Synchronization of Inhalation/Exhalation Ratio and Heart Rate Variability During Spontaneous Breathing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
- Individuals with respiratory diseases
- Individuals with cardiovascular diseases
- Individuals with neurological or muscular disorders
- Individuals diagnosed with sleep apnea syndrome (SAS)
- Individuals regularly taking medications that suppress respiration
- Individuals who have consumed caffeine or alcohol within the past three hours
- Smokers who have smoked within the past six hours
- Individuals with severe obesity (BMI ≥ 35)
- Pregnant or lactating individuals
- Other cases deemed inappropriate by the principal investigator
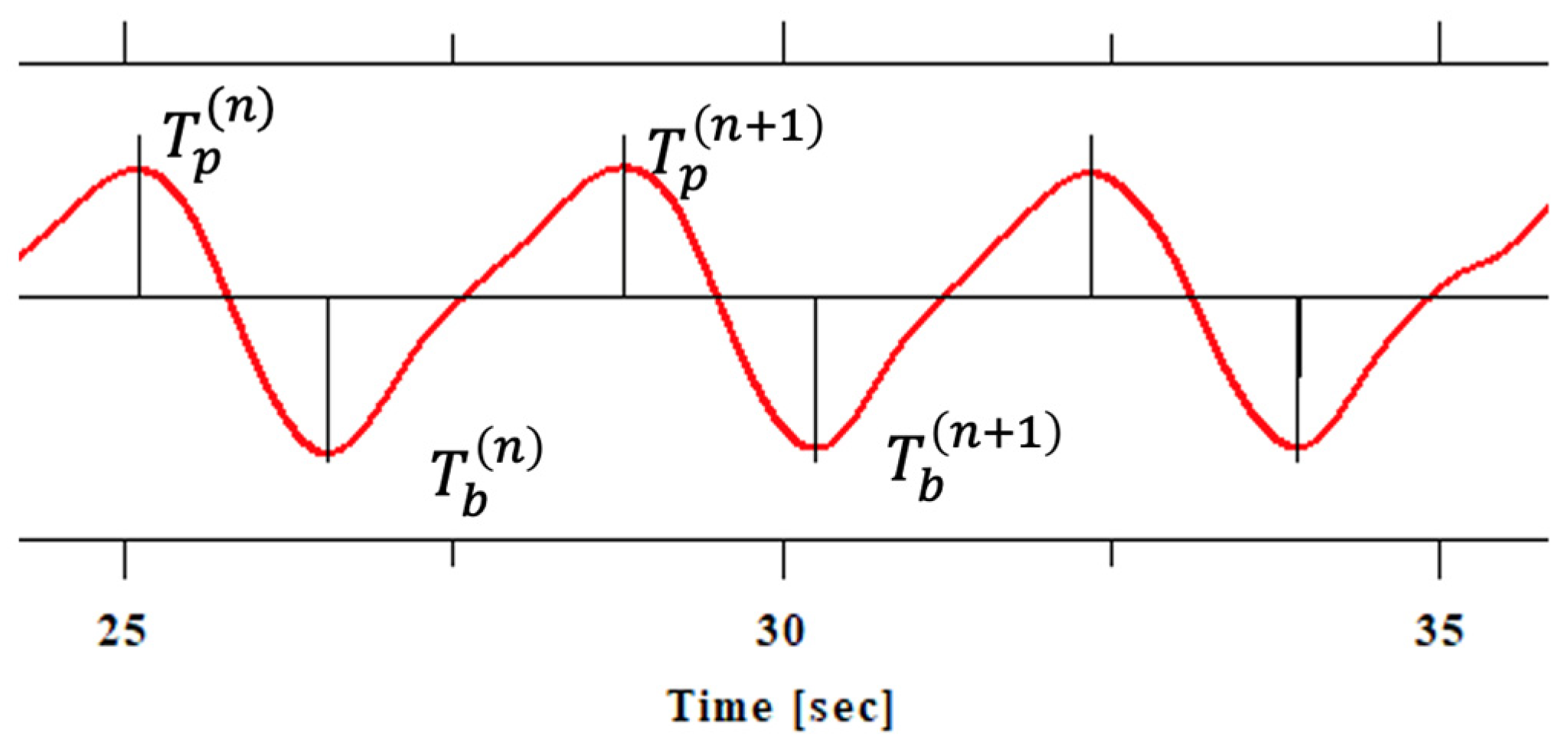
2.2. Measurement of Respiratory and Cardiac Signals
- Very low frequency (VLF) power: 0.0033–0.04 Hz. Reflects long-term regulatory mechanisms such as thermoregulation and the renin–angiotensin system.
