A 5 mW 28 nm CMOS Low-Noise Amplifier with Transformer-Based Electrostatic Discharge Protection for 60 GHz Applications
Abstract
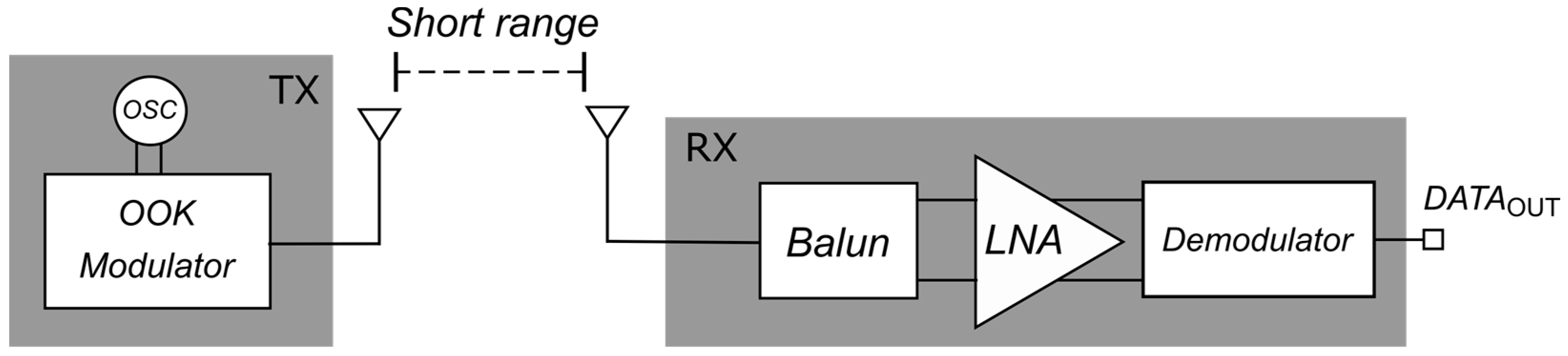
1. Introduction
2. LNA Description
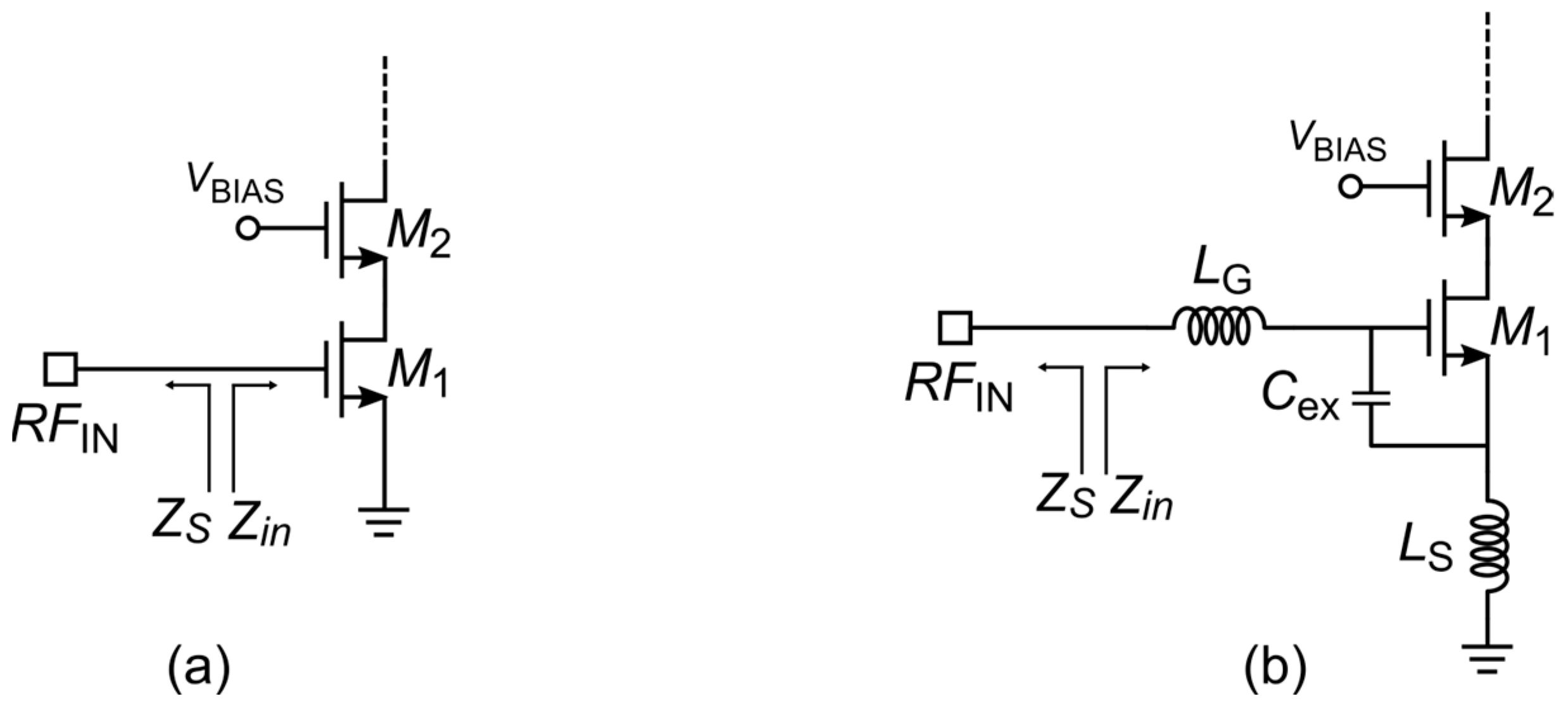
2.1. State-of-the-Art Design Strategies of RF/mm-Wave CMOS LNAs
2.2. Power-Efficient SNIM with Source Impedance Transformation (PE-SNIM)
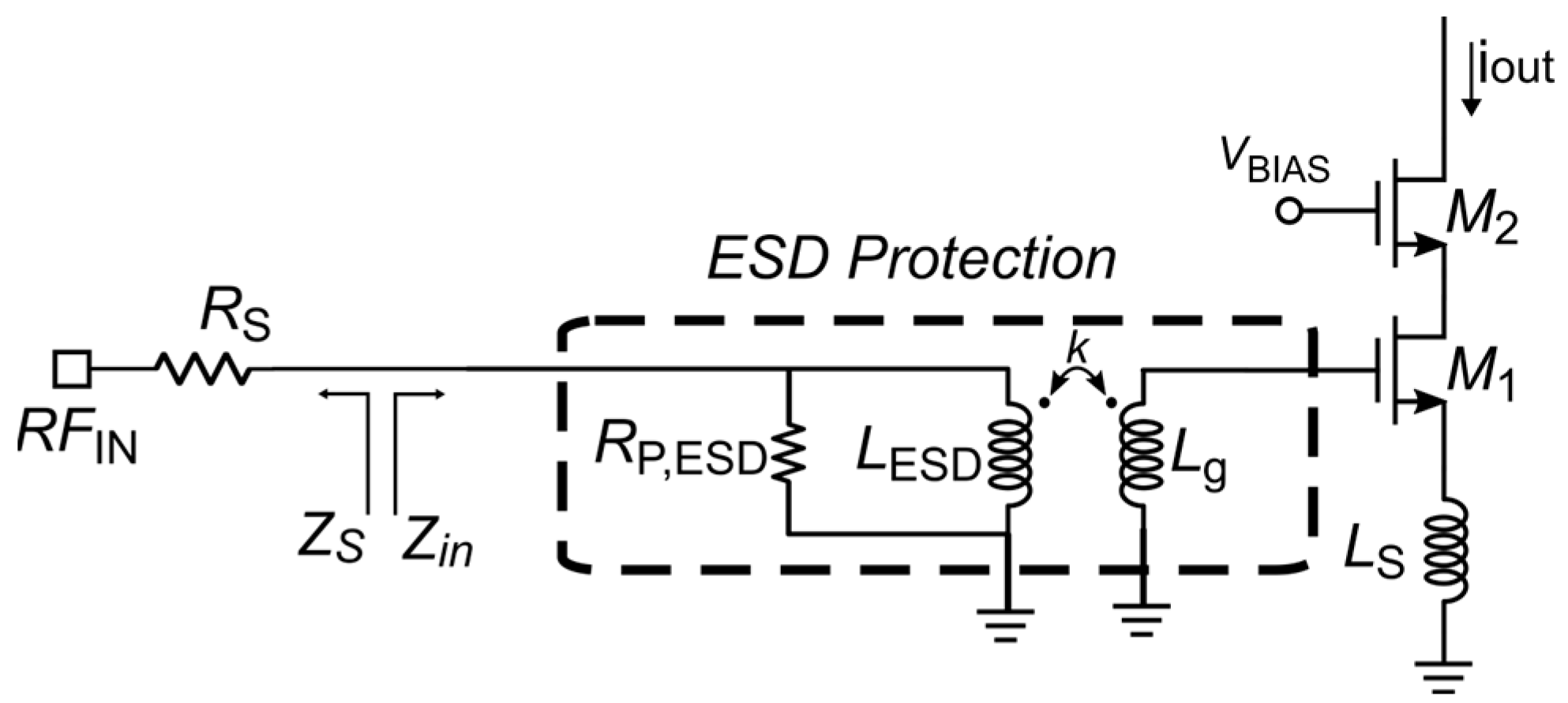
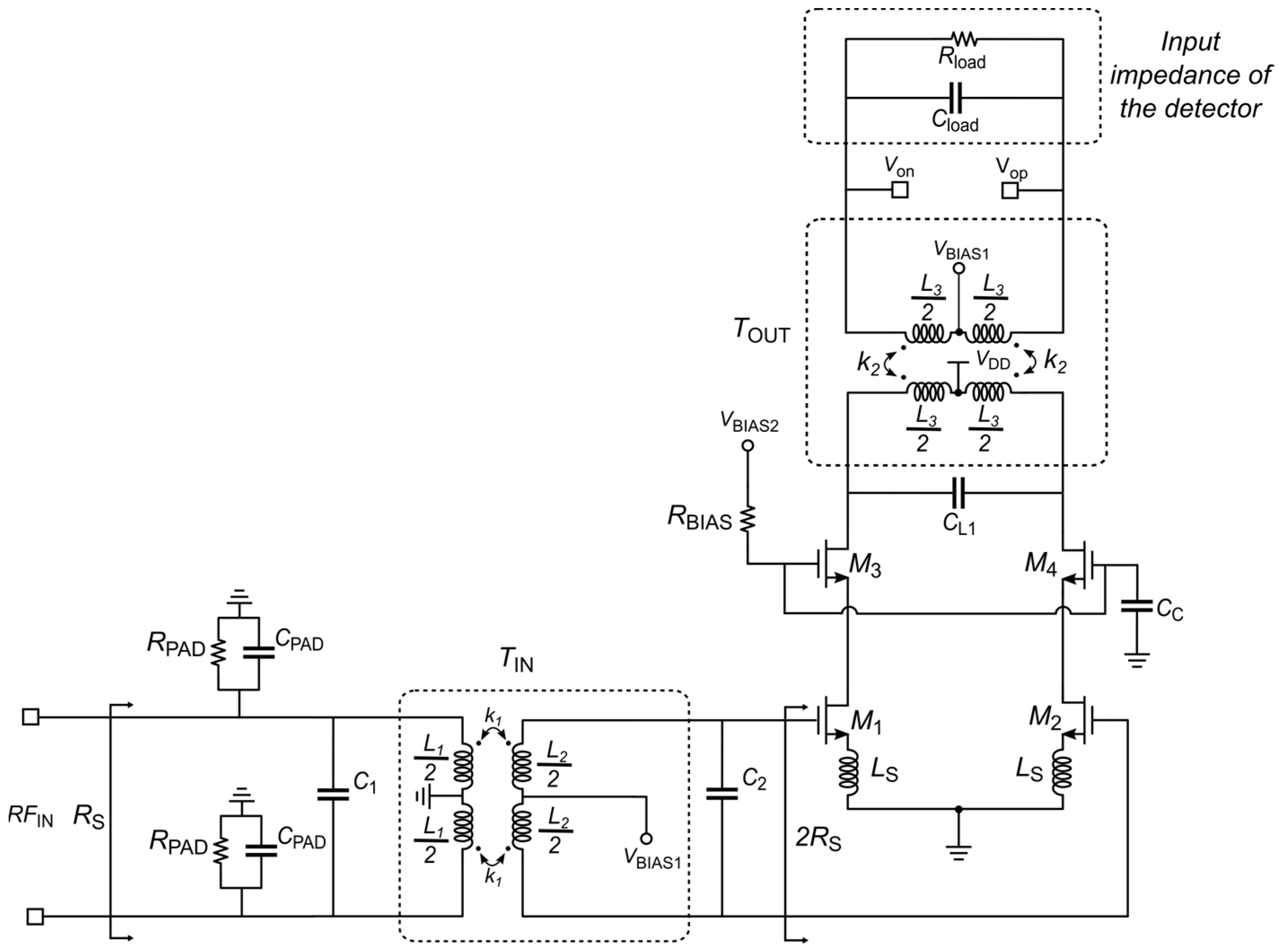
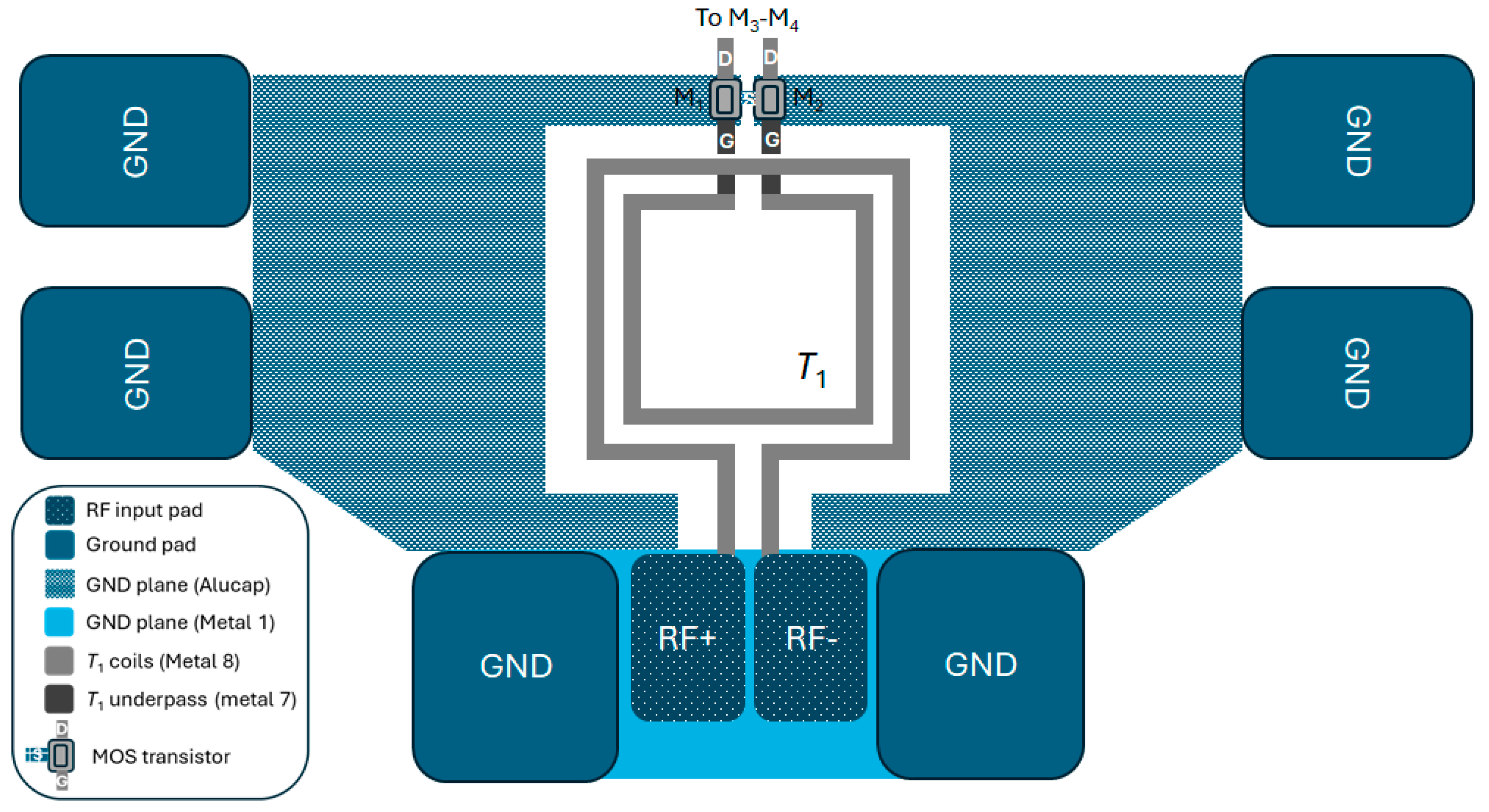
2.3. PE-SNIM Design of the 60 GHz LNA
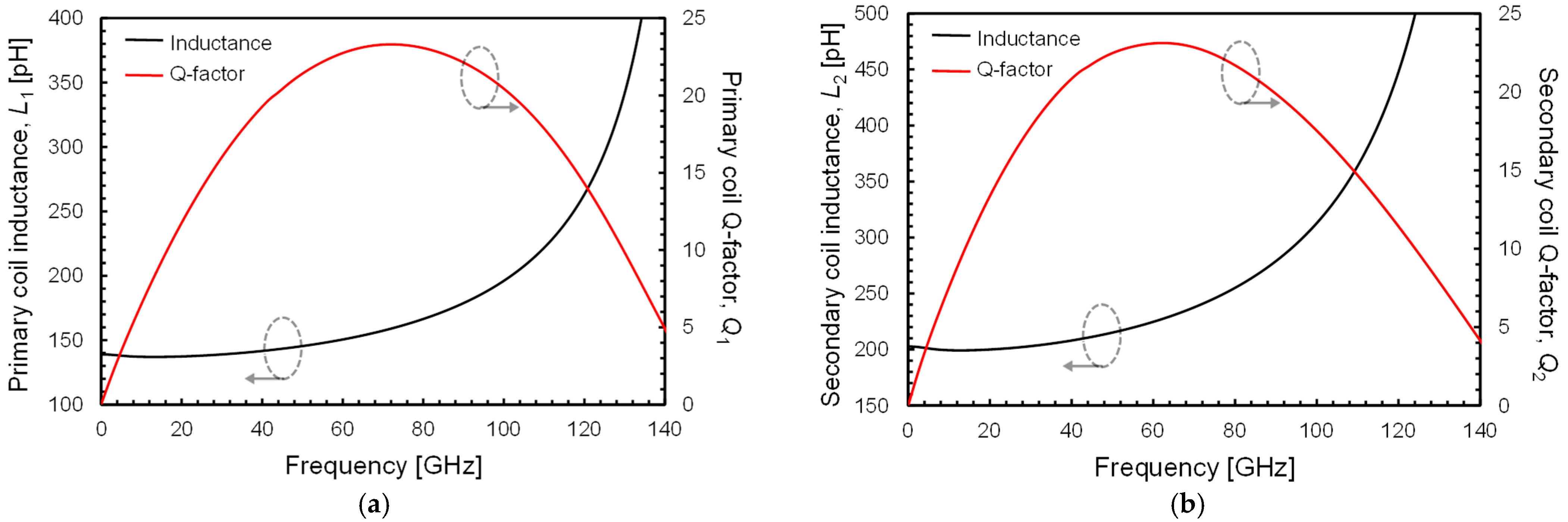
2.4. Transformer Design
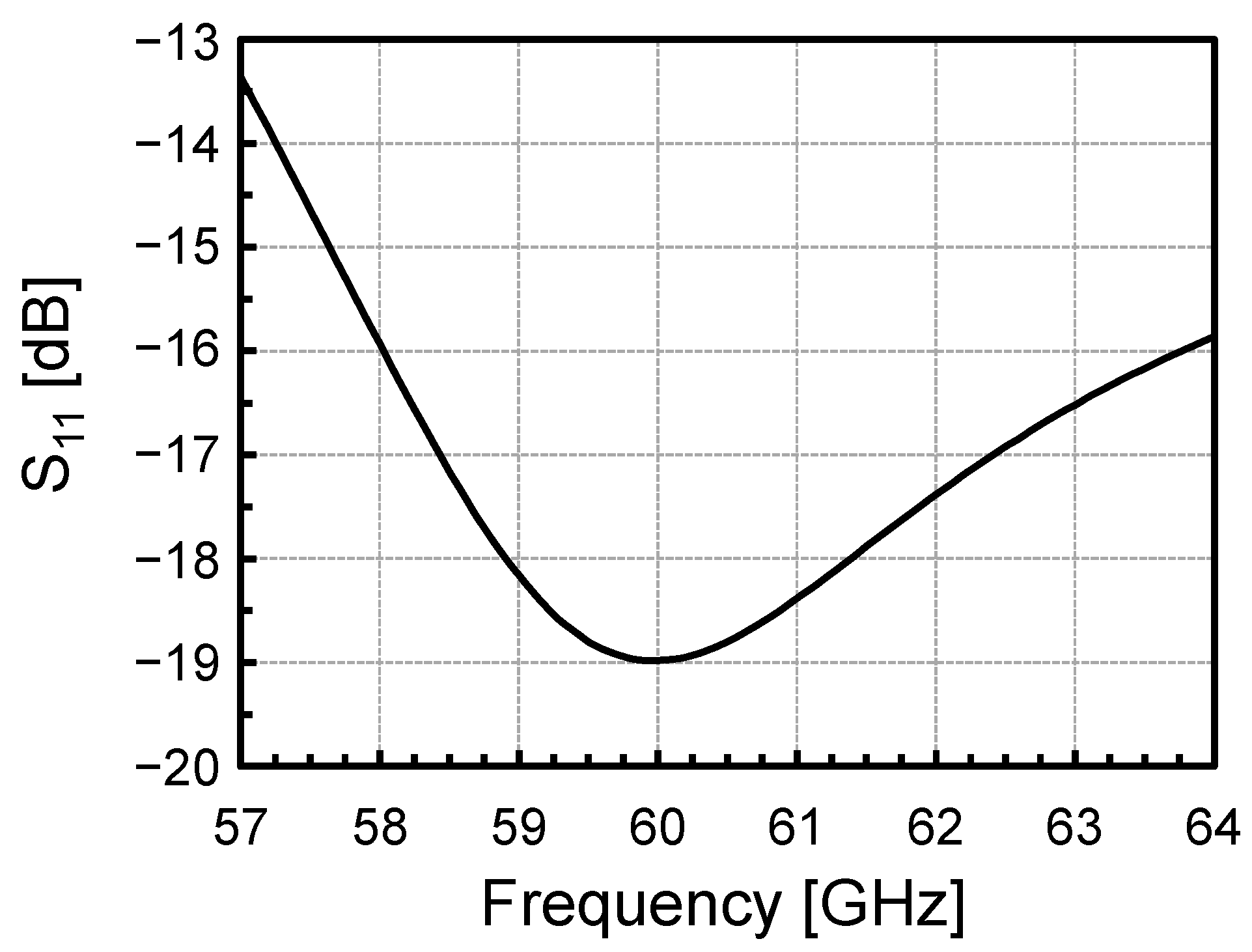
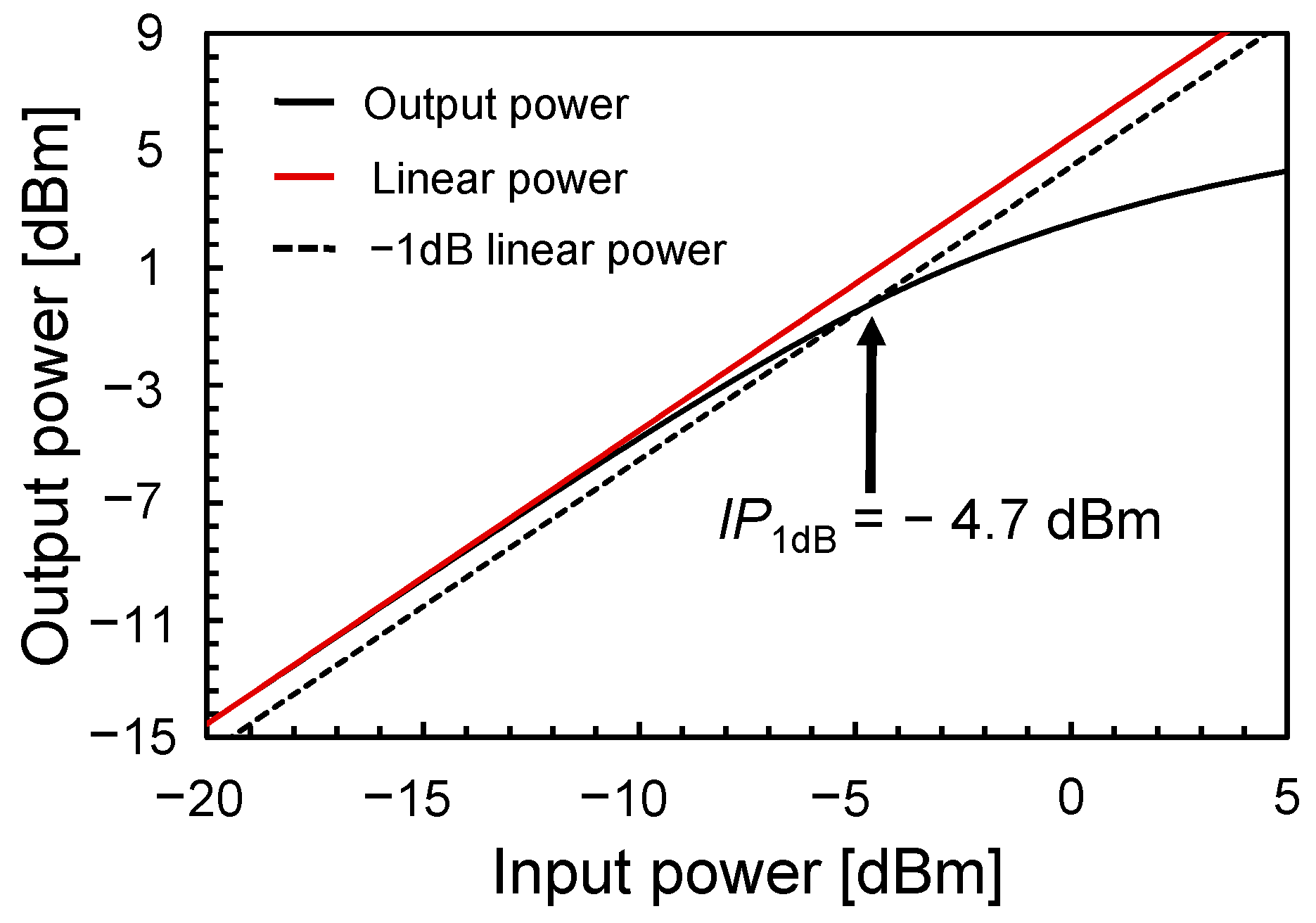
3. Simulation Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siligaris, A.; Richard, O.; Martineau, B.; Mounet, C.; Chaix, F.; Ferragut, R.; Dehos, C.; Lanteri, J.; Dussopt, L.; Yamamoto, S.D.; et al. A 65-nm CMOS fully integrated transceiver module for 60-GHz wireless HD applications. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2021, 46, 3005–3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomkins, A.; Aroca, R.A.; Yamamoto, T.; Nicolson, S.T.; Doi, Y.; Voinigescu, S.P. A zero-IF 60 GHz 65 nm CMOS transceiver with direct BPSK modulation demonstrating up to 6 Gb/s data rates over a 2 m wireless link. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2009, 44, 2085–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, K.; Li, N.; Matsushita, K.; Bunsen, K.; Murakami, R.; Musa, A.; Sato, T.; Asada, H.; Takayama, N.; Ito, S.; et al. A 60-GHz 16QAM/8PSK/QPSK/BPSK direct-conversion transceiver for IEEE802.15.3c. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2011, 46, 2988–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rappaport, T.S.; Murdock, J.N.; Gutierrez, F. State of the art in 60-GHz integrated circuits and systems for wireless communications. Proc. IEEE 2011, 99, 1390–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trotta, S.; Wintermantel, M.; Dixon, J.; Moeller, U.; Jammers, R.; Hauck, T.; Samulak, A.; Dehlink, B.; Shun-Meen, K.; Li, H.; et al. An RCP packaged transceiver chipset for automotive LRR and SRR systems in SiGe BiCMOS technology. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2012, 60, 778–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giammello, V.; Ragonese, E.; Palmisano, G. Transmitter chipset for 24/77-GHz automotive radar sensors. In Proceedings of the IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits Symposium, Anaheim, CA, USA, 23–25 May 2010; pp. 75–78. [Google Scholar]
