Smart Home Control Using Real-Time Hand Gesture Recognition and Artificial Intelligence on Raspberry Pi 5
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Aim and Scope
1.2. Research Tasks
- Adapting landmark-based gesture recognition to operate in real time on embedded CPU hardware.
- Constructing a compact, supervised, feed-forward model with a high accuracy whilst remaining TensorFlow Lite compatible.
- Integrating gesture recognition with GPIO-level actuation to realise smart-home control of binary and analogue hardware.
1.3. Contributions
- A fully on-device, Raspberry Pi 5-based implementation of hand-gesture recognition with responsive actuation, both binary and analogue, via GPIO.
- A lightweight training pipeline based on normalised hand landmarks and a modified (logical class merging and removal of unrequired classes) HaGRID dataset.
- Quantified performance (accuracy and frame rate) under specified environmental conditions, demonstrating feasibility for low-cost accessibility control.
1.4. Paper Structure
2. Literature Review
2.1. Overview
2.2. Computer Vision
2.3. Hand Detection
2.4. Gesture Datasets
2.5. The Machine Learning Model
2.6. Model Architecture
3. Technical Tools
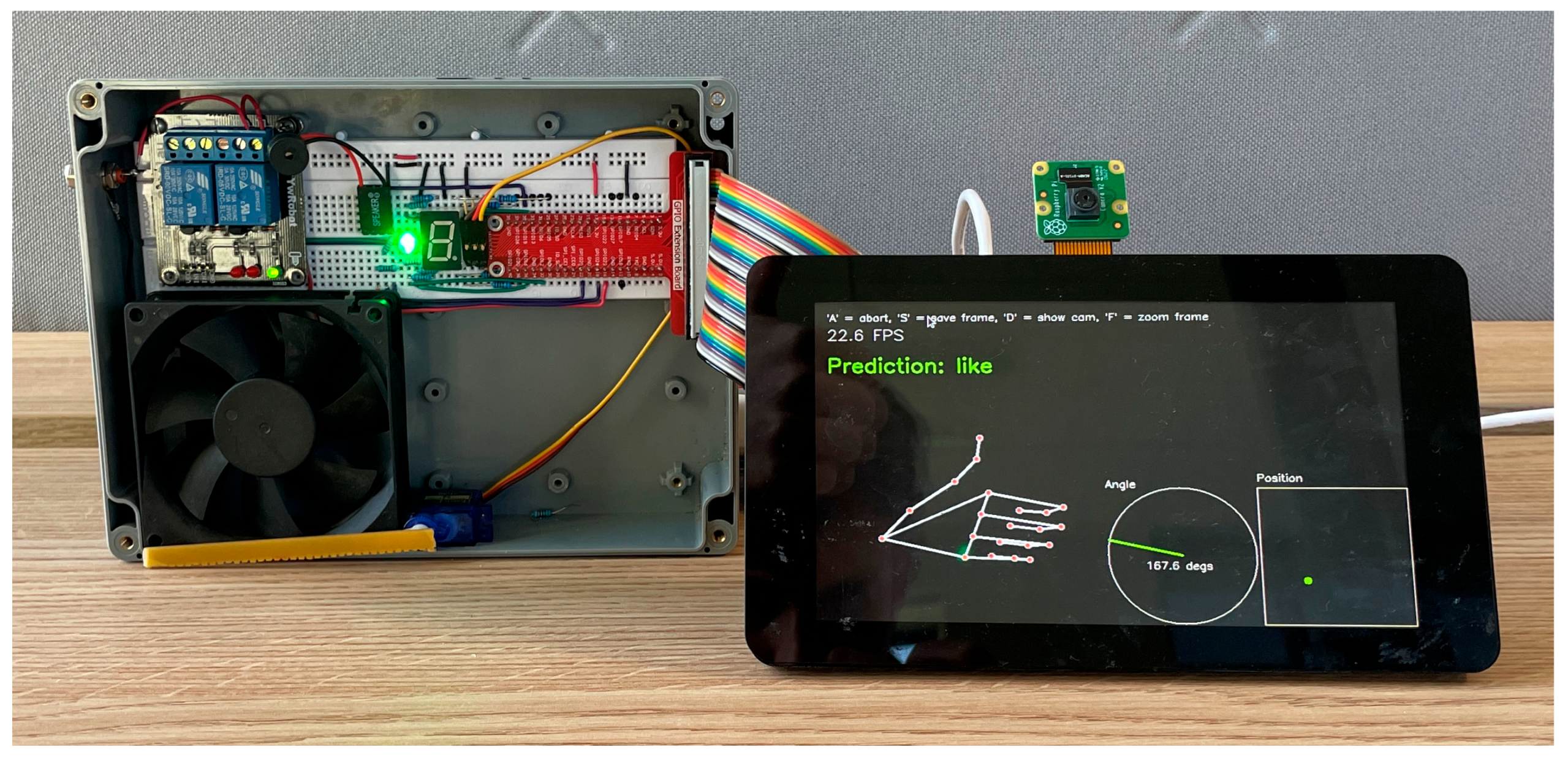
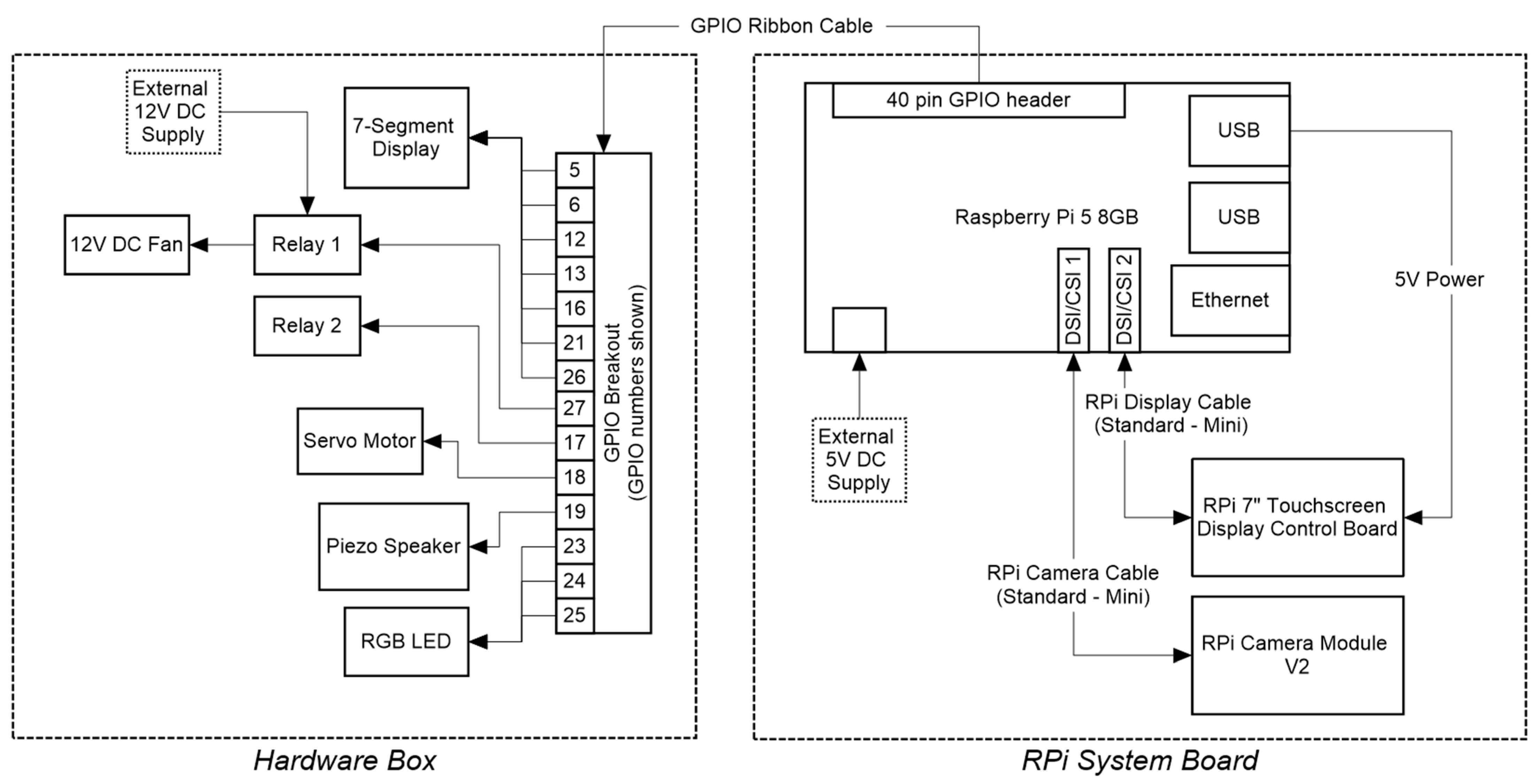
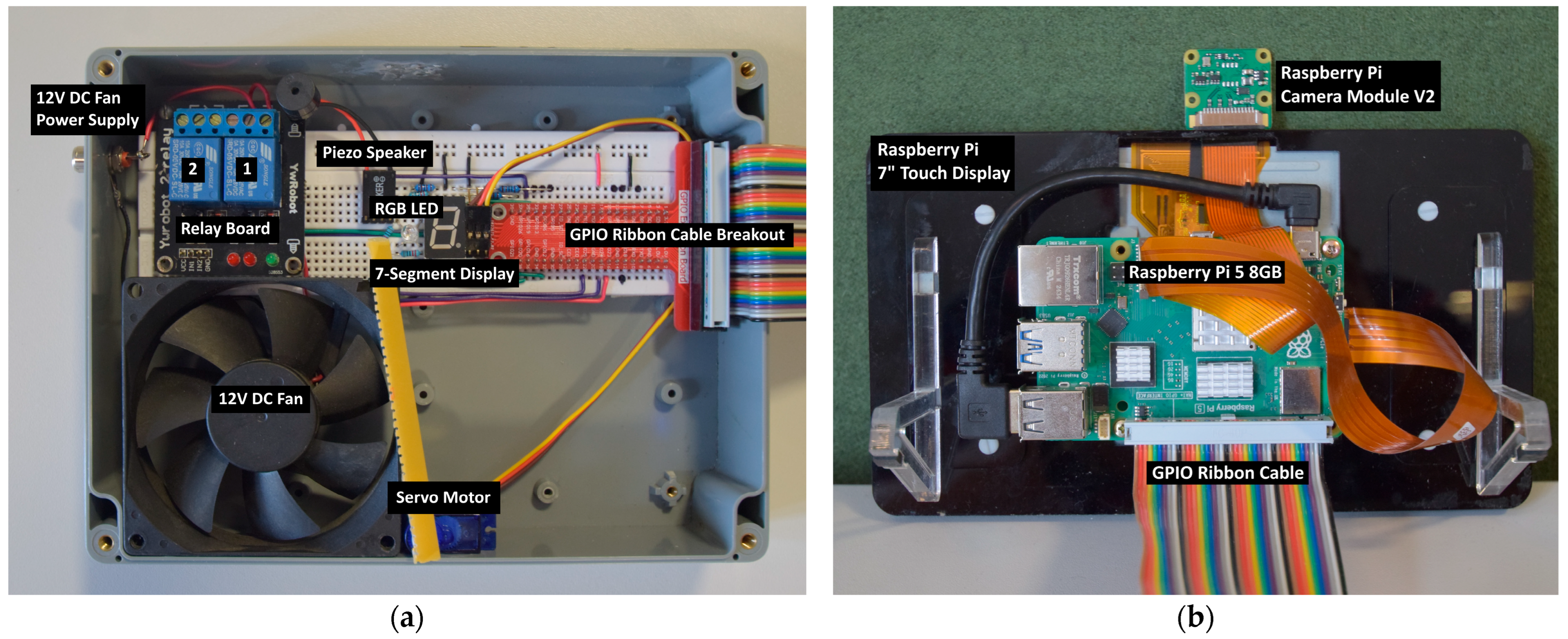
3.1. The Hardware Platform
3.2. Computer Vision
3.3. The Machine Learning Framework
3.4. System Integration
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Real-Time Hand Detection and Display
4.1.1. Camera Interfacing
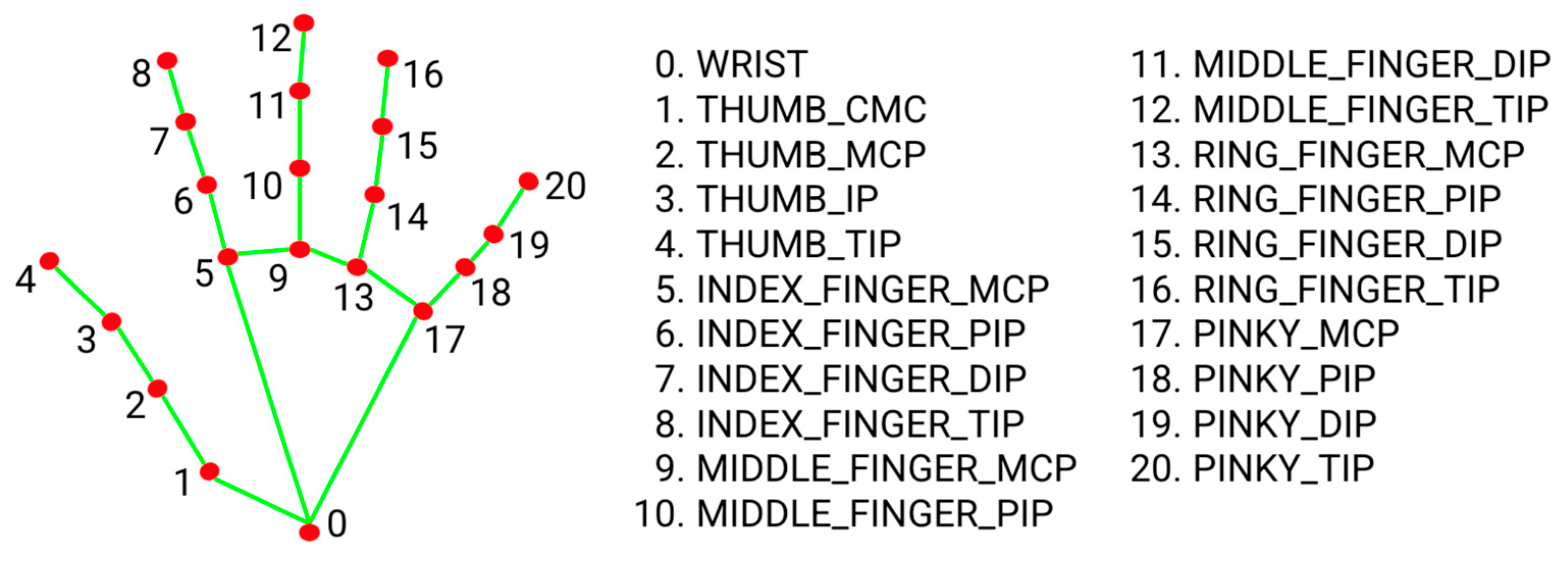
4.1.2. Hand Tracking and Landmark Assignment
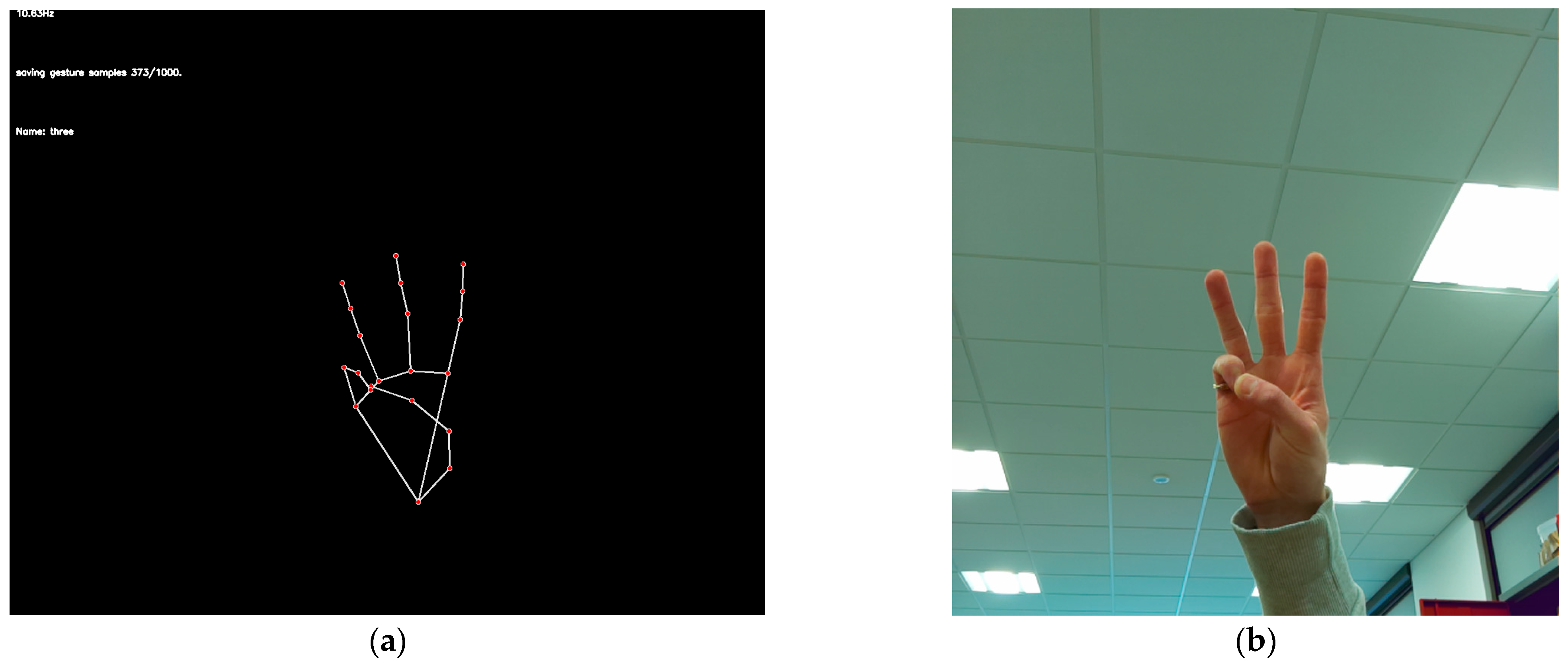
4.1.3. Landmark Display
4.2. Hand Gesture Recognition
4.2.1. Initial Training Data
