Twin-Space Decoupling and Interaction for Efficient Vision-Language Transfer
Abstract
1. Introduction
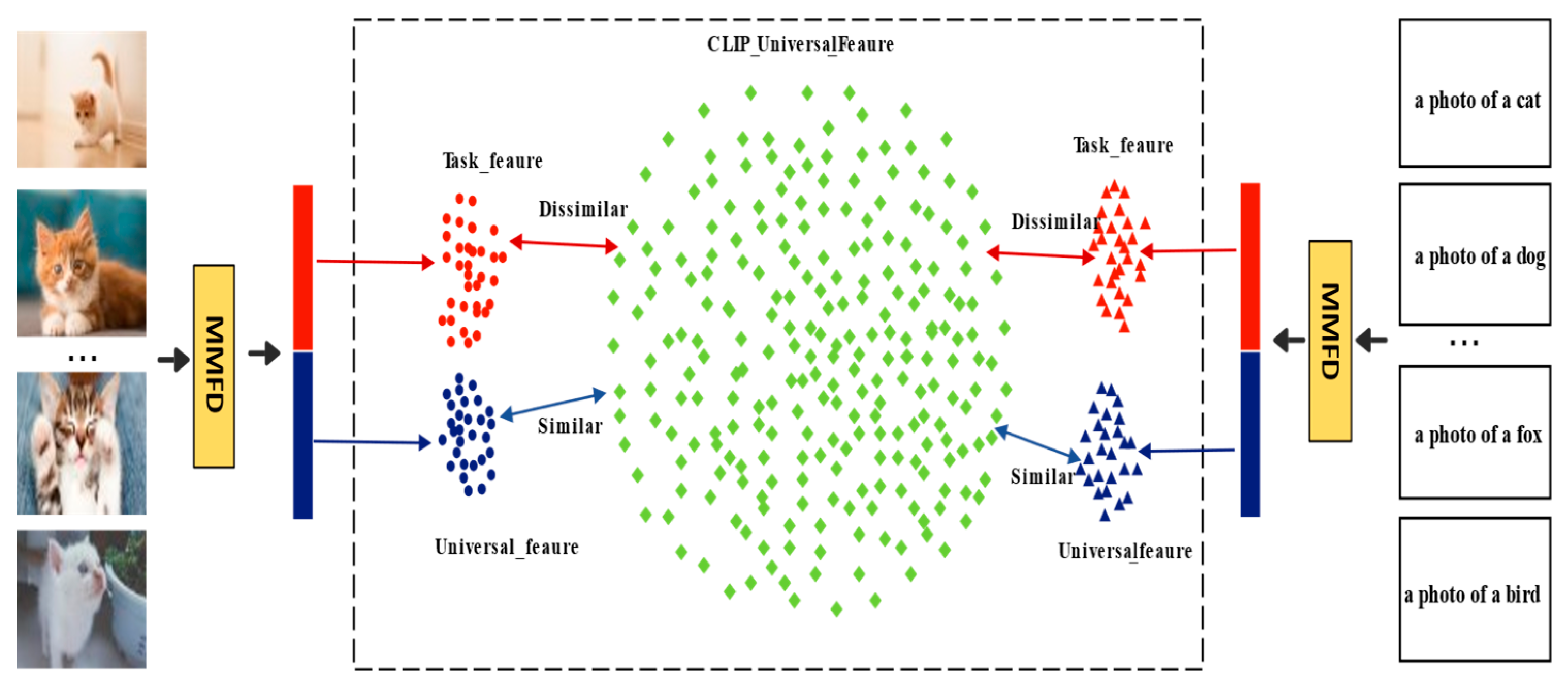
- A decentralized covariance dual-subspace decomposition method is developed to map visual and textual features into a shared subspace and a task-specific subspace. This design enables knowledge separation and collaborative modeling, effectively mitigating catastrophic forgetting of pre-trained knowledge and excessive feature coupling during task adaptation.
