Timekeeping Method with Dual Iterative Algorithm for GNSS Disciplined OCXO
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. OCXO Disciplined and Timekeeping System
3. Methodology
3.1. Timekeeping Model for OCXO
3.2. External Iterative Algorithm
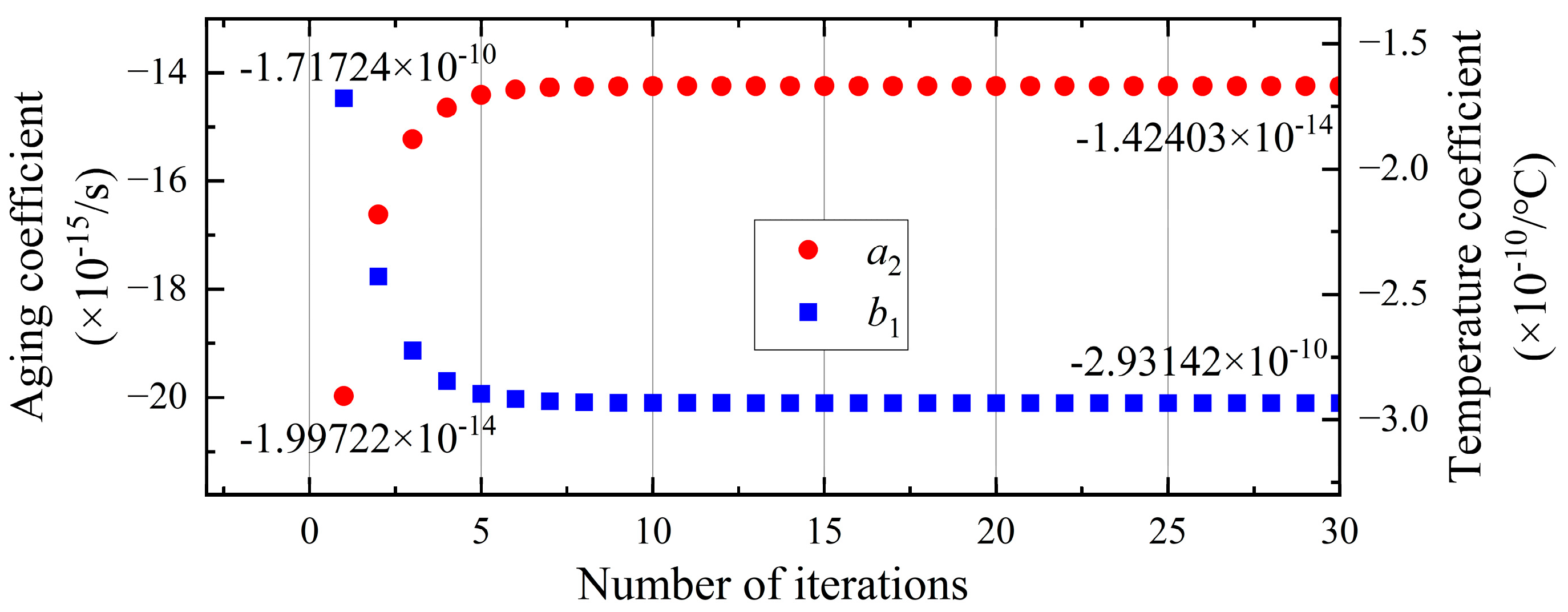
3.3. Internal Gauss–Seidel Iterative Algorithm
4. Experimental Validation and Result Analysis
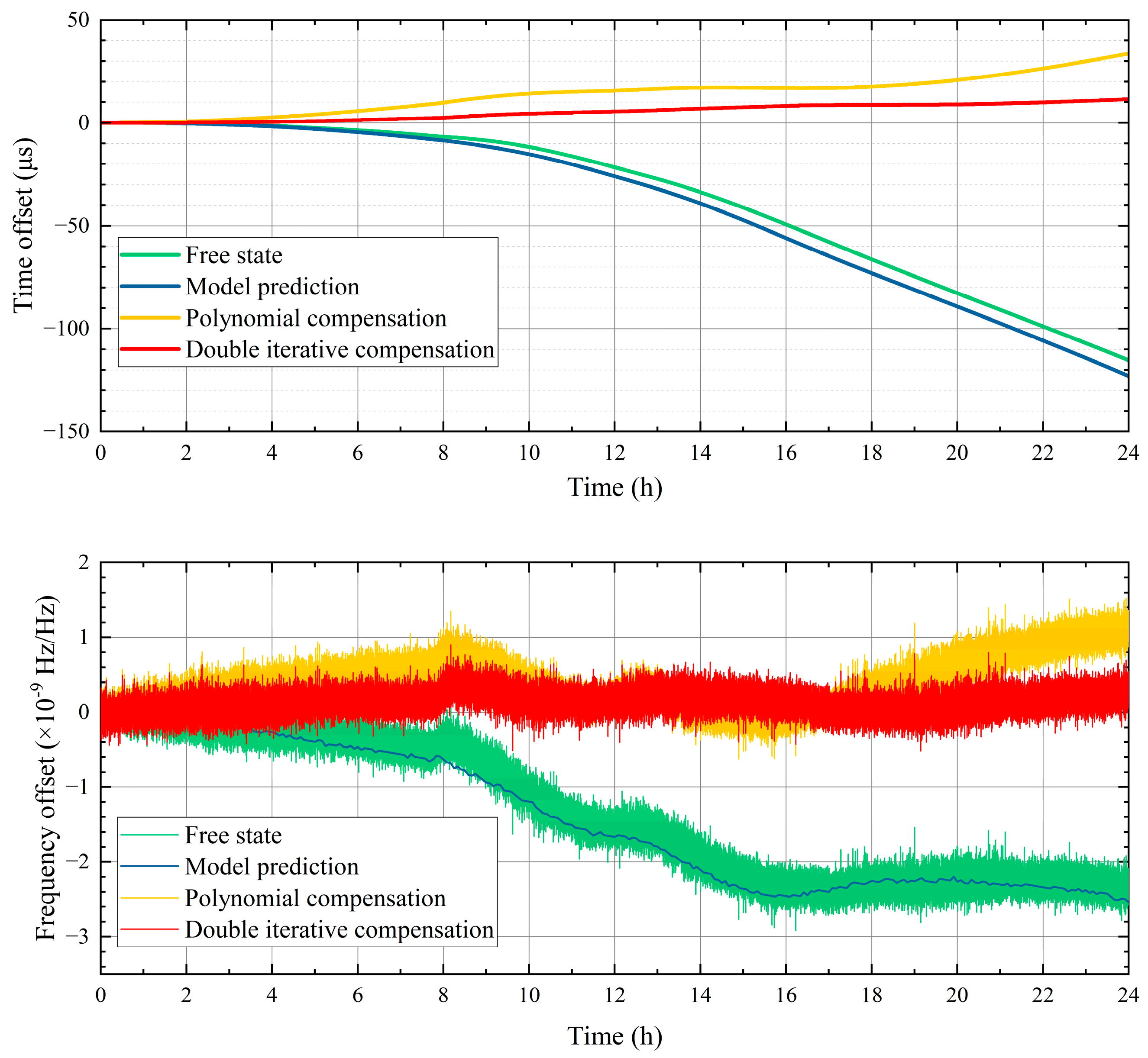
4.1. Experiment to Study the Timekeeping Capability of the Method
4.2. Effect of Disciplined Time on Timekeeping Capability
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GNSS | Global navigation satellite system |
| OCXO | Oven-controlled crystal oscillator |
| IEC | International Electrotechnical Commission |
| UTC | Universal Time Coordinated |
| DAC | Digital-to-analog converter |
References
- Meng, Y.S.; Lei, W.Y.; Bian, L.; Yan, T.; Wang, Y. Clock tuning technique for a disciplined high medium–long-stability GNSS oscillator with precise clock drifts for LEO users. GPS Solut. 2020, 24, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, X.W.; Cong, L.; Dong, X.H. Time synchronization error analysis and evaluation of TH-2 satellite. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2022, 51, 2455–2461. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.M. Research and Design of Key Technologies for Physical Layer to 5G V2X Standardization. Ph.D. Thesis, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.J.; Wu, Y.Y.; Zhang, J.X. Attitude synchronization control for multiple spacecraft: A preassigned finite-time scheme. Adv. Space Res. 2024, 73, 6094–6110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, X.; Liu, T.; Jiang, W.; Wang, J. Design of Universal Code Generator for Multi-Constellation Multi-Frequency GNSS Receiver. Electronics 2024, 13, 1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedi, A.A.; Mosavi, M.R. Low Computational-Complexity vector tracking for Low-Cost GNSS receivers. Measurement 2022, 195, 111171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eghtesadi, M.; Mosavi, M.R. A Pseudo-Differential LNA with Noise Improvement Techniques for Concurrent Multi-Band GNSS Applications. Electronics 2024, 13, 2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yu, X.; Guo, S. Inversion and characteristics of unmodeled errors in GNSS relative positioning. Measurement 2022, 195, 111151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Crystal Vibrators in Consumer Electronics Industry Market Space Measurement 2023. Available online: https://wenku.baidu.com/view/52098505b007e87101f69e3143323968011cf439.html?_wkts_=1752744636839 (accessed on 16 September 2023).
- Shi, C.; Zheng, F.; Lou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, D.; Song, W.; Wang, M.; Lin, Y.; et al. Theoretical approach and application of BeiDou high-precision time-frequency service. J. Wuhan Univ. Inf. Sci. Ed. 2023, 48, 1010–1018. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Peng, L.F. Constant temperature crystal taming method based on GPS/BDS dual mode receiver. GNSS World China 2021, 46, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, G. Research on GNSS Disciplined Crystal Oscillator and Holdover Technologies. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.X.; Ren, X.; Jia, X.L.; Sun, B.J. Development trends of the national secure PNT system based on BDS. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2023, 53, 917–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.H.; Zhao, Y. Crystal Oscillator; Science Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, B.; Lin, Y. Resilient timekeeping algorithm with multi-observation fusion Kalman filter. Satell. Navig. 2023, 4, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Wang, B.; Han, C. Resilient evaluation algorithm of caesium fountain clock based on robust adaptive observation model. Phys. Scr. 2023, 98, 115411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DIN EN IEC 62884-3; Measurement Techniques of Piezoelectric, Dielectric and Electrostatic Oscillators—Part 3: Frequency Aging Test Methods (IEC 62884-3:2018). German Version EN IEC 62884-3:2018. 2018. Available online: https://standards.cencenelec.eu/dyn/www/f?p=CENELEC:110:::::FSP_PROJECT,FSP_ORG_ID:64599,1258061&cs=10CCB2865C70EC9844C7794C8CE72DCBB (accessed on 15 July 2025).
