CMOS Low-Dropout Voltage Regulator Design Trends: An Overview
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Background
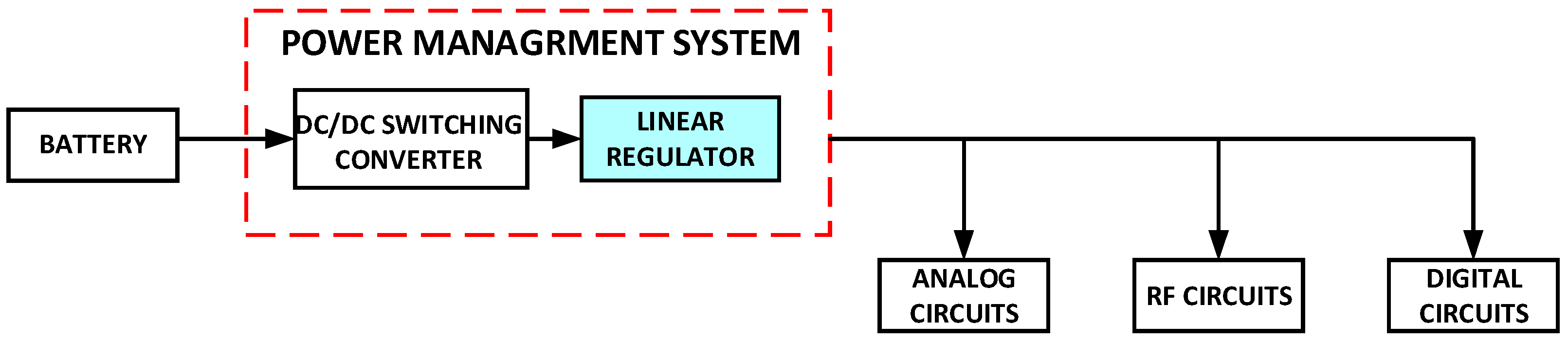
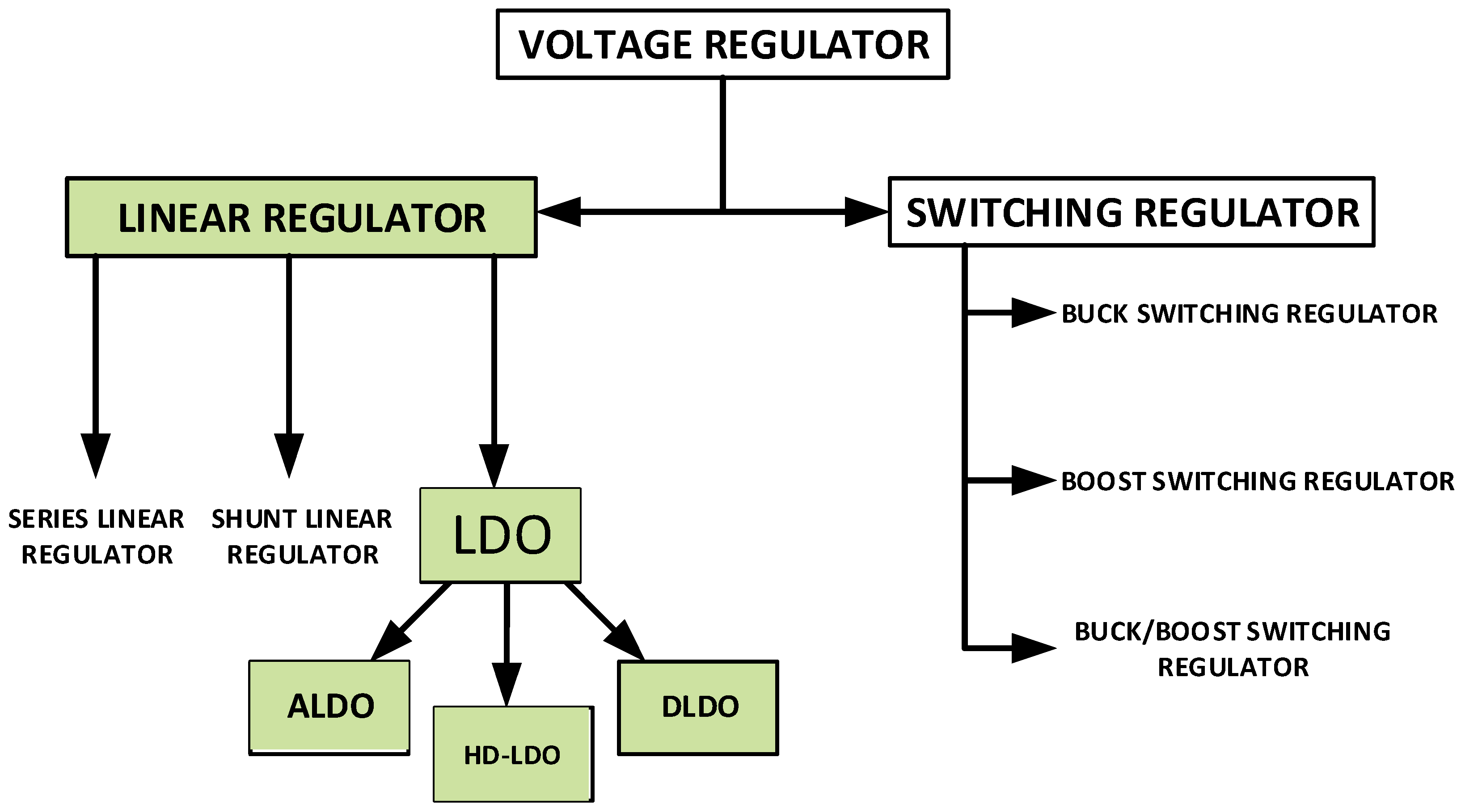
2.1. Overview of Different Categories of Voltage Regulators