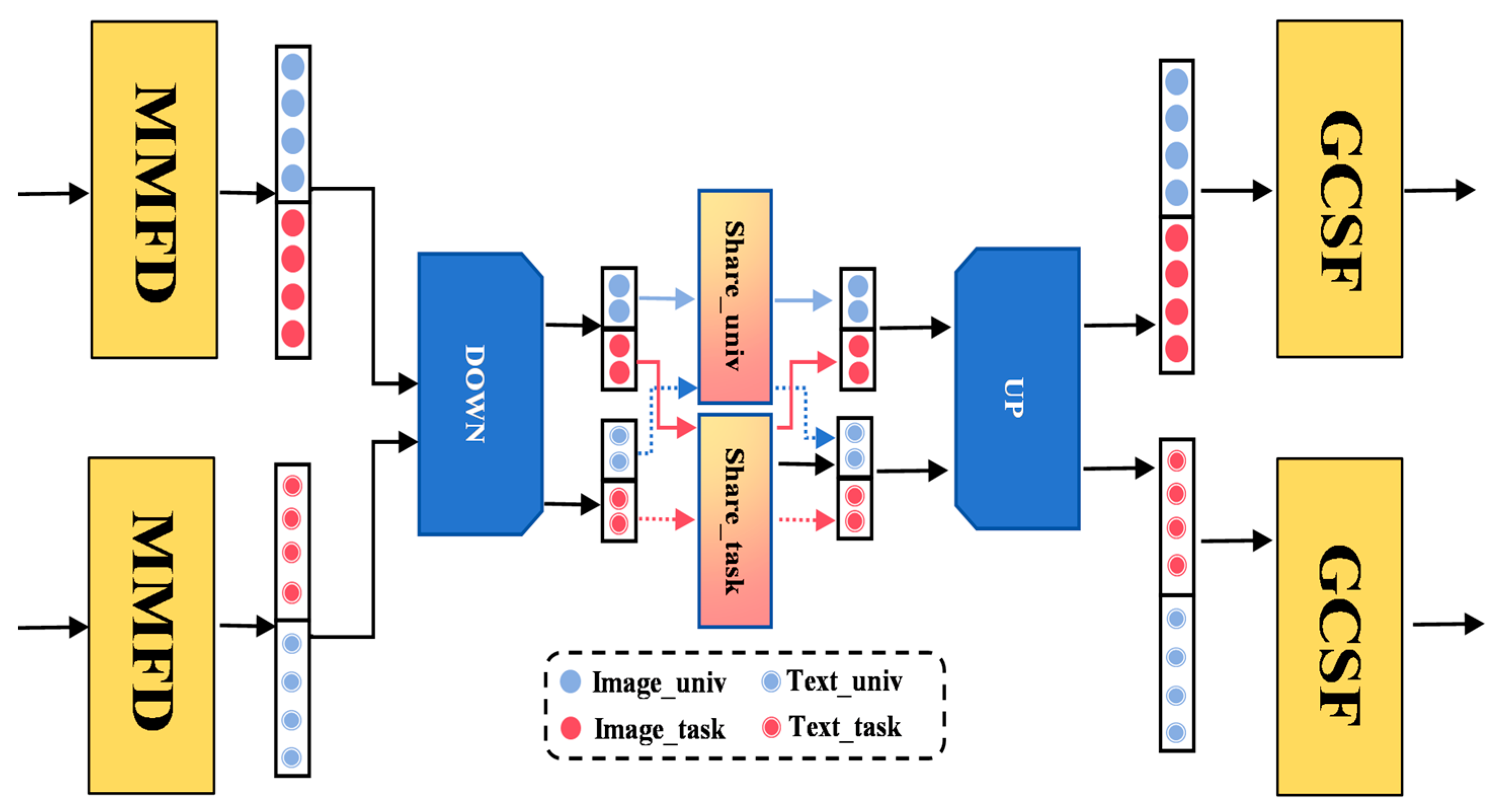
- Based on the dual-subspace architecture, a cross-modal semantic interaction adapter module and a gated cross-level semantic fusion module are introduced. The former performs independent interactions between shared and task-specific subspace features to avoid interference between general and task knowledge, while the latter employs a gating mechanism to dynamically adjust feature weights across levels, ensuring consistent semantic alignment.
- The proposed framework is evaluated on multiple benchmark datasets. Experimental results indicate that the method consistently achieves state-of-the-art performance compared with existing approaches, confirming its effectiveness and robustness.
