RTPO: A Domain Knowledge Base for Robot Task Planning
Abstract
1. Introduction
- It contributes a domain knowledge base RTPO for robots to have a better understanding of the task planning knowledge.
- An evaluation method of knowledge base is proposed and implemented to test scalability and responsiveness in this paper.
- A task planning algorithm based on RTPO is proposed which has good flexibility and avoids the shortcoming of manual editing domain knowledge in traditional task planners.
- We carried out the experimental research and applied the proposed approach on the real robot.
2. Building Considerations for Robot Task Planning Ontology (RTPO)
2.1. Purpose of Robot Task Planning Ontology (RTPO)
2.2. Requirements of Robot Task Planning Ontology (RTPO)
- With unambiguous knowledge representation, it is easy to be understood by humans and robots.
- With strong editability, it is easy to be operated and utilized by developers.
- With knowledge representation, it is consistent and free from contradictory knowledge or definitions.
3. The Building of Robot Task Planning Ontology (RTPO)
3.1. The Model of Robot Task Planning Ontology (RTPO)
3.2. The Approaches to Build Robot Task Planning Ontology (RTPO)
4. Knowledge Representation in Robot Task Planning Ontology (RTPO)
4.1. The Knowledge in Robot Task Planning Ontology (RTPO)
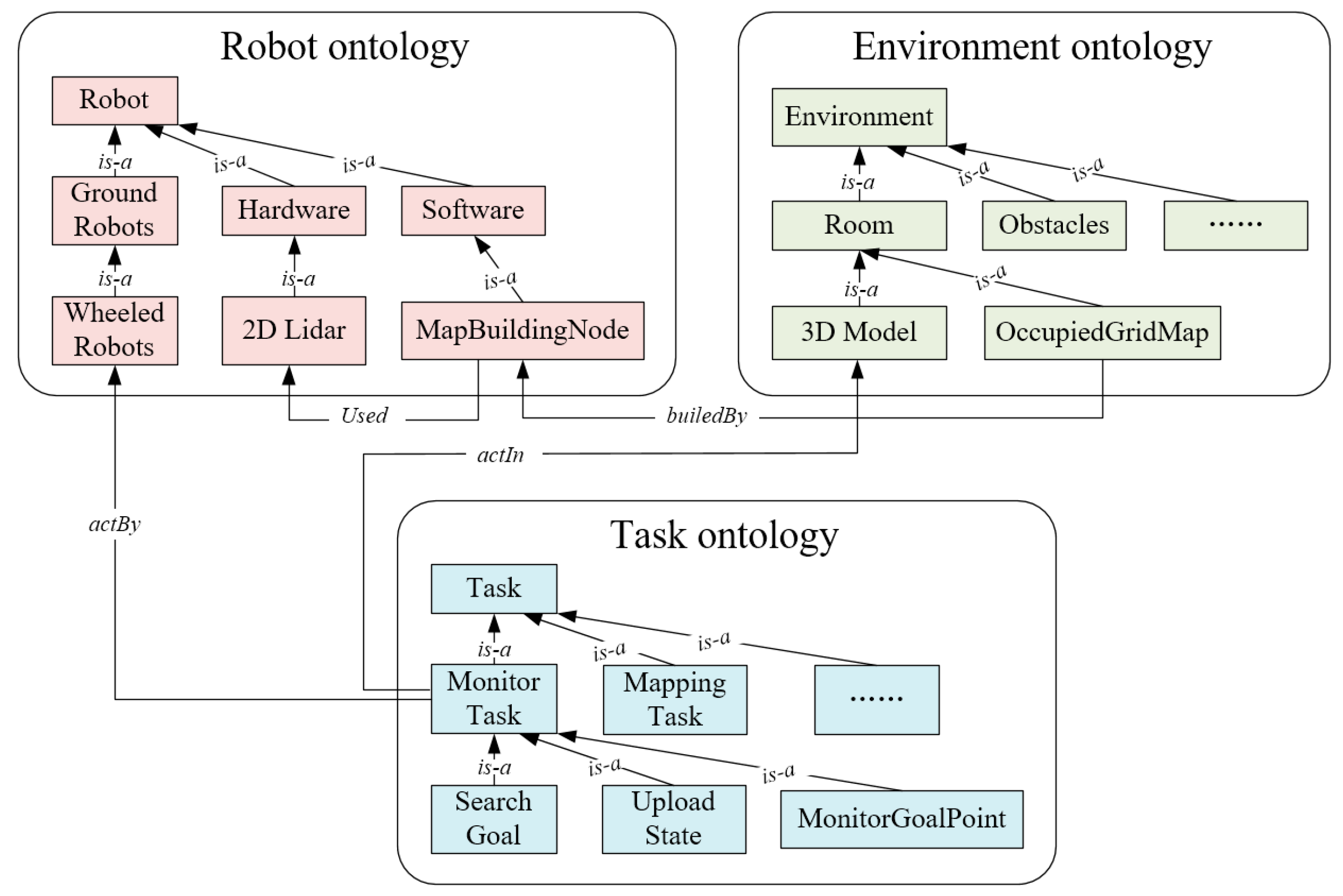
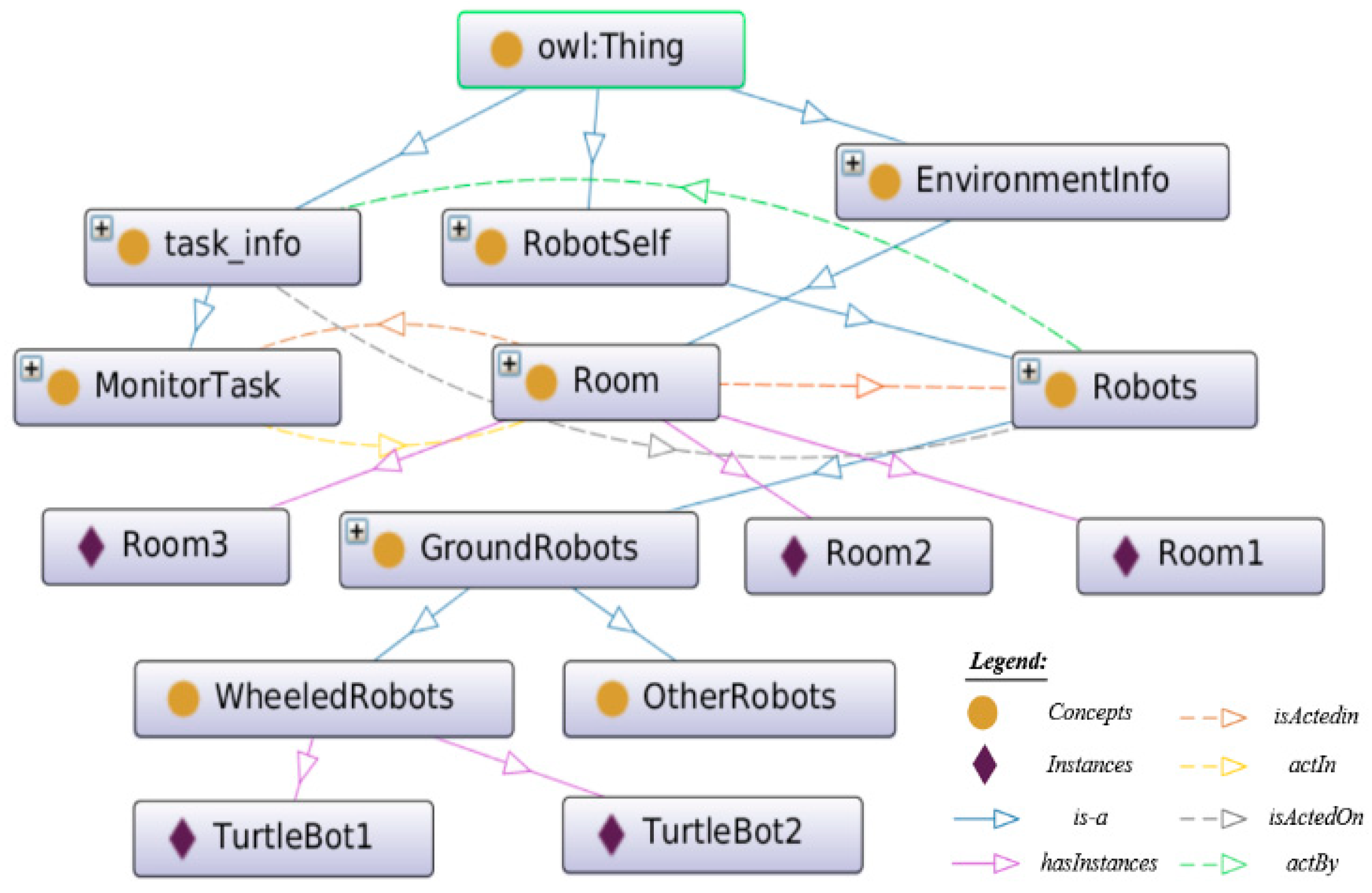
4.2. The Structure of Robot Task Planning Ontology (RTPO)
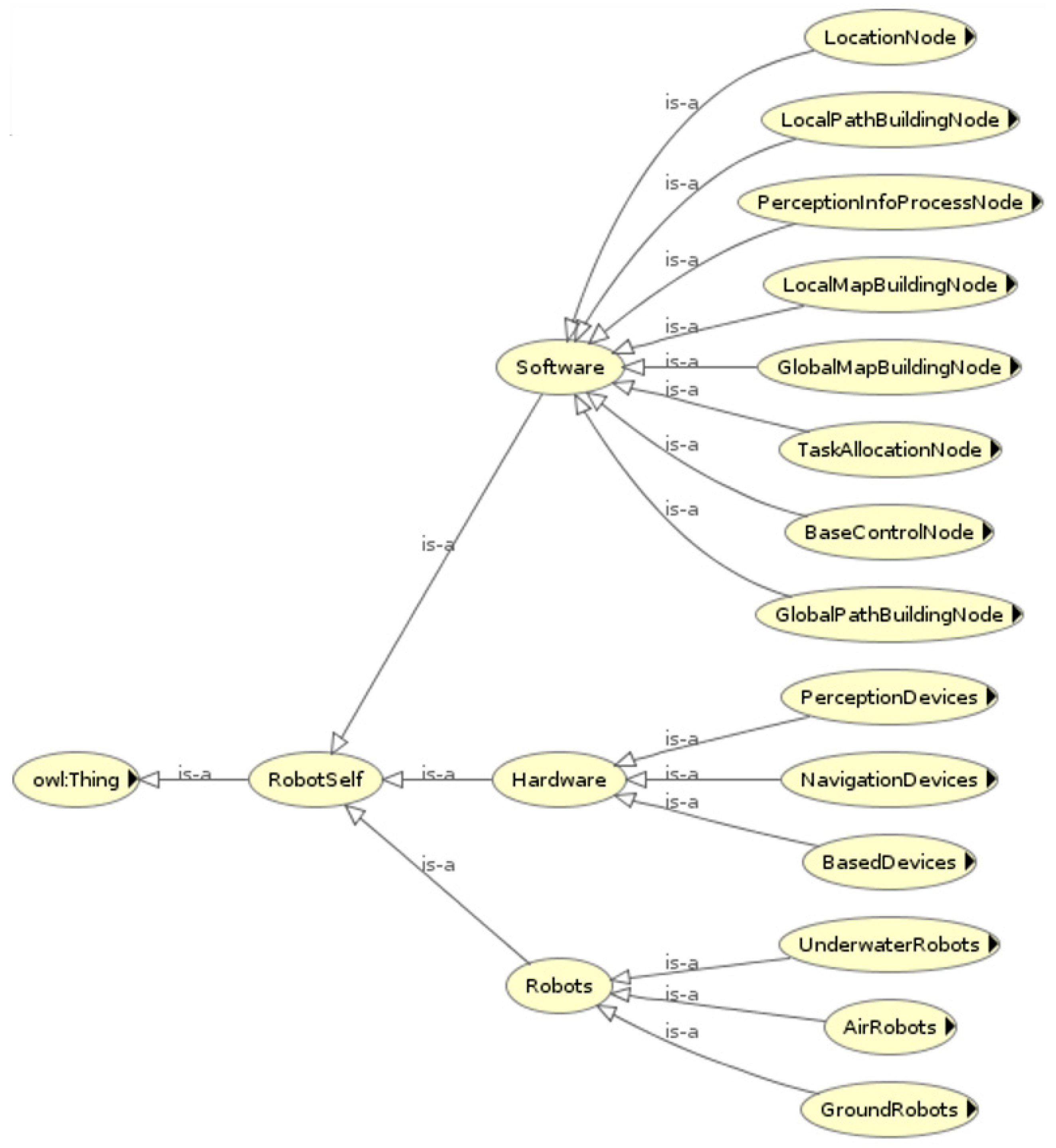
4.2.1. Robot Ontology