- Sapone, G.; Ragonese, E.; Italia, A.; Palmisano, G. A 0.13-μm SiGe BiCMOS colpitts-based VCO for W-band radar transmitters. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2013, 61, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomkins, A.; Poon, A.; Juntunen, E.; El-Gabaly, A.; Temkine, G.; To, Y.L.; Farnsworth, C.; Tabibiazar, A.; Fakharzadeh, M.; Jafarlou, S.; et al. A 60 GHz, 802.11ad/WiGig-compliant transceiver for infrastructure and mobile applications in 130 nm SiGe BiCMOS. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2015, 50, 2239–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papotto, G.; Nocera, C.; Finocchiaro, A.; Parisi, A.; Cavarra, A.; Castorina, A.; Ragonese, E.; Palmisano, G. A 27-mW W band radar receiver with effective TX leakage suppression in 28 nm FD-SOI CMOS. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2021, 69, 4132–4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocera, C.; Papotto, G.; Cavarra, A.; Ragonese, E.; Palmisano, G. A 13.5-dBm 1-V power amplifier for W-band automotive radar applications in 28-nm FD-SOI CMOS technology. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2021, 69, 1654–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kankuppe, A.; Park, S.; Renukaswamy, P.T.; Wambacq, P.; Craninckx, J. A Wideband 62-mW 60-GHz FMCW radar in 28-nm CMOS. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2021, 69, 2921–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragonese, E.; Papotto, G.; Nocera, C.; Cavarra, A.; Palmisano, G. CMOS automotive radar sensors: mm-Wave circuit design challenges. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2022, 69, 2610–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cathelin, A. Fully depleted silicon on insulator devices CMOS: The 28-nm node is the perfect technology for analog, RF, mmW, and mixed-signal system-on-chip integration. IEEE Solid-State Circuits Mag. 2017, 9, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preez, J.D.; Sinha, S.; Sengupta, K. SiGe and CMOS technology for state-of-the-art millimeter-wave transceivers. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 55596–55617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragonese, E.; Nocera, C.; Cavarra, A.; Papotto, G.; Spataro, S.; Palmisano, G. A comparative analysis between standard and mm-wave optimized BEOL in a nanoscale CMOS technology. Electronics 2020, 9, 2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferchischi, A.; Rehman, S.U.; Carta, C.; Ellinger, F. 22-Gb/s 60-GHz OOK demodulator in 0.13-µm SiGe BiCMOS for ultra-high-speed wireless communication. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium (IMS), Boston, MA, USA, 2–7 June 2019; pp. 247–250. [Google Scholar]
