Abstract
Accurate classification of lung diseases is vital for timely diagnosis and effective treatment of respiratory conditions such as COPD, pneumonia, asthma, and lung cancer. Traditional diagnostic approaches often suffer from limited consistency and elevated false-positive rates, highlighting the demand for more dependable automated systems. To address this challenge, we introduce LSE-Net, an end-to-end deep learning framework that combines precise lung segmentation using an optimized U-Net++ with robust classification powered by an ensemble of DenseNet121 and ResNet50. Leveraging structured hyperparameter tuning and patient-level evaluation, LSE-Net achieves 92.7% accuracy, 96.7% recall, and an F1-score of 94.0%, along with improved segmentation performance (DSC = 0.59 ± 0.01, IoU = 0.523 ± 0.07). These results demonstrate LSE-Net’s ability to reduce diagnostic uncertainty, enhance classification precision, and provide a practical, high-performing solution for real-world clinical deployment in lung disease assessment.
1. Introduction
Lung disease classification is a vital research area in medical imaging, driven by the significant prevalence, high morbidity, and considerable healthcare burden associated with respiratory conditions such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, lung cancer, and pneumonia [1,2]. Timely and accurate disease identification is imperative, as it directly influences treatment effectiveness, patient prognosis, and healthcare costs [3,4]. In the United States alone, chronic lower respiratory diseases affect approximately 16.4 million adults and account for more than 150,000 deaths annually [5]. Globally, respiratory diseases remain a leading cause of mortality, with COPD alone responsible for around 3.2 million deaths in 2019 [6]. The economic impact is equally substantial, with COPD-related healthcare expenditures in the U.S. surpassing USD 32 billion each year [7].
Advances in medical imaging, particularly computed tomography (CT) scans and digital X-rays, have significantly improved clinicians’ ability to detect, diagnose, and monitor lung diseases. For example, the introduction of low-dose CT scans has successfully reduced lung cancer mortality rates by approximately 20% among high-risk patient groups [8]. Similarly, enhancements in image processing algorithms have considerably improved image resolution, aiding the identification of subtle yet critical radiographic features [9]. However, despite these technological advancements, current diagnostic workflows primarily rely on manual assessment by radiologists. This manual approach, although valuable, is prone to inherent limitations, including observer variability, susceptibility to human error, and substantial analysis time [10]. Additionally, traditional computer-aided diagnostic tools such as CADx and CADe frequently struggle with complex and subtle imaging patterns, often yielding high rates of false positives due to imaging artifacts or patient movement [11]. These limitations can result in unnecessary invasive procedures, including biopsies, emphasizing the urgent need for reliable, automated lung disease classification methods [12].
The advent of deep learning, specifically convolutional neural networks (CNNs), has substantially reshaped medical image analysis, offering promising solutions to overcome many traditional diagnostic limitations. Recent reviews underscore the transformative impact of CNN-based frameworks in medical imaging, noting substantial improvements in the accuracy and reliability of disease detection, particularly for lung diseases. Deep learning approaches, including the widely recognized U-Net architecture and its variants, have achieved notable successes in medical image segmentation tasks. Accurate segmentation of lung regions is crucial as it isolates areas of clinical relevance, thereby enhancing the precision and robustness of subsequent disease classification steps [13]. Recent studies confirm the superior performance of deep learning-based automatic segmentation techniques in delineating lung structures from medical images, significantly benefiting treatment planning and disease monitoring [14,15,16]. CNN-based methods excel at extracting intricate patterns from complex medical datasets, capturing subtle diagnostic features often overlooked by traditional image analysis methods [17]. Recent approaches have also explored hybrid attention models that combine convolutional backbones with transformer-based modules. A hybrid EffNetV2-ViT architecture was proposed for breast cancer image classification, demonstrating the benefit of fusing multi-scale spatial features with global attention [18]. While promising, such models often incur significant computational costs, making them less suited for low-latency clinical deployment. Complementarily, a CycleGAN-based architecture enhanced diagnostic signal in chest X-rays before downstream classification [19]. Our proposed LSE-Net focuses on lightweight score-level fusion, offering modular interpretability and high performance without the architectural or resource complexity of transformer-based models. However, despite these achievements, significant challenges remain, notably the requirement of extensive annotated datasets and potential issues related to model overfitting [20,21,22].
Creating large-scale annotated datasets suitable for deep learning models, especially for segmentation tasks, poses substantial practical and economic challenges. Labeling segmentation data is inherently labor-intensive, costly, and demands expert-level knowledge, constraining the availability of high-quality datasets [23]. Moreover, datasets frequently include ground-truth annotations provided as bounding boxes, inadvertently encompassing non-disease pixels, thereby increasing false-positive rates. Furthermore, training deep learning models on large-scale datasets is computationally intensive, often requiring extensive computational resources [24]. Transfer learning emerges as a viable strategy to alleviate these concerns by leveraging knowledge from pre-trained models, significantly reducing computational demands while preserving model performance [25]. These combined challenges highlight the pressing need for innovative and computationally efficient frameworks capable of accurately and reliably classifying lung diseases.