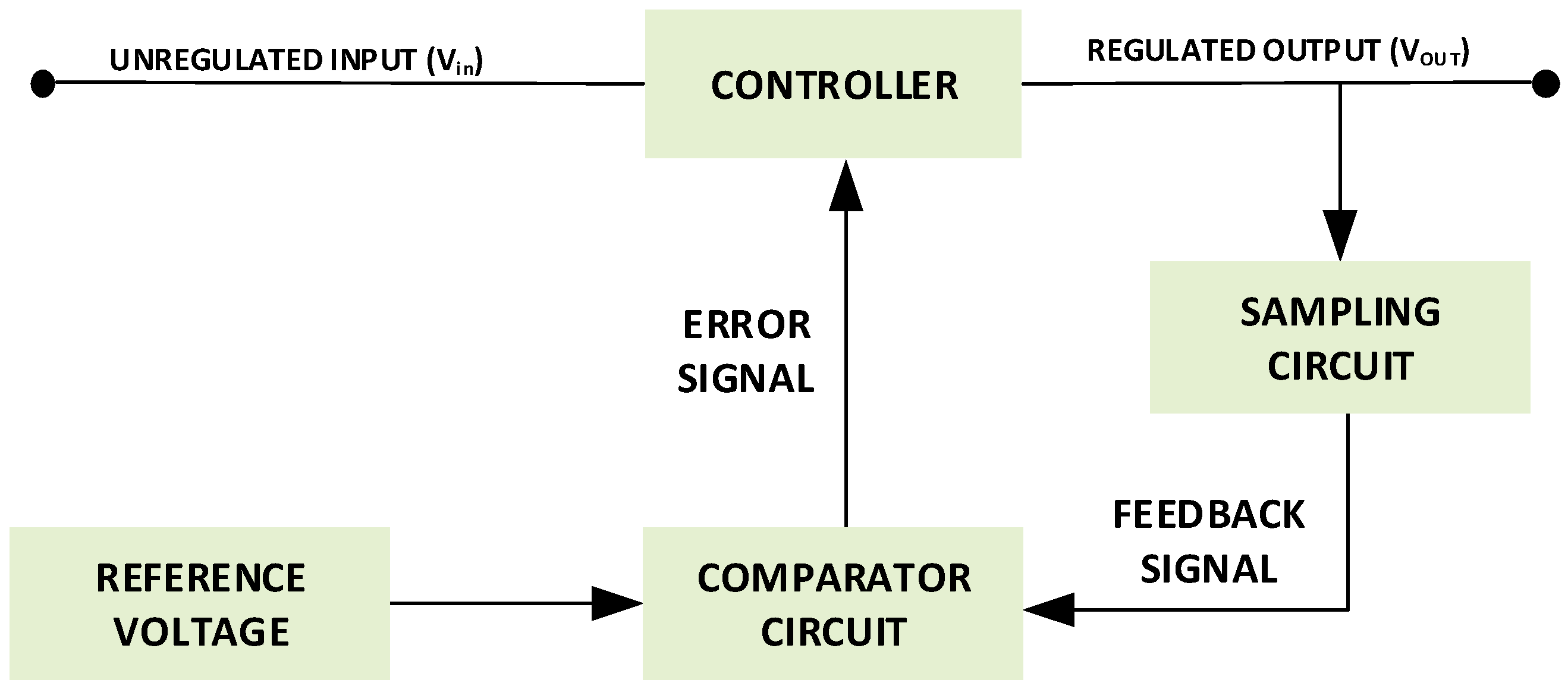
2.2. Linear Regulator Scheme
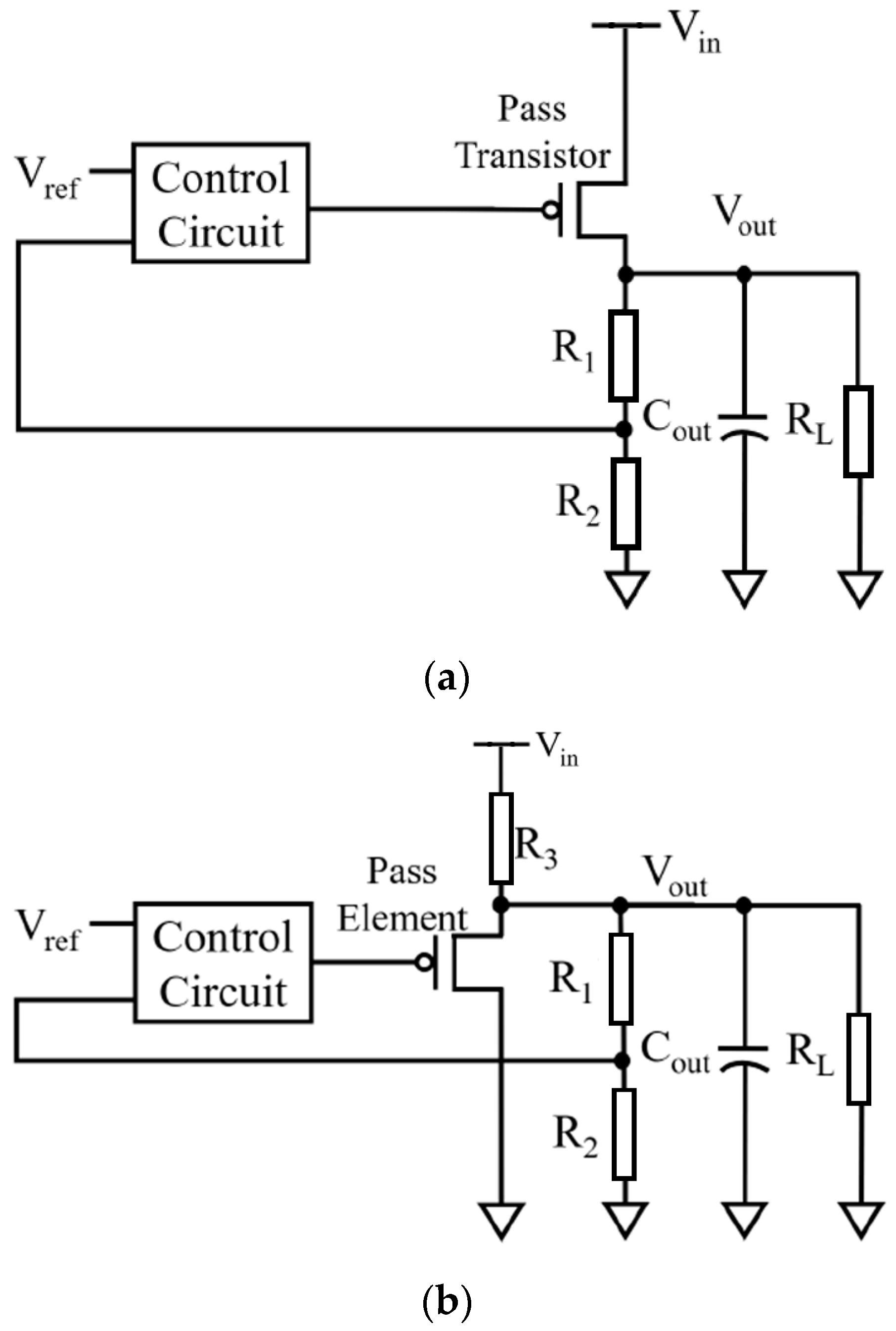
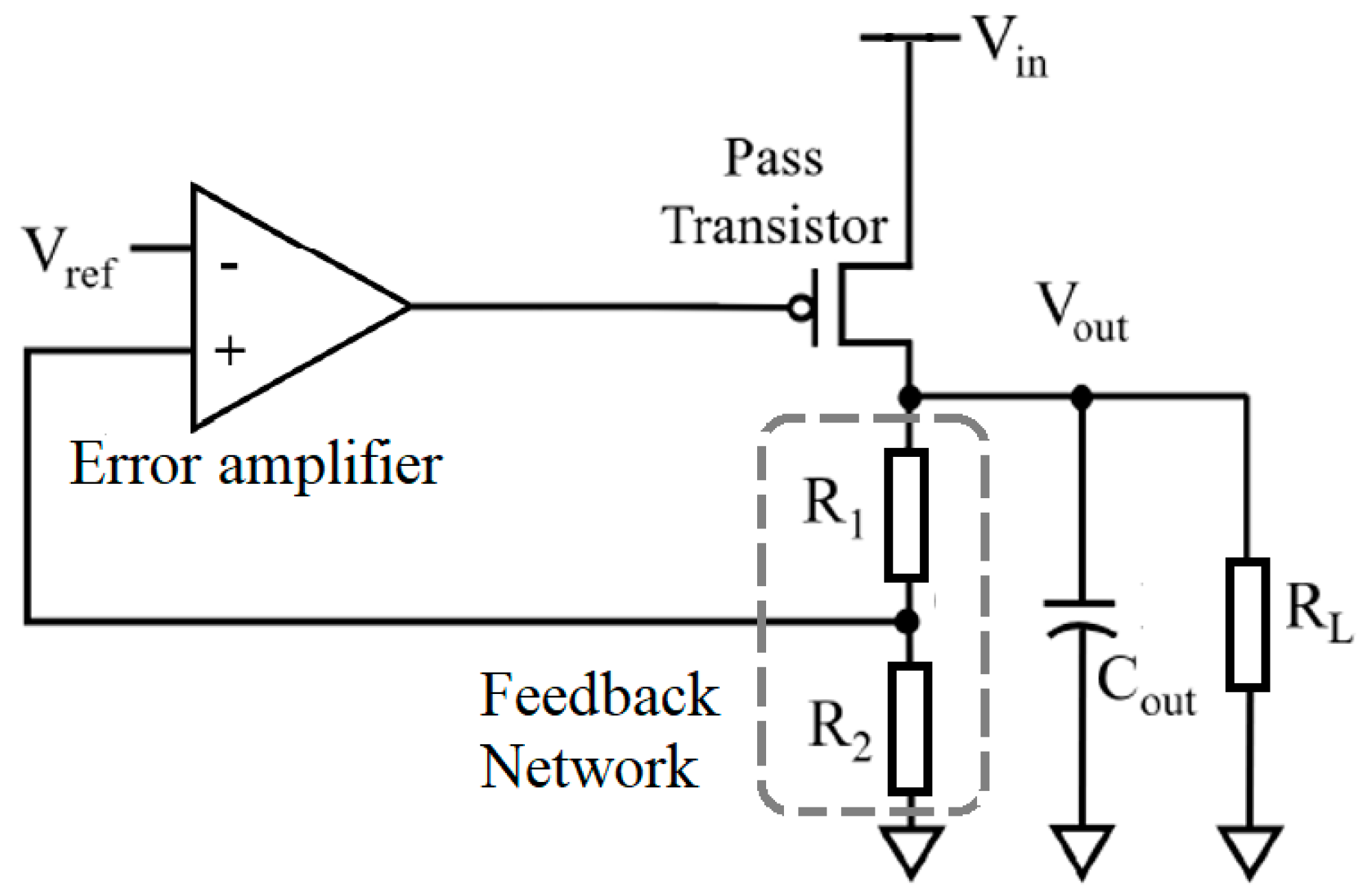
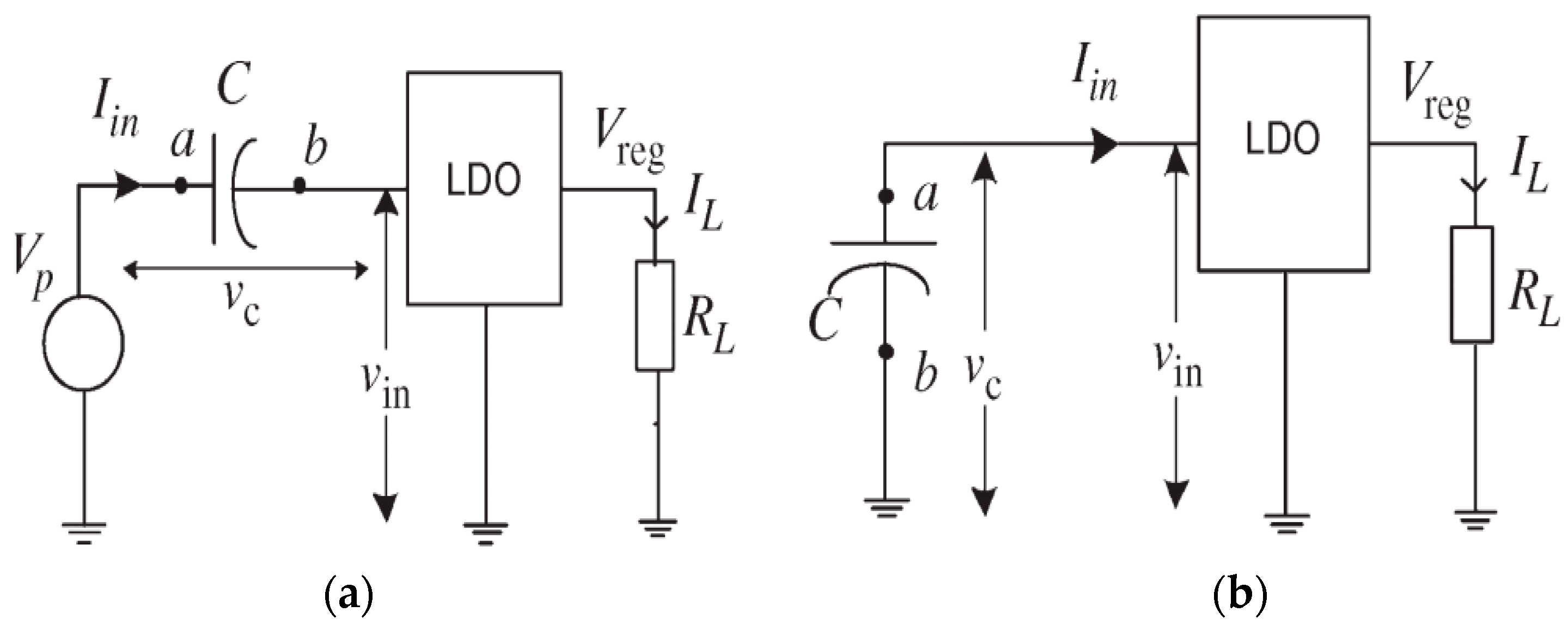
2.3. Low-Dropout (LDO) Voltage Regulator
2.4. LDO Design Parameters
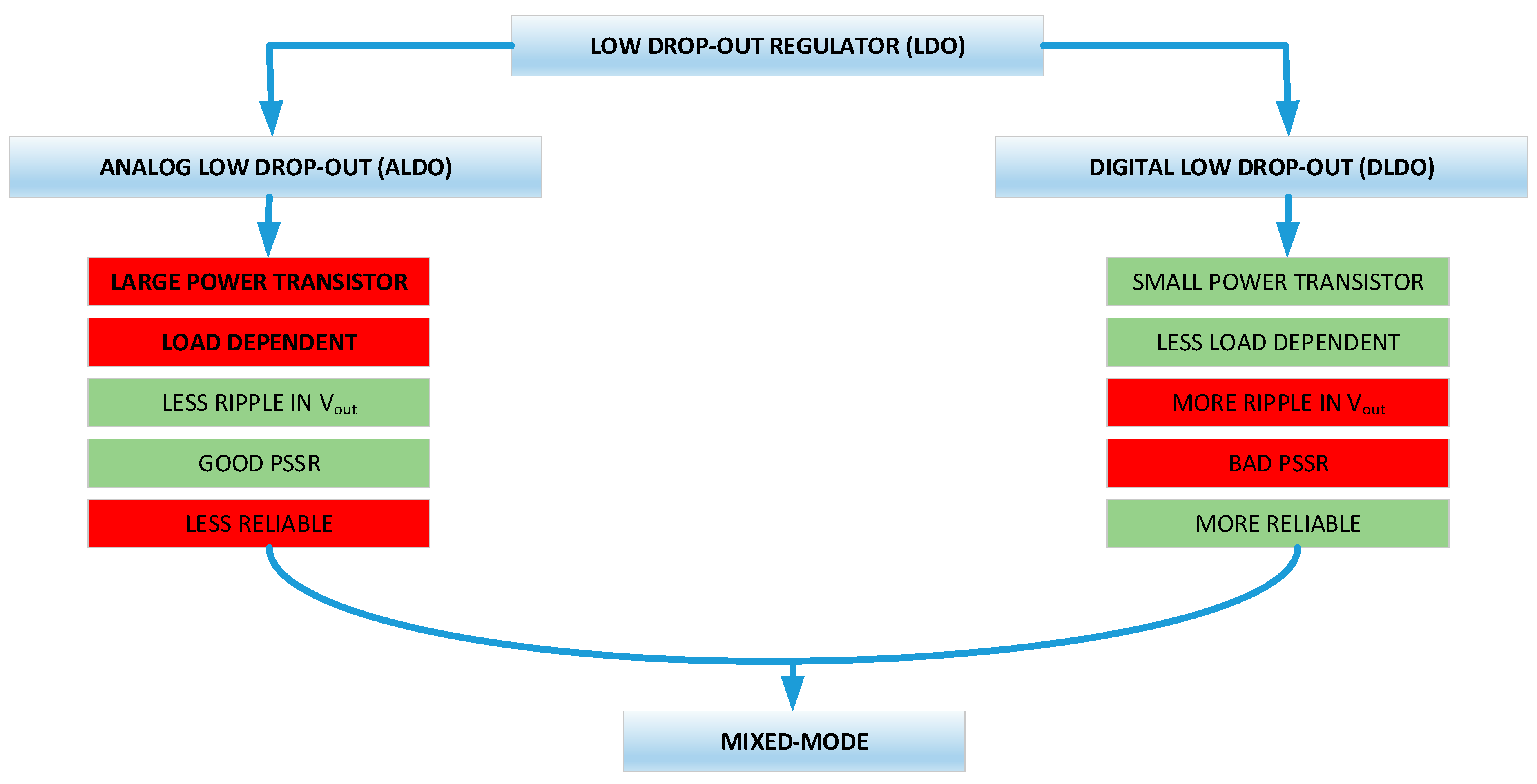
