Abstract
In traditional scheduling operations, dispatchers mainly rely on SCADA/EMS systems or personal experience. However, with access to a large number of new energy sources, the scale of the distribution network continues to expand, and its topology becomes increasingly complex, leading to potential security risks in scheduling operations. Therefore, it is very important to carry out risk assessments before scheduling operations. In this paper, risk theory is introduced into the field of distribution network scheduling operations, and a new risk assessment method is proposed considering various uncertain factors in the distribution network. In order to comprehensively analyze the influence of uncertainty factors in the operational process of a new distribution network, the output probability models of wind power, photovoltaic power, and load are first constructed in this study. Then, the improved Latin hypercube sampling method is used to extract the operating state of the distribution network system from the probability model, and the node voltage over-limit and line power flow overload are used as indicators to measure the severity of the consequences so as to establish a quantitative scheduling operation risk assessment system and analyze its framework in detail. Finally, simulation analysis is carried out in the improved IEEE-RTS79 test system: taking 15–25 lines from the operation state to the maintenance state as an example, this paper analyzes the influence of different locations and capacities of wind and solar access on the scheduling operation risk of distribution networks. The results can provide a reference for dispatchers to prevent risks before operation.
1. Introduction
A dispatching operation is an important means to achieve the safe and stable operation of the power grid and the rational and optimal use of power resources. Any operation made by the dispatcher will have different degrees of impact on the operation of the power grid, so the dispatching operation needs to follow guidelines for the safe operation of the power grid [1]. At present, the automatic generation–check–execution function of the operation ticket is determined mainly by means of a set of network dispatch systems [2,3,4], including some basic checks such as a ticket face check, topology check, and equipment status check. However, in the process of dispatching operations, due to factors such as weather, equipment status, and load changes, certain risks will be introduced into the dispatching operation process, resulting in operational risks such as voltage overrun and line power flow overload [5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13], so it is of great practical significance to carry out dispatching operation risk assessment for distribution networks. In reference [14], based on the characteristics of decomposing dispatching operations and having “no memory”, Markov chains are used to simulate the gradual execution of dispatching operations. Meanwhile, four indicators, namely, voltage over-limit, power flow overload, static voltage stability, and interlocking faults, are selected to quantify the consequences of the power grid, taking into account the impact of compliance fluctuations. In reference [15], a risk indicator severity solution function is proposed based on the improved utility theory. The authors use the Analytic Hierarchy Process to set the slopes of the indicator loss coefficient curves within different over-limit and overload intervals, and put forward the concept of the optimal risk assessment regional unit to eliminate the interference of data when calculating the severity of risk indicators. Risk assessment not only quantifies the consequences of an accident on its operation, but also considers the impact of uncertainties on scheduling operations [16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29]. In reference [30], a novel uncertainty-based reliability assessment approach is developed for microgrids considering uncertainties at both the supply and demand sides. A new reliability index is proposed and a risk quantification method is developed to measure the risk/probability of power inadequacy under uncertainties. In reference [31], considering the influence of human factors on scheduling jobs, a time-varying probability model for the reliability of human factors is established. Reference [32] mainly considers the influence of social, weather, and equipment factors on the risk assessment of distribution network dispatching operations, and references [33,34] investigate risk assessment from the perspectives of weather, operating equipment, and operation time, and propose a risk assessment method considering multi-dimensional operational factors. The above studies mainly carry out the risk assessment and analysis of dispatching operations from the perspectives of equipment, personnel, and weather, but do not consider the impact of uncertainty factors such as renewable energy in the dispatching operation.
Reference [35] proposes a technical framework for dynamic N-1 risk assessment while considering the failure risk of stable operations and the associated bus failure risk after the failure of switch operations, and proposes an assessment method to meet the risk completeness mentioned in reference [36], considering the degree of concern and the influence of social period. The authors of reference [37] proposed a topological analysis method for intelligent grid misoperation prevention based on fault tree analysis from the perspective of topological models, and constructed a multi-level fault tree model. However, with the large-scale integration of distributed power sources, the grid structure becomes increasingly complex, and the factors influencing the operation risk of the distribution network dispatch also increase. The uncertainty of renewable energy output brings certain operational risks to grid dispatching operations.