- Low frequency (LF) power: 0.04–0.15 Hz. Represents a mix of sympathetic and parasympathetic activity, associated with baroreflex sensitivity.
- High frequency (HF) power: 0.15–0.4 Hz. Indicates parasympathetic (vagal) activity and is closely related to respiratory sinus arrhythmia.
- Frequency to high frequency ratio (LF/HF): commonly used as an index of sympathovagal balance.
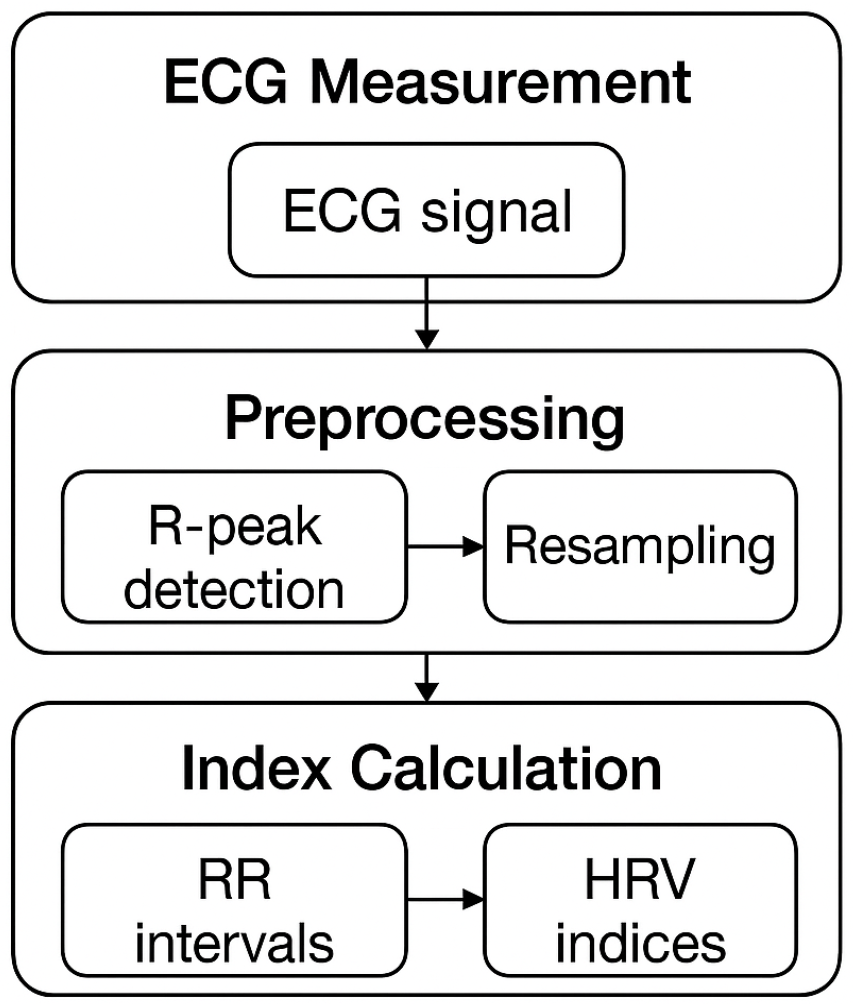
2.3. Data Processing and Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sarkar, M.; Madabhavi, I.V.; Mehta, S.; Mohanty, S. Use of Flow Volume Curve to Evaluate Large Airway Obstruction. Monaldi Arch. Chest Dis. 2022, 92, 1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Khlaiwi, T. Flow Volume Curve: A Diagnostic Tool in Extrathoracic Airway Obstruction. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 36, 846–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Toga, H.; Ohya, N. Flow-Volume Curve. Nihon Rinsho 1997, 55 (Suppl. 2), 15–18. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Guan, R.; Shi, M.; Dai, X.; Li, H.; Zhou, N.; Chen, D.; Mao, H. A Nanoforest-Based Humidity Sensor for Respiration Monitoring. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2022, 8, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, J.; Pavlidis, I. Thermistor at a Distance: Unobtrusive Measurement of Breathing. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 57, 988–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boparai, S.; Solomon, G.M. Interpretation of Spirometry, Peak Flow, and Provocation Testing for Asthma. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 2024, 57, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brigham, E.P.; West, N.E. Diagnosis of asthma: Diagnostic testing. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2015, 5 (Suppl. 1), S27–S30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, D.; Brusselle, G. Challenges of COPD diagnosis. Expert Opin. Med. Diagn. 2013, 7, 543–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormack, M.C.; Enright, P.L. Making the diagnosis of asthma. Respir. Care 2008, 53, 583–590. [Google Scholar]
- Ritsert, F.; Elgendi, M.; Galli, V.; Menon, C. Heart and Breathing Rate Variations as Biomarkers for Anxiety Detection. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, R. Stress Reappraisal Improves the Autonomic Nervous System Response of Test Anxious Individuals: Evidence from Heart Rate Variability. Neurosci. Lett. 2023, 812, 137372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immanuel, S.; Teferra, M.N.; Baumert, M.; Bidargaddi, N. Heart Rate Variability for Evaluating Psychological Stress Changes in Healthy Adults: A Scoping Review. Neuropsychobiology 2023, 82, 187–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shea, S.A. Behavioural and Arousal-Related Influences on Breathing in Humans. Exp. Physiol. 