed to reduce the speckle noise, of which holographic images are often affected.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.C. and C.P.; Funding acquisition, D.G. and C.P.; Investigation, C.P. and W.S.; Software, R.C.; Writing—original draft, R.C. and C.P.; Writing—review and editing, C.P., D.G., and A.L.
Funding
This research activity has been partially funded within the Cagliari2020 project (MIUR, PON04a2 00381) and the DigitArch Cluster Top-Down project (POR FESR, 2014-2020).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Maimone, A.; Georgiou, A.; Kollin, J.S. Holographic near-eye displays for virtual and augmented reality. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 2017, 36, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schelkens, P.; Ebrahimi, T.; Gilles, A.; Gioia, P.; Oh, K.J.; Pereira, F.; Perra, C.; Pinheiro, A.M. JPEG Pleno: Providing representation interoperability for holographic applications and devices. ETRI J. 2019, 41, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blinder, D.; Ahar, A.; Bettens, S.; Birnbaum, T.; Symeonidou, A.; Ottevaere, H.; Schretter, C.; Schelkens, P. Signal processing challenges for digital holographic video display systems. Signal Process. Image Commun. 2019, 70, 114–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazac, V.; Meshalkin, A.; Achimova, E.; Abashkin, V.; Katkovnik, V.; Shevkunov, I.; Claus, D.; Pedrini, G. Surface relief and refractive index gratings patterned in chalcogenide glasses and studied by off-axis digital holography. Appl. Opt. 2018, 57, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, X.; Kumar, M.; Matoba, O.; Awatsuji, Y.; Hayasaki, Y.; Hasegawa, S.; Wake, H. Three-dimensional stimulation and imaging-based functional optical microscopy of biological cells. Opt. Lett. 2018, 43, 5447–5450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, C.G.T.; Manuel, H.; Flores-Moreno, J.; Frausto-Reyes, C.; Santoyo, F.M. Cortical bone quality affectations and their strength impact analysis using holographic interferometry. Biomed. Opt. Express 2018, 9, 4818–4833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Shakher, C. Experimental characterization of the hygroscopic properties of wood during convective drying using digital holographic interferometry. Appl. Opt. 2016, 55, 960–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.P.; Tahara, T.; Hayasaki, Y.; Poon, T.C. Incoherent digital holography: A review. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poon, T.C. On the fundamentals of optical scanning holography. Am. J. Phys. 2008, 76, 738–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, J.; Brooker, G. Digital spatially incoherent Fresnel holography. Opt. Lett. 2007, 32, 912–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, P.W.M.; Poon, T.C. Review on the state-of-the-art technologies for acquisition and display of digital holograms. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2016, 12, 886–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makey, G.; Yavuz, Ö.; Kesim, D.K.; Turnalı, A.; Elahi, P.; Ilday, S.; Tokel, O.; Ilday, F.Ö. Breaking crosstalk limits to dynamic holography using orthogonality of high-dimensional random vectors. Nat. Photonics 2019, 13, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naughton, T.J.; Frauel, Y.; Javidi, B.; Tajahuerce, E. Compression of digital holograms for three-dimensional object reconstruction and recognition. Appl. Opt. 2002, 41, 4124–4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shortt, A.E.; Naughton, T.J.; Javidi, B. A companding approach for nonuniform quantization of digital holograms of three-dimensional objects. Opt. Express 2006, 14, 5129–5134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Pesquet-Popescu, B.; Dufaux, F. Comparative study of scalar and vector quantization on different phase-shifting digital holographic data representations. In Proceedings of the 2014 3DTV-Conference: The True Vision-Capture, Transmission and Display of 3D Video (3DTV-CON), Budapest, Hungary, 2–4 July 2014; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Shortt, A.E.; Naughton, T.J.; Javidi, B. Compression of digital holograms of three-dimensional objects using wavelets. Opt. Express 2006, 14, 2625–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, H.; Tamai, J. Holographic image compression by motion picture coding. In Proceedings of the Practical Holography X. International Society for Optics and Photonics, San Jose, CA, USA, 28 January–2 February 1996; Volume 2652, pp. 2–10. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, Y.H.; Choi, H.J.; Kim, D.W. 3D scanning-based compression technique for digital hologram video. Signal Process. Image Commun. 2007, 22, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanathan, K.; Gioia, P.; Morin, L. Wavelet compression of digital holograms: Towards a view-dependent framework. In Proceedings of the Applications of Digital Image Processing XXXVI. International Society for Optics and Photonics, San Diego, CA, USA, 25–29 August 2013; Volume 8856, p. 88561N. [Google Scholar]
- El Rhammad, A.; Gioia, P.; Gilles, A.; Cagnazzo, M.; Pesquet-Popescu, B. Color digital hologram compression based on matching pursuit. Appl. Opt. 2018, 57, 4930–4942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blinder, D.; Bruylants, T.; Ottevaere, H.; Munteanu, A.; Schelkens, P. JPEG 2000-based compression of fringe patterns for digital holographic microscopy. Opt. Eng. 2014, 53, 123102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peixeiro, J.P.; Brites, C.; Ascenso, J.; Pereira, F. Holographic data coding: Benchmarking and extending hevc with adapted transforms. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2018, 20, 282–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Lee, K.; Park, J.; Park, Y. Ultrahigh-definition dynamic 3D holographic display by active control of volume speckle fields. Nat. Photonics 2017, 11, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Lee, K.; Park, Y. Ultrathin wide-angle large-area digital 3D holographic display using a non-periodic photon sieve. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehtimäki, T.M.; Sääskilahti, K.; Näsänen, R.; Naughton, T.J. Visual perception of digital holograms on autostereoscopic displays. In Proceedings of the Three-Dimensional Imaging, Visualization, and Display 2009. International Society for Optics and Photonics, Orlando, FL, USA, 13–17 April 2009; Volume 7329, p. 73290C. [Google Scholar]
- Symeonidou, A.; Blinder, D.; Ceulemans, B.; Munteanu, A.; Schelkens, P. Three-dimensional rendering of computer-generated holograms acquired from point-clouds on light field displays. In Proceedings of the Applications of Digital Image Processing XXXIX. International Society for Optics and Photonics, San Diego, CA, USA, 28 August–1 September 2016; Volume 9971, p. 99710S. [Google Scholar]
- Lehtimäki, T.M.; Sääskilahti, K.; Pitkäaho, T.; Naughton, T.J. Comparing numerical error and visual quality in reconstructions from compressed digital holograms. In Proceedings of the Three-Dimensional Imaging, Visualization, and Display 2010 and Display Technologies and Applications for Defense, Security, and Avionics IV. International Society for Optics and Photonics, Orlando, FL, USA, 5–9 April 2010; Volume 7690, p. 769012. [Google Scholar]
- Darakis, E.; Kowiel, M.; Näsänen, R.; Naughton, T.J. Visually lossless compression of digital hologram sequences. In Proceedings of the Image Quality and System Performance VII. International Society for Optics and Photonics, San Jose, CA, USA, 17–21 January 2010; Volume 7529, p. 752912. [Google Scholar]
- Ahar, A.; Blinder, D.; Bruylants, T.; Schretter, C.; Munteanu, A.; Schelkens, P. Subjective quality assessment of numerically reconstructed compressed holograms. In Proceedings of the Applications of Digital Image Processing XXXVIII. International Society for Optics and Photonics, San Diego, CA, USA, 9–13 August 2015; Volume 9599, p. 95990K. [Google Scholar]
- ISO/IEC JPEG Pleno Database. Available online: https://jpeg.org/plenodb/ (accessed on 18 April 2019).
