Noise-Resilient Low-Light Image Enhancement with CLIP Guidance and Pixel-Reordering Subsampling
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We introduce the CLIP-LLA loss to inject semantic and perceptual priors from a foundation model into LLIE training, achieving faithful illumination and color consistency.
- We design a pixel-reordering subsampling (PRS) scheme that enhances robustness and noise suppression through multi-scale data regularization.
- We conduct extensive experiments on representative benchmarks such as LOL variations and SID. The results demonstrate consistent performance boosts, over PSNR and LPIPS improvement on SMID benchmark, validating the effectiveness of our proposed method.
2. Related Works
3. Method
3.1. Motivation and Preliminaries
3.2. CLIP-LLA Loss
- {“Good image”, “bad image”},
- {“Sharp image”, “blurry image”},
- {“sharp edges”, “blurry edges”},
- {“High resolution image”, “low resolution image”},
- {“Noise-free image”, “noisy image”}.
- {“A well lit image”, “A low light image”}.
3.3. Pixel-Reordering Subsampling (PRS): Multi-Scale Training for Noise Robustness
3.4. Summary of Proposed Algorithm
4. Experiment
4.1. Dataset and Implementation Details
4.1.1. sRGB Datasets
4.1.2. RAW Datasets
4.1.3. Evaluation Metrics
4.1.4. Training and Evaluation Protocol
4.2. Low-Light Image Enhancement
4.3. Ablation Study
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Detail on Network Framework and Algorithm

- Utilization of illumination features. IG-MSA multiplies the value vectors by the illumination map from the estimator before attention; standard blocks operate solely on the token features.
- Positional branch. IGAB adds a depthwise convolutional positional stream to the attention output; transformers rely on fixed or learned positional embeddings without extra conv branches.
- Channel-wise FFN. IGAB’s feed-forward path is all convolutional ( depthwise with GELU); transformers use linear layers.
- PreNorm placement. IGAB wraps only the FFN with PreNorm; attention path skips LayerNorm to keep illumination modulation raw, whereas standard blocks apply LayerNorm before both attention and FFN.
- Residual flow. IGAB applies residual adds after both attention + positional fusion and the conv MLP; transformers use two residuals but without the illumination gating step.
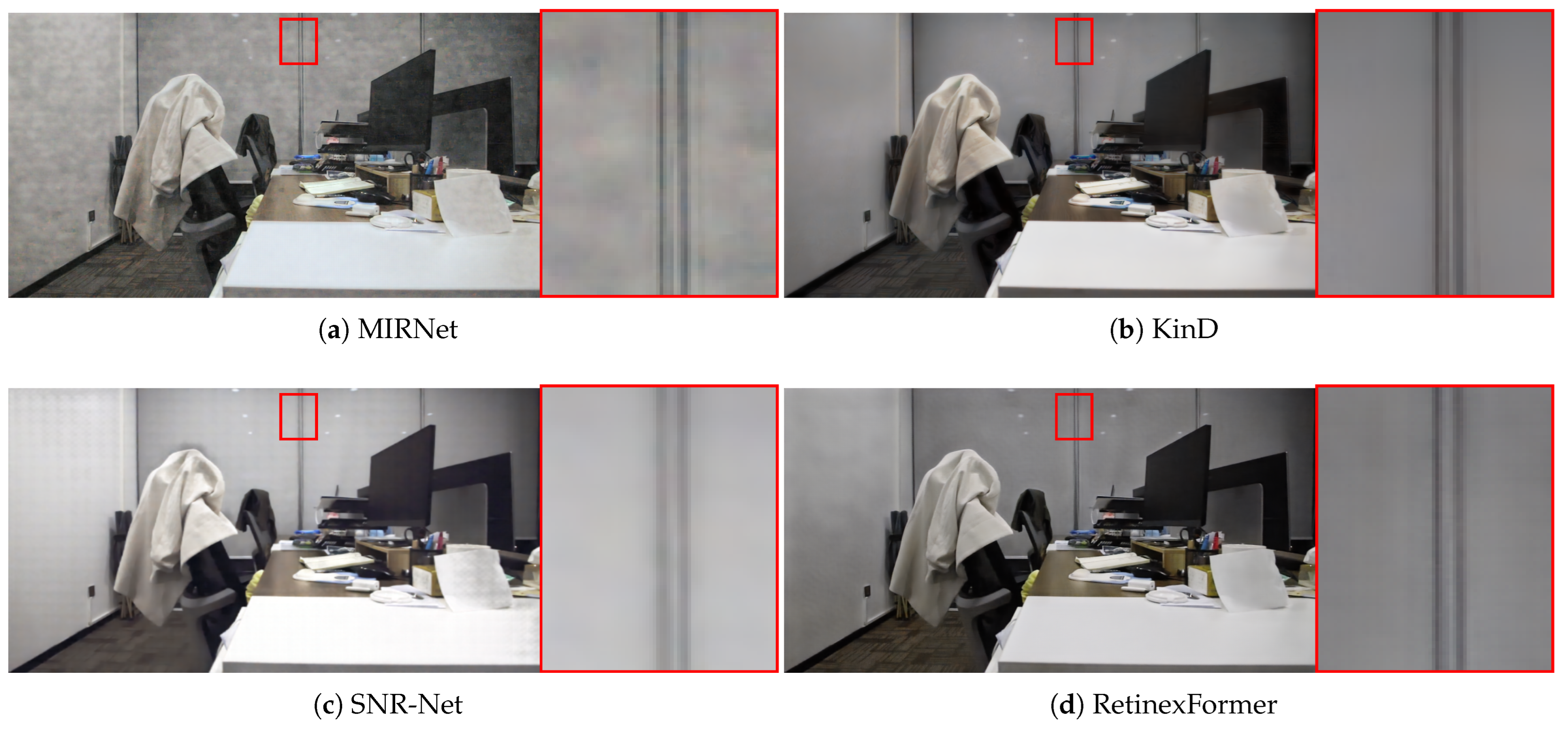
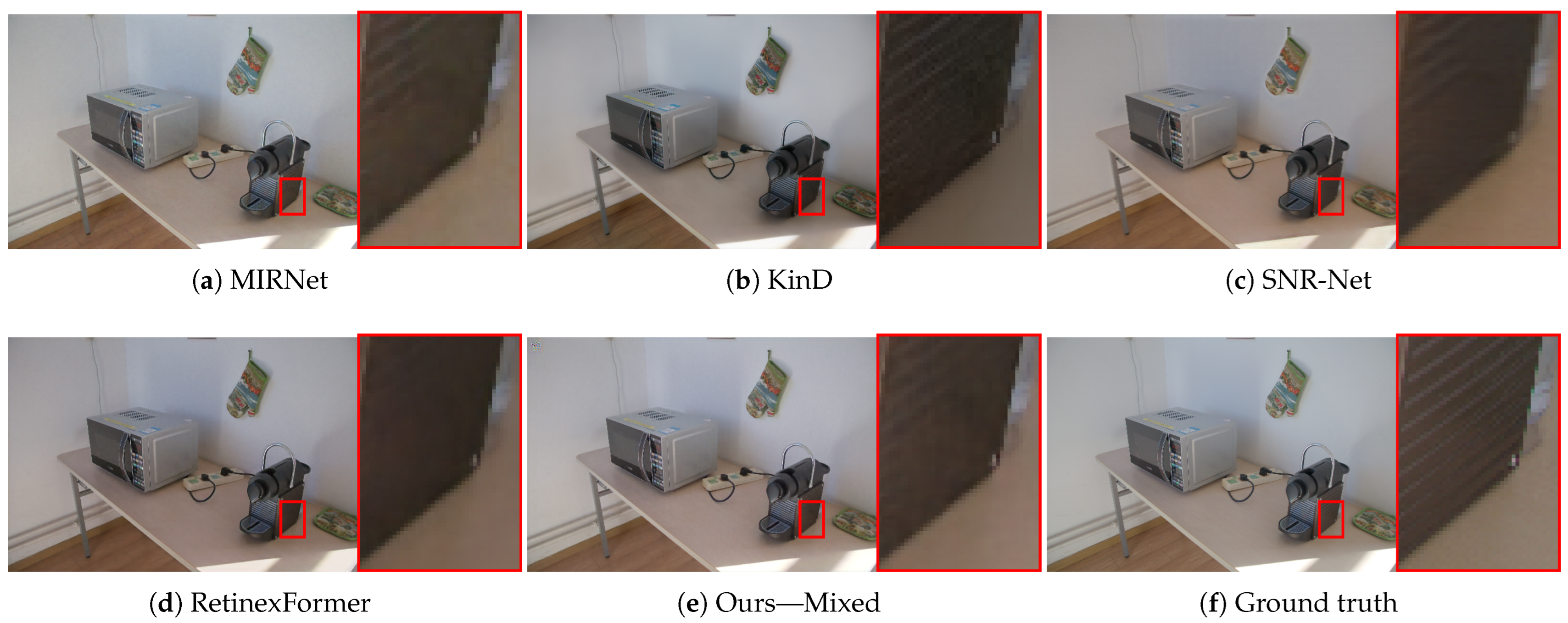
Appendix B. Additional Qualitative Results
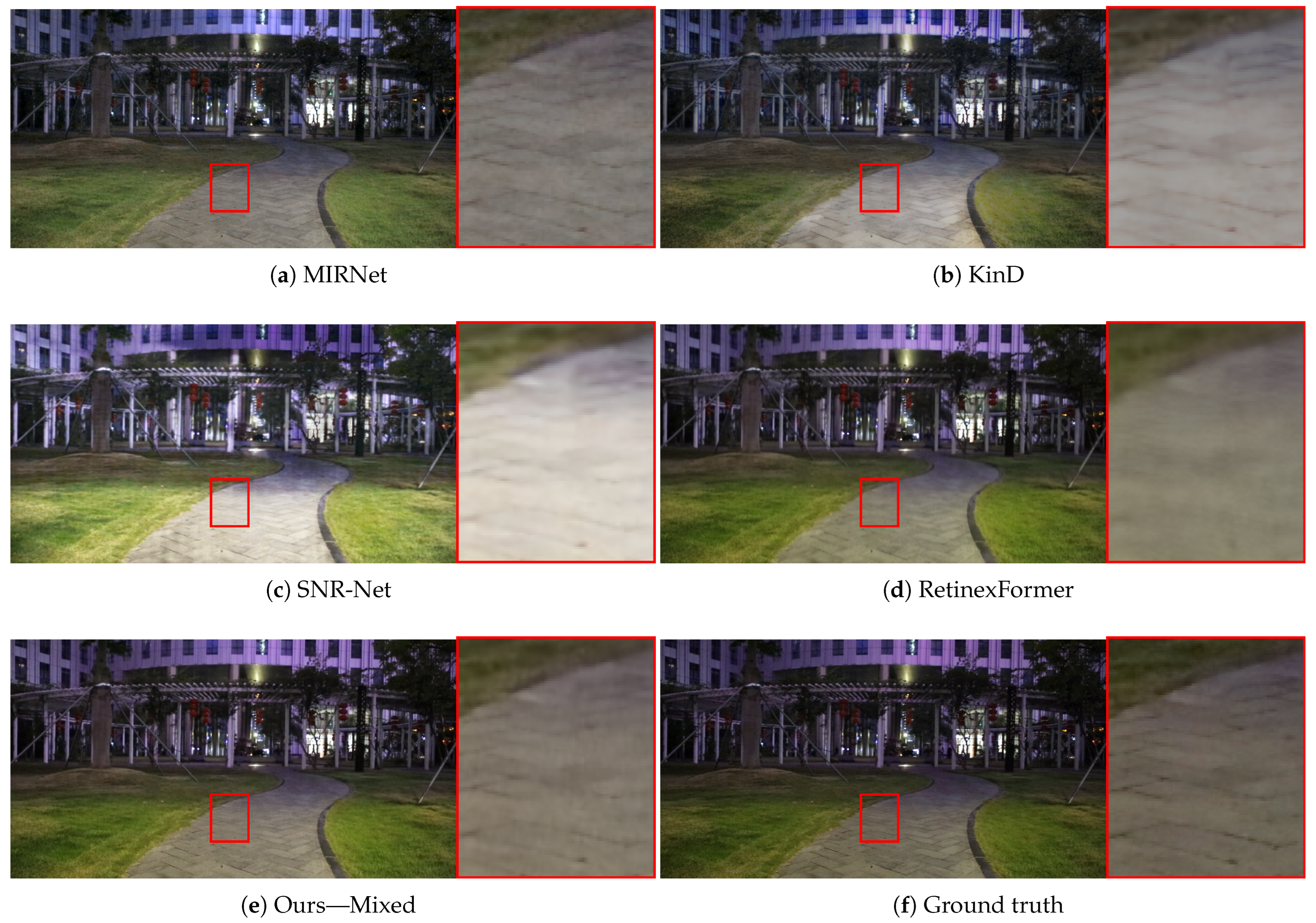
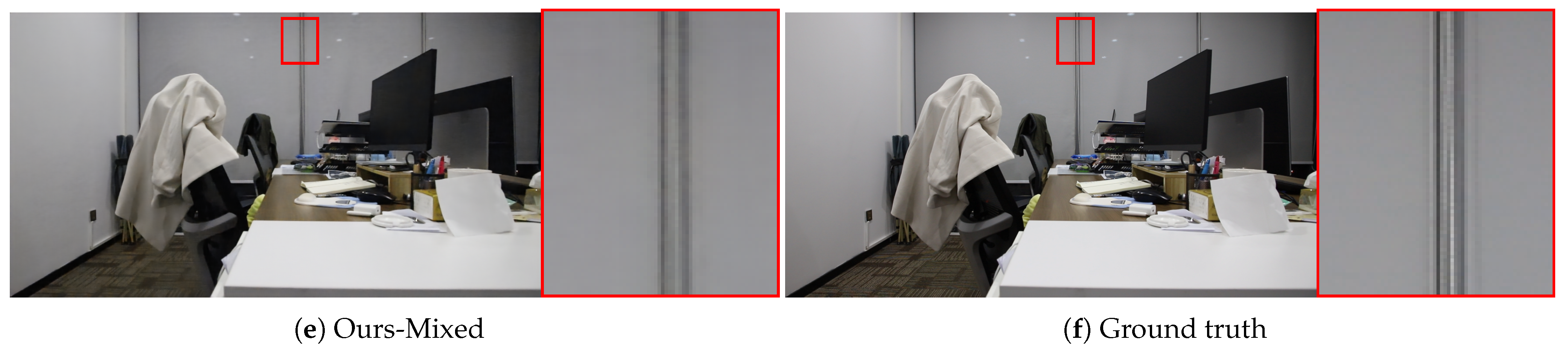



Appendix C. Influence of Loss Weight λ
| 0.25 | 0.5 | 1 | 2 | 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSNR↑ | 25.44 | 25.24 | 25.99 | 25.78 | 25.68 |
| SSIM↑ | 0.9318 | 0.9332 | 0.9556 | 0.9335 | 0.9324 |
| LPIPS↓ | 0.0567 | 0.0560 | 0.0546 | 0.0532 | 0.0544 |
| DISTS↓ | 0.0647 | 0.0644 | 0.0639 | 0.0627 | 0.0645 |
Appendix D. Detailed Computational Efficiency
