Stability Analysis and Virtual Inductance Control for Static Synchronous Compensators with Voltage-Droop Support in Weak Grid
Abstract
1. Introduction
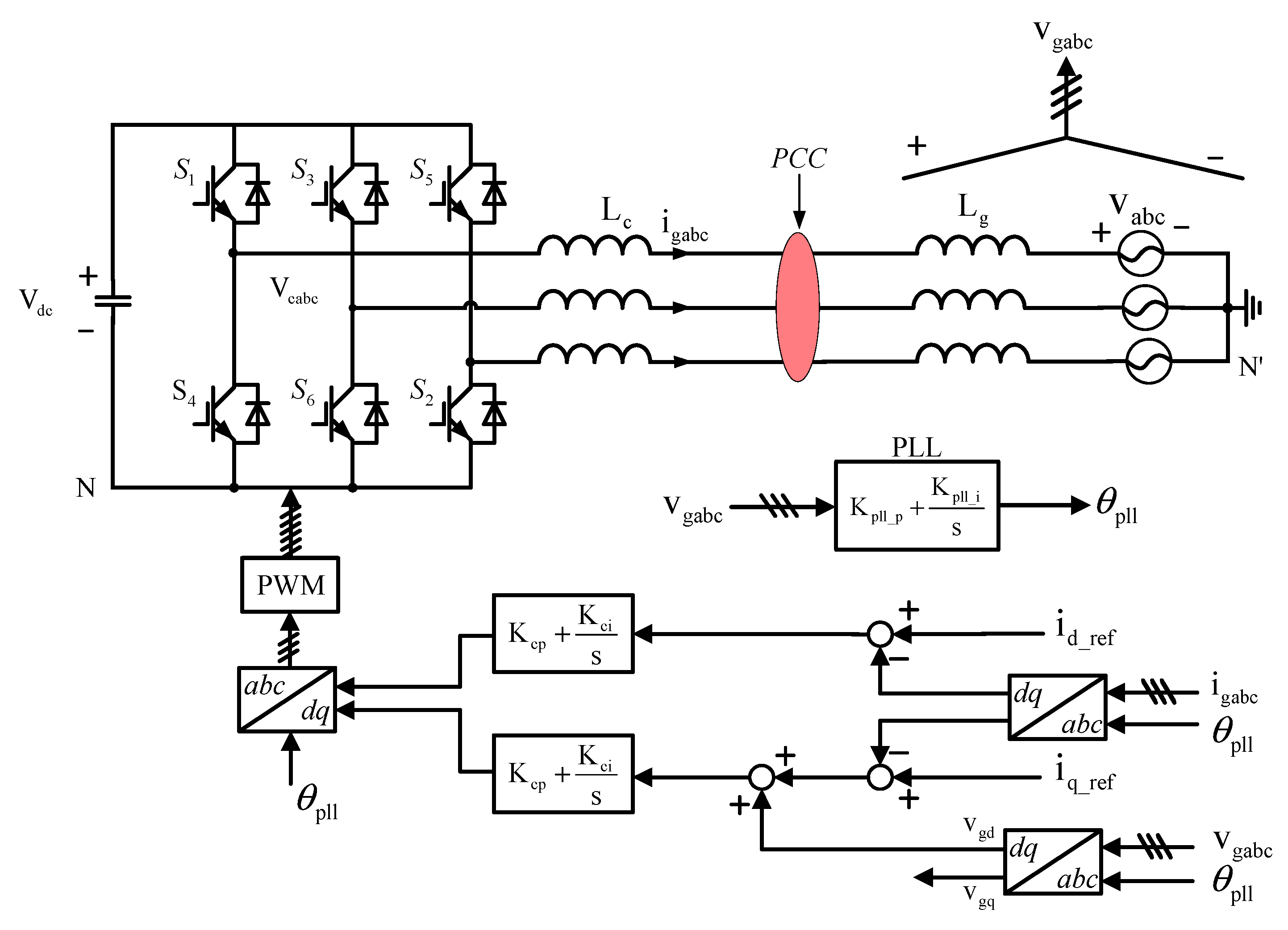
2. Introduction of STATCOMs in Weak Grid
2.1. Basic Operational Principle of STATCOM
2.2. Droop Control
3. Stability Analysis of STATCOMs in Weak Grid
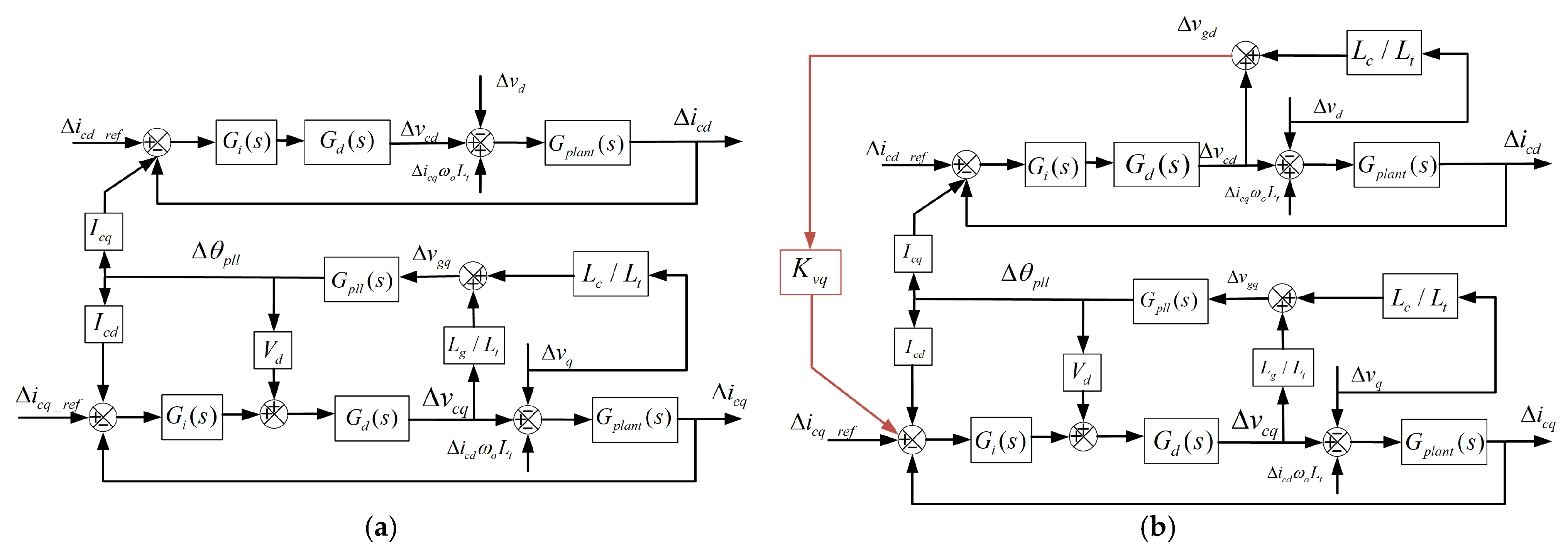
3.1. Derivation of the Small-Signal Control Block Diagram
3.2. Derivation of the Transfer Function
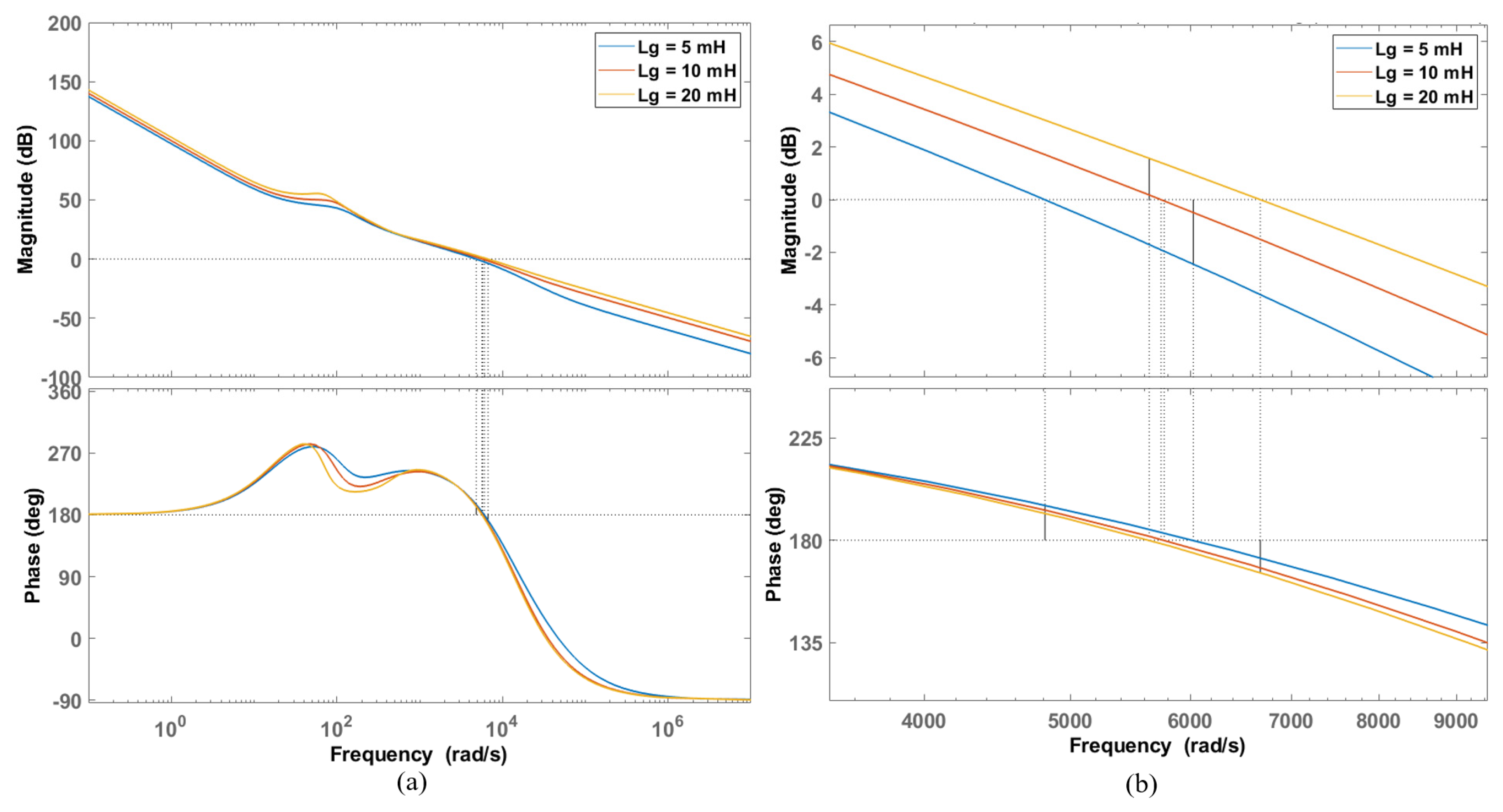
3.3. Stability Analysis
4. Virtual Inductance Control
4.1. Formula Derivation
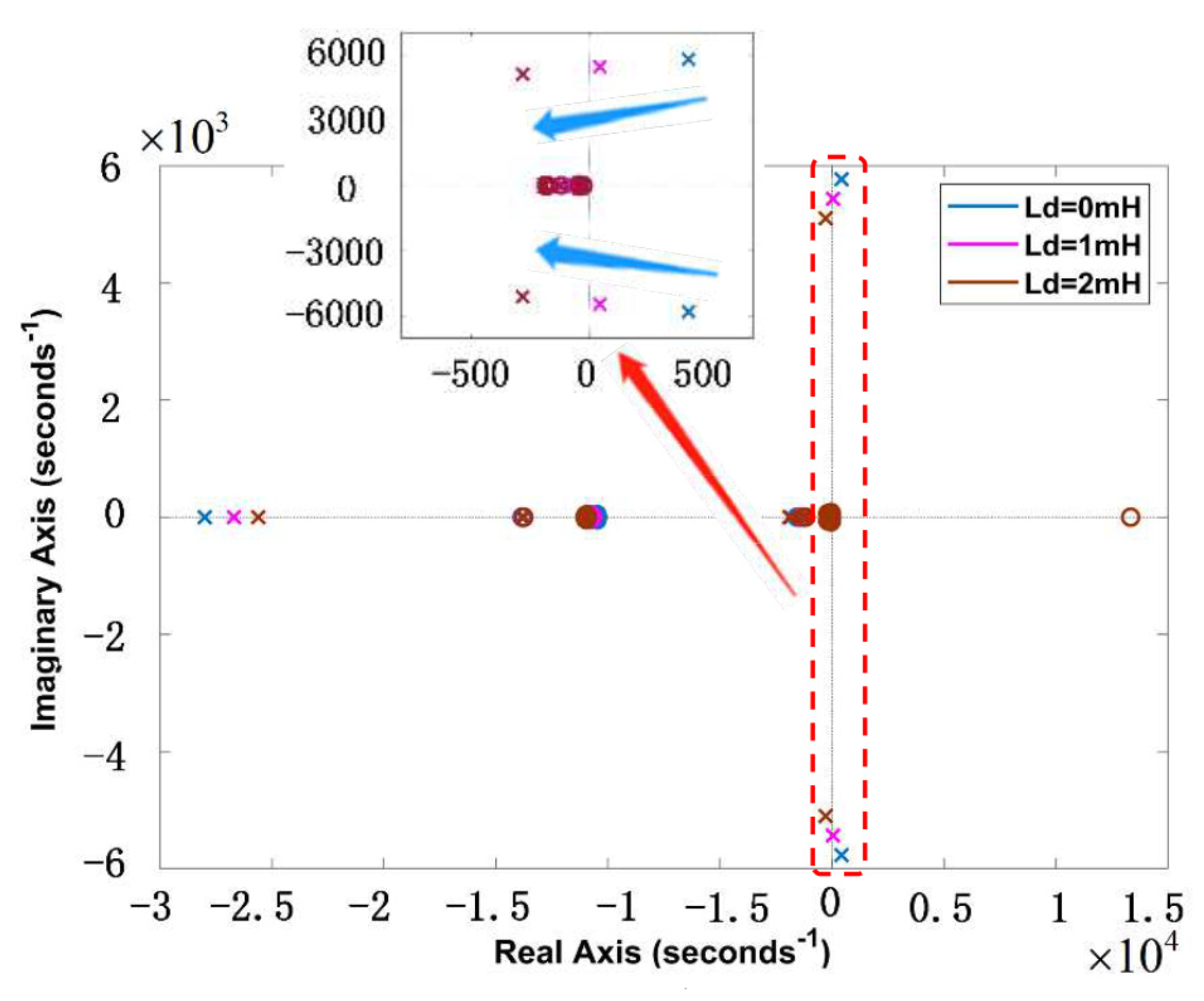
4.2. Stability Analysis
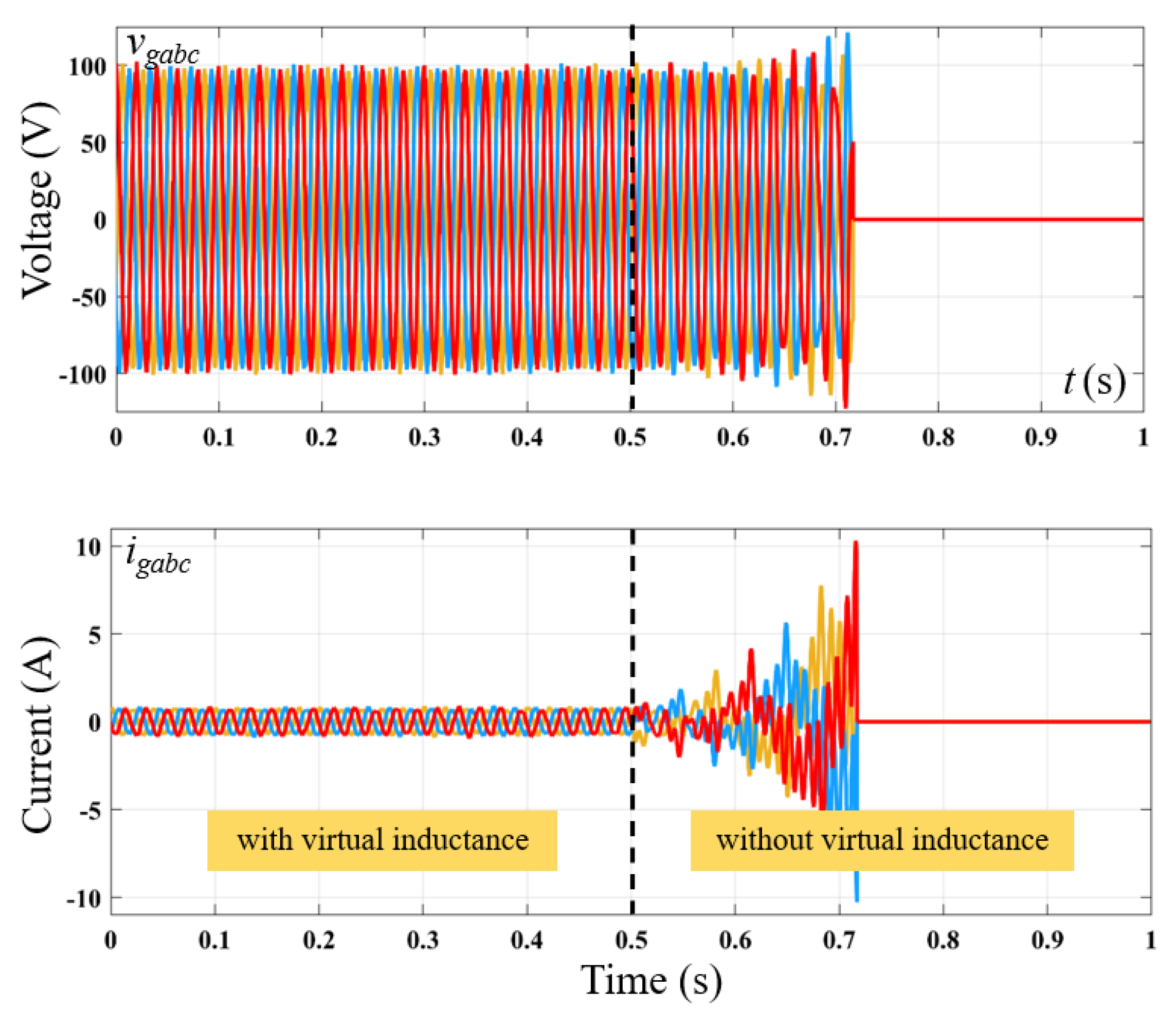
5. Simulation and Experimental Results
5.1. Simulation
5.1.1. Parameter Description
5.1.2. Analysis of SCR in the System
5.1.3. Stability Validation
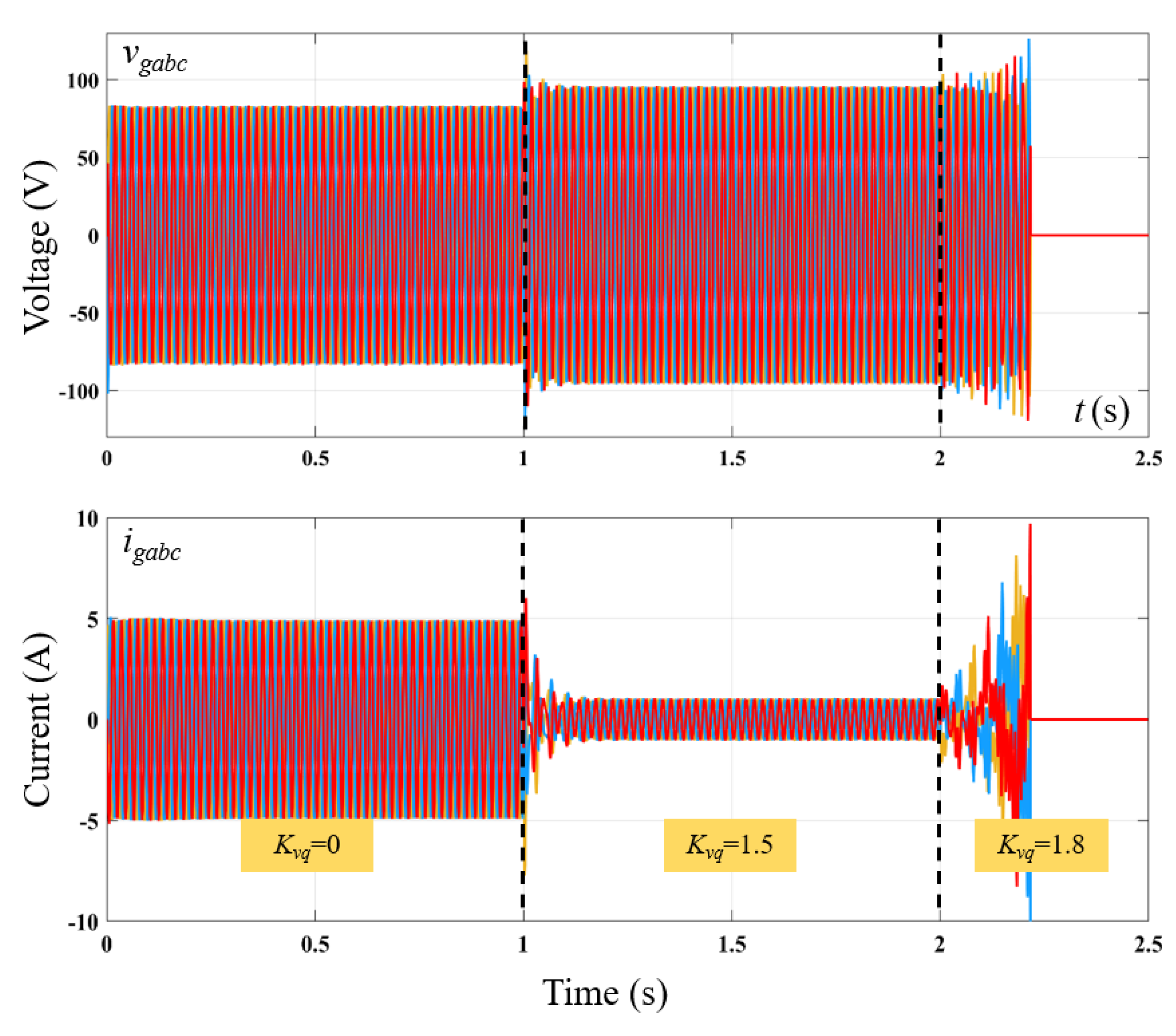
5.1.4. Functional Comparison
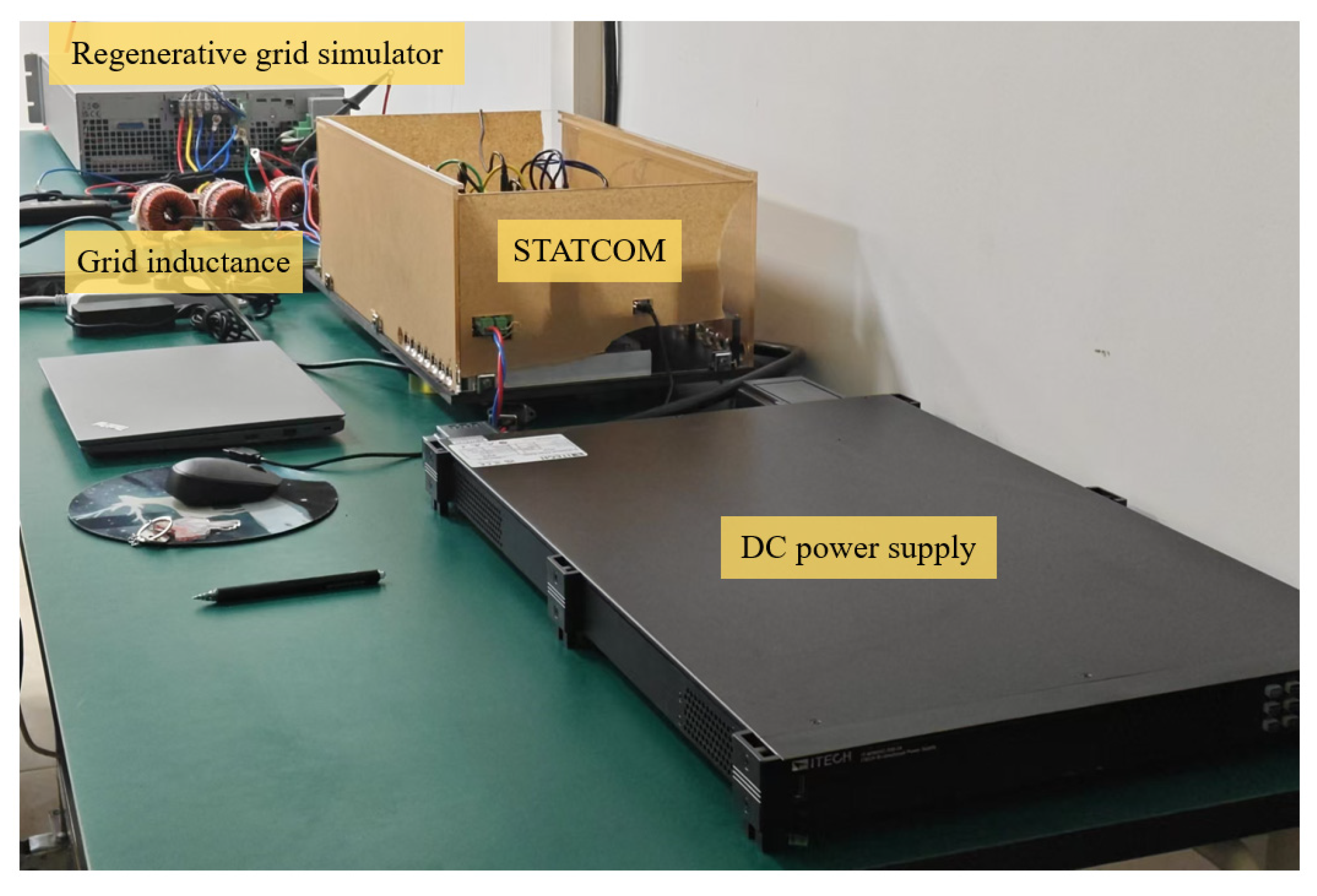
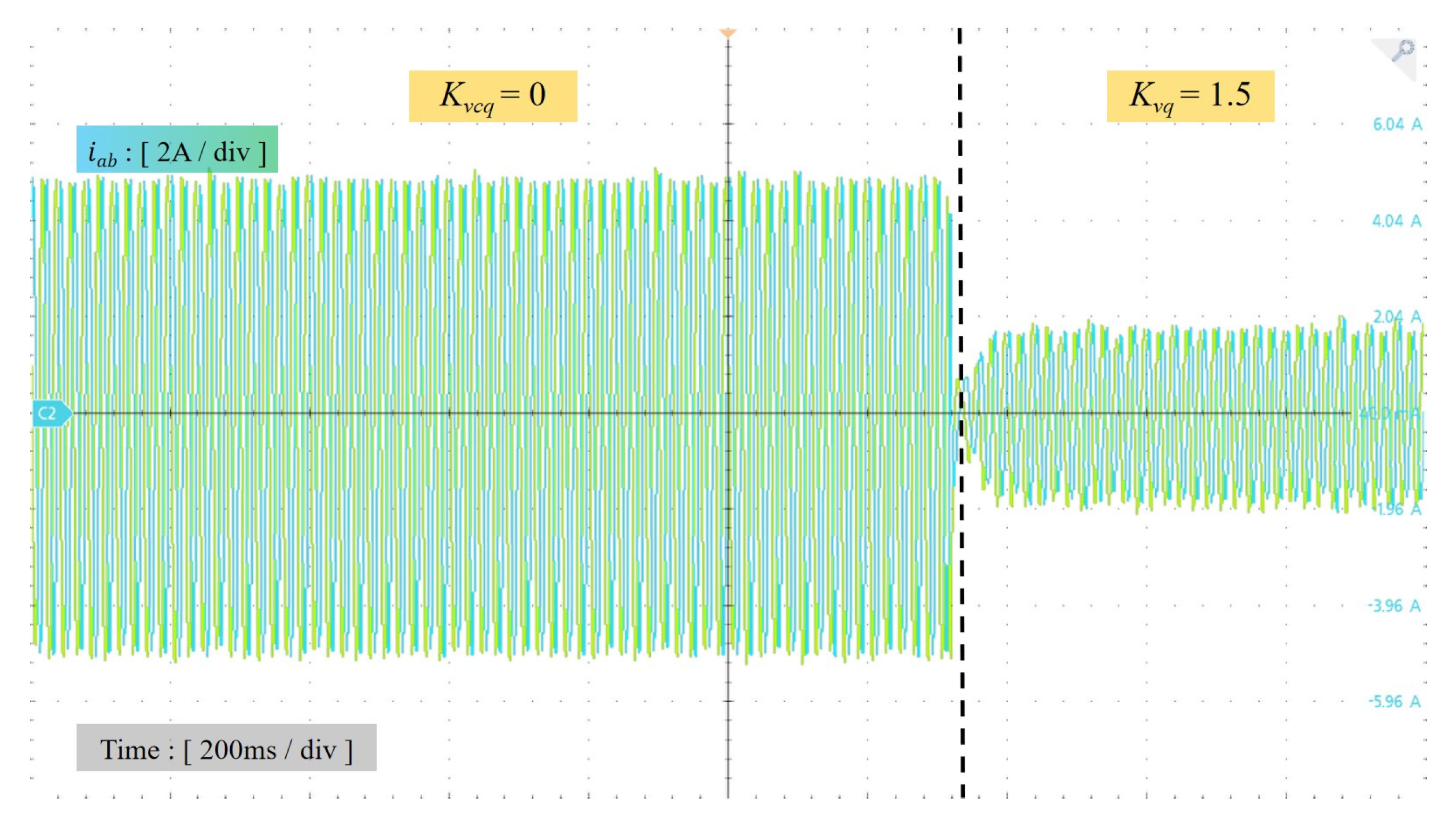
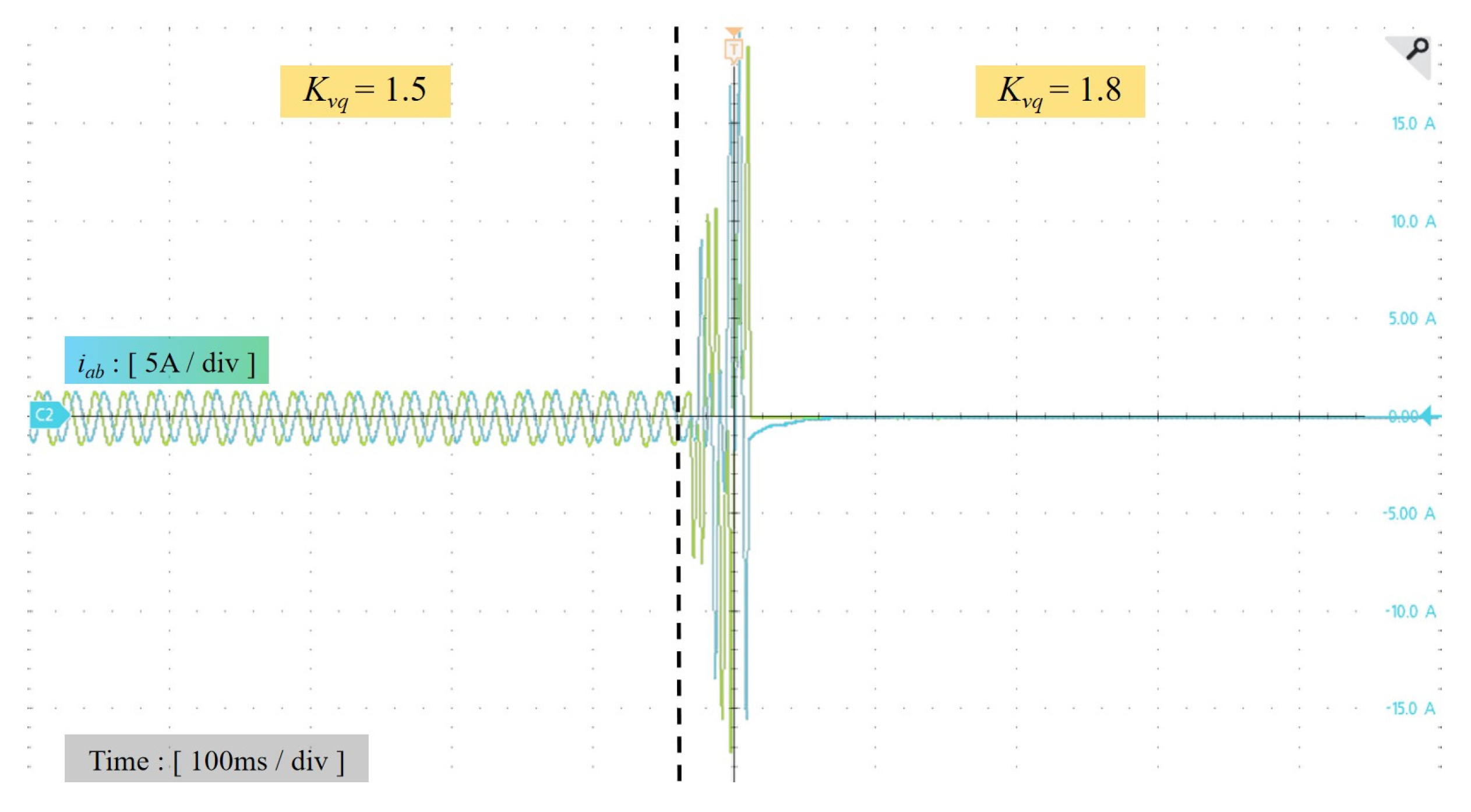
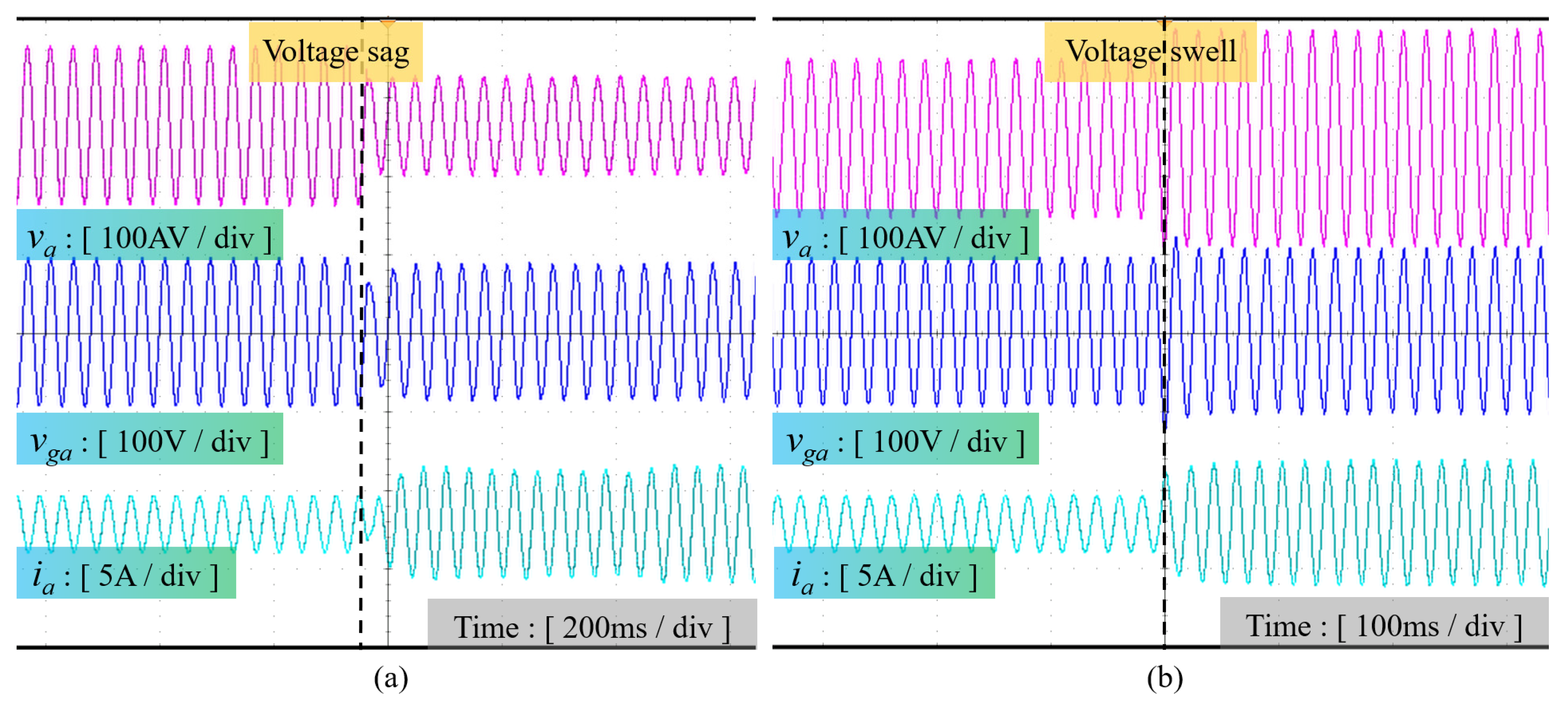
5.2. Experiment
6. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| STATCOMs | Static synchronous compensators |
| UPQCs | Unified power quality conditioners |
| SVCs | Static VAR compensators |
| DVRs | Dynamic voltage restorers |
| FACTS | Flexible AC transmission system |
| PLL | Phase-locked loop |
| SCR | Short-circuit ratio |
References
- Zeng, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Liu, Q.; Liang, G.; Rodriguez, E.; Zou, G.; Zhang, X.; Pou, J. Physics-Informed Deep Transfer Reinforcement Learning Method for the Input-Series Output-Parallel Dual Active Bridge-Based Auxiliary Power Modules in Electrical Aircraft. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2025, 11, 6629–6639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Jiang, S.; Konstantinou, G.; Pou, J.; Zou, G.; Zhang, X. Multi-Objective Controller Design for Grid-Following Converters with Easy Transfer Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2025, 40, 6566–6577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadkikar, V. Enhancing Electric Power Quality Using UPQC: A Comprehensive Overview. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 27, 2284–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LahuNikam, S.; Sandeep, K.K. Analysis of Modified Three-Phase Four-Wire UPQC Design. In Proceedings of the 2017 Third International Conference on Science Technology Engineering & Management (ICONSTEM), Chennai, India, 23–24 March 2017; pp. 586–590. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, S.A.O.D.; Modesto, R.A.; Sampaio, L.P.; Campanhol, L.B.G. Dynamic Improvement of a UPQC System Operating Under Grid Voltage Sag/Swell Disturbances. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II 2024, 71, 2844–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, Y.; Ma, C.; Fu, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, P.; Loh, P.C. The SVC Additional Adaptive Voltage Controller of Isolated Wind-Diesel Power System Based on Double Sliding-Mode Optimal Strategy. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2018, 9, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lam, C.-S.; Wong, M.-C. Multifunctional Hybrid Structure of SVC and Capacitive Grid-Connected Inverter (SVC//CGCI) for Active Power Injection and Nonactive Power Compensation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 1660–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadigh, A.K.; Smedley, K.M. Review of Voltage Compensation Methods in Dynamic Voltage Restorer (DVR). In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting, San Diego, CA, USA, 22–26 July 2012; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, J.; Beng Gooi, H. Phase Angle Control Based Three-Phase DVRwith Power Factor Correction at Point ofCommon Coupling. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2020, 8, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Xiao, L.; Cao, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Fang, B.; Tan, Y.; Zeng, L. Optimal Allocation of Multi-Type FACTS Devices in Power Systems Based on Power Flow Entropy. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2014, 2, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehraeen, S.; Jagannathan, S.; Crow, M.L. Novel Dynamic Representation and Control of Power Systems with FACTS Devices. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2010, 25, 1542–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schauder, C.; Stacey, E.; Lund, M.; Gyugyi, L.; Kovalsky, L.; Keri, A.; Mehraban, A.; Edris, A. AEP UPFC Project: Installation, Commissioning and Operation of the ±160 MVA STATCOM (Phase I). IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 1998, 13, 1530–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papic, I. Power Quality Improvement Using Distribution Static Compensator with Energy Storage System. In Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on Harmonics and Quality of Power. Proceedings (Cat. No.00EX441), Orlando, FL, USA, 1–4 October 2000; Volume 3, pp. 916–920. [Google Scholar]
- Barghi Latran, M.; Teke, A.; Yoldaş, Y. Mitigation of Power Quality Problems Using Distribution Static Synchronous Compensator: A Comprehensive Review. IET Power Electron. 2015, 8, 1312–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.; Li, M.; Weng, X. Droop Controlled Microgrid With DSTATCOM for Reactive Power Compensation and Power Quality Improvement. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 121602–121614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Gupta, S.; Zuhaib, M.; Bhuria, V.; Malik, H.; Almutairi, A.; Afthanorhan, A.; Hossaini, M.A. A Comprehensive Review on STATCOM: Paradigm of Modeling, Control, Stability, Optimal Location, Integration, Application, and Installation. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 2701–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Burgos, R.; Tang, Y.; Boroyevich, D. Stability Analysis on D-Q Frame Impedances in Power Systems with Multiple STATCOMs in Proximity. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Southern Power Electronics Conference (SPEC), Puerto Varas, Chile, 4–7 December 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.-L.; Liang, W.-G.; Gau, H.-S. Design of a Mode Decoupling STATCOM for Voltage Control of Wind-Driven Induction Generator Systems. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2010, 25, 1758–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, R.K.; Siavashi, E.M. Enhancement of Solar Farm Connectivity with Smart PV Inverter PV-STATCOM. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2019, 10, 1161–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lin, H. A Design Method of Phase-Locked Loop for Grid-Connected Converters Considering the Influence of Current Loops in Weak Grid. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2020, 8, 2420–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghazadeh, A.; Davari, M.; Nafisi, H.; Blaabjerg, F. Grid Integration of a Dual Two-Level Voltage-Source Inverter Considering Grid Impedance and Phase-Locked Loop. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2021, 9, 401–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasseter, R.H.; Chen, Z.; Pattabiraman, D. Grid-Forming Inverters: A Critical Asset for the Power Grid. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2020, 8, 925–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Chen, J.; Gong, C. Impedance-Phased Dynamic Control Method for Grid-Connected Inverters in a Weak Grid. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Li, H.; Tang, Y.; Blaabjerg, F. On the Inertia of Future More-Electronics Power Systems. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2019, 7, 2130–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Zou, X.; Zhu, D.; Tong, L.; Zhao, Y.; Kang, Y.; Yuan, X. An Improved Design of Current Controller for LCL-Type Grid-Connected Converter to Reduce Negative Effect of PLL in Weak Grid. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2018, 6, 648–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liserre, M.; Teodorescu, R.; Blaabjerg, F. Stability of Photovoltaic and Wind Turbine Grid-Connected Inverters for a Large Set of Grid Impedance Values. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2006, 21, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D. Impedance Shaping of the Grid-Connected Inverter with LCL Filter to Improve Its Adaptability to the Weak Grid Condition. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2024, 29, 5795–5805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Han, X.; Liu, L.; Pan, P.; Chen, G.; Wang, H. Stability Analysis and Interaction of VSC Grid-Connected System under Weak Grid Condition. In Proceedings of the 2023 Panda Forum on Power and Energy (PandaFPE), Chengdu, China, 27–30 April 2023; pp. 335–339. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J. Impedance-Based Stability Criterion for Grid-Connected Inverters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2011, 26, 3075–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etxegarai, A.; Eguia, P.; Torres, E.; Fernandez, E. Impact of Wind Power in Isolated Power Systems. In Proceedings of the 2012 16th IEEE Mediterranean Electrotechnical Conference, Yasmine Hammamet, Tunisia, 25–28 March 2012; pp. 63–66. [Google Scholar]