- Tsang, P.; Poon, T.C.; Wu, Y. Review of fast methods for point-based computer-generated holography. Photonics Res. 2018, 6, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucente, M.E. Interactive computation of holograms using a look-up table. J. Electron. Imaging 1993, 2, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimobaba, T.; Masuda, N.; Ito, T. Simple and fast calculation algorithm for computer-generated hologram with wavefront recording plane. Opt. Lett. 2009, 34, 3133–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, A.H.; Alam, M.A.; Jeon, S.H.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, N. Fast hologram generation of long-depth object using multiple wavefront recording planes. In Proceedings of the Practical Holography XXVIII: Materials and Applications. International Society for Optics and Photonics, San Francisco, CA, USA, 1–6 February 2014; Volume 9006, p. 900612. [Google Scholar]
- Shimobaba, T.; Ito, T. Fast generation of computer-generated holograms using wavelet shrinkage. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, D.; Shimobaba, T.; Nishitsuji, T.; Kakue, T.; Masuda, N.; Ito, T. An accelerated hologram calculation using the wavefront recording plane method and wavelet transform. Opt. Commun. 2017, 393, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H. Recent progress in computer-generated holography for three-dimensional scenes. J. Inf. Disp. 2017, 18, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Cao, L.; Zhang, H.; Kong, D.; Jin, G. Accurate calculation of computer-generated holograms using angular-spectrum layer-oriented method. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 25440–25449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.S.; Chu, D. Improved layer-based method for rapid hologram generation and real-time interactive holographic display applications. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 18143–18155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilles, A.; Gioia, P.; Cozot, R.; Morin, L. Hybrid approach for fast occlusion processing in computer-generated hologram calculation. Appl. Opt. 2016, 55, 5459–5470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.K.; Kim, E.S. Full-scale one-dimensional NLUT method for accelerated generation of holographic videos with the least memory capacity. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 12673–12691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsushima, K.; Nakahara, S. Extremely high-definition full-parallax computer-generated hologram created by the polygon-based method. Appl. Opt. 2009, 48, H54–H63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Kwon, J.; Hahn, J. Accelerated synthesis of wide-viewing angle polygon computer-generated holograms using the interocular affine similarity of three-dimensional scenes. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 16853–16874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimobaba, T.; Kakue, T.; Ito, T. Review of fast algorithms and hardware implementations on computer holography. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2016, 12, 1611–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakunami, K.; Yamaguchi, M. Calculation for computer generated hologram using ray-sampling plane. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 9086–9101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, H.; Kakue, T.; Ichihashi, Y.; Endo, Y.; Wakunami, K.; Oi, R.; Yamamoto, K.; Nakayama, H.; Shimobaba, T.; Ito, T. Real-time colour hologram generation based on ray-sampling plane with multi-GPU acceleration. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igarashi, S.; Nakamura, T.; Matsushima, K.; Yamaguchi, M. Efficient tiled calculation of over-10-gigapixel holograms using ray-wavefront conversion. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 10773–10786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, J.W. Introduction to Fourier Optics; Roberts and Company Publishers: Greenwood Village, CO, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Schnars, U.; Jüptner, W.P. Digital recording and numerical reconstruction of holograms. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2002, 13, R85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.K. Digital holographic microscopy. In Digital Holographic Microscopy; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2011; pp. 20–24. [Google Scholar]
- Atlan, M. Ultrahigh-throughput rendering of digital holograms. In Proceedings of the Digital Holography and Three-Dimensional Imaging. Optical Society of America, Orlando, Fl, USA, 25–28 June 2018; p. DM5F-4. [Google Scholar]