3. LDO Design Topologies
3.1. ALDO Design Topologies
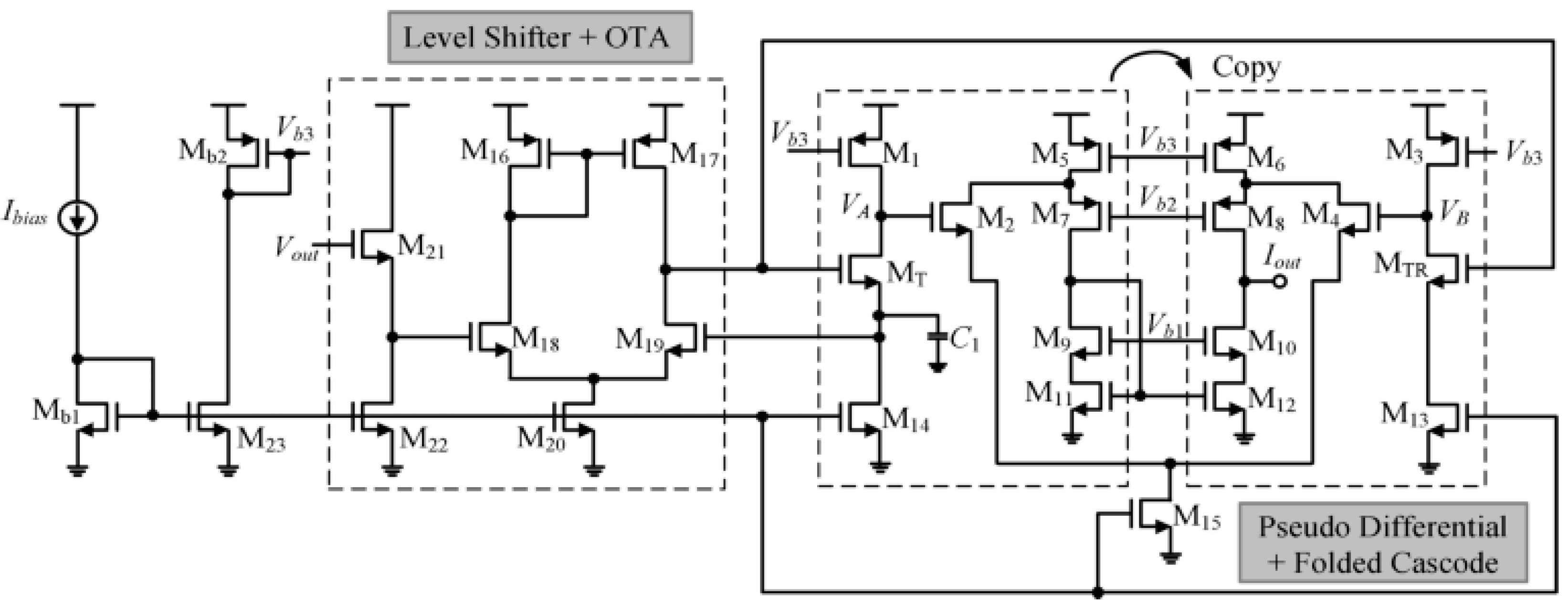
3.1.1. Folded Compensation Cascode Topology
3.1.2. Buffer Impedance Attenuation Topology
3.1.3. Current Steering—Fast Transient LDO
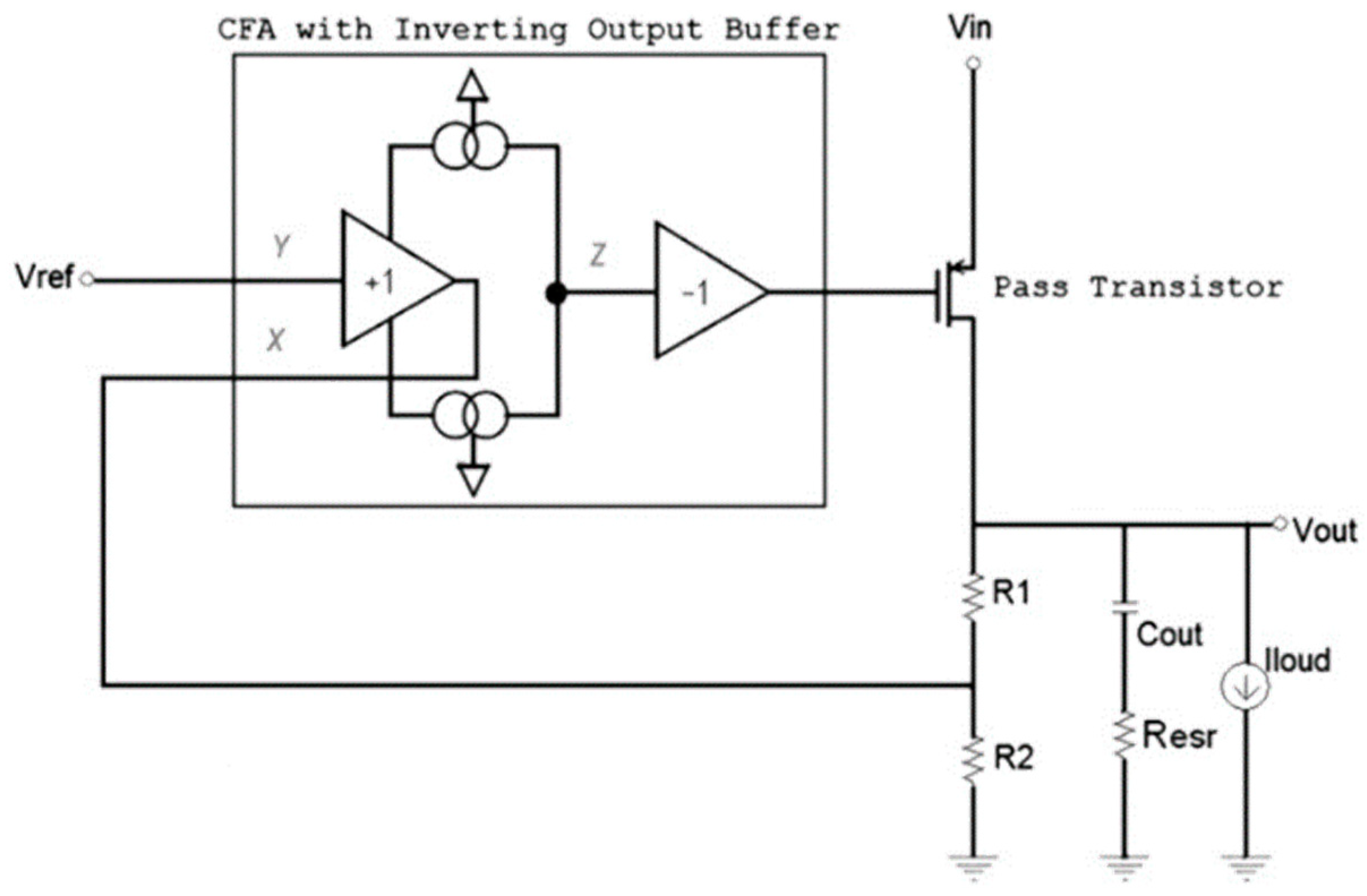
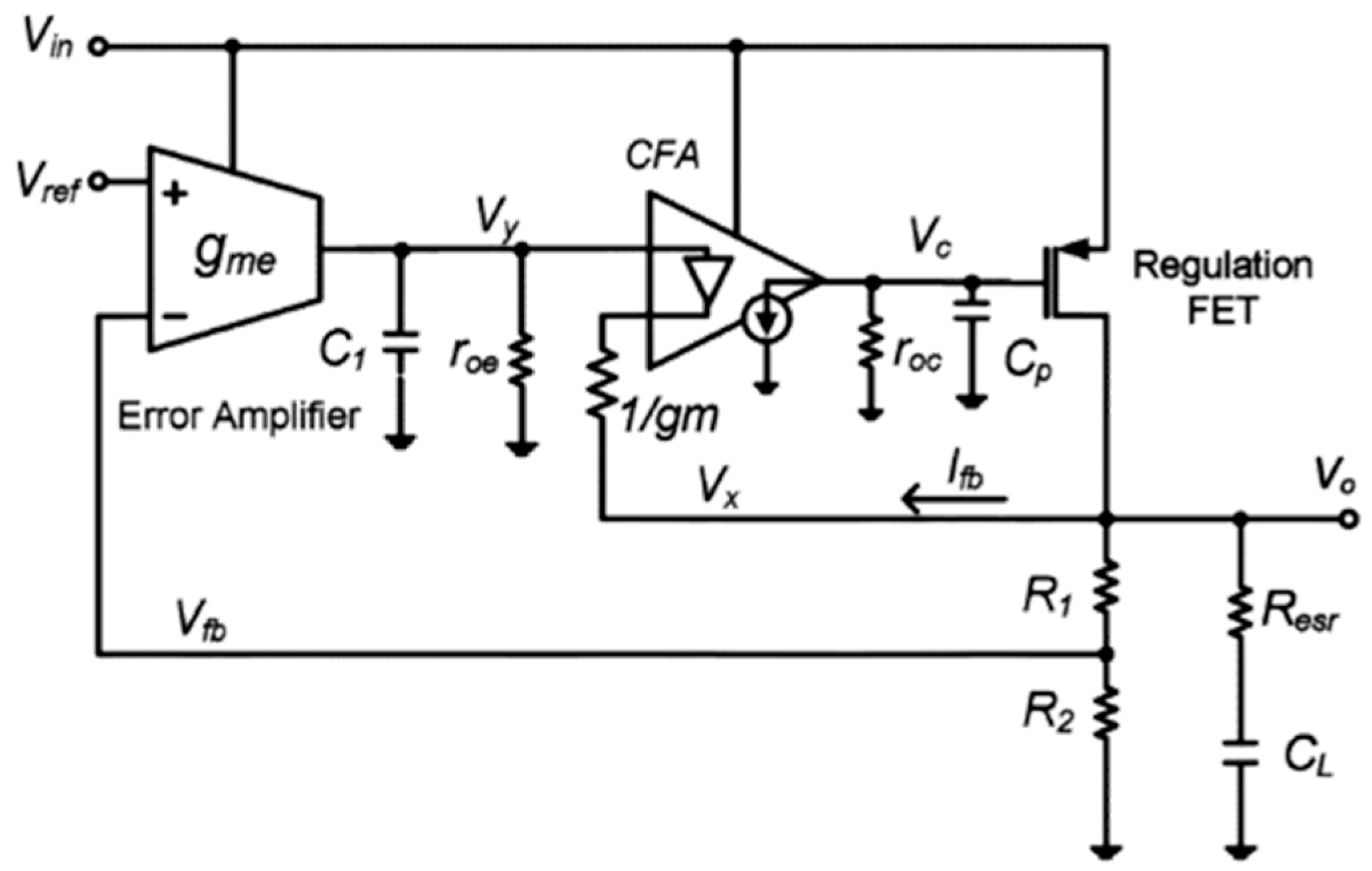
