Cross-Channel Color Image Encryption Scheme Based on Discrete Memristive Coupled Neurons and DWT Compression
Abstract
1. Introduction
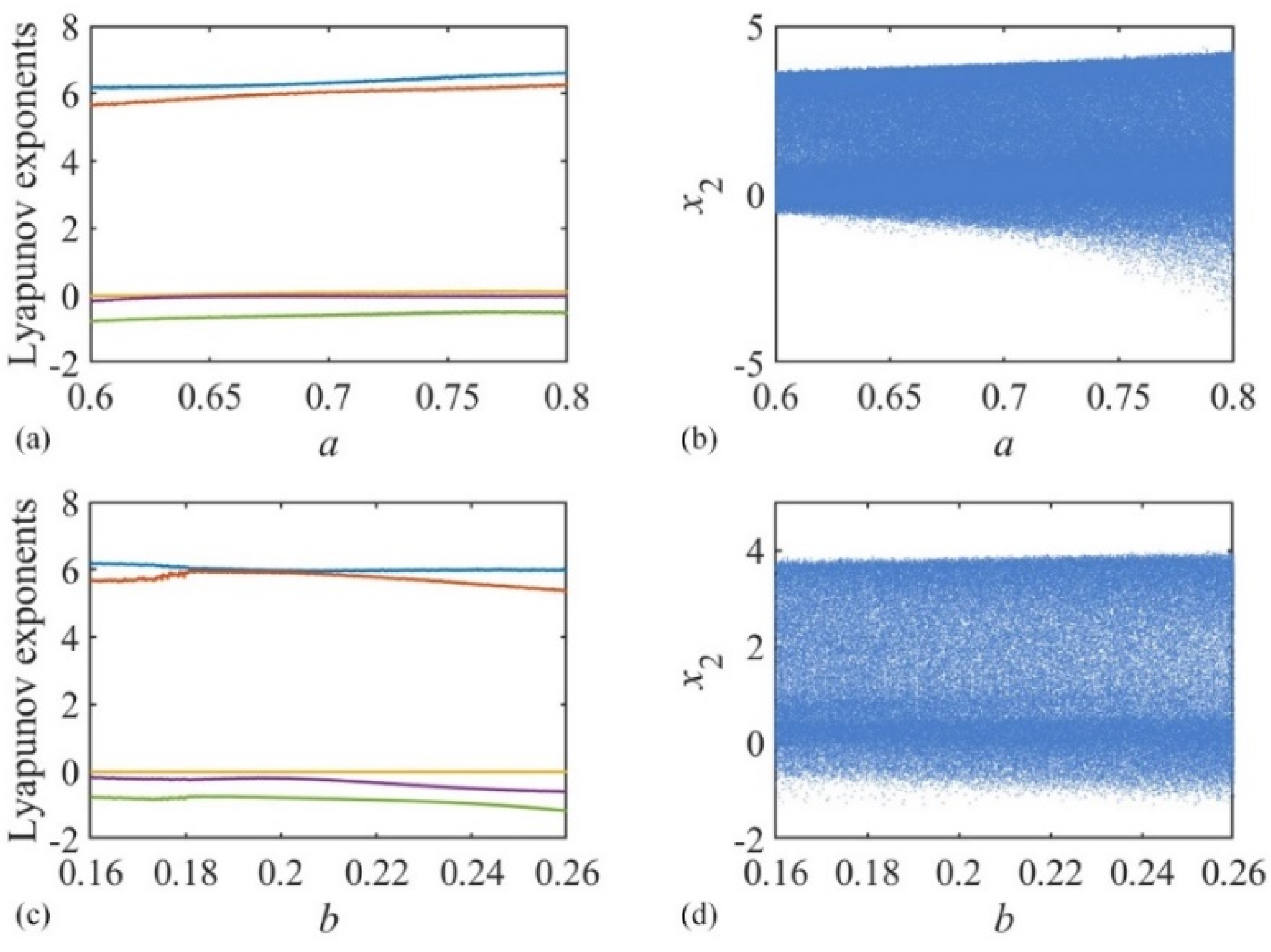
- Phase diagrams, bifurcation diagram, Lyapunov exponents (LEs) and the spectral entropy of the discrete memristive coupled neurons are analyzed;
- The color image is compressed using DWT technology, and it is clearly seen on the reduction side;
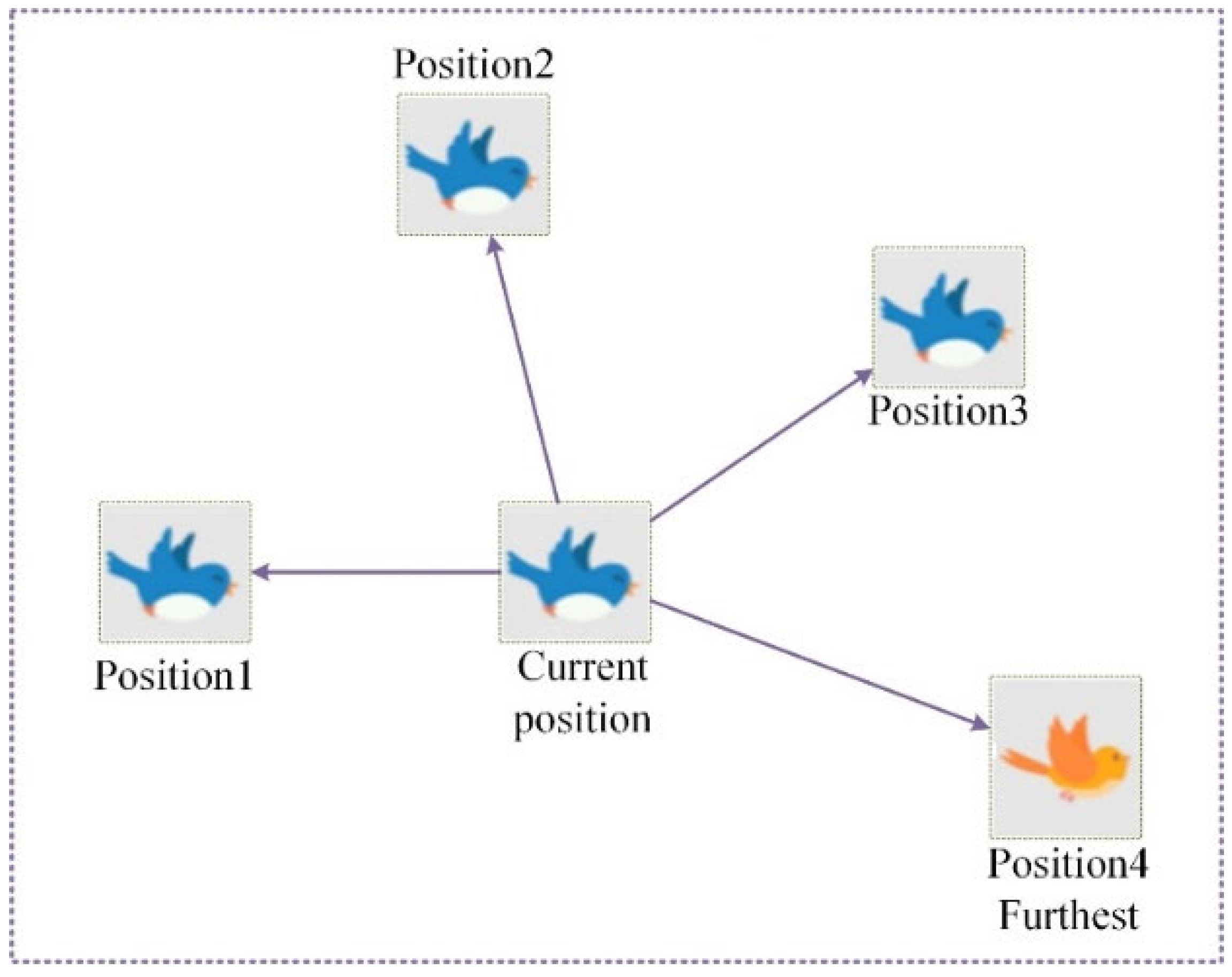
- Particle swarm foraging algorithms are designed to disrupt color image planar pixel positions cross-channel;
- Tests and performance analysis are conducted, and the scheme has good security and statistical performance.
2. Basic Theory
2.1. Five-Dimensional Discrete Map
2.1.1. Phase Diagram
2.1.2. LEs and Bifurcation Diagram
2.1.3. Spectral Entropy
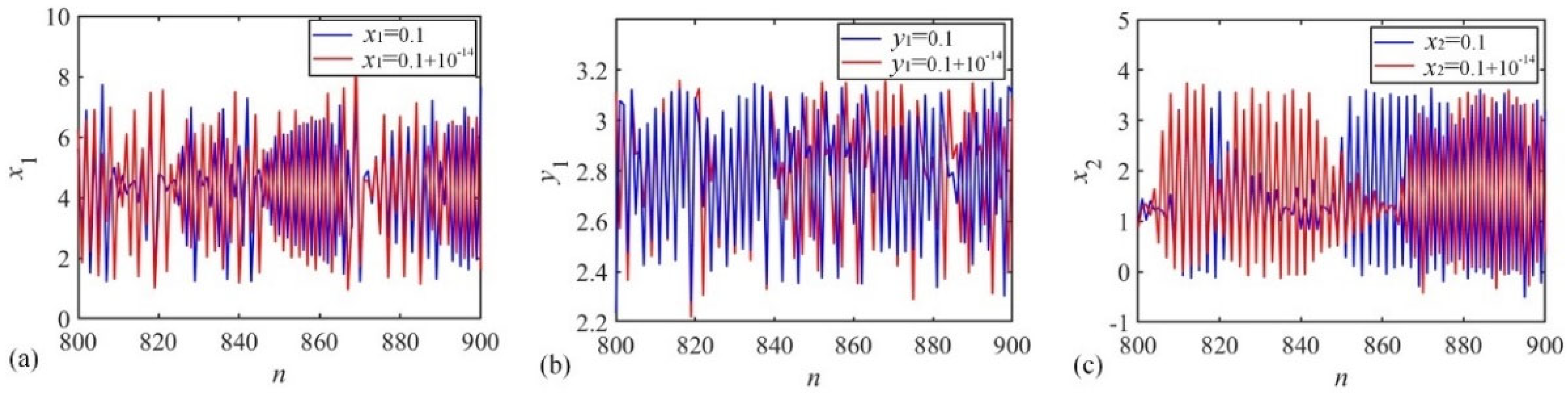
2.1.4. Initial Value Sensitivity
2.1.5. NIST Test
2.2. DWT Compression
2.3. Particle Swarm Foraging Algorithm (PSFA)
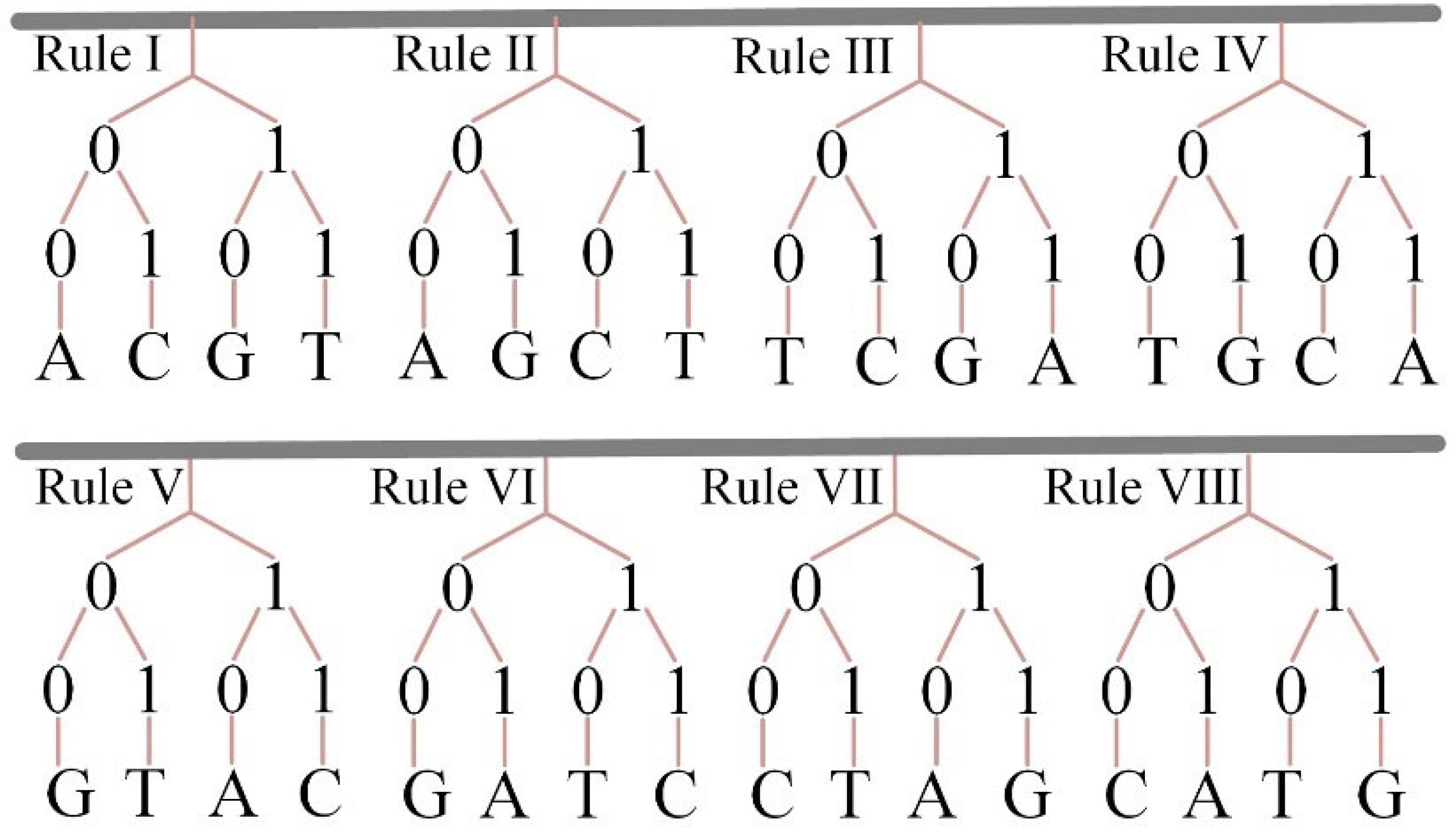
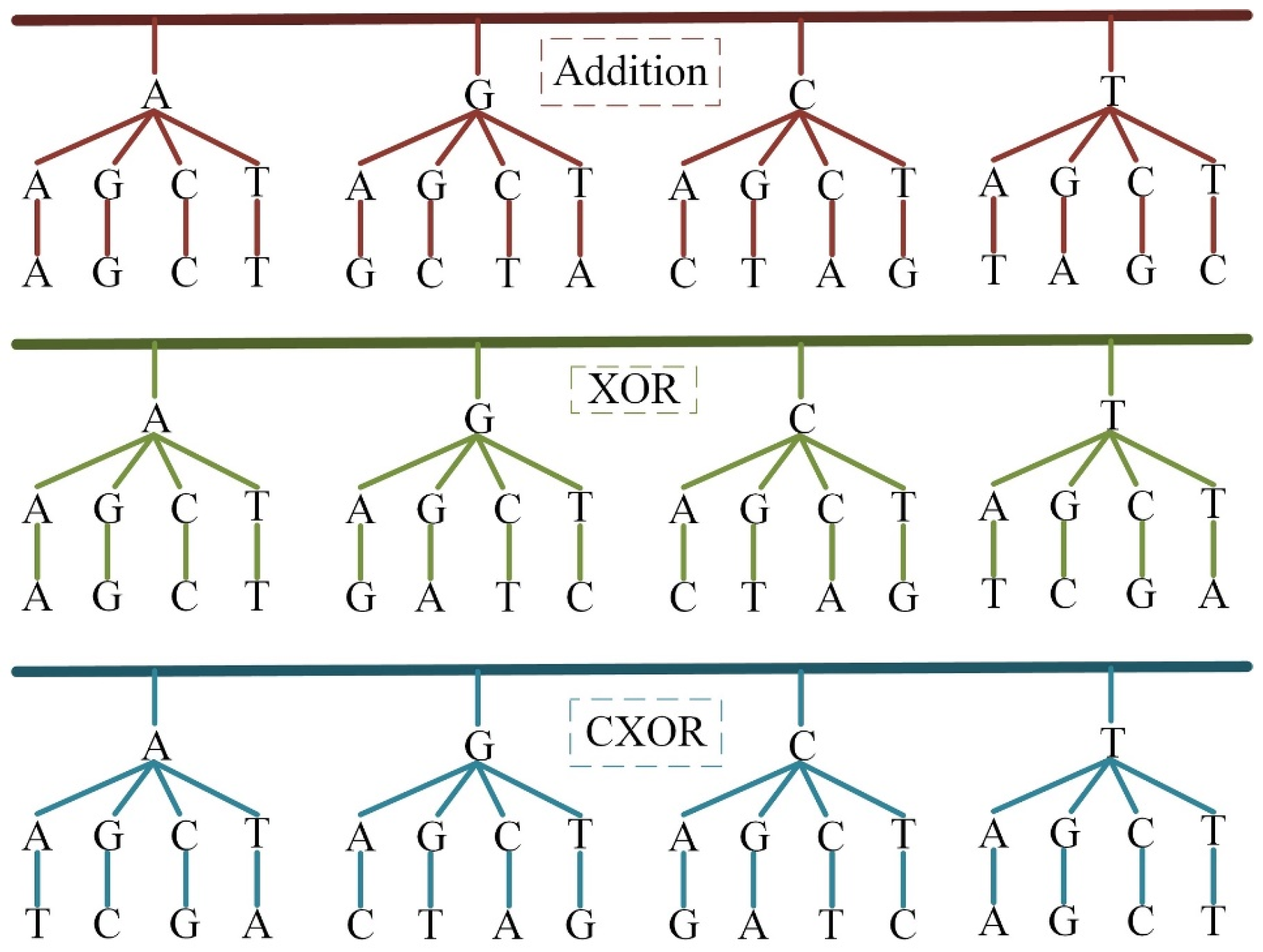
2.4. DNA Encoding
3. Encryption Scheme and Decryption Scheme
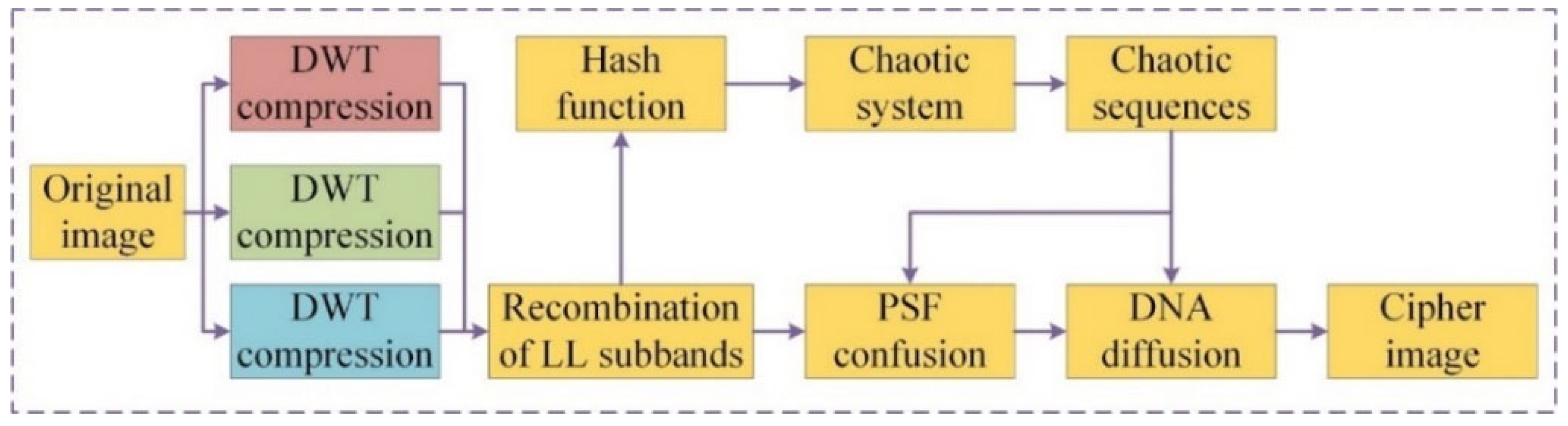
3.1. The Complete Encryption Process
3.2. Encryption Process
3.2.1. DWT Compression
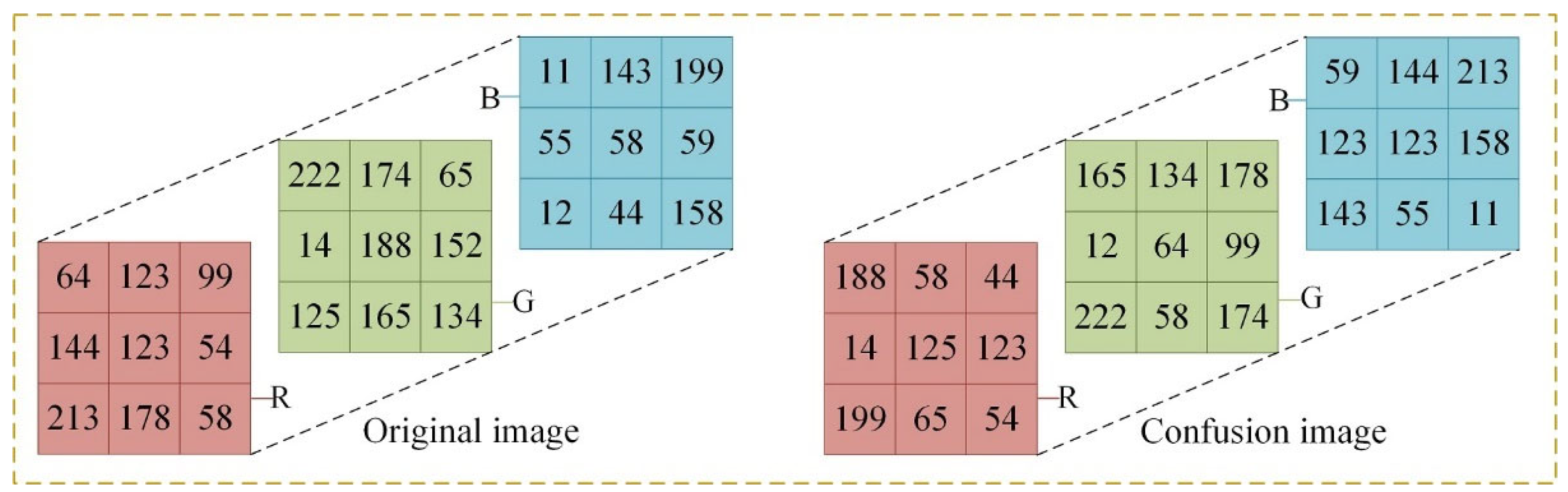
3.2.2. Confusion Process
3.2.3. Diffusion Process
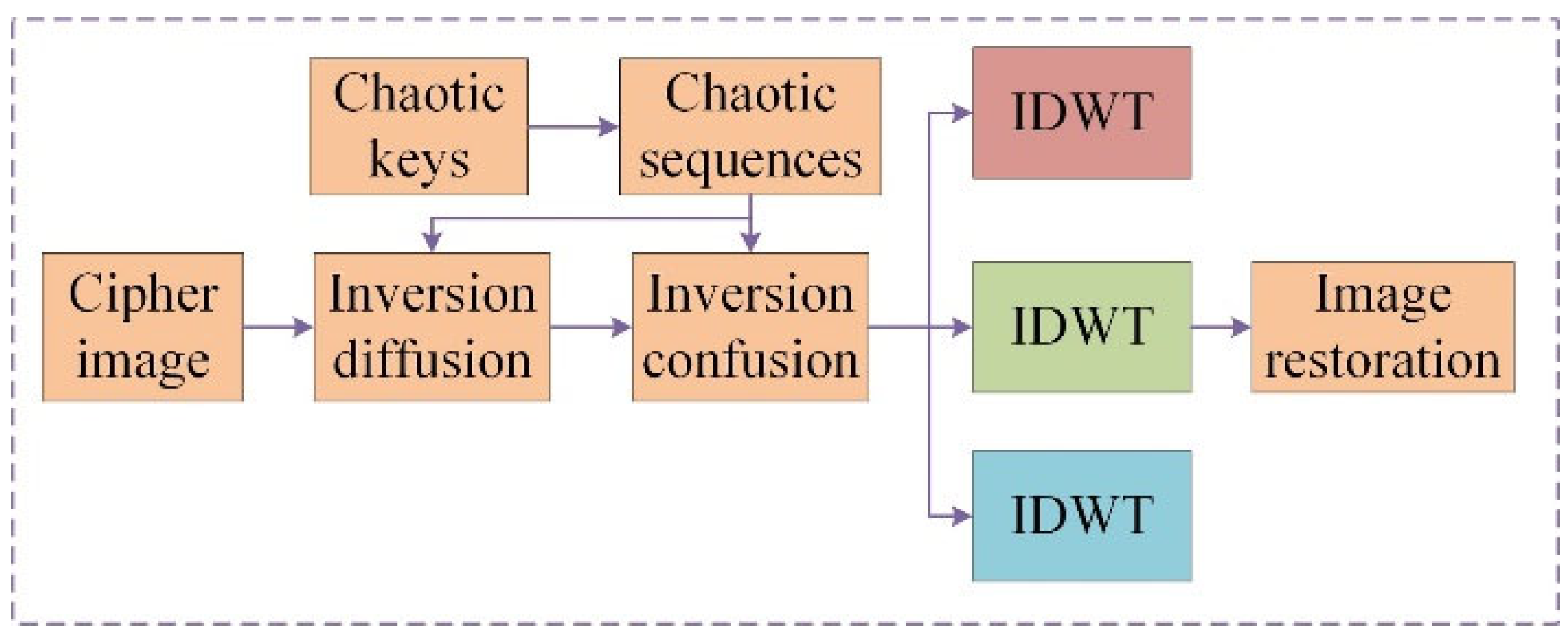
3.3. Decryption Process
3.4. Simulation Results
4. Security Analysis
4.1. Quality Reconstruction Analysis
4.2. Histogram Analysis
4.3. Correlation Analysis
4.4. Information Entropy
4.5. Key Space
4.6. Key Sensitivity
4.7. Differential Attack
4.8. Plain Attack
4.9. Robustness
4.9.1. Noise Attack Analysis
4.9.2. Shearing Attack Analysis
4.10. Comparing Our Scheme with Other Encryption Schemes
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, X.; Mou, J.; Cao, Y.; Banerjee, S. Chaotic Multiple-Image Encryption Algorithm Based on Block Scrambling and Dynamic DNA Coding. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2023, 33, 2350190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Cao, Y.; Jahanshahi, H.; Mou, J. Chaotic color multi-image compression-encryption/LSB data type steganography scheme for NFT transaction security. J. King Saud Univ.-Comput. Inf. Sci. 2023, 35, 101839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Mou, J.; Banerjee, S.; Cao, Y. A chaotic hierarchical encryption/watermark embedding scheme for multi-medical images based on row–column confusion and closed-loop bi-directional diffusion. Chin. Phys. B 2024, 33, 020503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Mou, J.; Zhou, N.; Banerjee, S.; Cao, Y. Multi-cube encryption scheme for multi-type images based on modified Klotski game