Real-Time True Wireless Stereo Wearing Detection Using a PPG Sensor with Edge AI
Abstract
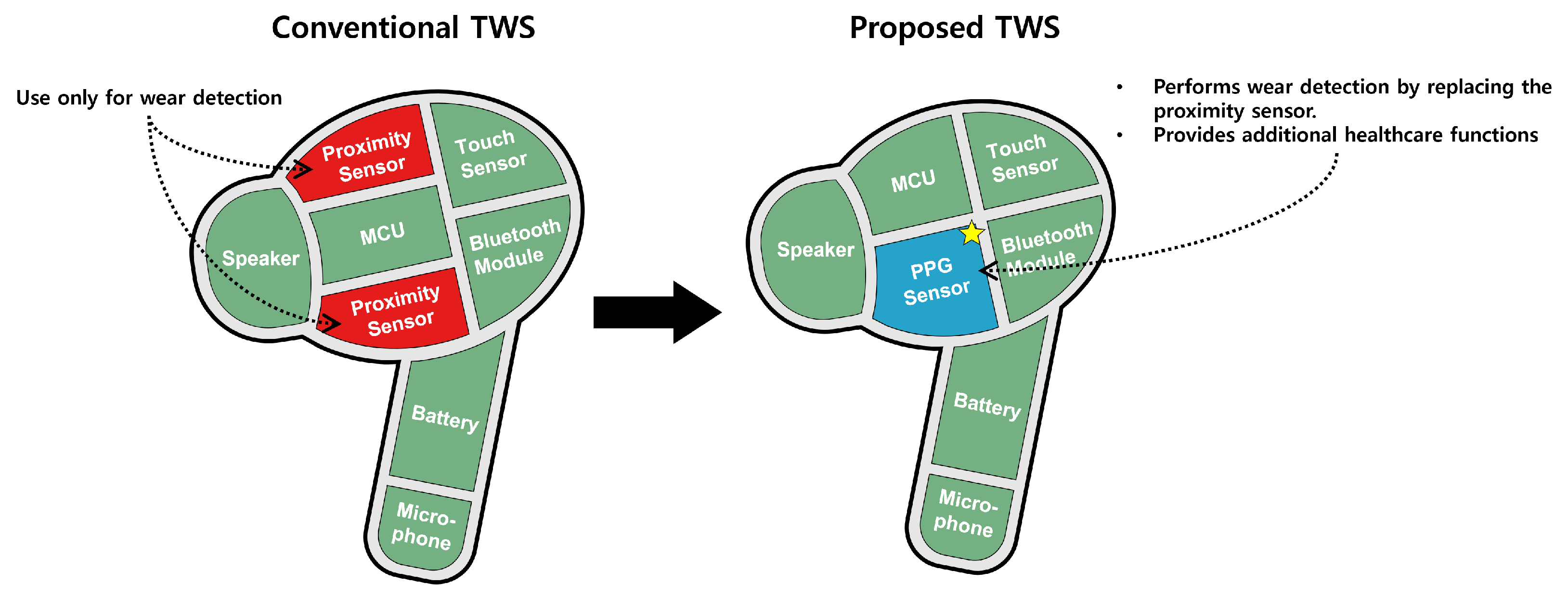
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
3. Photoplethysmography
- Heart rate monitoring;
- SpO2 monitoring;
- Blood pressure monitoring;
- Respiratory rate monitoring.
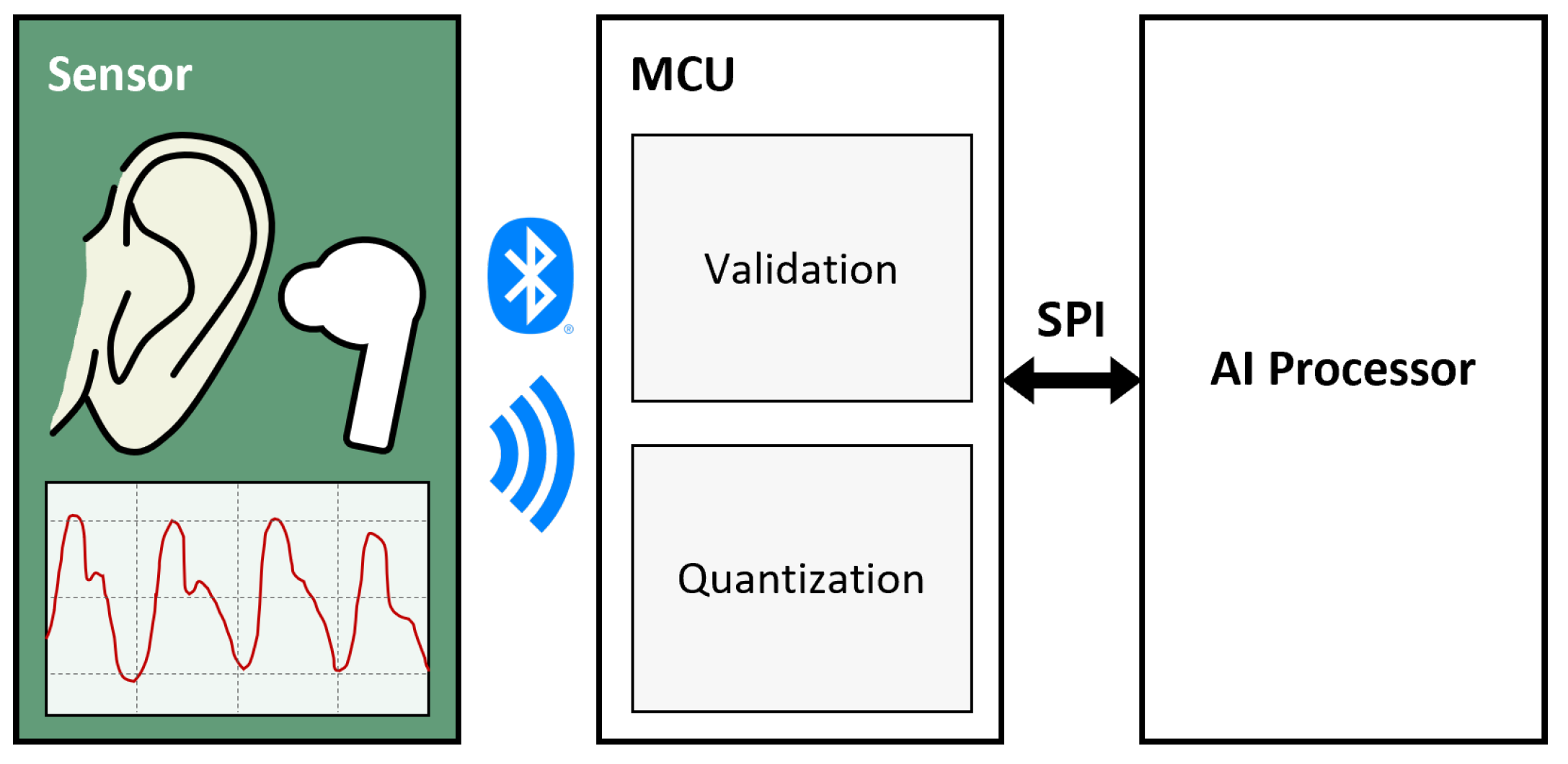
4. Methodology
- 1.