2. Related Work
2.1. Vision-Language Models
2.2. Efficient Transfer Learning
3. Model
3.1. Problem Definition
3.2. Overall Framework
3.3. Implement
3.3.1. Covariance-Guided Dual-Subspace Feature Decoupling Mechanism
3.3.2. Cross-Modal Semantic Interaction Adapter Module
3.3.3. Gated Cross-Level Semantic Fusion Module
| Algorithm 1 # Pseudocode for Dual-Subspace Cross-Modal Decoupling & Fusion |
| for each image I_i and text T_k: Xv, Xt = VisualEncoder(I_i), TextEncoder(T_k) for layer = 1 to L: # 1. Multi-Modal Feature Disentanglement Xv_univ, Xv_task = MMFD(Xv) Xt_univ, Xt_task = MMFD(Xt) # 2. Cross-Modal Semantic Interaction Adapter Xv_univ_mut, Xt_univ_mut = CMSIA(Xv_univ, Xt_univ) Xv_task_mut, Xt_task_mut = CMSIA(Xv_task, Xt_task) # 3. Gated Cross-Level Semantic Fusion beta_v = GatingNetwork(concat(Xv_task_mut, Xv_univ_mut)) beta_t = GatingNetwork(concat(Xt_task_mut, Xt_univ_mut)) Xv_fused = beta_v Xv_task_mut + (1-beta_v) Xv_univ_mut Xt_fused = beta_t Xt_task_mut + (1-beta_t) Xt_univ_mut # Residual connection Xv, Xt = Xv + alpha_res Xv_fused, Xt + alpha_res Xt_fused |
4. Experiments
4.1. Experimental Setup
4.1.1. Datasets
4.1.2. Baselines
4.1.3. Implementation Details
4.2. Base-to-Novel Generalization
4.3. Few-Shot Learning Evaluation
4.4. Cross-Dataset Evaluation
4.5. Domain Generalization
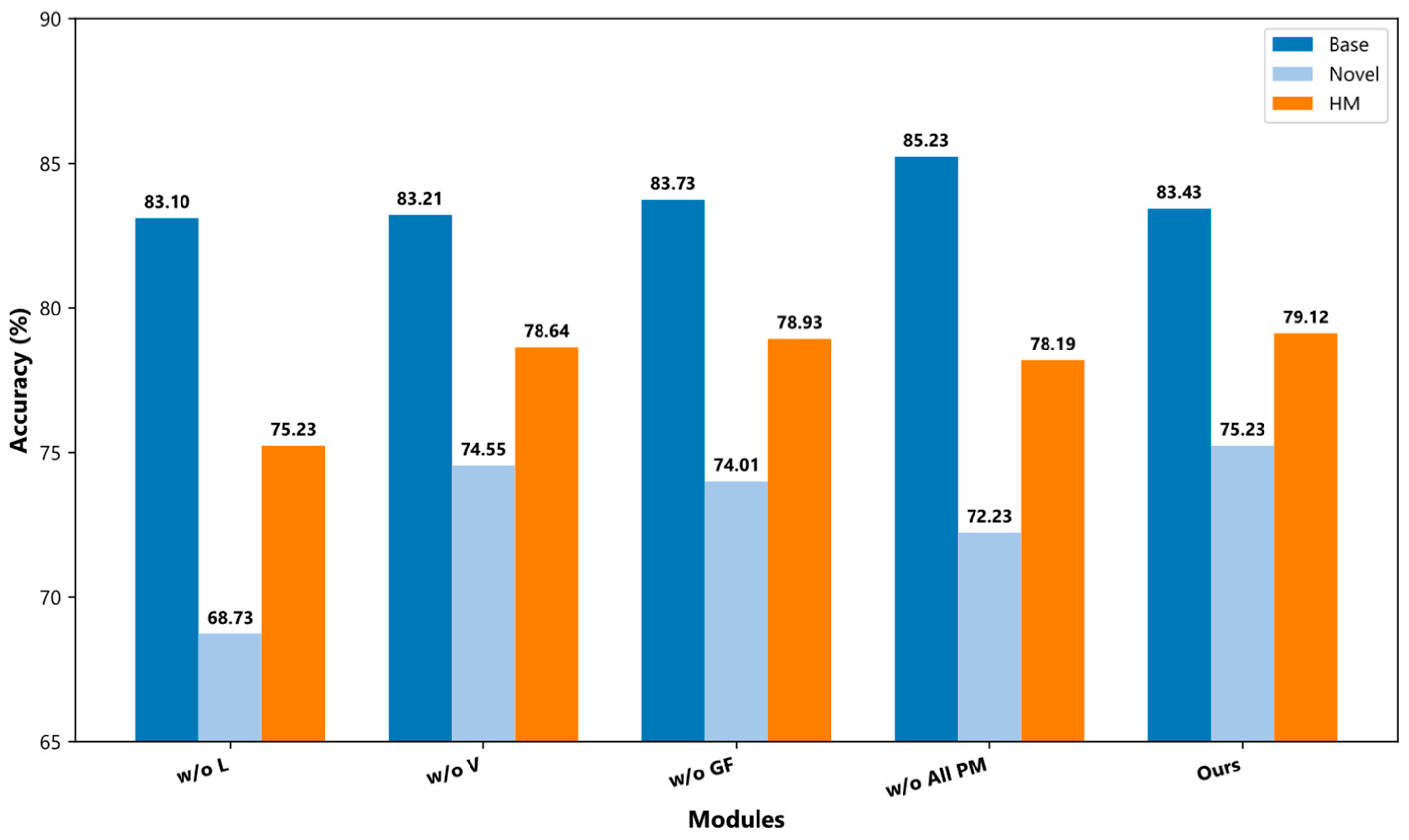
4.6. Ablation Analysis
4.7. Parameter Sensitivity Experiments
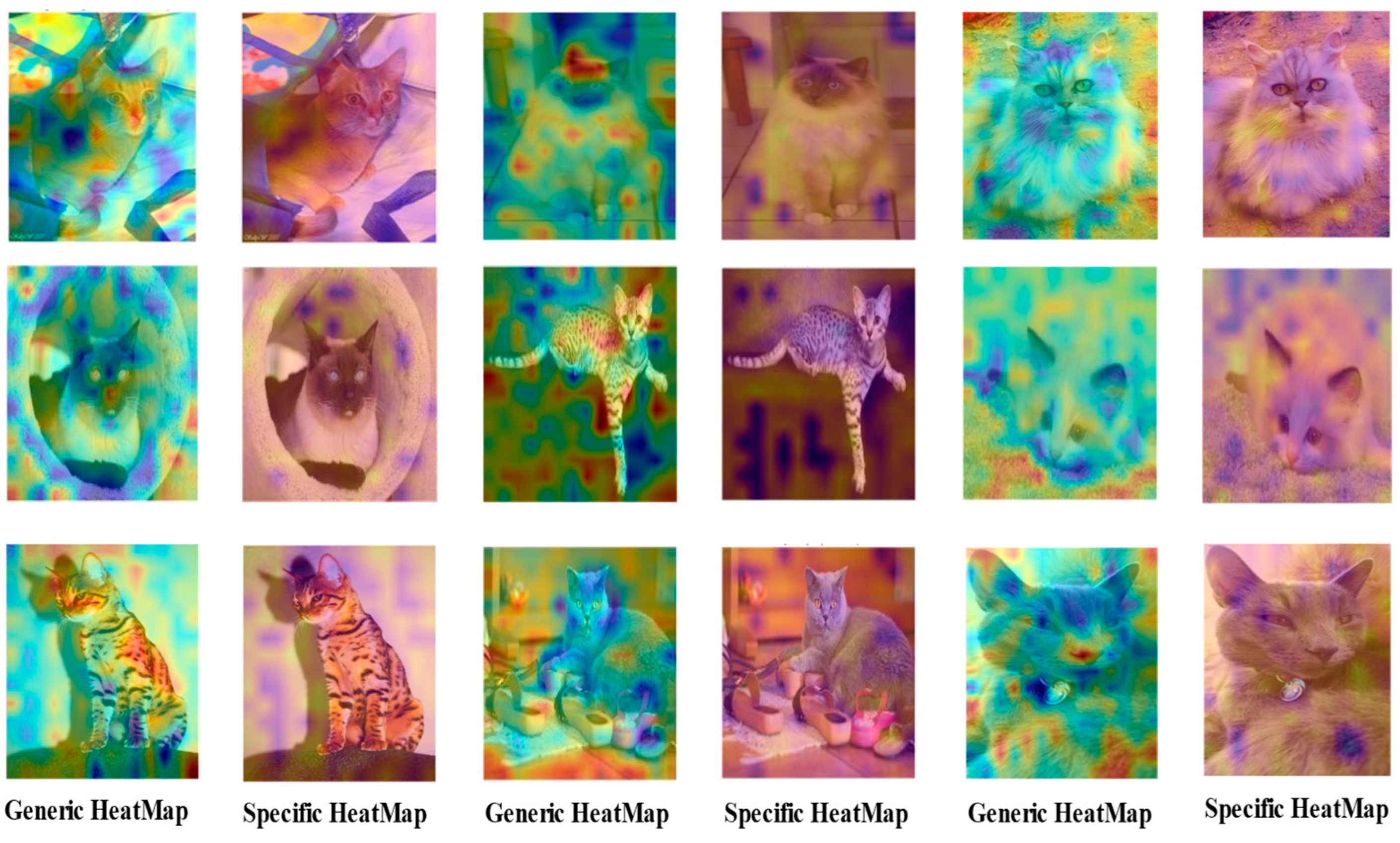
4.8. Feature Visualization
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alayrac, J.B.; Donahue, J.; Luc, P.; Miech, A.; Barr, I.; Hasson, Y.; Lenc, K.; Mensch, A.; Millican, K.; Reynolds, M.; et al. Flamingo: A visual language model for few-shot learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 23716–23736. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Hua, L.; Liu, H.; Song, W. Automatic tracking method for 3D human motion pose using contrastive learning. Int. J. Image Graph. 2024, 24, 2550037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Shan, Y.; Li, F.; Chen, X.; Zhang, S. CLSpell: Contrastive learning with phonological and visual knowledge for chinese spelling check. Neurocomputing 2023, 554, 126468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajare, N.; Rajawat, A.S. Black gram disease classification via deep ensemble model with optimal training. Int. J. Image Graph. 2025, 25, 2550033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, P.; Anoop, B.K. Improved invasive weed social ski-driver optimization-based deep convolution neural network for diabetic retinopathy classification. Int. J. Image Graph. 2025, 25, 2550012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Mori, K.; Tamura, S. Low-rank and sparse decomposition based shape model and probabilistic atlas for automatic pathological organ segmentation. Med. Image Anal. 2017, 38, 30–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lv, P.; Wang, H.; Shi, C. SAR-U-Net: Squeeze-and-excitation block and atrous spatial pyramid pooling based residual U-Net for automatic liver segmentation in Computed Tomography. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2021, 208, 106268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, P.