1996, 81, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutschmann, M.; Dick, T.E. Pontine Mechanisms of Respiratory Control. Compr. Physiol. 2012, 2, 2443–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thayer, J.F.; Åhs, F.; Fredrikson, M.; Sollers, J.J.; Wager, T.D. A Meta-Analysis of Heart Rate Variability and Neuroimaging Studies: Implications for Heart Rate Variability as a Marker of Stress and Health. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2012, 36, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szulczewski, M.T. Training of Paced Breathing at 0.1 Hz Improves CO2 Homeostasis and Relaxation during a Paced Breathing Task. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0218550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokogawa, M.; Kurebayashi, T.; Soma, K.; Miaki, H.; Nakagawa, T. Investigation into Deep Breathing through Measurement of Ventilatory Parameters and Observation of Breathing Patterns. J. Vis. Exp. 2019, 151, e60062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleicher, D.; Jarvers, I.; Kocur, M.; Kandsperger, S.; Brunner, R.; Ecker, A. Does It Need an App? Differences between App-Guided Breathing and Natural Relaxation in Adolescents after Acute Stress. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2024, 169, 107148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berntson, G.G.; Cacioppo, J.T.; Quigley, K.S. Respiratory Sinus Arrhythmia: Autonomic Origins, Physiological Mechanisms, and Psychophysiological Implications. Psychophysiology 1993, 30, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garssen, B.; de Ruiter, C.; van Dyck, R. Breathing Retraining: A Rational Placebo? Clin. Psychol. Rev. 1992, 12, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remmers, J.E.; Issa, F.G.; Suratt, P.M. Sleep and Respiration. J. Appl. Physiol. 1990, 68, 1286–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decker, M.J.; Haaga, J.; Arnold, J.L.; Atzberger, D.; Strohl, K.P. Functional Electrical Stimulation and Respiration during Sleep. J. Appl. Physiol. 1993, 75, 1053–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doheny, E.P.; Lowery, M.M.; Russell, A.; Ryan, S. Estimation of Respiration Rate and Sleeping Position Using a Wearable Accelerometer. Annu. Int. Conf. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2020, 2020, 4668–4671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Addison, P.S.; Antunes, A.; Montgomery, D.; Borg, U.R. Non-Contact Monitoring of Inhalation-Exhalation (I:E) Ratio in Non-Ventilated Subjects. IEEE J. Transl. Eng. Health Med. 2024, 12, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Zhang, X.; He, X.; Ling, L.; Zeng, C.; Luo, Y. The Independent and Combined Effects of Respiratory Events and Cortical Arousals on the Autonomic Nervous System across Sleep Stages. Sleep Breath. 