Privacy-Enhancing Technologies in Federated Learning for the Internet of Healthcare Things: A Survey
Abstract
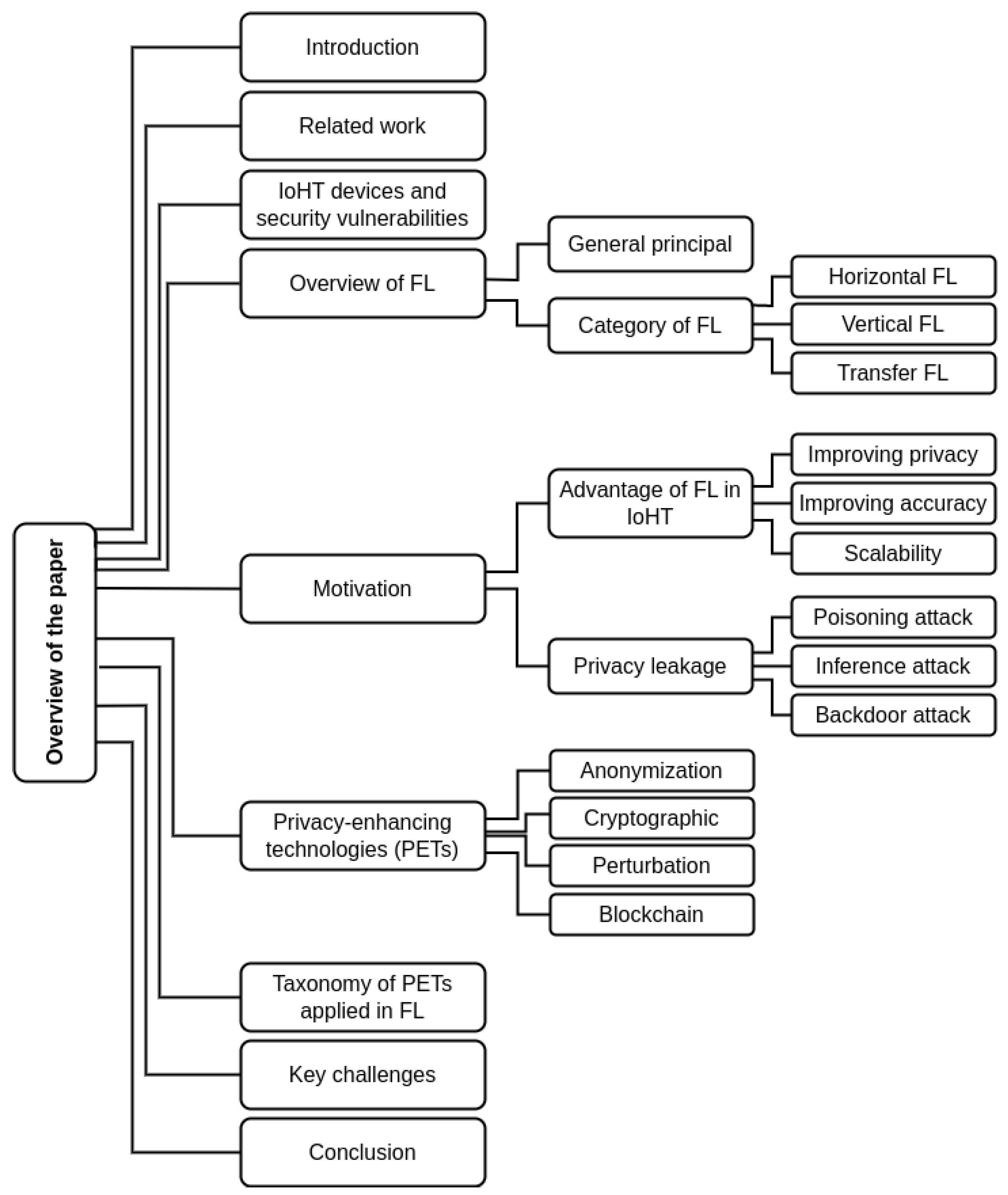
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. IoHT Devices and Security Vulnerabilities
3.1. Glucose Monitoring System
3.2. Smart Insulin Pumps
3.3. Pacemaker
3.4. Monitoring of Oxygen Levels
3.5. Security Vulnerabilities in the IoHT
3.5.1. IoHT Device Operating System Vulnerability
3.5.2. Communication Protocol Vulnerability
3.6. Data Leakage in IoHT Devices
3.7. Summary
4. Federated Learning for Healthcare
4.1. Principles of FL for Smart Healthcare
- Initialization. The aggregation server selects data generated by IoHT devices, such as blood sample readers or human motion detection devices, to perform a prediction or classification task. Furthermore, the central server chooses a group of participants to participate in the FL process;
- Local model training. The server sends an initial model to the devices for distributed training after choosing the IoHT devices for feeding the model. Each device computes its updated model by training a local model with its own dataset that is stored locally. Finally, each device sends its updated model to the central server, which is responsible for aggregating all the updated models;
- Model aggregation. After receiving the parameters from each IoHT device in the FL process, the aggregation step combines all parameters to generate a global learning model. The federated averaging (FedAvg) algorithm [36] is an averaging model that can be used to calculate the global model and send it to all IoHT devices to update the local models.