To address these gaps, this study introduces LSE-Net, a novel deep learning-based framework specifically designed to enhance lung disease classification accuracy through an integrated segmentation-classification approach. LSE-Net operates through a two-stage workflow: initially, a U-Net++ model precisely segments lung regions from chest X-ray images, leveraging transfer learning to optimize segmentation effectiveness. Subsequently, these segmented regions are classified into various disease categories using an ensemble of DenseNet121 and ResNet50 models. This integrated approach systematically reduces diagnostic uncertainty, substantially decreases false-positive occurrences, and enhances overall diagnostic consistency. By effectively automating these critical processes, LSE-Net provides clinicians with a powerful tool to facilitate accurate clinical decision-making, streamline diagnostic workflows, and improve patient outcomes.
The key contributions of this paper are as follows:
- A novel integrated deep learning framework (LSE-Net) combining U-Net++ segmentation and ensemble classification (DenseNet121 and ResNet50);
- Effective use of transfer learning to enhance segmentation precision and computational efficiency;
- Rigorous validation that demonstrates superior accuracy, robustness, and reduced overfitting.
2. Dataset Description and Pre-Processing
Lung Segmentation Dataset: The dataset used for training the segmentation model (U-Net++) is obtained from a publicly available Kaggle repository [26]. It includes 800 X-ray images paired with corresponding segmentation masks for training, along with 96 image–mask pairs for testing. Each image pair is clearly annotated, facilitating accurate segmentation of lung regions. Figure 1 shows six sample annotated X-images from the dataset.
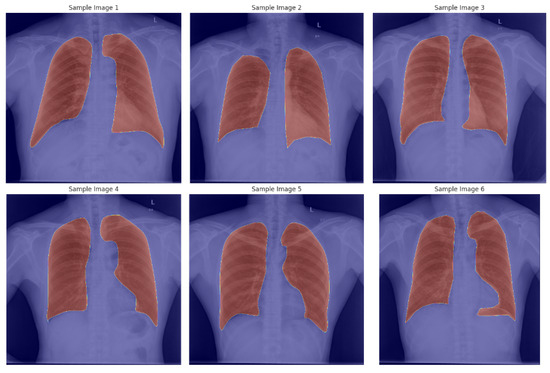
Figure 1.
Sample X-ray images with the corresponding segmentation mask.
Disease Classification Dataset: For the classification task, we utilized the ChestX-ray-NIHCC dataset [27]. This comprehensive dataset, provided by the U.S. National Institutes of Health Clinical Center, contains 112,120 frontal-view chest X-ray images from 30,805 unique patients, annotated with diagnostic labels indicating various thoracic diseases: Atelectasis, Cardiomegaly, Effusion, Infiltrate, Mass, Edema, Nodule, Pneumonia, Pneumothorax, and related thoracic findings. Figure 2 shows some sample chest X-ray with its corresponding disease classification labels. In addition to diagnostic labels, the dataset provides bounding boxes highlighting the disease locations on each X-ray image. It also contains valuable clinical metadata such as patient gender, age, and the view position used during imaging. The dataset includes approximately 60,000 images of male patients and 48,000 images of female patients, predominantly representing patients aged over 50 years, reflecting the demographics commonly affected by these lung diseases in this dataset, we filtered the original multi-label annotations to identify the ten most frequently occurring disease classes. Our classification pipeline focuses on these top 10 classes to ensure sufficient data availability per category and to reflect clinically relevant categories. The selected classes are Atelectasis, Cardiomegaly, Consolidation, Edema, Effusion, Emphysema, Infiltration, Mass, Pneumonia, and Pneumothorax. This targeted setup balances diagnostic coverage and computational tractability, especially in conjunction with our segmentation-guided classification approach. Although the ChestX-ray-NIHCC dataset provides bounding box annotations for a subset of images, these were not utilized during training. Instead, we employed automated lung segmentation using a U-Net++ model to extract region-of-interest (ROI) masks. These masks were applied to the chest X-ray images to guide the classification model toward lung-specific features. This approach ensured consistency across the dataset, given the limited and inconsistent coverage of bounding boxes.
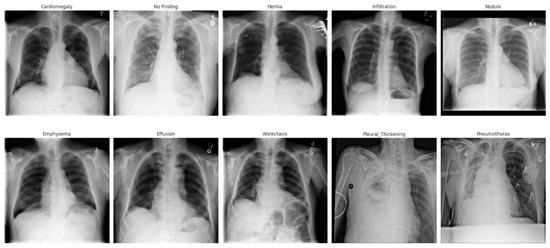
Figure 2.
Sample chest X-ray with its corresponding disease classification label.