4.2.2. The Initial Machine Learning Model
4.2.3. Landmark Normalisation
4.2.4. Improved Training Data
4.2.5. Machine Learning Model Development
4.2.6. Machine Learning Model Optimisation
4.3. Home Appliance Control
4.3.1. Binary Devices
4.3.2. Analogue Devices
5. Results
5.1. Real-Time Hand Detection and Display
5.2. Hand Gesture Recognition
5.3. Home Appliance Control
5.3.1. Digital Hardware
5.3.2. Analogue Hardware
6. Discussion
6.1. Conclusions
6.2. Further Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| API | Application Programming Interface |
| IoT | Internet of Things |
| RPi | Raspberry Pi |
| GPIO | General Purpose Input Output |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| BSL | British Sign Language |
| MP | MediaPipe |
| OpenCV | Open-Source Computer Vision Library |
| CV2 | OpenCV Version 2.0+ Python Interface Prefix |
| LED | Light Emitting Diode |
| FPS | Frames Per Second |
| TF | TensorFlow |
| HaGRID | Hand Gesture Recognition Image Dataset |
| CPU | Central Processing Unit |
| GPU | Graphical Processing Unit |
| RAM | Random Access Memory |
| RGB | Red–Green–Blue |
| GB | Gigabyte |
| NP | NumPy |
| ReLU | Rectified Linear Unit |
| PWM | Pulse Width Modulation |
References
- World Health Organization. Deafness and Hearing Loss; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2025; Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/deafness-and-hearing-loss (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- Wren, C.R.; Azarbayejani, A.; Darrell, T.; Pentland, A.P. Pfinder: Real-time tracking of the human body. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1997, 19, 780–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Bazarevsky, V.; Vakunov, A.; Tkachenka, A.; Sung, G.; Chang, C.L.; Grundmann, M. MediaPipe Hands: On-device Real-time Hand Tracking. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.10214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fezari, M.; Dahoud, A.A. Raspberry Pi 5: The New Raspberry Pi Family with More Computation Power and AI Integration. 2023. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/375552555_Raspberry_Pi_5_The_new_Raspberry_Pi_family_with_more_computation_power_and_AI_integration?channel=doi&linkId=654e81a5b86a1d521bcc2f0c&showFulltext=true (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- Culjak, I.; Abram, D.; Pribanic, T.; Dzapo, H.; Cifrek, M. A brief introduction to OpenCV. In Proceedings of the 35th International Convention MIPRO, Opatija, Croatia, 21–25 May 2012; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 1725–1730. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6240859 (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- Gujar, H.; Chile, S.; Shitole, S.; Mhatre, P.; Kadam, S.; Ghanate, S.; Kurle, D. Python based image processing. 2016. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/309208697_Python_Based_Image_Processing (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- van der Walt, S.; Schönberger, J.L.; Nunez-Iglesias, J.; Boulogne, F.; Warner, J.D.; Yager, N.; Gouillart, E.; Yu, T. Scikit-image: Image processing in Python. PeerJ 2014, 2, e453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raspberry Pi Ltd. The Picamera2 Library; Raspberry Pi Ltd.: Cambridge, UK, 2025; Available online: https://datasheets.raspberrypi.com/camera/picamera2-manual.pdf (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- Cao, Z.; Hidalgo, G.; Simon, T.; Wei, S.; Sheikh, Y. OpenPose: Realtime multi-person 2D pose estimation using affinity fields. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1812.08008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.Y.; Lin, Y.N.; Wang, S.K.; Shen, V.R.L.; Tung, Y.C.; Shen, F.H.C.; Huang, C.H. Smart Control of Home Appliances Using Hand Gesture Recognition in an IoT-Enabled System. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 37, 2176607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, A.; Pandey, A.; Mehndiratta, S.; Goyal, H.; Kaushik, P.; Rathore, R. Smart AI based volume control system: Gesture recognition with OpenCV & MediaPipe integration. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Smart Devices, Dehradun, India, 2–3 May 2024; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bora, J.; Dehingia, S.; Boruah, A.; Chetia, A.A.; Gogoi, D. Real-time Assamese Sign Language Recognition using MediaPipe and Deep Learning. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2023, 218, 1384–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Materzynska, J.; Berger, G.; Bax, I.; Memisevic, R. The Jester dataset: A Large-scale video dataset of human gestures. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27–28 October 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuzhdin, A.; Nagaev, A.; Sautin, A.; Kapitanov, A.; Kvanchiani, K. HaGRIDv2: 1M images for static and dynamic hand gesture recognition. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2412.01508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, J. Ultimate Neural Network Programming with Python; Orange Education Pvt Ltd., AVA: Delhi, India, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Paszke, A.; Gross, S.; Massa, F.; Lerer, A.; Bradbury, J.; Chanan, G.; Killeen, T.; Lin, Z.; Gimelshein, N.; Antiga, L.; et