4.2. FL Types for Smart Healthcare
4.3. Summary
5. Motivation for Using Privacy-Preserving FL in Smart Healthcare
- Preserving the privacy of patients and the confidentiality of patient healthcare data (i.e., preventing unauthorized access to health information);
- Ensuring the integrity of healthcare data (i.e., preventing unauthorized data manipulation);
- Granting access to health data to authorized people.
5.1. Benefits of FL in IoHT
5.1.1. Improving the Privacy of User Data
5.1.2. Less Biased Model
5.1.3. Improving Scalability
5.2. Privacy Leakage and Threats in FL
5.3. Summary
6. Privacy-Enhancing Technologies
6.1. Anonymization Techniques
6.2. Cryptographic Techniques
6.3. Perturbation Techniques
6.4. Blockchain Techniques
6.5. Summary
7. Applying PETs in FL
7.1. Anonymization Methods
7.2. Cryptographic Methods
7.3. Perturbation Methods
7.4. Blockchain Methods
7.5. Summary
8. Key Challenges for Future Research
8.1. Computation Costs
8.2. Privacy and Security
8.3. Linkage Attacks
8.4. Storage Cost
8.5. Energy Consumption
8.6. Communication Latency
8.7. Summary
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mani, N.; Singh, A.; Nimmagadda, S.L. An IoT guided healthcare monitoring system for managing real-time notifications by fog computing services. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2020, 167, 850–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Wu, W.; Cao, J.; Li, K. Fuzzy group-based intersection control via vehicular networks for smart transportations. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2016, 13, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojkoska, B.L.R.; Trivodaliev, K.V. A review of Internet of Things for smart home: Challenges and solutions. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 140, 1454–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Sivaparthipan, C.; Muthu, B. IoT based smart and intelligent smart city energy optimization. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2022, 49, 101724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aceto, G.; Persico, V.; Pescapé, A. Industry 4.0 and health: Internet of things, big data, and cloud computing for healthcare 4.0. J. Ind. Inf. Integr. 2020, 18, 100129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajotte, J.F.; Mukherjee, S.; Robinson, C.; Ortiz, A.; West, C.; Ferres, J.M.L.; Ng, R.T. Reducing bias and increasing utility by federated generative modeling of medical images using a centralized adversary. In Proceedings of the Conference on Information Technology for Social Good, Roma, Italy, 9–11 September 2021; pp. 79–84. [Google Scholar]
- Vayena, E.; Blasimme, A.; Cohen, I.G. Machine learning in medicine: Addressing ethical challenges. PLoS Med. 2018, 15, e1002689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Joshi, M.; Pal, A.; Sankarasubbu, M. Federated Learning for Healthcare Domain-Pipeline, Applications and Challenges. ACM Trans. Comput. Healthc. 2022, 3, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aouedi, O.; Sacco, A.; Piamrat, K.; Marchetto, G. Handling Privacy-Sensitive Medical Data with Federated Learning: Challenges and Future Directions. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2022, 27, 790–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Chen, T.; Tong, Y. Federated machine learning: Concept and applications. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2019, 10, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, R.S.; André da Costa, C.; Küderle, A.; Yari, I.A.; Eskofier, B. Federated Learning for Healthcare: Systematic Review and Architecture Proposal. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2022, 13, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asad, M.; Moustafa, A.; Yu, C. A critical evaluation of privacy and security threats in federated learning. Sensors 2020, 20, 7182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danezis, G. An Introduction to Privacy Enhancing Technologies. In Proceedings of the Internet Society Geneva’s Monthly Conferences Cycle, Barcelona, Spain, 10–14 May 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, A.; Al Amin, A.; Shin, S.Y. FBI: A federated learning-based blockchain-embedded data accumulation scheme using drones for Internet of Things. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2022, 11, 972–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagabir, S.; Ibrahim, N.K.; Bagabir, H.; Ateeq, R. COVID-19 and Artificial Intelligence: Genome sequencing, drug development and vaccine discovery. J. Infect. Public Health 2022, 15, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou El Houda, Z.; Hafid, A.S.; Khoukhi, L. MiTFed: A Privacy Preserving Collaborative Network Attack Mitigation Framework Based on Federated Learning using SDN and Blockchain. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Mao, W.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, C.; Xie, Y. A survey on federated learning in data mining. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2022, 12, e1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; Zhou, P.; Xu, Z.; Wang, X.; Xie, Y.; Ding, X.; Wen, S. A resource-constrained and privacy-preserving edge-computing-enabled clinical decision system: A federated reinforcement learning approach. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 9122–9138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, M.; Ye, D.; Wang, S.; Tan, B.; Yu, R. URLLC resource slicing and scheduling for trustworthy 6G vehicular services: A federated reinforcement learning approach. Phys. Commun. 2021, 49, 101470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Shen, B.; Barnawi, A.; Xi, S.; Kumar, N.; Wu, Y. FedDPGAN: Federated differentially private generative adversarial networks framework for the detection of COVID-19 pneumonia. Inf. Syst. Front. 