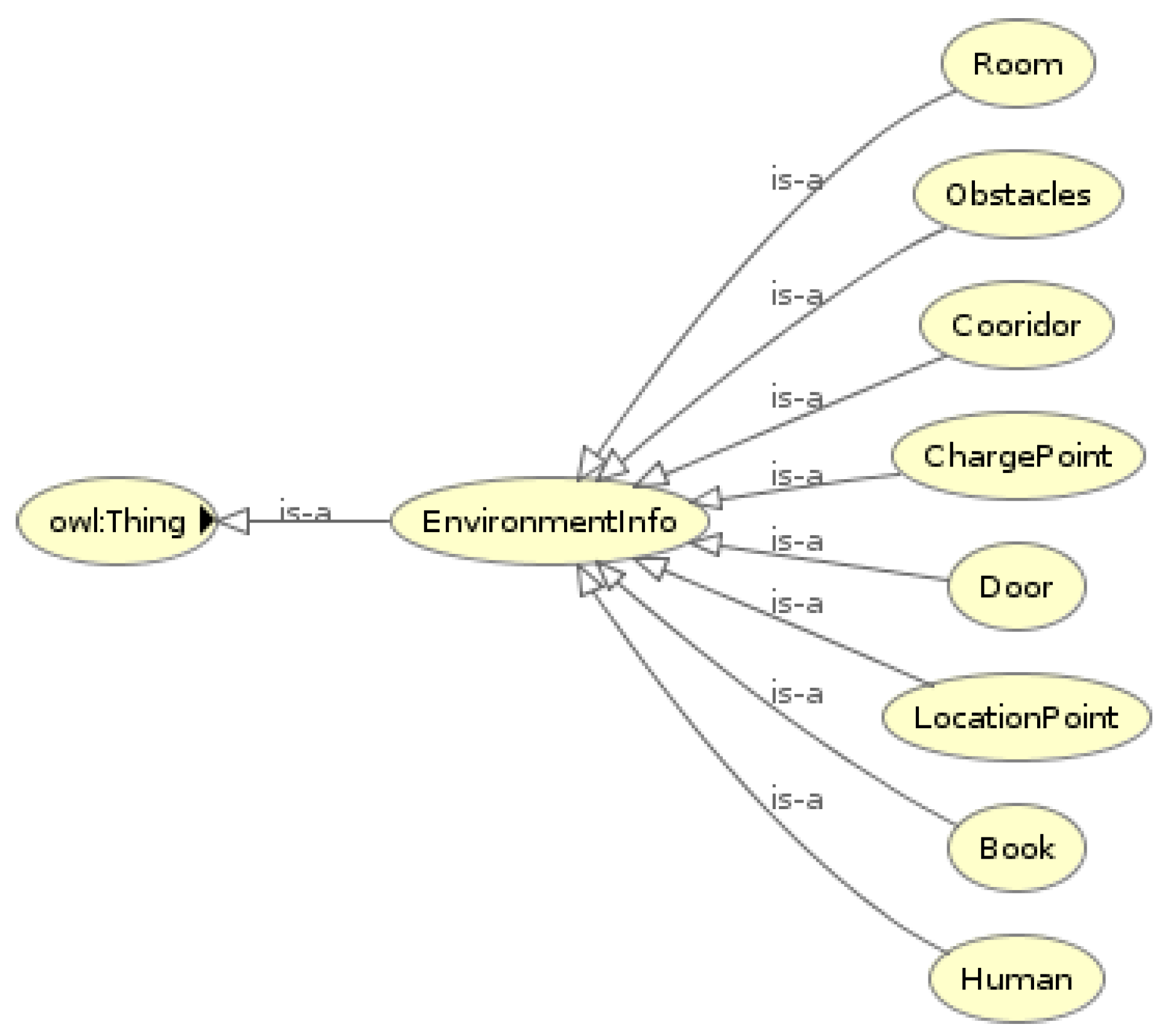
4.2.2. Environment Ontology
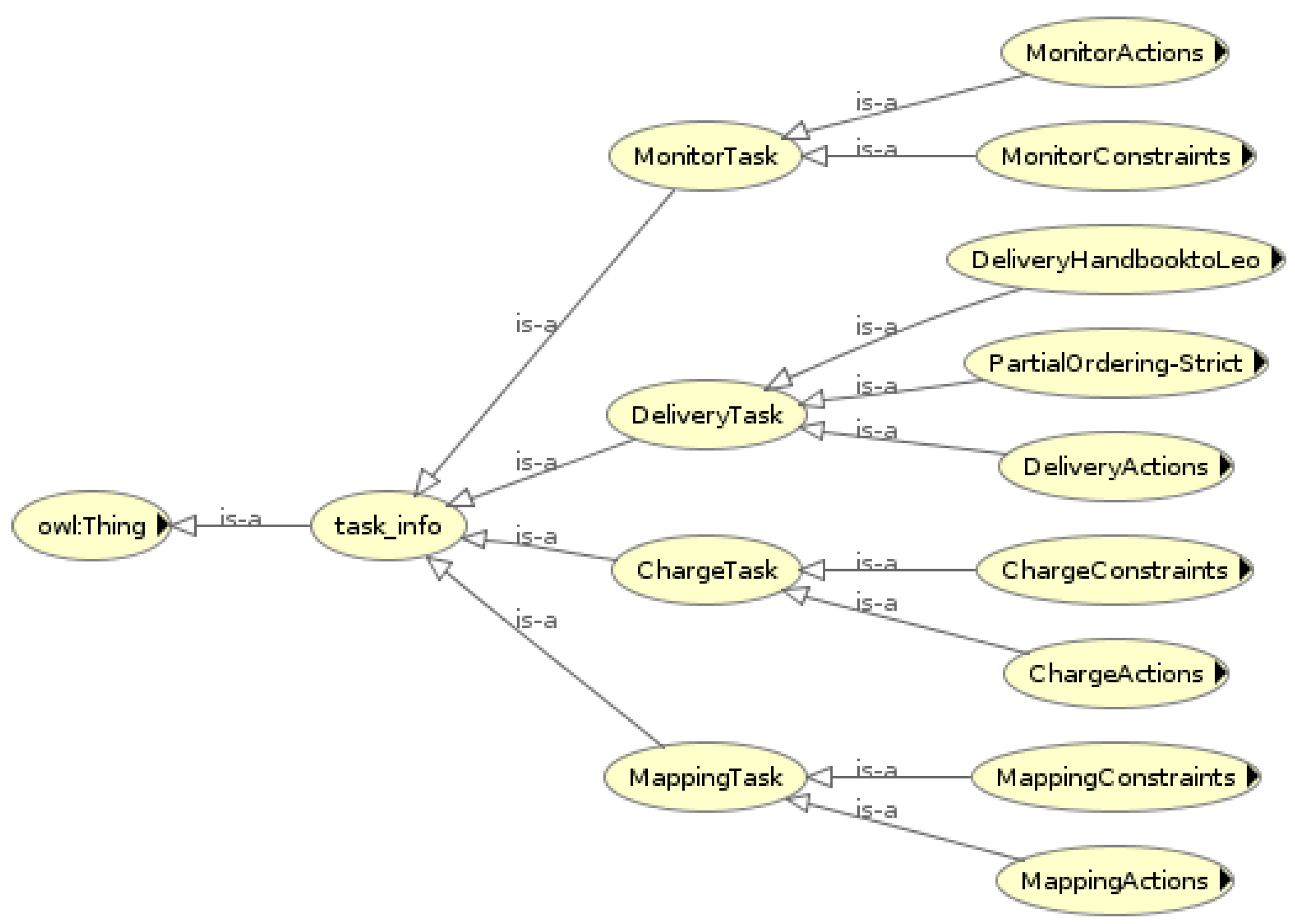
4.2.3. Task Ontology
4.2.4. Communications Among the Three Parts
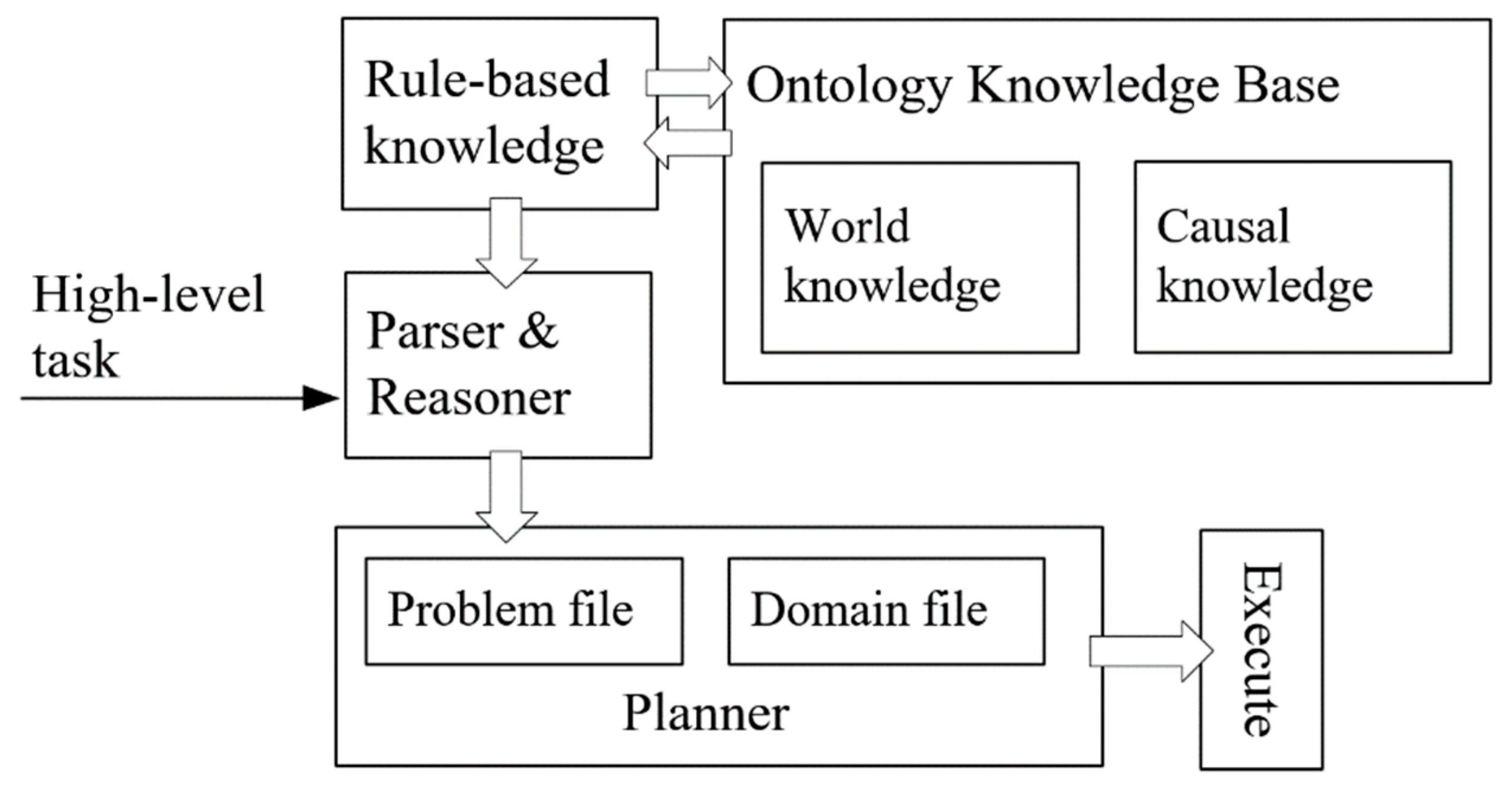
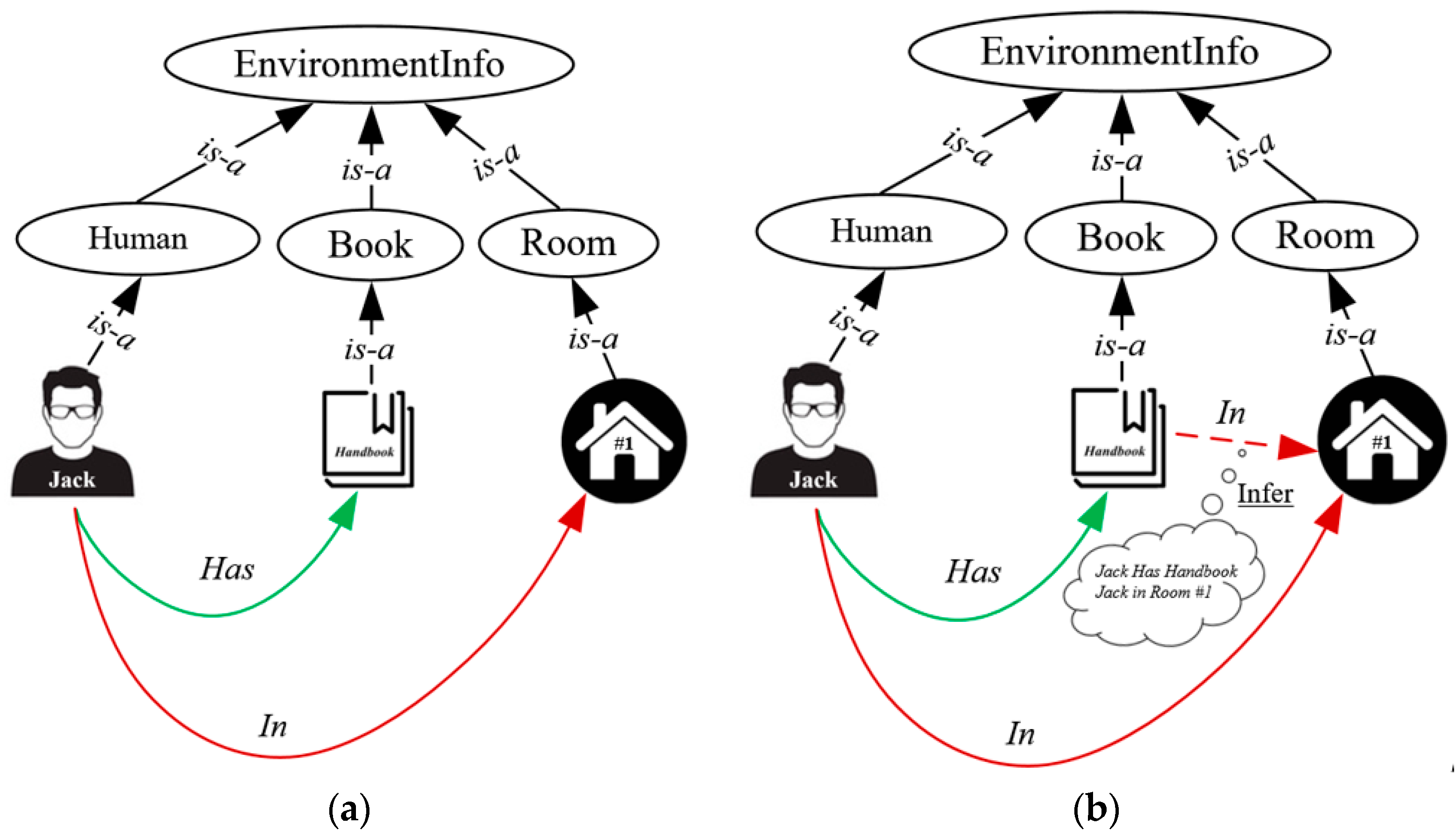
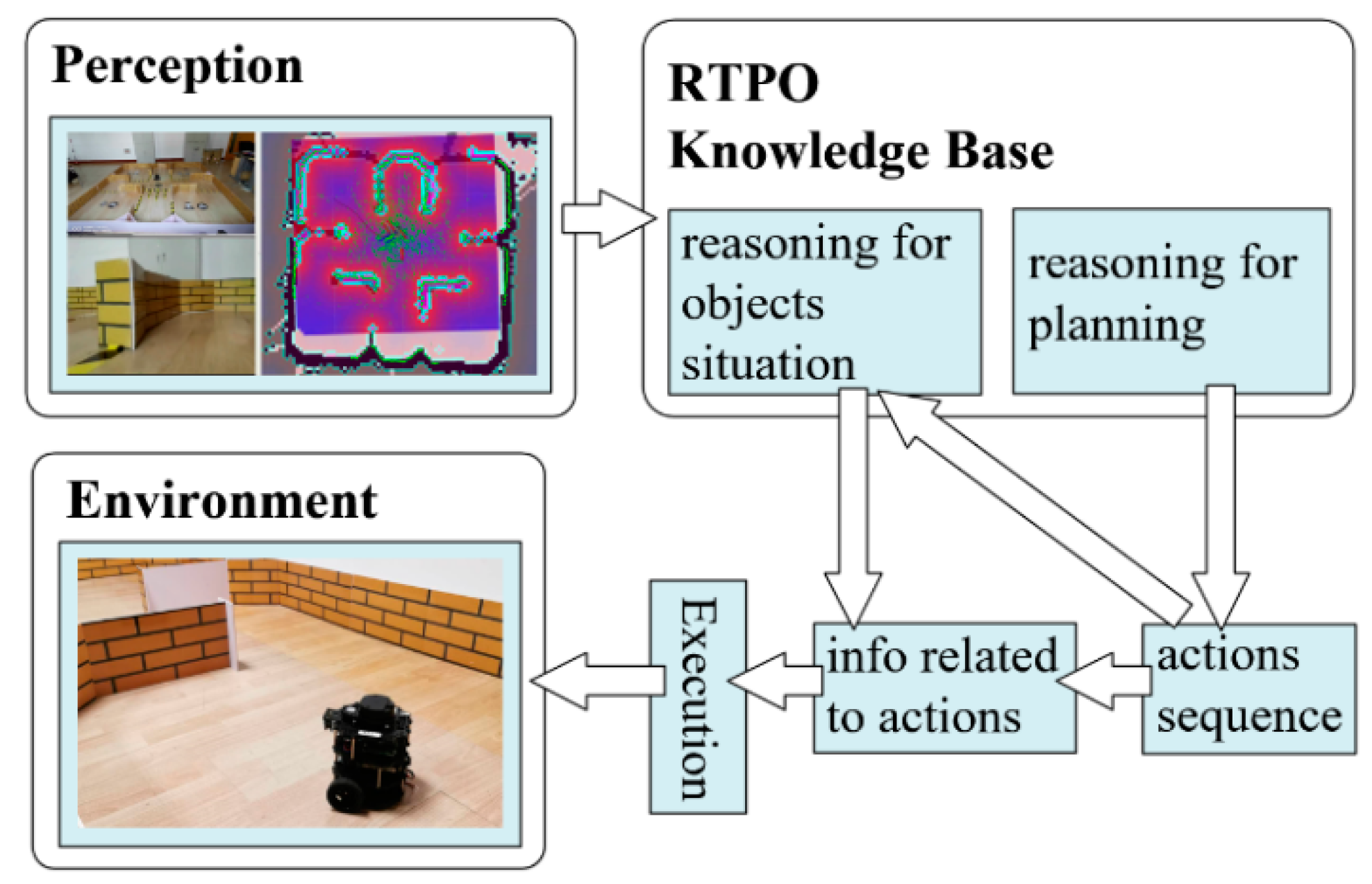
4.3. Knowledge Reasoning
5. Evaluation and Experiments
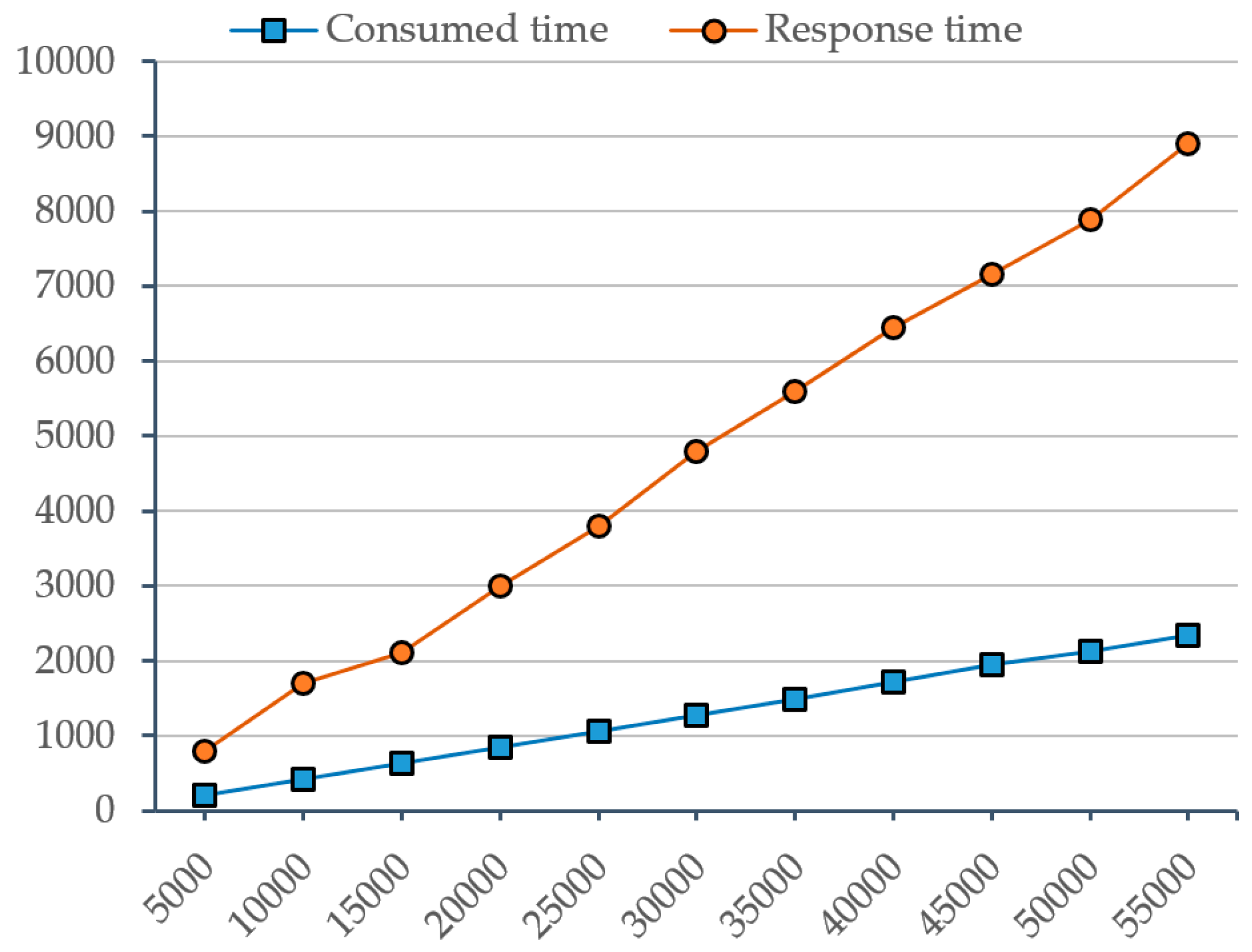
5.1. The Evaluation of Robot Task Planning Ontology (RTPO)
5.2. Verification Using a Case Study
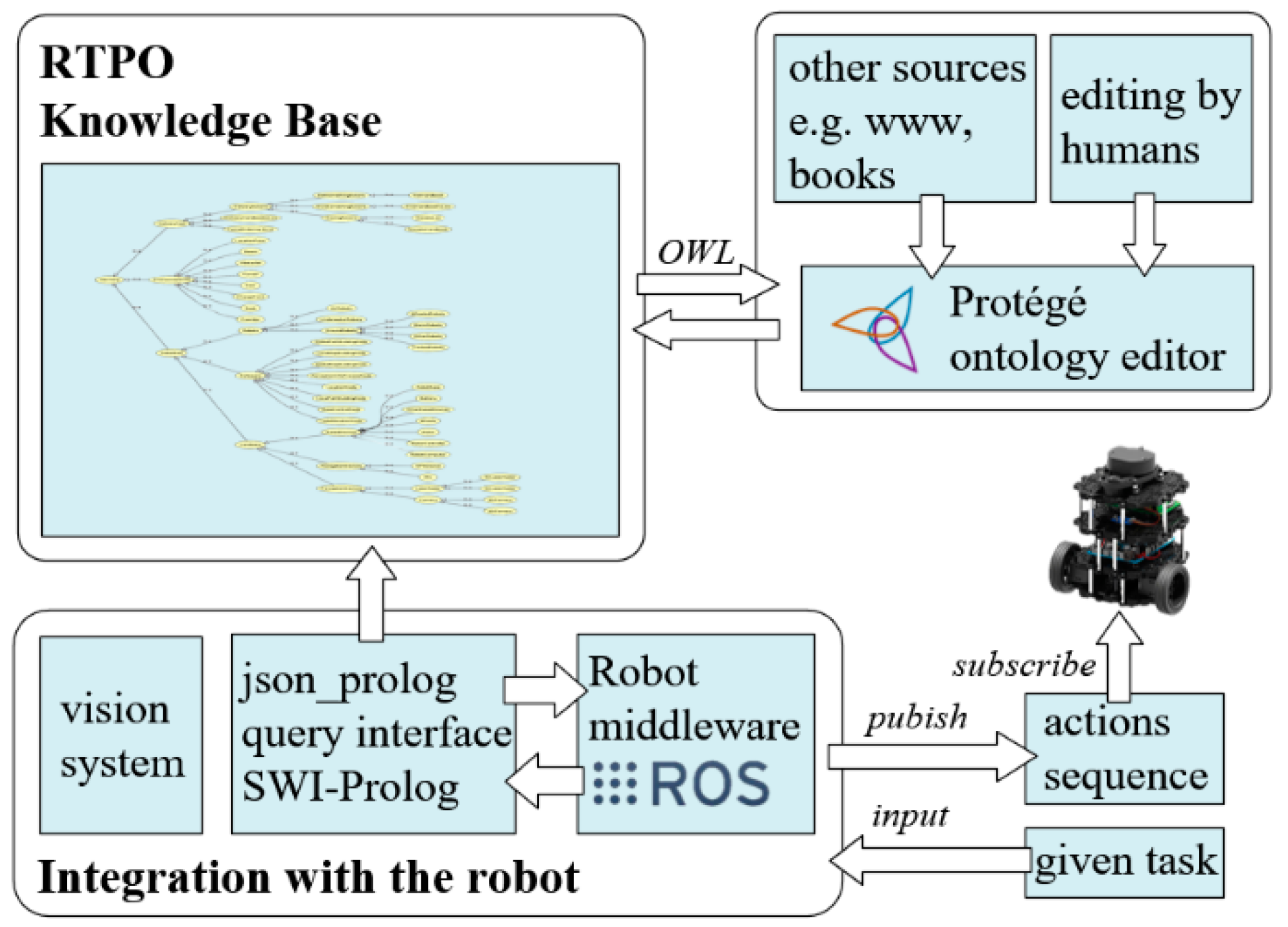
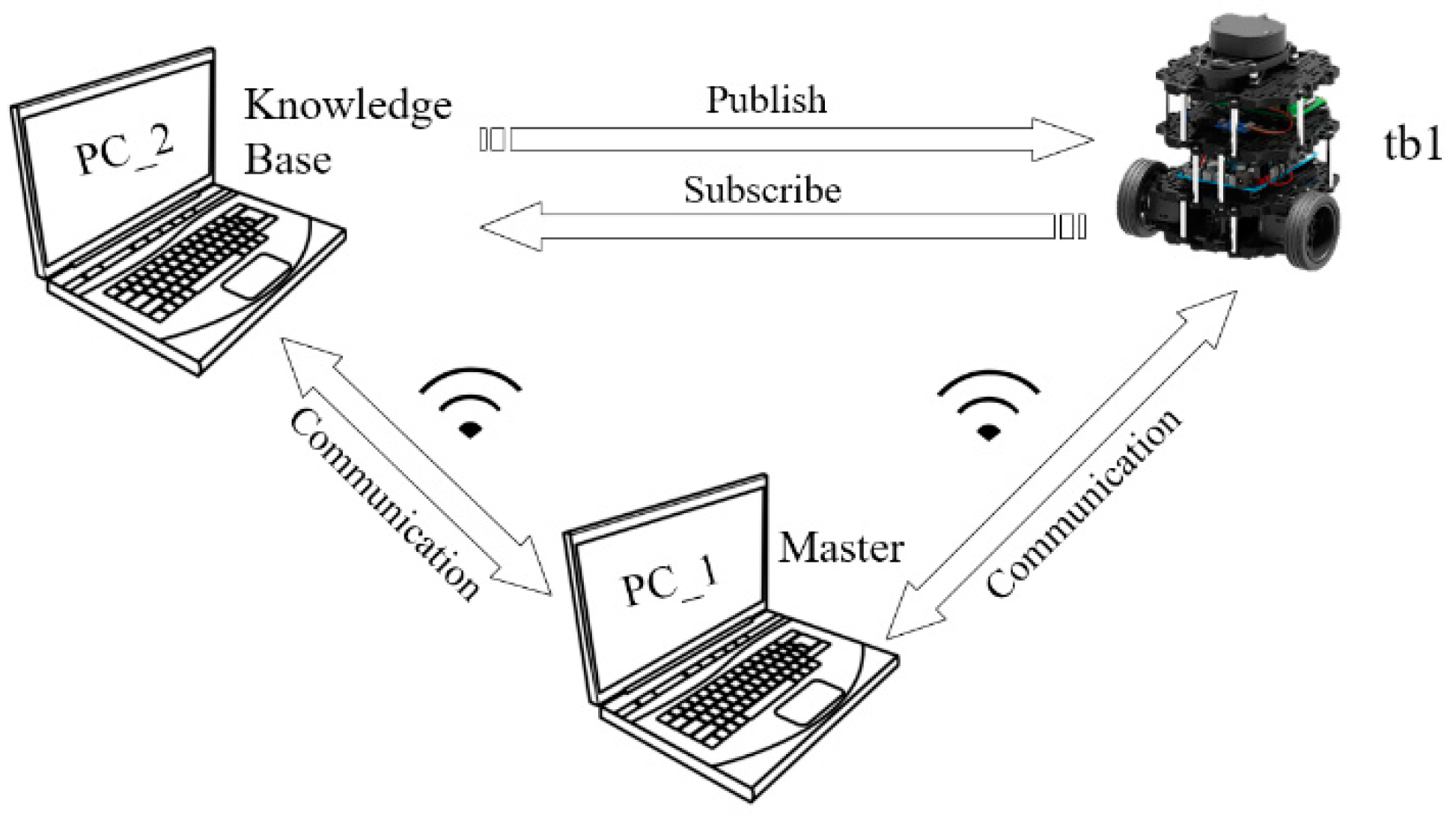
5.2.1. Hardware and Software
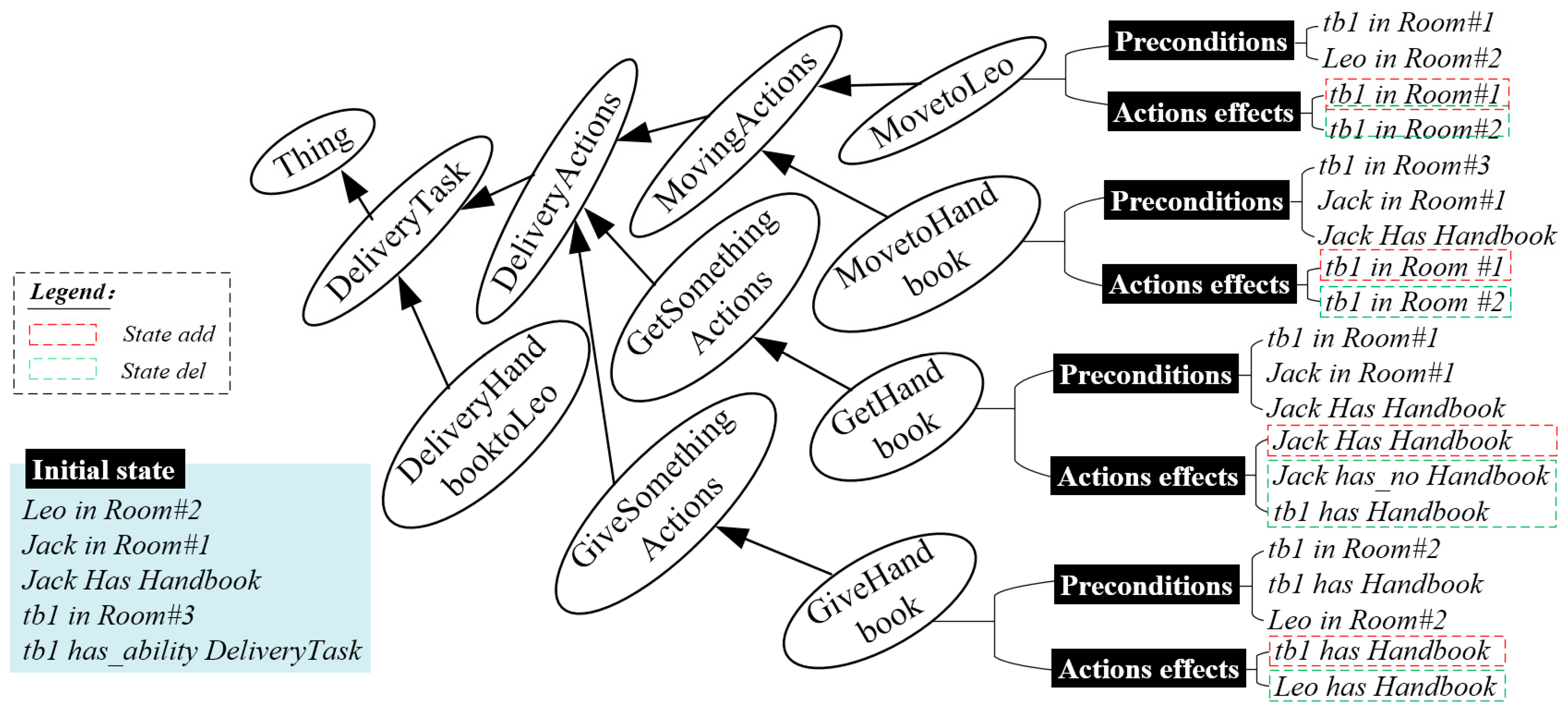
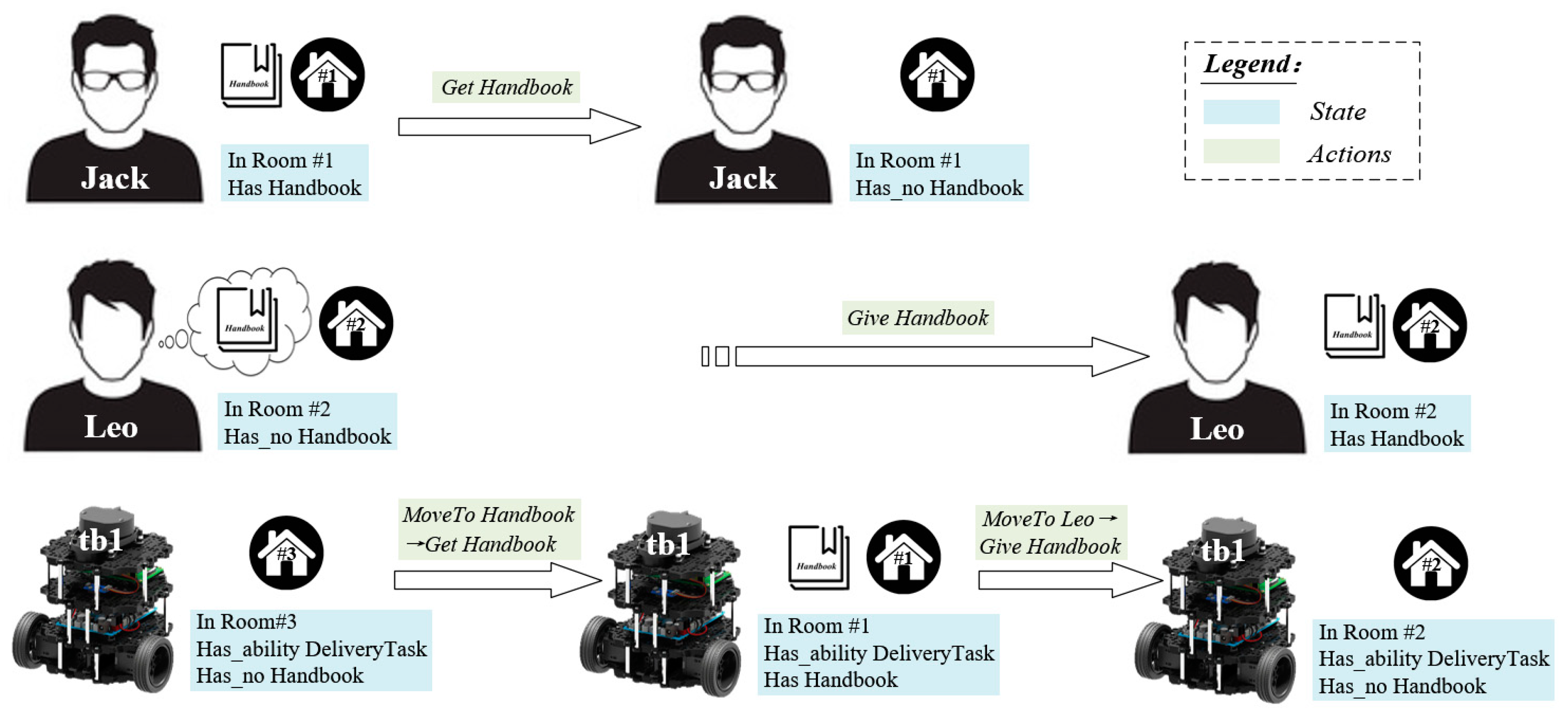
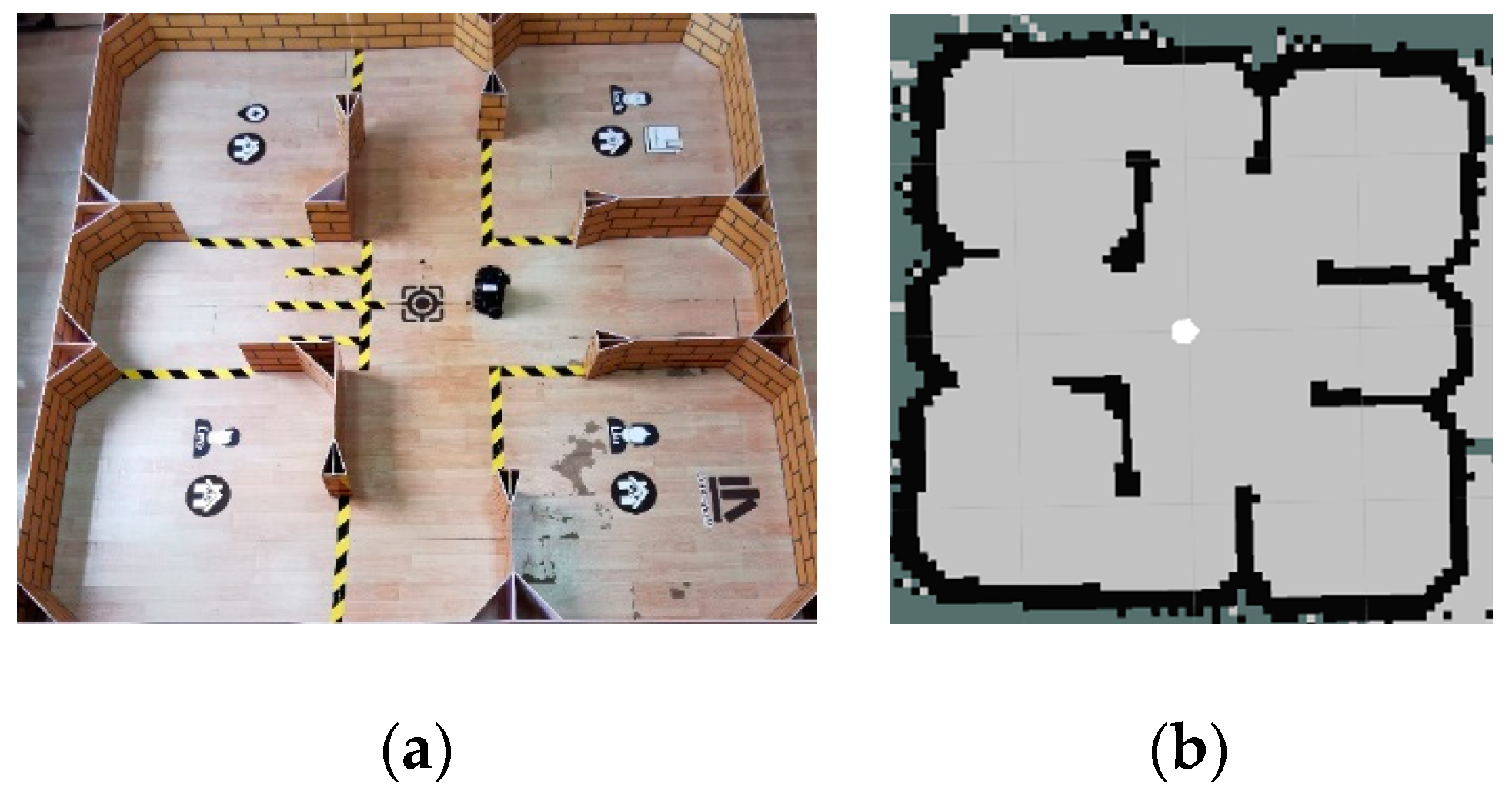
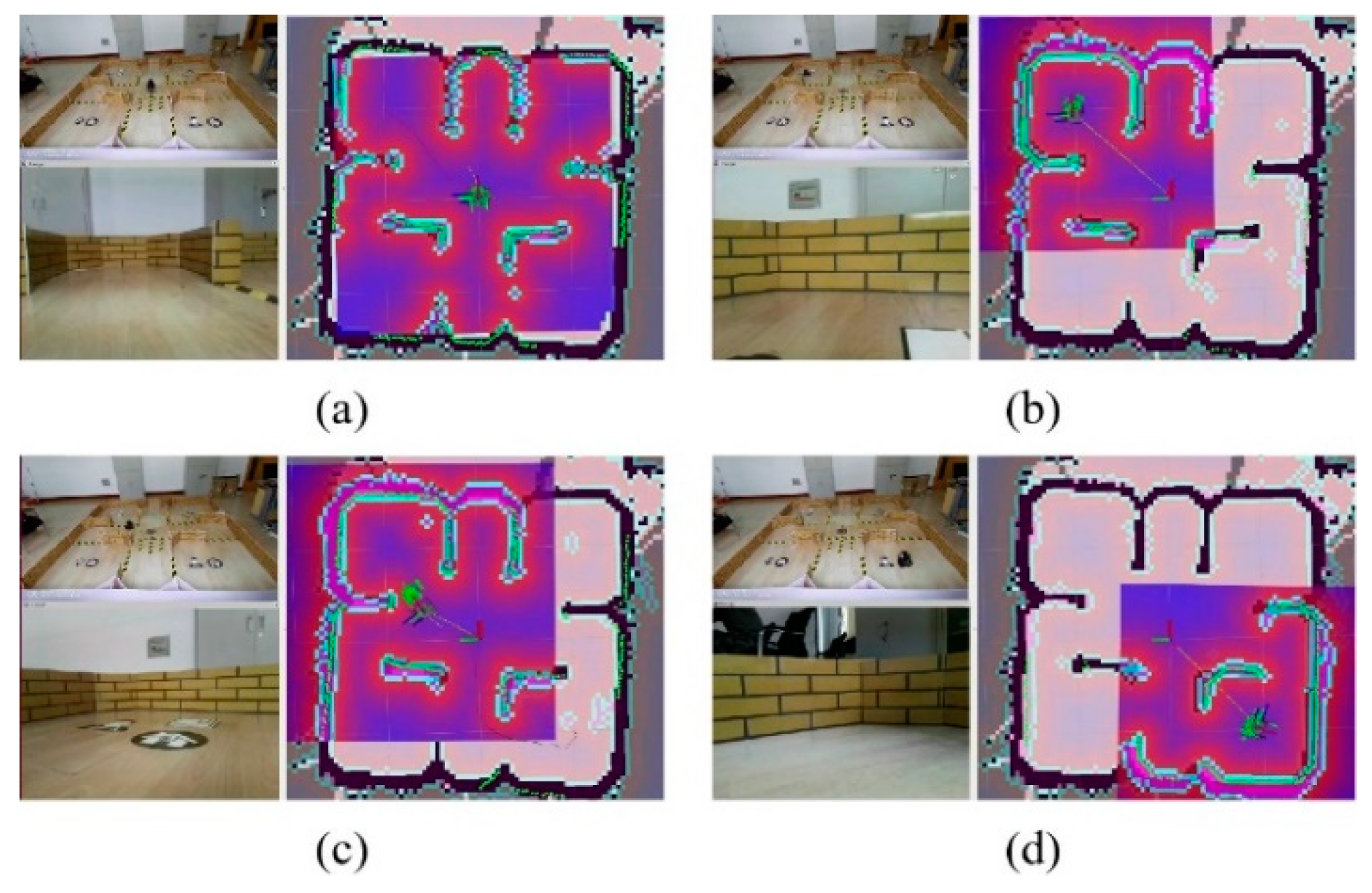
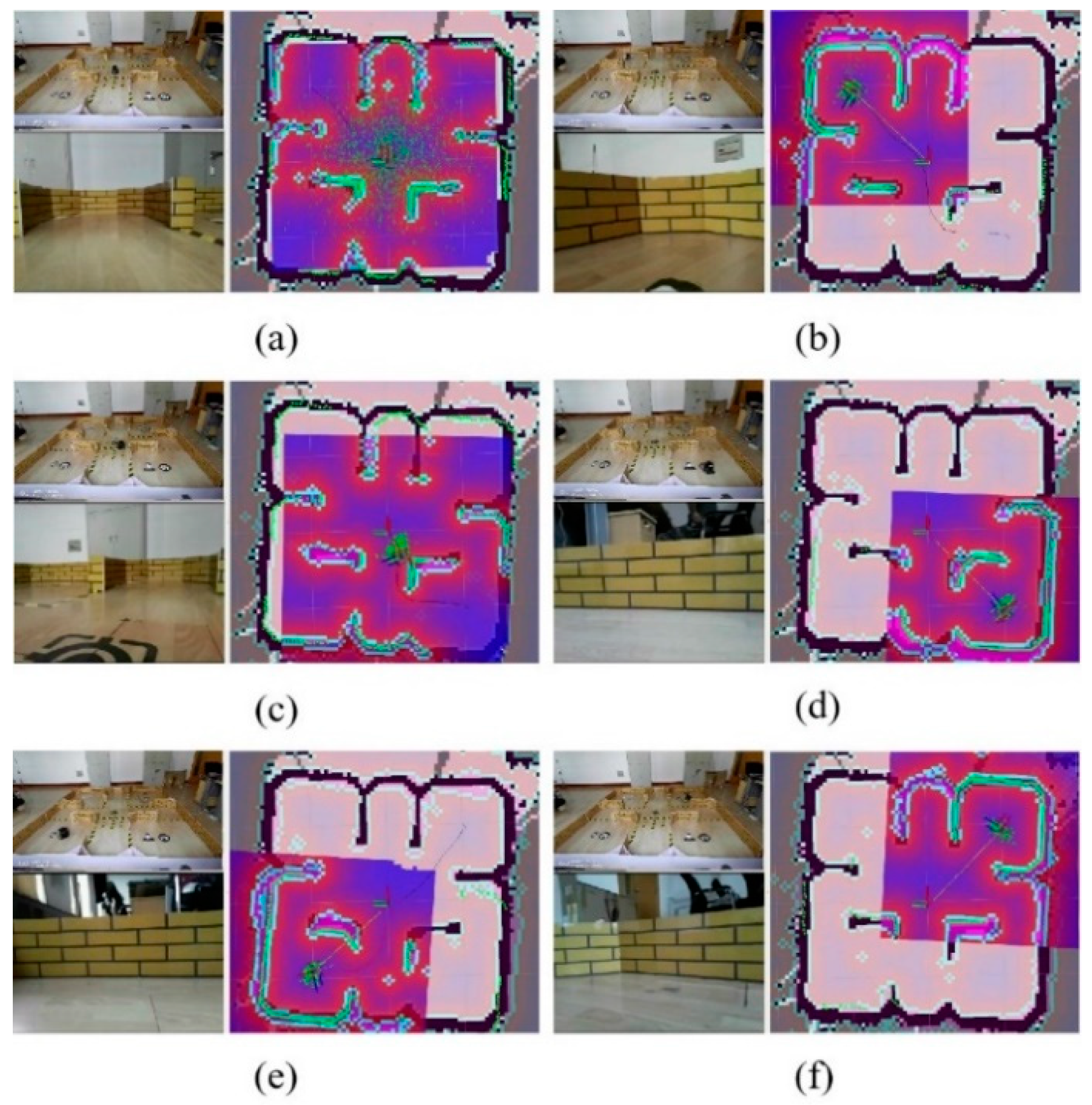
5.2.2. The Experimental Scenario
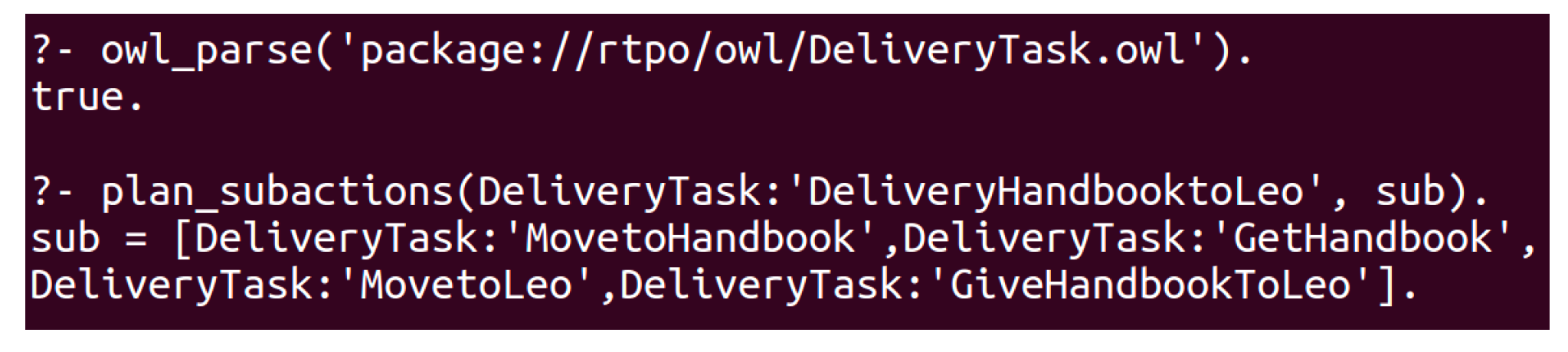
5.2.3. The Experiments and Results
| Algorithm 1 Task Planning Algorithm Based on Robot Task Planning Ontology (RTPO) |
| Input: s: the initial state; t: the given high-level task; O: the ontology knowledge Output: : A plan for accomplishing the t from the initial state; 1: procedure generate a plan for accomplishing the t 2: 3: function task_planning (t) 4: if t is a primitive task then 5: modify s by deleting del(t) and adding add(t) 6: append t to P 7: else 8: for all subtask in subtasks(t) do 9: if preconditions(subtask) matches the s then 10: task_planning (subtask) 11: return P 12: end procedure |
