1. Introduction
The Internet of Things (IoT) has established itself as the medium for global connectivity among all sorts of devices, with 20.4 billion estimated connected devices worldwide by 2020 [
1]. The IoT relies on Internet protocols, such as Machine-to-Machine (M2M) communications, to achieve interoperability and cater for the needs of domains such as e-health, smart grids, or smart cities [
2,
3,
4]. In the particular case of e-health, patients can be monitored using networked sensors that collect personal data and send it to medical or processing centers for tracking chronic conditions or for prophylactic reasons [
5,
6].
Continuous patient monitoring for quick response is also common in intensive care units. However, it can also be similarly important in emergency wards, where deaths and serious adverse events can occur if a prompt response is not enforced [
7,
8,
9]. This is particularly critical during overloads caused by catastrophic events, extreme weather or periods of high propensity, raising the awareness to the importance of continuous patient monitoring in emergency wards [
7,
10,
11].
Currently, monitoring physiological parameters in wards can be done with existing wearable devices, like wristbands or smartwatches, that collect heart beat frequency and variability, blood pressure, oxygen saturation level, and body and room temperatures. However, current devices rely on short-range communication protocols, typically Bluetooth, requiring a gateway (GW) for sustained Internet connection [
12,
13,
14,
15,
16]. GWs can be implemented using smartphones given their usability and enhanced connectivity, but this comes at a price. The GW functionality increases the power consumption of the smartphone severely reducing its autonomy, it also increases the communication delay due to relaying, and it increases the cost of the monitoring system [
12,
17,
18]. In the work by the authors of [
18], considerable depletion of smartphones’ battery was observed when using them as GWs for BT wearable devices, in an IoT e-health scenario with online remote monitoring, mainly due to network accesses. Moreover, there is currently a range of disparate non-interoperable e-health systems that use specific vertical solutions for communications and monitoring [
19,
20], contributing to a global high system cost.
In this paper we propose an open IoT architecture to track the physiological parameters of patients, fully integrated with the Internet from the wearable sensors up to the monitoring system. For this purpose we leverage an interoperable framework [
21] that relies on two de facto standards. oneM2M [
22] is a technical standard for interoperability concerning architecture, API specifications, and security for M2M/IoT technologies based on requirements contributed by a global partnership. openEHR [
23] is an open standard specification for data semantics, storage, and making health data available to the medical personnel in electronic health records (EHRs).
Then, we make use of low-cost and low-power WiFi-enabled sensor devices based on ESP8266 modules [
24] and embedded in wristbands with a 1000 mAh battery for continuous patient ambulatory monitoring. These devices connect directly to an existing Internet infrastructure, avoiding GWs and potentially reducing cost and communication latency, while improving usability. However, it is a significant challenge to control the power of the Wi-Fi devices to achieve sufficient autonomy while keeping enough computing capacity to execute sensor processing functions and Internet communication protocols.
Therefore, we carry out a feasibility study of the proposed open IoT architecture, showing the configuration and implementation of the services, the use protocol of the wristbands, the device’s consumption and autonomy in different module sleep modes, the end-to-end services latency, and the impact of the WiFi network configuration. We believe that integrating WiFi-enabled wearable sensors in e-health systems is novel and has the potential to provide a low-cost solution for continued tracking of patients physiological parameters as needed in emergency wards.
The rest of the paper is structured as follows. The next section presents a storyboard that we use as the motivating use case scenario. It is followed by the architecture and implementation of the framework in
Section 3. In
Section 4 and
Section 5 we provide, respectively, a qualitative comparison and quantitative performance analysis of the modules’ performance in terms of the power requirements as well as the end-to-end latency using normal and energy-saving modes. We analyze the impact of different WiFi network configurations on the modules power consumption in
Section 6 and conclude the paper in
Section 7.
2. The Emergency Ward Scenario
We envision a use case scenario in hospitals emergency departments where wristbands, containing not only a colored paper indicating the priority of patients’ treatments based on the severity of their condition [
25,
26], but also an optical (photoplethysmography (PPG)) sensor that tracks heart rate and pulse oxymetry [
27], are given to patients at the initial triage, allowing medical personnel or services to follow patients’ vital signs.
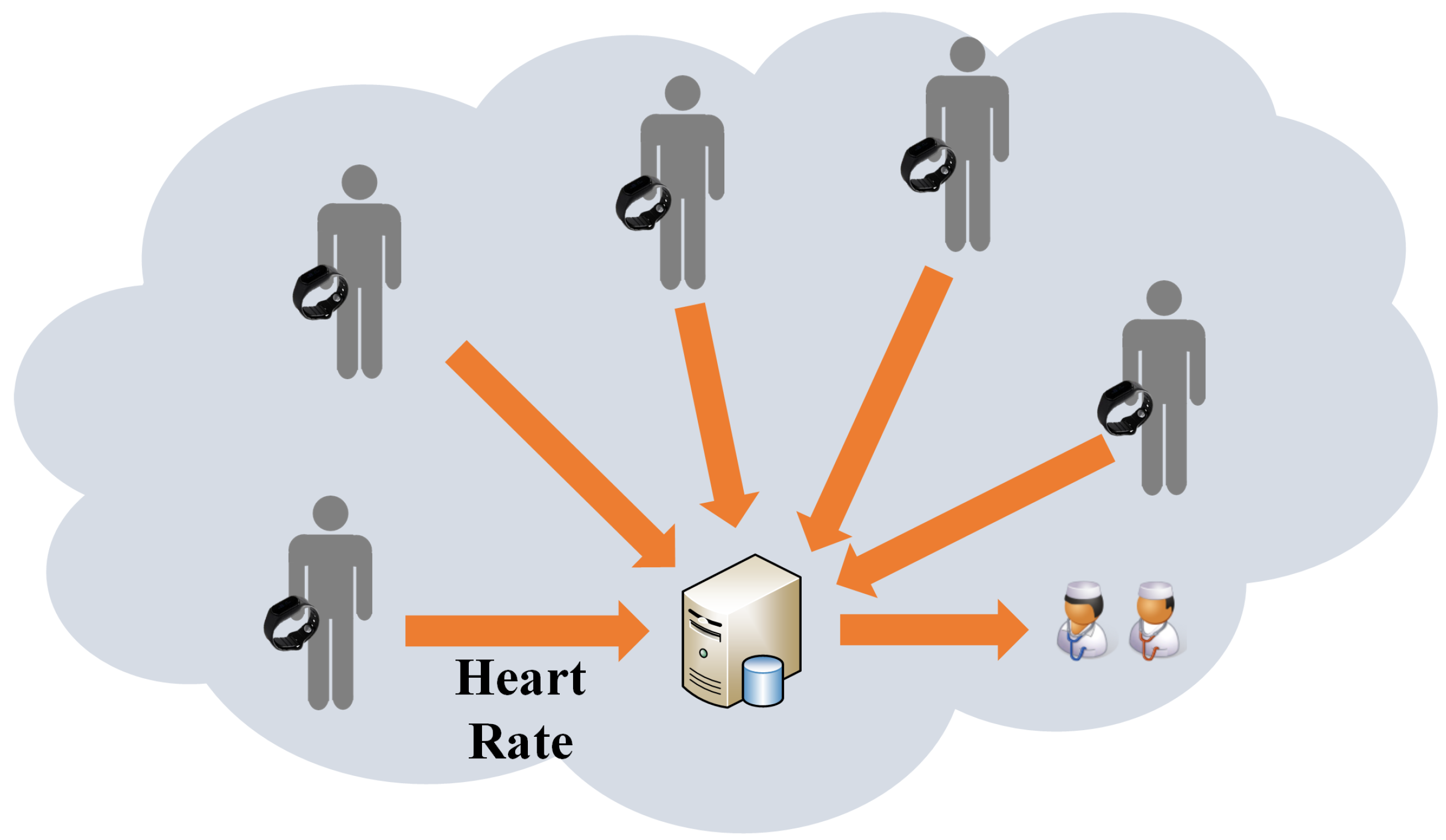
First, the medical personnel responsible for the triage accesses the patient’s EHR and registers the identification of the wristband that will be given to the patient. This triggers the collection and transmission of data by the wristband while a subscription is done to this data in a publish–subscribe communication model (see next section). Then, the EHR service is set up to start receiving the data from the wristband, updating the patient’s EHR history accordingly, allowing online remote monitoring while the wristband is connected. During this time, the wristband continuously uploads the sensor data with a frequency that is configurable, using the Wi-Fi hospital infrastructure, until the patient leaves the hospital, at which moment the medical personnel signals the stopping of the data collection and collects the wristband from the patient. If the wristband loses Wi-Fi connectivity temporarily, it can buffer the information for later upload.