3.1.4. Current-Mode Feedback Buffer Amplifier-Based LDO
3.1.5. High-Speed Compact Output Driver-Based LDO
3.1.6. Supercapacitor Assisted LDO
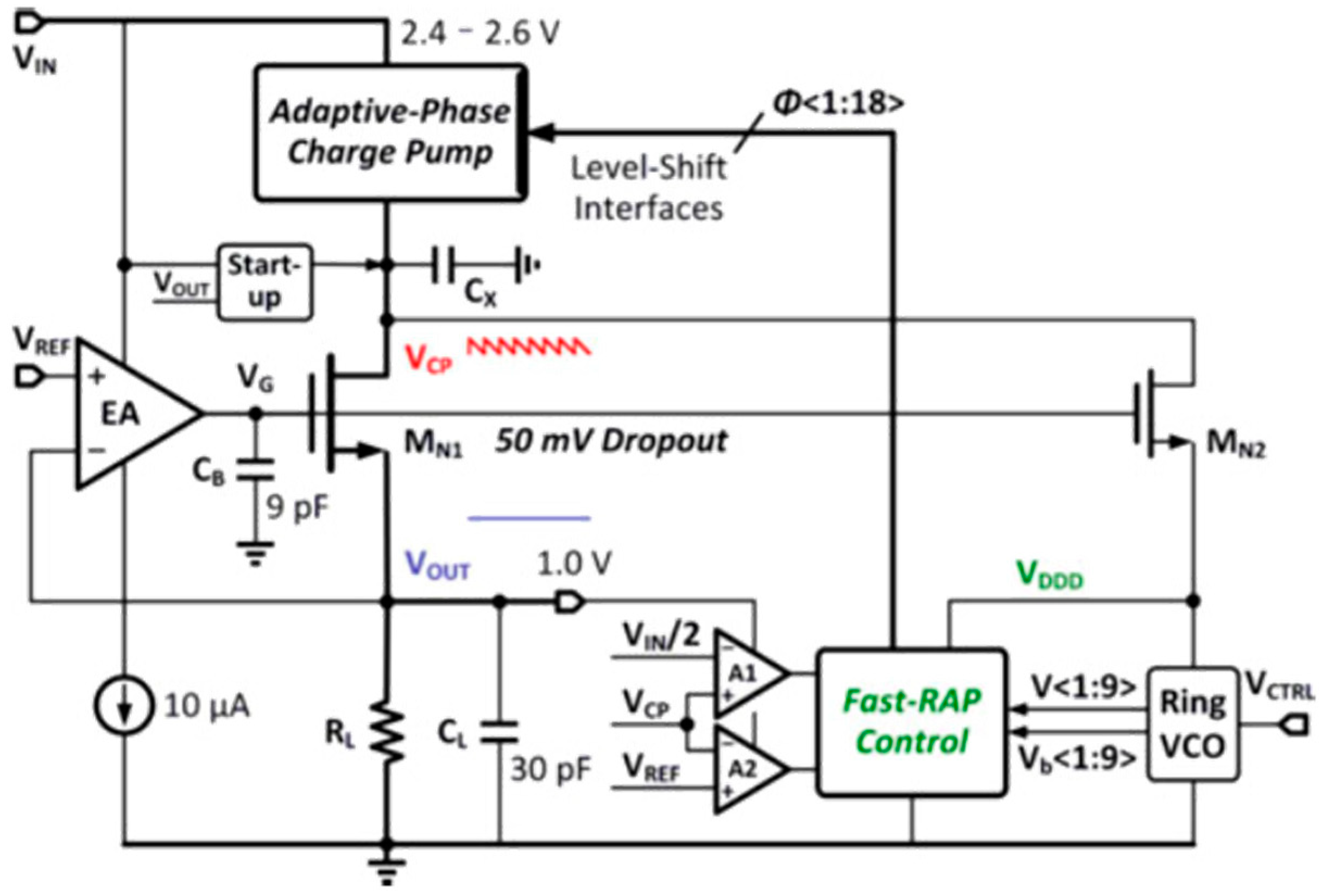
3.1.7. Fast-Response Adaptive-Phase LDO
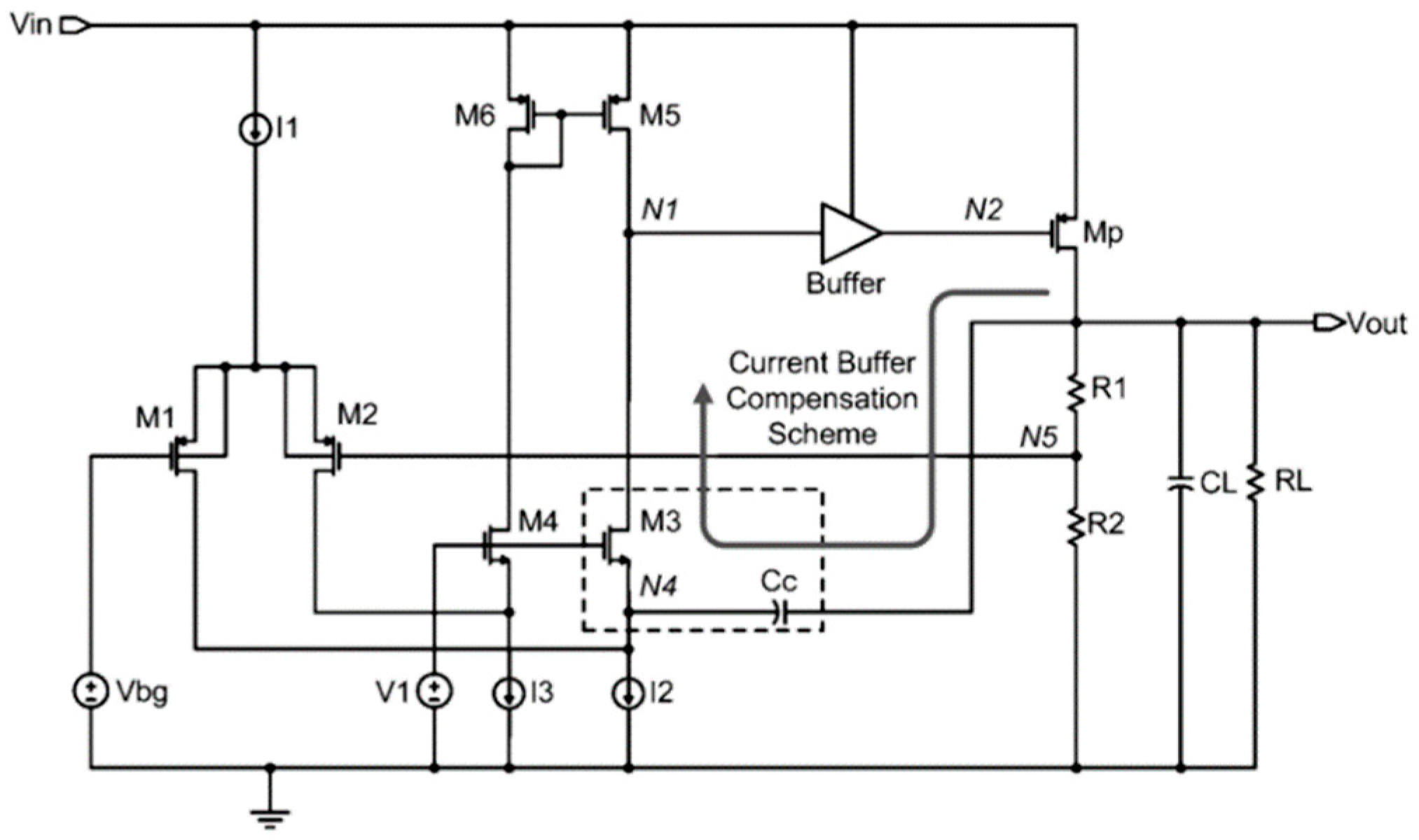