- Ferchichi, A.; Rehman, S.U.; Rieß, V.; Carta, C.; Ellinger, F. 20 Gb/s 60-GHz OOK receiver for high-data-rate short-range wireless communications. In Proceedings of the European Microwave Integrated Circuits Conference (EuMIC), Utrecht, The Netherlands, 10–15 January 2021; pp. 45–48. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, F.; Brinkhoff, J.; Kang, K.; Pham, D.D.; Yuan, X. A low power 60GHz OOK transceiver system in 90 nm CMOS with innovative onchip AMC antenna. In Proceedings of the IEEE Asian Solid-State Circuits Conference, Taipei, Taiwan, 6–18 November 2009; pp. 349–352. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Lu, H.; Chang, C. A low-power fully integrated 60 GHz transceiver system with OOK modulation and onboard antenna assembly. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference—Digest of Technical Papers, San Francisco, CA, USA, 8–12 February 2009; pp. 316–317 and 317a. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.J.; Byeon, C.W.; Eun, K.C.; Oh, I.Y.; Park, C.S. Gbps 60 GHz CMOS OOK modulator and demodulator. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Compound Semiconductor Integrated Circuit Symposium (CSICS), Monterey, CA, USA, 3–6 October 2010; pp. 145–149. [Google Scholar]
- Byeon, C.W.; Yoon, C.H.; Park, C.S. A 67-mW 10.7-Gb/s 60-GHz OOK CMOS transceiver for short-range wireless communications. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2013, 61, 3391–3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Hong, W.; Liang, W.F.; Chen, J.X.; Jiang, X.; Yan, P.P.; Wu, K. A low-power low-cost 45-GHz OOK transceiver system in 90-nm CMOS for multi-Gb/s transmission. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2014, 62, 2105–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzunkol, M.; Shin, W.; Rebeiz, G.M. Design and analysis of a low-power 3–6-Gb/s 55-GHz OOK receiver with high-temperature performance. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2012, 60, 3263–3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byeon, C.W.; Eun, K.C.; Park, C.S. A 2.65-pJ/Bit 12.5-Gb/s 60-GHz OOK CMOS transmitter and receiver for proximity communications. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2020, 68, 2902–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Kim, C.; Ihm, G.; Yang, M.; Lee, S. CMOS low-noise amplifier design optimization techniques. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2004, 5, 1433–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Chun, J.H.; Beebe, S.G.; Dutton, R.W. ESD design strategies for high-speed digital and RF circuits in deeply scaled silicon technologies. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Reg. Pap. 2010, 9, 2301–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amerasekera, E.A.; Duvvury, C. ESD in Silicon Integrated Circuits; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Voldman, S.H. ESD Basics: From Semiconductor Manufacturing to Product Use; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Pepe, D.; Chlis, I.; Zito, D. Transformer-based input integrated matching in cascode amplifiers: Analytical proofs. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2018, 5, 1495–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.H.; Hsu, S.S.H.; Hsueh, F.-L.; Jou, C.P.; Yeh, T.-J. A 17.5–26 GHz low-noise amplifier with over 8 kV ESD protection in 65 nm CMOS. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2012, 9, 483–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issakov, V.; Waas, S.K.; Ciocoveanu, R.; Simbürger, W.; Geiselbrechtinger, A. A 6 kV ESD-protected low-power 24 GHz LNA for radar applications in SiGe BiCMOS. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE BiCMOS and Compound Semiconductor Integrated Circuits and Technology Symposium (BCICTS), San Diego, CA, USA, 5–17 October 2018; pp. 194–197. [Google Scholar]
- Haus, H.A.; Atkinson, W.R.; Branch, G.M.; Davenport, W.B.; Fonger, W.H.; Harris, W.A.; Harrison, S.W.; Mcleod, W.W.; Stodola, E.K.; Talpey, T.E. Representation of noise in linear two ports. Proc. IRE 1960, 48, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voinigescu, S.P.; Maliepaard, M.C.; Showell, J.L.; Babcock, G.E.; Marchesan, D.; Schroter, M.; Schvan, P.; Harame, D.L. A scalable high-frequency noise model for bipolar transistors with application optimal transistor sizing for low-noise amplifier design. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 1997, 9, 1430–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaeffer, D.K.; Lee, T.H. A 1.5 V, 1.5 GHz CMOS low noise amplifier. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 1997, 5, 745–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreani, P.; Sjoland, H. Noise optimization of an inductively degenerated CMOS low noise amplifier. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. 2001, 9, 835–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borremans, J.; Thijs, S.; Wambacq, P.; Linten, D.; Rolain, Y.; Kuijk, M. A 5 kV HBM transformer-based ESD protected 5–6 GHz LNA. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Symposium on VLSI Circuits, Kyoto, Japan, 14–16 June 2007; pp. 100–101. [Google Scholar]
- Galal, S.; Razavi, B. 40-Gb/s amplifier and ESD protection circuit in 0.18-/spl mu/m CMOS technology. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2004, 39, 2389–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linten, D.; Thijs, S.; Jeamsaksiri, W.; Ramos, J.; Mercha, A.; Natarajan, M.I.; Wambacq, P.; Scholten, A.J.; Decoutere, S. An integrated 5 GHz low-noise amplifier with 5.5 kV HBM ESD protection in 90 nm RF CMOS. In Proceedings of the VLSI Circuits Symposium, Kyoto, Japan, 16–18 June 2005; pp. 86–89. [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua, A. Fundamentals of integrated transformers: From principles to applications. IEEE Solid-State Circuits Mag. 2020, 12, 86–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, B.; Kerherve, E.; Gueret, J.B.B.; Belot, D. Design of high transformation ratio millimeter-wave integrated transformers. Int. J. Microw. Wirel. Technol. 