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y. Dimensionality reduction in evolutionary algorithms-based feature selection for motor imagery brain-computer interface. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2020, 52, 100597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L. Global exponential convergence of neutral type shunting inhibitory cellular neural networks with D operator. Neural Process. Lett. 2017, 45, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Zhou, K. A dynamic local path planning method for outdoor robot based on characteristics extraction of laser rangefinder and extended support vector machine. Int. J. Pattern Recognit. Artif. Intell. 2016, 30, 1659004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Jiang, W. Human Behavior Recognition Method Based on Edge Intelligence. Discret. Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2022, 2022, 3955218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Yang, J.; Loy, C.C.; Liu, Z. Learning to prompt for vision-language models. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2022, 130, 2337–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khattak, M.U.; Rasheed, H.; Maaz, M.; Khan, S.; Khan, F.S. Maple: Multi-modal prompt learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 19113–19122. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, P.; Geng, S.; Zhang, R.; Ma, T.; Fang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Qiao, Y. Clip-adapter: Better vision-language models with feature adapters. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2023, 132, 581–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, W.; Fang, R.; Gao, P.; Li, K.; Dai, J.; Qiao, Y.; Li, H. Tipadapter: Training-free adaption of clip for few-shot classification. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 493–510. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Kim, J.W.; Hallacy, C.; Ramesh, A.; Goh, G.; Agarwal, S.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; Mishkin, P.; Clark, J.; et al. Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PmLR, Virtual, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 8748–8763. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, C.; Yang, Y.; Xia, Y.; Chen, Y.T.; Parekh, Z.; Pham, H.; Le, Q.; Sung, Y.H.; Li, Z.; Duerig, T. Scaling up visual and vision-language representation learning with noisy text supervision. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Virtual, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 4904–4916. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, L.; Huang, R.; Hou, L.; Lu, G.; Niu, M.; Xu, H.; Liang, X.; Li, Z.; Jiang, X.; Xu, C. Filip: Fine-grained interactive language-image pre-training. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Vienna, Austria, 4 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Liang, W.; Wang, K.I.-K.; Shimizu, S. Multi-modality behavioral influence analysis for personalized recommendations in health social media environment. IEEE Trans. Comput. Soc. Syst. 2019, 6, 888–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Liang, W.; Wang, K.I.