- Shimobaba, T.; Weng, J.; Sakurai, T.; Okada, N.; Nishitsuji, T.; Takada, N.; Shiraki, A.; Masuda, N.; Ito, T. Computational wave optics library for C++: CWO++ library. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2012, 183, 1124–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niwase, H.; Takada, N.; Araki, H.; Maeda, Y.; Fujiwara, M.; Nakayama, H.; Kakue, T.; Shimobaba, T.; Ito, T. Real-time electroholography using a multiple-graphics processing unit cluster system with a single spatial light modulator and the InfiniBand network. Opt. Eng. 2016, 55, 093108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugie, T.; Akamatsu, T.; Nishitsuji, T.; Hirayama, R.; Masuda, N.; Nakayama, H.; Ichihashi, Y.; Shiraki, A.; Oikawa, M.; Takada, N.; et al. High-performance parallel computing for next-generation holographic imaging. Nat. Electron. 2018, 1, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishitsuji, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Sugie, T.; Akamatsu, T.; Hirayama, R.; Nakayama, H.; Kakue, T.; Shimobaba, T.; Ito, T. Special-purpose computer HORN-8 for phase-type electro-holography. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 26722–26733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Nakayama, H.; Takada, N.; Nishitsuji, T.; Sugie, T.; Kakue, T.; Shimobaba, T.; Ito, T. Large-scale electroholography by HORN-8 from a point-cloud model with 400,000 points. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 34259–34265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Kim, Y.; Ji, H.; Park, H.; An, J.; Song, H.; Kim, Y.T.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, K. A Single-Chip FPGA Holographic Video Processor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 2066–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blinder, D.; Ahar, A.; Symeonidou, A.; Xing, Y.; Bruylants, T.; Schreites, C.; Pesquet-Popescu, B.; Dufaux, F.; Munteanu, A.; Schelkens, P. Open access database for experimental validations of holographic compression engines. In Proceedings of the 2015 Seventh International Workshop on Quality of Multimedia Experience (QoMEX), Pylos-Nestoras, Greece, 26–29 May 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Symeonidou, A.; Blinder, D.; Ahar, A.; Schretter, C.; Munteanu, A.; Schelkens, P. Speckle noise reduction for computer generated holograms of objects with diffuse surfaces. In Proceedings of the Optics, Photonics and Digital Technologies for Imaging Applications IV. International Society for Optics and Photonics, Brussels, Belgium, 3–7 April 2016; Volume 9896, p. 98960F. [Google Scholar]
- Symeonidou, A.; Blinder, D.; Schelkens, P. Colour computer-generated holography for point clouds utilizing the Phong illumination model. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 10282–10298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilles, A.; Gioia, P.; Cozot, R.; Morin, L. Computer generated hologram from multiview-plus-depth data considering specular reflections. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia & Expo Workshops (ICMEW), Seattle, WA, USA, 11–15 July 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Bernardo, M.V.; Fernandes, P.; Arrifano, A.; Antonini, M.; Fonseca, E.; Fiadeiro, P.T.; Pinheiro, A.M.; Pereira, M. Holographic representation: Hologram plane vs. object plane. Signal Process. Image Commun. 2018, 68, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.; Kim, K.; Yoon, J.; Park, Y. Active illumination using a digital micromirror device for quantitative phase imaging. Opt. Lett. 2015, 40, 5407–5410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.; Kim, K.; Park, H.; Choi, C.; Jang, S.; Park, Y. Label-free characterization of white blood cells by measuring 3D refractive index maps. Biomed. Opt. Express 2015, 6, 3865–3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomocube Dataset. Available online: http://www.tomocube.com/reference-resources/ (accessed on 18 April 2019).
- Gilles, A.; Gioia, P. Doc. ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 29/WG1 M82039. In Proceedings of the 82th Meeting, Lisbon, Portugal, 19–25 January 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Peixeiro, J.; Brites, C.; Ascenso, J.; Pereira, F. Digital holography: Benchmarking coding standards and representation formats. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), Seattle, WA, USA, 11–15 July 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- JPEG XT Reference Software. Available online: https://jpeg.org/jpegxt/software.html (accessed on 18 April 2019).
- Overview of JPEG XS. Available online: https://jpeg.org/jpegxs/index.html (accessed on 18 April 2019).
- JPEG 2000 Kakadu Software. Available online: http://kakadusoftware.com/downloads/ (accessed on 18 April 2019).
- JPEG LS Reference Software. Available online: https://jpeg.org/jpegls/software.html (accessed on 18 April 2019).
- FFmpeg Software. Available online: https://www.ffmpeg.org/ (accessed on 18 April 2019).
- HEVC Reference Software. Available online: https://hevc.hhi.fraunhofer.de/ (accessed on 18 April 2019).
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).