Multi-Scale Attention-Driven Hierarchical Learning for Fine-Grained Visual Categorization
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- Multi-scale hierarchical feature integration: We leverage hierarchical representations by integrating features from multiple intermediate and deep layers of the backbone network. This strategy enables the model to capture both low-level visual details and high-level semantic context for distinguishing between fine-grained categories that exhibit subtle inter-class variations.
- (2)
- Attention-driven region localization and progressive training: We incorporate a dynamic attention mechanism that identifies class-relevant spatial regions across different scales, and then reintroduce the attention-driven localized discriminating areas for progressive training refinement. With this strategy, MAHL potentially enhances the precision of feature learning and improves its ability to localize subtle but informative visual cues, ultimately leading to higher classification accuracy.
- (3)
- Generalized adaptive pooling: We introduce a pooling method that adaptively combines the top-ranked activations, achieving better spatial information retention and stronger feature discriminability for fine-grained classification.
2. Related Work
2.1. Attention Mechanism
2.2. Multi-Scale Feature Extraction
2.3. Pooling Methods
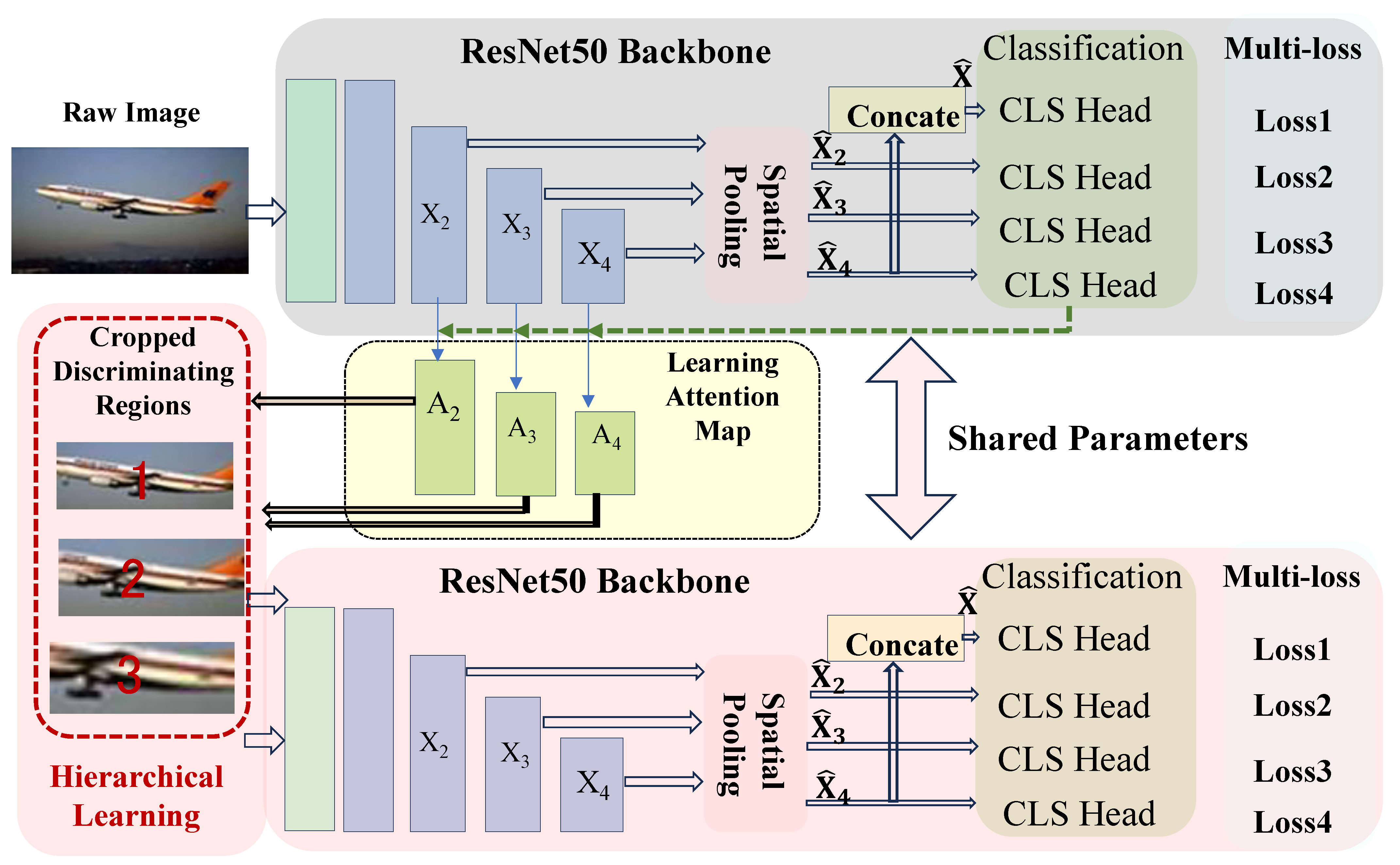
3. Proposed Multi-Scale Attention-Driven Hierarchical Learning (MAHL)
3.1. Overview
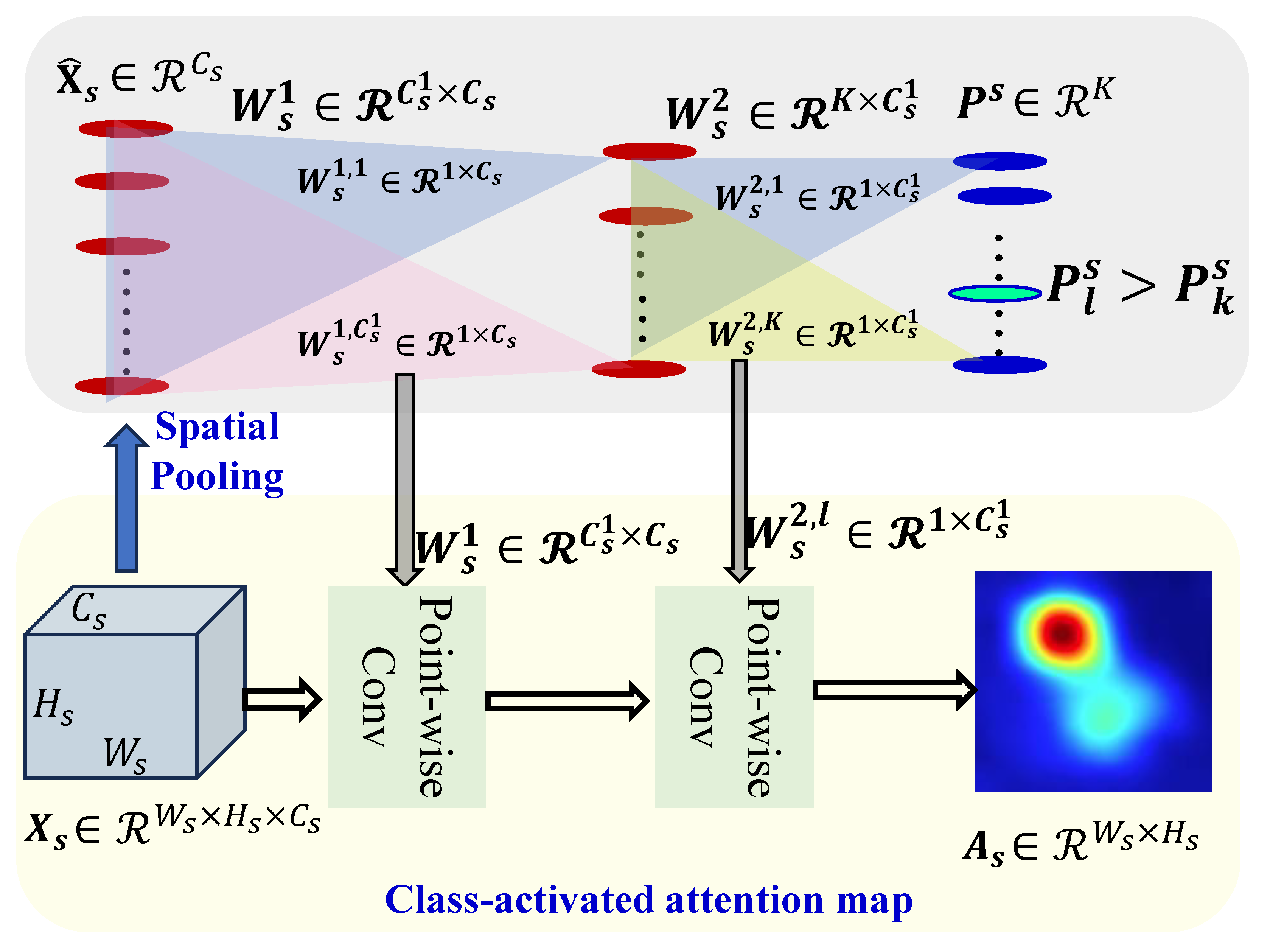
3.2. Attention-Driven Region Localization (ADRL)
3.3. Hierarchical Learning with the Localized Regions
3.4. Generalized Spatial Pooling
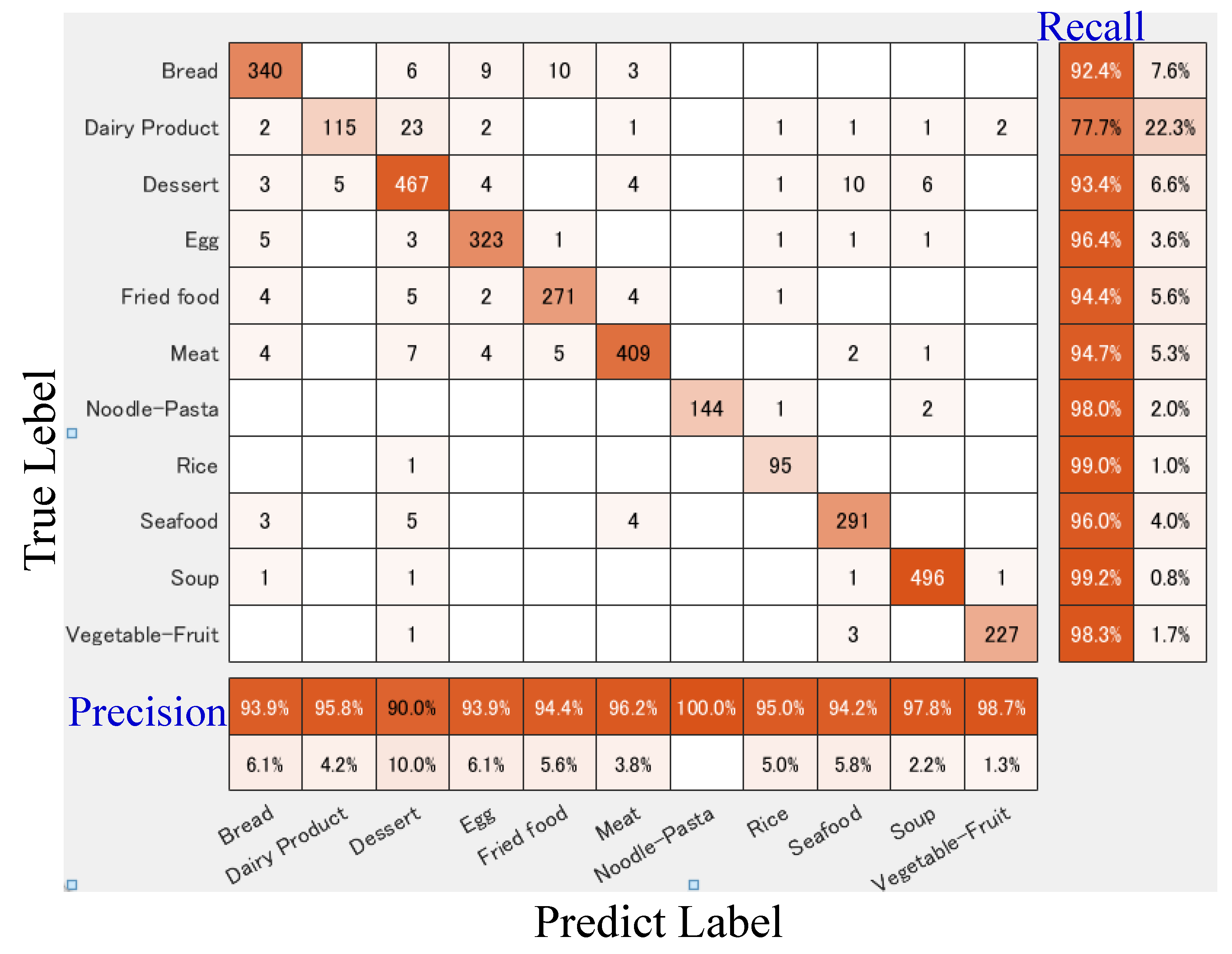
4. Experiments
4.1. Experimental Settings
4.2. Comparison with State-of-the-Art Methods
4.3. Ablation Study
4.4. Visualization of Multi-Scale Attention Maps
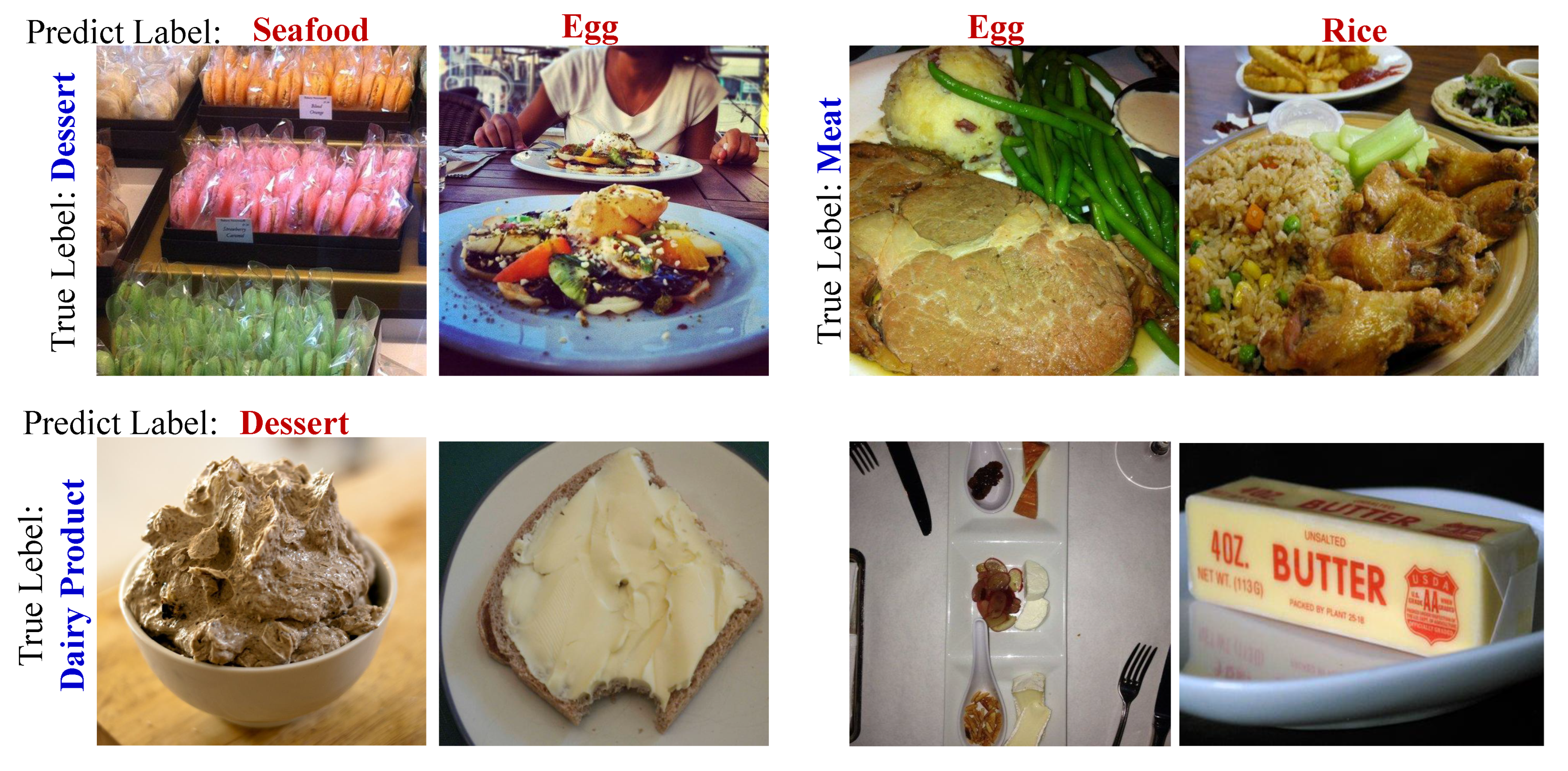
4.5. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, M.; Zhang, C.; Bai, H.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, Y. Cross-part learning for fine-grained image classification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 37, 748–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, C.; Deng, Y.; Xie, B.; Liu, T.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.F. Transifc: Invariant cues-aware feature concentration learning for efficient finegrained bird image classification. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2023, 27, 1677–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, R.; Yu, W.; Wang, H.; Lin, T.E.; Chang, D.; Ma, Z. Multi-view active finegrained visual recognition. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV2023), Paris, France, 4–6 October 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, S.; Zou, X.; Qian, J.; Wong, W.K. Learning structured relation embeddings for finegrained fashion attribute recognition. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2023, 26, 1652–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, W.