and hyperchaotic map. Nonlinear Dyn. 2024, 112, 5727–5747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhou, N.; Sun, B.; Banerjee, S.; Mou, J. Multimedia healthcare cloud personal archives security system based on compressed sensing and multi-image encryption. J. Frankl. Inst. 2024, 361, 106844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alawida, M. A novel DNA tree-based chaotic image encryption algorithm. J. Inf. Secur. Appl. 2024, 83, 103791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almasoud, A.S.; Alabduallah, B.; Alqahtani, H.; Aljameel, S.S.; Alotaibi, S.S.; Mohamed, A. Chaotic image encryption algorithm with improved bonobo optimizer and DNA coding for enhanced security. Heliyon 2024, 10, E25257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, P.; Teng, L. A chaotic image encryption algorithm based on sliding window and pseudo-random stack shuffling. Nonlinear Dyn. 2024, 112, 13539–13569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L. A novel chaotic map application in image encryption algorithm. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 252, 124316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, M.U. Quantum-enhanced chaotic image encryption: Strengthening digital data security with 1-D sine-based chaotic maps and quantum coding. J. King Saud Univ.-Comput. Inf. Sci. 2024, 36, 101980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Cao, Y.; Jahanshahi, H.; Mou, J.; Sun, B. 2D and 3D compatible chaotic image encryption system based on checkers rules and shift register. J. Frankl. Inst. 2024, 361, 106874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Wang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Sun, B.; Mou, J. Multiple remote sensing image encryption scheme based on saliency extraction and magic cube circular motion. Appl. Intell. 2024, 54, 5944–5960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Mou, J.; Banerjee, S.; Cao, Y.; Xiong, L.; Chen, X. An effective multiple-image encryption algorithm based on 3D cube and hyperchaotic map. J. King Saud Univ.-Comput. Inf. Sci. 2022, 34, 1535–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Mou, J.; Banerjee, S.; Zhang, Y. Color-gray multi-image hybrid compression–encryption scheme based on BP neural network and knight tour. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2023, 53, 5037–5047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sang, Y.; Sang, J.; Alam, M.S. Image encryption based on logistic chaotic systems and deep autoencoder. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2022, 153, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Li, Q.; Yan, X. Spiral-transform-based fractal sorting matrix for chaotic image encryption. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2022, 69, 3320–3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal, S.S.; Hazzazi, M.M.; Khan, M.F.; Bassfar, Z.; Aljaedi, A.; ul Islam, Z. Region of interest-based medical image encryption technique based on chaotic S-boxes. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 238, 122030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, X. Image encryption scheme based on improved four-dimensional chaotic system and evolutionary operators. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 7033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toktas, A.; Erkan, U.; Gao, S.; Pak, C. A robust bit-level image encryption based on Bessel map. Appl. Math. Comput. 2024, 462, 128340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toktas, F.; Erkan, U.; Yetgin, Z. Cross-channel color image encryption through 2D hyperchaotic hybrid map of optimization test functions. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 249, 123583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Hu, H. An image encryption algorithm based on a compound-coupled chaotic system. Digit. Signal Process. 2024, 146, 104367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Yu, S. Break an enhanced plaintext-related chaotic image encryption algorithm. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2024, 181, 114623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alawida, M. A Novel Image Encryption Algorithm Based on Cyclic Chaotic Map in Industrial IoT Environments. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darani, A.Y.; Yengejeh, Y.K.; Pakmanesh, H.; Navarro, G. Image encryption algorithm based on a new 3D chaotic system using cellular automata. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2024, 179, 114396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Es-sabry, M.; El Akkad, N.; Khrissi, L.; Satori, K.; El-Shafai, W.; Altameem, T.; Rathore, R.S. An efficient 32-bit color image encryption technique using multiple chaotic maps and advanced ciphers. Egypt. Inform. J. 2024, 25, 100449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocak, O.; Erkan, U.; Toktas, A.; Gao, S. PSO-based image encryption scheme using modular integrated logistic exponential map. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 237, 121452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Dua, M. Image encryption using a novel hybrid chaotic map and dynamic permutation−diffusion. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 32789–32812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Sharma, D. A chaotic based image encryption scheme using elliptic curve cryptography and genetic algorithm. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2024, 57, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.; Wang, C.; Lin, H. Chaotic dynamical system of Hopfield neural network influenced by neuron activation threshold and its image encryption. Nonlinear Dyn. 2024, 112, 6629–6646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.; Wang, C.; Lin, H. Memristive Hopfield neural network dynamics with heterogeneous activation functions and its application. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2024, 178, 114387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Al-Barakati, A.A.; Jahanshahi, H.; Mou, J. A novel circuit based on memristor-memcapacitor with extreme multistability. Nonlinear Dyn. 2024, 112, 4863–4877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Sun, B.; Banerjee, S.; Mou, J. Biological neuron modeling based on bifunctional memristor and its application in secure communication. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2024, 184, 115020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, C.; Deng, Q. Symmetric multi-double-scroll attractors in Hopfield neural network under pulse controlled memristor. Nonlinear Dyn. 2024, 112, 14463–14477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Wang, C.; Sun, Y. A universal variable extension method for designing multiscroll/wing chaotic systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2023, 71, 7806–7818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Mou, J.; Banerjee, S.; Miao, M. A quartic nonlinear flux-controlled memristor model and its application in chaotic system. Appl. Comput. Math. 2023, 22, 317–337. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, D.; Wang, C.; Lin, H.; Yu, F. Dynamics analysis and hardware implementation of multi-scroll hyperchaotic hidden attractors based on locally active memristive Hopfield neural network. Nonlinear Dyn. 2024, 112, 1511–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liang, J.; Deng, Q. Dynamics of heterogeneous Hopfield neural network with adaptive activation function based on memristor. Neural Netw. 2024, 178, 106408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Tang, D.; Lin, H.; Yu, F.; Sun, Y. High-dimensional memristive neural network and its application in commercial data encryption communication. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 242, 122513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Wang, Y.; Banerjee, S.; Cao, Y.; Mou, J. A discrete Chialvo–Rulkov neuron network coupled with a novel memristor model: Design, Dynamical analysis, DSP implementation and its application. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2024, 179, 114466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Lu, Y. Synchronization in scale-free neural networks under electromagnetic radiation. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 2024, 34, 033116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Xiong, K.; Li, Z.; He, S. Dynamical behavior of memristor-coupled heterogeneous discrete neural networks with synaptic crosstalk. Chin. Phys. B 2024, 33, 028706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, J.; Ma, T.; Banerjee, S.; Zhang, Y. A Novel Memcapacitive-Synapse Neuron: Bionic Modeling, Complex Dynamics Analysis and Circuit Implementation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2024, 71, 1771–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Mou, J.; Qin, L.; Jahanshahi, H. A memristor-coupled heterogeneous discrete neural networks with infinite multi-structure hyperchaotic attractors. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2023, 138, 1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Chu, R.; Cui, Y. Complex Dynamical Characteristics of the Fractional-Order Cellular Neural Network and Its DSP Implementation. Fractal Fract. 2023, 7, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Mou, J.; Banerjee, S.; Cao, Y. Analysis of the functional behavior of fractional-order discrete neuron under electromagnetic radiation. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2023, 176, 114113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Qin, L.; Jahanshahi, H.; Mou, J. Infinitely Many Coexisting Attractors and Scrolls in a Fractional-Order Discrete Neuron Map. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2023, 33, 2350197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, Y.; Chu, R. Dynamical analysis of the incommensurate fractional-order Hopfield neural network system and its digital circuit realization. Fractal Fract. 2023, 7, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Zhu, C. A new one-dimensional chaotic map for image encryption scheme based on random DNA coding. Opt. Laser Technol. 2023, 160, 109033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naim, M.; Ali Pacha, A. A new chaotic satellite image encryption algorithm based on a 2D filter and Fisher–Yates shuffling. J. Supercomput. 2023, 79, 17585–17618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Ma, L.; Liu, L.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, R.; Liu, Z.; Lin, W.; Wu, J.; Li, Y. High-quality restoration image encryption using DCT frequency-domain compression coding and chaos. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 16523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, Y.; Mou, J.; Banerjee, S.; Jahanshahi, H.; Cao, Y. Low-cost multiclass-image encryption based on compressive sensing and chaotic system. Nonlinear Dyn. 2023, 111, 7831–7857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SaberiKamarposhti, M.; Sahlabadi, M.; Lin, C.