| Model | Inference Time (s) | FLOPs (G) | Memory (MB) | #Params (M) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIRNet | 0.51 | 785 | 154 | 31.8 |
| KinD | 0.53 | 35.0 | 154 | 8.02 |
| SNR-Net | 0.11 | 26.4 | 149 | 4.01 |
| RetinexFormer | 0.33 | 15.6 | 572 | 1.61 |
| Ours | 0.34 | 15.6 | 572 | 1.61 |
References
- Loh, Y.P.; Chan, C.S. Getting to know low-light images with the exclusively dark dataset. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2019, 178, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Zhu, C.; Li, M.; Tang, W.; Zhou, W. LLVIP: A visible-infrared paired dataset for low-light vision. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 3496–3504. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Li, B.; Tu, Z.; Liu, X.; Guo, Q.; Juefei-Xu, F.; Xu, R.; Yu, H. Light the night: A multi-condition diffusion framework for unpaired low-light enhancement in autonomous driving. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 17–21 June 2024; pp. 15205–15215. [Google Scholar]
- Xian, X.; Zhou, Q.; Qin, J.; Yang, X.; Tian, Y.; Shi, Y.; Tian, D. CROSE: Low-light enhancement by CROss-SEnsor interaction for nighttime driving scenes. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 248, 123470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Huang, L.; Li, M.; Han, C.; Nie, T. Atmospheric Scattering Model and Non-Uniform Illumination Compensation for Low-Light Remote Sensing Image Enhancement. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Ai, H.; Zhou, P.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, G.; Chen, W. Low-Light Image Dehazing and Enhancement via Multi-Feature Domain Fusion. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizer, S.M.; Amburn, E.P.; Austin, J.D.; Cromartie, R.; Geselowitz, A.; Greer, T.; ter Haar Romeny, B.; Zimmerman, J.B.; Zuiderveld, K. Adaptive histogram equalization and its variations. Comput. Vis. Graph. Image Process. 1987, 39, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Cai, J.; Li, L.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, L. Learning image-adaptive 3d lookup tables for high performance photo enhancement in real-time. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 44, 2058–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lore, K.G.; Akintayo, A.; Sarkar, S. LLNet: A deep autoencoder approach to natural low-light image enhancement. Pattern Recognit. 2017, 61, 650–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, F.; Lu, F.; Wu, J.; Lim, C. MBLLEN: Low-light image/video enhancement using cnns. In Proceedings of the BMVC, Newcastle upon Tyne, UK, 3–6 September 2018; Volume 220, p. 4. [Google Scholar]