2018, 22, 1161–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernando, A.; Posada-Quintero, H.; Peláez-Coca, M.D.; Gil, E.; Chon, K.H. Autonomic Nervous System Characterization in Hyperbaric Environments Considering Respiratory Component and Non-Linear Analysis of Heart Rate Variability. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2022, 214, 106527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology. Heart Rate Variability: Standards of Measurement, Physiological Interpretation, and Clinical Use. Circulation 1996, 93, 1043–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, P.; Kollai, M. Respiratory Sinus Arrhythmia, Cardiac Vagal Tone, and Respiration: Within- and Between-Individual Relations. Psychophysiology 1993, 30, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, Y.; Furukawa, Y.; Ogasawara, H.; Yuda, E.; Hayano, J. Longer lying position causes lower LF/HF of heart rate variability during ambulatory monitoring. In Proceedings of the IEEE Global Conference on Consumer Electronics (GCCE), Kyoto, Japan, 11–14 October 2016; pp. 348–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porges, S.W. The Polyvagal Perspective. Biol. Psychol. 2007, 74, 116–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakakibara, M.; Hayano, J. Effect of Slowed Respiration on Cardiac Parasympathetic Response to Threat. Psychosom. Med. 1996, 58, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauss-Blasche, G.; Moser, M.; Voica, M.; McLeod, D.R.; Klammer, N.; Marktl, W. Relative Timing of Inspiration and Expiration Affects Respiratory Sinus Arrhythmia. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2000, 27, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berntson, G.G.; Bigger, J.T.; Eckberg, D.L.; Grossman, P.; Kaufmann, P.G.; Malik, M.; Nagaraja, H.N.; Porges, S.W.; Saul, J.P.; Stone, P.H.; et al. Heart Rate Variability: Origins, Methods, and Interpretive Caveats. Psychophysiology 1997, 34, 623–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayano, J.; Mukai, S.; Sakakibara, M.; Okada, A.; Takata, K.; Fujinami, T. Effects of Respiratory Interval on Vagal Modulation of Heart Rate. Am. J. Physiol. 1994, 267, H33–H40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaschillo, E.; Vaschillo, B.; Lehrer, P.M. Characteristics of Resonance in Heart Rate Variability Stimulated by Biofeedback. Appl. Psychophysiol. Biofeedback 2006, 31, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasuma, F.; Hayano, J. Respiratory Sinus Arrhythmia: Why Does the Heartbeat Synchronize with Respiratory Rhythm? Chest 2004, 125, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, H.M.; Rehder, K.; Hyatt, R.E. Respiratory Timing and Depth of Breathing in Dogs Anesthetized with Halothane or Enflurane. J. Appl. Physiol. Respir. Environ. Exerc. Physiol. 