al. PyTorch: An imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1912.01703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abadi, M.; Agarwal, A.; Barham, P.; Brevdo, E.; Chen, Z.; Citro, C.; Corrado, G.S.; Davis, A.; Dean, J.; Devin, M.; et al. TensorFlow: Large-scale machine learning on heterogeneous distributed systems. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1603.04467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine learning in Python. arXiv 2012, arXiv:1201.0490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keras. Introducing Keras 3.0. Keras. 2023. Available online: https://keras.io/keras_3/ (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- David, R.; Duke, J.; Jain, A.; Reddi, V.J.; Jeffries, N.; Li, J.; Kreeger, N.; Nappier, I.; Natraj, M.; Regev, S.; et al. TensorFlow Lite Micro: Embedded machine learning on TinyML systems. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2010.08678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remiro, M.Á.; Gil-Martín, M.; San-Segundo, R. Improving Hand Pose Recognition Using Localization and Zoom Normalizations over MediaPipe Landmarks. Eng. Proc. 2023, 58, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ake, A.A.R.; Esomonu, C. Improved Hand Gesture Recognition System Using Keypoints. 2023. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/375594763_Improved_Hand_Gesture_Recognition_System_Using_Keypoints?channel=doi&linkId=655148703fa26f66f4f750ae&showFulltext=true (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- Brownlee, J.; A Gentle Introduction to the Rectified Linear Unit (ReLU). Machine Learning Mastery. 