-K.; Wang, H.; Yang, L.T.; Jin, Q. Deep-learning-enhanced human activity recognition for internet of healthcare things. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 7, 6429–6438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Sun, W. The role of film and television big data in real-time image detection and processing in the Internet of Things era. J. Real-Time Image Process. 2021, 18, 1115–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Mo, C. High-speed real-time augmented reality tracking algorithm model of camera based on mixed feature points. J. Real-Time Image Process. 2021, 18, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Xu, X.; Liang, W.; Zeng, Z.; Yan, Z. Deep-learning-enhanced multitarget detection for end–edge–cloud surveillance in smart IoT. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 12588–12596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Liang, W.; Li, W.; Yan, K.; Shimizu, S.; Wang, K.I.-K. Hierarchical adversarial attacks against graph-neural-network-based IoT network intrusion detection system. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 9, 9310–9319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Yang, J. ELGONBP: A grouped neighboring intensity difference encoding for texture classification. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023, 82, 10311–10336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Wu, Y.; Liu, X.; Ma, M.; Liu, A.; Zhao, M. Learning-based synchronous approach from forwarding nodes to reduce the delay for Industrial Internet of Things. EURASIP J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2018, 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Yang, J.; Loy, C.C.; Liu, Z. Conditional prompt learning for vision-language models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 16816–16825. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, H.; Zhang, R.; Xu, C. Visual language prompt tuning with knowledge-guided context optimization. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 6757–6767. [Google Scholar]
- Goswami, K.; Karanam, S.; Udhayanan, P.; Joseph, K.J.; Srinivasan, B.V. Copl: Contextual prompt learning for vision-language understanding. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 20–27 February 2024; Volume 38, pp. 18090–18098. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tian, X. Prompt distribution learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; Volume 3, pp. 5206–5215. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Li, X.; Sun, J.; Xu, Z. Training Networks in Null Space of Feature Covariance with Self-Supervision for Incremental Learning. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2024, 47, 2563–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.J.; Li, K.; Li, F. Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA; pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar]
- Fei-Fei, L.; Fergus, R.; Perona, P. Learning generative visual models from few training examples: An incremental bayesian approach tested on 101 object categories. In Proceedings of the 2004 Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshop, Washington, DC, USA, 27 June–1 July 2004; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA; p. 178. [Google Scholar]