2012, 4, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Gao, H.; Dommele, R.V.; Kammerer, M.K.M.; Baltus, P.G.M. A 60 GHz low noise variable gain amplifier with small noise figure and IIP3 variation in a 40-nm CMOS technology. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE MTT-S International Wireless Symposium (IWS), Chengdu, China, 6–10 May 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Juntunen, E.; Leung MC, H.; Barale, F.; Rachamadugu, A.; Yeh, D.A.; Perumana, B.G.; Sen, P.; Dawn, D.; Sarkar, S.; Pinel, S. A 60-GHz 38-pJ/bit 3.5-Gb/s 90-nm CMOS OOK digital radio. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2010, 58, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, K. A millimeter-wave intra-connect solution. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2010, 45, 2655–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickson, T.O.; LaCroix, M.-A.; Boret, S.; Gloria, D.; Beerkens, R.; Voinigescu, S.P. 30–100-GHz inductors and transformers for millimeter-wave (Bi)CMOS integrated circuits. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2005, 53, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimmelspacher, J.; Breun, S.; Werthof, A.; Geiselbrechtinger, A.; Weigel, R.; Issakov, V. Experimental comparison of integrated transformers in a 28 nm bulk CMOS technology. In Proceedings of the 2018 48th European Microwave Conference (EuMC), Madrid, Spain, 23–27 September 2018; pp. 1097–1100. [Google Scholar]
- Ragonese, E.; Sapone, G.; Giammello, V.; Palmisano, G. Analysis and modeling of interstacked transformers for mm-wave applications. Analog Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 2012, 72, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavarra, A.; Nocera, C.; Papotto, G.; Ragonese, E.; Palmisano, G. Transformer design for 77-GHz down-converter in 28-nm FD-SOI CMOS technology. In Applications in Electronics Pervading Industry, Environment and Society; Saponara, S., De Gloria, A., Eds.; ApplePies 2018; Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 573. [Google Scholar]
- Nocera, C.; Cavarra, A.; Ragonese, E.; Palmisano, G.; Papotto, G. Down-converter solutions for 77-GHz automotive radar sensors in 28-nm FD-SOI CMOS technology. In Proceedings of the 2018 14th Conference on Ph.D. Research in Microelectronics and Electronics (PRIME), Prague, Czech Republic, 2–5 July 2018; pp. 153–156. [Google Scholar]