- IEEE. IEEE Guide for Planning DC Links Terminating at AC Locations Having Low Short-Circuit Capacities; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Qin, K.; Ruan, X.; Pan, D.; He, Y.; Liu, F. A Robust Grid-Voltage Feedforward Scheme to Improve Adaptability of Grid-Connected Inverter to Weak Grid Condition. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 36, 2384–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazaei, J.; Beza, M.; Bongiorno, M. Impedance Analysis of Modular Multi-Level Converters Connected to Weak AC Grids. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2018, 33, 4015–4025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Angquist, L.; Nee, H.-P. Investigation of StatComs with Capacitive Energy Storage for Reduction of Voltage Phase Jumps in Weak Networks. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2009, 24, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Burgos, R.; Wen, B.; Tang, Y.; Boroyevich, D. Stability Analysis of Power Systems with Multiple STATCOMs in Close Proximity. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 2268–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, D.; Gao, X. Sub- and Super-Synchronous Interactions between STATCOMs and Weak AC/DC Transmissions with Series Compensations. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 33, 7424–7437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, J.M.; GarciadeVicuna, L.; Matas, J.; Castilla, M.; Miret, J. A Wireless Controller to Enhance Dynamic Performance of Parallel Inverters in Distributed Generation Systems. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2004, 19, 1205–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, N.; Undeland, T.M.; Robbins, W.P. Power Electronics: Converters, Applications, and Design, 3rd ed.; Media Enhanced; [Nachdr.]; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; ISBN 978-0-471-22693-2. [Google Scholar]