- Parkhi, O.M.; Vedaldi, A.; Zisserman, A.; Jawahar, C.V. Cats and dogs. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2012; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA; pp. 3498–3505. [Google Scholar]
- Krause, J.; Stark, M.; Deng, J.; Fei-Fei, L. 3d object representations for fine-grained categorization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Sydney, Australia, 2–8 December 2013; pp. 554–561. [Google Scholar]
- Nilsback, M.-E.; Zisserman, A. Automated flower classification over a large number of classes. In Proceedings of the 2008 Sixth Indian Conference on Computer Vision, Graphics & Image Processing, Bhubaneswar, India, 16–19 December 2008; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA; pp. 722–729. [Google Scholar]
- Bossard, L.; Guillaumin, M.; Van Gool, L. Food-101–mining discriminative components with random forests. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2014: 13th European Conference, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; Proceedings, Part VI 13. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 446–461. [Google Scholar]
- Maji, S.; Rahtu, E.; Kannala, J.; Blaschko, M.; Vedaldi, A. Fine-grained visual classification of aircraft. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1306.5151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Hays, J.; Ehinger, K.A.; Oliva, A.; Torralba, A. Sun database: Large-scale scene recognition from abbey to zoo. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–18 June 2010; pp. 3485–3492. [Google Scholar]
- Cimpoi, M.; Maji, S.; Kokkinos, I.; Mohamed, S.; Vedaldi, A. Describing textures in the wild. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 3606–3613. [Google Scholar]
- Helber, P.; Bischke, B.; Dengel, A.; Borth, D. Eurosat: A novel dataset and deep learning benchmark for land use and land cover classification. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 2217–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soomro, K.; Zamir, A.R.; Shah, M. Ucf101: A dataset of 101 human actions classes from videos in the wild. arXiv 2012, arXiv:1212.0402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Niu, Y.; Han, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, H. Prompt-aligned gradient for prompt tuning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 15659–15669. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, G.; Kim, S.; Lee, S. Aapl: Adding attributes to prompt learning for vision-language models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 17–21 June 2024; pp. 1572–1582. [Google Scholar]
- Recht, B.; Roelofs, R.; Schmidt, L.; Shankar, V. Do imagenet classifiers generalize to imagenet? In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019; pp. 5389–5400. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Ge, S.; Lipton, Z.; Xing, E.P. Learning robust global representations by penalizing local predictive power. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2019, 32, 10506–10518. [Google Scholar]