Starting from the randomness of wind and solar output, this study analyzes the impact of grid dispatching operations on the risk of grid operations under the condition of the uncertainty of renewable energy output. It also conducts a probability sampling of wind and solar output scenarios through improved Latin hypercube sampling, takes node voltage overrun and branch power flow outpass as evaluation indexes to analyze the risk of dispatching operations on power grid operations, and, finally, uses the improved IEEE-RTS79 test system to verify the effectiveness of the proposed method.
2. Uncertainty Modeling of New Distribution Components
2.1. Probability Model of Photovoltaic Output
The output power of photovoltaics is related to the light intensity, which can be approximately described by the Beta distribution over a period of time, and its probability density function is as follows [38]:
where and represent the actual and maximum light intensity during this time, respectively; and and are the shape parameters of the beta distribution, respectively.
The formula for the output power of the photovoltaic panel is as follows:
where and are the actual output power and the maximum output power of the photovoltaic, respectively; is the total area of the photovoltaic panels; and is the photoelectric conversion efficiency of the photovoltaic panels.
According to the relationship between photovoltaic output and light intensity, the probability density function of photovoltaic cells can be deduced as follows:
The power factor is maintained at a fixed value, and the photovoltaic power generation system is used as a PQ node in the power flow calculation.
2.2. Probability Model of Wind Power Output
Wind turbine output also has strong randomness, and research shows that the wind speed distribution in most areas conforms to the Weibull distribution. The probability density function of wind speed can be expressed by the following formula [39]:
where denotes the wind speed, and and represent the shape parameters of the distribution function.
The relationship between the output power of a general wind turbine and the wind speed can be expressed by the following mathematical model:
where and are the active power and rated power output by the wind turbine, respectively; is the actual wind speed; and are cut-in and cut-out winds, respectively; and is the rated wind speed.
According to the wind speed Weibull distribution function and the relationship between the output power of the wind turbine and the wind speed, the probability density function of the output power of the wind turbine can be derived, and its mathematical model is as follows:
It can be used as a PQ node in power flow calculation.
2.3. Probabilistic Model of Load Demand Uncertainty
The randomness of load forecasting can be regarded as a random variable that obeys a normal distribution, and its corresponding probability density function is as follows:
where and are the active and reactive power of the load, respectively; and are mathematical expectations for active and reactive power, respectively; and and are the standard deviations of active and reactive power, respectively.
3. A New Distribution Network Dispatching Operation Risk Assessment Index System
The risk assessment of distribution network scheduling operations is based on the probability of scheduling operation failure and the severity of the risk consequences caused by it. The risk level of a distribution network scheduling operation can be quantitatively evaluated. In this paper, the distribution network risk assessment model mainly considers the uncertainty of wind power and photovoltaic output and the uncertainty of load demand, and takes the node voltage overrun and line power flow overrun caused by the scheduling operation as the evaluation index for risk assessment. The risk value is calculated as follows:
where is a probable event; represents the likelihood of an event occurring; and indicates the severity of the risk of the event occurring under the operating conditions of .
3.1. Node Voltage Overrun Risk Indicators
The distribution network generally stipulates that the voltage fluctuation does not exceed ±5% as the limit. The formula for calculating the probability of the node voltage exceeding the limit is as follows:
where is the voltage out-of-limit probability of node ; denotes the probability of each operating scenario; represents the voltage of node in the s-th scenario; and is the 0–1 flag quantity for the risk of voltage overrun, with 0 meaning that the voltage is not overrun, and 1 meaning that the voltage is out of limit.
The voltage out-of-limit severity function is as follows:
In the formula, represents the severity value of overvoltage and represents the severity value of low voltage.
In summary, the functional expression of the risk of node voltage overrun is as follows:
where represents the total number of buses in the grid, and represents the node voltage over-limit severity function.
3.2. Slip Flow Overrun Risk Indicator
The risk of the line power flow exceeding the limit is expressed in the risk that the apparent power carried by the line exceeds the maximum power limit that the line can pass under different operating conditions of the system. The function expression of the probability and risk of line overload is as follows:
where is the risk value of the branch power flow exceeding the limit; represents the total number of transmission lines in the grid; is the probability of carrying the apparent power of line j; indicates whether the line j is overloaded in the running state of s; represents the out-of-limit severity function of line j in the s running state; represents the power flow of line j in the S running scenario; and is the maximum power flow limits of line j.