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Luo, M.; Kang, L.; Wei, X.; Wei, X.; Jiang, S. Large scale visual food recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 45, 9932–9949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, R.; Kaneko, T.; Shiraishi, S. Framework for fine-grained recognition of retail products from a single exemplar. In Proceedings of the 2023 15th International Conference on Knowledge and Smart Technology (KST2023), Phuket, Thailand, 21–24 February 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; RoyChowdhury, A.; Maji, S. Bilinear CNN models for fine-grained visual recognition. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV2015), Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1449–1457. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, S.; Zuo, W.; Zhang, L. Higher-order integration of hierarchical convolutional activations for fine-grained visual categorization. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV2017), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 511–520. [Google Scholar]
- Engin, M.; Wang, L.; Zhou, L.; Liu, X. DeepKSPD: Learning kernel-matrix-based SPD representation for fine-grained image recognition. In Proceedings of the 2018 15th European Conference (ECCV2018), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 629–645. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, H.; Fu, J.; Zha, Z.J.; Luo, J. Learning deep bilinear transformation for fine-grained image representation. In Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS2019), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019; pp. 4277–4289. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Han, X.; Wang, X.; Huang, W.; Scott, M.R. Channel interaction networks for fine-grained image categorization. In Proceedings of the 34th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI2020), New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; pp. 10818–10825. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, G.; Cholakkal, H.; Khan, S.; Khan, F.S.; Shao, L. Fine-grained recognition: Accounting for subtle differences between similar classe. In Proceedings of the 34th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI2020), New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; pp. 12047–12054. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Luo, T.; Wang, D.; Hu, Z.; Gao, J.; Wang, L. Learning to Navigate for Fine-grained Classification. In Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 438–454. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, D.; Ding, Y.; Xie, J.; Bhunia, A.; Li, X.; Ma, Z.; Wu, M.; Guo, J.; Song, Y.Z. The devil is in the channels: Mutual-channel loss for fine-grained image classification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 4683–4695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, R.; Chang, D.; Bhunia, A.K.; Xie, J.; Song, Y.Z.; Ma, Z.; Guo, J. Fine-Grained Visual Classification via Progressive Multi-Granularity Training of Jigsaw Patches. In Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR2015), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 7–9 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR2016), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; van der Maaten, L.; Wein-berge, K.Q. Densely Connected Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR2017), Hawaii, HI, USA, 22–25 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An Image is Worth 16x16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR2021), Virtual, 3–7 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, M.; Xiao, B.; Codella, N.; Luo, P.; Wang, J.; Yuan, L. DaViT: Dual Attention Vision Transformer. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2204.03645. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, H.Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin Transformer: Hierarchical Vision Transformer using Shifted Windows. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV2021), Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Hu, H.; Lin, Y.; Yao, Z.; Xie, Z.; Wei, Y.; Ning, J.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Dong, L.; et al. Swin Transformer V2: Scaling Up Capacity and Resolution. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR2022), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1512.03385. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.E.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going Deeper with Convolutions. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.4842. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR2018), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. CBAM: Convolutional Block Attention Module. In Proceedings of the 2018 European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV2018), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Jetley, S.; Lord, N.A.; Lee, N.; Torr, P.H.S. Learn to pay attention. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.02391. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, B.; Wu, X.; Feng, J.; Peng, Q.; Yan, S. Diversified Visual Attention Networks for Fine-Grained Object Classification. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2017, 19, 1245–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Zheng, H.; Mei, T. Look Closer to See Better: Recurrent Attention Convolutional Neural Network for Fine-grained Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR2017), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4438–4446. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, W.; Yang, Y.; Yang, L. Fine-grained image classification method based on hybrid attention module. Front. Neurorobot. 2024, 18, 1391791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Li, M.; Zhai, G.; Liu, Y. Multi-branch and Multi-scale Attention Learning for Fine-Grained Visual Categorization. In International Conference on Multimedia Modeling; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 136–147. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, D.; Ge, H.; Zhang, Q.; Wei, X. Multi-Scale Attention Constraint Network for Fine-Grained Visual Classification. In IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME); IEEE Computer Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Xie, E.; Li, X.; Fan, D.P.; Song, K.; Liang, D.; Lu, T.; Luo, P.; Shao, L. Pyramid vision transformer: A versatile backbone for dense prediction without convolutions. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV2021), Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 568–578. [Google Scholar]
- Conde, M.V.; Turgutlu, K. Exploring Vision Transformers for Fine-grained Classification. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2106.10587. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Dollar, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature Pyramid Networks for Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR2017), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, H.; Fu, J.; Zha, Z.J.; Luo, J. Looking for the Devil in the Details: Learning Trilinear Attention Sampling Network for Fine-grained Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR2019), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 5012–5021. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Ye, Q.; Jiao, J. Selective Sparse Sampling for Fine-Grained Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV2019), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, P.; Wang, Y.; Qiao, Y. Learning Attentive Pairwise Interaction for Fine-Grained Classification. In Proceedings of the Thirty-Fourth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI2020), New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; pp. 13130–13137. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, W.; Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Wei, X.S. Learning semantically enhanced feature for fine-grained image classification. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2020, 27, 1545–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, S.; Li, H.; Dou, Z.; Li, J. Graph-propagation based correlation learning for weakly supervised fine-grained image classification. In Proceedings of the Thirty-Fourth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI2020), New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; pp. 12289–12296. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, S.; Yang, S.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Li, Z. Weakly supervised fine-grained image classification via gaussian mixture model oriented discriminative learning. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR2020), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 9749–9758. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; RoyChowdhury, A.; Maji, S. Bilinear convolutional neural networks for fine-grained visual recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 40, 1309–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, T.; Mei, T. Look-into-object: Self-supervised structure modeling for object recognition. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR2020), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 11774–11783. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, J.; Wang, D.; Xing, H.H.W.; Wang, L. Adcnn: Towards learning adaptive dilation for convolutional neural networks. Pattern Recognit. 2022, 123, 108369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Shi, G. Attention-shift based deep neural network for fine–grained visual categorization. Pattern Recognit. 2021, 116, 107947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Sreekumar, G.; Goodman, E.; Banzhaf, W.; Deb, K.; Boddeti, V. Neural architecture transfer. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 43, 2971–2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michaeli, E.; Fried, O. Advancing Fine-Grained Classification by Structure and Subject Preserving Augmentation. In Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeuIPS2024), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 10–15 December 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, Q.; Zhou, B.; Ji, W.; Xia, G.S. Universal Fine-grained Visual Categorization by Concept Guided Learning. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2025, 34, 394–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Chen, J.N.; Liu, S.; Kortylewski, A.; Yang, C.; Bai, Y.; Wang, C.; Yuille, A. TransFG: A Transformer Architecture for Fine-grained Recognition. In Proceedings of the 36th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI2022), Virtual, 22 February– 1 March 2022; pp. 852–860. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, L.; Hou, B.; Jian, Y.; Tu, X. TransFGVC: Transformer-based fine-grained visual classification. Vis. Comput. 2024, 41, 2439–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, S.; Fowlkes, C. Low-rank bilinear pooling for fine-grained classification. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR2017), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 365–374. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.; Zhao, X.; Zheng, Q.; Zhang, P.; You, X. Hierarchical bilinear pooling for fine-grained visual recognition. In Proceedings of the 2018 European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV2018), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 595–610. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Spatial Pyramid Pooling in Deep Convolutional Networks for Visual Recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 37, 1904–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Xie, J.; Zuo, W.; Zhang, L.; Li, P. Deep cnns meet global covariance pooling: Better representation and generalization. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 43, 2582–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, A.; Wharton, Z.; Hewage, P.R.P.G.; Bera, A. Context-aware Attentional Pooling (CAP) for Fine-grained Visual Classification. In Proceedings of the 35th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI2021), Virtual, 2–9 February 2021; pp. 929–937. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Huang, S.; Liu, W. Learning sequentially diversified representations for fine-grained categorization. Pattern Recognit. 2022, 121, 108219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikdar, A.; Liu, Y.; Kedarisetty, S.; Zhao, Y.; Ahmed, A.; Behera, A. Interweaving Insights: High-Order Feature Interaction for Fine-Grained Visual Recognition. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2024, 133, 1755–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singla, A.; Yuan, L.; Ebrahimi, T. Food/non-food image classification and food categorization using pre-trained googlenet model. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Workshop on Multimedia Assisted Dietary Management, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 16 October 2016; pp. 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Maji, S.; Kannala, J.; Rahtu, E.; Blaschko, M.; Vedaldi, A. Fine-grained visual classification of aircraft. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1306.5151. [Google Scholar]
- Krause, J.; Stark, M.; Deng, J.; Fei-Fei, L. 3D object representations for fine-grained categorization. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Sydney, NSW, Australia, 2–8 December 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Y.; Kato, J. Learn from each other to Classify better: Cross-layer mutual attention learning for fine-grained visual classification. Pattern Recognit. 2023, 140, 109550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, R.; Zhang, W.; Yin, J.; Wang, J. Data-free Knowledge Distillation for Fine-grained Visual Categorization. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV2023), Paris, France, 2–6 October 2023; pp. 1515–1525. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, M.; Siddique, B.; Rahman, S.; Jabid, T. Food image classification with convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Informatics and Biomedical Sciences (ICIIBMS2018), Bangkok, Thailand, 21–24 October 2018; Volume 3, pp. 257–262. [Google Scholar]
- McAllister, P.; Zheng, H.; Bond, R.; Moorhead, A. Combining deep residual neural network features with supervised machine learning algorithms to classify diverse food image datasets. Comput. Biol. Med. 2018, 95, 217–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yigit, G.O.; Ozyildirim, B. Comparison of convolutional neural network models for food image classification. J. Inf. Telecommun. 2018, 2, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, K.; Wijewickrema, S.; Pervez, S.O.M. An exploration of deep transfer learning for food image classification. In Proceedings of the Digital Image Computing: Techniques and Applications (DICTA2018), Canberra, Australia, 10–13 December 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, R.; Chew, X.; Khaw, K. Neural architecture search for lightweight neural network in food recognition. Mathematics 2021, 9, 1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-CAM: Visual Explanations from Deep Networks via Gradient-based Localization. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV2017), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W.; Luo, M.; Zhou, P.; Si, C.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.; Feng, J.; Yan, S. Metaformer is actually what you need for vision. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR2022), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022. [Google Scholar]

| Method | Core Idea | Limitation vs. MAHL |
|---|---|---|
| MC-Loss [14] | Enhances channel diversity via mutual-channel loss. | Lacks spatial attention and hierarchical refinement. |
| SEF [39] | Semantic enhancement of features. | No iterative or scale-adaptive attention. |
| GCL [40] | Graph-based correlation modeling. | Relies on graph structures instead of direct spatial attention. |
| DFGMM [41] | GMM-based part localization. | Uses statistical parts, not adaptive attention maps. |
| B-CNN [42] | Bilinear pooling for high-order interactions. | No dynamic attention or hierarchical processing. |
| GCP [54] | Global covariance pooling. | Misses fine-grained local attention mechanisms. |
| LIO [43] | Self-supervised structure learning. | Not tailored for discriminative refinement in FGVC. |
| PGT [15] | Multi-granularity jigsaw learning. | Fixed patches, lacks adaptive attention integration. |
| NAT [46] | Neural architecture search. | Focuses on architecture, not attention/pooling mechanisms. |
| AS-DNN [45] | Attention shift mechanisms. | No classifier-guided spatial attention or hierarchy. |
| ADCNN [44] | Adaptive dilation in convolutions. | Emphasizes receptive fields over attention structure. |
| SDR [56] | Sequentially diversified representations. | Lacks focus on spatial attention and region hierarchy. |
| I2-HOFI [57] | High-order feature interactions. | No spatial refinement or multiscale integration. |
| SaSPA [47] | Augmentation preserving structure. | Data-focused, not a learning framework innovation. |
| CGL [48] | Concept-guided semantic learning. | Focuses on semantics over spatial attention integration. |
| MAHL (Ours) | Hierarchical learning with multi-scale attention and generalized pooling. | Increased training process |
| Dataset | Dataset Content | Categories | Training Images | Testing Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FGVC-Aircraft [59] | Aircraft Models | 100 | 6667 | 3333 |
| Stanford Cars [60] | Car Models | 196 | 8144 | 8041 |
| Food-11 [58] | Dishes | 11 | 9866 | 3347 |
| (a) on FGVC-Aircraft and Stanford Cars datasets | ||||
| Methods | Publication venue | Backbone | FGVC-aircraft | Cars |
| SEF [39] | Signal Processing Letters, 2020 | ResNet50 | 92.1 | 94.0 |
| MC Loss [14] | TIP, 2020 | B-CNN | 92.9 | 94.4 |
| GCL [40] | AAAI, 2020 | ResNet50 | 93.20 | 94.0 |