- Hendrycks, D.; Zhao, K.; Basart, S.; Steinhardt, J.; Song, D. Natural adversarial examples. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 15262–15271. [Google Scholar]
- Hendrycks, D.; Basart, S.; Mu, N.; Kadavath, S.; Wang, F.; Dorundo, E.; Desai, R.; Zhu, T.; Parajuli, S.; Guo, M.; et al. The many faces of robustness: A critical analysis of out-of-distribution generalization. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 8340–8349. [Google Scholar]





| Datasets | Classes | Train | Val | Test | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ImageNet | 1000 | 1.28 M | ~ | 50,000 | Recognition of generic objects |
| Caltech101 | 100 | 4128 | 1649 | 2465 | Recognition of generic objects |
| OxfordPets | 37 | 2944 | 736 | 3669 | Fine-grained classification of pets |
| StanfordCars | 196 | 6509 | 1635 | 8041 | Fine-grained classification of cars |
| Flowers102 | 102 | 4093 | 1633 | 2463 | Fine-grained classification of flowers |
| Food101 | 101 | 50,500 | 20,200 | 30,300 | Fine-grained classification of foods |
| FGVCAircraft | 100 | 3334 | 3333 | 3333 | Fine-grained classification of aircrafts |
| SUN397 | 397 | 15,880 | 3970 | 19,850 | Scene classification |
| DTD | 47 | 2820 | 1128 | 1692 | Texture classification |
| EuroSAT | 10 | 13,500 | 5400 | 8100 | Land use & cover classification with satellite images |
| UCF101 | 101 | 7639 | 1898 | 3783 | Action recognition |
| Datasets | Metric | CLIP | CoOp | CoCoOp | ProGrad | KgCoOp | AAPL | Ours |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ImgNet | Base | 72.42 | 76.47 | 75.98 | 77.02 | 75.83 | 76.53 | 77.50 |
| New | 68.14 | 67.88 | 70.43 | 66.66 | 69.96 | 70.57 | 71.30 | |
| H | 70.22 | 71.92 | 73.10 | 71.46 | 72.78 | 73.43 | 73.81 | |
| Caltech | Base | 96.84 | 98.00 | 97.96 | 98.02 | 97.72 | 97.87 | 98.23 |
| New | 94.00 | 89.31 | 93.81 | 93.89 | 94.39 | 95.10 | 93.00 | |
| H | 95.40 | 93.73 | 95.84 | 95.91 | 96.03 | 96.46 | 95.54 | |
| Pets | Base | 91.17 | 93.67 | 92.50 | 95.07 | 94.65 | 95.63 | 95.68 |
| New | 97.26 | 95.29 | 97.69 | 97.63 | 97.60 | 97.40 | 97.93 | |
| H | 94.12 | 94.47 | 96.43 | 96.33 | 96.18 | 96.51 | 96.79 | |
| Cars | Base | 63.37 | 78.12 | 70.49 | 77.68 | 71.76 | 70.33 | 78.00 |
| New | 74.89 | 60.40 | 73.59 | 68.68 | 75.04 | 73.50 | 70.33 | |
| H | 68.65 | 68.13 | 72.01 | 72.88 | 73.56 | 71.88 | 73.97 | |
| Flowers | Base | 72.08 | 97.60 | 94.87 | 95.54 | 95.00 | 95.10 | 96.80 |
| New | 77.80 | 59.67 | 71.75 | 71.87 | 74.73 | 70.63 | 71.73 | |
| H | 74.83 | 74.06 | 81.71 | 82.03 | 83.65 | 81.06 | 82.40 | |
| Food101 | Base | 90.10 | 88.33 | 90.70 | 90.37 | 90.50 | 90.70 | 90.43 |
| New | 91.22 | 82.26 | 91.29 | 89.59 | 91.70 | 91.60 | 91.17 | |
| H | 90.66 | 85.19 | 90.99 | 89.98 | 91.09 | 91.15 | 90.80 | |
| Aircraft | Base | 27.19 | 40.44 | 33.41 | 40.54 | 36.21 | 34.07 | 40.83 |
| New | 36.29 | 22.30 | 23.71 | 27.57 | 33.55 | 24.17 | 33.27 | |
| H | 31.09 | 28.75 | 27.74 | 32.82 | 34.83 | 28.28 | 36.66 | |
| SUN397 | Base | 69.36 | 80.6 | 79.74 | 81.26 | 80.29 | 79.65 | 82.10 |
| New | 75.35 | 65.89 | 76.86 | 74.17 | 76.53 | 76.90 | 77.37 | |
| H | 72.23 | 72.51 | 78.27 | 77.55 | 78.36 | 78.25 | 79.66 | |
| DTD | Base | 53.24 | 79.44 | 77.01 | 77.35 | 77.55 | 73.90 | 82.63 |