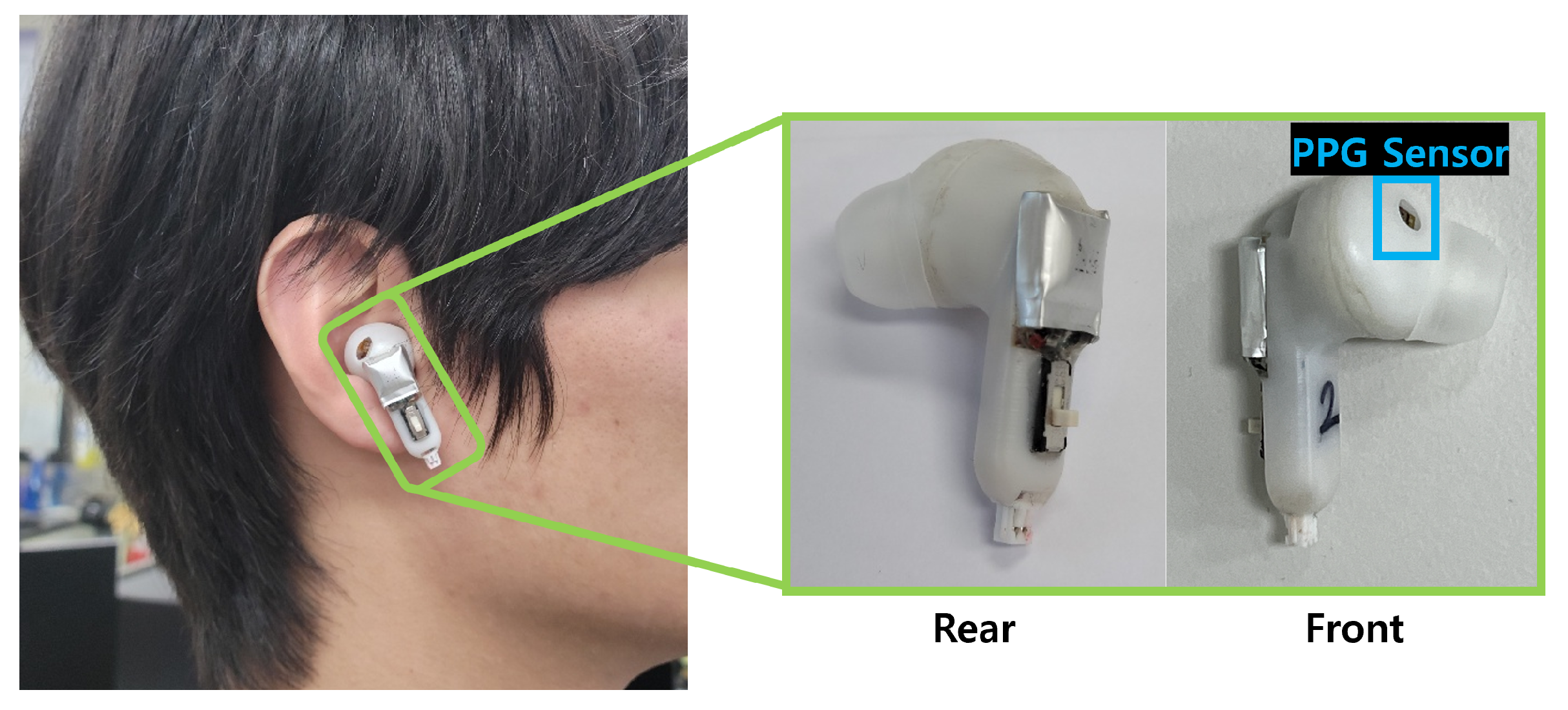
- Signal acquisition: The PPG sensor embedded in the TWS prototype measures blood flow changes in the ear canal. The analog signal is digitized and transmitted to the microcontroller unit (MCU) via Bluetooth.
- 2.
- Segment buffering: The MCU accumulates the incoming signal until a specified segment length is reached, ensuring consistent windowed processing.
- 3.
- Validity check: For each buffered segment, the MCU applies the finite difference method to evaluate signal quality. This step filters out segments corrupted by noise or motion artifacts.
- 4.