2020. Available online: https://machinelearningmastery.com/rectified-linear-activation-function-for-deep-learning-neural-networks/ (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- Gil-Martín, M.; Marini, M.R.; Martín-Fernández, I.; Esteban-Romero, S.; Cinque, L. Hand gesture recognition using MediaPipe landmarks and deep learning networks. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence, Porto, Portugal, 23–25 February 2025; SciTePress: Setubal, Portugal, 2025; Volume 3, pp. 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, C.R.; Millman, K.J.; van der Walt, S.J.; Gommers, R.; Virtanen, P.; Cournapeau, D.; Wieser, E.; Taylor, J.; Berg, S.; Smith, N.J.; et al. Array programming with NumPy. Nature 2020, 585, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Google AI for Developers [Internet]. Google AI; [Date Unknown]. [Image], Hand Landmarks Detection Guide; [About 2 Screens]. Available online: https://ai.google.dev/edge/mediapipe/solutions/vision/hand_landmarker (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- Raspberry Pi Ltd. Raspberry Pi Camera Module 3; Raspberry Pi Ltd.: Cambridge, UK, 2024; Available online: https://datasheets.raspberrypi.com/camera/camera-module-3-product-brief.pdf (accessed on 28 July 2025).
- Yang, H.; Liu, Z.; Ma, N.; Wang, X.; Liu, W.; Wang, H. CSRM-MIM: A Self-Supervised Pretraining Method for Detecting Catenary Support Components in Electrified Railways. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2025, 11, 10025–10037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, F.; Li, M.; Zhou, N.; Jin, B.; Wang, H.; Yang, H.; Zhang, W. Research on multimodal techniques for arc detection in railway systems with limited data. Struct. Health Monit. 2025, 14759217251336797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



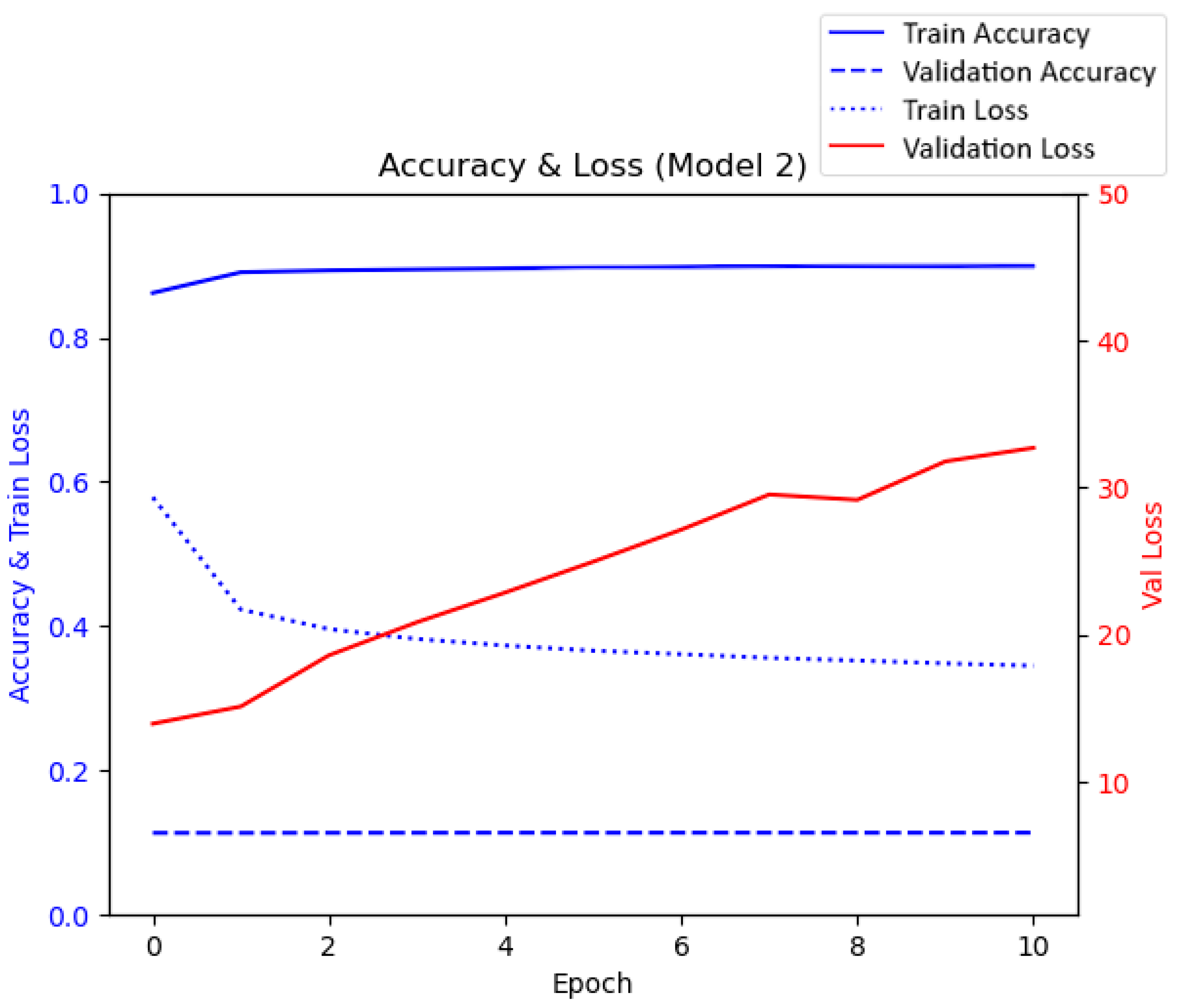