- Spataro, S.; Salerno, N.; Papotto, G.; Ragonese, E. The effect of a metal PGS on the Q-factor of spiral inductors for RF and mm-wave applications in a 28-nm CMOS technology. Int. J. RF Microw. Comput.-Aided Eng. 2020, 30, e22368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spataro, S.; Ragonese, E. Design and optimization of silicon-integrated inductive components for automotive radar applications in K- and W-bands. In Proceedings of the AEIT International Conference of Electrical and Electronic Technologies for Automotive (AEIT AUTOMOTIVE), Turin, Italy, 18–20 November 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Maksimović, D.; Notermans, G. Simulating electrostatic discharge. In Proceedings of the Small Systems Simulation Symposium, Niš, Serbia, 12–14 February 2010; pp. 6–12. [Google Scholar]
- JEDEC Publication JEP155; Recommended ESD Target Levels for HBM/MM Qualification. JEDEC Solid State Technology Association: Arlington, VA, USA, 2008.
- Carrara, F.; Italia, A.; Ragonese, E.; Palmisano, G. Design methodology for the optimization of transformer loaded RF circuits. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Reg. Pap. 2006, 53, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-C.; Kuo, H.-C.; Huang, T.-H.; Chuang, H.-R. Low-power, high-gain V-band CMOS low noise amplifier for microwave radiometer applications. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2011, 21, 104–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gramegna, G.; Paparo, M.; Erratico, P.G.; De Vita, P. A sub-1-dB NF ±2.3-kV ESD-protected 900-MHz CMOS LNA. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2001, 36, 1010–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, M.-T.; Lin, Y.-H.; Yang, J.-C. Design of UWB CMOS LNA based on current-reused topology and forward body-bias for high figure of merit. In Proceedings of the 2013 Asia-Pacific Microwave Conference Proceedings (APMC), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 5–8 November 2013; pp. 772–774. [Google Scholar]
- Asgaran, S.; Deen, M.J.; Chen, C.-H. Design of the input matching network of RF CMOS LNAs for low-power operation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Reg. Pap. 2007, 54, 544–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritsche, D.; Tretter, G.; Carta, C.; Ellinger, F. Millimeter-wave low-noise amplifier design in 28-nm low-power digital CMOS. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2015, 63, 1910–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, J.; Feng, G.; Wang, Y. A compact 60 GHz LNA with 22.7-dB gain and 4.4-dB NF in 40nm CMOS. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Integrated Circuits, Technologies and Applications, Xi’an, China, 28–30 October 2022; pp. 152–153. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, B.J.; Wang, C.H.; Chen, C.C.; Lei, M.F.; Huang, P.C.; Lin, K.Y.; Wang, H. Design and analysis for a 60-GHz low-noise amplifier with RF ESD protection. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2009, 57, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.H.; Hsu, S.S.H.; Hsueh, F.L.; Jou, C.P.; Yeh, T.J. Design of 60-GHz low-noise amplifiers with low NF and robust ESD protection in 65-nm CMOS. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2013, 61, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.Y.; Chu, L.W.; Ker, M.D. ESD protection design for 60-GHz LNA with inductor-triggered SCR in 65-nm CMOS process. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2012, 60, 714–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eghtesadi, M.; Giustolisi, G.; Pennisi, S.; Ragonese, E. A 28-nm CMOS 60-GHz LNA for OOK low-power receivers. In Proceedings of the 2024 19th Conference on Ph.D Research in Microelectronics and Electronics (PRIME), Larnaca, Cyprus, 9–12 June 2024; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Yaghoobi, M.; Yavari, M.; Kashani, M.H.; Ghafoorifard, H.; Mirabbasi, S. A 55–64-GHz low-power small-area LNA in 65-nm CMOS with 3.8-dB average NF and 12.8-dB power gain. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2019, 29, 128–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, P.Y.; Su, S.H.; Hsu, S.S.H.; Cho, W.H.; Jin, J.D. An ultra-low-power transformer-feedback 60 GHz low-noise amplifier in 90 nm CMOS. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2012, 22, 197–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morath, H.P.E.; Testa, P.V.; Wagner, J.; Ellinger, F. A 3.6 mW 60 GHz low-noise amplifier with 0.6 ns settling time for duty-cycled receivers. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2021, 31, 977–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
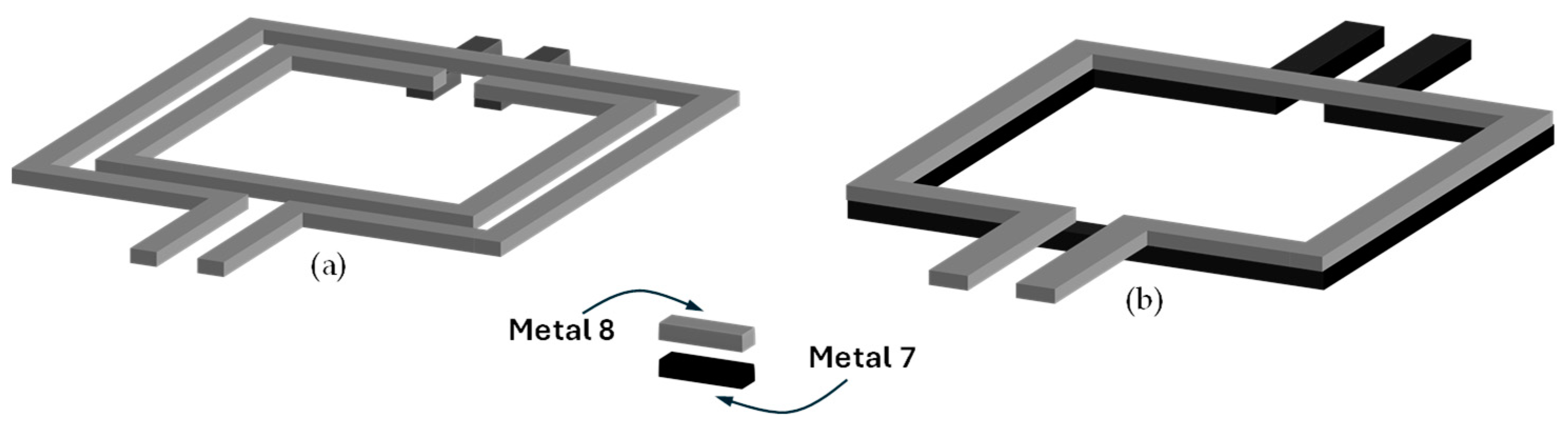

| Parameters | TIN | TOUT | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transformer topology | Interleaved | Stacked | |
| Primary/secondary inner diameter (dIN) | 50/68 | 40 | µm |
| Metal width (w)/spacing (s) | 4/5 | 3/- | µm |
| Number of turns (n) | 1 | 1 | - |
| Primary coil inductance @ 60 GHz | 151 | 122 | pH |
| Secondary coil inductance @ 60 GHz | 225 | 122 | pH |
| Primary coil Q-factor @ 60 GHz | 22.7 | 18.7 | - |
| Secondary coil Q-factor @ 60 GHz | 23.1 | 18.5 | - |
| Magnetic coupling factor (k) @ 60 GHz | 0.41 | 0.72 | - |
| Self-resonance frequency (SRF) | 150 | 140 | GHz |
| Parameters | [21] (S) | [64] (S) | [65] (S) | [59] (P) | [66] (S) | [41] (S) | [60] (M) | [61] (M) | [62] (M) | [63] (S) | This Work (S) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. stages/topology | 6 CS | 2 CAS | 4 CS | 2 CS | 2 CAS | 2 CAS | 3 CAS | 2 CAS | 2 CAS | 2 CAS | 1 CAS |