- Buso, S.; Mattavelli, P. Digital Control in Power Electronics; Synthesis Lectures on Power Electronics; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, J.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Tang, Y. Stability Improvement for Three-Phase Grid-Connected Converters through Impedance Reshaping in Quadrature-Axis. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 8365–8375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Taul, M.G.; Wu, H.; Liao, Y.; Blaabjerg, F.; Harnefors, L. Grid-Synchronization Stability of Converter-Based Resources—An Overview. IEEE Open J. Ind. Appl. 2020, 1, 115–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





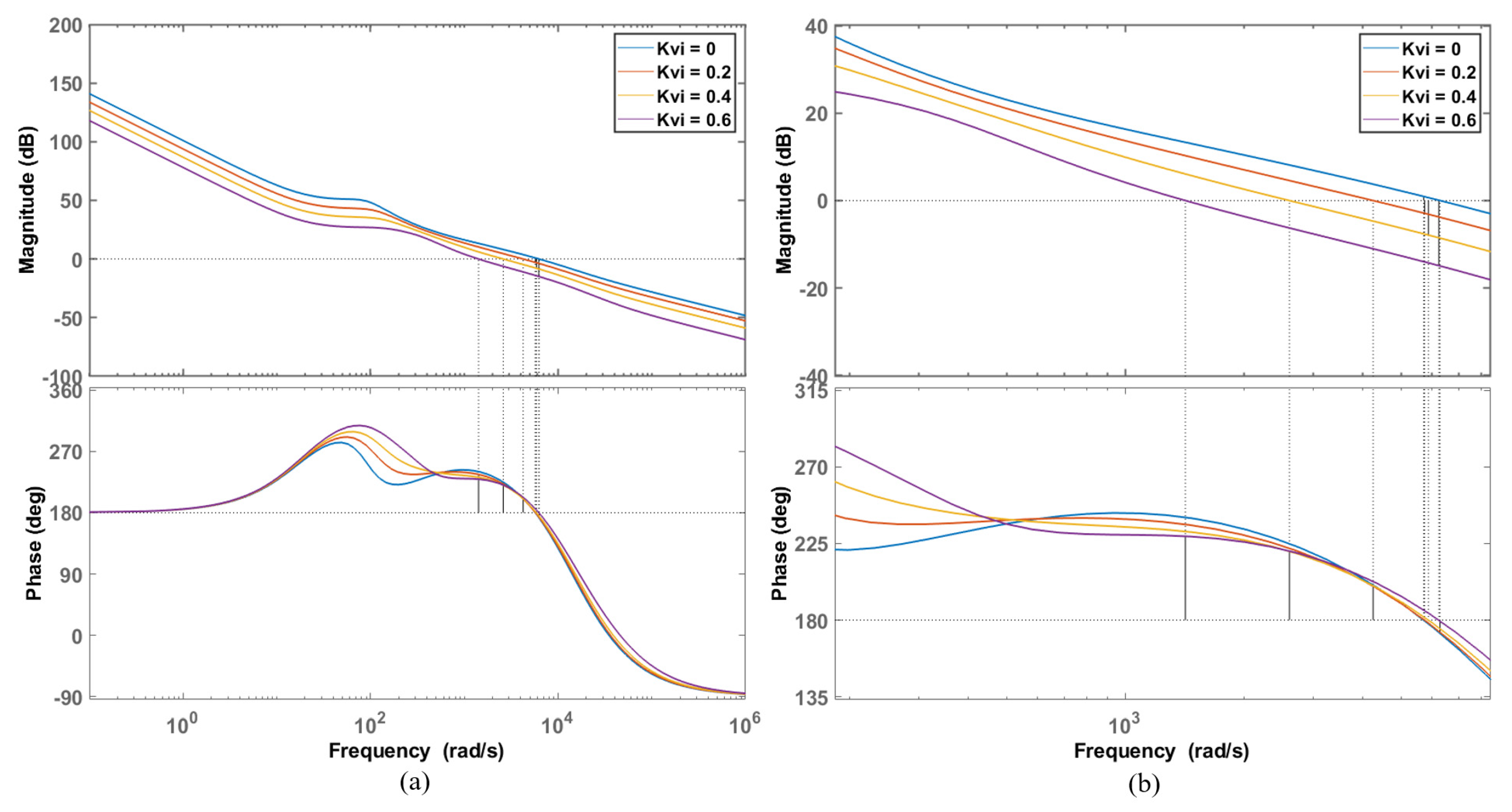
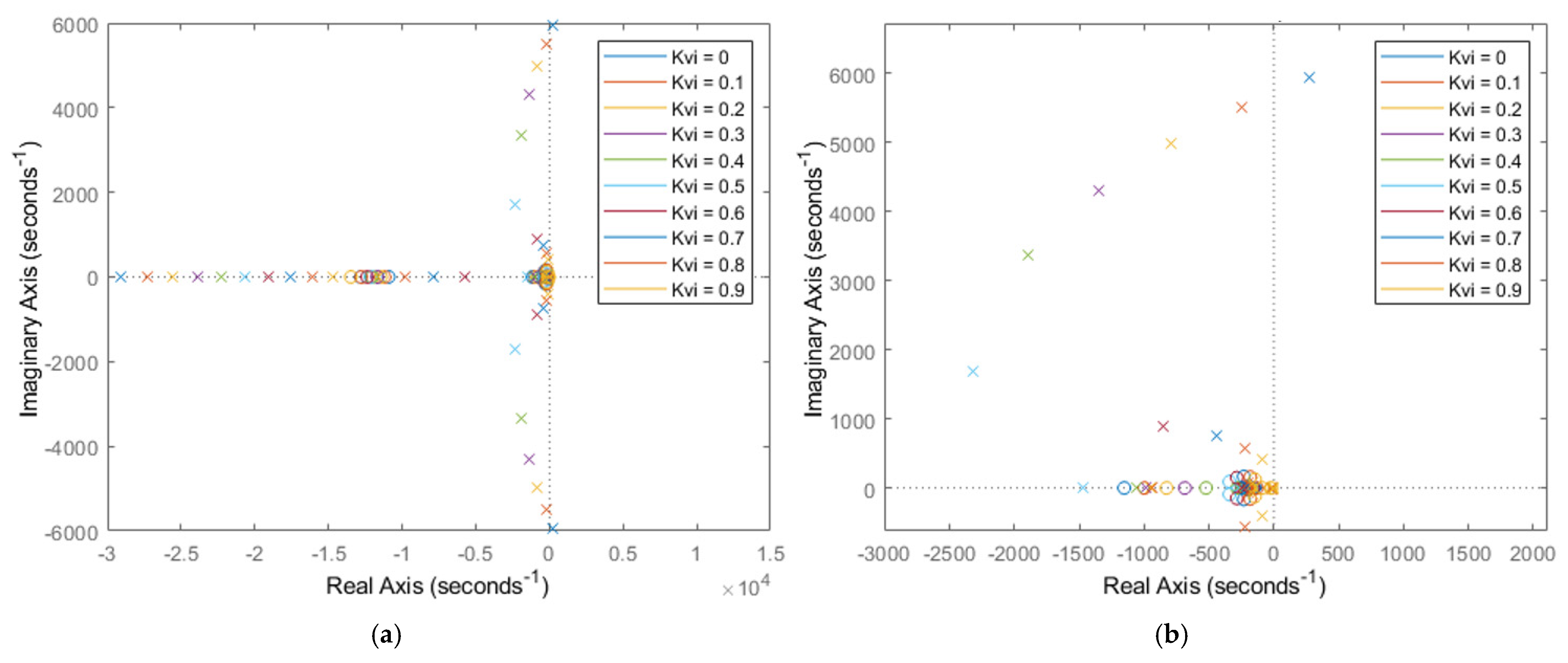

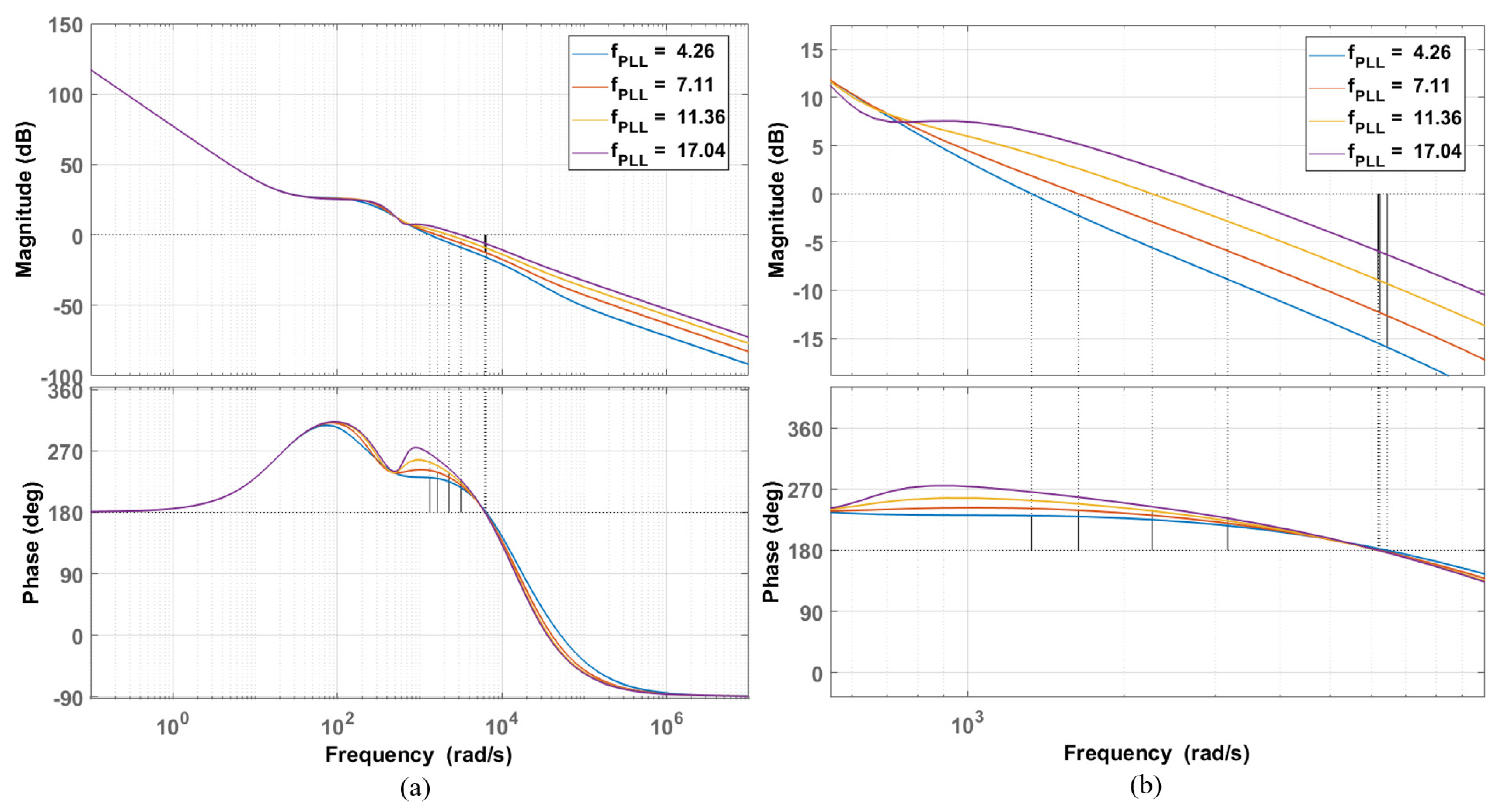




| Gain Margin/dB | Phase Margin/Deg | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 22 | 69 |
| 0.5 | 9.44 | 50.7 |
| 1 | 3.94 | 26.9 |
| 1.6 | 0.0443 | 0.353 |
| 1.7 | −0.464 | −3.76 |
| 1.8 | −0.944 | −7.8 |
| 2 | −1.83 | −15.6 |
| Gain Margin/dB | Phase Margin/Deg | |
|---|---|---|
| 4.26 | 15.9 | 51.1 |
| 7.11 | 12.3 | 58.9 |
| 11.36 | 8.92 | 58 |
| 17.04 | 5.96 | 47.3 |
| Symbol | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Vdc | DC-link voltage | 500 V |
| Lc | Filter inductance | 4 mH |
| Vgd | Grid voltage amplitude | 100 V |
| Lg | Grid inductance | 10 mH |
| fs | Sampling/switching frequency | 10 KHz |
| Kpll_p | PLL proportional gain | 3 |
| Kpll_i | PLL integral gain | 300 |
| Kcp | Current regulator proportional gain | 15 |
| Kci | Current regulator integral gain | 300 |
| Icd_ref | Current reference of d axis | 0 A |
| Icq_ref | Current reference of q axis | 5 A |
| Symbol | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Vdc | DC-link voltage | 500 V |
| Lc | Filter inductance | 4 mH |
| Vgd | Grid voltage amplitude | 100 V |