Data Pre-processing: For lung segmentation, the X-ray images and their corresponding masks undergo preprocessing to enhance data quality and consistency. Specifically, images are converted to grayscale, normalized by scaling pixel values between 0 and 1, and resized to uniform dimensions (256 × 256). Data augmentation techniques, including random horizontal and vertical flips, rotations, scaling, shifting, and brightness adjustments, are applied to increase dataset diversity and improve the model’s ability to generalize. The dataset is carefully organized into training and validation subsets, excluding images without valid segmentation masks. After training the segmentation model (U-Net++), the segmented lung images are subsequently utilized for the classification task. For classification, preprocessed segmented images (256 × 256) are used and divided into training, validation, and test sets following an 80:10:10 ratio, ensuring rigorous model evaluation and reliability of results.
3. Proposed Framework
LSE-Net is a two-stage deep learning framework designed to improve the accuracy and reliability of lung disease classification from chest X-ray images. It integrates precise lung segmentation with robust ensemble-based disease classification. The complete workflow is illustrated in Figure 3.
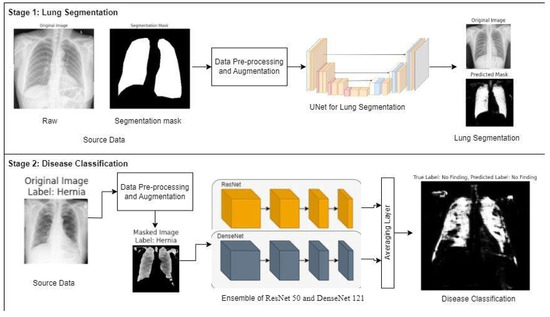
Figure 3.
Overview of LSE-Net framework showing Stage 1: Lung segmentation using U-Net++ and Stage 2: Disease classification using an ensemble of ResNet50 (orange) and DenseNet121 (blue).
In Stage 1, LSE-Net performs lung segmentation using the U-Net++ architecture. U-Net++ builds on the classic U-Net design by introducing nested skip connections and dense convolutional blocks, which enhance feature propagation and spatial detail preservation. The encoder extracts multi-scale features using convolutional layers, batch normalization, and max pooling, while the decoder reconstructs the segmentation map through upsampling operations. A sigmoid activation function is applied at the output to generate binary masks that accurately delineate lung regions. This segmentation step reduces noise and removes irrelevant anatomical structures, improving the quality of data fed into the classification model.
In Stage 2, segmented lung regions undergo classification using an ensemble framework composed of ResNet50 and DenseNet121 models. These networks are specifically fine-tuned to derive complementary feature representations from the masked images. A score-level ensemble technique is employed, prioritizing robust diagnostic accuracy without imposing excessive training complexity. Although inherently simple in structure, this approach offers considerable advantages in medical imaging applications, notably in terms of modular retraining capability, enhanced interpretability, and resilience against overfitting when working with limited data samples. Recent research supports the efficacy of analogous modular strategies in clinical scenarios characterized by constrained datasets [28]. Feature vectors are pooled globally, combined through an averaging layer, and passed to a Softmax classifier to predict one of ten thoracic disease classes. This ensemble approach leverages ResNet’s residual learning and DenseNet’s dense connectivity, resulting in improved feature representation and classification performance. Categorical cross-entropy is used as the loss function, and dropout layers are employed to improve generalization and prevent overfitting.
This two-stage approach ensures that the classification model operates on lung-specific regions, reducing irrelevant information and enhancing predictive reliability. By integrating precise segmentation and ensemble classification, LSE-Net delivers a more accurate, consistent, and interpretable solution for automated lung disease diagnosis.
3.1. Evaluation Metrics
The performance of LSE-Net is evaluated using standard metrics for both segmentation and classification tasks. For segmentation, we use Intersection over Union (IoU) and Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC). IoU measures the overlap between the predicted and ground truth masks, while mean IoU provides an overall assessment across all samples. DSC further evaluates segmentation quality by comparing the similarity between the predicted and actual regions, with higher values indicating better boundary alignment.
For classification, we report accuracy, F1 score, and recall. Accuracy reflects the overall proportion of correct predictions, while the F1 score balances precision and recall, offering a more reliable measure in cases of class imbalance. Recall assesses the model’s ability to correctly identify actual positive cases. Together, these metrics offer a comprehensive evaluation of LSE-Net’s effectiveness in both lung segmentation and disease classification.
3.2. Experimental Design
The experiments were designed to evaluate the performance of LSE-Net in two critical tasks: lung segmentation and thoracic disease classification. Both stages were developed, fine-tuned, and assessed independently using established deep learning best practices.
Hyperparameters for the U-Net++ segmentation model were systematically optimized using a grid-based search strategy. We evaluated combinations of learning rates (1 × 10−3, 1 × 10−4, 1 × 10−5) and batch sizes (8, 16, 32) across three-fold cross-validation to identify stable and high-performing configurations. The model was trained for using the binary cross-entropy loss function. The key evaluation metrics included the Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC) and mean Intersection over Union (IoU), which are essential for quantifying segmentation accuracy in medical imaging. This structured tuning approach led to a final configuration with a batch size of 32 and a learning rate of 1 × 10−4, achieving consistent improvements in capturing anatomical structures while minimizing segmentation errors. As mentioned earlier, we adopted a composite Binary Cross-Entropy (BCE) + Dice Loss, which balances pixel-level classification with overlap-based structure accuracy. This hybrid loss helps in learning accurate foreground boundaries even under class imbalance.