The data sent by the wristband is also formatted at the end according to the semantics required for the correct interpretation by the EHR interface service that runs in the healthcare unit. Medical personnel can analyze the patient’s information anytime, or anywhere with Wi-Fi coverage, accessing the EHR which is responsible for storing and making the data available. The EHR itself can also be configured to trigger alarms whenever the sensor values cross predefined thresholds. The scenario is shown in
Figure 1. Communications are based on the publish–subscribe model, using a message broker as intermediary.
3. OneM2M-Based E-Health Framework
Among the diversity of IoT communications middleware available, we picked oneM2M to enable our interoperable framework for its suitable performance to support e-health real-time applications [
28,
29,
30]. OneM2M supports two communication models, namely, publish–subscribe and request–response. In this work, we focus on the former only, as it is more efficient for sensing and remote monitoring, while also providing more flexibility and scalability [
31].
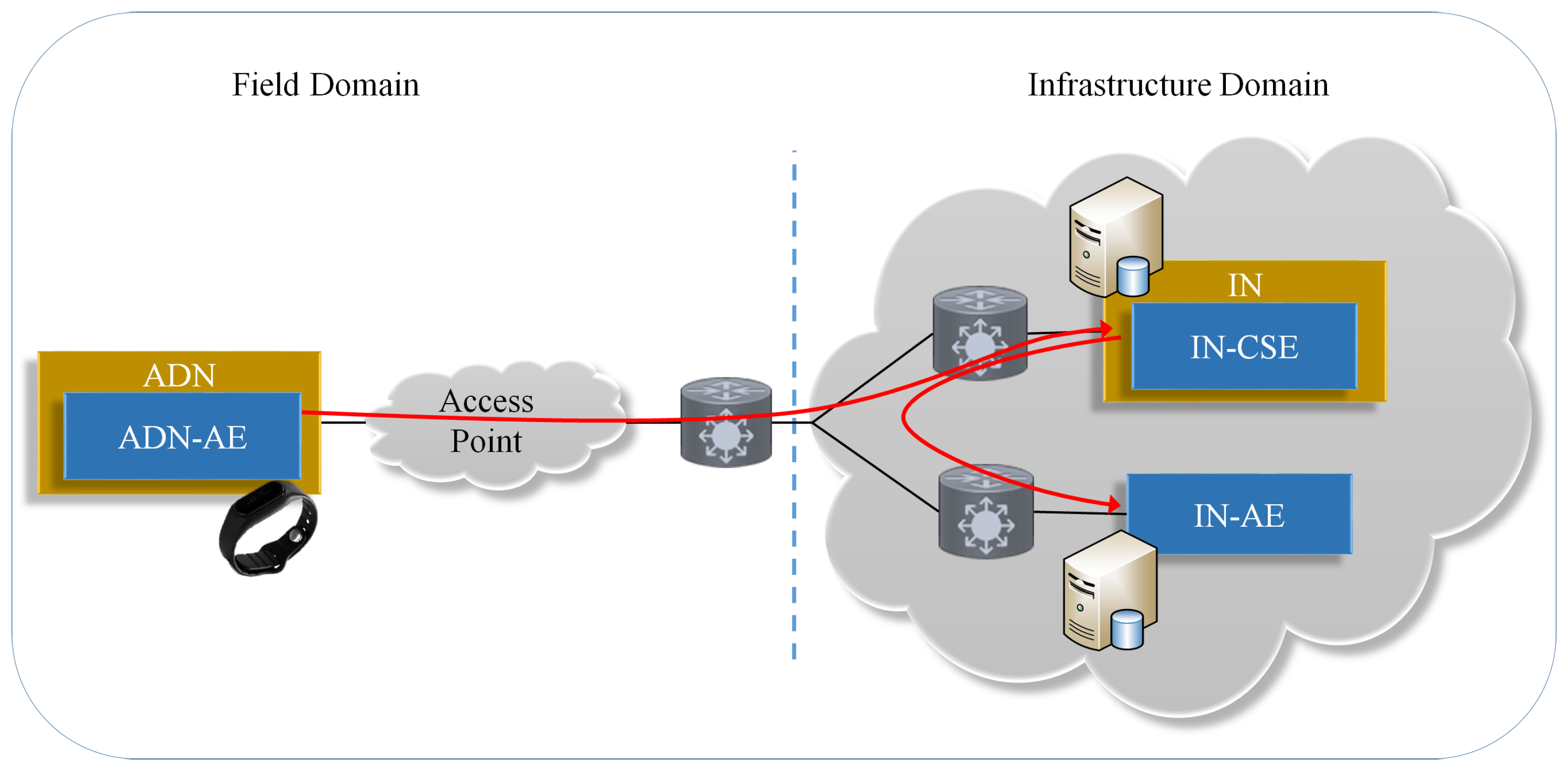
Figure 2 shows how the elements of our system are mapped onto a oneM2M standard-based ecosystem. As referred before, current wearable wristbands do not possess M2M capabilities nor do they use standardized interfaces, and thus the need for the use of GWs that act as proxies on their behalf. However, by enabling the wristbands with such capabilities, we can surpass the use of GWs.
In the proposed oneM2M-based architecture, the wristbands are Application Dedicated Nodes (ADN) in the field domain, containing at least one Application Entity (AE). As defined in the standard, the AE is an entity in the application layer that implements an M2M application service logic. The infrastructure domain contains central architectural elements for information management, namely, Infrastructure Nodes (IN) containing Common Service Entities (CSE). According to the standard, a CSE is an instance of a set of “common service functions” that are exposed to other entities through defined reference points, namely, Mca and Mcc. The Mca reference point is the communications interface between a CSE and an AE, whereas the Mcc reference point is the communications interface between two CSEs. In our scenario, the AE in the ADN communicates with a CSE in the IN using the Mca reference point.
oneM2M uses “resources” to represent information, according to the RESTful architecture style [
32]. Resources can change over time and use unique addresses called Universal Resource Identifiers (URI). The resources are hosted in a hierarchical tree structure within the IN-CSE, where information is maintained. The subscriptions are resources in the resource tree, where they can be dynamically handled.
The ADN-AE manages the wristband internal sensor and its data and runs in the ESP8266 module. It can decide when it should transmit, periodically or aperiodically, to control the battery lifetime of the wristband, or it can receive remote actuation commands for such. For such, the ADN-AE supports the use of buffers, which can also be used for temporary connectivity losses. The data is sent to the IN-CSE that acts as a broker in the communication model.
