Internal Model-Based Dynamic Power Control of Grid-Following Voltage-Source Inverters
Abstract
1. Introduction
- −
- A reliable IMC is developed to ensure stable performance of GFLIs with improved adaptability to various grid conditions, including weak and highly fluctuating grids.
- −
- The proposed control approach enables independent regulation of active and reactive power.
- −
- Passive damping techniques are integrated into the LCL filter design to effectively reduce resonance.
- −
- The control strategy maintains high power quality by minimizing total harmonic distortion (THD) that ensures the injected current and output voltage of the inverter comply with grid standards.
2. Literature Survey
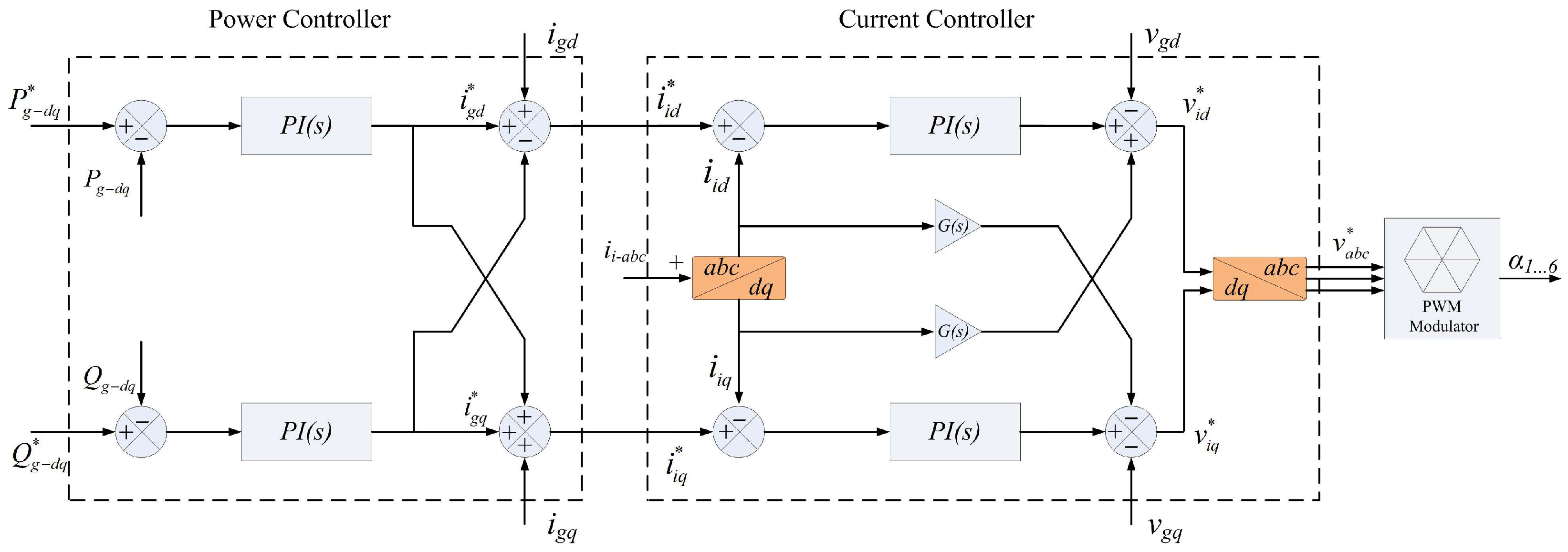
3. Modelling of the System and Design of the Controller
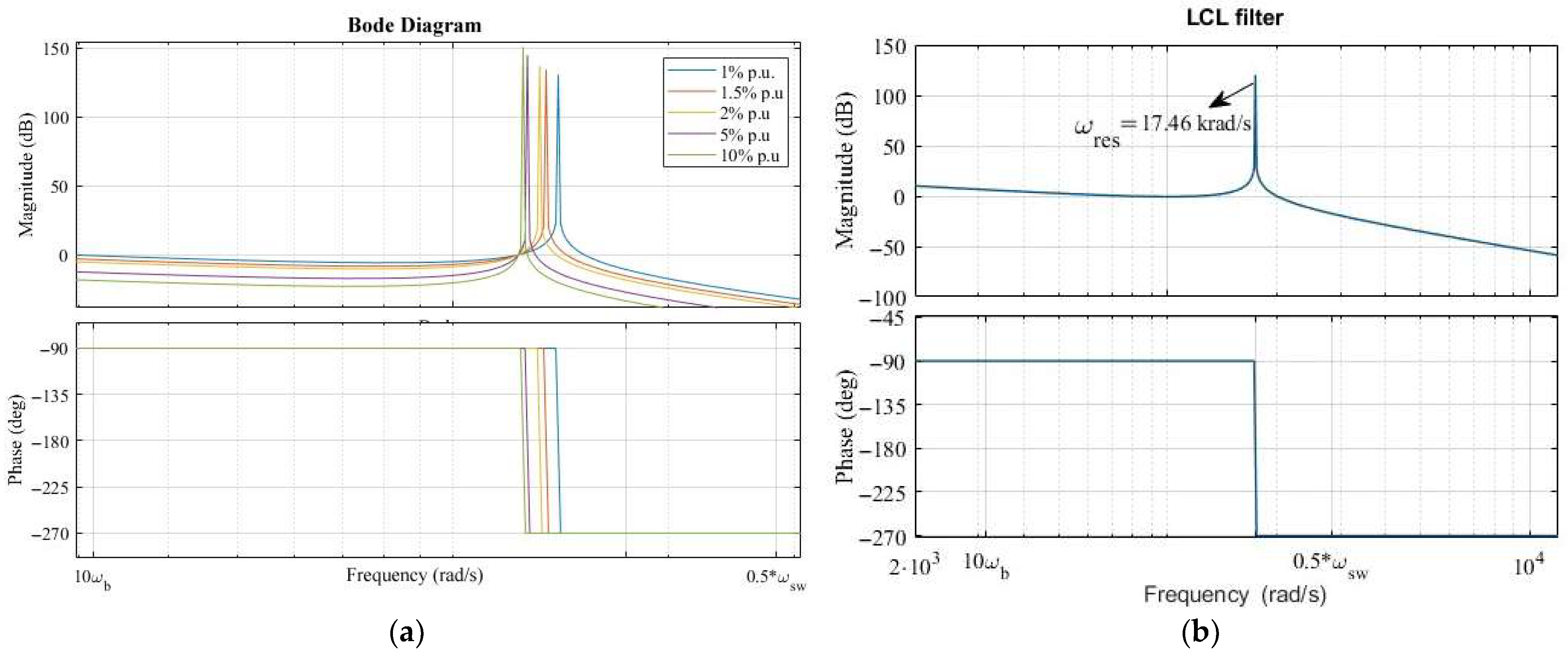
3.1. Design and Dynamics Analysis of LCL Filter
3.2. Design Studies of IMC and Its Control Objectives
4. Simulation Setup and Modelling Studies
4.1. Simulation Environment
4.1.1. LCL Filter Modelling
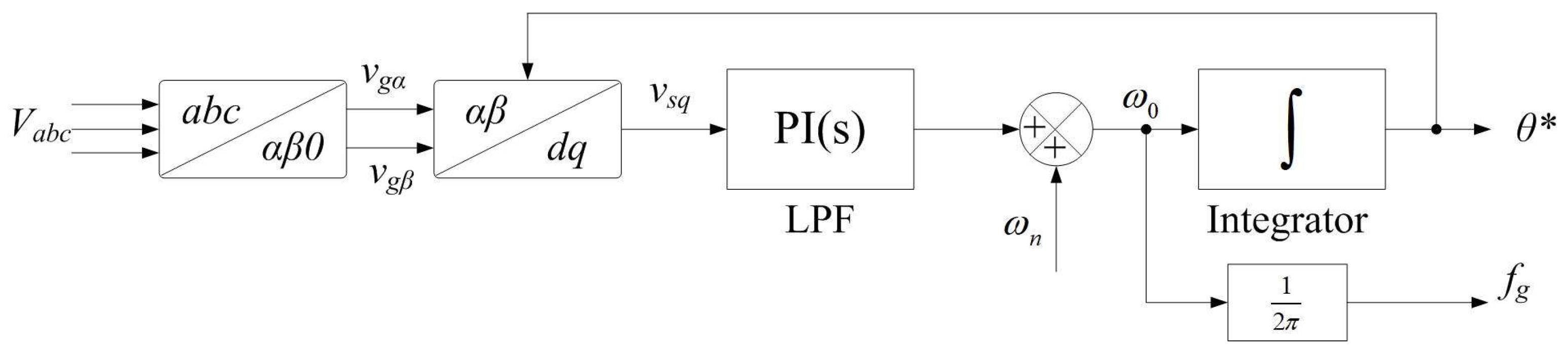
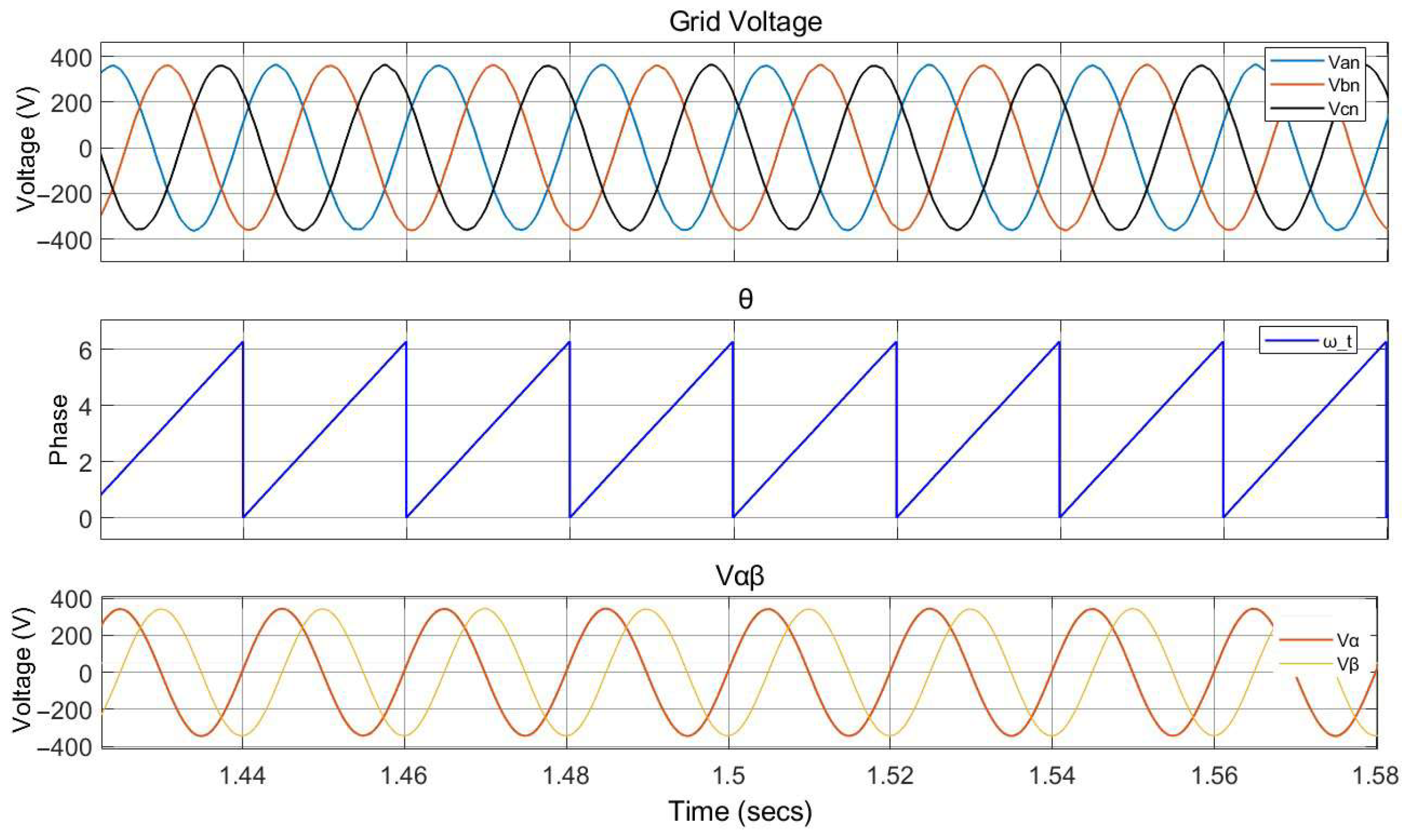
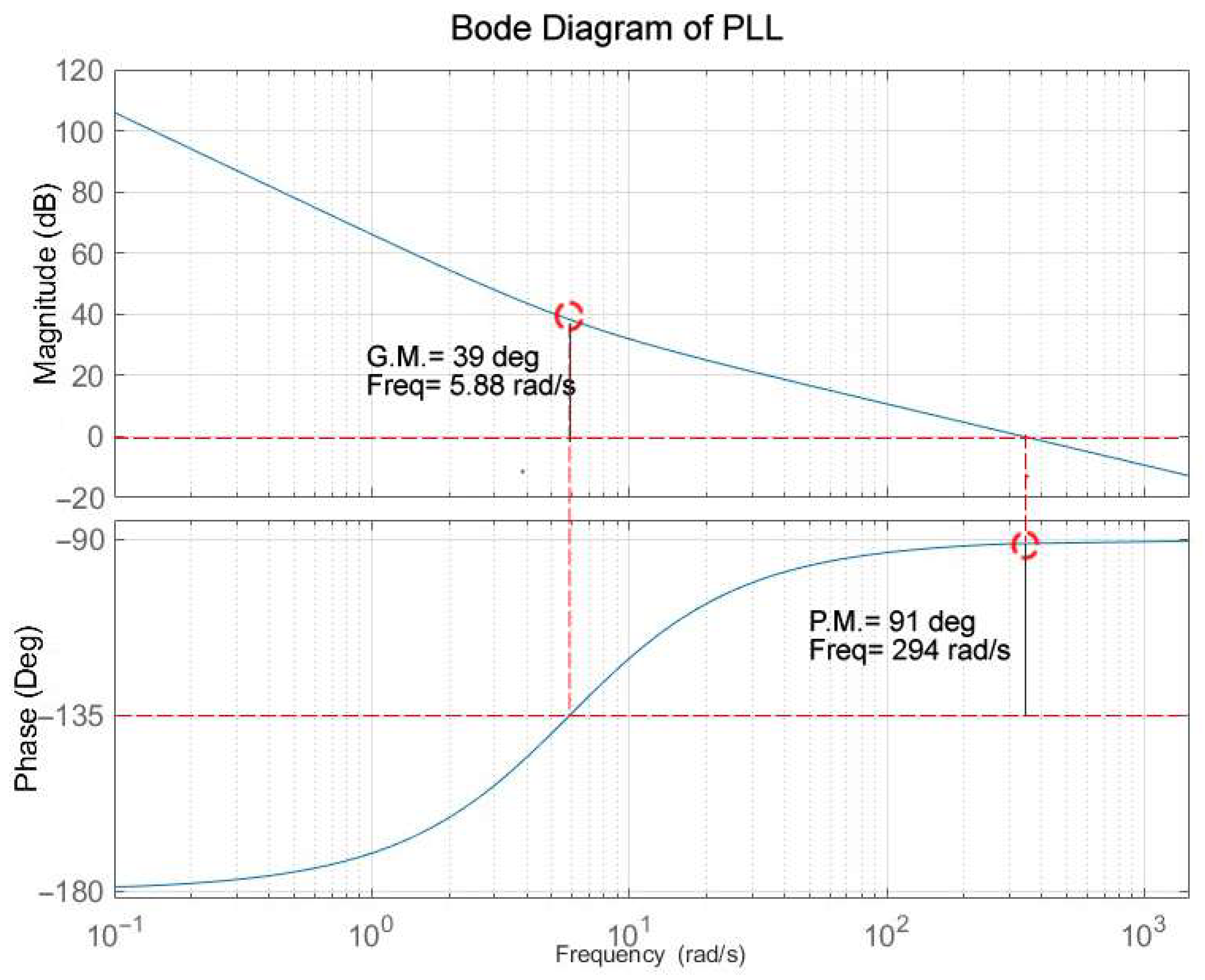
4.1.2. Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) Modelling
5. Analysis and Case Studies
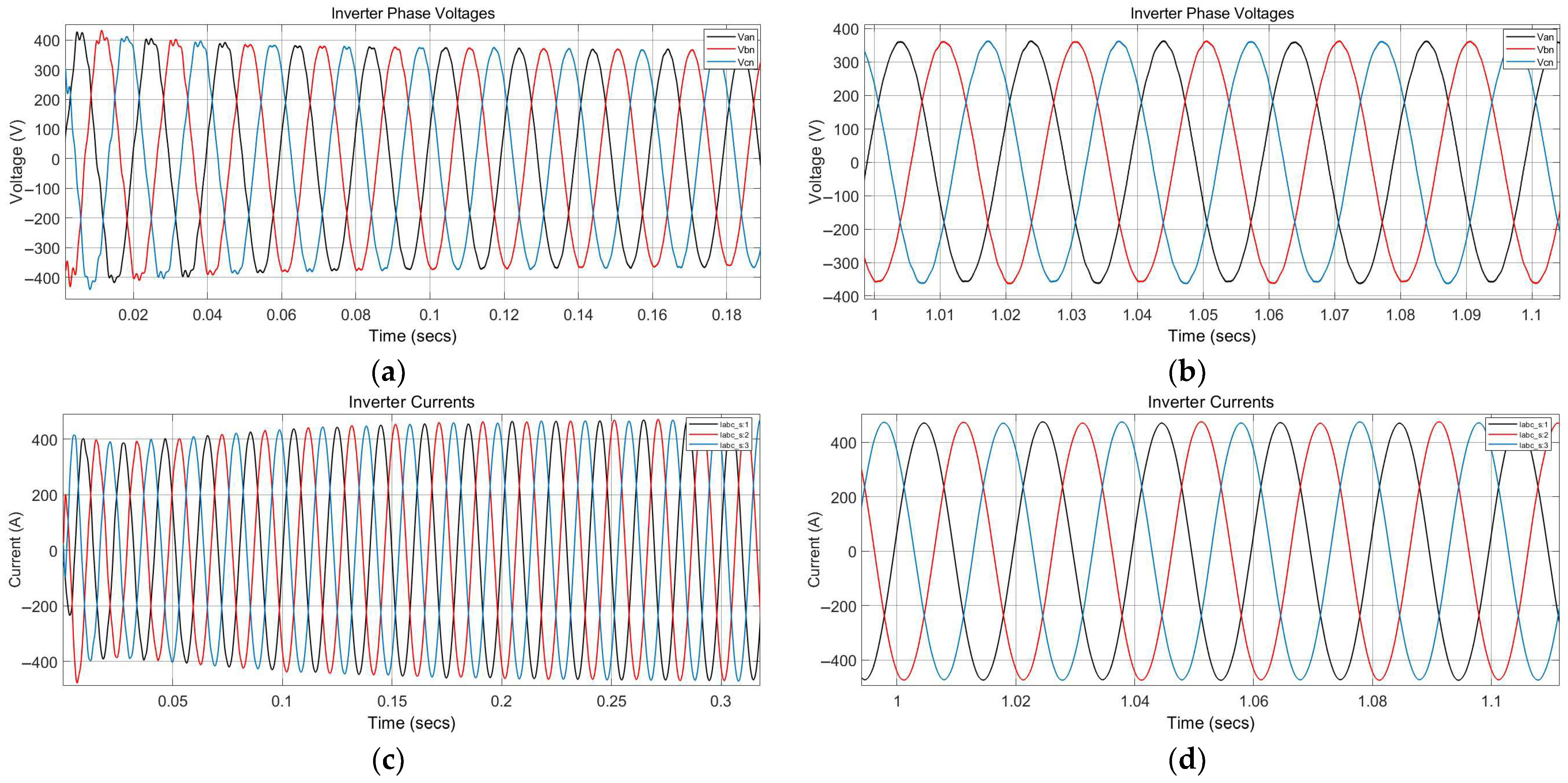
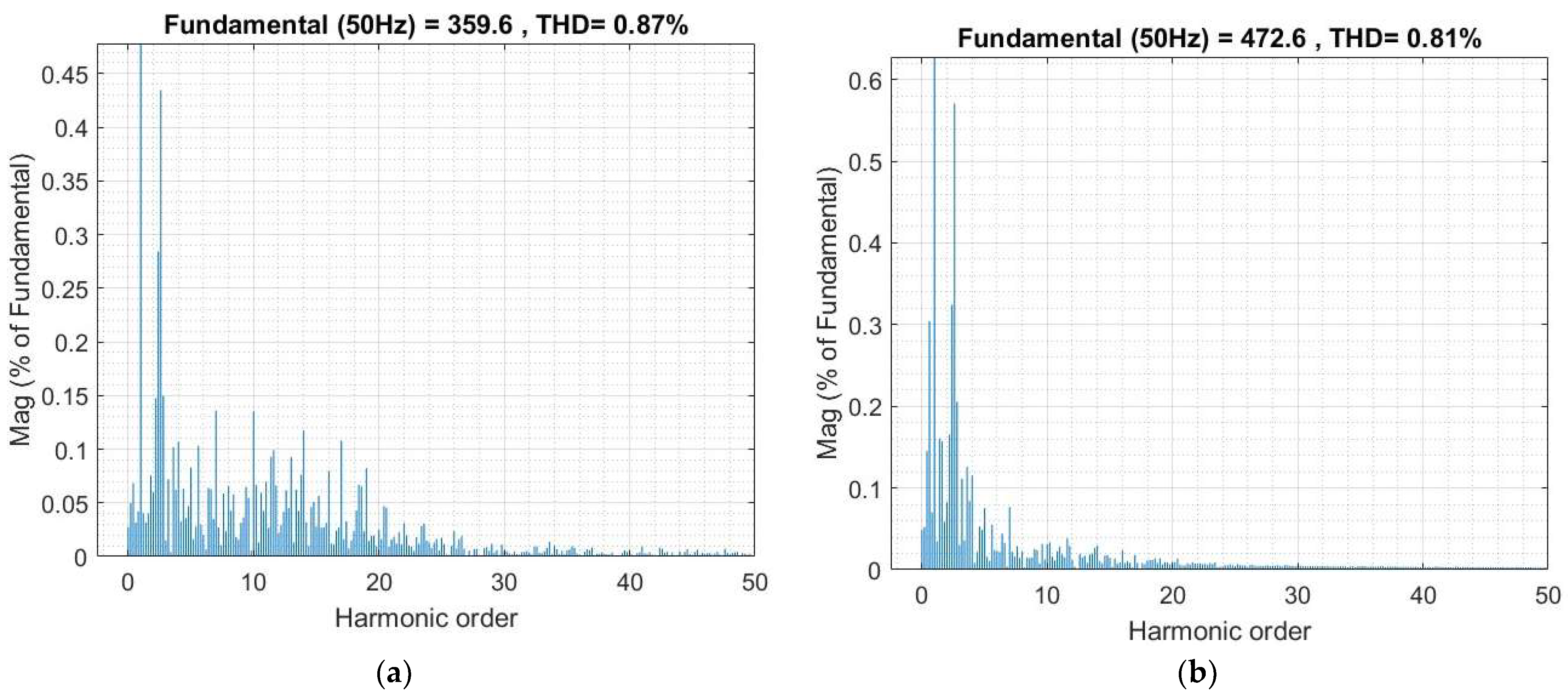
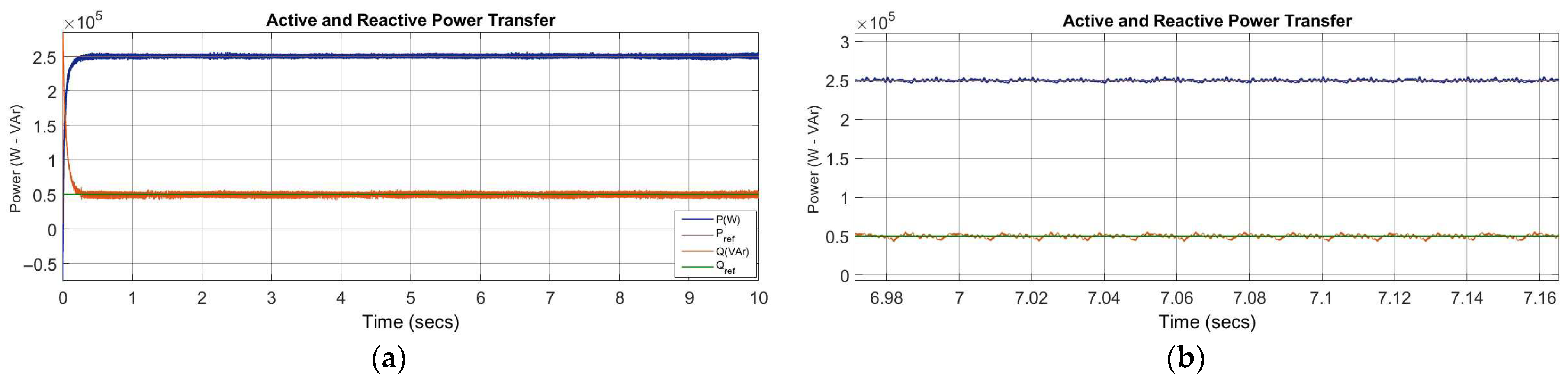
5.1. Scenario 1: Steady-State Operation Under Nominal Grid Conditions
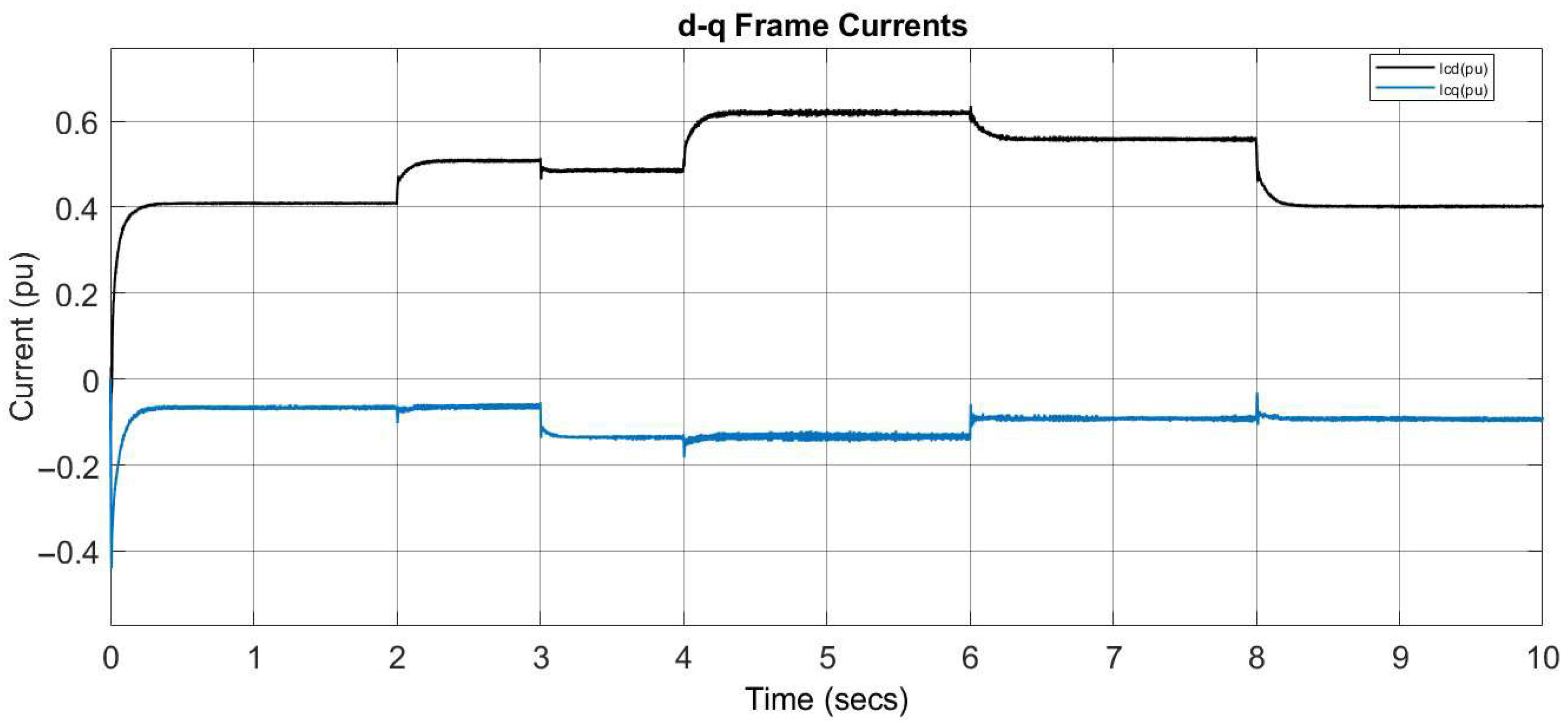
5.2. Scenario 2: System Performance Under Grid Disturbances
5.3. Scenario 3: Dynamic Response to Sudden Load Deviation
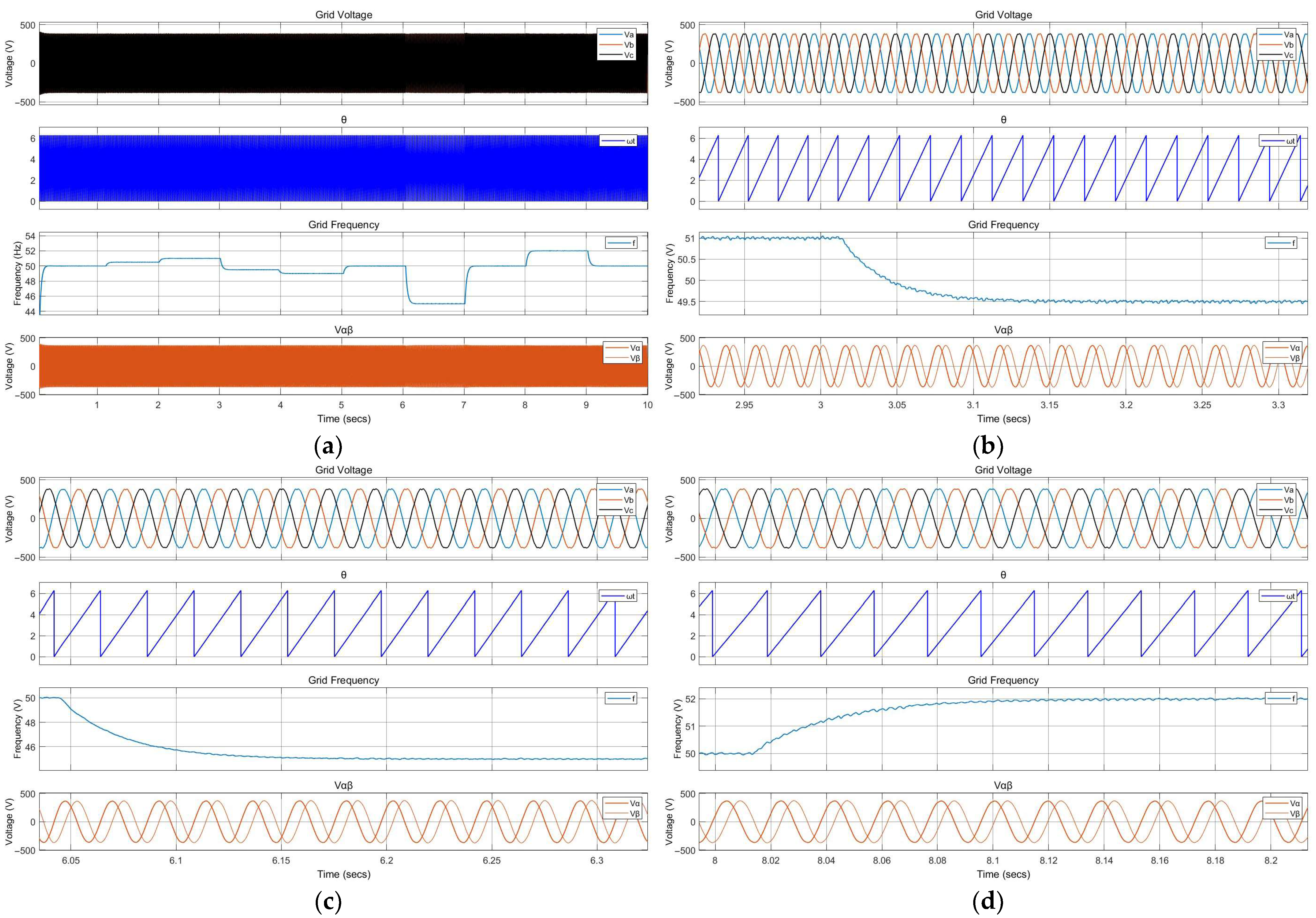
5.4. Scenario 4: Efficiency of Grid-Following Operation Under Frequency Deviations
6. Discussions
6.1. Scenario 1: Steady-State Operation Under Nominal Grid Conditions
6.2. Scenario 2: Performance Under Grid Disturbances
6.3. Scenario 3: Dynamic Response to Sudden Load Deviations
6.4. Scenario 4: Grid-Following Operation Under Frequency Deviations
7. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Q.; Caldognetto, T.; Buso, S. Review and Comparison of Grid-Tied Inverter Controllers in Microgrids. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 7624–7639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Zou, Z.; Yang, J.; Wang, Z.; Chen, W.; Buticchi, G. Transient Stability Analysis and Enhancement of Grid-Forming and Grid-Following Converters. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Ind. Electron. 2024, 5, 1396–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Kar, R.; Miao, Z.; Fan, L. A Novel Design for Switchable Grid-Following and Grid-Forming Control. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2025, 16, 1301–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zhou, D.; Anvari-Moghaddam, A.; Blaabjerg, F. Stability Analysis of Grid-Following and Grid-Forming Converters Based on State-Space Modelling. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2024, 60, 4910–4920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, H.; Huang, Y.; He, G.; Liu, C.; Wang, W. Dynamic Interaction and Stability Analysis of Grid-Following Converter Integrated into Weak Grid. CSEE J. Power Energy Syst. 2025, 11, 552–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Wang, Q.; Fang, W.; Wang, Y.; Diao, H.; Xu, H.; Guo, L. Research on Dynamic and Steady-State Characteristics of Grid-Following/Grid-Forming Hybrid Control Based on Model Predictive Control. IEEE Open J. Power Electron. 2025, 6, 909–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE. IEEE Guide for Planning DC Links Terminating at AC Locations Having Low Short-Circuit Capacities; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawda, G.S.; Shaik, A.G.; Su, W. Efficient Wind Energy Integration in Weak AC Grid with a DLMF-Based Adaptive Approach. Appl. Energy 2024, 372, 123779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saranchimeg, S.; Nair, N.K.C. A Novel Framework for Integration Analysis of Large-Scale Photovoltaic Plants into Weak Grids. Appl. Energy 2021, 282, 116141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigneysh, T.; Pachauri, N.; Suresh, V. Internal Model-Based Cascaded Control Approach for Multi-Functional Grid Interactive Converters. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 19862–19874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Eull, M.; Wang, W.; Preindl, M. Modular Model-Predictive Control with Regulated Third-Harmonic Injection for Zero-Sequence Stabilized Inverter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2022, 58, 7634–7647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.N.; Babu, P.N.; Kiranmayi, R.; Siano, P.; Panda, G. Improved Power Quality in a Solar PV Plant Integrated Utility Grid by Employing a Novel Adaptive Current Regulator. IEEE Syst. J. 2020, 14, 4308–4319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, M.; Rashid, U.; Arshad, R.; Khan, M.N.; Gilani, S.O.; Ayaz, Y. Robust Repetitive Current Control of Two-Level Utility-Connected Converter Using LCL Filter. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2015, 40, 2653–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, N.N.; Nguyen, N.-D.; Lee, Y.I. Model Predictive Control for a Voltage Sensorless Grid-Connected Inverter with LCL Filter Using Lumped Disturbance Observer. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2023, 11, 3050–3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, V.R.; Singh, A. Adaptive Internal Model Based Current Control with Embedded Active Damping of a Three-Phase Grid-Connected Inverter with LCL Filter for PV Application. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Detroit, MI, USA, 9 October 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, F.; Zhu, M.; Ye, Y. The Stability of LCL-Type Grid-Tied Inverter Based on Repetitive Control and Grid Voltage Feed-Forward. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2023, 11, 1496–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Xu, B.; Kang, K.; Zuo, S. Research on the Control Strategy of LCL Grid-Connected Inverters Based on Improved Auto Disturbance Rejection. Sci. Prog. 2023, 106, 00368504231208520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, W.; Yao, Z. An Improved Three-Level Cascaded Control for LCL-Filtered Grid-Connected Inverter in Complex Grid Impedance Condition. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 65485–65495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, M.; Waris, A.; Gilani, S.O.; Khawaja, B.A.; Khan, M.N.; Raza, A. Design of Robust Higher-Order Repetitive Controller Using Phase Lead Compensator. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 30603–30614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korada, D.M.R.; Mishra, M.K. Fixed Switching Frequency Model Predictive Current Control for Grid-Connected Inverter with Improved Dynamic and Steady State Performance. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 104094–104105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morari, M. Internal Model Control—Theory and Applications. IFAC Proc. Vol. 1983, 16, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, D.E.; Morari, M.; Skogestad, S. Internal Model Control: PID Controller Design. Ind. Eng. Chem. Proc. Des. Dev. 1986, 25, 252–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnefors, L.; Nee, H.-P. Model-Based Current Control of AC Machines Using the Internal Model Control Method. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1998, 34, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdanian, M.; Mehrizi-Sani, A. Internal Model-Based Current Control of the RL Filter-Based Voltage-Sourced Converter. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2014, 29, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Wang, X.; Harnefors, L. Rethinking Current Controller Design for PLL-Synchronized VSCs in Weak Grids. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 37, 1369–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitner, S.; Yazdanian, M.; Ziaeinejad, S.; Mehrizi-Sani, A.; Muetze, A. Internal Model-Based Active Resonance Damping Current Control of a Grid-Connected Voltage-Sourced Converter with an LCL Filter. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2018, 33, 6025–6036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Zhou, D.; Li, Y. Hybrid Model Predictive Current and Voltage Control for LCL-Filtered Grid-Connected Inverter. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2021, 9, 5747–5760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdani, S.; Ferdowsi, M.; Shamsi, P. Internal Model Based Smooth Transition of a Three-Phase Inverter Between Islanded and Grid-Connected Modes. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2020, 35, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, V.R. Internal Model Based Grid Voltage Estimation and Control of a Three-Phase Grid Connected Inverter for PV Application. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2021, 36, 3568–3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamanakos, P.; Nahalparvari, M.; Geyer, T. Fixed Switching Frequency Direct Model Predictive Control with Continuous and Discontinuous Modulation for Grid-Tied Converters with LCL Filters. IEEE Trans. Contr. Syst. Technol. 2021, 29, 1503–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reznik, A.; Simoes, M.G.; Al-Durra, A.; Muyeen, S.M. LCL Filter Design and Performance Analysis for Grid-Interconnected Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2014, 50, 1225–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollweg, G.V.; Khan, S.A.; Chaturvedi, S.; Fan, Y.; Wang, M.; Su, W. Grid-Connected Converters: A Brief Survey of Topologies, Output Filters, Current Control, and Weak Grids Operation. Energies 2023, 16, 3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman, R.; De Vicuna, L.G.; Castilla, M.; Miret, J.; De La Hoz, J. Variable Structure Control for Three-Phase LCL-Filtered Inverters Using a Reduced Converter Model. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrani, B.; Rufer, A. A Cascade Voltage Controller for Three-Phase Islanded Microgrids. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 21–25 July 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Leitner, S.; Yazdanian, M.; Mehrizi-Sani, A.; Muetze, A. Small-Signal Stability Analysis of an Inverter-Based Microgrid with Internal Model-Based Controllers. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2018, 9, 5393–5402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdanian, M.; Mehrizi-Sani, A. Case Studies on Cascade Voltage Control of Islanded Microgrids Based on the Internal Model Control. IFAC-Pap. 2015, 48, 578–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi-Ghartemani, M. Enhanced Phase-Locked Loop Structures for Power and Energy Applications; John Wiley & Sons Inc: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; ISBN 978-1-118-79513-2. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez, P.; Pou, J.; Bergas, J.; Candela, J.I.; Burgos, R.P.; Boroyevich, D. Decoupled Double Synchronous Reference Frame PLL for Power Converters Control. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2007, 22, 584–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabalci, E. Multilevel Inverters: Control Methods and Advanced Power Electronic Applications; Academic Press: London, UK, 2021; ISBN 978-0-323-90725-5. [Google Scholar]
- IEEE. IEEE Recommended Practice and Requirements for Harmonic Control in Electric Power Systems; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Electrotechnical Commission. Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC)—Part 3-2: Limits—Limits for Harmonic Current Emissions. 2018. Available online: https://webstore.iec.ch/en/publication/28164 (accessed on 1 December 2025).
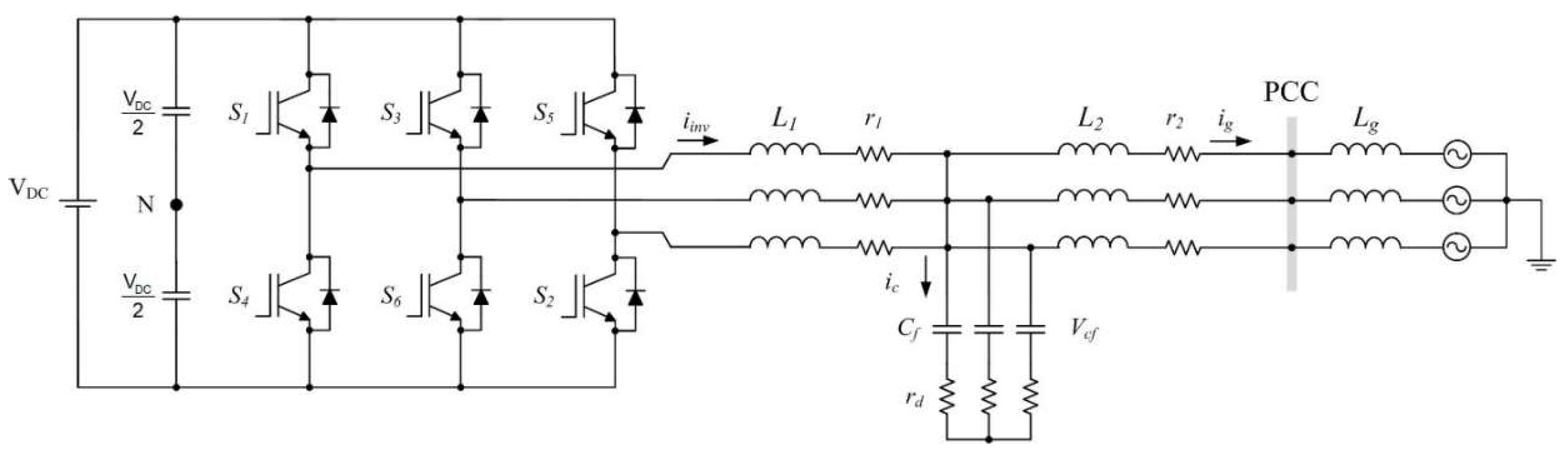
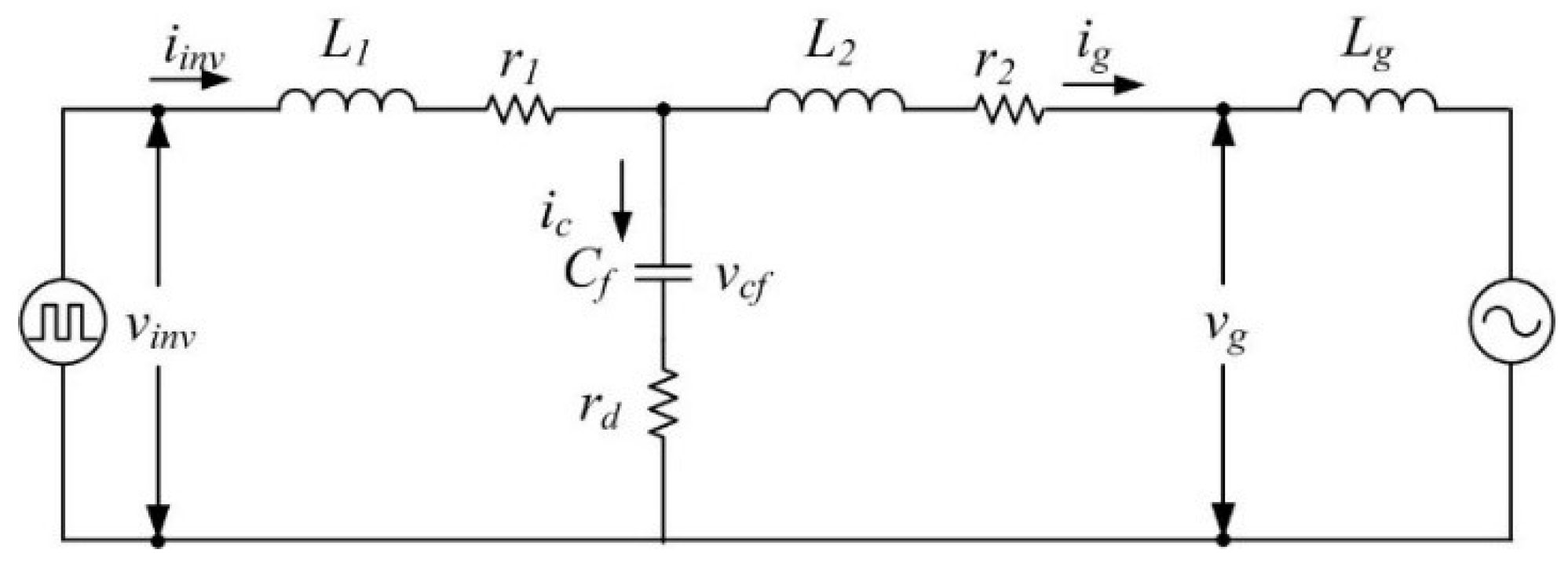
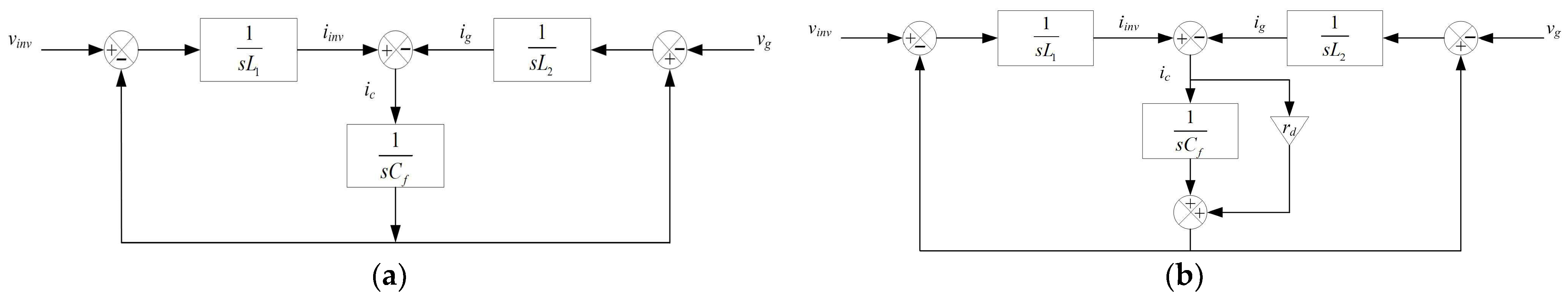