- Invalid segment handling: If the data is deemed invalid, the system does not forward it to the AI processor. Instead, the previously inferred result is retained to prevent erroneous changes in classification.
- 5.
- Quantization: When the data is valid, the signal is quantized into 8-bit resolution to reduce computational load while preserving key features.
- 6.
- Data transmission: The quantized segment is transferred from the MCU to the edge AI processor through a serial peripheral interface (SPI), enabling efficient communication.
- 7.
- Classification: The edge AI processor applies the k-nearest neighbor (k-NN) algorithm. For each valid input, distances to the stored training data are computed, and the label with the highest majority vote is assigned. This real-time classification determines the wearing status of the TWS (fully worn, partially worn, or not worn).
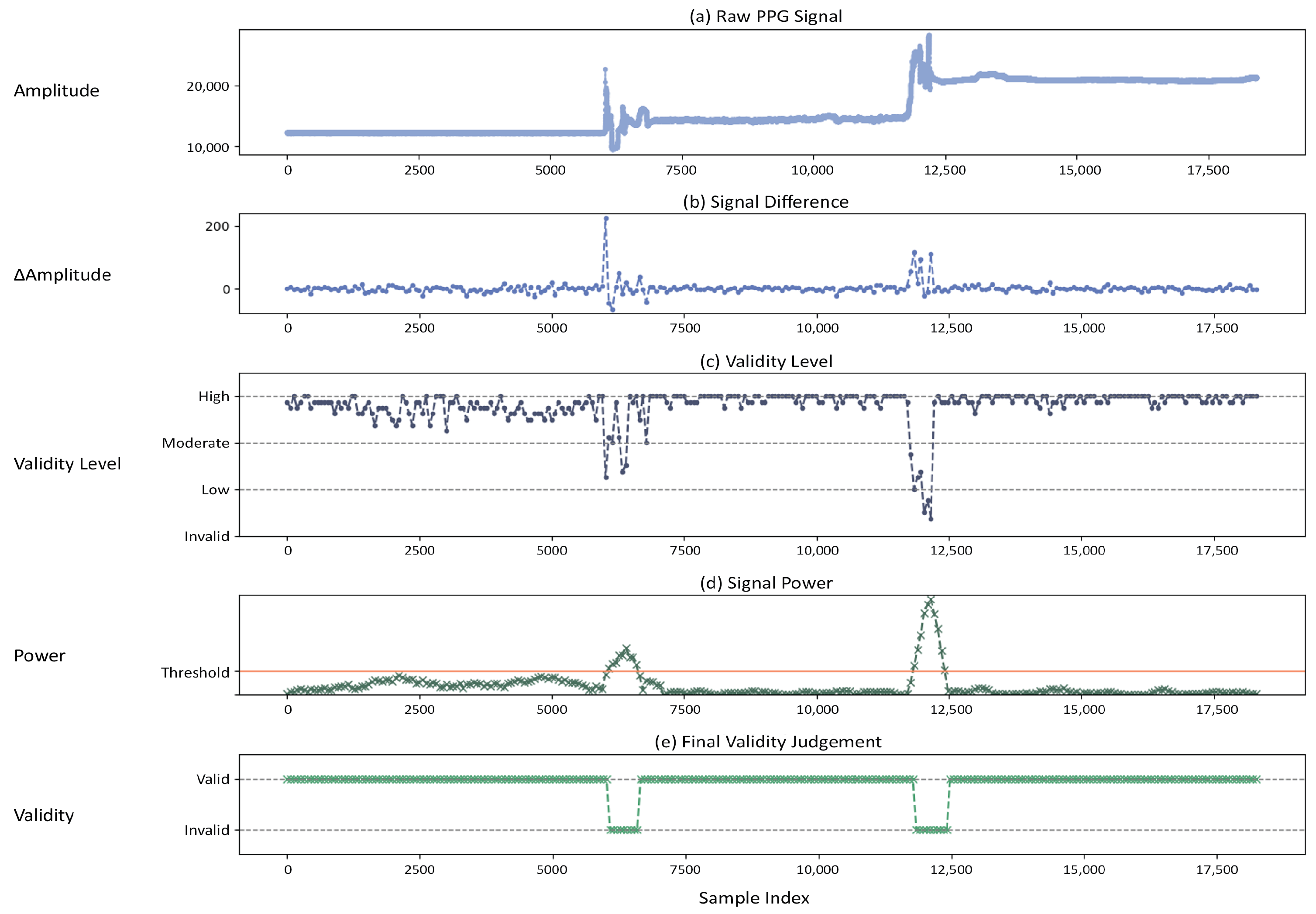
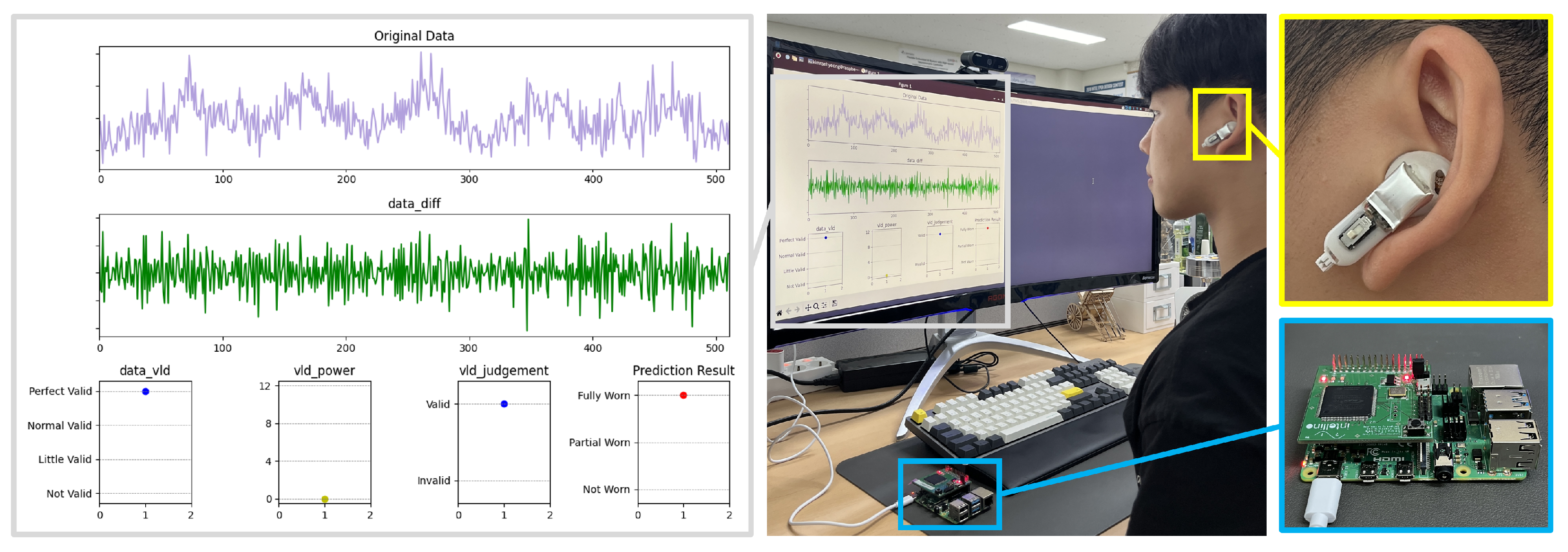
4.1. Validation
- Panel (a) shows the raw data from the PPG sensor, which includes two segments affected by noise.