3.1.8. Feedforward Compensated High-Voltage Linear Regulator LDO
3.1.9. High Power Supply Rejection Linear Regulator LDO
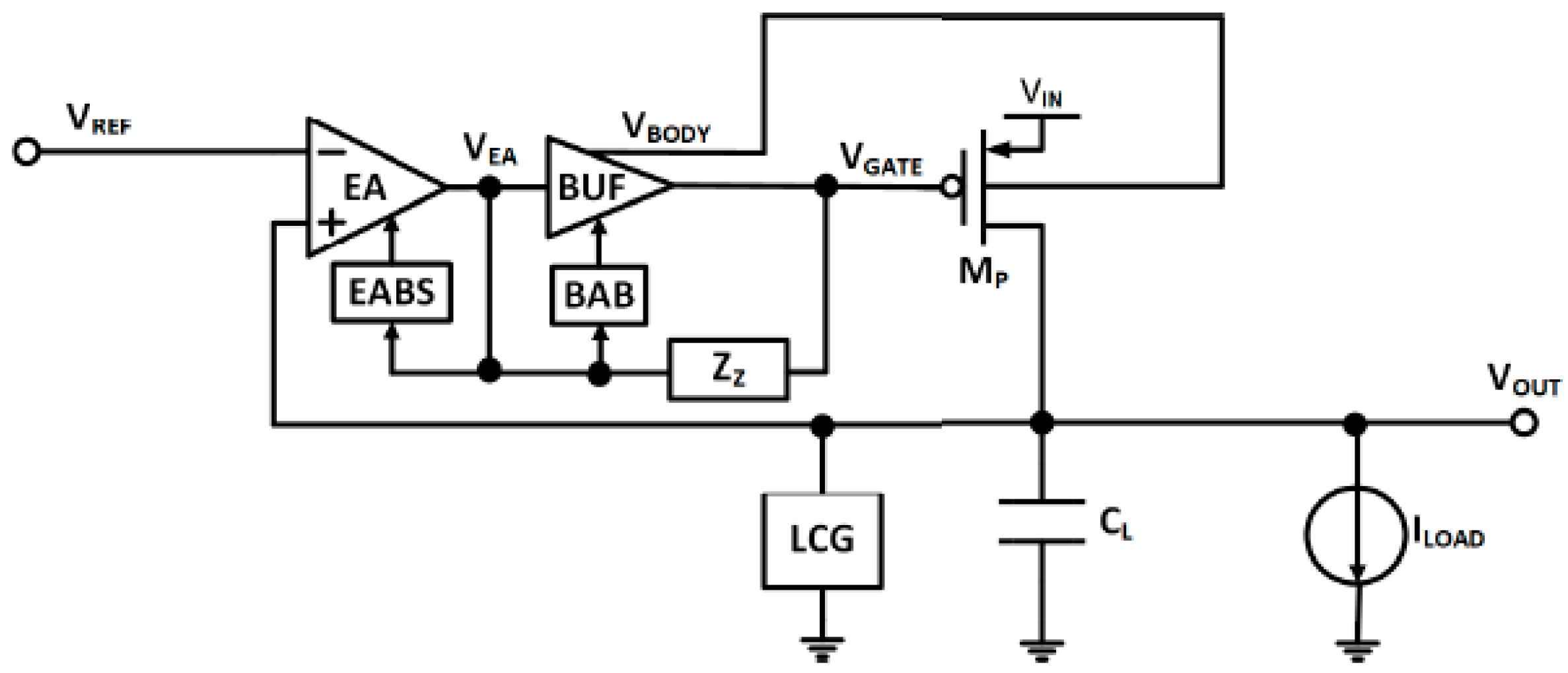
3.1.10. Concurrent Bulk Modulation and Forward Body Bias
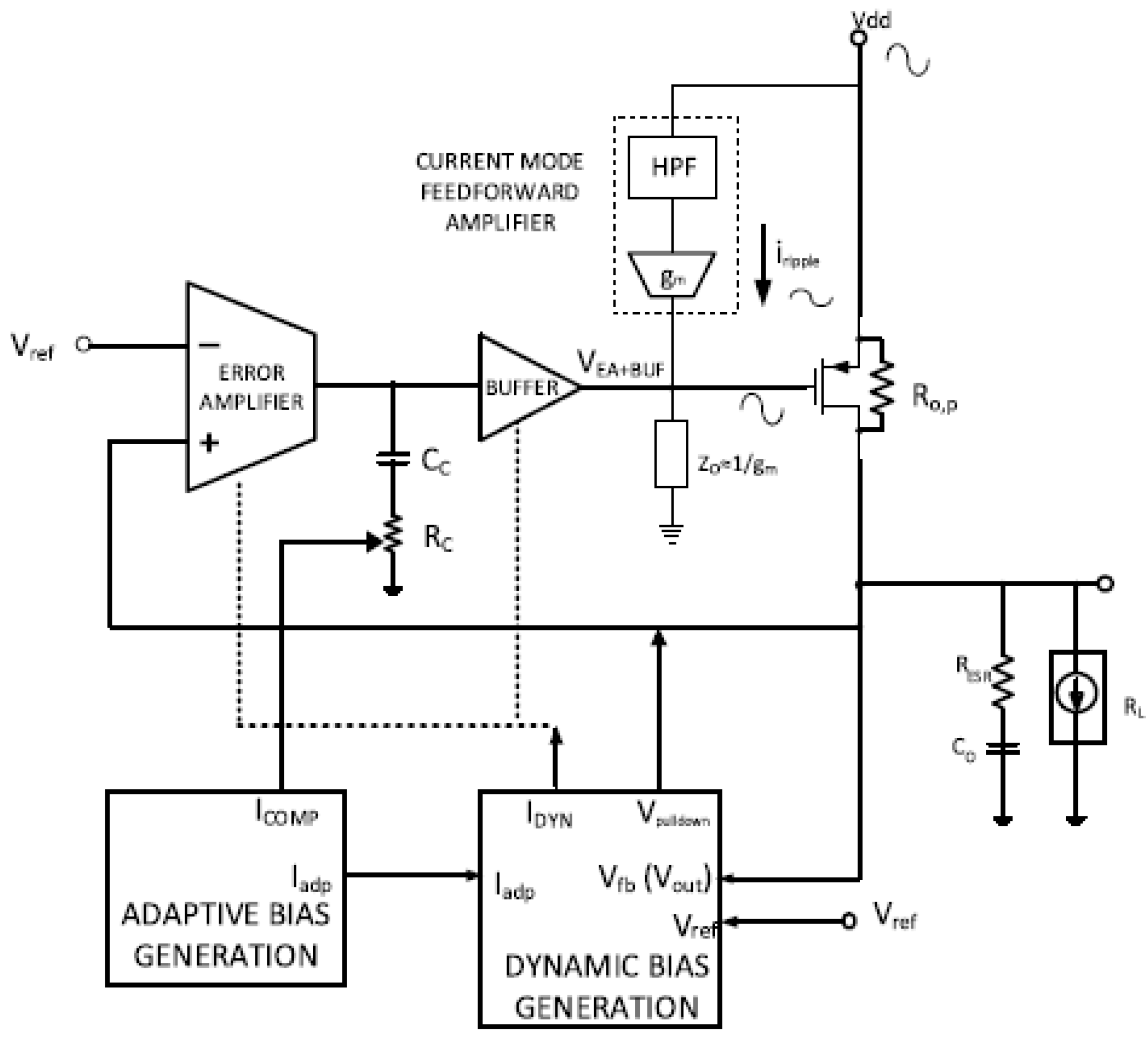
3.1.11. Current-Mode Feedforward Ripple Canceller