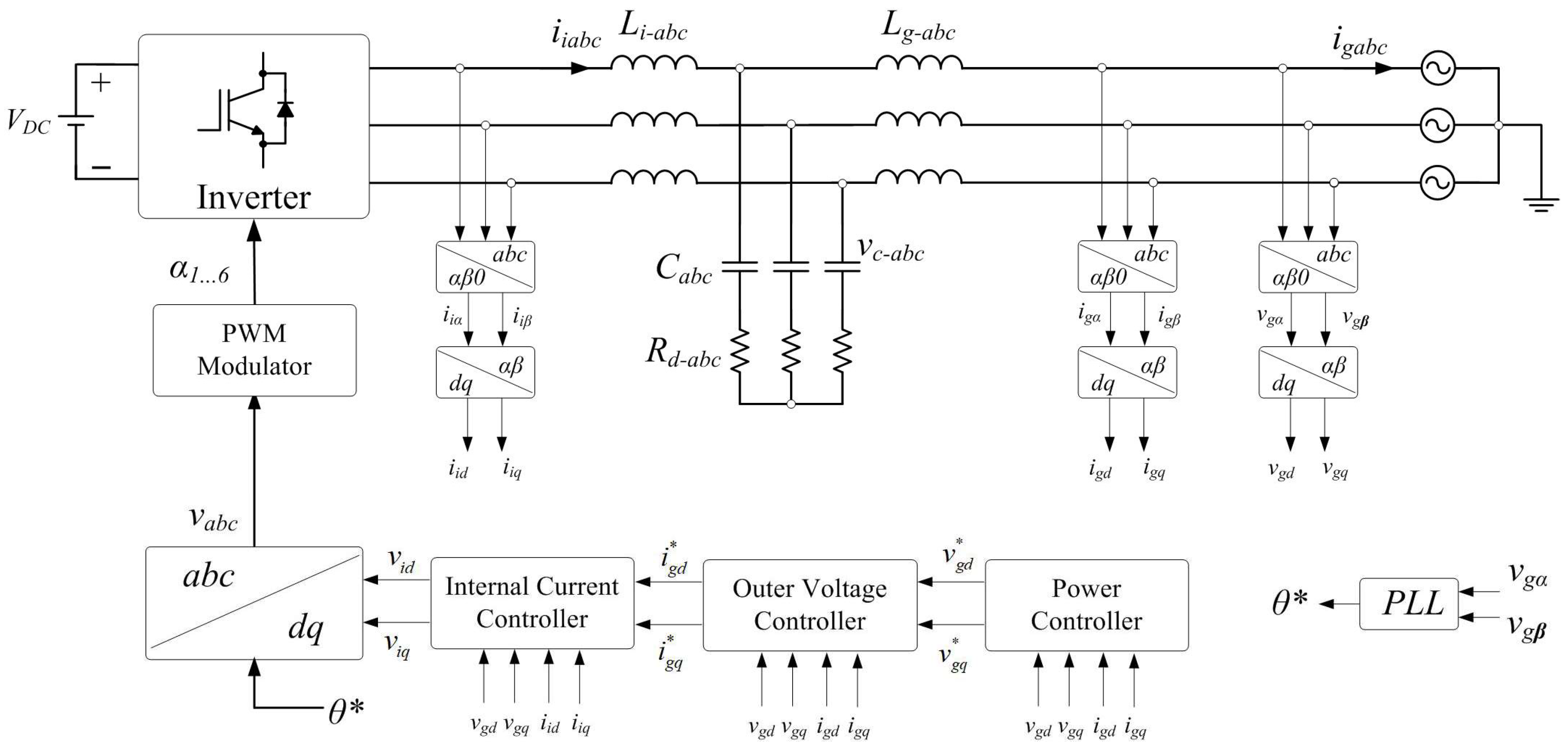
| Parameter | Description | Expression |
|---|---|---|
| Li | Inverter-side filter inductance | 155 μH |
| Ri | Inverter-side filter resistance | 0.0267 Ω |
| λ | IMC tuning parameter | Selected based on robustness and SCR |
| KP | Proportional gain of PI controller | |
| Ki | Integral gain of the PI controller |
| Inverter Parameters | ||
| DC bus voltage | Vdc | 800 V |
| Rated Power | Sn | 400 kVA |
| Inverter side inductor | Li | 155 μH (0.135 pu) |
| Grid-side inductor | Lg | 2.87 μH (0.0025 pu) |
| Filter capacitor | Cf | 110 μF (0.05 pu) |
| Filter resistance | Rf | 0.0267 Ω (0.074 pu) |
| Nominal line voltage | Viabc | 380 V |
| System frequency | fi | 50 Hz |
| Base impedance | Zb | 0.361 Ω |
| Base voltage | Vb | 310.26 V |
| Base current | Ib | 607.75 A |
| Base current (dq-frame) | Ib-dq | 859.50 A |
| Grid Parameters | ||
| Grid voltage | Vgabc | 380 V |
| Angular frequency | ωg | 314 rad/s |
| Short circuit ratio | SCR | 1.5–8 |
| Reactance to resistance ratio | X/R | 1.5–5 |
| Controller Parameters | ||
| Switching frequency | fsw | 9 kHz |
| Sampling time | Ts | 10 μs |
| Angular resonance frequency | ωres | 17,461 rad/s |
| Angular switching frequency | ωsw | 56,549 rad/s |
| Proportional gain of power controller | Kp-p | 0.0018 |
| Integral gain of the power controller | Ki-p | 0.053 |
| Proportional gain of the current controller | Kp-c | 0.2994 |
| Integral gain of the current controller | Ki-c | 0.0025 |
| Parameter | Case 1: Steady-State Operation | Case 2: Grid Disturbances | Case 3: Sudden Load Deviations | Case 4: Frequency Deviations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grid SCR | Low | Medium/Low | Medium/Low/Very Low | Low |
| Operating Mode | Normal grid-following | Fault/disturbed grid | Load transient | Frequency-varying grid |
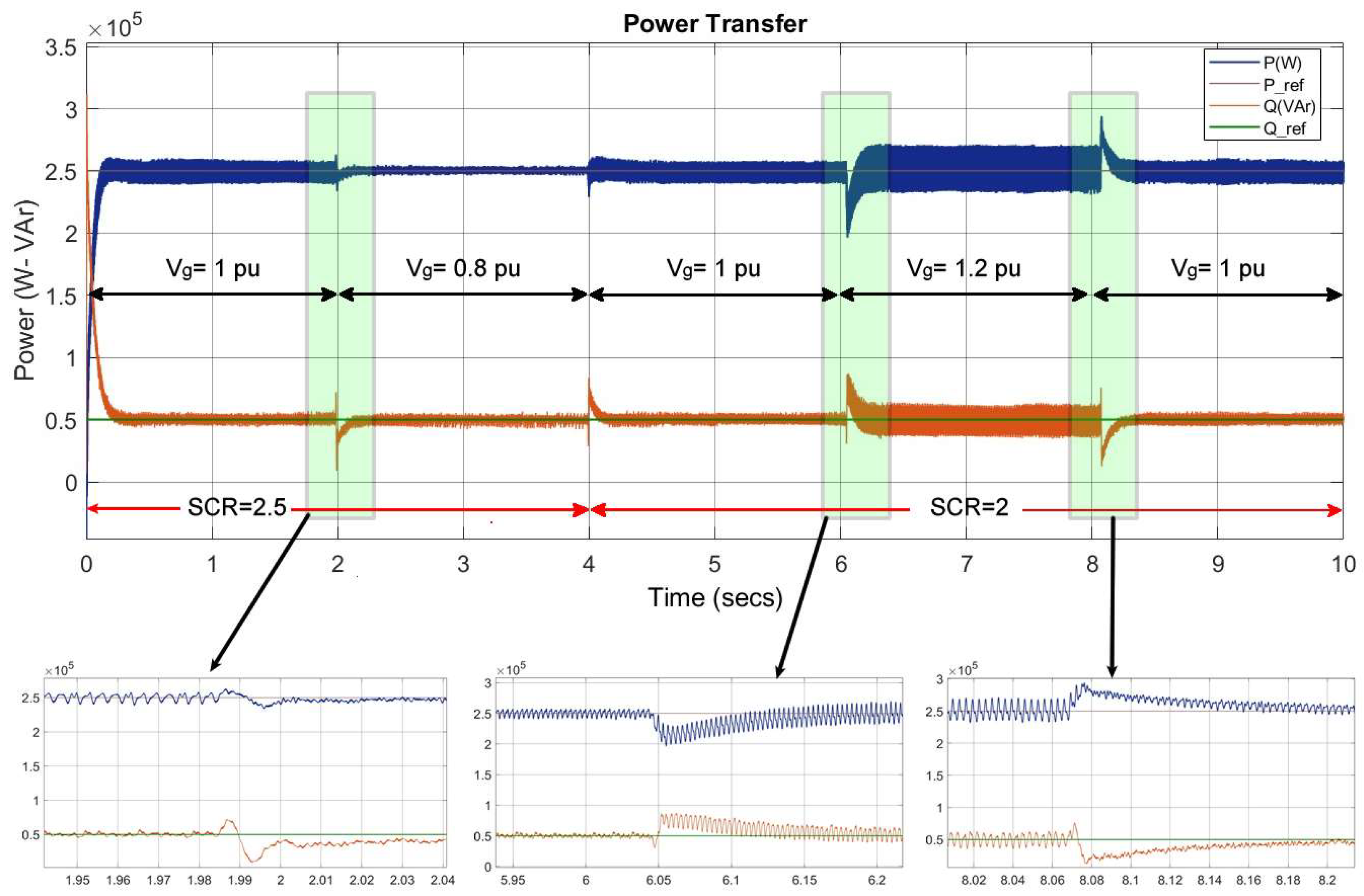
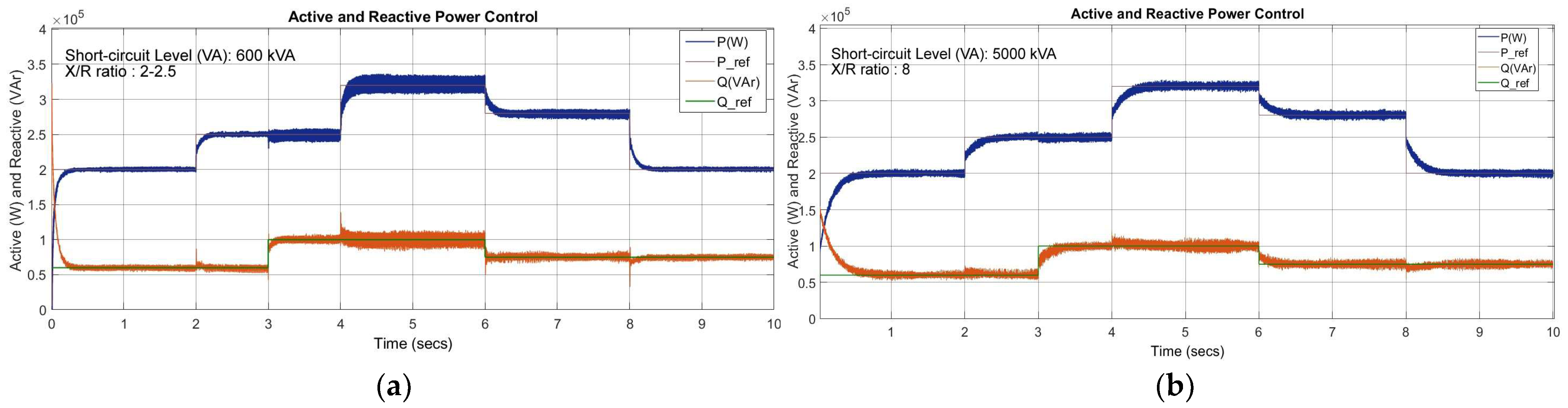