- Panel (b) shows the signal after applying a finite difference filter, which removes the direct current component and retains only the rate of change.
- Panel (c) computes the absolute value of selected samples, averages them, and classifies the validity into four levels, High, Moderate, Low, and Invalid, based on a predefined threshold.
- Panel (d) assigns different weights to each validity level, sums them, and calculates the signal power, which is then compared against the Validity Threshold.
- Panel (e) presents the Final Validity Judgment as a binary output (Valid or Invalid). In this example, the noisy sections are successfully classified as Invalid. This method is computationally efficient since it avoids complex operations such as multiplication and division, making it well suited for resource-constrained hardware environments such as true wireless stereo (TWS) devices.
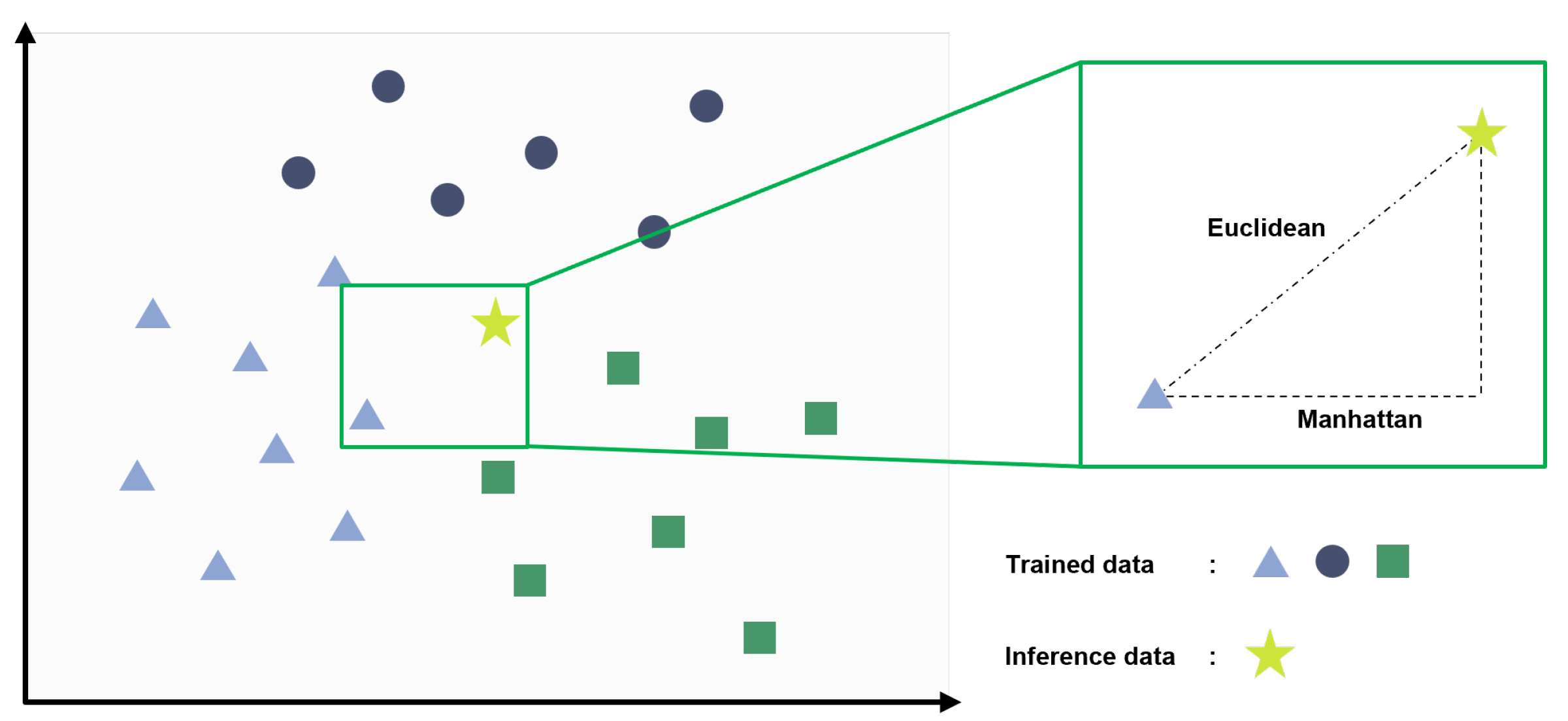
4.2. k-Nearest Neighbor (k-NN)
- Training: Stores all available data points and their corresponding class labels. This phase involves no explicit training processes like parameter estimation in other models, such as neural networks or decision trees.