The IN-AE is an AE that is registered with the CSE in the IN, and communicates with the IN-CSE through the Mca reference point. In our scenario, the IN-AE is the openEHR service instance enabled with M2M capabilities. Every time a patient’s wristband is assigned to the patient’s EHR, the IN-AE makes a subscription to the respective resource in the IN-CSE. Then, the IN-AE starts receiving notifications of the data published by the device, i.e., the ADN-AE. Note that the device starts transmitting after receiving a command, only, for efficiency reasons. Access control is verified in every resource access by the IN-CSE. TLS or DTLS can be used to ensure privacy and security. Reliability and fault tolerance of the system can be handled by the communications’ protocols or by the service entities themselves.
The openEHR standard is non-proprietary and aims at providing interoperability and openness in e-health concerning data, models, and application programming interfaces, for both systems and components. It offers a standardized EHR architecture based on a multilevel modeling approach that separates information from knowledge. The specifications define a reference model and archetypes for health information together with a query language [
23]. The archetypes define how to capture the health information and are typically associated to a single clinical concept. The IN-AE receives physiological data such as heart rate and oxymetry from the wristbands and converts it to a form suitable for interpretation and storage in the EHR.
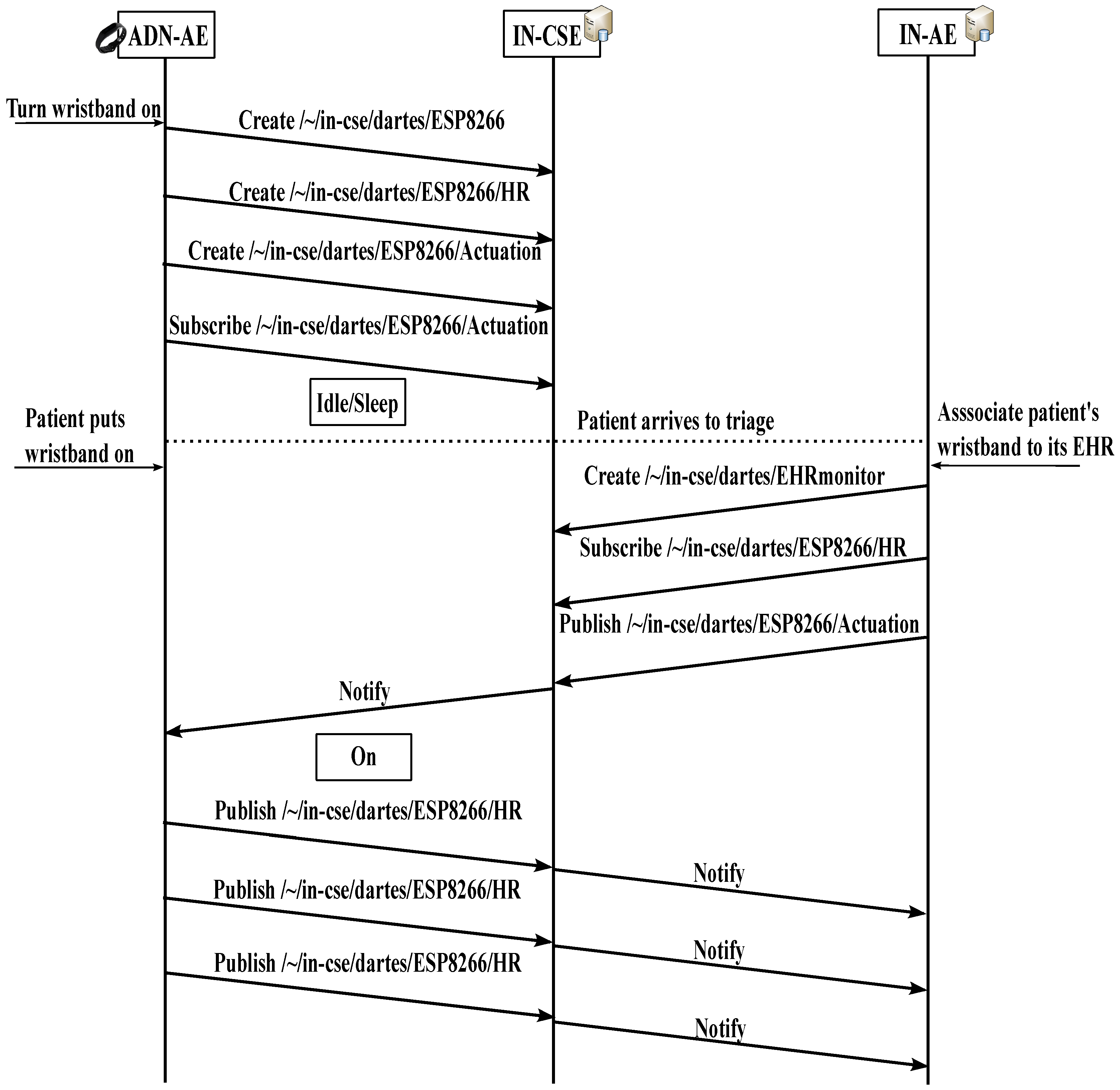
Figure 3 shows a normal message sequence among the entities during the start of operation of a wristband, from the moment it is turned on until the patient puts it on at the triage. When the wristband is switched on, the corresponding ADN-AE registers itself at the IN-CSE (at
/∼/in-cse/dartes in the figure) and creates the heart rate (HR) container inside a content instance resource to store the corresponding data that will be shared by means of publications. The ADN-AE also creates a subscription under a specific container (“Actuation” in the figure) to receive remote commands published by the IN-AE. The IN-AE subscribes at the IN-CSE to the HR container from the patient’s ADN-AE, mapping the specific patient’s wristband to the patient’s EHR.
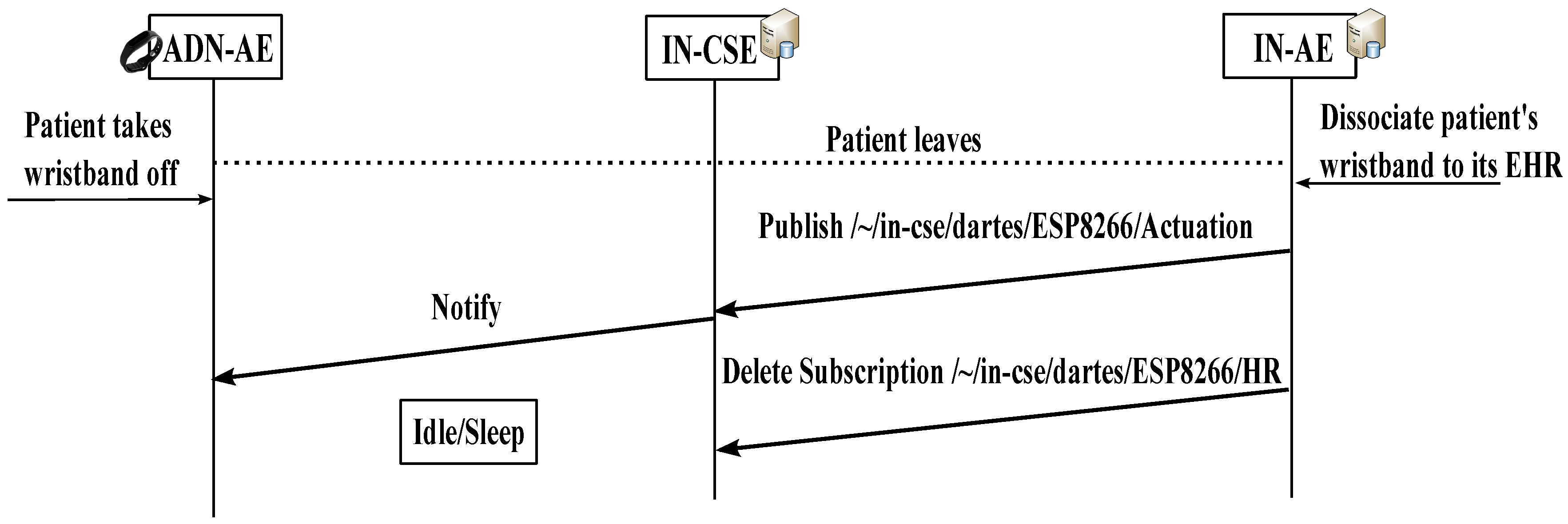
Figure 4 shows the messages exchanged to stop the remote monitoring when the patient leaves the ward. The medical personnel collects the wristband from the patient and signals the openEHR to request the dissociation. For this purpose, the IN-AE sends a command to the ADN-AE, via IN-CSE, causing it to stop publishing, and then it deletes its subscription from the IN-CSE.