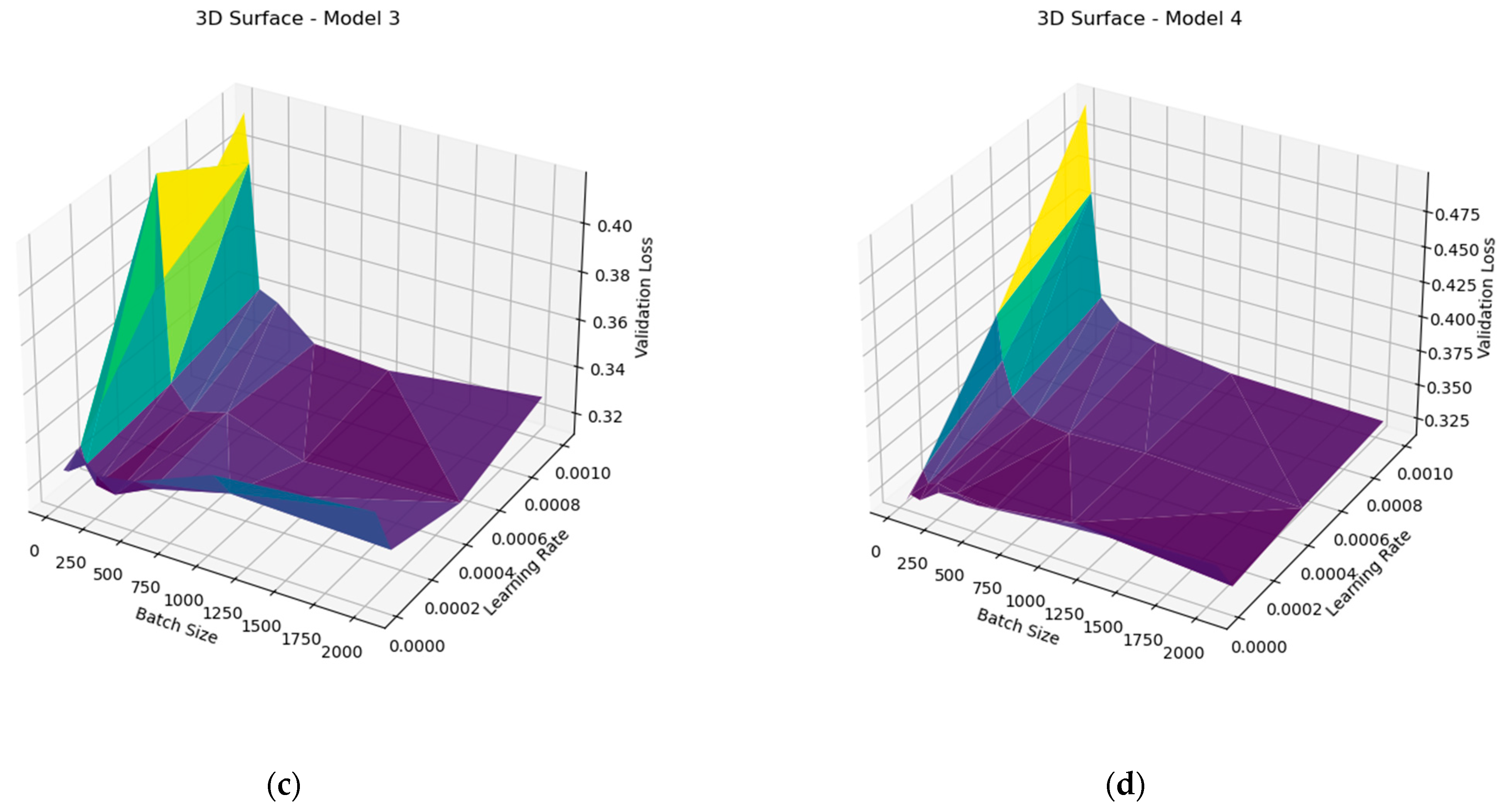
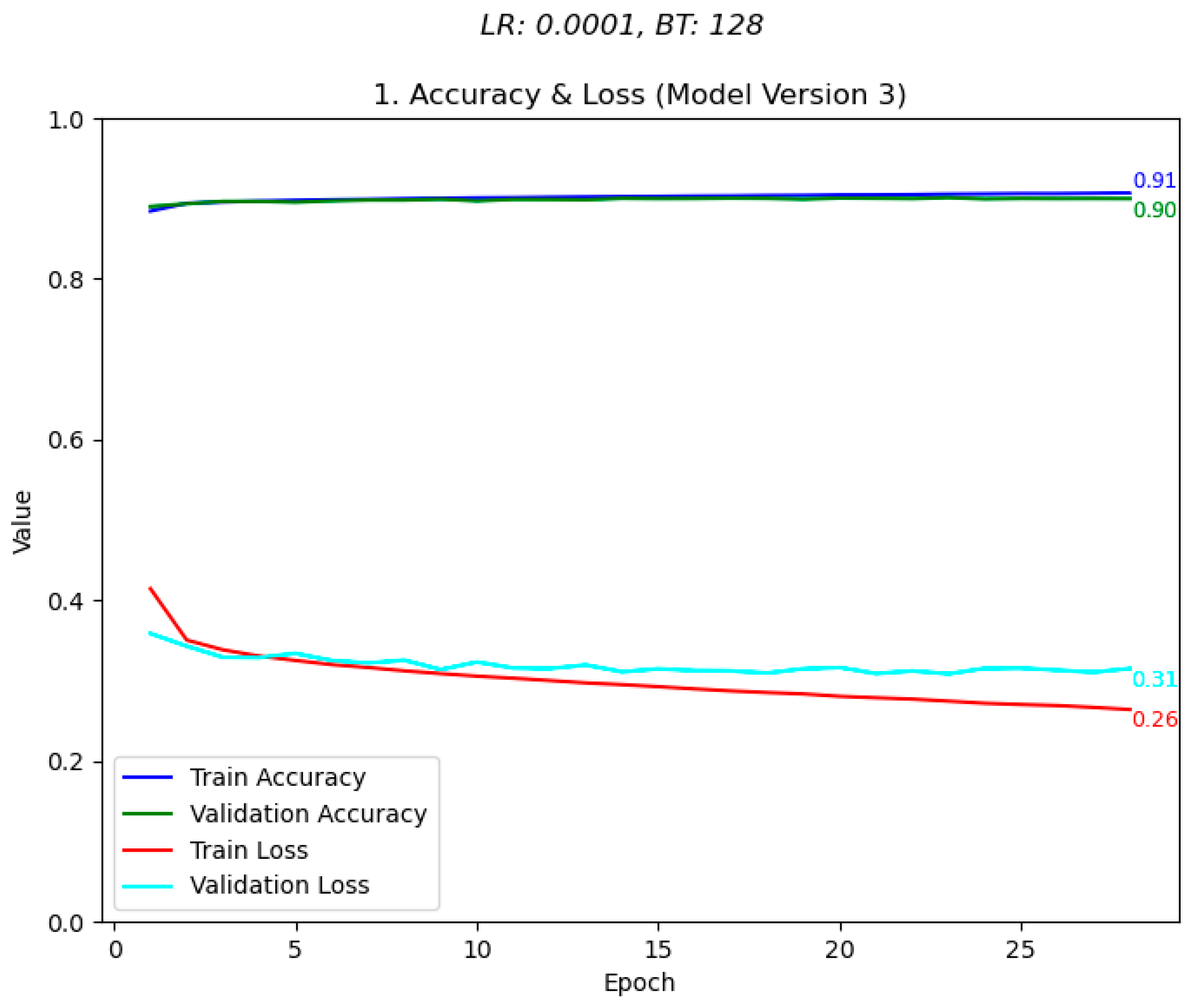

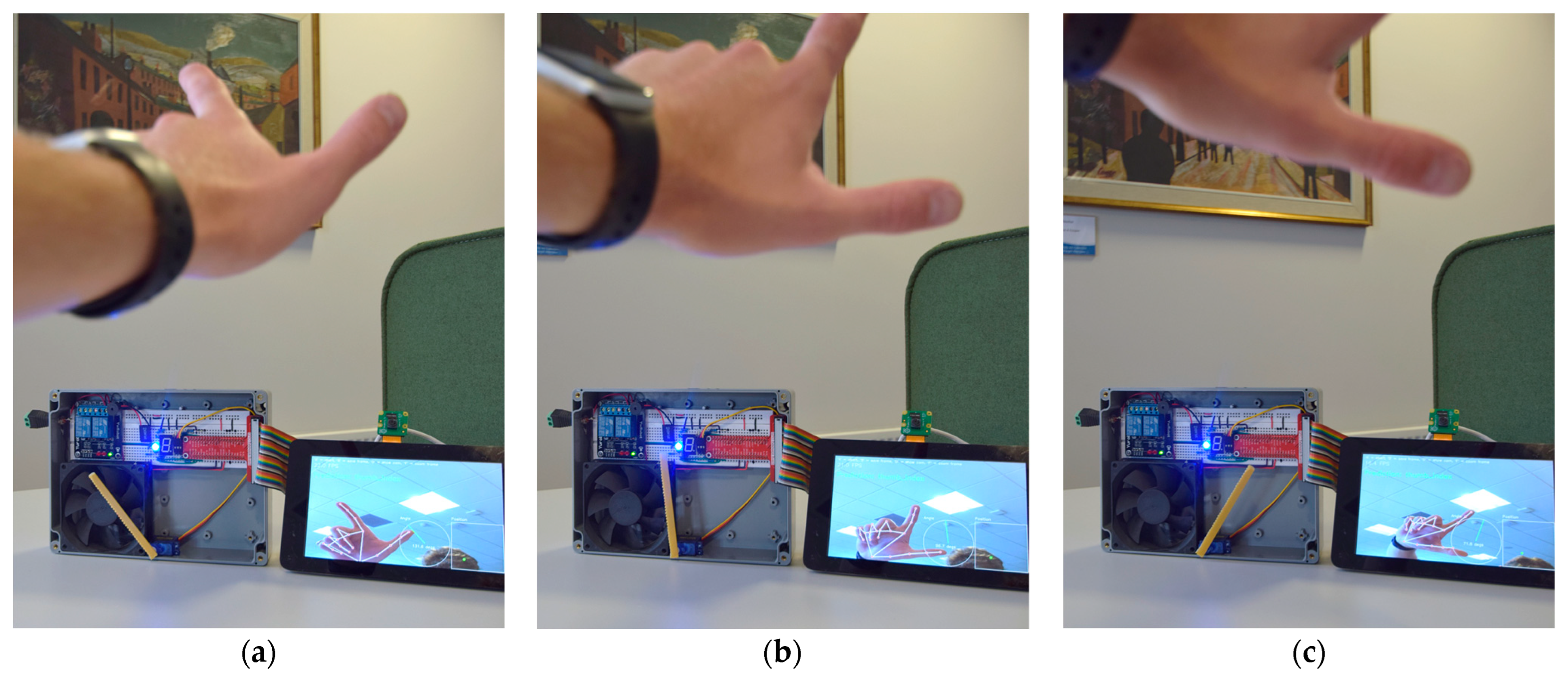

| Rajput’s Initial Keras Model [15] (p. 251) | Modified Keras Model |
|---|---|
| model = Sequential() model.add(Flatten(input_shape = (28, 28))) model.add(Dense(128, activation = ’relu’)) model.add(Dense(128, activation = ’relu’)) model.add(Dense(10, activation = ’softmax’)) | model = Sequential() model.add(Input(shape = (63,))) model.add(Dense(256, activation = ‘relu’)) model.add(Dense(128, activation = ‘relu’)) model.add(Dense(64, activation = ‘relu’)) model.add(Dense(num_classes, activation = ‘softmax’)) |
| ID | Successful Samples | Success Rate | Assigned Name | HaGRID Originals | Assigned Hardware |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 52,783 | 94.050% | Call | Call | Relay 2 |
| 1 | 56,370 | 89.125% | dislike | Dislike | RGB red |
| 2 | 244,279 | 94.222% | Five | stop, stop2, palm, grab | 7-sgmt ‘5’ |
| 3 | 59,229 | 94.206% | Four | Four | 7-sgmt ‘4’ |
| 4 | 71,021 | 97.540% | Grip | Grip | N/A |
| 5 | 56,444 | 90.328% | Like | Like | RGB green |
| 6 | 70,803 | 93.079% | middle | Middle | N/A |
| 7 | 4234 | 97.828% | no_gesture | no_gesture | N/A |
| 8 | 59,215 | 95.039% | ok | Ok | RGB blue |
| 9 | 187,057 | 91.785% | one | one, mute, point | 7-sgmt ‘1’ |
| 10 | 70,908 | 97.667% | pinkie | Pinkie | Piezo speaker |
| 11 | 59,326 | 92.173% | rock | Rock | Relay 1 |
| 12 | 267,291 | 96.674% | three | three, three2, three3 | 7-sgmt ‘3’ |
| 13 | 91,586 | 97.442% | thumbindex | Thumbindex | Servo Motor |
| 14 | 227,499 | 92.987% | two | two, two2, peace, peace2 | 7-sgmt ‘2’ |
| 15 | 57,900 | 91.779% | zero | Fist | 7-sgmt ‘0’ |
| Total | Average | ||||
| 16 | 1,635,945 | 94.120% | |||