-C.; Muniyand, R.C. Using 2d hénon map, cycling chaos and dna sequence for new secure color image encryption algorithm. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2024, 49, 4125–4137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, C.; Cui, M.; Luo, Y.; Wu, T.; Liang, X. Joint compressed sensing and JPEG coding based secure compression scheme in OFDM-PON. Opt. Commun. 2022, 510, 127901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Huang, L.; Cai, S.; Xiong, X.; Liu, Y. Novel and secure plaintext-related image encryption algorithm based on compressive sensing and tent-sine system. IET Image Process. 2022, 16, 1544–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Su, Y. Image encryption based on compressed sensing and DNA encoding. Signal Process. Image Commun. 2021, 95, 116246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadj Brahim, A.; Ali Pacha, A.; Hadj Said, N. A new image compression-encryption scheme based on compressive sensing & classical AES algorithm. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023, 82, 42087–42117. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Saveriades, G.; Agaian, S.; Noonan, J.P.; Natarajan, P. Local Shannon entropy measure with statistical tests for image randomness. Inf. Sci. 2013, 222, 323–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyedzadeh, S.M.; Norouzi, B.; Mosavi, M.R.; Mirzakuchaki, S. A novel color image encryption algorithm based on spatial permutation and quantum chaotic map. Nonlinear Dyn. 2015, 81, 511–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, Z.; Li, Q.; Chen, H.; Cai, S.; Xiong, X.; Huang, L. Medical image encryption system based on a simultaneous permutation and diffusion framework utilizing a new chaotic map. Phys. Scr. 2024, 99, 055249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, H. Cosine-transform-based chaotic system for image encryption. Inf. Sci. 2019, 480, 403–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naim, M.; Pacha, A.A.; Serief, C. A novel satellite image encryption algorithm based on hyperchaotic systems and Josephus Problem. Adv. Space Res. 2021, 67, 2077–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, X. Multiple-image encryption algorithm based on bit planes and chaos. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020, 79, 20753–20771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Hu, Y. Multiple-image encryption algorithm based on the 3D scrambling model and dynamic DNA coding. Opt. Laser Technol. 