4. Risk Assessment of Distribution Network Scheduling Operation Based on Improved Latin Hypercube Sampling
4.1. The Principle of Latin Hypercube Sampling
Latin hypercube sampling is a sampling method that uses sampling values to reflect the overall distribution of random variables. In 1979, Mackay et al. [40] proposed that the sampling process is divided into two steps: the first step is the sampling process, which is mainly to divide the probability density function sample space of the input variable into N subspaces. All subspaces are independent of each other and do not affect each other, and separate probability sampling is carried out in each subspace. Then, M input variables form the initial sampling matrix X of M × N after N sampling. The second step is the sorting process: first, a sequential matrix T is formed. Then, the elements in the initial sampling matrix X are sorted according to the position of the corresponding elements in the sequential matrix T, and the final sampling matrix is formed. The principle of the sampling process is shown in Figure 1.
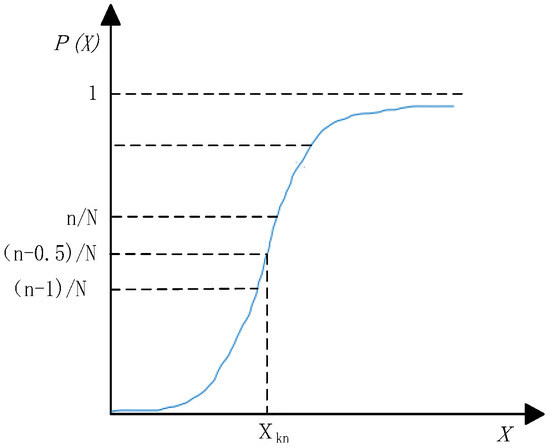
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the LHS sampling process.
P(X) is the probability density function of the random variable X. The interval [0, 1] is divided into N sub-intervals with a spacing of 1/N. Each sub-interval is represented by Kn, n = 1, 2, …, N; the element i(i = 1, 2, …, n) is randomly sampled, the random number C(0,1) is generated from the interval (0,1), Kn is randomly selected, and then the sampling point XKn is calculated according to the P(X) inverse function. If XKn > , the component is in normal operation in the sub-section (Xi = 0). Otherwise, it is in an invalid state (Xi = 1). The next sampling is carried out randomly from the remaining sub-intervals, and if one sub-interval sampling completed, the remaining sub-intervals of the sample are sampled until the convergence condition is satisfied. Latin hypercube sampling, through the abovementioned process of stratified sampling, makes the sampling distribution more uniform and can cover the whole sample space. The sampling produces more fault states, avoids a large number of repeated sampling of the whole system sample, and improves the sampling efficiency.
4.2. The Principle of the Important Sampling Method
The basic principle of the important sampling method is to change the probability distribution of the original spatial samples without changing their expected value, so as to reduce the variance of the samples, reduce the amount of sampling, and improve the sampling efficiency. The formula is expressed as follows:
where is the probability function of the original sample distribution; is the state function of the spatial distribution of the original sample; and are the probability and state functions of the spatial distribution of the new sample, respectively; and and , respectively, are the variances and expected values of . The important sampling method focuses on how to select the probability distribution function of the system in the new distribution so that the sample of the new distribution can reduce the variance of the sample while the desired value remains unchanged.
4.3. Risk Assessment Scenario Generation Based on Improved Latin Hypercube Sampling
4.3.1. Comparison of Sampling Effects Based on LHS+ Important Sampling Method
Taking an object with a variable of 2 and a sampling size of 100 as an example, the distribution of the sampling results obtained using conventional random sampling, Latin hypercube sampling, and the improved sampling method in this study is shown in Figure 2. As can be seen from the figure, Latin hypercubic sampling has a more uniform distribution of variables and a larger coverage space than conventional sampling. Comparing the results obtained by LHS+ important sampling with the results of the other two samples, it can be seen that the LHS+ important sampling method embodies the principle of importance. The key lies in selecting the points close to the expected value boundary, which integrates the ideas of “stratification” and “importance”, which makes the sampling more targeted, reduces the sampling of non-fault states, and improves the sampling efficiency.