- Inference: Measures the distance between the input feature vector and each stored training data point. It then identifies the labels of the k-NN and uses majority voting to determine the final classification result.
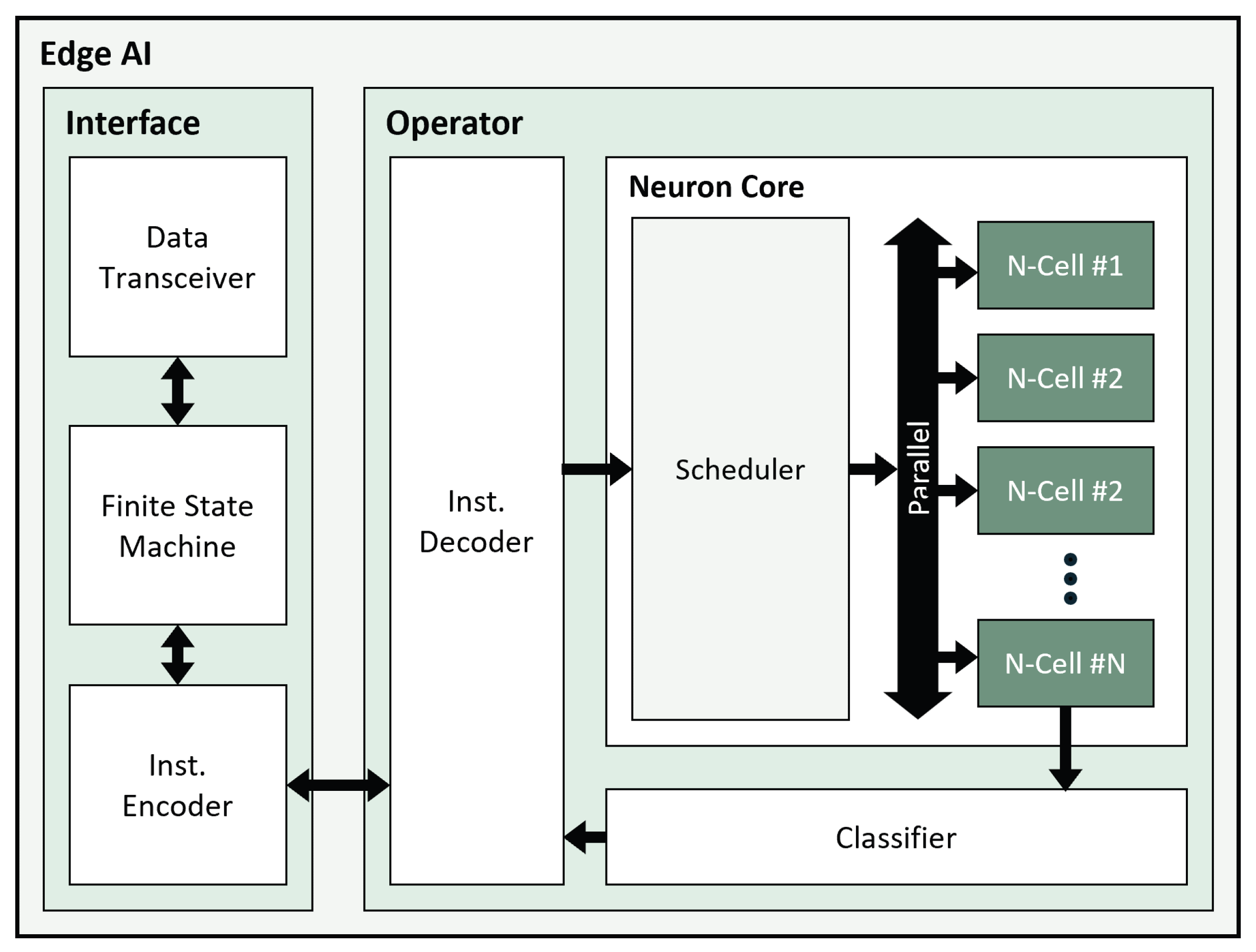
4.3. Edge AI Processor
- Interface: Manages data exchange with external sources, comprising the Data Transceiver, Finite State Machine (FSM), and Instruction Encoder. The Data Transceiver receives datasets or instructions for learning and inference. The FSM interprets the received data per specific protocols, and the Instruction Encoder encodes the interpreted data for transmission to the Operator.
- Operator: Includes the Instruction Decoder, Neuron Core (N-core), and Classifier, performing learning and inference based on input data. The Instruction Decoder processes encoded information about data, categories, distances, and algorithm details, directing the N-core’s operations. N-core, with a Scheduler and parallel-connected Neuron Cells (N-cells), stores training data and corresponding categories during training. In recognition tasks, N-core calculates distances between input data and stored data in each N-cell. Results are sent to the Classifier, which determines the category of the input data based on the smallest distance, utilizing either the k-NN algorithm employed in this paper or the radial basis function neural network algorithm.