2021, 23, 1403–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrido, G.M.; Sedlmeir, J.; Uludağ, Ö.; Alaoui, I.S.; Luckow, A.; Matthes, F. Revealing the landscape of privacy-enhancing technologies in the context of data markets for the IoT: A systematic literature review. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2022, 207, 103465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aledhari, M.; Razzak, R.; Parizi, R.M.; Saeed, F. Federated Learning: A Survey on Enabling Technologies, Protocols, and Applications. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 140699–140725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Xie, Y.; Bai, H.; Yu, B.; Li, W.; Gao, Y. A survey on federated learning. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2021, 216, 106775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mothukuri, V.; Parizi, R.M.; Pouriyeh, S.; Huang, Y.; Dehghantanha, A.; Srivastava, G. A Survey on Security and Privacy of Federated Learning. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2021, 115, 619–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.C.; Ding, M.; Pathirana, P.N.; Seneviratne, A.; Li, J.; Vincent Poor, H. Federated Learning for Internet of Things: A Comprehensive Survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2021, 23, 1622–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novikova, E.; Fomichov, D.; Kholod, I.; Filippov, E. Analysis of privacy-enhancing technologies in open-source federated learning frameworks for driver activity recognition. Sensors 2022, 22, 2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.C.; Pham, Q.V.; Pathirana, P.N.; Ding, M.; Seneviratne, A.; Lin, Z.; Dobre, O.; Hwang, W.J. Federated Learning for Smart Healthcare: A Survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2022, 55, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuehong, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Chen, X.; Fan, Y. The internet of things in healthcare: An overview. J. Ind. Inf. Integr. 2016, 1, 3–13. [Google Scholar]
- Joy, A.; Hafsiya, T.; King, G. A Review on Glucose Monitoring Using Enabling Technologies of Internet of Things. In Proceedings of the 2021 7th International Conference on Advanced Computing and Communication Systems (ICACCS), Coimbatore, India, 19–20 March 2021; Volume 1, pp. 270–273. [Google Scholar]
- Ketu, S.; Mishra, P.K. Internet of Healthcare Things: A contemporary survey. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2021, 192, 103179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Cai, H.; Liu, H.H.; Su, X.J.; Zhou, C.Y.; Li, J.; Tang, Y.L.; Jackson, T.; Xiang, Y.T. Prevalence of depression and its association with quality of life in patients after pacemaker implantation during the COVID-19 pandemic: A network analysis. Front. Psychiatry 2023, 14, 1084792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, V.A.; Vu Khanh, Q.; Nguyen, V.H.; Nguyen, T.; Nguyen, D.C. Intelligent Healthcare: Integration of Emerging Technologies and Internet of Things for Humanity. Sensors 2023, 23, 4200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyakina, J.N.; Taher, B.H. A survey of healthcare sector digitization strategies: Vulnerabilities, countermeasures and opportunities. World J. Adv. Eng. Technol. Sci. 2023, 8, 282–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, J.; Ahmad, R.; Kiani, A.K.; Ahmad, T.; Saeed, S.; Almuhaideb, A.M. Data protection and privacy of the internet of healthcare things (IoHTs). Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghili, S.F.; Mala, H.; Shojafar, M.; Peris-Lopez, P. LACO: Lightweight three-factor authentication, access control and ownership transfer scheme for e-health systems in IoT. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2019, 96, 410–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahan, B.; Moore, E.; Ramage, D.; Hampson, S.; y Arcas, B.A. Communication-efficient learning of deep networks from decentralized data. In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics (PMLR), Lauderdale, FL, USA, 20–22 April 2017; pp. 1273–1282. [Google Scholar]
- Konečnỳ, J.; McMahan, H.B.; Yu, F.X.; Richtárik, P.; Suresh, A.T.; Bacon, D. Federated learning: Strategies for improving communication efficiency. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1610.05492. [Google Scholar]
- Mammen, P.M. Federated learning: Opportunities and challenges. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2101.05428. [Google Scholar]
- Pfitzner, B.; Steckhan, N.; Arnrich, B. Federated learning in a medical context: A systematic literature review. ACM Trans. Internet Technol. 2021, 21, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Mao, S. An introduction to the federated learning standard. GetMobile Mob. Comput. Commun. 2022, 25, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shyu, C.R.; Putra, K.T.; Chen, H.C.; Tsai, Y.Y.; Hossain, K.T.; Jiang, W.; Shae, Z.Y. A systematic review of federated learning in the healthcare area: From the perspective of data properties and applications. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11191. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Qin, X.; Wang, J.; Yu, C.; Gao, W. Fedhealth: A federated transfer learning framework for wearable healthcare. IEEE Intell. Syst. 2020, 35, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, H.; Zhou, J.; Li, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Hou, G. Wearable indoor localisation approach in Internet of Things. IET Netw. 2016, 5, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooney, G. Is HIPAA Compliant with the GDPR? 2018. Available online: https://www.ipswitch.com/blog/is-hipaa-compliant-with-the-gdpr (accessed on 3 May 2018).