4. Qualitative Assessment
This section shows a qualitative comparison between wristbands that use Bluetooth relying on smartphones as GWs and those that connect directly to WiFi and the M2M system, based on the ESP8266 modules. This comparison also assesses the feasibility of the Wi-Fi wristbands as M2M devices. We consider four important qualitative dimensions: capabilities, performance, ease of use, and cost.
Table 1 summarizes the qualitative analysis for each approach.
4.1. Capabilities
IoT applications frequently exploit the growing number of smartphone users. Smartphones have acquired well-known powerful capabilities in terms of connectivity, memory and processing, which surpass that of most constrained devices.
On the other hand, ESP8266 modules alone have very limited capabilities; however, they are highly integrated. They bear a 32-bit processor @ 80 MHz (160 MHz maximum), 36 KB of on-chip SRAM, and can support up to 16 MB of external SPI Flash memory [
24]. Only 20% of its MIPS are occupied by the Wi-Fi stack, therefore the rest can all be used for user application programming and development. Therefore, storage and transmission scheduling can still be optimized when using these modules. The WiFi interface is compliant with IEEE 802.11b/g/n/e/i (including transmission power and receiver sensitivity), it is tightly integrated with a full TCP/IP stack, and supports WPA and WPA2 security. These modules offer multiple sleep modes that grant the ultra-low-power feature, allowing different trade-offs between time to wake-up and energy consumption, with all modes maintaining a clock running for wake-up control. Thus, despite its lower capabilities, it is expected that the ESP8266 module can run M2M middleware with very low energy demands. Finally, these modules still offer a reasonable computing capacity, allowing them to perform actions such as preprocessing the PPG sensor data, detection of critical conditions and sending alarms. This is particularly suited to mission-critical IoT applications that require low latency, integrating well with recent paradigms like Fog Computing [
33].
4.2. Performance—Latency and Power Requirements
Few studies have benchmarked the performance of devices in M2M middleware, as performance evaluations of reference middleware implementations and protocols are only now becoming available [
28,
29,
30,
34].
Smartphones’ ubiquity is mainly powered by the use of cellular networks, which are known to have long and inefficient transitions between the different states of the network interface [
28,
35,
36]. This fact becomes crucial as latency between GWs and broker plays an important role in the fulfillment of time requirements [
28]. Moreover, additional delay can be introduced by the GW functionality, protocol conversion, etc.
M2M communications can be the middleware that glues together the IoT, but the interoperability and standardization usually comes with the cost of additional overhead in communications. This means an increased amount of information will be transmitted in each transmission and on the additional time the transmissions take. Currently, smartphones are mainly used for other purposes such as Web browsing, instant messaging, phone calls, etc, and the use of smartphones as M2M GWs can have a considerable impact on the smartphones’ usability, introducing undesired battery depletion due to continued network accesses [
12,
17,
18]. The additional use of external BT wearables can lead to considerable depletion of smartphones’ battery, easily reducing the battery life to less than 6 h for transmissions every second [
18].
Conversely, the performance of the ESP8266 modules for IoT communications is still unknown, despite the claimed ultra-low-power consumption. The next section shows a quantitative analysis focused on power requirements and latency performance of these modules in a test scenario.
4.3. Ease of Use
Ease of use is an important requirement for a wearable monitoring system. The use of smartphones as GWs requires one additional device besides the wristband and can lead to extra configurations required for the communications. The standalone use of the wristband clearly has advantage in terms of ease of use, reducing the human interaction to the minimum.
4.4. Cost
The current costs of ESP8266 and BT modules range from 0.10 to 1.00 USD in regular component suppliers, e.g., Alibaba (
www.alibaba.com). ESP8266 modules have a very low retail price, and thus the main cost comes from integrating the battery and the PPG sensor to produce the wristbands. The final cost of these wristbands is expected to be similar to that of BT-based counter parts. However, the BT solution, for online remote monitoring, also needs to consider the cost of a personal gateway, such as a smartphone, of which the average selling price, according to a market statistics service (
www.statista.com), is currently in the range of 200 USD.
5. Performance of the ESP8266 Modules
This section shows a quantitative characterization of the energy consumption and latency achievable with the ESP8266 modules when integrated in the M2M architecture shown in
Section 3 and as a function of multiple sleep and message configurations. The energy consumption of the PPG sensor (MAX86150), is negligible compared to the processor module.
5.1. Test Set-Up
We carried out several experiments in our department, using a oneM2M broker (IN-CSE) running on a dedicated server and an openEHR subscriber client (IN-AE) running on another computer. The server had an Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-2500 CPU, clocked at 3.3 GHz, 8 GB of RAM, and running the CentOS 6.9 OS, whereas the client had an Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-4700HQ CPU, clocked at 2.4 GHz, 8 GB of RAM, and running the Ubuntu 16.04 LTS OS. These two machines were connected through a Fast Ehernet network (100 Mb/s).
The ESP8266 publisher client (ADN-AE) connects to the broker via WiFi through an ASUS RT-AC87U dual-band AC2400 [
37] access point (AP) using the default 802.11 protocol with a typical beacon interval of 100 ms and DTIM of 3. The ESP8266 software framework is provided by Espressif Systems, v1.2 [
38], running on FreeRTOS. The specific module hardware version we used is powered by a Tensilica 32-bit CPU clocked at 80 MHz, featuring 36 KB of on-chip SRAM and 4 MB of external SPI Flash memory. The wireless AP is connected to the broker through the referred Fast Ethernet network.
The OM2M broker [
39] was used as reference implementation for the oneM2M standard. The CoAP protocol over UDP with nonconfirmable messages was used between the publisher and the broker to reduce publishing overhead.
Between the broker and the subscriber, we used the HTTP protocol over TCP for high reliability. We use the POST method for publications and notifications, and we added a short token to every message for access control.
We implemented the ESP8266 publisher client in C and the openEHR subscriber client in Java. The communication between the broker and both the publisher and subscriber clients was accomplished through the Mca reference point.
5.2. Methodology
We first assessed the ESP8266 modules power requirements, measuring the current consumed by the modules through a USB connection using the Monsoon power monitor [
40]. The sampling rate is 5000 Hz, and our trace contains two fields: time and current. For the sake of completeness, we measured the current in different modes of operation:
Normal mode, which is the default configuration in which the module’s CPU and Wi-Fi circuit remain always on;
Modem-sleep mode, in which the module’s Wi-Fi circuit is shut off when idle for a certain time, but without breaking Wi-Fi connectivity; the
Light-sleep mode, which differs from the Modem-sleep in that the module’s CPU also becomes pending, shutting down the crystal oscillator-based system clock, keeping a less precise RTC clock; and, finally, the
Deep-sleep mode, where the whole module is shut down, breaking the Wi-Fi connectivity.