| DF-GMM [41] | CVPR, 2020 | ResNet50 | 93.8 | 94.8 |
| LIO [43] | CVPR, 2020 | ResNet50 | 92.7 | 94.5 |
| PMG [15] | ECCV, 2020 | ResNet50 | 92.8 | 95.1 |
| GCP [54] | TPAMI, 2021 | ResNet101 | 91.4 | 93.3 |
| B-CNN [42] | TPAMI, 2021 | VGG-M + VGG-D | 84.1 | 90.6 |
| NAT [46] | TPAMI, 2021 | NAT-M4 | 90.8 | 92.9 |
| AS-DNN [45] | Pattern Recognition, 2021 | AS-DNN | 92.3 | 94.1 |
| ADCNN [44] | Pattern Recognition, 2022 | W-ResNet101 | 92.5 | 91.3 |
| SDNs [56] | Pattern Recognition, 2022 | ResNet101 | 92.7 | 94.6 |
| I2-HOFI [57] | IJCV, 2024 | ResNet50 | 92.26 | 94.33 |
| SaSPA [47] | NeurIPS, 2024 | ResNet50 | 90.79 | 95.34 |
| CGL [48] | TIP, 2025 | ResNet50 | 94.2 | - |
| Ours | - | ResNet-50 | 93.03 | 97.11 |
| DFKD [62] | ICCV, 2023 | ResNet-34 | 65.76 | 71.89 |
| (b) on Food-11 dataset | ||||
| Methods | Publication venue | Backbone | Food-11 | |
| Inception-TL [63] | ICIIBMS, 2018 | Inception V3 | 92.9 | |
| ANN [64] | Computers in Biology and Medicine, 2018 | ResNet152 | 91.3 | |
| Food-DCNN [65] | JIT, 2018 | Alexnet | 86.9 | |
| ResNet50-TL [66] | DICTA, 2018 | ResNet50 | 88.1 | |
| LNAS [67] | Mathematics, 2021 | LNAS-net | 89.1 | |
| CMAL [61] | Pattern Recognition, 2023 | ResNet50 | 96.3 | |
| CMAL [61] | Pattern Recognition, 2023 | Res2Next50 | 96.5 | |
| Ours | - | ResNet-50 | 97.01 | |
| Methods | Food-11 | FGVC-Aircraft | Stanford Cars |
|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 88.1% | 88.5% | 91.7% |
| +MAHL | 96.3% | 92.8% | 97.27% |
| +MAHL& GP | 97.01% | 93.03% | 97.11% |
| (a) Different settings in MAHL | |||||
| Shallow2 | Deep2 | Scale4 | Scale3 with Grad-CAM | Scale3 (Our) | |
| Acc. | 94.59% | 94.14% | 94.26% | 93.30% | 94.95% |
| (b) Different settings in GP strategy (d refers to the element number in the pooling region) | |||||
| Top- | (MP) | (AP) | |||
| Acc. | 94.47% | 94.95% | 93.92% | 93.52% | 93.87% |
| (c) Different attention threshod to produce discriminating regions | |||||
| Threshod | |||||
| Acc. | 94.20% | 94.68% | 94.95% | 94.68% | 93.92% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, Z.; Kojima, R.; Han, X.-H. Multi-Scale Attention-Driven Hierarchical Learning for Fine-Grained Visual Categorization. Electronics 2025, 14, 2869. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14142869
Hu Z, Kojima R, Han X-H. Multi-Scale Attention-Driven Hierarchical Learning for Fine-Grained Visual Categorization. Electronics. 2025; 14(14):2869. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14142869
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Zhihuai, Rihito Kojima, and Xian-Hua Han. 2025. "Multi-Scale Attention-Driven Hierarchical Learning for Fine-Grained Visual Categorization" Electronics 14, no. 14: 2869. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14142869
APA StyleHu, Z., Kojima, R., & Han, X.-H. (2025). Multi-Scale Attention-Driven Hierarchical Learning for Fine-Grained Visual Categorization. Electronics, 14(14), 2869. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14142869