| New | 59.90 | 41.18 | 56.00 | 52.35 | 54.99 | 53.43 | 63.00 | |
| H | 56.37 | 54.24 | 64.85 | 62.45 | 64.35 | 62.02 | 71.49 | |
| EuroSAT | Base | 56.48 | 92.19 | 87.49 | 90.11 | 85.64 | 87.00 | 89.60 |
| New | 64.05 | 54.74 | 60.04 | 60.89 | 64.34 | 66.30 | 79.57 | |
| H | 60.03 | 68.69 | 71.21 | 72.67 | 73.48 | 75.25 | 84.29 | |
| UCF101 | Base | 70.53 | 84.69 | 82.33 | 84.33 | 82.89 | 82.20 | 86.10 |
| New | 77.50 | 56.05 | 73.45 | 74.94 | 76.67 | 74.27 | 78.90 | |
| H | 73.85 | 67.46 | 77.64 | 79.35 | 79.65 | 78.03 | 82.34 | |
| Avg ACC | Base | 69.37 | 82.69 | 80.47 | 82.48 | 80.73 | 80.27 | 83.43 |
| New | 74.22 | 63.22 | 71.69 | 70.75 | 73.60 | 72.17 | 75.23 | |
| H | 71.70 | 71.66 | 75.83 | 76.16 | 77.00 | 76.01 | 79.12 |
| Method | Source | Target | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ImgNet | Caltech | Pets | Cars | Flowers | Food101 | Aircraft | SUN397 | DTD | EuroSAT | UCF101 | |
| CoOp | 71.51 | 93.70 | 89.14 | 64.51 | 68.71 | 85.30 | 18.47 | 64.15 | 41.92 | 46.39 | 66.55 |
| CoCoOp | 71.02 | 94.43 | 90.14 | 65.32 | 71.88 | 86.06 | 22.94 | 67.36 | 45.73 | 45.37 | 68.21 |
| KgCoOp | 71.26 | 94.35 | 89.96 | 65.40 | 71.25 | 86.38 | 23.05 | 66.20 | 46.38 | 46.04 | 68.63 |
| AAPL | 71.37 | 94.17 | 90.73 | 65.32 | 71.77 | 86.00 | 23.03 | 66.80 | 44.80 | 41.83 | 69.30 |
| Ours | 71.70 | 93.50 | 90.10 | 64.37 | 71.96 | 85.40 | 24.30 | 67.50 | 44.13 | 40.30 | 69.50 |
| Method | Source | Target | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ImgNet | ImgNet-V2 | ImgNet-Sketch | ImgNet-A | ImgNet-R | |
| CLIP | 66.73 | 60.83 | 46.15 | 47.77 | 73.96 |
| CoOp | 71.51 | 64.20 | 47.99 | 49.71 | 75.21 |
| CoCoOp | 71.02 | 64.07 | 48.75 | 50.63 | 76.18 |
| KgCoOp | 71.20 | 64.10 | 48.90 | 50.60 | 76.70 |
| AAPL | 71.37 | 64.20 | 48.80 | 50.60 | 76.87 |
| Ours | 71.70 | 64.64 | 49.27 | 48.27 | 77.17 |
| Methods | CLIP | CoOp | CoCoOp | Maple | Ours |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | 124,324,281 | 2048 | 35,360 | 3,555,072 | 6,815,744 |
| HM | 71.70 | 71.66 | 75.83 | 78.55 | 79.12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, W.; Li, J.; Guo, Z.; Peng, Z.; Li, X.; Yang, J.; Li, C.; Long, W. Twin-Space Decoupling and Interaction for Efficient Vision-Language Transfer. Electronics 2025, 14, 4314. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14214314
Liang W, Li J, Guo Z, Peng Z, Li X, Yang J, Li C, Long W. Twin-Space Decoupling and Interaction for Efficient Vision-Language Transfer. Electronics. 2025; 14(21):4314. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14214314
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Wei, Junqiang Li, Zhengkai Guo, Zhiwei Peng, Xiaocui Li, Junfeng Yang, Chuang Li, and Wei Long. 2025. "Twin-Space Decoupling and Interaction for Efficient Vision-Language Transfer" Electronics 14, no. 21: 4314. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14214314
APA StyleLiang, W., Li, J., Guo, Z., Peng, Z., Li, X., Yang, J., Li, C., & Long, W. (2025). Twin-Space Decoupling and Interaction for Efficient Vision-Language Transfer. Electronics, 14(21), 4314. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14214314