- Barrows, R.C., Jr.; Clayton, P.D. Privacy, confidentiality, and electronic medical records. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 1996, 3, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ng, D.; Lan, X.; Yao, M.M.S.; Chan, W.P.; Feng, M. Federated learning: A collaborative effort to achieve better medical imaging models for individual sites that have small labelled datasets. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2021, 11, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhao, J.; Jiang, L.; Tan, R.; Niyato, D.; Li, Z.; Lyu, L.; Liu, Y. Privacy-preserving blockchain-based federated learning for IoT devices. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 8, 1817–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahab, O.A.; Mourad, A.; Otrok, H.; Taleb, T. Federated machine learning: Survey, multi-level classification, desirable criteria and future directions in communication and networking systems. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2021, 23, 1342–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheller, M.J.; Edwards, B.; Reina, G.A.; Martin, J.; Pati, S.; Kotrotsou, A.; Milchenko, M.; Xu, W.; Marcus, D.; Colen, R.R.; et al. Federated learning in medicine: Facilitating multi-institutional collaborations without sharing patient data. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rieke, N.; Hancox, J.; Li, W.; Milletari, F.; Roth, H.R.; Albarqouni, S.; Bakas, S.; Galtier, M.N.; Landman, B.A.; Maier-Hein, K.; et al. The future of digital health with federated learning. NPJ Digit. Med. 2020, 3, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, W.Y.B.; Luong, N.C.; Hoang, D.T.; Jiao, Y.; Liang, Y.C.; Yang, Q.; Niyato, D.; Miao, C. Federated learning in mobile edge networks: A comprehensive survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2020, 22, 2031–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, L.U.; Saad, W.; Han, Z.; Hossain, E.; Hong, C.S. Federated learning for internet of things: Recent advances, taxonomy, and open challenges. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2021, 23, 1759–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, L.U.; Pandey, S.R.; Tran, N.H.; Saad, W.; Han, Z.; Nguyen, M.N.; Hong, C.S. Federated learning for edge networks: Resource optimization and incentive mechanism. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2020, 58, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melis, L.; Song, C.; De Cristofaro, E.; Shmatikov, V. Exploiting unintended feature leakage in collaborative learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy, San Francisco, CA, USA, 20–22 May 2019; pp. 691–706. [Google Scholar]
- Bhowmick, A.; Duchi, J.; Freudiger, J.; Kapoor, G.; Rogers, R. Protection against reconstruction and its applications in private federated learning. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1812.00984. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.; Liu, Z.; Han, S. Deep leakage from gradients. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2019, 32, 14774–14784. [Google Scholar]
- Aono, Y.; Hayashi, T.; Wang, L.; Moriai, S. Privacy-preserving deep learning via additively homomorphic encryption. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2017, 13, 1333–1345. [Google Scholar]
- Bhagoji, A.N.; Chakraborty, S.; Mittal, P.; Calo, S. Analyzing federated learning through an adversarial lens. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (PMLR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019; pp. 634–643. [Google Scholar]
- Ying, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X. Privacy-preserving in defending against membership inference attacks. In Proceedings of the 2020 Workshop on Privacy-Preserving Machine Learning in Practice, Virtual Event, 9 November 2020; pp. 61–63. [Google Scholar]
- Bagdasaryan, E.; Veit, A.; Hua, Y.; Estrin, D.; Shmatikov, V. How to backdoor federated learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics (PMLR), Online Event, Palermo, Italy, 26–28 August 2020; pp. 2938–2948. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Xu, M.; Wu, Y.; Zheng, N. Deep model poisoning attack on federated learning. Future Internet 2021, 13, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolpegin, V.; Truex, S.; Gursoy, M.E.; Liu, L. Data poisoning attacks against federated learning systems. In Proceedings of the European Symposium on Research in Computer Security, Guildford, UK, 14–18 September 2020; Springer: Guildford, UK, 2020; pp. 480–501. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, D.; Chang, S.; Lin, Z.; Liu, G.; Sun, D. Understanding distributed poisoning attack in federated learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE 25th International Conference on Parallel and Distributed Systems (ICPADS), Tianjin, China, 4–6 December 2019; pp. 233–239. [Google Scholar]
- Lyu, L.; Yu, H.; Yang, Q. Threats to federated learning: A survey. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.02133. [Google Scholar]