- Land, E.H.; McCann, J.J. Lightness and retinex theory. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1971, 61, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Li, Y.; Ling, H. LIME: Low-light image enhancement via illumination map estimation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2016, 26, 982–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liu, J.; Yang, W.; Sun, X.; Guo, Z. Structure-Revealing Low-Light Image Enhancement Via Robust Retinex Model. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 27, 2828–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Wang, W.; Yang, W.; Liu, J. Deep retinex decomposition for low-light enhancement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1808.04560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Guo, X. Kindling the darkness: A practical low-light image enhancer. In Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Nice, France, 21–25 October 2019; pp. 1632–1640. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.; Bian, H.; Lin, J.; Wang, H.; Timofte, R.; Zhang, Y. Retinexformer: One-stage retinex-based transformer for low-light image enhancement. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2–6 October 2023; pp. 12504–12513. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, X.; Xu, H.; Zhang, H.; Tang, L.; Ma, J. Diff-retinex: Rethinking low-light image enhancement with a generative diffusion model. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2–6 October 2023; pp. 12302–12311. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, W.; Stenger, B.; Lu, T.; Kim, T.K.; Liu, W. LLDiffusion: Learning degradation representations in diffusion models for low-light image enhancement. Pattern Recognit. 2025, 166, 111628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Yang, Z.; Yang, Y. Pyramid diffusion models for low-light image enhancement. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.10028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Luo, A.; Fan, H.; Han, S.; Liu, S. Low-light image enhancement with wavelet-based diffusion models. ACM Trans. Graph. 2023, 42, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radford, A.; Kim, J.W.; Hallacy, C.; Ramesh, A.; Goh, G.; Agarwal, S.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; Mishkin, P.; Clark, J.; et al. Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Virtual Event, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 8748–8763. [Google Scholar]
- Poynton, C. Digital Video and HD: Algorithms and Interfaces; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Jobson, D.J.; Rahman, Z.u.; Woodell, G.A. A multiscale retinex for bridging the gap between color images and the human observation of scenes. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 1997, 6, 965–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Zhang, Q.; Fu, C.W.; Shen, X.; Zheng, W.S.; Jia, J. Underexposed photo enhancement using deep illumination estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 6849–6857. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Gong, X.; Liu, D.; Cheng, Y.; Fang, C.; Shen, X.; Yang, J.; Zhou, P.; Wang, Z. Enlightengan: Deep light enhancement without paired supervision. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 2340–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.; Li, C.; Guo, J.; Loy, C.C.; Hou, J.; Kwong, S.; Cong, R. Zero-reference deep curve estimation for low-light image enhancement. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Virtual Event, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 1780–1789. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 5998–6008. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Virtual Event, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 10012–10022. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Cun, X.; Bao, J.; Zhou, W.; Liu, J.; Li, H. Uformer: A general u-shaped transformer for image restoration. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–24 June 2022; pp. 17683–17693. [Google Scholar]
- Zamir, S.W.; Arora, A.; Khan, S.; Hayat, M.; Khan, F.S.; Yang, M.H. Restormer: Efficient transformer for high-resolution image restoration. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–24 June 2022; pp. 5728–5739. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, K.; Shen, T.; Luo, W.; Stenger, B.; Lu, T. Ultra-high-definition low-light image enhancement: A benchmark and transformer-based method. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2023, 37, 2654–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Yang, X. Retinexformer+: Retinex-Based Dual-Channel Transformer for Low-Light Image Enhancement. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2025, 82, 1969–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Rahman Siddiquee, M.M.; Tajbakhsh, N.; Liang, J. Unet++: A nested u-net architecture for medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis, Granada, Spain, 20 September 2018; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, J.; Yin, Y.; He, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X. Retinexmamba: Retinex-based mamba for low-light image enhancement. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Neural Information Processing, Auckland, New Zealand, 2–6 December 2024; pp. 427–442. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, A.; Goel, K.; Ré, C. Efficiently modeling long sequences with structured state spaces. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.00396. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, A.; Dao, T. Mamba: Linear-time sequence modeling with selective state spaces. In Proceedings of the First Conference on Language Modeling, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 7–9 October 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Liang, X.; Han, J.; Geng, W. Spike-RetinexFormer: Rethinking Low-light Image Enhancement with Spiking Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the Thirty-Ninth Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, San Diego, CA, USA, 2–7 December 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Tavanaei, A.; Ghodrati, M.; Kheradpisheh, S.R.; Masquelier, T.; Maida, A. Deep learning in spiking neural networks. Neural Netw. 2019, 111, 47–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, S.; Hussain, B.; Fareed, S.; Arif, A.; Ali, B. Real-world adaptation of retinexformer for low-light image enhancement using unpaired data. Int. J. Ethical AI Appl. 2025, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Chen, Q.; Hu, H.; Peng, L.; Tao, W. An unsupervised fine-tuning strategy for low-light image enhancement. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2025, 110, 104480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feijoo, D.; Benito, J.C.; Garcia, A.; Conde, M.V. Darkir: Robust low-light image restoration. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 11–15 June 2025; pp. 10879–10889. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, R.; Niu, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, H.; Liu, W.; Chen, Y. URWKV: Unified RWKV Model with Multi-state Perspective for Low-light Image Restoration. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 11–15 June 2025; pp. 21267–21276. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Chan, K.C.; Loy, C.C. Exploring clip for assessing the look and feel of images. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2023, 37, 2555–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, K.; Lee, M.; Shim, H. Psynet: Self-supervised approach to object localization using point symmetric transformation. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2020, 34, 10451–10459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Li, S.; Jia, X.; Lu, H.; Liu, J. Neighbor2neighbor: Self-supervised denoising from single noisy images. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Virtual Event, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 14781–14790. [Google Scholar]
- Mansour, Y.; Heckel, R. Zero-shot noise2noise: Efficient image denoising without any data. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2023; pp. 14018–14027. [Google Scholar]
- Yun, S.; Han, D.; Oh, S.J.; Chun, S.; Choe, J.; Yoo, Y. Cutmix: Regularization strategy to train strong classifiers with localizable features. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 6023–6032. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.; Wang, W.; Huang, H.; Wang, S.; Liu, J. Sparse gradient regularized deep retinex network for robust low-light image enhancement. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 2072–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, Q.; Do, M.N.; Koltun, V. Seeing motion in the dark. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 3185–3194. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Chen, Q.; Xu, J.; Koltun, V. Learning to see in the dark. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 3291–3300. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Xu, X.; Fu, C.W.; Lu, J.; Yu, B.; Jia, J. Seeing dynamic scene in the dark: A high-quality video dataset with mechatronic alignment. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Online, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 9700–9709. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pambrun, J.F.; Noumeir, R. Limitations of the SSIM quality metric in the context of diagnostic imaging. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Quebec City, QC, Canada, 27–30 September 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 2960–2963. [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson, J.; Akenine-Möller, T. Understanding ssim. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.13846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A.; Shechtman, E.; Wang, O. The unreasonable effectiveness of deep features as a perceptual metric. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 586–595. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, K.; Ma, K.; Wang, S.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image quality assessment: Unifying structure and texture similarity. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 44, 2567–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Wang, S.; Fang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J. Band representation-based semi-supervised low-light image enhancement: Bridging the gap between signal fidelity and perceptual quality. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 3461–3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosugi, S.; Yamasaki, T. Unpaired image enhancement featuring reinforcement-learning-controlled image editing software. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2020, 34, 11296–11303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, S.; Marza, P.; McDonagh, S.; Parisot, S.; Slabaugh, G. Deeplpf: Deep local parametric filters for image enhancement. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Online, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 12826–12835. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Wang, Y.; Guo, T.; Xu, C.; Deng, Y.; Liu, Z.; Ma, S.; Xu, C.; Xu, C.; Gao, W. Pre-trained image processing transformer. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Online, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 12299–12310. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.; Ma, L.; Zhang, J.; Fan, X.; Luo, Z. Retinex-inspired unrolling with cooperative prior architecture search for low-light image enhancement. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Virtual Event, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 11197–11206. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, K.; Yang, X.; Yin, B.; Lau, R.W. Learning to restore low-light images via decomposition-and-enhancement. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Online, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 2281–2290. [Google Scholar]