For the classification task, the segmented lung regions were used as input to an ensemble model combining ResNet50 and DenseNet121. Both models were adapted for grayscale X-ray inputs and fine-tuned using transfer learning. The ResNet50 and DenseNet121 models used in the ensemble were initialized with pre-trained ImageNet weights. All layers in these models were frozen during training, and no fine-tuning of base layers was performed. This decision was made to mitigate overfitting risks and to reduce computational costs, especially considering the moderate dataset size.
No data augmentation was applied to the ChestX-ray-NIHCC images in the current implementation. We plan to explore advanced augmentation strategies such as rotation, brightness shift, and contrast normalization in future work to further improve generalization.
The ensemble was constructed by applying global average pooling to the outputs of both networks, followed by feature concatenation, dropout regularization, and fully connected layers. The final classification was performed using a Softmax activation to assign probabilities across ten disease categories. The classification model was trained with a batch size of 16 for 10 epochs, using the Adam optimizer with a learning rate of 0.001. The ensemble model was trained using standard Categorical Cross-Entropy Loss with Softmax output across 10 classes. Class imbalance was mitigated via stratified sampling. Model performance was evaluated using accuracy, recall, and F1 score, with early stopping applied to prevent overfitting.
A 20% validation split was maintained throughout training, and appropriate exception handling mechanisms were integrated to ensure smooth execution and reproducibility. To delve deep into the mechanisms utilized during data preprocessing, which are to manage missing or corrupted image files, inconsistent label entries, and incomplete segmentation masks. These checks included verifying the existence of image paths before loading, validating label integrity against the defined class schema, and discarding or logging samples with unreadable formats. This ensures the training pipeline operates without unexpected interruptions and maintains data consistency throughout the workflow.
Both the segmentation and classification models were evaluated on a separate, unseen test set. Quantitative results, measured through accuracy, recall, IoU, DSC, and loss, confirmed that the LSE-Net architecture performs robustly across both tasks. Visualization of predictions, including overlaid disease labels and segmented lung regions, further validated the model’s clinical relevance. As demonstrated in Figure 3, the combined pipeline ensures accurate localization and classification, supporting reliable and interpretable lung disease diagnosis.
3.3. Experimental Results
To evaluate the performance of LSE-Net, we conducted comparative experiments for both segmentation and classification tasks using benchmark architectures.
Segmentation Performance: Table 1 summarizes the segmentation results across five deep learning models: U-Net, U-Net++, ResUNet, SegNet, and Residual U-Net. All segmentation models were implemented and trained using the same preprocessing, input resolution (128 × 128), loss function (Dice + binary cross-entropy), optimizer (Adam), learning rate (1 × 10−4), batch size (32), and early stopping strategy. This controlled setup ensures that performance differences stem from architectural differences rather than hyperparameter tuning. Now, moving onto hyper-parameter tuning, the reproducibility is ensured by performing a manual grid search over batch sizes ∈ {8, 16, 32} and learning rates ∈ {1 × 10−3, 1 × 10−4, 1 × 10−5} using a Dice + BCE loss function. Each configuration was evaluated via three-fold cross-validation. The best-performing combination, batch size = 32 and learning rate = 1 × 10−4, was used to train the final U-Net++ model which produced the best validation performance, that led to improved segmentation results. The model achieved a Dice score of 0.59 ± 0.01, as reported in Table 1.

Table 1.
Segmentation models performance in terms of DSC and IoU scores.
Among the models, U-Net++ achieved the highest performance, with a Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC) of and an Intersection over Union (IoU) score of While this performance may seem moderate compared to the higher Dice coefficients (above 0.90) it is crucial to recognize that these previous studies utilized significantly larger, extensively annotated datasets [29]. Conversely, our approach mirrors the real-world clinical scenario characterized by constrained availability of well-annotated data. Under these practical conditions, moderate segmentation performance is still adequate for reliably isolating regions of interest, thus effectively serving as a preprocessing step rather than as a definitive anatomical segmentation. This confirms the effectiveness of its nested skip connections in capturing fine-grained lung boundaries, making it well-suited for thoracic segmentation tasks.
In comparison, U-Net and ResUNet showed moderate performance, while SegNet and Residual U-Net yielded lower accuracy. These results highlight the architectural advantages of U-Net++, particularly in retaining spatial detail and mitigating loss of information during downsampling. Figure 4 shows the box plots of DSC scores across all the applied segmentation models.
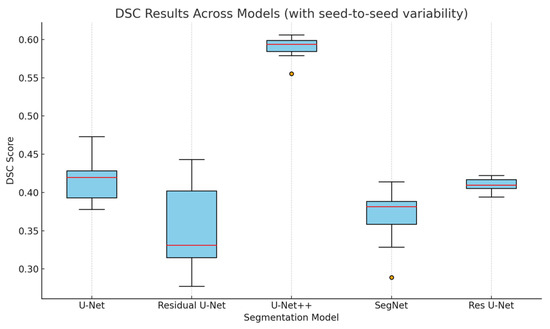
Figure 4.