| Model Number | Model Details | Python Model Layers |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Initial Model | Dense (256, activation = ‘relu’) Dense (128, activation = ‘relu’) Dense (64, activation = ‘relu’) |
| 2 | Reduced Initial Model | Dense (128, activation = ‘relu’) Dense (64, activation = ‘relu’) |
| 3 | Expanded Initial Model | Dense (1024, activation = ‘relu’) Dense (512, activation = ‘relu’) Dense (256, activation = ‘relu’) Dense (128, activation = ‘relu’) Dense (64, activation = ‘relu’) |
| 4 | Expanded Initial Model with Dropout Layers | Dense (1024, activation = ‘relu’) Dropout (0.3) Dense (512, activation = ‘relu’) Dropout (0.2)) Dense (256, activation = ‘relu’) Dropout (0.1) Dense (128, activation = ‘relu’) Dense (64, activation = ‘relu’) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hobbs, T.; Ali, A. Smart Home Control Using Real-Time Hand Gesture Recognition and Artificial Intelligence on Raspberry Pi 5. Electronics 2025, 14, 3976. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14203976
Hobbs T, Ali A. Smart Home Control Using Real-Time Hand Gesture Recognition and Artificial Intelligence on Raspberry Pi 5. Electronics. 2025; 14(20):3976. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14203976
Chicago/Turabian StyleHobbs, Thomas, and Anwar Ali. 2025. "Smart Home Control Using Real-Time Hand Gesture Recognition and Artificial Intelligence on Raspberry Pi 5" Electronics 14, no. 20: 3976. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14203976
APA StyleHobbs, T., & Ali, A. (2025). Smart Home Control Using Real-Time Hand Gesture Recognition and Artificial Intelligence on Raspberry Pi 5. Electronics, 14(20), 3976. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14203976