For measuring the end-to-end latency, synchronization is required between publisher and subscriber as they are not located in the same machine. For that, we use the Network Time Protocol (NTP) for clock synchronization over the network [
41], selecting for that the same server on both ends, residing on the machine running the OM2M broker. NTP time updates were set with a period of 20 s in the publisher. For the case of the Deep-sleep mode, as the module erases several counters and memory related elements, we perform an NTP update every time the Wi-Fi connection to the access point is reestablished. We acquire timestamps at application-level, and consider the end-to-end latency as the time difference between the arrival of the notifications at the subscriber and the corresponding publication at the publisher.
We do not consider the current required to periodically collect data from the sensor, as this is negligible compared to the module current (below 0.5 mA in operation and 1 A when shut down, for the MAX86150). We use just HR sensor data that is stored in memory so that accesses to the flash memory are minimized. Each HR measurement is published by creating a new content instance resource in an individual container resource already existing in the broker and representing a single ESP8266 module. The content instance’s payload is marshaled in JSON format.
By default the publisher transmits data every 1s, but we also performed measurements for transmissions every 10 s to measure the impact of the transmission frequency on the power consumption. We kept the CoAP data goodput in both cases, though, transmitting one HR measurement in the first case (85 B) and 10 HR measurements in the second (850 B). The exception is the Deep-sleep mode, in which we only used transmissions at 10 s intervals, due to the time required for reestablishing the Wi-Fi connection. All publish requests used one of these two payload sizes, only.
To eliminate possible deviations in channel conditions during measurements, we performed every measurement by setting the module approximately one meter away from the wireless access point. This minimizes the possibility of random errors and other interference. The measurements were sequential to avoid interference between different measurements. We do not consider the initial message exchange (registration, creating containers, etc.) in the measurements. We measured every scenario for an interval corresponding to 100 publications.
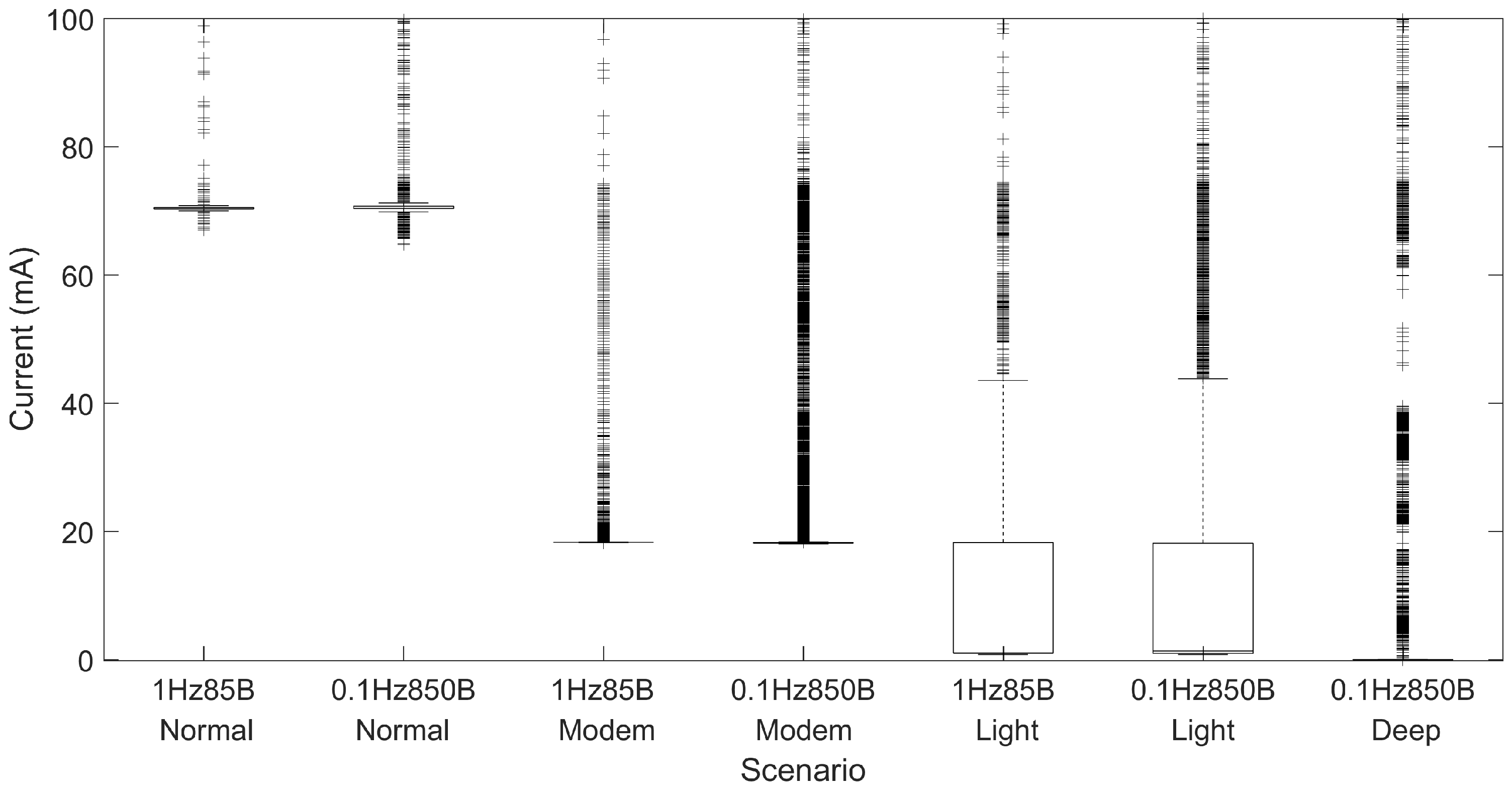
5.3. Results on Power Requirements
Figure 5 shows the distribution of the current measurements for each referred test scenario. The Y-axis was truncated for better visualization. The average current consumed throughout the entire measurement in the Normal mode was approximately 70.9 mA for transmissions every second and 70.8 mA for transmissions every 10 s. As the Wi-Fi circuit remains on, the module does not explore energy-saving techniques and requires more current than in the other modes. Moreover, the figure shows that in Modem-sleep, the average current consumption is considerably reduced when compared to the Normal mode. The scenario that transmits every 1 s required an average current of 27.0 mA (61.9% reduction w.r.t. Normal), and the scenario that transmits every 10 s required an average current of 23.6 mA (66.7% reduction w.r.t. Normal). Further power efficiency can be obtained using the Light-sleep modes with which we achieved an average current of 22.1 mA (18.2% reduction w.r.t. Modem-sleep) when transmitting every 1 s and 15.3 mA (35.2% reduction w.r.t. Modem-sleep) when transmitting every 10 s.
The most energy-efficient mode for transmissions with a frequency of 0.1 Hz is Deep-sleep, as expected. This mode required an average current of 9.8 mA (36.0% decrease w.r.t. Light-sleep). This difference is essentially controlled by the time taken to reestablish the Wi-Fi connection, during which the current consumption is high.
On the other hand, these results also show that there are substantial differences of power requirements between the two transmitting frequencies and that there is a clear advantage in reducing the transmission frequency. This difference is higher in Light-sleep (30.8% reduction), as more components are idle/off.
Table 2 summarizes the average current consumption values and shows the respective estimated battery lifetime defined as the time to reach 10% of battery capacity, assuming the module was powered by a battery with a capacity of 1000 mAh and the battery depletion was linear. Using energy-saving moves, the battery lifetime can easily surpass one day, thus allowing daily charging cycles.
