Lightweight Multi-Scale Dilated U-Net for Crop Disease Leaf Image Segmentation
Abstract
1. Introduction
- LWMSDU-Net is constructed by retaining local and multi-scale detail information;
- Dilated convolution is introduced into U-Net to enlarge the receptive field of the convolution layer, improve the feature learning ability of U-Net, and obtain more information about leaf spot image;
- A residual path (Respath) connection instead of the skip connection is employed to allow gradient information to flow better through the network and overcome gradient vanishing and degradation.
2. Related Works
2.1. Residual Block
2.2. Dilated Convolution
2.3. U-Net
2.4. Summarization
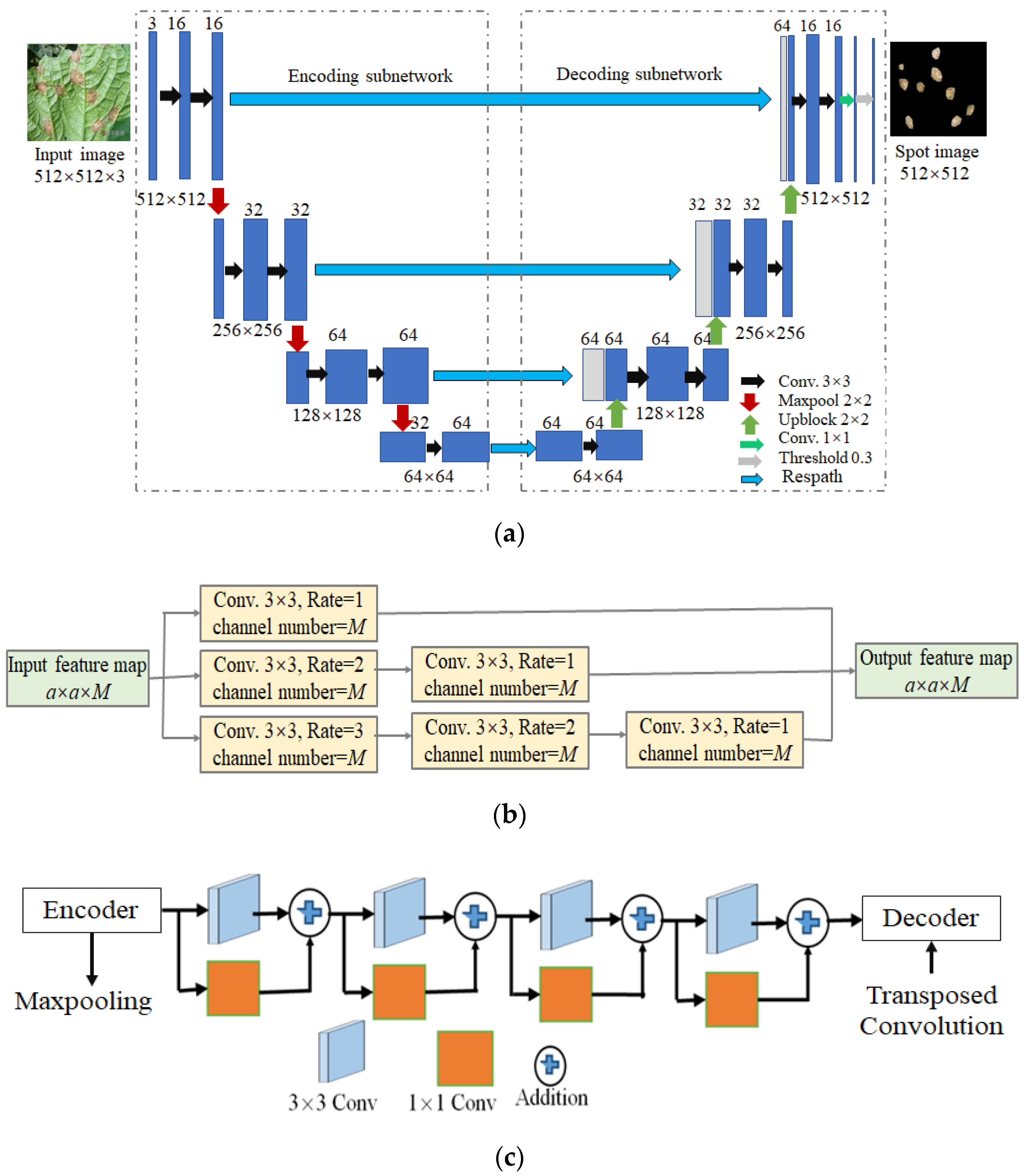
3. Lightweight Multi-Scale Dilated U-Net (LWMSDU-Net)
3.1. LWMSDU-Net Architecture
3.2. Process of CDLIS
4. Experiments and Analysis
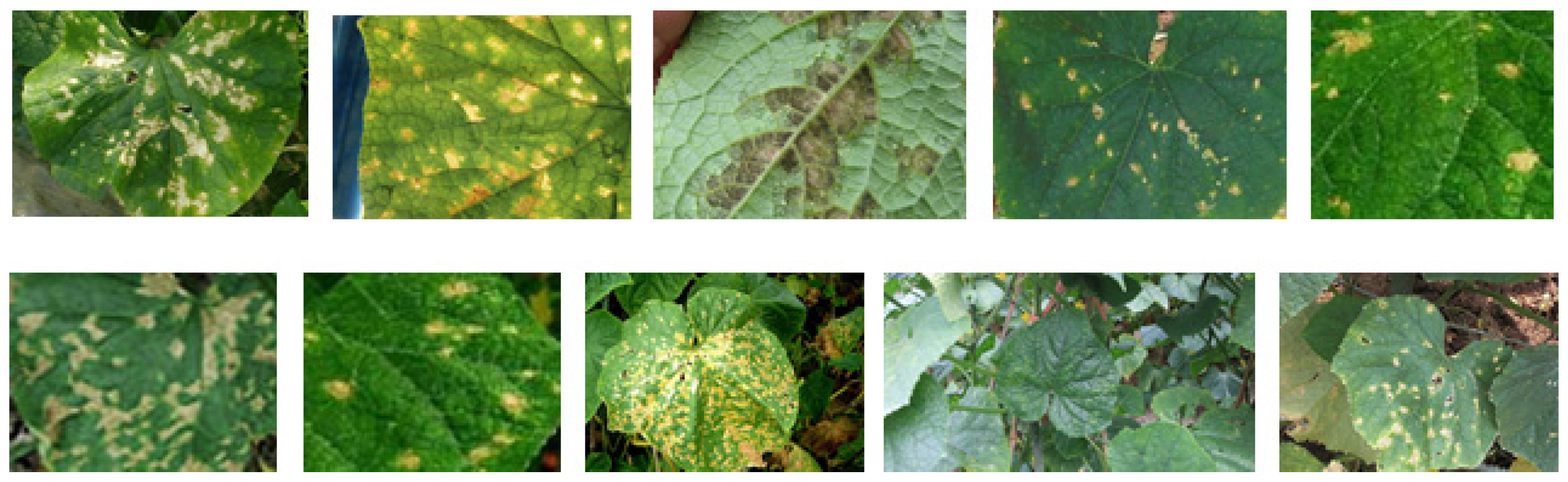
4.1. Dataset
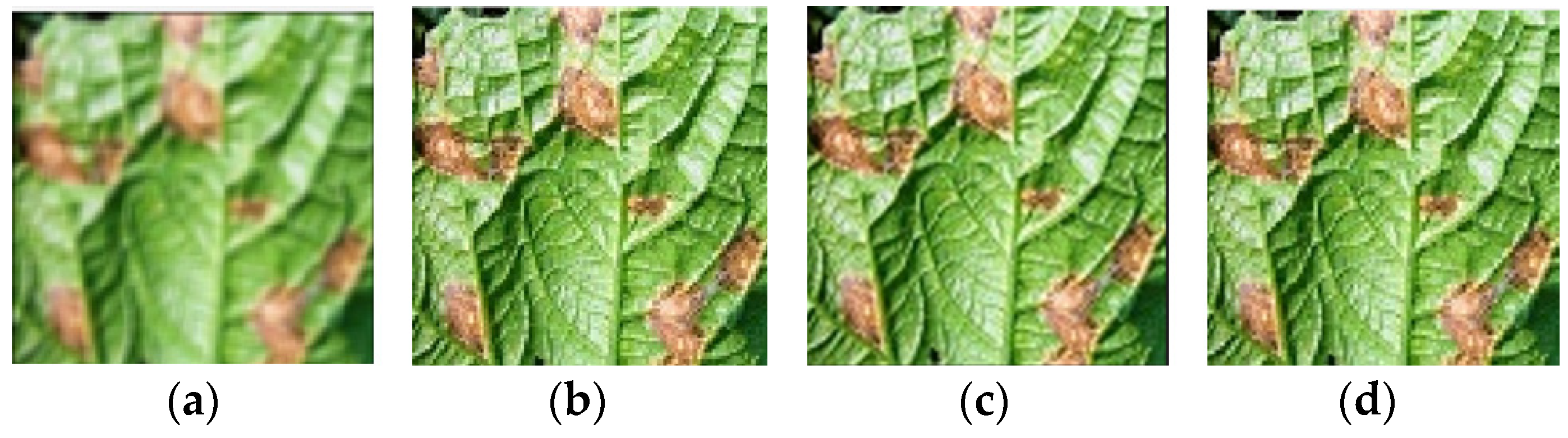
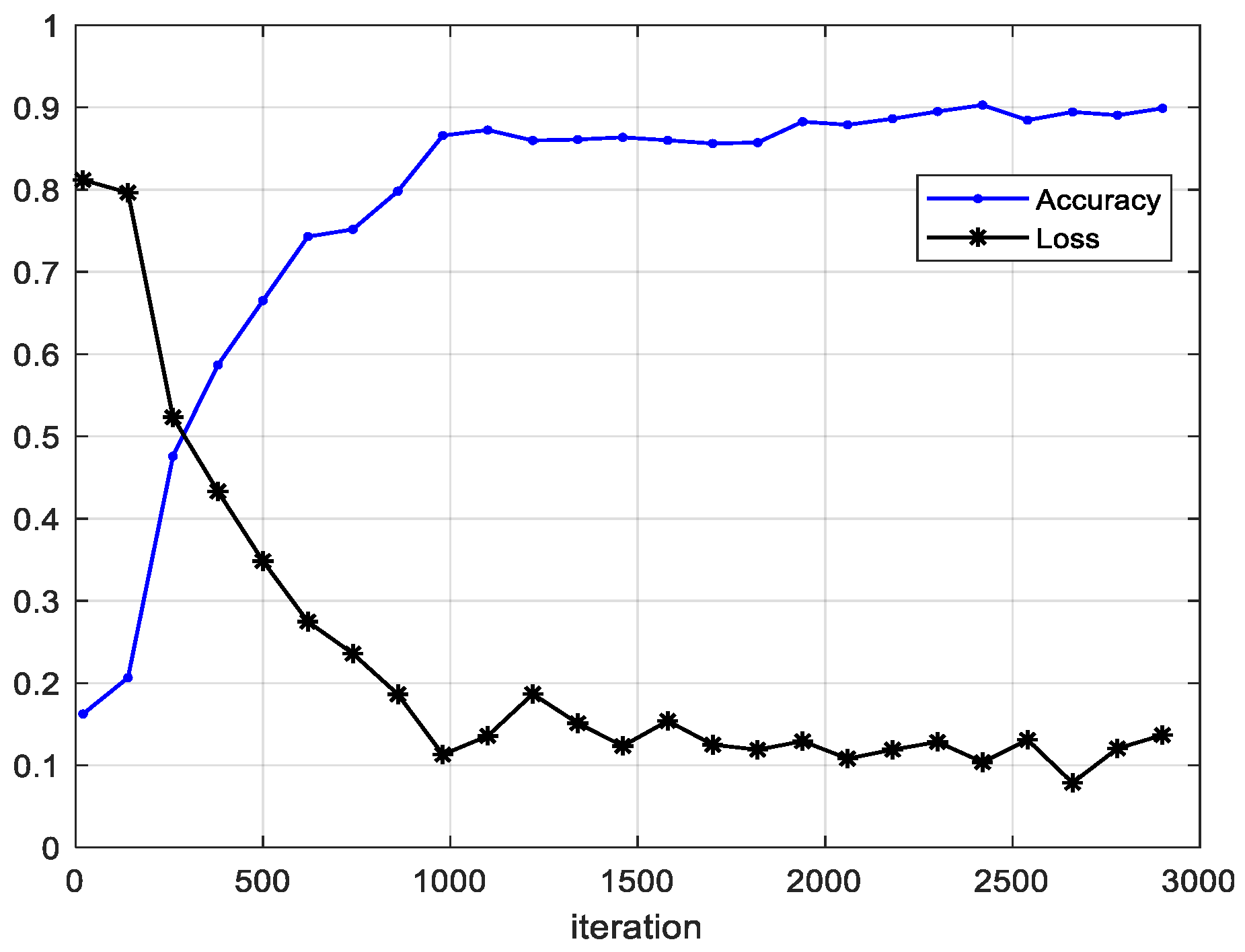
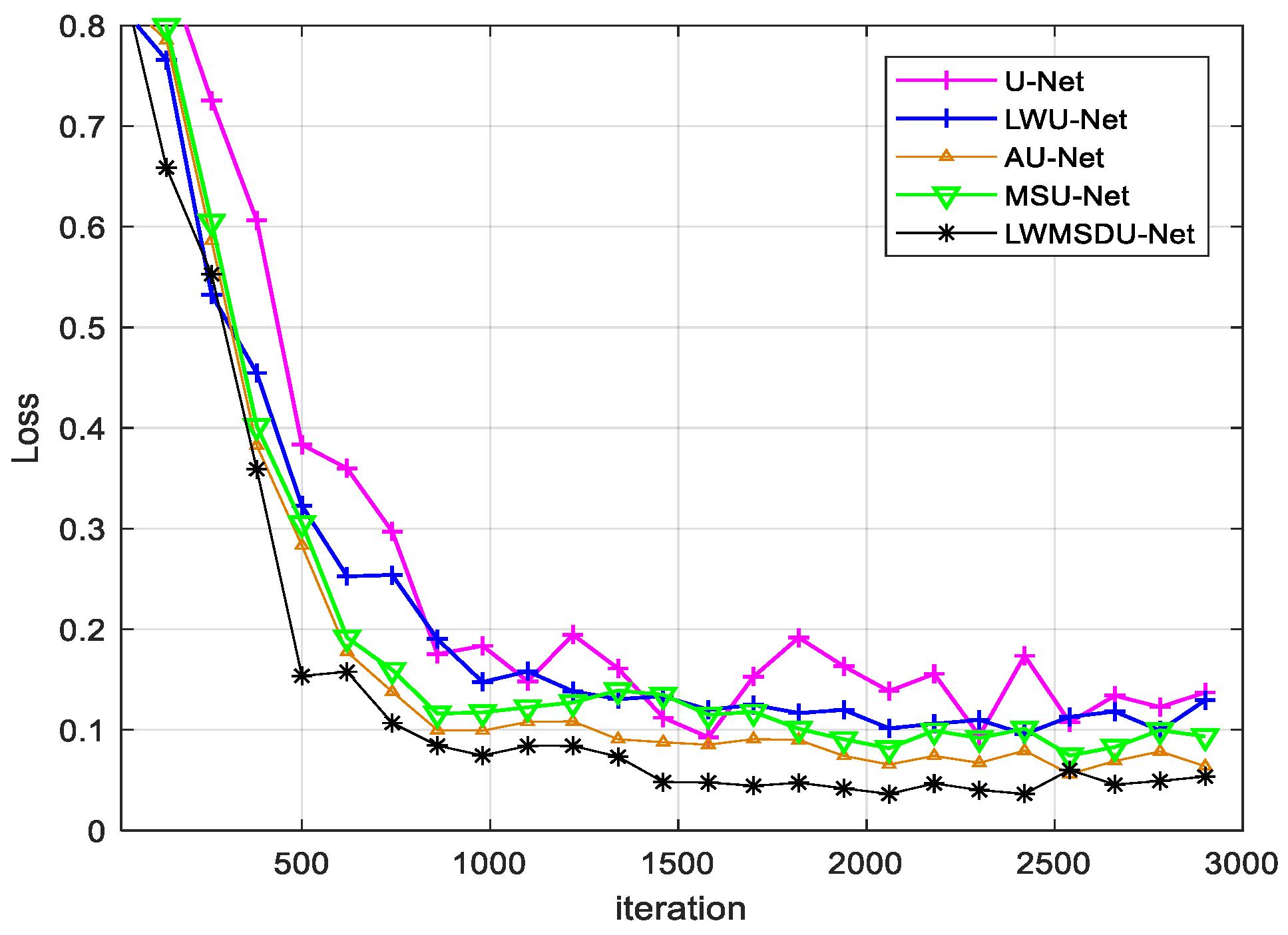
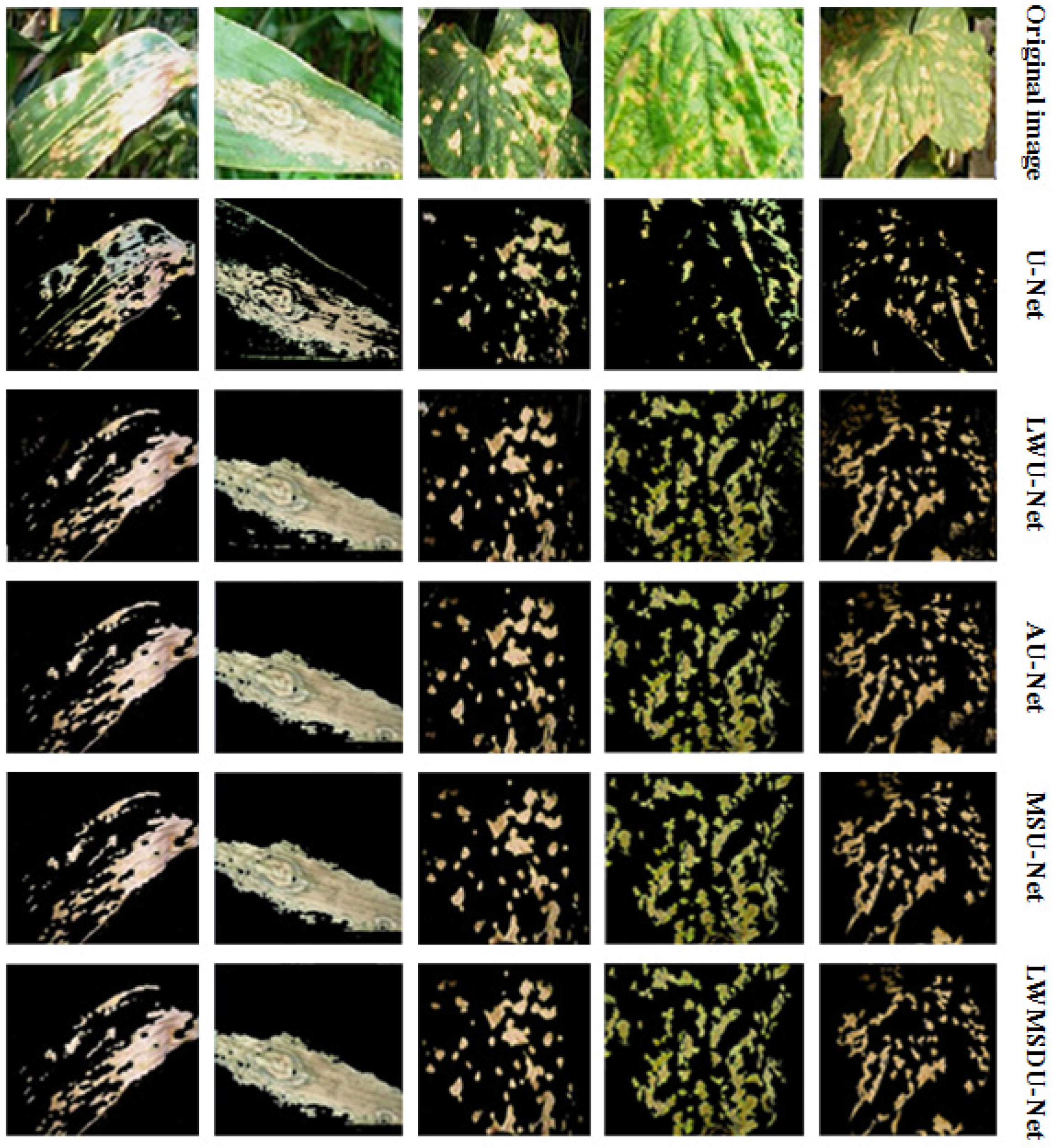
4.2. Results
4.3. Ablation Experiments and Results