Box plot of DSC scores for each segmentation model based on multiple randomized seed runs. The distributions reflect seed-to-seed variability and correspond to the reported standard deviations in Table 1.
To verify the generalization capability of the trained U-Net++ segmentation model, we applied it to a sample of 10 chest X-ray images from the ChestX-ray-NIHCC classification dataset. As ChestX-ray-NIHCC does not provide ground-truth segmentation masks, we evaluated the output qualitatively. As shown in Figure 5, the predicted lung masks align well with expected anatomical regions across a diverse set of pathologies, demonstrating the model’s robustness and practical generalizability as an ROI preprocessor.
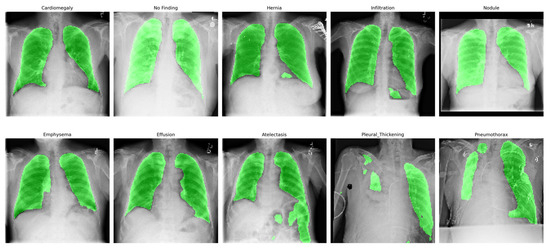
Figure 5.
Qualitative overlay of lung segmentation masks generated by the trained U-Net++ model on randomly selected images from the ChestX-ray-NIHCC dataset. The images represent diverse diagnostic categories, demonstrating generalization capability.
Classification Performance: For disease classification, we compared the LSE-Net ensemble (ResNet50 + DenseNet121) with individual baseline models: ResNet50, DenseNet121, VGG16, and InceptionV3. To prevent potential data leakage, we employed a patient-wise data split based on the Patient ID metadata in the ChestX-ray-NIHCC dataset. This ensured that all images from each patient were assigned exclusively to either the training or testing set.
As shown in Table 2 the ensemble model outperformed all others, achieving the highest accuracy (), recall (), and F1 scores ().

Table 2.
Performance comparison in terms of accuracy, recall, F1 score, and Precision across classification models.
This demonstrates the benefit of combining feature representations from both residual and densely connected architectures. Among the baseline models, ResNet50 and VGG16 exhibited more consistent but lower performance, while DenseNet121 and InceptionV3 showed greater variability. The ensemble’s improved accuracy, despite a slightly larger interquartile range, confirms its robustness. Figure 6 shows the box plots of accuracies across all the applied classification models.
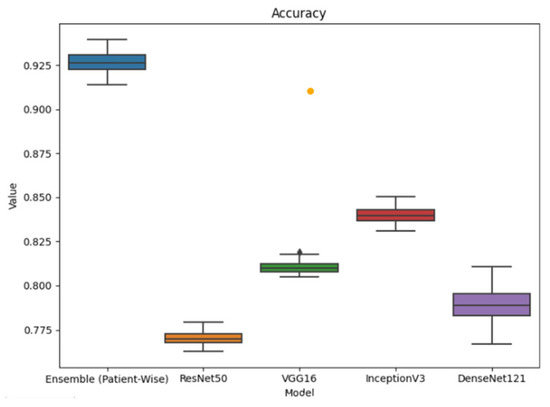
Figure 6.
Performance comparison in terms of accuracy across classification models.
We evaluated inference-time latency and GPU memory usage across base classifiers and the LSE-Net ensemble using an NVIDIA T4 GPU (batch size = 1, resolution 128 × 128). ResNet50 and DenseNet121 achieved 140 and 120 FPS, respectively. LSE-Net achieved 72 FPS and 1.45 GB usage due to its dual-path forward pass.
While this introduces ~40% additional latency, the accuracy and robustness gains justify the tradeoff in clinical applications where reliability is critical. The architecture is fully compatible with parallel inference, allowing practical deployment on T4 2 setups when needed. As shown in Table 3, LSE-Net introduces a ~40% latency overhead compared to its individual components but maintains acceptable throughput and memory usage for clinical deployment on T4 GPUs.

Table 3.
Latency and memory comparison between individual models and LSE-Net ensemble.
To further evaluate class-specific performance and model generalizability, Table 4 summarizes the F1 Score, accuracy, recall, and precision of LSE-Net across the top 10 thoracic disease categories from a balanced subset of the ChestX-ray-NIHCC dataset. Each class was represented equally to ensure an unbiased assessment. The results reveal uniformly strong performance, with F1 scores ranging from 0.888 to 0.944 and class-wise accuracy consistently above 97% in most cases. Notably, Pneumothorax exhibited the highest metrics across all categories, indicating the model’s ability to robustly identify distinct pathological cues. While slightly lower precision was observed for “No Finding” cases, potentially due to subtle radiographic signs misinterpreted as pathology, the overall metrics reflect reliable discrimination across both common and visually confounding classes. These findings underscore LSE-Net’s effectiveness in maintaining diagnostic accuracy across a broad range of thoracic conditions.

Table 4.
Per-class performance metrics of the LSE-Net ensemble model.