5.4. Results on End-to-End Latency
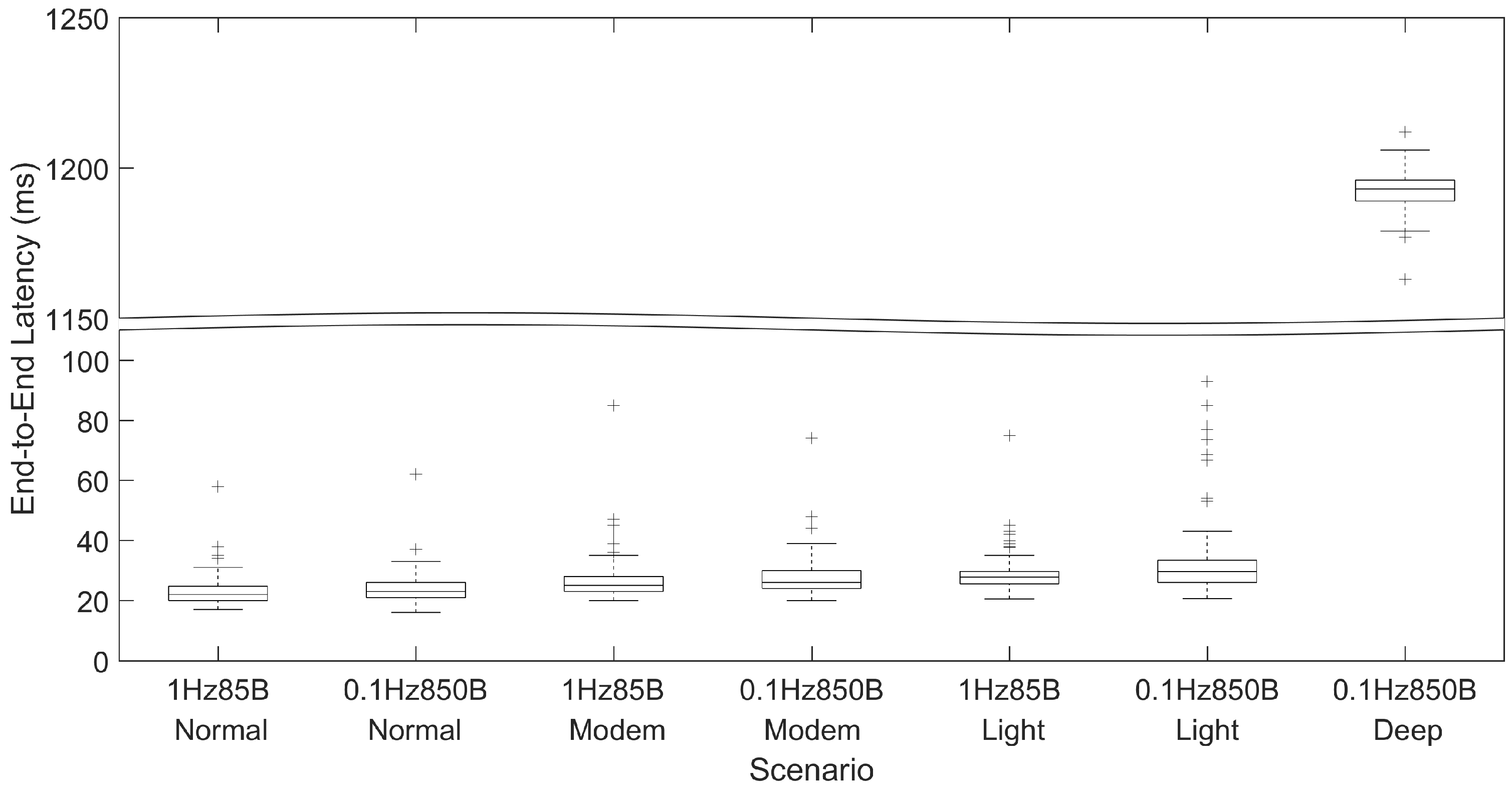
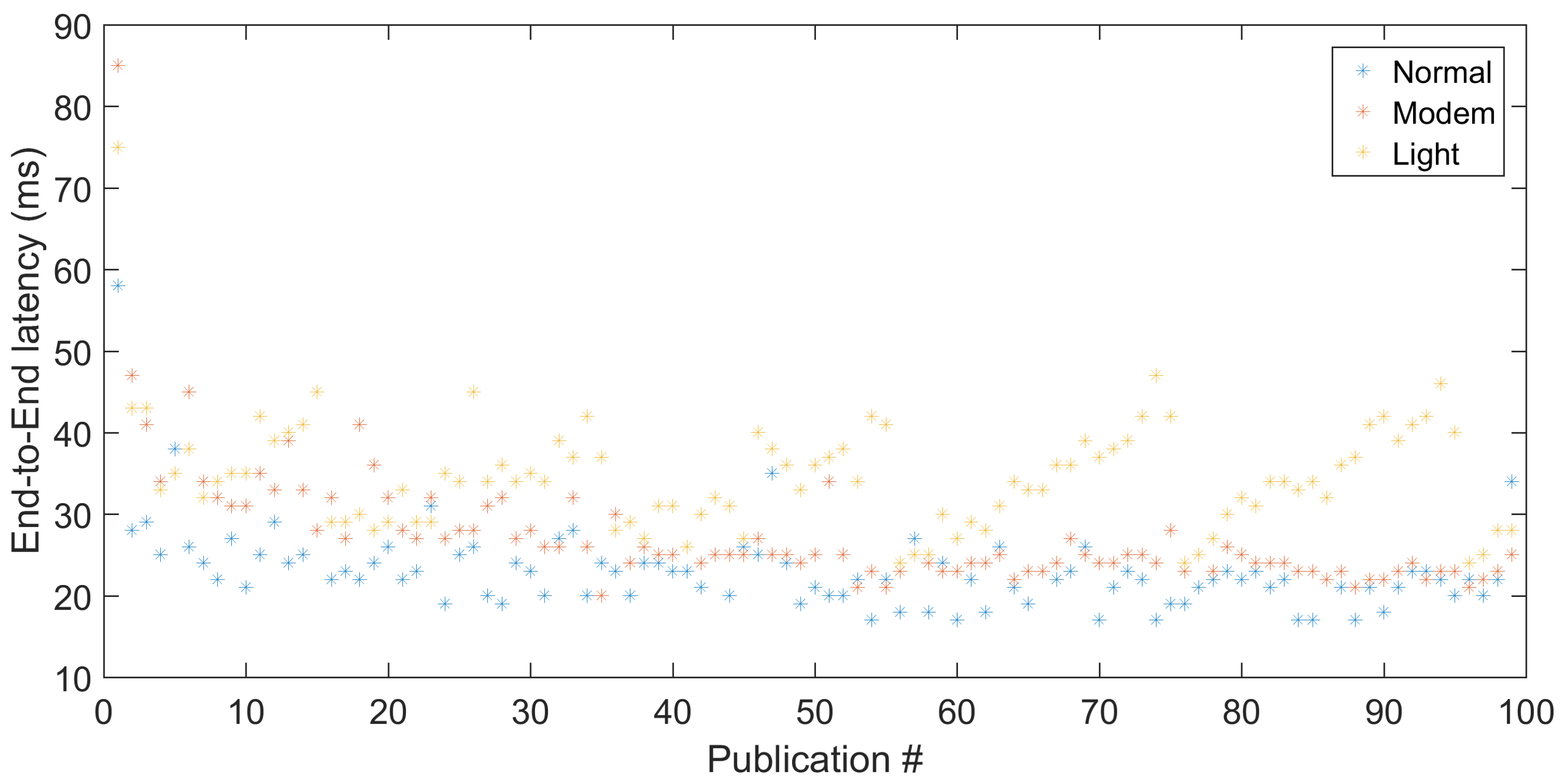
Figure 6 shows the distribution of the end-to-end latency measurements for each test scenario. Additionally,
Figure 7 shows the detailed end-to-end latency measurements for transmissions every 1 s. It allows observing a strong clock drift in Light-sleep, caused by the low precision of the RC clock that is used in this mode. Every 20 s, the clock drift is corrected by NTP. The average drift rate per second is approximately 0.73%, and we used this value to correct the measurements in
Figure 6.