| Active Power Tracking Error (ΔP, %) | 0.01% | SCR = 2: 25% (1 ms transient) SCR = 2: 5% (50 ms transient) SCR = 2: 2% (steady state) | SCR = 1.5: 10% (max) SCR = 1.5: 2% (min) SCR = 12.5: 3% (max) | – |
| Reactive Power Tracking Error (ΔQ, %) | 0.01% | SCR = 2: 50% (1 ms transient) SCR = 2: 9% (50 ms transient) SCR = 2: 2% (steady state) | SCR = 1.5: 10% (max) SCR = 1.5: 2% (min) SCR = 12.5: 5% (max) | – |
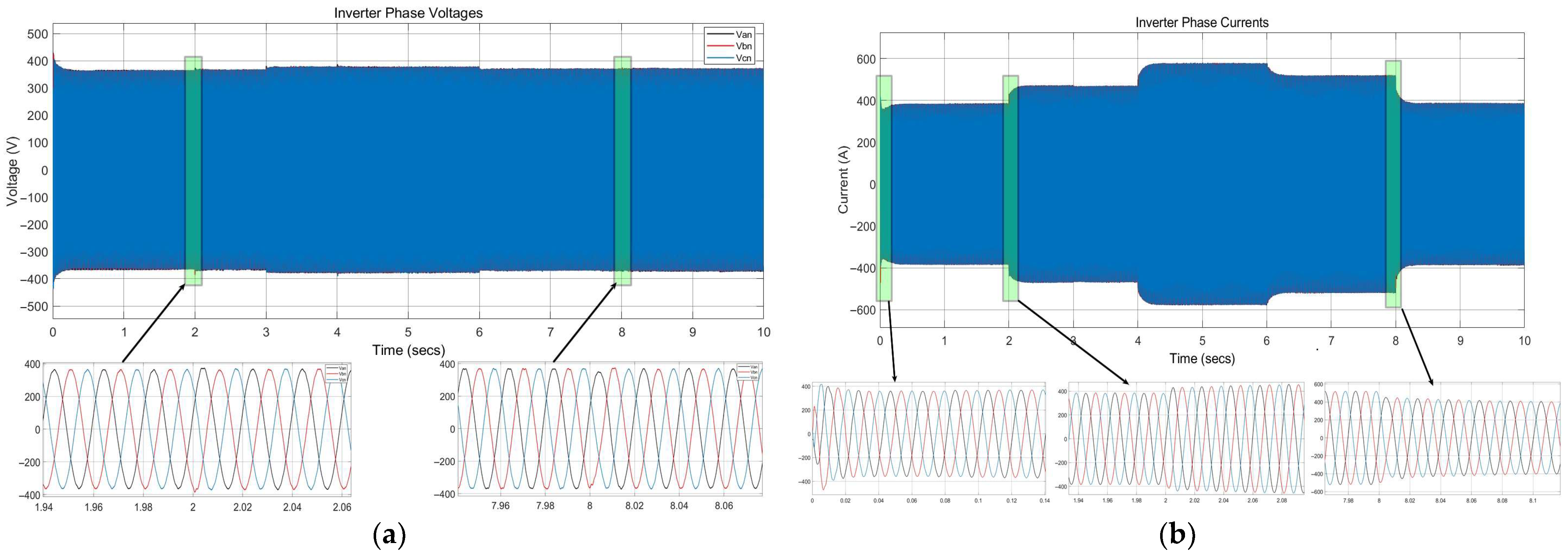
| id Overshoot (%) | 0% | 2.2% | ≈2% | ≈2% |
| iq Overshoot (%) | 3.2% | ≈5% | ≈3% | ≈2% |
| Current Settling Time (ms) | ≈90 | ≈80 | ≈100 @ SCR = 1.5 | ≈40 |
| Voltage Deviation at PCC (ΔV, pu) | 1.03 | 1.05 | ≈1.02@ SCR = 1.5 | ≈1.02 |
| PLL Phase Error (Δθ, rad/s) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Frequency Tracking Error (Δf, %) | – | 0 | – | – |
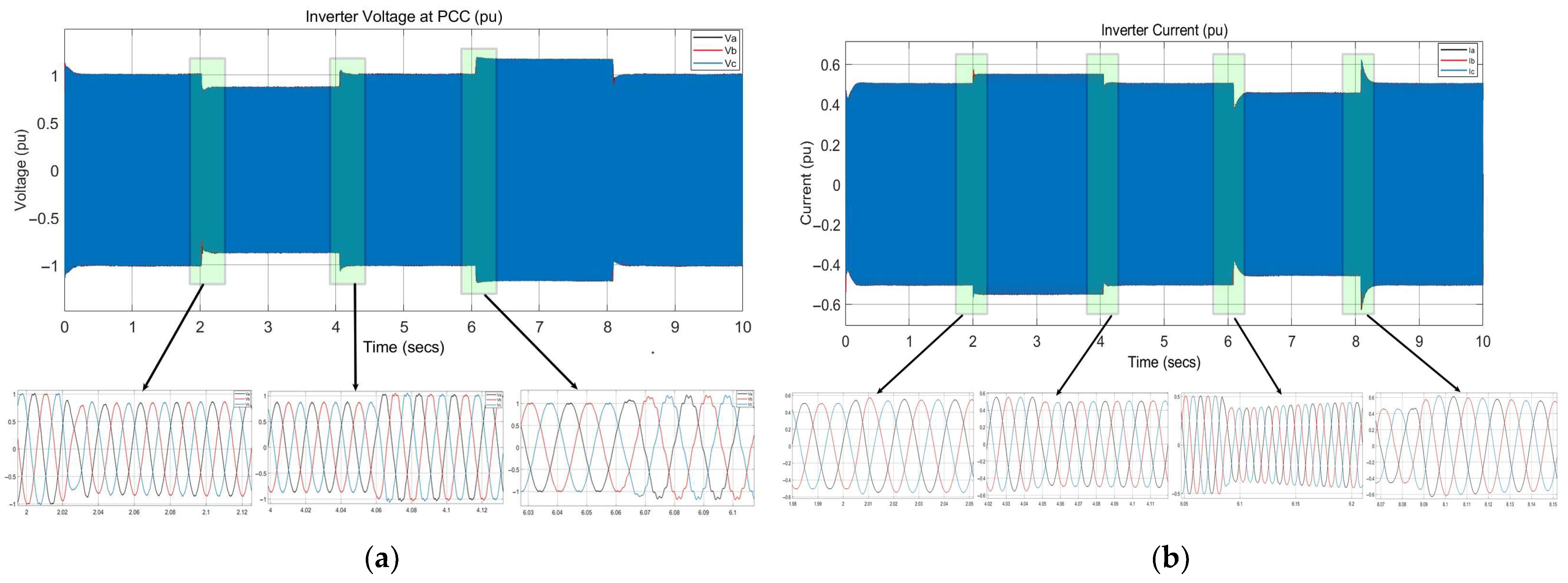
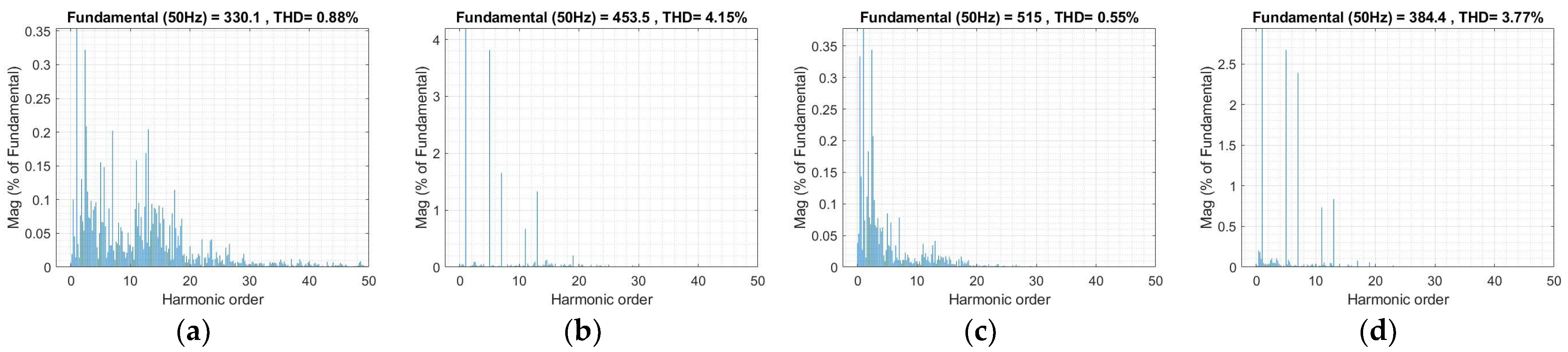
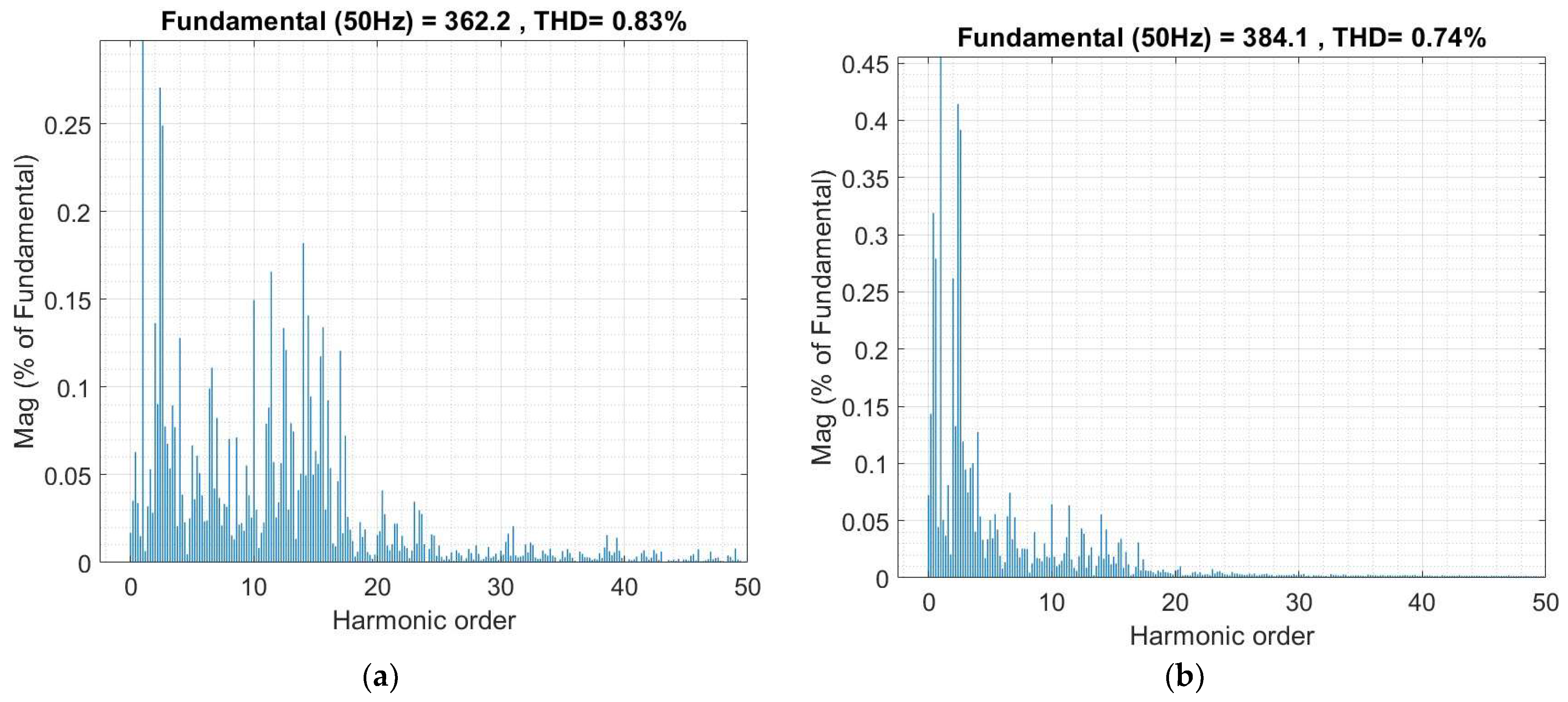
| THD of Injected Current (%) | 0.81% | 0.55% at Vgrid = 0.8 pu 3.77% at Vgrid = 1.2 pu | 0.74% | – |
| THD of Injected Voltage (%) | 0.87% | 0.88% at Vgrid = 0.8 pu 4.15% at Vgrid = 1.2 pu ✓ | 0.83% | – |
| Compliance with International Standards | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Kabalci, E. Internal Model-Based Dynamic Power Control of Grid-Following Voltage-Source Inverters. Electronics 2026, 15, 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics15010185
Kabalci E. Internal Model-Based Dynamic Power Control of Grid-Following Voltage-Source Inverters. Electronics. 2026; 15(1):185. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics15010185
Chicago/Turabian StyleKabalci, Ersan. 2026. "Internal Model-Based Dynamic Power Control of Grid-Following Voltage-Source Inverters" Electronics 15, no. 1: 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics15010185
APA StyleKabalci, E. (2026). Internal Model-Based Dynamic Power Control of Grid-Following Voltage-Source Inverters. Electronics, 15(1), 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics15010185