1981, 51, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, D.L.; Cover, D.; Hughes, J.M. Effect of Respiratory Apparatus on Timing and Depth of Breathing in Man. Respir. Physiol. 1985, 61, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giardino, N.D.; Glenny, R.W.; Borson, S.; Chan, L. Respiratory Sinus Arrhythmia Is Associated with Efficiency of Pulmonary Gas Exchange in Healthy Humans. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2003, 284, H1585–H1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, G.R.; Breen, P.P.; Jayarathna, T.; Tong, B.K.; Eckert, D.J.; Gargiulo, G.D. Morphic Sensors for Respiratory Parameters Estimation: Validation against Overnight Polysomnography. Biosensors 2023, 13, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, P.; Karemaker, J.; Wieling, W. Prediction of Tonic Parasympathetic Cardiac Control Using Respiratory Sinus Arrhythmia: The Need for Respiratory Control. Psychophysiology 1991, 28, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, B. Sleep, Sleep Loss, and Breathing. South. Med. J. 1985, 78, 1483–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Chen, W.; Nemoto, T.; Kanemitsu, Y.; Kitamura, K.; Yamakoshi, K.; Wei, D. Real-Time Monitoring of Respiration Rhythm and Pulse Rate during Sleep. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2006, 53, 2553–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobson, J.A.; Goldfrank, F.; Snyder, F. Respiration and Mental Activity in Sleep. J. Psychiatr. Res. 1965, 3, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaiduk, M.; Perea, J.J.; Seepold, R.; Martinez Madrid, N.; Penzel, T.; Glos, M.; Ortega, J.A. Estimation of Sleep Stages Analyzing Respiratory and Movement Signals. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2022, 26, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balady, G.J.; Arena, R.; Sietsema, K.; Myers, J.; Coke, L.; Fletcher, G.F.; Forman, D.; Franklin, B.; Guazzi, M.; Gulati, M.; et al. Clinician’s Guide to cardiopulmonary exercise testing in adults: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2010, 122, 191–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalanza, J.F.; Lorente, S.; Bullich, R.; García, C.; Losilla, J.M.; Capdevila, L. Methods for Heart Rate Variability Biofeedback (HRVB): A Systematic Review and Guidelines. Appl. Psychophysiol. Biofeedback 2023, 48, 275–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehrer, P.M.; Vaschillo, E.; Vaschillo, B.; Lu, S.