- Zamir, S.W.; Arora, A.; Khan, S.; Hayat, M.; Khan, F.S.; Yang, M.H.; Shao, L. Learning enriched features for real image restoration and enhancement. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Online, 23–28 August 2020; pp. 492–511. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Wang, R.; Fu, C.W.; Jia, J. Snr-aware low-light image enhancement. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–24 June 2022; pp. 17714–17724. [Google Scholar]
- Blau, Y.; Michaeli, T. The perception-distortion tradeoff. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 6228–6237. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, R.; Kligvasser, I.; Rivlin, E.; Freedman, D. Looks too good to be true: An information-theoretic analysis of hallucinations in generative restoration models. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2024, 37, 22596–22623. [Google Scholar]






| Method | Complexity | LOL-v1 | LOL-v2-real | LOL-v2-syn | SID | SMID | SDSD-in | SDSD-out | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FLOPS | Params | PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | |
| SID [50] | 13.73 | 7.76 | 14.35 | 0.436 | 13.24 | 0.442 | 15.04 | 0.610 | 16.97 | 0.591 | 24.78 | 0.718 | 23.29 | 0.703 | 24.90 | 0.693 |
| 3DLUT [8] | 0.075 | 0.59 | 14.35 | 0.445 | 17.59 | 0.721 | 18.04 | 0.800 | 20.11 | 0.592 | 23.86 | 0.678 | 21.66 | 0.655 | 21.89 | 0.649 |
| DeepUPE [24] | 21.1 | 1.02 | 14.38 | 0.446 | 13.27 | 0.452 | 15.08 | 0.623 | 17.01 | 0.604 | 23.91 | 0.690 | 21.70 | 0.662 | 21.94 | 0.698 |
| RF [59] | 46.23 | 21.54 | 15.23 | 0.452 | 14.05 | 0.458 | 15.97 | 0.632 | 16.44 | 0.596 | 23.11 | 0.681 | 20.97 | 0.655 | 21.21 | 0.689 |
| DeepLPF [60] | 5.86 | 1.77 | 15.28 | 0.473 | 14.10 | 0.480 | 16.02 | 0.587 | 18.07 | 0.600 | 24.36 | 0.688 | 22.21 | 0.664 | 22.76 | 0.658 |
| IPT [61] | 6887 | 115.31 | 16.27 | 0.504 | 19.80 | 0.813 | 18.30 | 0.811 | 20.53 | 0.561 | 27.03 | 0.783 | 26.11 | 0.831 | 27.55 | 0.850 |
| UFormer [30] | 12 | 5.29 | 16.36 | 0.771 | 18.82 | 0.771 | 19.66 | 0.871 | 18.54 | 0.577 | 27.20 | 0.792 | 23.17 | 0.859 | 23.85 | 0.748 |
| RetinexNet [14] | 587.47 | 0.84 | 16.77 | 0.560 | 15.47 | 0.567 | 17.13 | 0.798 | 16.48 | 0.578 | 22.83 | 0.684 | 20.84 | 0.617 | 20.96 | 0.629 |
| SparseRN [49] | 53.26 | 2.33 | 17.20 | 0.640 | 20.06 | 0.816 | 22.05 | 0.905 | 18.68 | 0.606 | 25.48 | 0.766 | 23.25 | 0.863 | 25.28 | 0.804 |
| EnGAN [25] | 61.01 | 114.35 | 17.48 | 0.650 | 18.23 | 0.617 | 16.57 | 0.734 | 17.23 | 0.543 | 22.62 | 0.674 | 20.02 | 0.604 | 20.10 | 0.616 |
| RUAS [62] | 0.83 | 0.003 | 18.23 | 0.720 | 18.37 | 0.723 | 16.55 | 0.652 | 18.44 | 0.581 | 25.88 | 0.744 | 23.17 | 0.696 | 23.84 | 0.743 |
| FIDE [63] | 28.51 | 8.62 | 18.27 | 0.665 | 16.85 | 0.678 | 15.20 | 0.612 | 18.34 | 0.578 | 24.42 | 0.692 | 22.41 | 0.659 | 22.20 | 0.629 |
| DRBN [58] | 48.61 | 5.27 | 20.13 | 0.830 | 20.29 | 0.831 | 23.22 | 0.927 | 19.02 | 0.577 | 26.60 | 0.781 | 24.08 | 0.868 | 25.77 | 0.841 |
| KinD [15] | 34.99 | 8.02 | 20.86 | 0.790 | 14.74 | 0.641 | 13.29 | 0.578 | 18.02 | 0.583 | 22.18 | 0.634 | 21.95 | 0.672 | 21.97 | 0.654 |