- Jere, M.S.; Farnan, T.; Koushanfar, F. A taxonomy of attacks on federated learning. IEEE Secur. Priv. 2020, 19, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Li, A.; Wang, B.; Yang, H.; Li, H.; Chen, Y. Soteria: Provable defense against privacy leakage in federated learning from representation perspective. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 9311–9319. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Yu, S. Gan enhanced membership inference: A passive local attack in federated learning. In Proceedings of the ICC 2020-2020 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Virtual Conference, 7–11 June 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Song, M.; Wu, L.; Xue, F.; Ren, K. Poisoning-assisted property inference attack against federated learning. IEEE Trans. Dependable Secur. Comput. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Q.; Hu, S.; Deng, R.; Lu, Z. Combined federated and split learning in edge computing for ubiquitous intelligence in internet of things: State-of-the-art and future directions. Sensors 2022, 22, 5983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hitaj, B.; Ateniese, G.; Perez-Cruz, F. Deep models under the GAN: Information leakage from collaborative deep learning. In Proceedings of the 2017 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Dallas, TX, USA, 30 October–3 November 2017; pp. 603–618. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Song, M.; Zhang, Z.; Song, Y.; Wang, Q.; Qi, H. Beyond inferring class representatives: User-level privacy leakage from federated learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE INFOCOM 2019-IEEE Conference on Computer Communications, Paris, France, 29 April–2 May 2019; pp. 2512–2520. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, M.; Wang, H.; Zhang, B.; Zhu, L.; Xu, K.; Li, Q.; Du, X. Exploiting unintended property leakage in blockchain-assisted federated learning for intelligent edge computing. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 8, 2265–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Liu, L.; Loper, M.; Chow, K.H.; Gursoy, M.E.; Truex, S.; Wu, Y. A framework for evaluating client privacy leakages in federated learning. In Proceedings of the European Symposium on Research in Computer Security, Guildford, UK, 14–18 September 2020; Springer: Guildford, UK, 2020; pp. 545–566. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, H.; Zhou, T.; Wu, X.; Cai, Z. Never Too Late: Tracing and Mitigating Backdoor Attacks in Federated Learning. In Proceedings of the 2022 41st International Symposium on Reliable Distributed Systems (SRDS), Vienna, Austria, 19–22 September 2022; pp. 69–81. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Guo, P.; Zhou, P. Backdoor attacks on federated learning with lottery ticket hypothesis. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2109.10512. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.; Kairouz, P.; Suresh, A.T.; McMahan, H.B. Can you really backdoor federated learning? arXiv 2019, arXiv:1911.07963. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer-Hübner, S. IT-Security and Privacy: Design and Use of Privacy-Enhancing Security Mechanisms; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, A.; Khan, S.U. A review on the state-of-the-art privacy-preserving approaches in the e-health clouds. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2014, 18, 1431–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra-Arnau, J.; Rebollo-Monedero, D.; Forné, J. Privacy-enhancing technologies and metrics in personalized information systems. In Advanced Research in Data Privacy; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 423–442. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Crespo, R.G.; Martínez, O.S. Enhancing privacy and data security across healthcare applications using blockchain and distributed ledger concepts. Healthcare 2020, 8, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhiman, G.; Juneja, S.; Mohafez, H.; El-Bayoumy, I.; Sharma, L.K.; Hadizadeh, M.; Islam, M.A.; Viriyasitavat, W.; Khandaker, M.U. Federated learning approach to protect healthcare data over big data scenario. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarati, P.; Sweeney, L. Protecting Privacy When Disclosing Information: K-Anonymity and Its Enforcement through Generalization and Suppression; Technical Report; SRI International: Menlo Park, CA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Choudhury, O.; Gkoulalas-Divanis, A.; Salonidis, T.; Sylla, I.; Park, Y.; Hsu, G.; Das, A. Anonymizing data for privacy-preserving federated learning. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2002.09096. [Google Scholar]
- Machanavajjhala, A.; Kifer, D.; Gehrke, J.; Venkitasubramaniam, M. l-diversity: Privacy beyond k-anonymity. ACM Trans. Knowl. Discov. Data 2007, 1, 3-es. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sei, Y.; Okumura, H.; Takenouchi, T.; Ohsuga, A. Anonymization of sensitive quasi-identifiers for l-diversity and t-closeness. IEEE Trans. Dependable Secur. Comput. 2017, 16, 580–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo-Ferrer, J.; Soria-Comas, J. From t-closeness to differential privacy and vice versa in data anonymization. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2015, 74, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blanco-Justicia, A.; Domingo-Ferrer, J.; Martínez, S.; Sánchez, D.; Flanagan, A.; Tan, K.E. Achieving security and privacy in federated learning systems: Survey, research challenges and future directions. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2021, 106, 104468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Fan, Y.; Tse, M.; Lin, K.Y. A review of applications in federated learning. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2020, 149, 106854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Huang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Ji, S.; Xiong, H.; Dou, D. From distributed machine learning to federated learning: A survey. Knowl. Inf. Syst. 2022, 64, 885–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, A.C. Protocols for secure computations. In Proceedings of the 23rd Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, Chicago, IL, USA, 3–5 November 1982; pp. 160–164. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, X.; Zhu, Y.; Hu, J. A comprehensive survey of privacy-preserving federated learning: A taxonomy, review, and future directions. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 2021, 54, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Liao, L.; Li, Z.; Lai, R.X.; Zhang, M. Applying Federated Learning in Software-Defined Networks: A Survey. Symmetry 2022, 14, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldwasser, S.; Micali, S.; Rackoff, C. The knowledge complexity of interactive proof systems. SIAM J. Comput. 1989, 18, 186–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Liu, Z.; Li, J.; Gao, J.; Hou, B.; Dong, C.; Baker, T. Verifl: Communication-efficient and fast verifiable aggregation for federated learning. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2020, 16, 1736–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wang, X.; Peng, W. Secure remote multi-factor authentication scheme based on chaotic map zero-knowledge proof for crowdsourcing internet of things. IEEE Access 2019, 8, 8754–8767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Wang, G.; Gehrke, J. Differential privacy via wavelet transforms. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2010, 23, 1200–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Chaudhuri, K.; Sarwate, A.D. Stochastic gradient descent with differentially private updates. In Proceedings of the IEEE Global Conference on Signal and Information Processing, Austin, TX, USA, 3–5 December 2013; pp. 245–248. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Wu, Z.; Wen, Z.; He, B. Privacy-preserving gradient boosting decision trees. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34, pp. 784–791. [Google Scholar]
- Jordan, S.; Fontaine, C.; Hendricks-Sturrup, R. Selecting Privacy-Enhancing Technologies for Managing Health Data Use. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 814163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, T.H.H.; Li, M.; Shi, E.; Xu, W. Differentially private continual monitoring of heavy hitters from distributed streams. In Proceedings of the 12th International Symposium on Privacy Enhancing Technologies Symposium, Vigo, Spain, 11–13 July 2012; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 140–159. [Google Scholar]
- Cormode, G.; Jha, S.; Kulkarni, T.; Li, N.; Srivastava, D.; Wang, T. Privacy at scale: Local differential privacy in practice. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Management of Data, Houston, TX, USA, 10–15 June 2018; pp. 1655–1658. [Google Scholar]
- Kaaniche, N.; Laurent, M.; Belguith, S. Privacy enhancing technologies for solving the privacy-personalization paradox: Taxonomy and survey. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2020, 171, 102807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, I.T.; Alharbi, F.; Margaria, T.; Crespi, N.; Qureshi, K.N. PETchain: A blockchain-based privacy enhancing technology. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 41129–41143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, N.B.; Sun, K.; Lee, G.M.; Guo, Y. Gdpr-compliant personal data management: A blockchain-based solution. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2019, 15, 1746–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alamri, B.; Javed, I.T.; Margaria, T. Preserving patients’ privacy in medical IoT using blockchain. In Proceedings of the Edge Computing–EDGE 2020: 4th International Conference, Held as Part of the Services Conference Federation (SCF 2020), Honolulu, HI, USA, 18–20 September 2020; Springer: Honolulu, HI, USA, 2020; pp. 103–110. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Huang, X.; Zhang, K.; Maharjan, S.; Zhang, Y. Blockchain and federated learning for 5G beyond. IEEE Netw. 2020, 35, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.C.; Ding, M.; Pham, Q.V.; Pathirana, P.N.; Le, L.B.; Seneviratne, A.; Li, J.; Niyato, D.; Poor, H.V. Federated learning meets blockchain in edge computing: Opportunities and challenges. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 12806–12825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Yan, Z.; Ding, W.; Yang, L.T. A survey on data provenance in IoT. World Wide Web 2020, 23, 1441–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Orekondy, T.; Oh, S.J.; Zhang, Y.; Schiele, B.; Fritz, M. Gradient-leaks: Understanding and controlling deanonymization in federated learning. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.05838. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, W.; Mehta, N.; Liang, K.J.; Cheng, P.; El-Khamy, M.; Carin, L. Waffle: Weight anonymized factorization for federated learning. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 49207–49218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Song, Y.; Wang, Q.; Ren, J.; Qi, H. Analyzing user-level privacy attack against federated learning. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2020, 38, 2430–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marulli, F.; Verde, L.; Marrone, S.; Barone, R.; De Biase, M.S. Evaluating Efficiency and Effectiveness of Federated Learning Approaches in Knowledge Extraction Tasks. In Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Virtual Event, 18–22 July 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Choudhury, O.; Gkoulalas-Divanis, A.; Salonidis, T.; Sylla, I.; Park, Y.; Hsu, G.; Das, A. A syntactic approach for privacy-preserving federated learning. In ECAI 2020; IOS Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 1762–1769. [Google Scholar]