2021, 141, 107073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Dieu, N.J.; Ruben, F.S.V.; Nestor, T.; Zeric, N.T.; Jacques, K. Dynamic analysis of a novel chaotic system with no linear terms and use for DNA-based image encryption. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 81, 10907–10934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, G.; Guo, L. A visual meaningful encryption and hiding algorithm for multiple images. Nonlinear Dyn. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, G.; Wu, H.; Liu, M.; Shi, Y. Image encryption scheme based on blind signature and an improved Lorenz system. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 205, 117709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Chen, S.-H.; Zhou, L.; Gong, L.-H. Optical image encryption and authentication scheme with computational ghost imaging. Appl. Math. Model. 2024, 131, 49–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H. A novel image encryption scheme with adaptive Fourier decomposition. J. Frankl. Inst. 2024, 361, 106630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
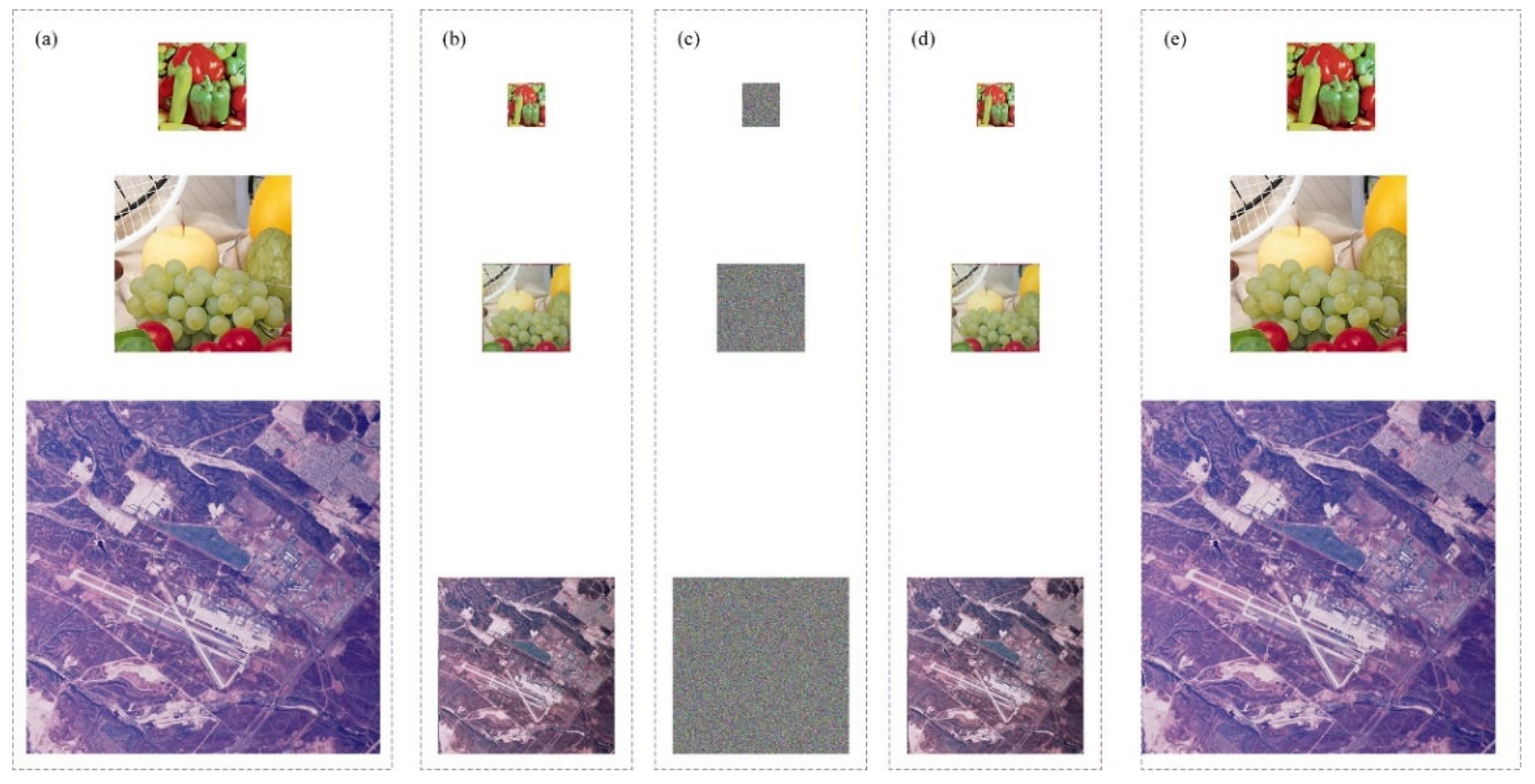











| Test | p-Value | Pass Pate | Pass/Fail |
|---|---|---|---|
| The Frequency Test | 0.2192 | 100% | Pass |
| Frequency Test within a Block | 0.3325 | 98% | Pass |
| The Run Test | 0.2627 | 96% | Pass |
| Tests for the Longest-Run-of-Ones in a Block | 0.5240 | 98% | Pass |
| The Binary Matrix Rank Test | 0.3165 | 99% | Pass |
| The Discrete Fourier Transform Test | 0.2163 | 99% | Pass |
| The Non-Overlapping Template Matching Test | 0.3197 | 98% | Pass |
| The Overlapping Template Matching Test | 0.4249 | 99% | Pass |
| Universal Statistical Test | 0.5414 | 100% | Pass |
| The Liner Complexity Test | 0.2396 | 100% | Pass |
| The Serial Test | 0.9740 | 100% | Pass |
| The Approximate Entropy Test | 0.1017 | 100% | Pass |
| The Cumulative Sums Test | 0.4248 | 100% | Pass |
| The Random Excursions Test | 0.5881 | 98% | Pass |
| The Random Excursions Variant Test | 0.6957 | 98% | Pass |
| Peppers | Size | PSNR | Fruits | Size | PSNR | 2.2.05 | Size | PSNR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | 256 × 256 | 29.5744 | R | 512 × 512 | 33.0693 | R | 1024 × 1024 | 29.2794 |
| G | 256 × 256 | 26.6075 | G | 512 × 512 | 32.3118 | G | 1024 × 1024 | 30.0306 |
| B | 256 × 256 | 29.3594 | B | 512 × 512 | 32.5318 | B | 1024 × 1024 | 31.6912 |
| Scheme | [53] | [54] | [55] | [56] | Proposed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSNR (dB) | 26.2896 | 27.6917 | 27.3366 | 27.4886 | 28.5137 |
| Peppers | Horizontal | Vertical | Diagonal | Pass/Fail |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | 0.8780 | 0.8559 | 0.8406 | Fail |
| G | 0.8542 | 0.8863 | 0.8109 | Fail |