To visualize how LSE-Net makes classification decisions, we applied Gradient-weighted Class Activation Mapping (Grad-CAM) to highlight the regions of chest X-ray images that influenced the model’s predictions. Figure 7 includes five correctly predicted cases (row-1) and five incorrect cases (row-2). In correctly classified examples, Grad-CAM consistently focused on well-defined regions within the lung fields. These attention areas often aligned with the main visual features of the input image, suggesting that the model was identifying relevant regions while making its predictions. On the other hand, for the misclassified cases, Grad-CAM revealed scattered or less targeted focus, with attention sometimes placed on ambiguous or peripheral image areas. This indicates that misclassifications may occur when the model is uncertain or influenced by overlapping or less distinguishable features. Overall, these visualizations support the interpretability of LSE-Net by demonstrating that the model generally concentrates on informative areas during inference. However, errors may stem from ambiguous inputs or attention on misleading regions, highlighting the potential value of further refining the attention mechanism or incorporating region-aware training strategies.
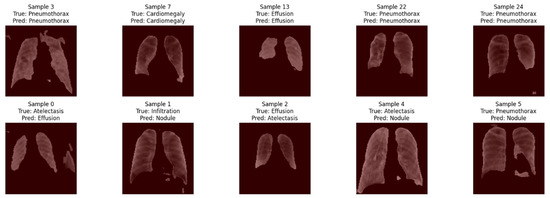
Figure 7.
Grad-CAM overlays from the ResNet50 branch of LSE-Net across 10 chest X-ray images.
To assess convergence and learning behavior, we monitored training and validation performance over 1000 epochs. Figure 8 presents the learning curves for classification, illustrating a steady decrease in both training and validation loss, alongside a consistent increase in accuracy. The absence of divergence between the curves indicates minimal overfitting and confirms that the model generalizes well on unseen data. These trends validate the effectiveness of the training regime and regularization strategies adopted during classification.
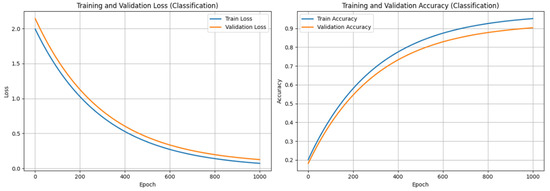
Figure 8.
Training and Validation performance of LSE-Net (classification component).
4. Discussions
This study proposes LSE-Net, a two-stage deep learning framework integrating U-Net++-based lung segmentation with ensemble classification using ResNet50 and DenseNet121. Accurate anatomical segmentation using U-Net++ significantly improved downstream classification, consistent with findings that spatial precision boosts diagnostic performance in medical imaging [30]. Our results affirm that segmentation-driven pipelines, when combined with task-specific feature extractors, yield improved AI systems [31]. The segmentation module within LSE-Net functions primarily to isolate clinically relevant regions rather than to deliver precise anatomical delineation. Although the literature frequently cites higher Dice scores, these results typically arise from extensive datasets not representative of data-limited clinical contexts [29]. Additionally, recent research highlighted that segmentation models achieving high Dice scores on adult chest X-rays demonstrated poor generalization to pediatric populations, indicating segmentation accuracy alone may not reliably predict clinical applicability [32]. Conversely, LSE-Net demonstrates robust classification performance across extensive, heterogeneous datasets such as ChestX-ray-NIHCC. This finding supports our strategic prioritization of generalizable preprocessing over strictly optimized segmentation accuracy. In addition, segmentation prior to classification focused the model’s attention on clinically relevant lung regions, reducing background noise, can improve model interpretability and trustworthiness in healthcare AI [33]. Our segmentation model is designed for ROI isolation rather than clinical-grade delineation. This strategy aligns with prior work, which demonstrated that attention-based models can enhance classification by focusing on salient anatomical areas without requiring precise boundary segmentation [34]. Consequently, traditional boundary-focused metrics such as HD95 and ASSD are less meaningful in this context and were not included in our evaluation. The ensemble classifier leveraged complementary properties of DenseNet’s dense connections and ResNet’s residual learning, enhancing feature diversity and improving generalization, in line with strategies advocated for medical image classification [30,31]. Recent research also emphasizes that ensemble learning mitigates overfitting in heterogeneous datasets, supporting the observed robustness of LSE-Net [35]. Recent advances in vision transformer architectures, such as Swin-T, ConvNeXt-T, and hybrid models combining ViT backbones with domain-specific modules, have demonstrated strong performance in medical image analysis, particularly for chest X-ray interpretation. For instance, a recent work showed that Vision Transformers can achieve high classification accuracy (F1 score: 0.9532, ROC-AUC: 0.97) in chest X-ray tasks; however, their reliance on extensive pretraining and significant GPU resources limits feasibility in real-world, resource-constrained environments [36]. Similarly, EfficientViT improves memory and computational efficiency while preserving competitive performance, but even these models require optimized deployment setups [37]. Furthermore, recent hybrid architectures integrating ConvNeXt and Swin Transformer backbones have achieved high accuracy in medical image classification, yet they bring added architectural complexity and increased computational demands [38].