5. Analysis and Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sharma, V.; Tripathi, A.K.; Mittal, H. Technological Advancements in Automated Crop Pest and Disease Detection: A Review & Ongoing Research. International Conference on Computing, Communication. In Security and Intelligent Systems (IC3SIS); IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, N.; Khan, M.A.; Tariq, U.; Kadry, S.; Yar, M.A.E.; Mostafa, A.M.; Alnuaim, A.A.; Ahmad, S. Multiclass Cucumber Leaf Diseases Recognition Using Best Feature Selection. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2022, 2, 3281–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praveen, P.; Nischitha, M.; Supriya, C.; Yogitha, M.; Suryanandh, A. To Detect Plant Disease Identification on Leaf Using Machine Learning Algorithms. In Intelligent System Design; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, M.; Tan, J. Overview: Research Progress on Pest and Disease Identification. In Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 404–415. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, K.; Pan, S.; Han, Y. Segmentation of Crop Disease Images with an Improved K-means Clustering Algorithm. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2018, 34, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Luo, P.; Mu, Y.; Zhou, R.; Tjahjadi, T.; Ren, Y. Leaf image based plant disease identification using transfer learning and feature fusion. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 196, 106892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Sreenivasu, S.; Mahalaxmi, U.; Sharma, H.; Patil, D.; Asenso, E. Hybrid Feature-Based Disease Detection in Plant Leaf Using Convolutional Neural Network, Bayesian Optimized SVM, and Random Forest Classifier. Hindawi J. Food Qual. 2022, 2020, 2845320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Bai, X.; Wang, L.; Ren, B.; Lu, S. Review and Trend Analysis of Knowledge Graphs for Crop Pest and Diseases. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 62251–62264. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez, C.I.; Leblon, B.; Wang, J.; Haddadi, A.; Wang, K. Cucumber powdery mildew detection using hyperspectral data. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2022, 1, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, J.; Jan, B.; Farman, H.; Ahmad, W.; Ullah, A. Disease Detection in Plum Using Convolutional Neural Network under True Field Conditions. Sensors 2020, 20, 5569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Shao, K.; Bai, M.; Fang, G. Shan and M. Chen. Fully convolutional network-based multi-output