| B | 0.8247 | 0.8572 | 0.8082 | Fail |
| Cipher | Horizontal | Vertical | Diagonal | Pass/Fail |
| R | 0.0029 | 0.0023 | −0.0061 | Pass |
| G | 0.0092 | −0.0107 | 0.0015 | Pass |
| B | −0.0033 | 0.0025 | −0.0008 | Pass |
| Images | Plain Image | Cipher Image | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Size | R | G | B | Size | R | G | B | |
| Peppers | 256 × 256 | 7.3318 | 7.5242 | 7.0792 | 128 × 128 | 7.9901 | 7.9887 | 7.9889 |
| Fruits | 512 × 512 | 7.0555 | 7.3527 | 7.7134 | 256 × 256 | 7.9968 | 7.9968 | 7.9969 |
| 2.2.05 | 1024 × 1024 | 7.4445 | 7.2346 | 6.5895 | 512 × 512 | 7.9992 | 7.9992 | 7.9993 |
| Parameters | Key Space |
|---|---|
| c, γ, σ, f2, f3 | 1015 |
| ε, kr, a, b, μ, α, β, f1, f2, f5 | 1016 |
| Total key space | 10235 ≈ 2780 |
| Scheme | Ref. [59] | Ref. [60] | Ref. [61] | Proposed |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Key space | 2192 | 2256 | 2358 | 2780 |
| Key Space | Δ Value | NPCR (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Ε | Δ = 10−16 | 99.6052 |
| kr | Δ = 10−16 | 99.6033 |
| a | Δ = 10−16 | 99.6113 |
| b | Δ = 10−16 | 99.6193 |
| c | Δ = 10−15 | 99.6048 |
| r | Δ = 10−15 | 99.6155 |
| μ | Δ = 10−16 | 99.6124 |
| σ | Δ = 10−15 | 99.6231 |
| α | Δ = 10−16 | 99.6243 |
| β | Δ = 10−16 | 99.6185 |
| f1 | Δ = 10−16 | 99.6075 |
| f2 | Δ = 10−15 | 99.6123 |
| f3 | Δ = 10−15 | 99.6105 |
| f4 | Δ = 10−16 | 99.6090 |
| f5 | Δ = 10−16 | 99.5975 |
| Average value | Δ = 10−15 | 99.6116 |
| Images | NPCR (%) | UACI (%) |
|---|---|---|
| ‘Peppers’ | 99.5850 | 33.3926 |
| ‘Fruits’ | 99.6017 | 33.4460 |
| ‘2.2.05’ | 99.6235 | 33.4601 |
| Proposed | 99.6034 | 33.4329 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, Y.; Cai, C.; Xu, X.; Bi, X. Cross-Channel Color Image Encryption Scheme Based on Discrete Memristive Coupled Neurons and DWT Compression. Electronics 2024, 13, 2647. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13132647
Cao Y, Cai C, Xu X, Bi X. Cross-Channel Color Image Encryption Scheme Based on Discrete Memristive Coupled Neurons and DWT Compression. Electronics. 2024; 13(13):2647. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13132647
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Yinghong, Chang Cai, Xianying Xu, and Xiuguo Bi. 2024. "Cross-Channel Color Image Encryption Scheme Based on Discrete Memristive Coupled Neurons and DWT Compression" Electronics 13, no. 13: 2647. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13132647
APA StyleCao, Y., Cai, C., Xu, X., & Bi, X. (2024). Cross-Channel Color Image Encryption Scheme Based on Discrete Memristive Coupled Neurons and DWT Compression. Electronics, 13(13), 2647. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13132647