| Differential (d) /Single-ended (s) | d | s | s | d | s | s | s | s | s | d | d |
| ESD protection HBM Level (kV) | NO | NO | NO | NO | NO | NO | 6.5/1.5 | >8 | 3 | 2 | 2 |
| Frequency (GHz) | 60 | 60 | 60 | 58 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 |
| NF (dB) | 4.9 (M) | 3.5 | 4 | 4.4 | 4.9 | 3.5 | 8.6 | 5.3 | 8.6 | 6.9 | 6.3 |
| Gain (dB) | 24.5 | 13 | 13 | 22.7 | 18.1 | 6.7 | 20.4 | 17.5 | 10.2 | 19.3 | 21.4 |
| BW3dB (GHz) | 14 (53–67) | 9 (55–64) | 6 (55.2–61.2) | 9 (54–63) | 18.3 (49.8–68.1) | 7 (57–64) | 7 (55–62) | 7 (54.5–61.5) | 10 (55–65) | 6 (56.8–62.8) | 2 (59–61) |
| IP1dB (dBm) | −27 (M) | −17.8 (M) | −16 (M) | −16.1 | −21.1 (M) | −22.4 | −20 | −20.63 | −11 | −14 | −4.7 |
| Voltage supply (V) | 1.2 | 1 | 1 | - | 0.85 | 1.1 | 2.4 | 1.5 | 1 | 0.9 | 0.9 |
| Current consumption (mA) | 14 | 8.8 | 4.4 | - | 4.2 | 12 | 27 | 12 | 30 | 9.18 | 5.8 |
| Power consumption (mW) | 16.8 | 8.8 | 4.4 | 29.9 | 3.6 | 13.2 | 65 | 18 | 30 | 8.3 | 5.2 |
| CMOS process | 90 nm | 65 nm | 90 nm | 40 nm | 22 nm FD SOI | 40 nm | 130 nm | 65 nm | 65 nm | 28 nm | 28 nm |
| FoM1/FoM2 | 0.08/20 | 1.19/178 | 2.95/295 | 0.62/96 | 1.12/342 | 0.1/12 | 0.03/3.52 | 0.21/24.65 | 0.26/43.25 | 1.42/142.5 | 25.5/851 |
| (S): simulations (M): measurements (P): post-layout simulations | |||||||||||
| [57] FoM1 = Gain [dB] ∙ Freq [GHz] ∙ IP1dB [mW]/(F − 1) ∙ PDC [mW]; | |||||||||||
| [58] FoM2 = Gain [dB] ∙ IP1dB [mW] ∙ BW [MHz]/(F − 1) ∙ PDC [mW] (where F is the noise factor) | |||||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eghtesadi, M.; Giustolisi, G.; Ballo, A.; Pennisi, S.; Ragonese, E. A 5 mW 28 nm CMOS Low-Noise Amplifier with Transformer-Based Electrostatic Discharge Protection for 60 GHz Applications. Electronics 2024, 13, 4285. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13214285
Eghtesadi M, Giustolisi G, Ballo A, Pennisi S, Ragonese E. A 5 mW 28 nm CMOS Low-Noise Amplifier with Transformer-Based Electrostatic Discharge Protection for 60 GHz Applications. Electronics. 2024; 13(21):4285. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13214285
Chicago/Turabian StyleEghtesadi, Minoo, Gianluca Giustolisi, Andrea Ballo, Salvatore Pennisi, and Egidio Ragonese. 2024. "A 5 mW 28 nm CMOS Low-Noise Amplifier with Transformer-Based Electrostatic Discharge Protection for 60 GHz Applications" Electronics 13, no. 21: 4285. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13214285
APA StyleEghtesadi, M., Giustolisi, G., Ballo, A., Pennisi, S., & Ragonese, E. (2024). A 5 mW 28 nm CMOS Low-Noise Amplifier with Transformer-Based Electrostatic Discharge Protection for 60 GHz Applications. Electronics, 13(21), 4285. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13214285