The scenarios with a transmission frequency of 1 Hz experienced an average end-to-end latency of 23.1 ms, 27.4 ms, and 29.1 ms for the Normal, Modem-sleep, and Light-sleep modes, respectively. The scenarios with a transmission frequency of 0.1 Hz experienced an average end-to-end latency of 23.8 ms, 27.6 ms, and 33.0 ms for the Normal, Modem-sleep, and Light-sleep modes, respectively. We can observe that transmissions when the module is on Normal mode experience a smaller average end-to-end latency than on Modem-sleep. This is due to the time it takes to activate the Wi-Fi circuit from the sleep mode. Although the precise characterization of this difference would require more investigation, we observe that in our measurements it is approximately 4 ms, which is compatible with the average time to activate the Wi-Fi interface referred in the module datasheet.
The latency values for transmissions every 1 s are similar to those of transmissions every 10 s for the same operation mode, which shows that this size difference has a negligible impact on the experienced end-to-end latency.
Finally, we obtained an average end-to-end latency of 1193 ms for the Deep-sleep scenario, due to the time needed to reestablish the Wi-Fi connection. This long latency has to be taken into account when assessing the adequacy of the Deep-sleep mode to each specific application scenario.
Taken together, these results show that the ESP8266 modules can support a working M2M standardized framework. Nonetheless, careful planning of applications must be performed, as different transmission frequencies and operation modes can provide very different quality of service levels, in terms of expected battery lifetime, end-to-end latency, and synchronization, which are conflicting goals.
6. Impact of WiFi Network Configuration
In the previous section, we used the ESP8266 modules within an infrastructured Wi-Fi network, which uses beacons for synchronization and (Delivery) Traffic Indication Maps (TIM / DTIM) to allow battery operated nodes to exploit sleep modes. All nodes wake up every beacon (or every x beacons) to receive the TIM (DTIM) and see whether they have any traffic for them (or broadcast/multicast traffic) pending in the AP and retrieve it. Thus, the beacon interval and the DTIM period (x) impact on the modules power consumption. These parameters are configured in the AP, and thus we carried out another set of experiments to assess their impact on the ESP8266 modules power consumption in our M2M scenario.
In this case, we followed a different methodology and inhibited all module transmissions and NTP updates, leaving it in an idle state in which it would respond to automatic infrastructure interactions only, such as beacons. This approach allows observing the impact of the infrastructure configuration without interference of the actual traffic pattern. In particular, we measured the current consumption for various beacon intervals (100 ms, 300 ms, 500 ms, and 1000 ms) and DTIM periods (1, 3, and 5). We also considered two different sleep modes only, namely, Modem-sleep and Light-sleep. We did not consider Normal mode, because it keeps the Wi-Fi interface on all the time, or Deep-sleep, because it ignores the AP beacons. The average and median current measured for each scenario are shown in
Table 3.
We observed that modules in the Modem-sleep mode show a small reduction of the average current consumption as the beacon interval and DTIM period increase. The median values, however, remain constant. Curiously, the experiments with Light-sleep show the opposite behavior, with the average current slightly increasing with the beacon interval and the DTIM period. The median, in turn, shows two very different values, with the smallest for combinations of short beacon interval and low DTIM period. By performing a visual inspection of the current consumption profile for the Light-sleep mode, we observed that the module transitions to a very low energy consumption state for a certain time but then returns to a state that has similar consumption to that of Modem-sleep until the next DTIM arrives. This behavior still requires further investigation.
Nevertheless, these results already provide guidelines for the right AP configuration according to the sleep mode used. Curiously, the most favorable configuration we found for Light-sleep mode is with a beacon interval of 100 ms and a DTIM of 3, which is a typical default WiFi network configuration.
7. Conclusions
Following the current trend towards e-health IoT applications, we focused on a potentially high-impact use case, which is the tracking of patients vital signs in emergency wards. We proposed a vertical IoT architecture based on open standards, fully integrated with the Internet. Our proposal includes an e-health framework that settles in the use of the oneM2M and openEHR standards, thus allowing interoperability between different devices and software, from the wearable sensors to the databases.
A critical element in this architecture is the design of efficient M2M-capable sensors. We showed that such sensors can be designed resorting to new low-cost, ultra-low-power ESP8266 Wi-Fi modules that can be integrated in wristbands and connect directly to the Internet, using M2M standardized protocols.
We then carried out a feasibility study, assessing the performance of the ESP8266 modules in terms of power requirements and end-to-end latency. Using sleep states allowed extending the lifetime of a 1000 mAh battery between 1 and 2 days with end-to-end latency in the range of 20–40 ms. Longer lifetime could be achieved with a deep-sleep mode which, however, caused a jump to over 1 s in the latency, due to the time taken to reestablish Wi-Fi connection. We also carried out experiments to provide guidelines for the WiFi network configuration concerning beacon interval and DTIM period.
We conclude that emerging Wi-Fi nodes, such as the ESP8266, are indeed adequate to develop IoT-enabled wearables that can be integrated in open, interoperable e-health frameworks, thus playing a key role in the rise and adoption of low-cost solutions. Nevertheless, further work is underway to characterize the modules operation in more situations, particularly with different transmitting powers and modulations as well as under loaded wireless media. Future work will also address time guarantees or availability for scenarios where different quality of service might be required, focusing on deployment in a real-life scenario. Due to their enhanced processing capacities and reduced battery consumption, these modules could also be used to explore forms of edge computing concerning patients’ data.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.P., F.S., L.A. and A.A.; methodology, C.P. and L.A.; software, C.P., J.M. and D.G.; validation, C.P and L.A.; formal analysis, C.P.; investigation, C.P., J.M. and D.G.; resources, C.P. and L.A.; data curation, C.P., J.M. and D.G.; writing–original draft preparation, C.P. and L.A.; writing–review and editing, C.P. and L.A.; visualization, C.P.; supervision, L.A.; project administration, C.P., F.S., L.A. and A.A.; funding acquisition, L.A. and A.A.
Funding
This work is a result of the project MobiWise (SAICTPAC/0011/2015, POCI-01-0145-FEDER-016426) and IT (UID/EEA/50008/2019) Research Units, funded by the applicable financial framework: Fundo Europeu de Desenvolvimento Regional (FEDER), Programa Operacional Competitividade e Internacionalização (POCI), FCT/MCTES (Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Gartner. Press Release: Gartner Says 8.4 Billion Connected “Things” Will Be in Use in 2017, Up 31 Percent from 2016. 2017. Available online: https://www.gartner.com/newsroom/id/3598917 (accessed on 15 May 2019).