| Restormer [31] | 144.25 | 26.13 | 22.43 | 0.823 | 19.94 | 0.827 | 21.41 | 0.830 | 22.27 | 0.649 | 26.97 | 0.758 | 25.67 | 0.827 | 24.79 | 0.802 |
| MIRNet [64] | 785 | 31.76 | 24.14 | 0.830 | 20.02 | 0.820 | 21.94 | 0.876 | 20.84 | 0.605 | 25.66 | 0.762 | 24.38 | 0.864 | 27.13 | 0.837 |
| SNR-Net [65] | 26.35 | 4.01 | 24.61 | 0.842 | 21.48 | 0.849 | 24.14 | 0.928 | 22.87 | 0.625 | 28.49 | 0.805 | 29.44 | 0.894 | 28.66 | 0.866 |
| RetinexFormer [16] | 15.57 | 1.61 | 22.78 | 0.883 | 20.06 | 0.862 | 25.61 | 0.955 | 24.38 | 0.677 | 29.12 | 0.813 | 27.38 | 0.886 | 28.54 | 0.864 |
| Ours—Textual | 15.57 | 1.61 | 22.71 | 0.876 | 20.98 | 0.851 | 24.70 | 0.919 | 24.12 | 0.668 | 28.60 | 0.802 | 27.84 | 0.876 | 28.45 | 0.856 |
| Ours—Visual | 23.47 | 0.883 | 20.23 | 0.864 | 25.64 | 0.954 | 24.22 | 0.670 | 31.34 | 0.832 | 28.08 | 0.886 | 28.21 | 0.862 | ||
| Ours—Mixed | 22.66 | 0.882 | 20.23 | 0.844 | 25.99 | 0.956 | 24.49 | 0.675 | 31.85 | 0.834 | 26.65 | 0.881 | 28.87 | 0.867 | ||
| Method | LOL-v1 | LOL-v2-real | LOL-v2-syn | SID | SMID | SDSD-in | SDSD-out | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LPIPS | DISTS | LPIPS | DISTS | LPIPS | DISTS | LPIPS | DISTS | LPIPS | DISTS | LPIPS | DISTS | LPIPS | DISTS | |
| RetinexFormer | 0.145 | 0.141 | 0.168 | 0.148 | 0.059 | 0.067 | 0.357 | 0.209 | 0.164 | 0.133 | 0.137 | 0.123 | 0.167 | 0.117 |
| Ours—Textual | 0.160 | 0.139 | 0.195 | 0.156 | 0.124 | 0.134 | 0.358 | 0.210 | 0.179 | 0.136 | 0.152 | 0.120 | 0.165 | 0.106 |
| Ours—Visual | 0.149 | 0.142 | 0.163 | 0.142 | 0.057 | 0.067 | 0.352 | 0.211 | 0.157 | 0.129 | 0.133 | 0.121 | 0.176 | 0.120 |
| Ours—Mixed | 0.140 | 0.137 | 0.164 | 0.142 | 0.055 | 0.064 | 0.355 | 0.210 | 0.154 | 0.131 | 0.129 | 0.119 | 0.164 | 0.118 |
| Model | PSNR (dB)↑ | SSIM↑ | LPIPS↓ | DISTS↓ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 25.61 | 0.9545 | 0.0594 | 0.0673 |
| w/o PRS | 25.30 | 0.9313 | 0.0603 | 0.0671 |
| w/o CL | 25.10 | 0.9308 | 0.0584 | 0.0656 |
| Ours—Mixed | 25.99 | 0.9556 | 0.0546 | 0.0639 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, S. Noise-Resilient Low-Light Image Enhancement with CLIP Guidance and Pixel-Reordering Subsampling. Electronics 2025, 14, 4839. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14244839
Song S. Noise-Resilient Low-Light Image Enhancement with CLIP Guidance and Pixel-Reordering Subsampling. Electronics. 2025; 14(24):4839. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14244839
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Seongjong. 2025. "Noise-Resilient Low-Light Image Enhancement with CLIP Guidance and Pixel-Reordering Subsampling" Electronics 14, no. 24: 4839. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14244839
APA StyleSong, S. (2025). Noise-Resilient Low-Light Image Enhancement with CLIP Guidance and Pixel-Reordering Subsampling. Electronics, 14(24), 4839. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14244839