-E.; Eckberg, D.L.; Edelberg, R.; Shih, W.J.; Lin, Y.; Kuusela, T.A.; Tahvanainen, K.U.O.; et al. Heart Rate Variability Biofeedback Increases Baroreflex Gain and Peak Expiratory Flow. Psychosom. Med. 2003, 65, 796–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitzalis, M.V.; Mastropasqua, F.; Massari, F.; Passantino, A.; Colombo, R.; Mannarini, A.; Forleo, C.; Rizzon, P. Effect of Respiratory Rate on the Relationship between RR Interval and Systolic Blood Pressure Fluctuations: A Frequency-Dependent Phenomenon. Cardiovasc. Res. 1998, 38, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.-S.; Lehrer, P.M. The Effects of Specific Respiratory Rates on Heart Rate and Heart Rate Variability. Appl. Psychophysiol. Biofeedback 2003, 28, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seipäjärvi, S.M.; Tuomola, A.; Juurakko, J.; Rottensteiner, M.; Rissanen, A.E.; Kurkela, J.L.O.; Kujala, U.M.; Laukkanen, J.A.; Wikgren, J. Measuring Psychosocial Stress with Heart Rate Variability-Based Methods in Different Health and Age Groups. Physiol. Meas. 2022, 43, 055003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Zwan, J.E.; de Vente, W.; Huizink, A.C.; Bögels, S.M.; de Bruin, E.I. Physical Activity, Mindfulness Meditation, or Heart Rate Variability Biofeedback for Stress Reduction: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Appl. Psychophysiol. Biofeedback 2015, 40, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


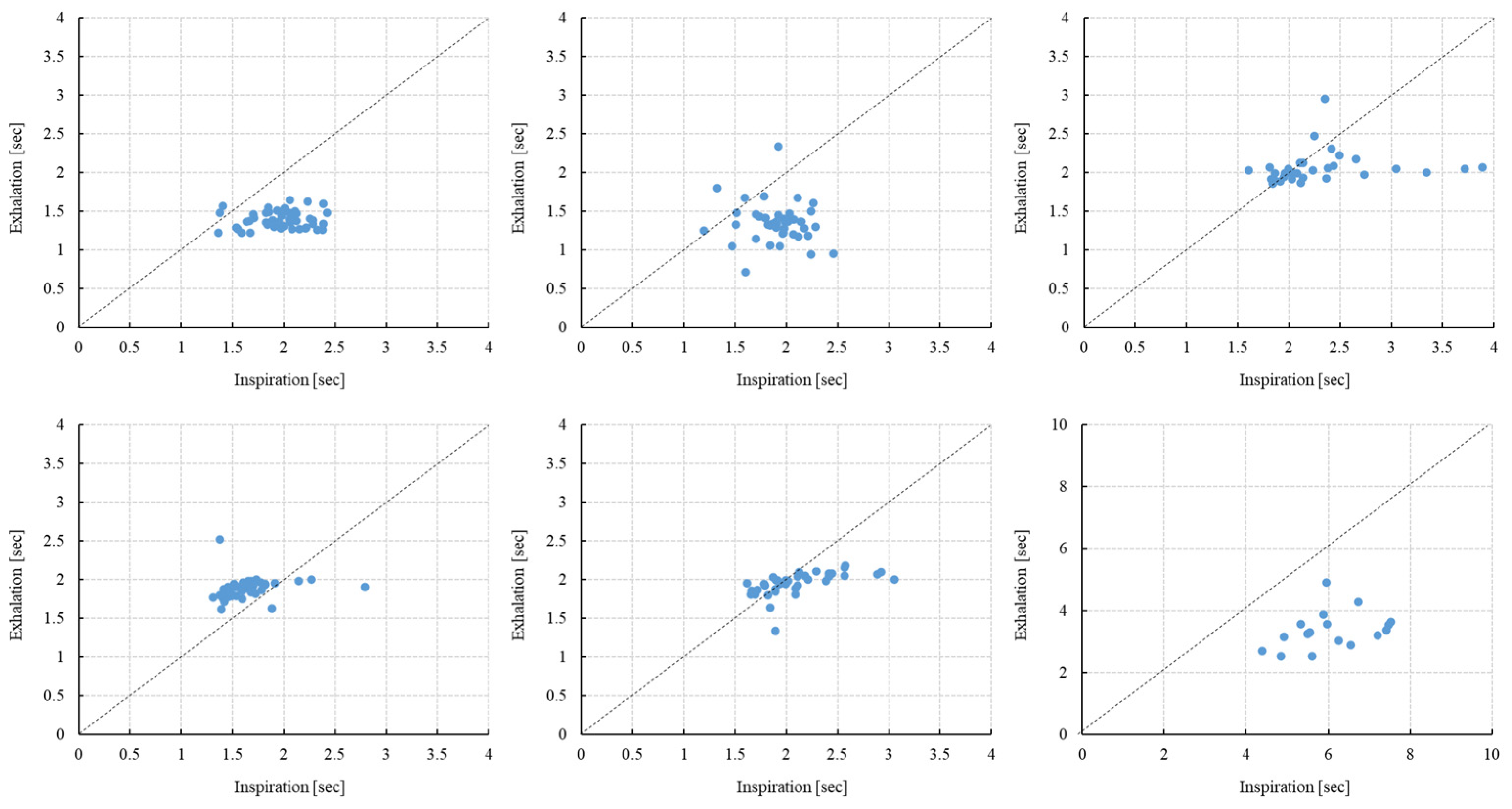

| Subjects | Inspiration [s] | Exhalation [s] | p-Value (Insp. vs. Exha.) | Insp./Exha. [Ratio] | Insp. +Exha. [s] | Peak Power [Ratio] | Peak Frequency [Hz] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Coefficient of Variation) | (Coefficient of Variation) | (Coefficient of Variation) | |||||
| 1 | 2.006 ± 0.267 | 1.425 ± 0.152 | <0.001 | 1.423 ± 0.230 | 3.431 | 0.0626 | 0.282 |
| −0.132 | −0.106 | −0.162 | |||||
| 2 | 1.828 ± 0.386 | 1.360 ± 0.260 | <0.001 | 1.418 ± 0.474 | 3.188 | 0.0485 | 0.275 |
| −0.21 | −0.19 | −0.334 | |||||
| 3 | 2.322 ± 0.585 | 2.041 ± 0.184 | <0.001 | 1.138 ± 0.266 | 4.363 | 0.0409 | 0.21 |
| −0.25 | −0.089 | −0.234 | |||||
| 4 | 1.591 ± 0.288 | 1.843 ± 0.151 | <0.001 | 0.865 ± 0.145 | 3.434 | 0.0638 | 0.237 |
| −0.18 | −0.082 | −0.168 | |||||
| 5 | 2.133 ± 0.370 | 1.958 ± 0.135 | <0.001 | 1.074 ± 0.160 | 4.091 | 0.0938 | 0.244 |
| −0.172 | −0.067 | −0.149 | |||||
| 6 | 5.655 ± 1.096 | 3.871 ± 1.558 | <0.001 | 1.667 ± 0.577 | 9.526 | 0.0644 | 0.103 |
| −0.191 | −0.402 | −0.346 |
| Subjects | Inspiration [s] | Exhalation [s] | p-Value (Insp. vs. Exha.) | Insp./Exha. [Ratio] | Insp. +Exha. [s] | Peak Power [mV2] | Peak Frequency [Hz] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Coefficient of Variation) | (Coefficient of Variation) | (Coefficient of Variation) | |||||
| 1 | 1.963 ± 0.273 | 1.395 ± 0.110 | <0.001 | 1.414 ± 0.216 | 3.358 | 0.091 | 0.282 |
| −0.139 | −0.079 | −0.153 | |||||
| 2 | 1.912 ± 0.252 | 1.352 ± 0.245 | <0.001 | 1.462 ± 0.348 | 3.264 | 0.057 | 0.289 |