model for automatic segmentation of organs at risk in thorax. Sci. Prog. 2021, 104, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Mukherjee, A.; Phadikar, S. A Deep Learning Approach for the Classification of Rice Leaf Diseases. In Intelligence Enabled Research; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 61–69. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, W.; Li, H.; Hu, G.; Liang, D. Lightweight dense-scale network (LDSNet) for corn leaf disease identification. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 197, 106943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashwinkumar, S.; Rajagopal, S.; Manimaran, V.; Jegajoth, B. Automated plant leaf disease detection and classification using optimal MobileNet based convolutional neural networks. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 51, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Ye, J.C. Framing U-Net via Deep Convolutional Framelets: Application to Sparse-View CT. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 37, 1418–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Jia, W.; Sun, M.; Hou, S.; Zheng, Y. A novel green apple segmentation algorithm based on ensemble U-Net under complex orchard environment. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 180, 105900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasiewicz, T.; Kawulok, M.; Nalepa, J. Lightweight U-Nets for Brain Tumor Segmentation. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2021, 12659, 3–14. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, Y.J.; Gao, Y.B.; Wu, H.; Yao, Y. Attention U-Net with Feature Fusion Module for Robust Defect Detection. J. Circuits. Syst. Comput. 2021, 31, 2150272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Peng, Y.; Guo, Y.; Ren, Y.; Xue, Q. DCAU-Net: Dense convolutional attention U-Net for segmentation of intracranial aneurysm images. Vis. Comput. Ind. Biomed. Art 2022, 5, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zheng, J.; Li, D. Precise segmentation of non-enhanced computed tomography in patients with ischemic stroke based on multi-scale U-Net deep network model. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2021, 208, 106278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Hu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Ma, H.; Liu, J. Multi-scale U-net with Edge Guidance for Multimodal Retinal Image Deformable Registration. In Proceedings of the 42nd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 July 2020; pp. 1360–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zou, Y.; Liu, P.X. Hybrid Dilation and Attention Residual U-Net for Medical Image Segmentation. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 134, 104449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, L.; Li, S.; Sun, Y. Lightweight Convolutional Neural Network for Apple Leaf Disease Identification. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 831219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, A.; Seyedali, M.; Mohammed, E.; Sherif, S.M.G.; Mosleh, M.A.; Tare, F.I.; EI-Sayed, M.E. Wind speed ensemble forecasting based on deep learning using adaptive dynamic optimization algorithm. IEEE Access. 2021, 9, 125787–125804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, N.; Zhao, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, W. Iron ORE Region Segmentation Using High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images Based on Res-U-Net. In IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium; IEEE: Piscataway Township, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 2563–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punn, N.S.; Agarwal, S. Inception U-Net Architecture for Semantic Segmentation to Identify Nuclei in Microscopy Cell Images. ACM Trans. Multimed. Comput. Commun. Appl. (TOMM) 2020, 16, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




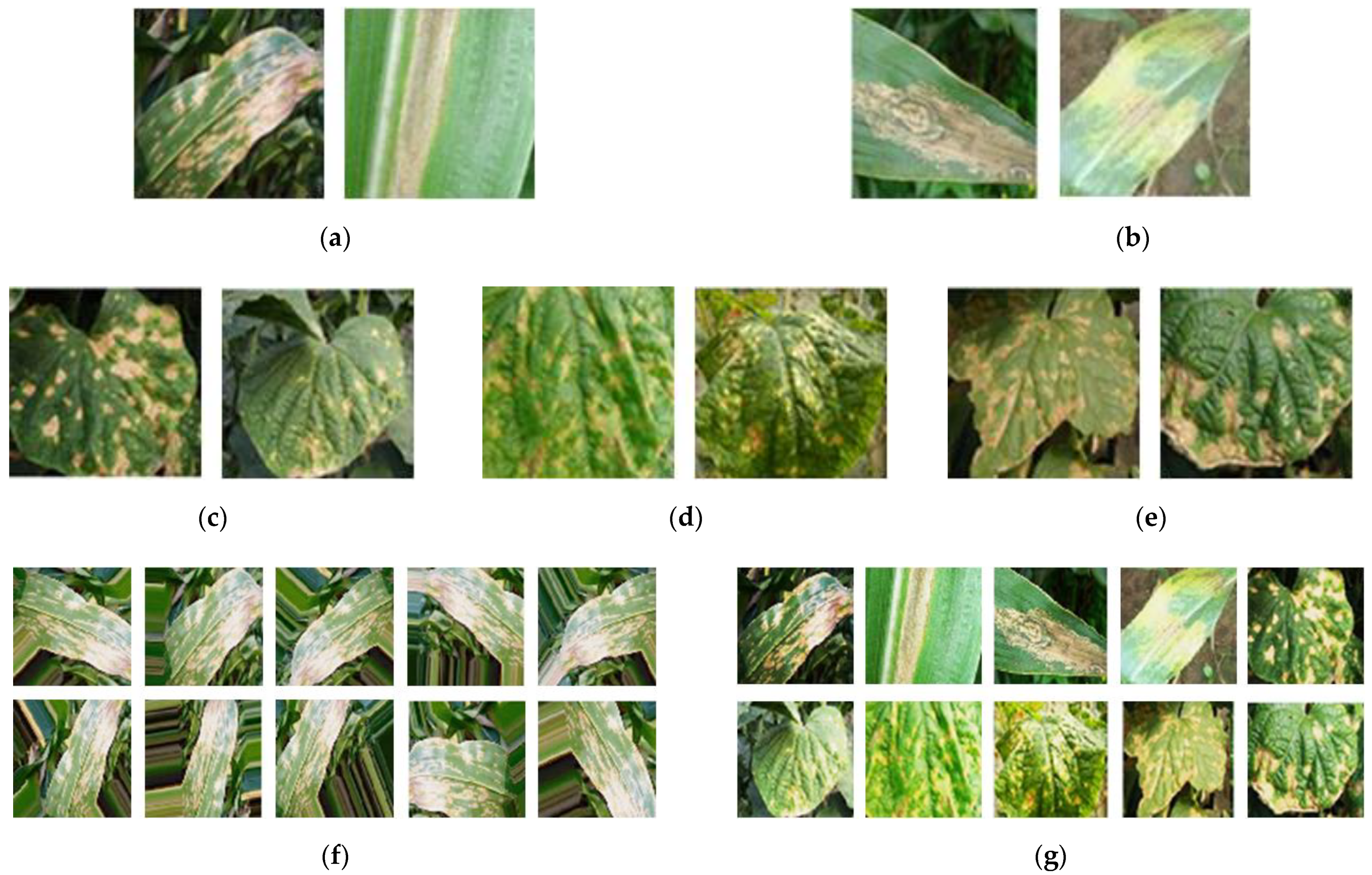

| Disease Type | Number of Original Images | Number of Augmented Images | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corn | Leaf blight | 20 | 200 | 220 |
| Brown spot | 20 | 200 | 220 | |
| Cucumber | Target spot | 20 | 200 | 220 |
| Brown spot | 20 | 200 | 220 | |
| Anthracnose | 20 | 200 | 220 | |
| Total number of images | 100 | 1000 | 1100 | |
| Method | U-Net | LWU-Net | AU-Net | MSU-Net | LWMSDU-Net |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precision | 86.13 | 89.86 | 92.54 | 93.25 | 94.18 |
| Recall | 82.36 | 81.18 | 84.31 | 85.25 | 89.10 |
| F1-score | 84.20 | 85.30 | 88.23 | 89.07 | 91.57 |
| Pixel accuracy | 85.66 | 90.24 | 91.50 | 91.45 | 93.71 |
| Training Time | 12.51 h | 6.42 h | 10.52 h | 11.14 h | 5.17 h |
| Testing time | 5.64 s | 5.18 s | 5.42 s | 4.85 s | 4.73 s |
| Combination Mode | Precision | Training Time |
|---|---|---|
| U-Net: 3 × 3 conv.+ Skip connection | 86.13 | 12.51 h |
| U-Net: 3 × 3 conv. + Respath connection | 87.22 | 11.36 h |
| Res-U-Net: residual block + Skip connection | 90.14 | 11.75 h |
| Inception U-Net: Inception + Skip connection | 92.16 | 10.46 h |
| U-Net: Inception module + Respath connection | 91.57 | 9.73 h |
| U-Net: dilated Inception module + skip connection | 92.46 | 7.13 h |
| LWMSDU-Net: dilated Inception + Respath connection | 94.18 | 5.17 h |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, C.; Yu, C.; Zhang, S. Lightweight Multi-Scale Dilated U-Net for Crop Disease Leaf Image Segmentation. Electronics 2022, 11, 3947. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11233947
Xu C, Yu C, Zhang S. Lightweight Multi-Scale Dilated U-Net for Crop Disease Leaf Image Segmentation. Electronics. 2022; 11(23):3947. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11233947
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Cong, Changqing Yu, and Shanwen Zhang. 2022. "Lightweight Multi-Scale Dilated U-Net for Crop Disease Leaf Image Segmentation" Electronics 11, no. 23: 3947. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11233947
APA StyleXu, C., Yu, C., & Zhang, S. (2022). Lightweight Multi-Scale Dilated U-Net for Crop Disease Leaf Image Segmentation. Electronics, 11(23), 3947. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11233947