5. Experiment
5.1. Data Collection
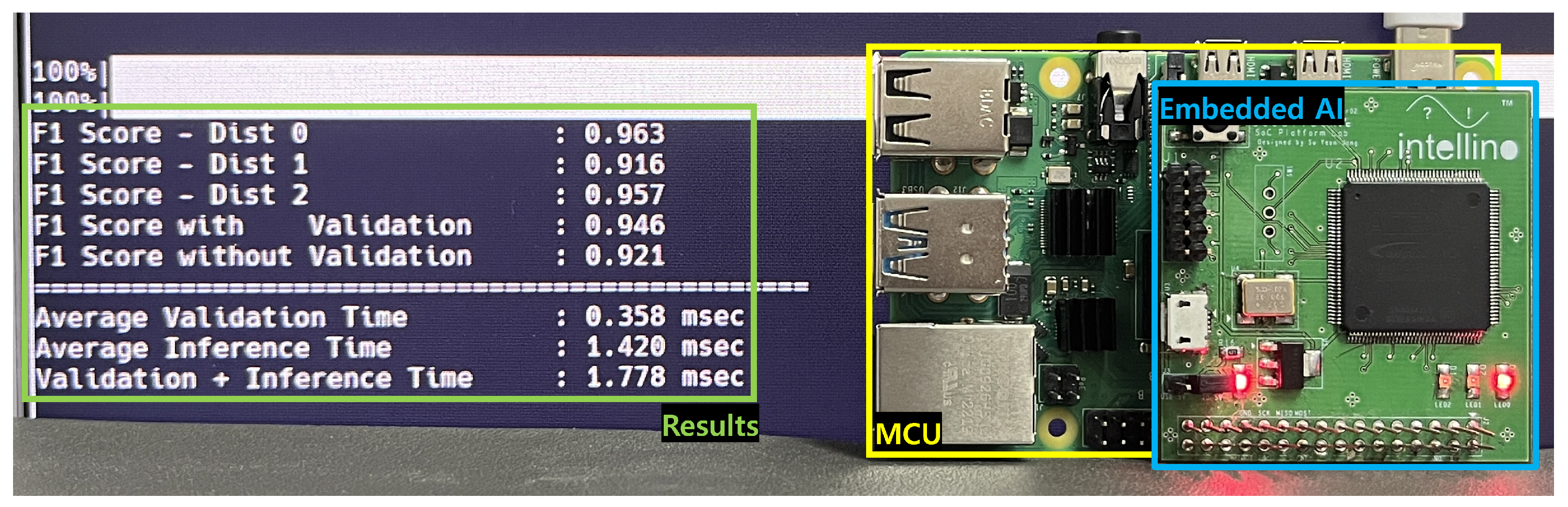
5.2. Implementation
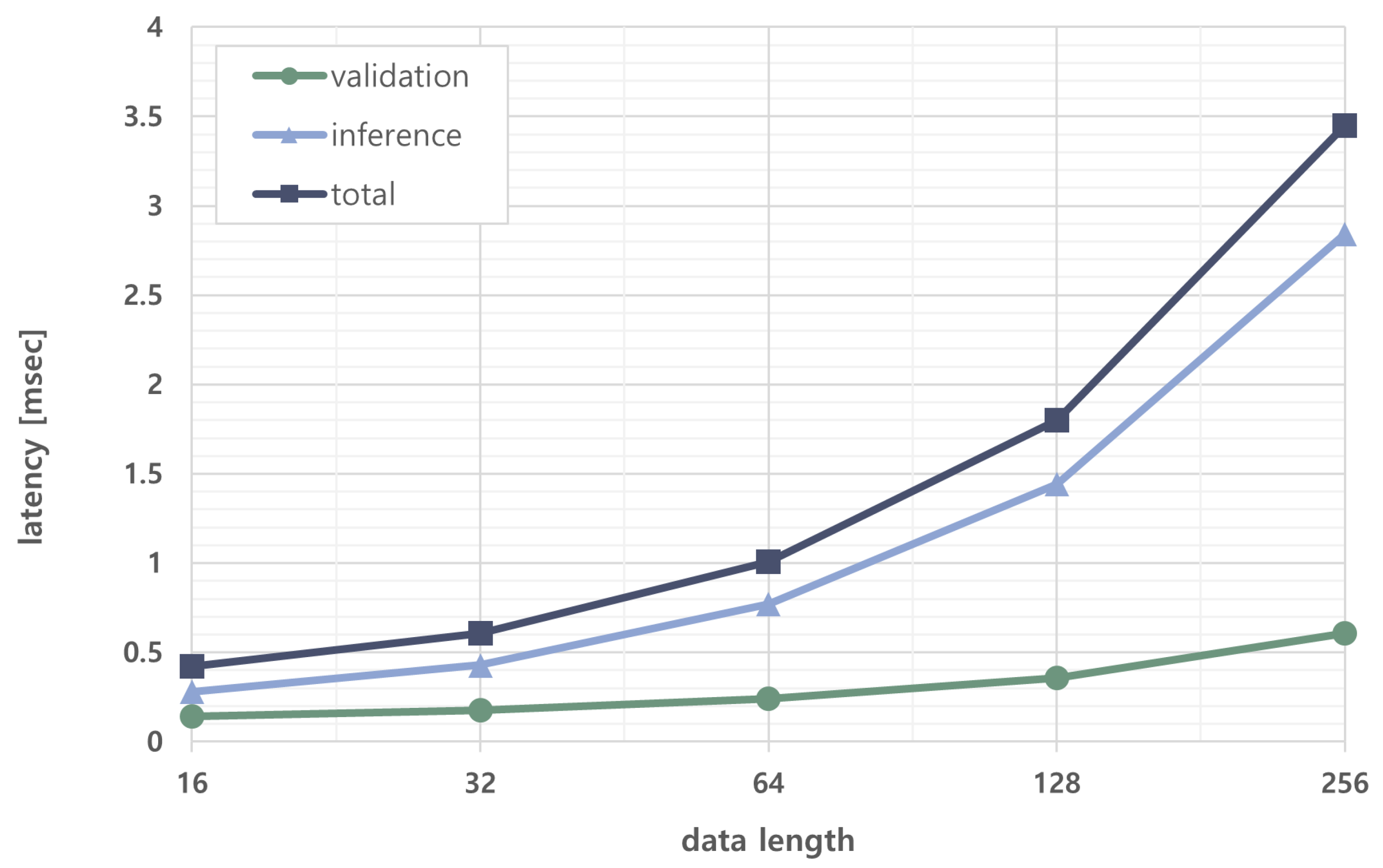
5.3. Evaluation
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alarfaj, A.A.; AlAhmmed, L.M.; Ali, S.I. Perception of earbuds side effects among teenager and adults in Eastern Province of Saudi Arabia: A cross sectional study. Clin. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2021, 12, 100784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röddiger, T.; Clarke, C.; Breitling, P.; Schneegans, T.; Zhao, H.; Gellersen, H.; Beigl, M. Sensing with Earables: A Systematic Literature Review and Taxonomy of Phenomena. Proc. ACM Interact. Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol. 2022, 6, 1–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, S.; Mitra, S.; Gan, W.S. Active noise control system for headphone applications. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2006, 14, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlini, A.; Montanari, A.; Mascolo, C.; Harle, R. Head Motion Tracking Through in-Ear Wearables. In Proceedings of the 1st International Workshop on Earable Computing, New York, NY, USA, 10 September 2019; EarComp’19. pp. 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkiek, K.; Harras, K.A.; Youssef, M. EarGest: Hand Gesture Recognition with Earables. In Proceedings of the 2022 19th Annual IEEE International Conference on Sensing, Communication, and Networking (SECON), Stockholm, Sweden, 20–23 September 2022; pp. 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saulsbury, A.N.; J, M.T. Wireless Ear Buds with Proximity Sensors. U.S. Patent 20230247341A1, 3 August 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Song, H.; Shin, G.W.; Yoon, Y. The Effects of Ear Dimensions and Product Attributes on the Wearing Comfort of Wireless Earphones. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarasinghe, Y.; Sandaruwan, D.; Madusanka, T.; Perera, I.; Meegahapola, L. Multimodal Earable Sensing for Human Energy Expenditure Estimation. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.00517. [Google Scholar]
- Loncar-Turukalo, T.; Zdravevski, E.; Machado da Silva, J.; Chouvarda, I.; Trajkovik, V. Literature on Wearable Technology for Connected Health: Scoping Review of Research Trends, Advances, and Barriers. J. Med. Internet Res. 2019, 21, e14017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakar, A.; Rahim, S.; Razali, A.; Noorsal, E.; Radzali, R.; Abd Rahim, A. Wearable Heart Rate and Body Temperature Monitoring Device for Healthcare. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1535, 012002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, A.; Montree, R.J.H.; Que, S.; Peri, E.; Vullings, R. An Overview of the Sensors for Heart Rate Monitoring Used in Extramural Applications. Sensors 2022, 22, 4035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.H.; Meng, X.; Xiao, X.; Suh, I.Y.; Kim, D.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.W. Triboelectric energy harvesting technology for self-powered personal health management. Int. J. Extrem. Manuf. 2025, 7, 022005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laput, G.; Chen, X.A.; Harrison, C. SweepSense: Ad Hoc Configuration Sensing Using Reflected Swept-Frequency Ultrasonics. In Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Intelligent User Interfaces, New York, NY, USA, 7–10 March 2016; IUI’16. pp. 332–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Shangguan, L.; Rupavatharam, S.; Zhang, Y.; Xiong, J.; Ma, Y.; Howard, R. HeadFi: Bringing intelligence to all headphones. In Proceedings of the 27th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, New York, NY, USA, 25–29 October 2021; MobiCom’21. pp. 