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goodfellow, I.; Bengio, Y.; Courville, A. Deep Learning; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, P.-C.; Suzuki, K.; Kase, K.; Sasaki, K.; Sugano, S.; Ogata, T. Repeatable folding task by humanoid robot worker using deep learning. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2016, 2, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, S.; Pastor, P.; Krizhevsky, A.; Ibarz, J.; Quillen, D. Learning hand-eye coordination for robotic grasping with deep learning and large-scale data collection. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2018, 37, 421–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiang, C.W.; Tee, F.S.; Halin, A.A.; Yap, N.K.; Hong, P.C. Ontology reuse for multiagent system development through pattern classification. Softw. Pract. Exp. 2018, 48, 1923–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sappagh, S.; Alonso, J.M.; Ali, F.; Ali, A.; Jang, J.-H.; Kwak, K.-S. An ontology-based interpretable fuzzy decision support system for diabetes diagnosis. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 37371–37394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Tian, X.; Sangaiah, A.K.; Wang, J. Towards Semantic Sensor Data: An Ontology Approach. Sensors 2019, 19, 1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, L.; Zhou, C.; Xiao, C.; Zhang, F.; Peng, X.; Zhan, W.; Sui, Z. Semantic Modelling of Ship Behavior in Harbor Based on Ontology and Dynamic Bayesian Network. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.E.; Yang, Y.; Ndzi, D.L.; Yang, G.; Al-Maliki, M. Ontology-based personalized course recommendation framework. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 5180–5199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, H.; Yang, K.-M.; Park, S.; Choi, J.; Lim, Y. An Ontology-Based Home Care Service Robot for Persons with Dementia; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 540–545. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, G.; Cao, Y.; Ren, Y.; Li, X.; Feng, Z. Network security situation awareness based on semantic ontology and user-defined rules for Internet of Things. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 21046–21056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, S.; Mansouri, M.; Pecora, F.; Hertzberg, J. Hierarchical Hybrid Planning in a Mobile Service Robot; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 309–315. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, H.; Chen, G.; Jia, Q.; Yu, B. Hierarchical task planning for multiarm robot with multiconstraint. Math. Probl. Eng. 2016, 2016, 2508304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo, C.; Fernández-Madrigal, J.-A.; González, J.; Saffiotti, A. Robot task planning using semantic maps. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2008, 56, 955–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cashmore, M.; Fox, M.; Long, D.; Magazzeni, D.; Ridder, B.; Carrera, A.; Palomeras, N.; Hurtos, N.; Carreras, M. Rosplan: Planning in the robot operating system. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Fifth International Conference on Automated Planning and Scheduling, Jerusalem, Israel, 7–11 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, F.; Tian, G.; Li, Q. Autonomous cognition and planning of robot service based on ontology. Jiqiren/Robot 2017, 39, 423–430. [Google Scholar]
- IsaacSaito.Wiki: ROS [EB/OL]. Available online: http://wiki.ros.org/ROS/ (accessed on 23 April 2013).
- Tenorth, M. Knowledge Processing for Autonomous Robots. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universität München, Munich, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Tenorth, M.; Beetz, M. KNOWROB—Knowledge processing for autonomous personal robots. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, St. Louis, MO, USA, 11–15 October 2009; pp. 4261–4266. [Google Scholar]
- Tenorth, M.; Beetz, M. Representations for robot knowledge in the KnowRob framework. Artif. Intell. 2015, 247, 151–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenorth, M.; Perzylo, A.C.; Lafrenz, R.; Beetz, M. Representation and Exchange of Knowledge about Actions, Objects, and Environments in the RoboEarth Framework. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2013, 10, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waibel, M.; Beetz, M.; Civera, J.; d’Andrea, R.; Elfring, J.; Galvez-Lopez, D.; Häussermann, K.; Janssen, R.; Montiel, J.M.M.; Perzylo, A.; et al. Roboearth—A world wide web for robots. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. (RAM) 2011, 18, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riazuelo, L.; Civera, J.; Montiel, J.; Montiel, J.M.M. C2tam: A cloud framework for cooperative tracking and mapping. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2014, 62, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemaignan, S. Grounding the Interaction: Knowledge Management for Interactive Robots. KI-Künstliche Intell. 2013, 27, 183–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemaignan, S.; Ros, R.; Mösenlechner, L.; Alami, R.; Beetz, M. ORO, a knowledge management platform for cognitive architectures in robotics. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Taipei, Taiwan, 18–22 October 2010; pp. 3548–3553. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Bilbao, S.; Martín-Wanton, T.; Bastos, J.; Rodriguez, J. SWARMs ontology: A common information model for the cooperation of underwater robots. Sensors 2017, 17, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landa-Torres, I.; Manjarres, D.; Bilbao, S.; Del Ser, J. Underwater robot task planning using multi-objective meta-heuristics. Sensors 2017, 17, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadik, A.R.; Urban, B. An Ontology-Based Approach to Enable Knowledge Representation and Reasoning in Worker–Cobot Agile Manufacturing. Future Internet 2017, 9, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diab, M.; Akbari, A.; Din, M.U.; Rosell, J. PMK—A Knowledge Processing Framework for Autonomous Robotics Perception and Manipulation. Sensors 2019, 19, 1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlenoff, C.; Prestes, E.; Madhavan, R.; Goncalves, P.; Li, H.; Balakirsky, S.; Kramer, T.; Miguelanez, E. An IEEE standard ontology for robotics and automation. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Algarve, Portugal, 7–12 October 2012; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 1337–1342. [Google Scholar]
- Khandelwal, P.; Zhang, S.; Sinapov, J.; Leonetti, M.; Thomason, J.; Yang, F.; Gori, I.; Svetlik, M.; Khante, P.; Lifschitz, V.; et al. Bwibots: A platform for bridging the gap between ai and human–robot interaction research. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2017, 36, 635–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandelwal, P.; Yang, F.; Leonetti, M.; Lifschitz, V.; Stone, P. Planning in Action Language BC while Learning Action Costs for Mobile Robots. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Fourth International Conference on Automated Planning and Scheduling, Portsmouth, NH, USA, 21–26 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Lifschitz, V.; Yang, F. Action Language BC: Preliminary Report. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Third International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Beijing, China, 3–9 August 2013; pp. 983–989. [Google Scholar]
- McGuinness, D.L.; Van Harmelen, F. OWL web ontology language overview. W3C Recomm. 2004, 10, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- OWL Working Group. OWL—Semantic Web Standard [EB/OL]. Available online: https://www.w3.org/2001/sw/wiki/OWL,2-013-12-21 (accessed on 21 August 2019).