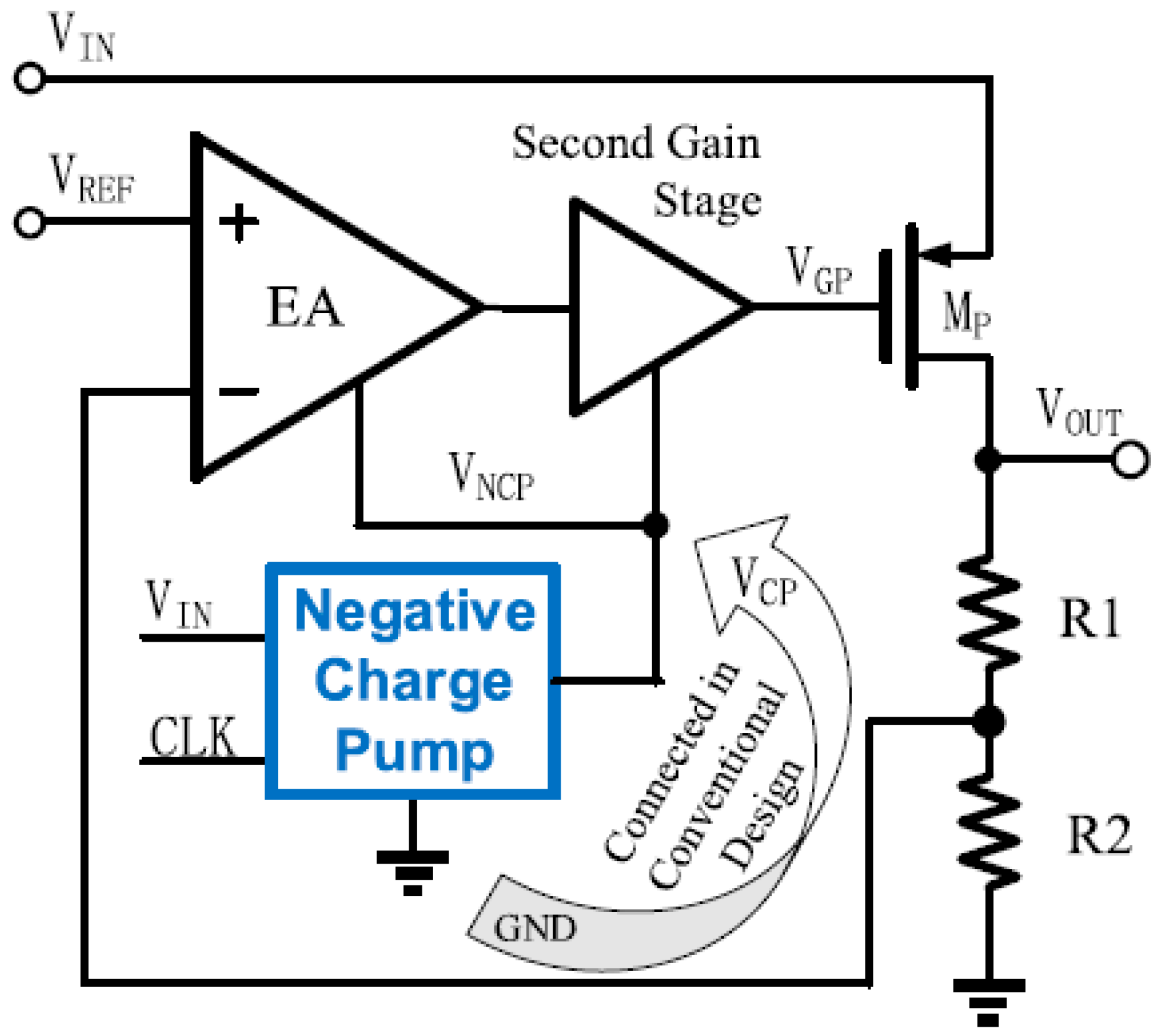
3.1.12. Negative Charge Pump-Enhanced (NCPE) LDO
3.1.13. Low-VDD Inverting Buffer with Efficient Feedforward Path
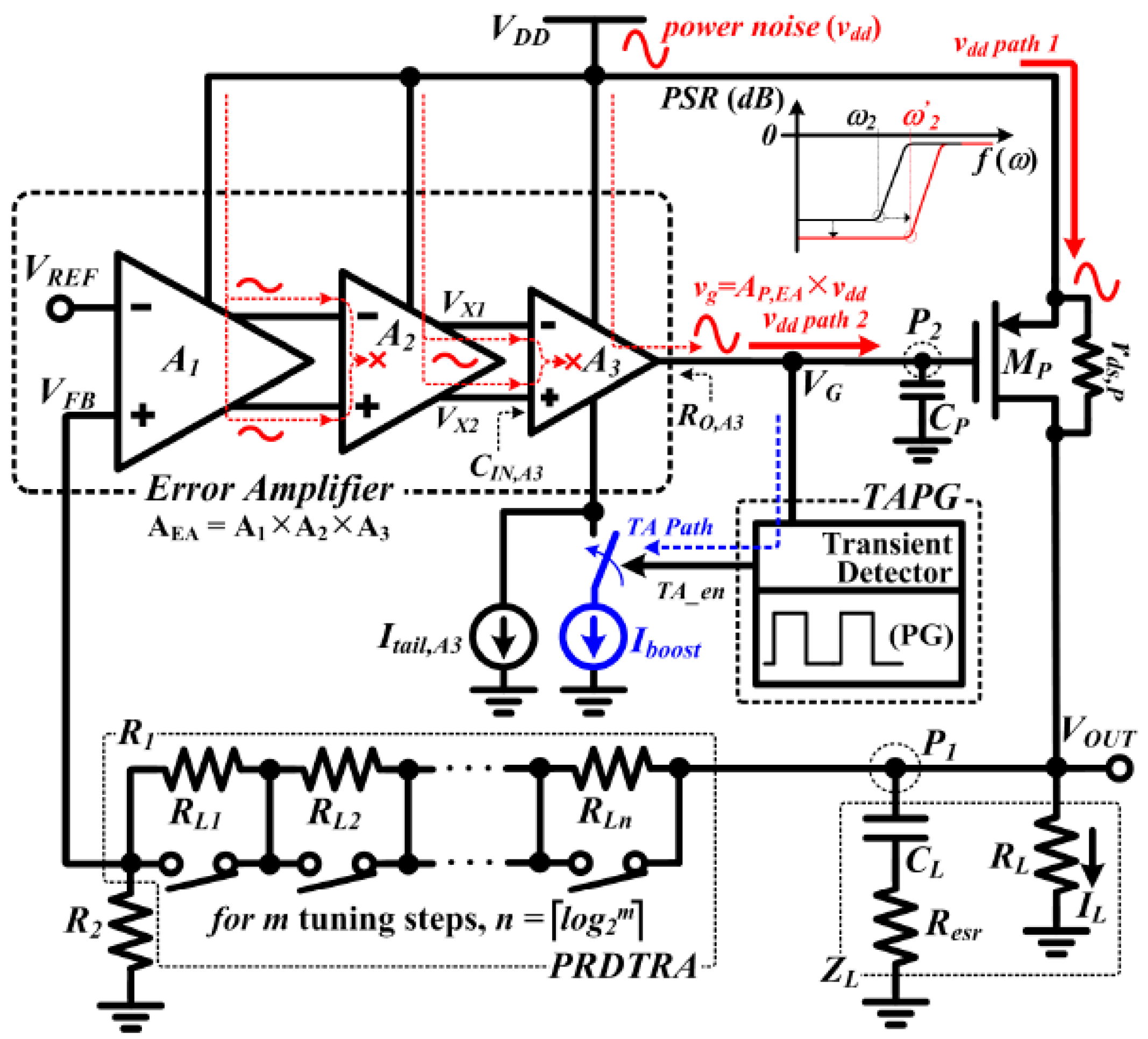
3.1.14. Multistage Error Amplifier and PRDTRA-Based LDO