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumura, K.; Sakamoto, D.; Inami, M.; Igarashi, T. Universal earphones: Earphones with automatic side and shared use detection. In Proceedings of the 2012 ACM International Conference on Intelligent User Interfaces, New York, NY, USA, 14–17 February 2012; IUI’12. pp. 305–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.; Park, J.; Kwon, S.B.; Lee, S.E. Photoplethysmography-Based Distance Estimation for True Wireless Stereo. Micromachines 2023, 14, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahiya, E.S.; Kalra, A.M.; Lowe, A.; Anand, G. Wearable Technology for Monitoring Electrocardiograms (ECGs) in Adults: A Scoping Review. Sensors 2024, 24, 1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, J. Photoplethysmography and its application in clinical physiological measurement. Physiol. Meas. 2007, 28, R1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancilla-Palestina, D.E.; Jimenez-Duarte, J.A.; Ramirez-Cortes, J.M.; Hernandez, A.; Gomez-Gil, P.; Rangel-Magdaleno, J. Embedded System for Bimodal Biometrics with Fiducial Feature Extraction on ECG and PPG Signals. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference (I2MTC), Dubrovnik, Croatia, 25–28 May 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vostrikov, S.; Benini, L.; Cossettini, A. Complete Cardiorespiratory Monitoring via Wearable Ultra Low Power Ultrasound. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS), Montreal, QC, Canada, 3–8 September 2023; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlesinger, O.; Vigderhouse, N.; Eytan, D.; Moshe, Y. Blood Pressure Estimation From PPG Signals Using Convolutional Neural Networks And Siamese Network. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2020—2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 4–9 May 2020; pp. 1135–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, T.; Elahi, A.; Ganly, S.; Wijns, W.; Shahzad, A. Photoplethysmography-Based Respiratory Rate Estimation Algorithm for Health Monitoring Applications. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 2022, 42, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagha, S.; Shaw, L. A Real Time Analysis of PPG Signal for Measurement of SpO2 and Pulse Rate. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2011, 36, 45–50. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, V. Mental Stress Assessment Using PPG Signal a Deep Neural Network Approach. IETE J. Res. 2020, 69, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vulcan, R.S.; André, S.; Bruyneel, M. Photoplethysmography in Normal and Pathological Sleep. Sensors 2021, 21, 2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlini, A.; Montanari, A.; Min, C.; Li, H.; Sassi, U.; Kawsar, F. In-Ear PPG for Vital Signs. IEEE Pervasive Comput. 2022, 21, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azudin, K.; Gan, K.B.; Jaafar, R.; Ja’afar, M.H. The Principles of Hearable Photoplethysmography Analysis and Applications in Physiological Monitoring—A Review. Sensors 2023, 23, 6484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, S.; Boukhayma, A.; Caizzone, A. Ear and Finger PPG Wearables for Night and Day Beat-to-Beat Interval Detection. In Proceedings of the 2021 43rd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Virtual, 1–5 November 2021; pp. 1686–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivanjaneyulu, Y.; Manikandan, M.S.; Boppu, S. CNN Based PPG Signal Quality Assessment Using Raw PPG Signal for Energy-Efficient PPG Analysis Devices in Internet of Medical Things. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence of Things (ICAIoT), Istanbul, Turkey, 29–30 December 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Singh, A.; Sharma, A. Denoising and Analysis of PPG Acquired From Different Body Sites Using Savitzky Golay Filter. In Proceedings of the TENCON 2022—2022 IEEE Region 10 Conference (TENCON), Hong Kong, China, 1–4 November 2022; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, R.; Mehmood, A.; Rahman, M.M.U.; Dobre, O.A. A Deep Learning and Fast Wavelet Transform-Based Hybrid Approach for Denoising of PPG Signals. IEEE Sens. Lett. 2023, 7, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, Y. Asynchronous noise removal for earbud-based PPG sensors. In Proceedings of the 2016 38th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Orlando, FL, USA, 16–20 August 2016; pp. 259–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, L.E. K-nearest