Figure 2.
Comparison of sampling distributions.
4.3.2. Scenario Reduction Based on K-Medoids Algorithm
Compared with the K-means clustering algorithm, which uses the mean value of samples within the cluster as the particle, the K-medoids algorithm used in this paper takes the closest point to the center as the representative point of the cluster, which is less sensitive to outliers and noise pollution, and effectively avoids the distortion of clustering scenes [41]. The clustering algorithm is used to reduce and screen typical scenarios, and the specific process is as follows:
(1). K initial cluster centers are selected according to the “maximum and minimum distance principle”, and if m cluster centers are known, then the m + 1 cluster center selection principle is shown as follows: the minimum distance from the remaining candidate sample points to the known cluster centers is calculated, and the candidate sample corresponding to the largest minimum distance is the latest cluster center.
where is the i-th candidate sample, and is the center of cluster j. The middle distance is the Euclidean.
(2). According to the principle of minimum distance, the remaining n-k samples are assigned to the center of each cluster, and then the objective function value is calculated. The expression is as follows:
where is the number of the i-th candidate sample cluster; is the j-th cluster sample candidate set; and is the i-th sample within the j-th.
(3). Update the center of the cluster. For each cluster, all other sample points except the cluster center are calculated, and the sample with the smallest sum of distances is selected as the new cluster center.
(4). Repeat steps (2) and (3) until the objective function no longer changes or the preset maximum number of iterations has been reached.
(5). The final scenario is output, and the probability of a typical scenario is calculated, with the expression as follows:
where is the total number of initial sample scenes, and is the membership of the i-th sample to the class centered on the s-th typical scene, with 0 representing non-belonging and 1 representing belonging.
(6). Simulation analysis
According to the probability distribution model of wind power, photovoltaic power, and load, 200 initial scenarios were sampled by LHS+ important sampling method, and the K-medoids clustering algorithm was used to reduce them into five typical scenarios. The sampling results of the initial scenarios and reduction scenarios are shown in Figure 3 and Figure 4, and the probability of each scenario generated by the reduction is shown in Figure 5.
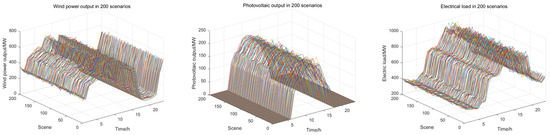
Figure 3.
Scenario generation results.

Figure 4.
Scenario reduction results.
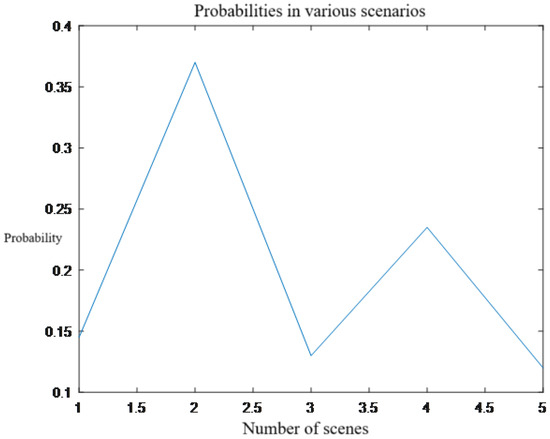
Figure 5.
Reducing the probability of each scenario generated.
4.4. Analysis of the Risk Assessment Process of Distribution Network Scheduling Operation
In this paper, the process of the risk assessment of the scheduling operation includes the sampling and reduction of scheduling operation scenarios, analysis of operational risk status, calculation of the severity of operational risk consequences, and calculation of operational risk indicators. The operation risk analysis part is mainly based on the data analysis of the type of scheduling operation and the distribution network, the risk state of the scheduling operation, and the probability of its operation state. The section on calculating the severity of operational risks includes node voltage overrun and branch power flow out-of-limit. The operation risk assessment index calculation module is calculated according to the obtained state probability and risk severity value, and, finally, the comprehensive risk assessment value is calculated.
Figure 6 shows the overall process framework of the risk assessment of distribution network scheduling operations.