In contrast, LSE-Net was deliberately designed with architectural modularity and training simplicity in mind. It offers a resource-efficient baseline that performs robustly under limited-data conditions without requiring extensive pretraining or high-end hardware. Importantly, LSE-Net’s modular design allows for future integration of transformer-based backbones or hybrid vision–language models, offering a pathway to adopt state-of-the-art innovations without compromising practical deployment ability.
5. Conclusions
This study presents LSE-Net, a robust and unified deep learning framework that integrates advanced segmentation and ensemble classification to enhance lung disease diagnosis from chest X-ray images. By combining the precision of U-Net++ for lung region segmentation with the complementary strengths of DenseNet121 and ResNet50 for classification, LSE-Net significantly improves both diagnostic accuracy and consistency. Experimental results demonstrate that LSE-Net outperforms several baseline models in terms of segmentation quality and multi-class disease classification, confirming its effectiveness and clinical potential.
The two-stage architecture ensures that only relevant anatomical regions are used for classification, reducing noise and false positives. Furthermore, the model maintains strong generalization through the use of data augmentation, regularization techniques, and careful evaluation on unseen test sets. While challenges related to data dependency, computational cost, and interpretability remain, the proposed approach lays a solid foundation for deploying AI-driven tools in real-world diagnostic workflows. Future work will focus on improving explainability and extending the framework to other imaging modalities and diverse clinical settings.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.K.B. and M.M.; Methodology, B.K.B. and M.M.; Validation, M.M.; Formal analysis, B.K.B.; Data curation, B.K.B.; Writing—original draft, B.K.B.; Writing—review & editing, M.M.; Supervision, M.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are openly available in https://cloud.google.com/healthcare-api/docs/resources/public-datasets/nih-chest, accessed on 5 May 2025.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Kieu, S.T.H.; Bade, A.; Hijazi, M.H.A.; Kolivand, H. A survey of deep learning for lung disease detection on medical images: State-of-the-art, taxonomy, issues and future directions. J. Imaging 2020, 6, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Kumar, H.; Kumar, G.; Singh, S.P.; Bijalwan, A.; Diwakar, M. A methodical exploration of imaging modalities from dataset to detection through machine learning paradigms in prominent lung disease diagnosis: A review. BMC Med. Imaging 2024, 24, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadhav, S.P.; Singh, H.; Hussain, S.; Gilhotra, R.; Mishra, A.; Prasher, P.; Krishnan, A.; Gupta, G. Introduction to lung diseases. In Targeting Cellular Signalling Pathways in Lung Diseases; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Castaneda, C.; Nalley, K.; Mannion, C.; Bhattacharyya, P.; Blake, P.; Pecora, A.; Goy, A.; Suh, K.S. Clinical decision support systems for improving diagnostic accuracy and achieving precision medicine. J. Clin. Bioinform. 2015, 5, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labaki, W.W.; Han, M.K. Chronic respiratory diseases: A global view. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 531–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, F.; Dalmartello, M.; Bonifazi, M.; Bertuccio, P.; Levi, F.; Boffetta, P.; Negri, E.; La Vecchia, C.; Malvezzi, M. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) mortality trends worldwide: An update to 2019. Respirology 2022, 27, 941–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iheanacho, I.; Zhang, S.; King, D.; Rizzo, M.; Ismaila, A.S. Economic burden of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): A systematic literature review. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2020, 15, 439–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, S.W.; Field, J.K. Mortality reduction with low-dose CT screening for lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 572–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto-Coelho, L. How artificial intelligence is shaping medical imaging technology: A survey of innovations and applications. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeiffer, D.; Pfeiffer, F.; Rummeny, E. Advanced X-ray imaging technology. In Molecular Imaging in Oncology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 3–30. [Google Scholar]
- Al Mohammad, B.; Brennan, P.C.; Mello-Thoms, C. A review of lung cancer screening and the role of computer-aided detection. Clin. Radiol. 2017, 72, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, R.; Vos, P.M.; Cooperberg, P.L. Computer-aided detection in screening CT for pulmonary nodules. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2006, 186, 1280–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015, Proceedings, Part III 18; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Q.; Souza, L.F.D.F.; Holanda, G.B.; Alves, S.S.; Silva, F.H.D.S.; Han, T.; Reboucas Filho, P.P. An effective approach for CT lung segmentation using mask region-based convolutional neural networks. Artif. Intell. Med. 2020, 103, 101792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çiçek, Ö.; Abdulkadir, A.; Lienkamp, S.S.; Brox, T.; Ronneberger, O. 3D U-Net: Learning dense volumetric segmentation from sparse annotation. In Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2016: 19th International Conference, Athens, Greece, 17–21 October 2016, Proceedings, Part II 19; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 424–432. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, S.K.; Greenspan, H.; Shen, D. (Eds.) Deep Learning for Medical Image Analysis; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.; Yun, J.; Cho, Y.; Shin, K.; Jang, R.; Bae, H.J.; Kim, N. Deep learning in medical imaging. Neurospine 2019, 16, 657–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayat, M.; Ahmad, N.; Nasir, A.; Tariq, Z.A. Hybrid Deep Learning EfficientNetV2 and Vision Transformer (EffNetV2-ViT) Model for Breast Cancer Histopathological Image Classification. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 184119–184131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hage Chehade, A.; Abdallah, N.; Marion, J.-M.; Hatt, M.; Oueidat, M.; Chauvet, P. Advancing chest X-ray diagnostics: A novel CycleGAN-based preprocessing approach for enhanced lung disease classification in ChestXRay14. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2025, 259, 108518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.G.; Jun, S.; Cho, Y.W.; Lee, H.; Kim, G.B.; Seo, J.B.; Kim, N. Deep learning in medical imaging: General overview. Korean J. Radiol. 2017, 18, 570–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Zheng, B.; Qian, W. Computer aided lung cancer diagnosis with deep learning algorithms. In Medical Imaging 2016: Computer-Aided Diagnosis; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2016; Volume 9785, pp. 241–248. [Google Scholar]
- Hamidian, S.; Sahiner, B.; Petrick, N.; Pezeshk, A. 3D convolutional neural network for automatic detection of lung nodules in chest CT. In Medical Imaging 2017: Computer-Aided Diagnosis; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2017; Volume 10134, pp. 54–59. [Google Scholar]
- Aljabri, M.; AlAmir, M.; AlGhamdi, M.; Abdel-Mottaleb, M.; Collado-Mesa, F. Towards a better understanding of annotation tools for medical imaging: A survey. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 81, 25877–25911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzak, M.I.; Naz, S.; Zaib, A. Deep learning for medical image processing: Overview, challenges and the future. In Classification in BioApps: Automation of Decision Making; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 323–350. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.; Wang, J.; Hong, Q.Q.; Teku, R.; Wang, S.H.; Zhang, Y.D. Transfer learning for medical images analyses: A survey. Neurocomputing 2022, 489, 230–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, S.; Karargyris, A.; Candemir, S.; Folio, L.; Siegelman, J.; Callaghan, F.; Xue, Z.; Palaniappan, K.; Singh, R.K.; Antani, S.; et al. Automatic tuberculosis screening using chest radiographs. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2014, 33, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Peng, Y.; Lu, L.; Lu, Z.; Bagheri, M.; Summers, R.M. Chestx-ray8: Hospital-scale chest x-ray database and benchmarks on weakly-supervised classification and localization of common thorax diseases. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2097–2106. [Google Scholar]
- Kuzinkovas, D.; Clement, S. The Detection of COVID-19 in Chest X-rays Using Ensemble CNN Techniques. Information 2023, 14, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nillmani Sharma, N.; Saba, L.; Khanna, N.N.; Kalra, M.K.; Fouda, M.M.; Suri, J.S. Segmentation-Based Classification Deep Learning Model Embedded with Explainable AI for COVID-19 Detection in Chest X-ray Scans. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Rahman Siddiquee, M.M.; Tajbakhsh, N.; Liang, J. Unet++: A nested u-net architecture for medical image segmentation. In Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis and Multimodal Learning for Clinical Decision Support: 4th International Workshop, DLMIA 2018, and 8th International Workshop, ML-CDS 2018, Held in Conjunction with MICCAI 2018, Granada, Spain, 20 September 2018, Proceedings 4; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Vranay, D.; Hliboký, M.; Kovács, L.; Sinčák, P. Using Segmentation to Boost Classification Performance and Explainability in CapsNets. Mach. Learn. Knowl. Extr. 2024, 6, 1439–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaraman, S.; Yang, F.; Zamzmi, G.; Xue, Z.; Antani, S.K. Generalizability of Deep Adult Lung Segmentation Models to the Pediatric Population: A Retrospective Study. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2211.02475. [Google Scholar]
- Muhammad, D.; Bendechache, M. Unveiling the black box: A systematic review of Explainable Artificial Intelligence in medical image analysis. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2024, 24, 542–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlemper, J.; Oktay, O.; Schaap, M.; Heinrich, M.; Kainz, B.; Glocker, B.; Rueckert, D. Attention gated networks: Learning to leverage salient regions in medical images. Med. Image Anal. 2019, 53, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.; Kora, R. A comprehensive review on ensemble deep learning: Opportunities and challenges. J. King Saud Univ.-Comput. Inf. Sci. 2023, 35, 757–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regmi, S.; Subedi, A.; Tomar, N.K.; Bagci, U.; Jha, D. Vision transformer for efficient chest X-ray and gastrointestinal image classification. In Medical Imaging 2025: Computer-Aided Diagnosis; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2025; Volume 13407, pp. 912–923. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Peng, H.; Zheng, N.; Yang, Y.; Hu, H.; Yuan, Y. Efficientvit: Memory efficient vision transformer with cascaded group attention. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 14420–14430. [Google Scholar]
- Qezelbash-Chamak, J.; Hicklin, K. A Hybrid Learnable Fusion of ConvNeXt and Swin Transformer for Optimized Image Classification. IoT 2025, 6, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).