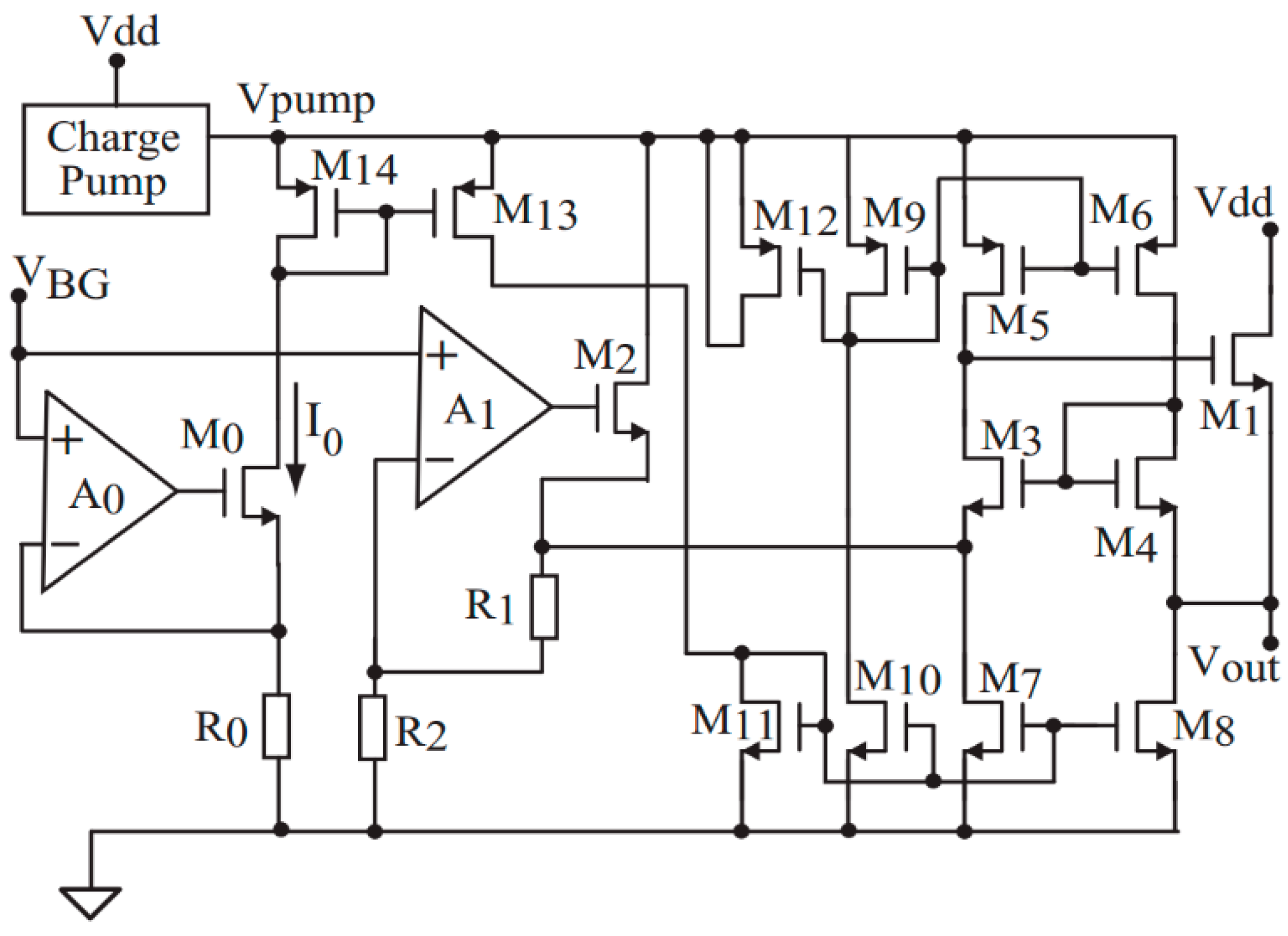
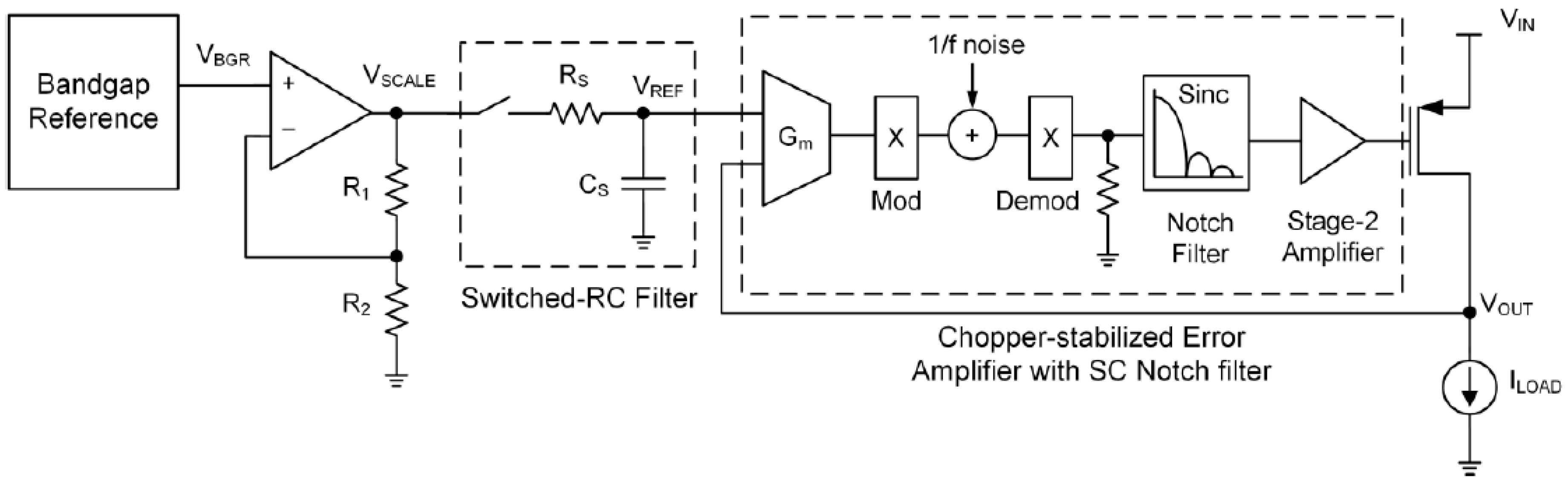
3.1.15. Switched RC Bandgap Reference LDO
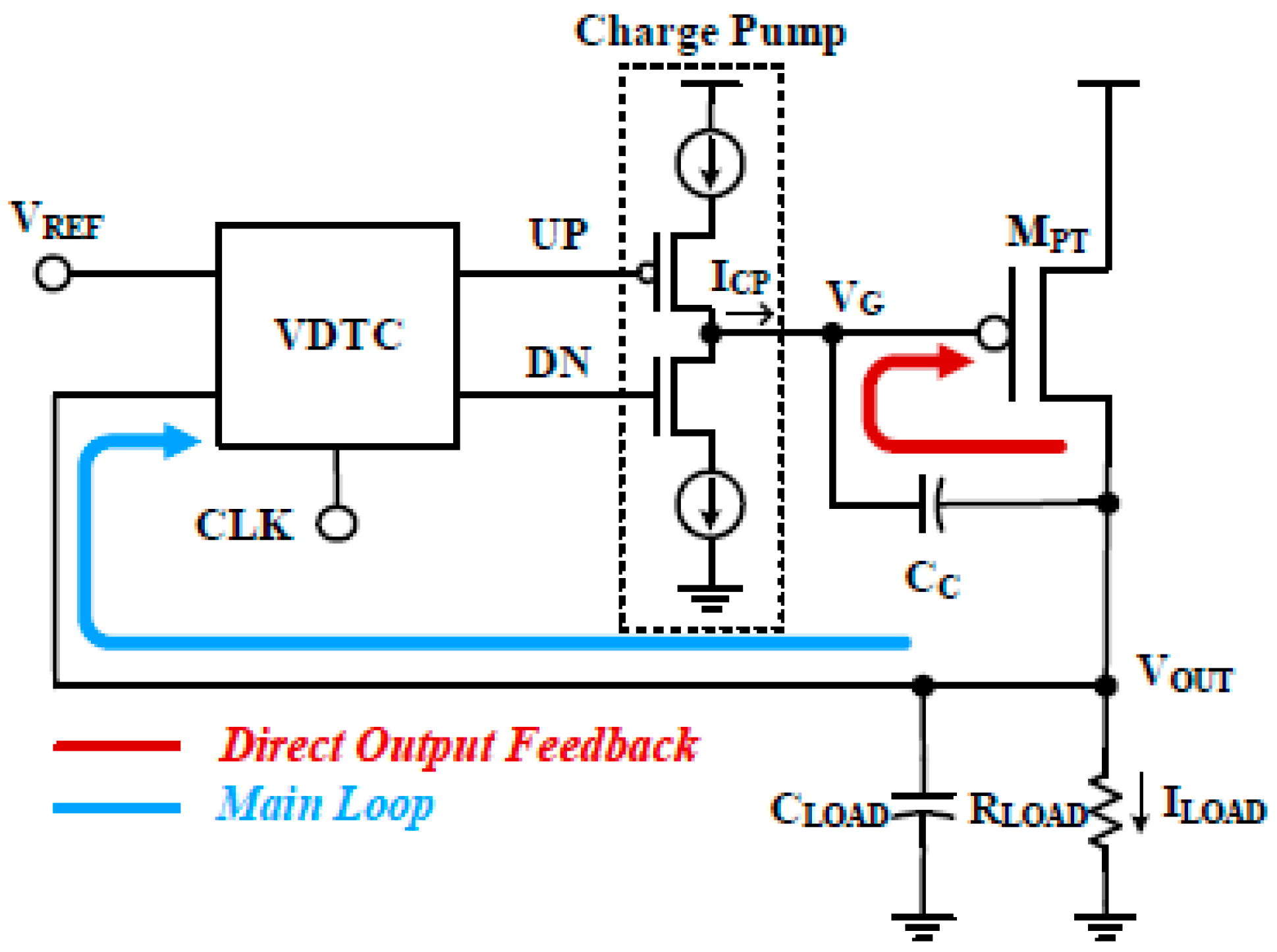
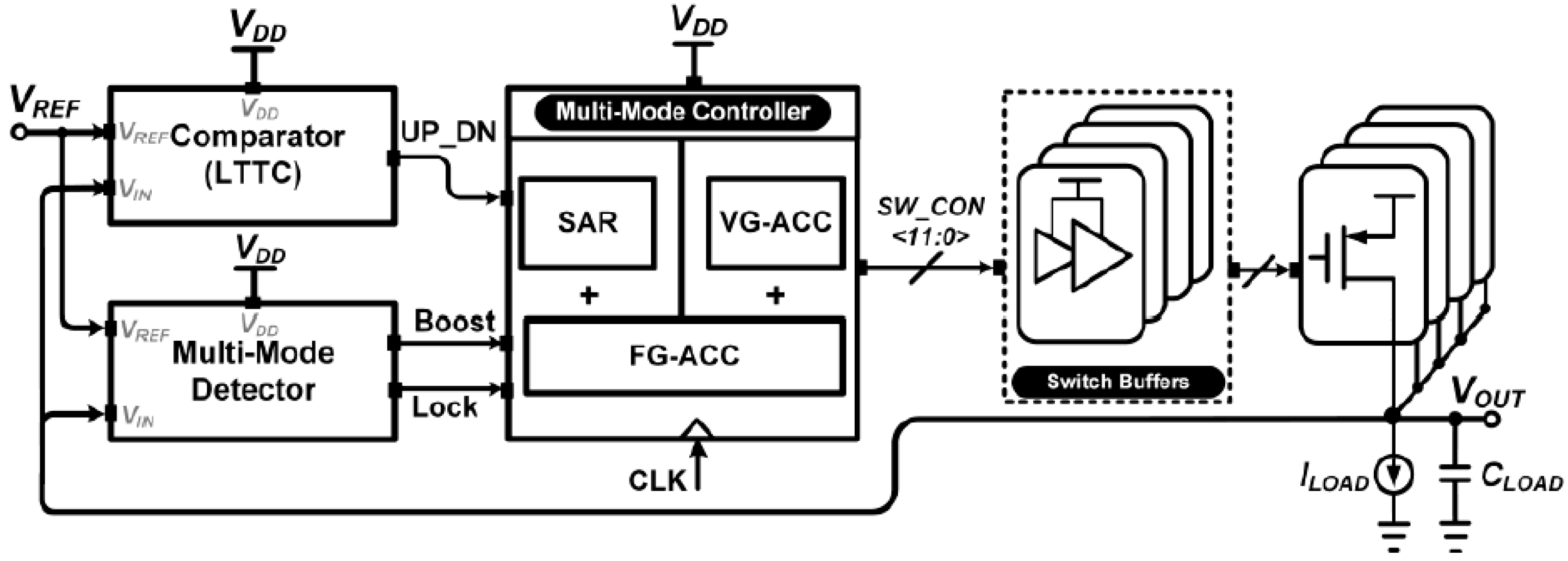
3.1.16. Voltage Difference to Time Converter with Direct Output Feedback
3.1.17. Performance Comparison of ALDO