- Zhai, Z.; Ortega, J.-F.M.; Martínez, N.L.; Castillejo, P. A Rule-Based Reasoner for Underwater Robots Using OWL and SWRL. Sensors 2018, 18, 3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- TaniaTudorache. Protégé Wiki [EB/OL]. Available online: https://protegewiki.stanford.edu/wiki/Main_Page (accessed on 23 May 2016).
- Maedche, A.; Staab, S. Ontology learning for the Semantic Web. Intell. Syst. IEEE 2001, 16, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clocksin, W.F.; Mellish, C.S. Programming in Prolog; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1981. [Google Scholar]

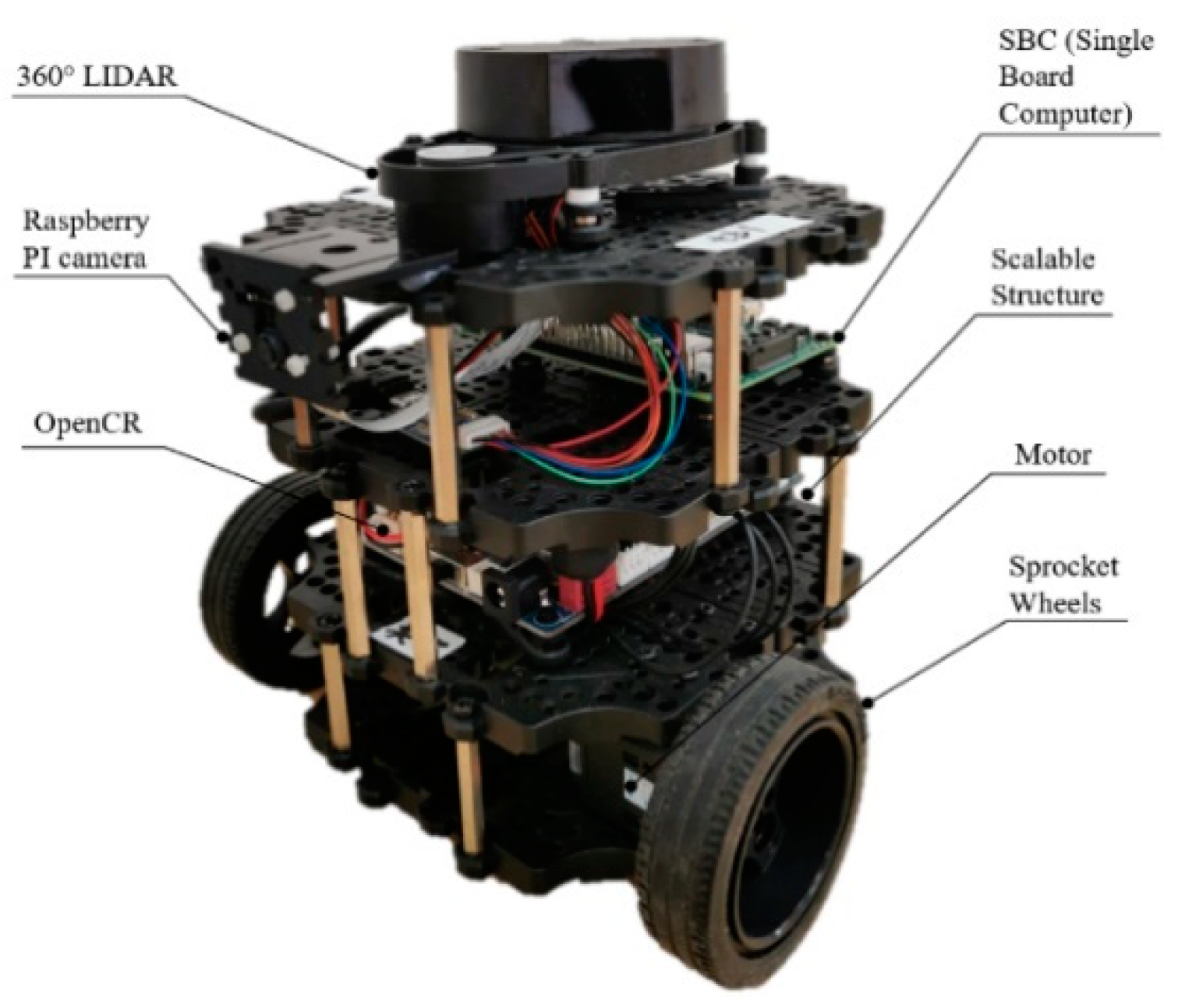
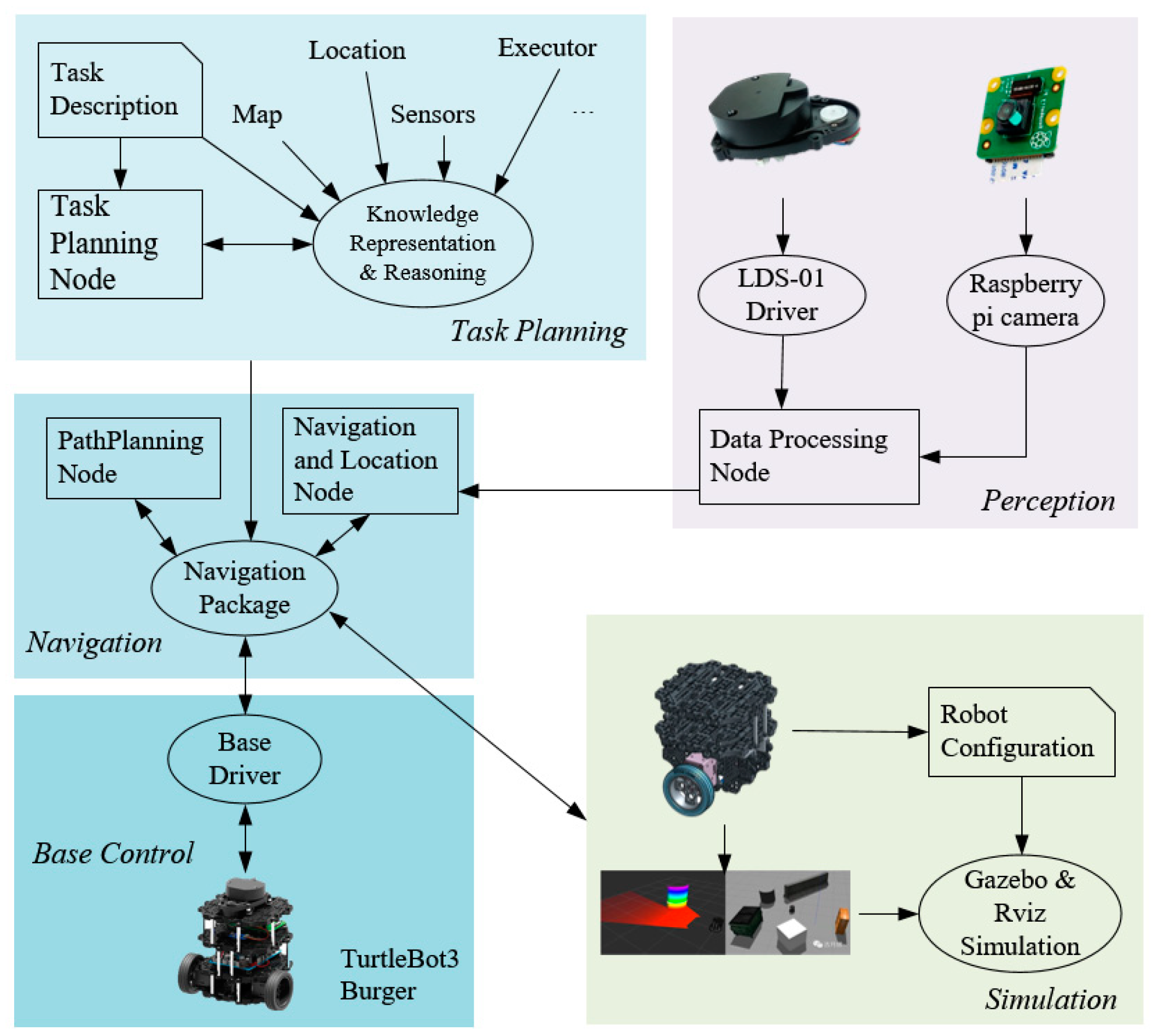
| Items | Configuration |
|---|---|
| LIDAR | 360-degree laser LIDAR LDS-01 (HLS-LFCD2) |
| SBC | Raspberry PI 3 and Intel Joule 570x |
| Battery | Lithium polymer 11.1 V 1800 mAh |
| IMU | Gyroscope 3 Axis |
| Accelerometer 3 Axis | |
| Magnetometer 3 Axis | |
| MCU | OpenCR (32-bit ARM Cortex® M7) |
| Motor | DYNAMIXEL(XL430) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J. RTPO: A Domain Knowledge Base for Robot Task Planning. Electronics 2019, 8, 1105. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8101105
Sun X, Zhang Y, Chen J. RTPO: A Domain Knowledge Base for Robot Task Planning. Electronics. 2019; 8(10):1105. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8101105
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Xiaolei, Yu Zhang, and Jing Chen. 2019. "RTPO: A Domain Knowledge Base for Robot Task Planning" Electronics 8, no. 10: 1105. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8101105
APA StyleSun, X., Zhang, Y., & Chen, J. (2019). RTPO: A Domain Knowledge Base for Robot Task Planning. Electronics, 8(10), 1105. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8101105