- Grama, M.; Musat, M.; Muñoz-González, L.; Passerat-Palmbach, J.; Rueckert, D.; Alansary, A. Robust aggregation for adaptive privacy preserving federated learning in healthcare. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2009.08294. [Google Scholar]
- Alsulaimawi, Z. A non-negative matrix factorization framework for privacy-preserving and federated learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE 22nd International Workshop on Multimedia Signal Processing (MMSP), Tampere, Finland, 21–24 September 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, J.; Zhu, H.; Deng, H.; Chen, Z.; Liu, D. FeARH: Federated machine learning with anonymous random hybridization on electronic medical records. J. Biomed. Inform. 2021, 117, 103735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wibawa, F.; Catak, F.O.; Kuzlu, M.; Sarp, S.; Cali, U. Homomorphic Encryption and Federated Learning based Privacy-Preserving CNN Training: COVID-19 Detection Use-Case. In Proceedings of the 2022 European Interdisciplinary Cybersecurity Conference, Barcelona, Spain, 15–16 June 2022; pp. 85–90. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Y.; Fan, M. A Method to Improve the Privacy and Security for Federated Learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE 6th International Conference on Computer and Communication Systems (ICCCS), Chengdu, China, 23–26 April 2021; pp. 704–708. [Google Scholar]
- Wibawa, F.; Catak, F.O.; Sarp, S.; Kuzlu, M. BFV-Based Homomorphic Encryption for Privacy-Preserving CNN Models. Cryptography 2022, 6, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xu, J.; Vijayakumar, P.; Sharma, P.K.; Ghosh, U. Homomorphic Encryption-based Privacy-preserving Federated Learning in IoT-enabled Healthcare System. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Naas, S.A.; Sigg, S.; Lyu, X. Privacy-preserving federated learning based on multi-key homomorphic encryption. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2022, 37, 5880–5901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stripelis, D.; Saleem, H.; Ghai, T.; Dhinagar, N.; Gupta, U.; Anastasiou, C.; Ver Steeg, G.; Ravi, S.; Naveed, M.; Thompson, P.M.; et al. Secure neuroimaging analysis using federated learning with homomorphic encryption. In Proceedings of the 17th International Symposium on Medical Information Processing and Analysis (SPIE), Campinas, Brazil, 17–19 November 2021; Volume 12088, pp. 351–359. [Google Scholar]
- Rachakonda, A.S.; Moorthy, B.S.; Jain, C.A.; Bukharev, D.A.; Bucur, E.A.; Manni, F.F.; Quiterio, G.T.M.; Joosten, H.L.; Mendez, I.N.I. Privacy enhancing and scalable federated learning to accelerate AI implementation in cross-silo and IoMT environments. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2022, 27, 744–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heiss, J.; Grünewald, E.; Haimerl, N.; Schulte, S.; Tai, S. Advancing Blockchain-based Federated Learning through Verifiable Off-chain Computations. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2206.11641. [Google Scholar]
- Kerkouche, R.; Acs, G.; Castelluccia, C.; Genevès, P. Privacy-preserving and bandwidth-efficient federated learning: An application to in-hospital mortality prediction. In Proceedings of the Conference on Health, Inference, and Learning, New York, NY, USA, 8–10 April 2021; pp. 25–35. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, T.U.; Ghasemi, R.; Mohammed, N. Privacy-Preserving Federated Learning Model for Healthcare Data. In Proceedings of the IEEE 12th Annual Computing and Communication Workshop and Conference (CCWC), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26–29 January 2022; pp. 0281–0287. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Yuan, S.; Xie, N.; Leng, J.; Wang, G. A Federated Adversarial Learning Method for Biomedical Named Entity Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), Houston, TX, USA, 9–12 December 2021; pp. 2962–2969. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Meng, Y.; Ma, L.; Du, S.; Zhu, H.; Pei, Q.; Shen, X. A federated learning based privacy-preserving smart healthcare system. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2021, 18, 2021–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.C.; Ding, M.; Pathirana, P.N.; Seneviratne, A.; Zomaya, A.Y. Federated learning for COVID-19 detection with generative adversarial networks in edge cloud computing. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 9, 10257–10271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, O.; Omojo, A.; Onuja, A.; Sunday, Y.; Tiwari, P.; Gupta, D.; Hafeez, G.; Yahaya, A.; Fatoba, O.; Shamshirband, S. IoMT: A COVID-19 Healthcare System driven by Federated Learning and Blockchain. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2022, 27, 823–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aich, S.; Sinai, N.K.; Kumar, S.; Ali, M.; Choi, Y.R.; Joo, M.I.; Kim, H.C. Protecting personal healthcare record using blockchain & federated learning technologies. In Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Advanced Communication Technology (ICACT), Pyeongchang, Republic of Korea, 13–16 February 2022; pp. 109–112. [Google Scholar]
- Lakhan, A.; Mohammed, M.A.; Nedoma, J.; Martinek, R.; Tiwari, P.; Vidyarthi, A.; Alkhayyat, A.; Wang, W. Federated-Learning Based Privacy Preservation and Fraud-Enabled Blockchain IoMT System for Healthcare. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2022, 27, 664–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Rathore, S.; Alfarraj, O.; Tolba, A.; Yoon, B. A framework for privacy-preservation of IoT healthcare data using Federated Learning and blockchain technology. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2022, 129, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Khan, A.A.; Kumar, J.; Golilarz, N.A.; Zhang, S.; Ting, Y.; Zheng, C.; Wang, W. Blockchain-federated-learning and deep learning models for covid-19 detection using ct imaging. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 16301–16314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| References | IoHT Environment | Healthcare Domain | Privacy Mechanisms | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anonymization | Cryptography | Perturbation | Blockchain | |||