- Xue, C. Analysis on Characteristics and Standard Demand of Crystal Oscillator Analysis on Characteristics and Standard Demand of Crystal Oscillator. China Stand. 2020, 201, 153–157. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, D.S.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.H. Crystal oscillator disciplined method based on Kalman filter. Time Freq. 2019, 42, 224–229. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Y.J. Study on the Taming and Holding Technology of the Oven Controlled Crystal Oscillator. Ph.D. Thesis, Xidian University, Xi’an, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H. Research on High Stability Crystal Taming and Holding System Based on GPS 1PPS. Ph.D. Thesis, Xi’an University of Science and Technology, Xi’an, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, W.F.; Gong, Q.R.; Zhu, M.M.; Shi, C. Method and performance of time timekeeping for RT-PPT receivers utilizing on-line estimation of clock parameters. GPS Solut. 2024, 28, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Y.; Zhang, Y.J. A Greedy Gauss-Seidel Method for Solving the Large Linear Least Squares Problem. Tongji Univ. Nat. Sci. 2021, 49, 1514–1521. [Google Scholar]
- Kunzi, F.; Montenbruck, O. Precise disciplined of a chip-scale atomic clock using PPP with broadcast ephemerides. GPS Solut. 2023, 27, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.Y. Analysis of Atomic Clock Performance and Clock Difference Prediction Algorithm. Master’s Thesis, Xi’an University of Science and Technology, Xi’an, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.W. Research on Algorithms of Precisie Clock Offset and Quality Evaluation of GNSS Satellite Clocks A. Ph.D. Thesis, Chang’an University, Xi’an, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, G.S. Method and Apparatus to Improve Performance of GPSDO’s and Other Oscillators. U.S. Patent US8362845 B2, 29 January 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, Z.Y. Research on a Clock Disciplining and Holding System Based on Beidou Time Service. Ph.D. Thesis, Xidian University, Xi’an, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, Z.; Lu, J.F. Fundamentals of Numerical Analysis, 3rd ed.; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2010; pp. 79–82. [Google Scholar]
- Li, A.Q. Iterative solution of systems of linear equations. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2007, 14, 3357–3364. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.Q. Atomic Clocks and Time-Frequency Systems: An Anthology; National Defense Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]