| −0.132 | −0.181 | −0.238 | |||||
| 3 | 2.342 ± 0.606 | 2.068 ± 0.205 | 0.011 | 1.135 ± 0.282 | 4.41 | 0.033 | 0.214 |
| −0.259 | −0.099 | −0.248 | |||||
| 4 | 1.643 ± 0.250 | 1.885 ± 0.130 | <0.001 | 0.873 ± 0.129 | 3.528 | 0.116 | 0.237 |
| −0.152 | −0.069 | −0.148 | |||||
| 5 | 2.113 ± 0.360 | 1.955 ± 0.152 | 0.003 | 1.080 ± 0.157 | 4.068 | 0.127 | 0.214 |
| −0.17 | −0.078 | −0.145 | |||||
| 6 | 6.069 ± 0.970 | 3.370 ± 0.610 | <0.001 | 1.833 ± 0.326 | 9.439 | 0.127 | 0.099 |
| −0.16 | −0.181 | −0.178 |
| Subjects | RRI [ms] | SDRR [ms] | VLF [ln,ms2] | LF [ln,ms2] | HF [ln,ms2] | LF/HF [ratio] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 609 | 18 | 4.57 | 4.37 | 3.09 | 3.59 |
| 2 | 805 | 36 | 6.73 | 4.98 | 3.83 | 3.15 |
| 3 | 781 | 23 | 5.73 | 5.28 | 4.32 | 2.63 |
| 4 | 602 | 18 | 5.32 | 3.68 | 3.48 | 1.22 |
| 5 | 741 | 63 | 6.7 | 6.91 | 7.24 | 0.72 |
| 6 | 810 | 34 | 4.9 | 6.8 | 4.19 | 13.57 |
| Subjects | RRI [ms] | SDRR [ms] | VLF [ln,ms2] | LF [ln,ms2] | HF [ln,ms2] | LF/HF [ratio] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 599 | 13 | 4.18 | 4.47 | 2.44 | 7.67 |
| 2 | 782 | 29 | 6.69 | 5.84 | 3.83 | 7.44 |
| 3 | 782 | 25 | 5.83 | 5.47 | 4.57 | 2.47 |
| 4 | 593 | 14 | 4.83 | 4.26 | 3.46 | 2.21 |
| 5 | 730 | 59 | 5.27 | 6.06 | 7.25 | 0.3 |
| 6 | 808 | 30 | 4.92 | 6.78 | 4.03 | 15.54 |
| HRV Index | RRI | SDRR | VLF | LF | HF | LF/HF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | 0.481 | −0.007 | −0.292 | 0.396 | −0.252 | 0.806 |
| p-value | 0.331 | 0.998 | 0.5738 | 0.435 | 0.63 | 0.053 |
| HRV Index | RRI | SDRR | VLF | LF | HF | LF/HF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | 0.518 | −0.029 | 0.01 | 0.63 | −0.277 | 0.944 |
| p-value | 0.292 | 0.956 | 0.985 | 0.184 | 0.596 | 0.005 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuda, E.; Yoshida, Y. Synchronization of Inhalation/Exhalation Ratio and Heart Rate Variability During Spontaneous Breathing. Electronics 2025, 14, 1903. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14091903
Yuda E, Yoshida Y. Synchronization of Inhalation/Exhalation Ratio and Heart Rate Variability During Spontaneous Breathing. Electronics. 2025; 14(9):1903. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14091903
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuda, Emi, and Yutaka Yoshida. 2025. "Synchronization of Inhalation/Exhalation Ratio and Heart Rate Variability During Spontaneous Breathing" Electronics 14, no. 9: 1903. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14091903
APA StyleYuda, E., & Yoshida, Y. (2025). Synchronization of Inhalation/Exhalation Ratio and Heart Rate Variability During Spontaneous Breathing. Electronics, 14(9), 1903. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14091903