Figure 6.
The risk assessment process of distribution network scheduling operation.
5. Case Analysis
5.1. An Introduction to the Example
In this paper, an improved IEEE-RTS79 node test system is used for a case analysis [42], which has a total installed capacity of 3405 MW and a total load of 2850 MW, including 24 nodes and 38 transmission lines. It multiplies the maximum allowable power of each branch in the system by 0.8, and connects to wind power and photovoltaic units of a certain capacity. The candidate nodes that can be connected to wind and solar in the test system are #6, #9, #10, #15, #22, and #23. In this paper, the risk assessment of the scheduling operation is carried out by taking the operation of lines 15–24 in the test system as an example. A topology expansion diagram of the system is shown in Figure 7, which can be decomposed into the following operation steps, as shown in Table 1. According to the analysis of the historical data of a power grid, the probability of success of the dispatching operation can be set to 0.98. In this paper, the risk assessment of the dispatch operation order is carried out as a whole, regardless of the internal operation steps.

Figure 7.
One-line diagram of the IEEE-RTS79 test system.

Table 1.
Line 15–24 operation to maintenance operation steps.
5.2. Scenario Analysis
In order to consider the influence of the uncertainty factors of wind power and photovoltaic power on the risk assessment of distribution network dispatching operations, the risk assessment of the adjustment operation is divided into three wind and solar access distribution network scenarios.
Scenario 1: At nodes 6 and 9, photovoltaic and wind power with total capacities of 75 MW and 100 MW, 100 MW and 150 MW, and 145 MW and 200 MW are connected under three scenarios, respectively.
Scenario 2: At nodes 10 and 15, photovoltaic and wind power with total capacities of 75 MW and 100 MW, 100 MW and 150 MW, and 145 MW and 200 MW are connected under three scenarios, respectively.
Scenario 3: At nodes 22 and 23, photovoltaic and wind power with total capacities of 75 MW and 100 MW, 100 MW and 150 MW, and 145 MW and 200 MW are connected under three scenarios, respectively.
(1). Scenario 1 analysis
In order to analyze the dispatching operation risk of connecting wind power and photovoltaic power with different capacities at the same node, photovoltaic and wind turbines are connected to nodes 6 and 9 respectively. Table 2 shows the risk assessment results for the scheduling operation after the operation. It can be seen from the table that with the continuous increase in the wind and solar capacity of the node bus, the risk of voltage loss of nodes 3 and 24 decreases, but the risk of branch power flow exceeding the limit also decreases. This is because after the disconnection of lines 15–24, with the increase in the capacity of wind and solar access, wind and solar replace the traditional energy power supply and reduce the transmission power to lines 14–16.

Table 2.
Scenario 1 risk assessment results for scheduling operations.
(2). Scenario 2 analysis
When wind power and photovoltaic power are connected to nodes 10 and 15, respectively, the risk assessment of the dispatching operation is carried out. The risk assessment results obtained after the operation are shown in Table 3. As can be seen from the table, when the capacity of wind and solar turbines connected to the node keeps increasing, the risk of branch power flow exceeding the limit also keeps rising, while the risk of the loss of pressure on node buses 3 and 24 decreases, and the risk value of the total scheduling operation shows an increasing trend due to the increase in the risk of power flow over-limit. Therefore, during the process of scheduling operations, it is necessary to guard against the operational risk caused by the over-limit of the power flow.

Table 3.
Scenario 2 scheduling operation risk assessment results.
(3). Scenario 3 Analysis
When wind power and photovoltaic power are connected to nodes 22 and 23, respectively, the risk assessment of the dispatching operation is carried out. The risk assessment results obtained after the operation are shown in Table 4. As can be seen from the table, with the increase in the access capacity of wind power and photovoltaic units, the risk of power flow and voltage limit increases. Because the wind and solar access nodes 22 and 23 are on the 230 KV high-voltage side of the system and the line load rate is high, when the wind and solar capacity continuously increases, the dispatching operation will lead to a power out-of-limit situation on the line. The risk of voltage out-of-limit will be affected by the change in the system power flow distribution caused by the power out-of-limit of the branch, and will also increase accordingly. The risk of the power flow exceeding the limit is more serious, so it is necessary to prevent the risk caused by the power flow exceeding the limit before the scheduling operation.