| Free State | Second-Order Polynomial | Proposed Method | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Drift rate of frequency (/s) | −3.48 × 10−14 | 5.15 × 10−15 | 8.33 × 10−16 |
| Improvement percentage | 85.20% | 97.61% |
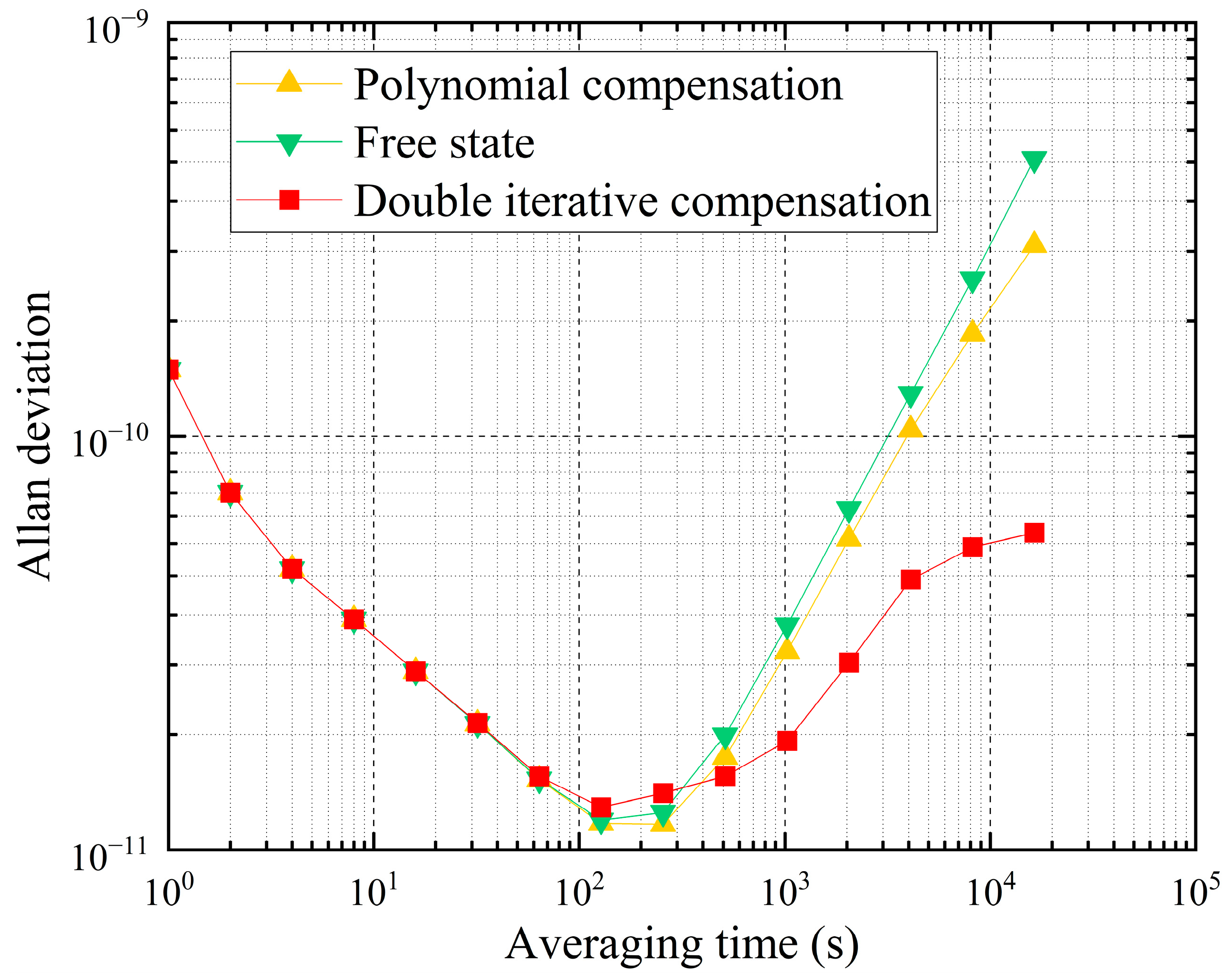
| Tau | 512 | 1024 | 2048 | 4096 | 8192 | 16,384 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Free state (×10−11) | 1.89 | 3.50 | 6.68 | 12.7 | 24.0 | 46.9 |
| Compensated (×10−11) | 1.51 | 1.84 | 2.84 | 4.50 | 5.39 | 5.85 |
| Improvement (%) | 20.45 | 47.52 | 57.52 | 64.47 | 77.49 | 87.53 |
| Free State | 24 h | 48 h | 72 h | 96 h | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drift rate (×10−15/s) | −34.8 | 0.833 | −2.04 | −2.30 | −2.88 |
| Improvement (%) | 97.61 | 94.15 | 93.40 | 91.73 |
| Experiment | Free State (μs) | Compensation (24 h) | Compensation (48 h) | Compensation (72 h) | Compensation (96 h) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bias (μs) | Radio | Bias (μs) | Radio | Bias (μs) | Radio | Bias (μs) | Radio | ||
| 1 | 98.97 | 35.44 | 64.19% | 4.57 | 95.38% | 1.63 | 98.36% | 0.55 | 99.45% |
| 2 | 87.49 | 7.89 | 90.98% | 0.58 | 99.34% | 0.40 | 99.54% | 0.05 | 99.94% |
| 3 | 74.88 | 8.98 | 88.01% | 4.44 | 94.07% | 0.96 | 98.72% | 3.37 | 95.50% |
| 4 | 91.02 | 19.41 | 78.68% | 9.49 | 89.58% | 6.22 | 93.17% | 3.05 | 96.65% |
| 5 | 115.36 | 11.48 | 90.04% | 0.38 | 99.67% | 0.48 | 99.58% | 2.10 | 98.18% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Xu, L.; Wang, X.; Wu, Z.; Lai, J.; Yu, W. Timekeeping Method with Dual Iterative Algorithm for GNSS Disciplined OCXO. Electronics 2025, 14, 2870. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14142870
Zhang L, Xu L, Wang X, Wu Z, Lai J, Yu W. Timekeeping Method with Dual Iterative Algorithm for GNSS Disciplined OCXO. Electronics. 2025; 14(14):2870. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14142870
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Linghe, Longwei Xu, Xiaobin Wang, Zhongwang Wu, Jiangfeng Lai, and Wenqian Yu. 2025. "Timekeeping Method with Dual Iterative Algorithm for GNSS Disciplined OCXO" Electronics 14, no. 14: 2870. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14142870
APA StyleZhang, L., Xu, L., Wang, X., Wu, Z., Lai, J., & Yu, W. (2025). Timekeeping Method with Dual Iterative Algorithm for GNSS Disciplined OCXO. Electronics, 14(14), 2870. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14142870