| Lg | Grid inductance | 10 mH |
| fs | Sampling/switching frequency | 10 KHz |
| kpPLL | PLL proportional gain | 3 |
| kiPLL | PLL integral gain | 300 |
| kpi | Current controller proportional gain | 15 |
| kii | Current controller integral gain | 300 |
| kpac | AC voltage controller proportional gain | 0.01 |
| kiac | AC voltage controller integral gain | 5 |
| kpdc | DC voltage controller proportional gain | 1.25 |
| kidc | DC voltage controller integral gain | 0.225 |
| Qref | Current reference of d axis | 500 W |
| Vdc_ref | Current reference of q axis | 500 V |
| Overshoot | Settling Time/ms | |
|---|---|---|
| 20% | 20% | 21.7 |
| 40% | 26% | 22.7 |
| 60% | 34% | 23.5 |
| 80% | 40% | 28 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Feng, F.; Peng, L.; Xiao, P.; Li, Z. Stability Analysis and Virtual Inductance Control for Static Synchronous Compensators with Voltage-Droop Support in Weak Grid. Electronics 2025, 14, 2203. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14112203
Wang X, Feng F, Peng L, Xiao P, Li Z. Stability Analysis and Virtual Inductance Control for Static Synchronous Compensators with Voltage-Droop Support in Weak Grid. Electronics. 2025; 14(11):2203. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14112203
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xueyuan, Fan Feng, Linyu Peng, Peng Xiao, and Zhenglin Li. 2025. "Stability Analysis and Virtual Inductance Control for Static Synchronous Compensators with Voltage-Droop Support in Weak Grid" Electronics 14, no. 11: 2203. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14112203
APA StyleWang, X., Feng, F., Peng, L., Xiao, P., & Li, Z. (2025). Stability Analysis and Virtual Inductance Control for Static Synchronous Compensators with Voltage-Droop Support in Weak Grid. Electronics, 14(11), 2203. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14112203