neighbor. Scholarpedia 2009, 4, 1883, revision #137311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, Y.H.; Hwang, D.H.; Yang, J.H.; Lee, S.E. Intellino: Processor for Embedded Artificial Intelligence. Electronics 2020, 9, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Shin, J.; Kim, R.; An, S.; Lee, S.; Kim, J.; Oh, J.; Jeong, Y.; Kim, S.; Jeong, Y.R.; et al. Accelerating Strawberry Ripeness Classification Using a Convolution-Based Feature Extractor along with an Edge AI Processor. Electronics 2024, 13, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Park, J.; Jeong, Y.; Lee, S.E. Intelligent Monitoring System with Privacy Preservation Based on Edge AI. Micromachines 2023, 14, 1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.Y.; Ho Lee, S.; Go, K.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.E. AI Processor based Data Correction for Enhancing Accuracy of Ultrasonic Sensor. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 5th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence Circuits and Systems (AICAS), Hangzhou, China, 11–13 June 2023; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Go, K.H.; Han, C.Y.; Cho, K.N.; Lee, S.E. Crime Prevention System: Crashing Window Sound Detection Using AI Processor. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics (ICCE), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 10–12 January 2021; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Source | Sensor | Proposed Approach | Pros | Cons | Acc. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [13] Laput, G. et al., 2016 | speaker, microphone | Emit an inaudible frequency through a speaker and monitor the frequency with a microphone. | Use only the built-inspeaker and microphone. | Sound leakage occurs if the earbuds are partially inserted, making accurate predictions difficult. | 94.8% |
| [14] Fan, X. et al., 2021 | speaker, microphone | Measure ambient noise resonance when wearing headphones | Not sensitive to noise. | Requires additional pairing devices. | 97.93% |
| [15] Matsumura, K. et al., 2012 | skin conductance sensor | Detect the wearing of both earphones by measuring microcurrent flow through the body when both are worn. | Achieves high accuracy by directly measuring the current flowing through the skin. | Requires both earphones to determine wearing status; low utility of skin conductivity sensors. | - |
| [16] Jeong, Y. et al., 2023 | PPG sensor | Classify PPG input data based on the wearing condition with a WA filter and MobileNet. | Classifies wearing status with a single PPG sensor. | Does not account for noise generated by movement. | 92.5% |
| 16 | 32 | 64 | 128 | 256 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| With validation | 0.913 | 0.936 | 0.950 | 0.953 | 0.967 |
| Without validation | 0.914 | 0.914 | 0.915 | 0.911 | 0.907 |
| 16 | 32 | 64 | 128 | 256 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fully worn | 0.894 | 0.941 | 0.971 | 0.974 | 0.982 |
| Partially worn | 0.909 | 0.933 | 0.923 | 0.928 | 0.950 |
| Not worn | 0.937 | 0.934 | 0.956 | 0.957 | 0.968 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, R.; Park, J.; Kim, J.; Oh, J.; Lee, S.E. Real-Time True Wireless Stereo Wearing Detection Using a PPG Sensor with Edge AI. Electronics 2025, 14, 3911. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14193911
Kim R, Park J, Kim J, Oh J, Lee SE. Real-Time True Wireless Stereo Wearing Detection Using a PPG Sensor with Edge AI. Electronics. 2025; 14(19):3911. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14193911
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Raehyeong, Joungmin Park, Jaeseong Kim, Jongwon Oh, and Seung Eun Lee. 2025. "Real-Time True Wireless Stereo Wearing Detection Using a PPG Sensor with Edge AI" Electronics 14, no. 19: 3911. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14193911
APA StyleKim, R., Park, J., Kim, J., Oh, J., & Lee, S. E. (2025). Real-Time True Wireless Stereo Wearing Detection Using a PPG Sensor with Edge AI. Electronics, 14(19), 3911. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14193911