Table 4.
Scenario 3 scheduling operations risk assessment results.
5.3. Scenario Comparison Analysis
(1). Comparison of scenarios 1 and 2. Comparing the risk assessment results in Table 2 and Table 3, it can be seen that when the wind and solar access capacity is the same but the wind and solar access different nodes, the risk from the dispatching operation is also different. The power flow overrun risk and voltage overrun risk from the adjustment of the wind and solar access nodes 6 and 9 are significantly smaller than those of access nodes 10 and 15; this is because nodes 6 and 9 are on the 138 KV low-voltage side of the system. The installed capacity and load of the power supply on the low-voltage side are lower, the line has a larger residual transmission capacity, and node 15 is located on the 230 KV side of the system. Most of the installed power supply and load of the system are concentrated on the high-voltage side and the transmission capacity of the line is small. The risk of voltage over-limit and branch power flow over-limit also increases accordingly when the dispatching operation is carried out. Comparison curves of the power flow over-limit risk and the voltage over-limit risk of the dispatching operation in different scenarios are shown in Figure 8 and Figure 9. The comparison table shows the comprehensive risk of dispatching operations when wind and solar access to the low-voltage side is smaller than that of the high-voltage side. Therefore, for the wind and solar connected to the high-voltage side, it is necessary to guard against operational risks before carrying out the dispatching operation.

Figure 8.
Comparison curves of power flow overrun risk under different scenarios.

Figure 9.
Comparison curves of power flow overrun risk under different scenarios.
(2). Comparison of scenarios 2 and 3. Comparing the evaluation results in Table 3 and Table 4, it can be seen that when the wind and solar access capacity is the same and when the wind and solar access nodes 22 and 23, the risk of voltage overrun caused by the scheduling operation is much greater than that of access nodes 10 and 15. This is because the access wind and solar nodes 10 and 15 are close to lines 15–24 of the dispatching operation, and when the line is switched from operation to cold standby, the node bus loses voltage. When the wind and solar capacity increases, voltage support for the bus is provided and the risk of voltage overrun is reduced. Figure 10 shows the voltage overrun risk comparison curves for the different scenarios.

Figure 10.
Comparison curves of voltage overrun risk in different scenarios.
6. Conclusions
This paper introduces risk theory into the risk assessment of dispatching operations, and proposes a risk analysis model for dispatching operations considering a variety of uncertainties including wind power and photovoltaic output. An improved Latin hypercube sampling model is also proposed that samples and simulates the uncertainty model, so as to quantitatively assess the risk of dispatching operations under various wind and solar output and access scenarios. A comparative analysis is conducted of the dispatching operation risks of different access capacities and access locations of wind and solar power. The results show that the risk values of dispatching operations vary when different capacities are accessed at different locations. In areas with dense loads and high voltages, the access of wind and solar power has a greater impact on the risk of dispatching operations, and the larger the access capacity, the higher the risk of node voltage and branch power flow over-limit, which can guide dispatching operators to prevent risks before operation. The model can provide important theoretical support for dispatchers to quickly and scientifically quantify and evaluate the potential risks in the process of grid dispatching operations. Subsequently, the risk values of each operational step can be further studied, and the influences of factors such as equipment, human factors, and weather on the dispatching operation risks can be considered in combination.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.Y. and S.Y.; Methodology, L.P. and S.Y.; Software, X.Y.; Validation, L.P., X.Y. and S.Y.; Formal Analysis, H.X.; Investigation, J.L.; Resources, L.P.; Data Curation, L.P.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, L.P.; Writing—Review & Editing, L.P.; Visualization, J.L.; Supervision, L.P.; Project Administration, L.P.; Funding Acquisition, Science and Technology Project of Guangxi Power Grid Corporation. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the Science and Technology Project of Guangxi Power Grid Corporation (046000KC24040005).