- Chen, K. Machine-to-machine communications for healthcare. J. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2012, 6, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Qian, Y.; Sharif, H.; Tipper, D. A Survey on Smart Grid Communication Infrastructures: Motivations, Requirements and Challenges. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2013, 15, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caragliu, A.; Del Bo, C.; Nijkamp, P. Smart cities in Europe. In Proceedings of the 3rd Central European Conference in Regional Science, Kosice, Slovakia, 7–9 October 2009; pp. 49–59. [Google Scholar]
- Norris, A.; Stockdale, R.; Sharma, S. A strategic approach to m-health. Health Inform. J. 2009, 15, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ETSI. ETSI TR 102 732 V1.1.1 (2013-09) Machine-to-Machine Communications (M2M). Use Cases of M2M Applications for eHealth. 2013. Available online: http://www.etsi.org/deliver/etsi_tr/102700_102799/102732/01.01.01_60/tr_102732v010101p.pdf (accessed on 15 May 2019).
- Cardona-Morrell, M.; Prgomet, M.; Turner, R.M.; Nicholson, M.; Hillman, K. Effectiveness of continuous or intermittent vital signs monitoring in preventing adverse events on general wards: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2016, 70, 806–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donaldson, L.J.; Panesar, S.S.; Darzi, A. Patient-Safety-Related Hospital Deaths in England: Thematic Analysis of Incidents Reported to a National Database, 2010–2012. PLoS Med. 2014, 11, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillman, K.M.; Bristow, P.J.; Chey, T.; Daffurn, K.; Jacques, T.; Norman, S.L.; Bishop, G.F.; Simmons, G. Antecedents to hospital deaths. Intern. Med. J. 2001, 31, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, D.; Mitchell, I.; Hillman, K.; Story, D. Defining clinical deterioration. Resuscitation 2013, 84, 1029–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, M.; Coventry, A. Critical care: The eight vital signs of patient monitoring. Br. J. Nurs. 2012, 21, 621–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morón, M.J.; Luque, R.; Casilari, E. On the Capability of Smartphones to Perform as Communication Gateways in Medical Wireless Personal Area Networks. Sensors 2014, 14, 575–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Costa, C.A.; Pasluosta, C.F.; Eskofier, B.; da Silva, D.B.; da Rosa Righi, R. Internet of Health Things: Toward intelligent vital signs monitoring in hospital wards. Artif. Intell. Med. 2018, 89, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albahri, O.; Albahri, A.; Mohammed, K.; Zaidan, A.; Zaidan, B.; Hashim, M.; Salman, O.H. Systematic review of real-time remote health monitoring system in triage and priority-based sensor technology: Taxonomy, open challenges, motivation and recommendations. J. Med. Syst. 2018, 42, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulić, P.; Kojek, G.; Biasizzo, A. Data Transmission Efficiency in Bluetooth Low Energy Versions. Sensors 2019, 19, 3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.; Shahjalal, M.; Chowdhury, M.Z.; Jang, Y.M. Real-Time Healthcare Data Transmission for Remote Patient Monitoring in Patch-Based Hybrid OCC/BLE Networks. Sensors 2019, 19, 1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, C.; Rodrigues, J.; Pinto, A.; Rocha, P.; Santiago, F.; Sousa, J.; Aguiar, A. Smartphones as M2M gateways in smart cities IoT applications. In Proceedings of the 2016 23rd International Conference on Telecommunications (ICT), Thessaloniki, Greece, 16–18 May 2016; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, C.; Pinto, A.; Aguiar, A.; Rocha, P.; Santiago, F.; Sousa, J. IoT interoperability for actuating applications through standardised M2M communications. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 17th International Symposium on A World of Wireless, Mobile and Multimedia Networks (WoWMoM), Coimbra, Portugal, 21–24 June 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreps, G.L.; Neuhauser, L. New directions in eHealth communication: Opportunities and challenges. Patient Educ. Couns. 2010, 78, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogac, A. Interoperability in eHealth Systems. Proc. VLDB Endow. 2012, 5, 2026–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pereira, C.; Frade, S.; Brandao, P.; Correia, R.; Aguiar, A. Integrating data and network standards into an interoperable e-Health solution. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE 16th International Conference on e-Health Networking, Applications and Services (Healthcom), Natal, Brazil, 15–18 October 2014; pp. 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OneM2M. OneM2M Standardization. 2017. Available online: http://www.onem2m.org (accessed on 15 May 2019).
- OpenEHR. OpenEHR. 2018. Available online: http://www.openehr.org/ (accessed on 15 May 2019).
- Espressif. ESP8266 Technical Reference. Available online: http://espressif.com/sites/default/files/documentation/esp8266-technical_reference_en.pdf (accessed on 15 May 2019).
- Robertson-Steel, I. Evolution of triage systems. Emerg. Med. J. 2006, 23, 154–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, C. Emergency Triage. BMJ 1997, 314, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaneda, D.; Esparza, A.; Ghamari, M.; Soltanpur, C.; Nazeran, H. A review on wearable photoplethysmography sensors and their potential future applications in health care. Int. J. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 4, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, C.; Pinto, A.; Ferreira, D.; Aguiar, A. Experimental Characterization of Mobile IoT Application Latency. IEEE Internet Things J. 2017, 4, 1082–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medvedev, A.; Hassani, A.; Zaslavsky, A.; Jayaraman, P.P.; Indrawan-Santiago, M.; Delir Haghighi, P.; Ling, S. Data Ingestion and Storage Performance of IoT Platforms: Study of OpenIoT. In Interoperability and Open-Source Solutions for the Internet of Things: Second International Workshop, InterOSS-IoT 2016, Held in Conjunction with IoT 2016, Stuttgart, Germany, November 7, 2016, Invited Papers; Podnar Žarko, I., Broering, A., Soursos, S., Serrano, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, J.; Pereira, C.; Aguiar, A.; Morla, R. Benchmarking IoT middleware platforms. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 18th International Symposium on A World of Wireless, Mobile and Multimedia Networks (WoWMoM), Macau, China, 12–15 June 2017; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, E.G.; Calveras, A.; Demirkol, I. Improving Packet Delivery Performance of Publish/Subscribe Protocols in Wireless Sensor Networks. Sensors 2013, 13, 648–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fielding, R.T. Architectural Styles and the Design of Network-Based Software Architectures. Ph.D. Thesis, University of California, Irvine, CA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Kraemer, F.A.; Braten, A.E.; Tamkittikhun, N.; Palma, D. Fog computing in healthcare—A review and discussion. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 9206–9222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, P.; Sisinni, E.; Brandão, D.; Rocha, M. Evaluation of communication latency in industrial IoT applications. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Workshop on Measurement and Networking (MN), Naples, Italy, 27–29 September 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Balasubramanian, N.; Balasubramanian, A.; Venkataramani, A. Energy Consumption in Mobile Phones: A Measurement Study and Implications for Network Applications. In Proceedings of the 9th ACM SIGCOMM Conference on Internet Measurement Conference, Chicago, IL, USA, 4–6 November 2009; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 280–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Qian, F.; Gerber, A.; Mao, Z.M.; Sen, S.; Spatscheck, O. A Close Examination of Performance and Power Characteristics of 4G LTE Networks. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Mobile Systems, Applications, and Services, Lake District, UK, 25–29 June 2012; pp. 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asus. Asus RT-AC87U. Available online: https://www.asus.com/pt/Networking/RTAC87U/ (accessed on 15 May 2019).
- Espressif. Espressif ESP8266 SDK Based on FreeRTOS. Available online: https://github.com/espressif/ESP8266_RTOS_SDK (accessed on 15 May 2019).
- Eclipse. Eclipse OM2M. Available online: http://www.eclipse.org/om2m/ (accessed on 15 May 2019).
- Monsoon. Monsoon Power Monitor. Available online: https://www.msoon.com/online-store (accessed on 15 May 2019).
- Mills, D. Network Time Protocol (Version 3): Specification, Implementation and Analysis. IETF RFC 1305. 1992. Available online: https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc1305 (accessed on 15 May 2019).
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).