| Aledhari et al. [22] | × | √ | × | × | × | × |
| Zhang et al. [23] | × | × | × | √ | √ | × |
| Mothukuri et al. [24] | × | × | × | √ | √ | √ |
| Nguyen et al. [25] | √ | √ | × | × | √ | √ |
| Novikova et al. [26] | × | × | × | √ | √ | × |
| Nguyen et al. [27] | √ | √ | × | × | √ | × |
| Our work | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Ref. | Aim | Dataset | Dataset Available | Open-Source | Privacy Attack | Privacy-Enhancing Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Choudhury et al. [113] | Maximize data utility and model performance | MIMIC III and LCED | √ | × | Inference attack | Syntactic anonymization |
| Grama et al. [114] | Applying data privacy engineering without reducing the accuracy | Pima Indians diabetes and Cleveland heart disease | √ | × | Poisoning attack | k-anonymity |
| Alsulaimawi [115] | Preserving private data with high accuracy | MNIST and HARUS | √ | × | - | Non-negative matrix factorization |
| Cui et al. [116] | Avoiding an attack from an untrustworthy central analyzer in FL, obtaining similar performance compared to a centralized model | eICU | √ | × | Inference attack | Anonymous random hybridization |
| Ref. | Aim | Dataset | Dataset Available | Open-Source | Privacy Attack | Privacy-Enhancing Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zhang et al. [120] | Preserving privacy in skin cancer detection while ensuring reliable accuracy | HAM10000 | √ | × | Inference attack | Homomorphic encryption and secure multi-party computation |
| Ma et al. [121] | Securing the FL environment with IoHT devices | UP-FALL | √ | × | Inference attack | xMK-CKKS multi-key homomorphic encryption |
| Stripelis et al. [122] | Enhancing patients’ data privacy | 3D brain MRI | √ | × | Membership inference attack | Fully homomorphic encryption (FHE) |
| Rachakonda et al. [123] | Protecting medical data privacy with IoHT devices | eICU | √ | × | Reverse engineering attack | Secure multi-party computation |
| Heiss et al. [124] | Privacy-enhanced decentralized applications | Daily and Sports Activities | √ | × | Global aggregation and poisoning attack | Zero-knowledge proofs |
| Ref. | Aim | Dataset | Dataset Available | Open-Source | Privacy Attack | Privacy-Enhancing Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kerkouche et al. [125] | Enhancing privacy and bandwidth efficiency | Two real-world electronic health records | √ | √ | Inference attack | Differential privacy |
| Islam et al. [126] | Preserving privacy and predicting risk of heart failure | BC-TCGA | √ | × | - | Differential privacy |
| Zhao et al. [127] | Avoiding medical data leakage during data exchange | Dataset from a tumor hospitals | × | × | Adversarial attack | Differential privacy |
| Li et al. [128] | Privacy-preserving IoHT and Alzheimer’s disease detection | ADReSS | √ | × | Man-in-the-middle attack | Differential privacy |
| Nguyen et al. [129] | Preserving privacy and improving COVID-19 detection | DarkCOVID and ChestCOVID | √ | × | - | Differential privacy |
| Ref. | Aim | Dataset | Dataset Available | Open-Source | Privacy Attack | Privacy-Enhancing Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Samuel et al. [130] | IoMT privacy preservation and prediction of COVID-19 | - | × | × | Backdoor and inference attacks | Blockchain |
| Aich et al. [131] | Preserving data privacy and predicting COVID-19 | - | × | × | - | Blockchain |
| Lakhan et al. [132] | Fraud detection for the IoHT | ECG heartbeat E-heart videos Blood pressure | × | × | Fraud attack | Blockchain |
| Singh et al. [133] | Privacy preservation for the IoHT in clouds | Healthcare data | × | × | Replay attack | Blockchain |
| Kumar et al. [134] | Preserving patients’ privacy and detecting COVID-19 from CT scans | CC-19 | √ | √ | - | Blockchain |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mosaiyebzadeh, F.; Pouriyeh, S.; Parizi, R.M.; Sheng, Q.Z.; Han, M.; Zhao, L.; Sannino, G.; Ranieri, C.M.; Ueyama, J.; Batista, D.M. Privacy-Enhancing Technologies in Federated Learning for the Internet of Healthcare Things: A Survey. Electronics 2023, 12, 2703. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12122703
Mosaiyebzadeh F, Pouriyeh S, Parizi RM, Sheng QZ, Han M, Zhao L, Sannino G, Ranieri CM, Ueyama J, Batista DM. Privacy-Enhancing Technologies in Federated Learning for the Internet of Healthcare Things: A Survey. Electronics. 2023; 12(12):2703. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12122703
Chicago/Turabian StyleMosaiyebzadeh, Fatemeh, Seyedamin Pouriyeh, Reza M. Parizi, Quan Z. Sheng, Meng Han, Liang Zhao, Giovanna Sannino, Caetano Mazzoni Ranieri, Jó Ueyama, and Daniel Macêdo Batista. 2023. "Privacy-Enhancing Technologies in Federated Learning for the Internet of Healthcare Things: A Survey" Electronics 12, no. 12: 2703. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12122703
APA StyleMosaiyebzadeh, F., Pouriyeh, S., Parizi, R. M., Sheng, Q. Z., Han, M., Zhao, L., Sannino, G., Ranieri, C. M., Ueyama, J., & Batista, D. M. (2023). Privacy-Enhancing Technologies in Federated Learning for the Internet of Healthcare Things: A Survey. Electronics, 12(12), 2703. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12122703