Data Availability Statement
The data is included in the article.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Lianrong Pan, Xiao Yang and Shangbing Yuan are employed by thecompany Electric Power Dispatching and Control Center of Guangxi Electric Power Grid Co., Ltd. Author Jiaan Li is employed by the company Laibin Power Supply Bureau of Guangxi Electric Power Grid Co., Ltd. Author Haowen Xue is employed by the company Hechi Power Supply Bureau of Guangxi Electric Grid Co., Ltd. The authors declare that this study received funding from Science and Technology Project of Guangxi Power Grid Corporation. The funder was not involved in the study design, collection, analysis, interpretation ofdata, the writing of this article or the decision to submit it for publication.
References
- Li, W. Risk Assessment of Electric Power Systems: Models, Methods, and Applications; Wiley-IEEE Press: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 1–325. [Google Scholar]
- Kirschen, D.S.; Jayaweera, D. Comparison of risk-based and deterministic security assessments. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2007, 1, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciapessoni, E.; Cirio, D.; Kjølle, G.; Massucco, S.; Pitto, A.; Sforna, M. Probabilistic Risk-Based Security Assessment of Power Systems Considering Incumbent Threats and Uncertainties. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2016, 7, 2890–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, F.; Vittal, V.; Raja, A. Probabilistic Power Flow Studies for Transmission Systems with Photovoltaic Generation Using Cumulants. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2012, 27, 2251–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Lin, Z.; Xu, X.; Chen, R.; Ma, W.; Shi, J.; Xu, X. A dispatch risk assessment method based on fuzzification accident rating index. Power Syst. Prot. Control. 2021, 49, 98–104. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Pan, B.; Yang, Y. Large-group risk dynamic emergency decision method based on the dual influence of preference transfer and risk preference. Soft Comput. 2018, 22, 7479–7490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Tian, Q.; Jiao, H.; Guo, C.; Lin, X.; Li, J.; He, L. Power grid risk assessment of dispatching operation considering multi-risk elements. J. Electr. Power Sci. Technol. 2016, 31, 109–115. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, J.; Hu, C.-H.; Yu, S.-Q.; Cheng, P.-F. An extended EDAS method under four-branch fuzzy environments and its application in credit evaluation for micro and small entrepreneurs. Soft Comput. 2021, 25, 2777–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Dong, K.; Li, J.; Yang, M.; Cai, X. Research on day-ahead quantitative evaluation system for Guangdong power griddispatching. Electr. Eng. 2021, 12, 128–129+160. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, W.; Jin, Q.; Lu, Z.; Wu, M.; Hu, C. Analyzing of research patterns based on a temporal tracking and assessing model. Pers. Ubiquitous Comput. 2016, 20, 933–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Zheng, H. A mortality risk assessment approach on ICU patients clinical medication events using deep learning. Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 2021, 128, 161–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Liu, J.; Chen, D.; Li, Y.; Lu, D.; Zeng, Y. Fast risk assessment technique for dispatching operations. Proc. CSU-EPSA 2016, 28, 83–88. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, L.; Dou, W.; Hu, C.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, J. A context-aware service evaluation approach over big data for cloud applications. IEEE Trans. Cloud Comput. 2015, 8, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Chen, Y.; Ma, X.; Dong, S.; Tang, K. Risk assessment method for power grid dispatching operation based on markov chain and two-point estimation method. Power Capacit. React. Power Compens. 2022, 43, 127–133. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Xie, M.; Lan, Q.; Wu, L.; Jia, Y. Risk assessment of scheduling operation based on improved utility theory. Electr. Autom. 2019, 41, 44–46+63. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W. Power System Risk Assessment Models, Methods and Applications; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2006; pp. 115–159. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, F.; Dong, L.; Wang, K.; Yang, K.; Pan, C. Distributed resource scheduling for large-scale MEC systems: A multiagent ensemble deep reinforcement learning with imitation acceleration. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 9, 6597–6610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashal, I. Smart grid reliability evaluation and assessment. Kybernetes 2022, 52, 3261–3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, W.; Xu, X.; Meng, S.; Zhang, X.; Hu, C.; Yu, S.; Yang, J. An energy-aware virtual machine scheduling method for service QoS enhancementin clouds over big data. Concurr. Comput. Pract. Exp. 2017, 29, e3909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Q.; Tang, J.; Zhang, Y.; He, J. Design of dispatching operation risk assessment and auxiliary decision-making system based on multi-source data fusion. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2018, 34, 38–45. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Y.; Liu, A.; Mao, X.; Li, F. An intelligent charging scheme maximizing the utility for rechargeable network in smart city. Pervasive Mob. Comput. 2021, 77, 101457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Luo, Z.; Zhao, S.; Wang, Z.; Xie, J.; Zeng, S. Risk assessment of a power system containing wind power and photovoltaic based on improved Monte Carlo mixed sampling. Power Syst. Prot. Control. 2022, 50, 75–83. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, W.; Hu, C.; Wu, M.; Jin, Q. A data intensive heuristic approach to the two-stage streaming scheduling problem. J. Comput. Syst. Sci. 2017, 89, 64–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaduru, R.; Mercy, P.; Srinivas, G.N. Power distribution system reliability evaluation using weight-optimised ANN approach. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 13905–13927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.-S.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X.-J.; Chin, K.-S.; Tsui, K.-L. Fostering linguistic decision-making under uncertainty: A proportional interval type-2 hesitant fuzzy TOPSIS approach based on Hamacher aggregation operators and andness optimization models. Inf. Sci. 2019, 500, 229–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Chen, X. Generalized archimedean intuitionistic fuzzy averaging aggregation operators and their application to multicriteria decision-making. Int. J. Inf. Technol. Decis. Mak. 2016, 15, 311–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, H.; Chen, X.; Yang, M. Reliability evaluation of distribution network considering multi-state reliability model of new distribution components. Distrib. Util. 2023, 40, 74–82. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, F.; Wang, K.; Li, D.; Pan, C.; Yang, K. Stacked autoencoder-based deep reinforcement learning for online resource scheduling in large-scale MEC networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 7, 9278–9290. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Ni, Z.; Xu, Y.; Luo, E.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y. A trustworthy industrial data management scheme based on redactable blockchain. J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 2021, 152, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Li, H.; Wang, S. A quantitative reliability assessment and risk quantification method for microgrids considering supply and demand uncertainties. Appl. Energy 2022, 328, 120130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Zhu, L.; Wei, K. Risk assessmentand application for dispatching operation considering human reliability. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2018, 18, 240–245. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, W.; Wang, E.; Liu, Z. Real-time probabilistic model based risk assessment of dispatching operations process. Power Syst. Technol. 2013, 37, 3509–3514. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, D.X.; Xu, D.; Liao, H.; Guo, J.; Guo, X. Risk assessment and control strategy on dispatching operation of power grid. Energy Eng. 2020, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, K.; Zeng, Y.; Jia, H.; Lu, E.; Liu, J.; Hu, S. Risk assessment and optimization method for markov chain-based scheduling operations. Autom. Electr. Power Syst. 2015, 39, 142–148. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Z.; Hu, Z.; Xu, X.; He, X.; Zou, Z.; Liu, X. Dynamic N-1 risk assessment technology considering the entire process of scheduling operations. Autom. Electr. Power Syst. 2019, 43, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Q.; Tang, J.; Liu, Y.; He, J. A risk quantitative evaluation method of the dispatching operation considering the complete risk. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2017, 33, 32–40+45. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Li, Z. Topology analysis of anti-misoperation in smart grid dispatching based on fault tree. Electr. Power Equip. Manag. 2024, 24, 57–59. [Google Scholar]
- Schilling, M.T.; Leite da Silva, A.M.; Billington, R.; El-Kady, M.A. Bibliography on power system probabilistic analysis (1962–1988). IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 1990, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Shuyong, C.; Huizhu, D.; Xiaomin, B.; Zhou, X. Evaluation of grid connected wind power plants. In Proceedings of the POWERCON’98. 1998 International Conference on Power System Technology, Beijing, China, 18–21 August 1998; pp. 1208–1212. [Google Scholar]
- McKay, M.D.; Beckman, R.J.; Conover, W.J. A comparison of three methods for selecting values of input variables in the analysis of output from a computer code. Technometrics 2000, 42, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Q. Design and application of smart city internet of things service platform based on fuzzy clustering algorithm. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2022, 2022, 8405306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subcommittee, P.M. IEEE reliability test system. IEEE Trans. Power Appar. Syst. 1979, 6, 2047–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).