3.2. DLDO Design Topologies
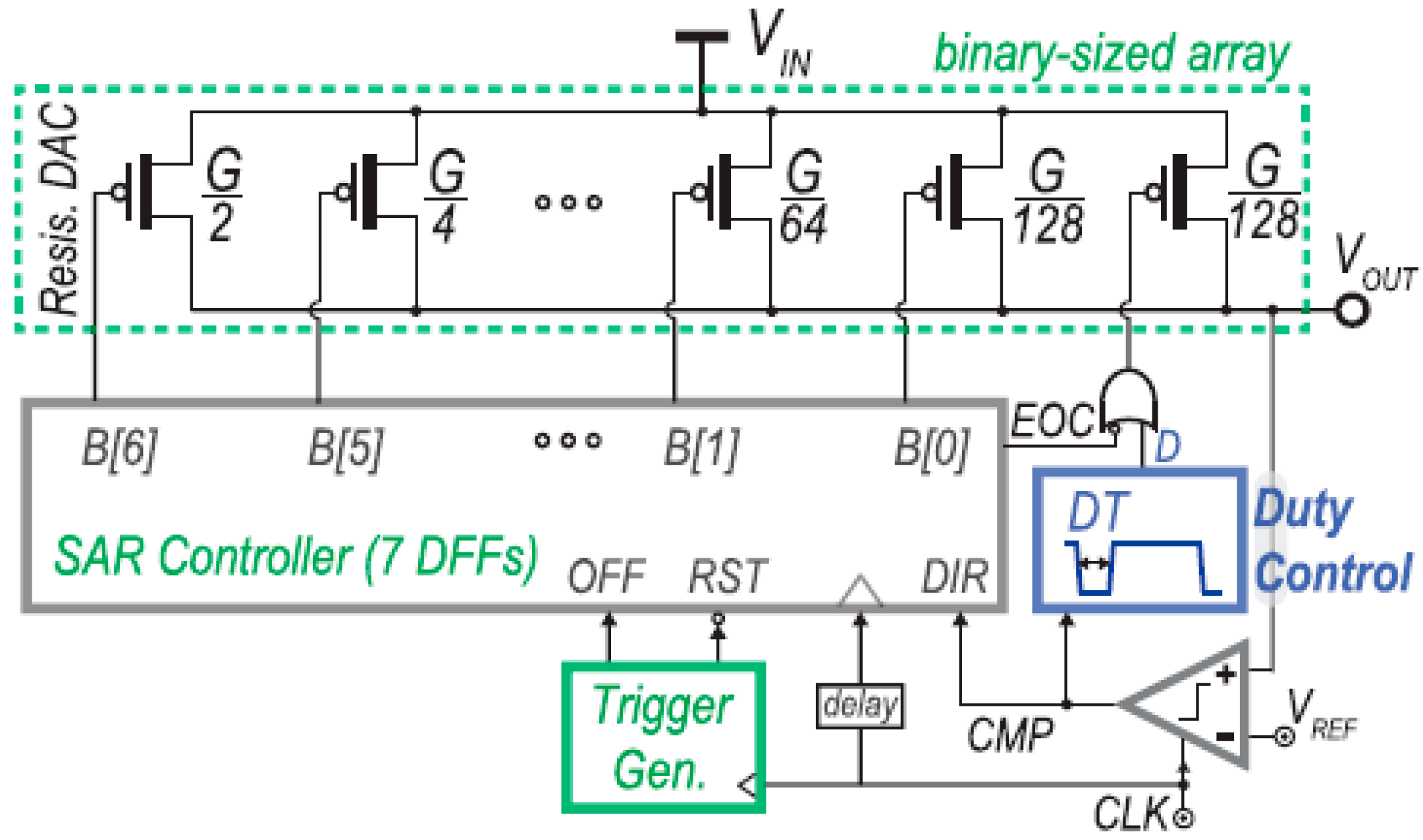
3.2.1. Proportional Derivative (PD) Compensation and Sub-LSB Duty Control
3.2.2. Fully Standard Cell-Based Digital LDO
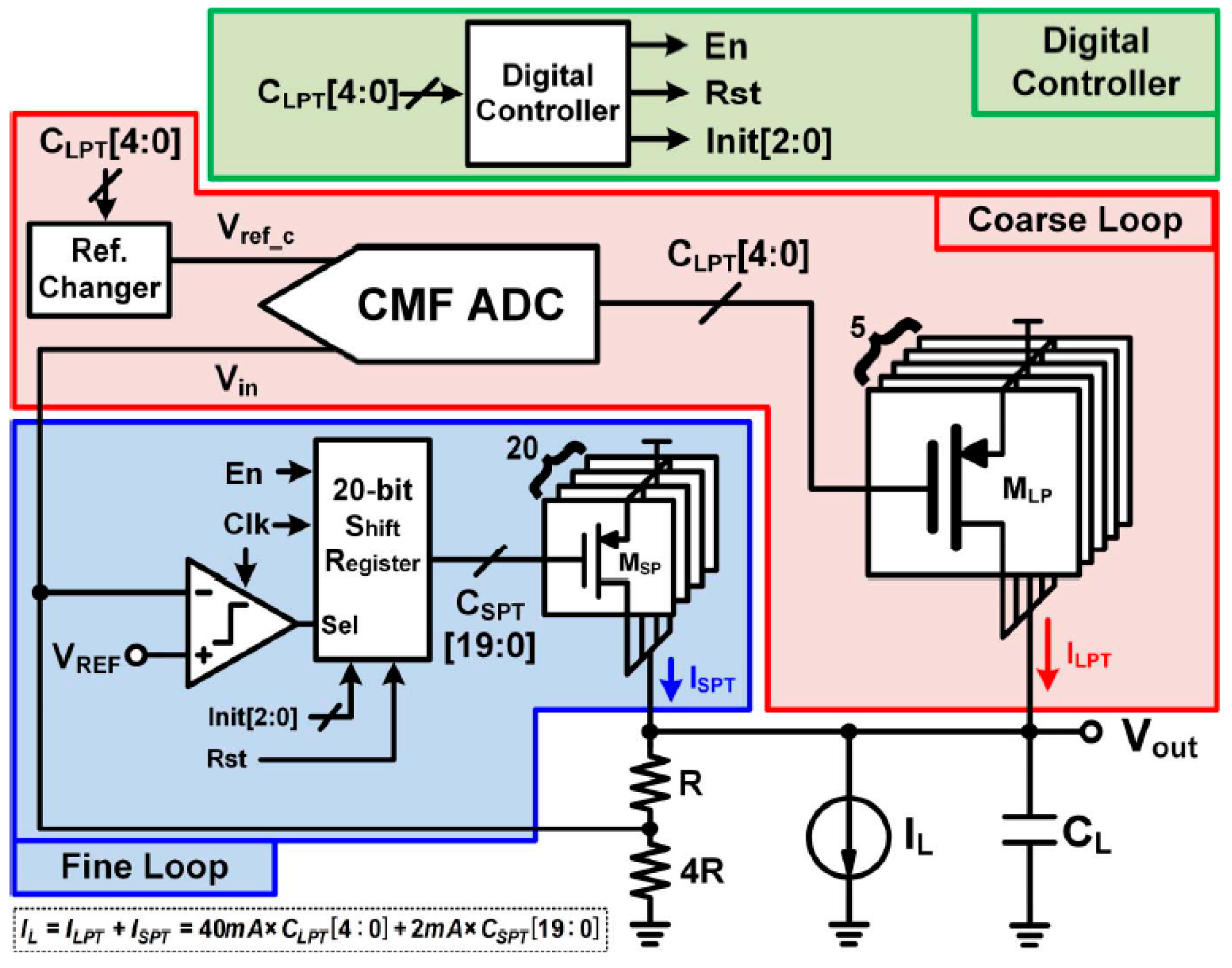
3.2.3. Coarse–Fine Dual Loop Digital LDO
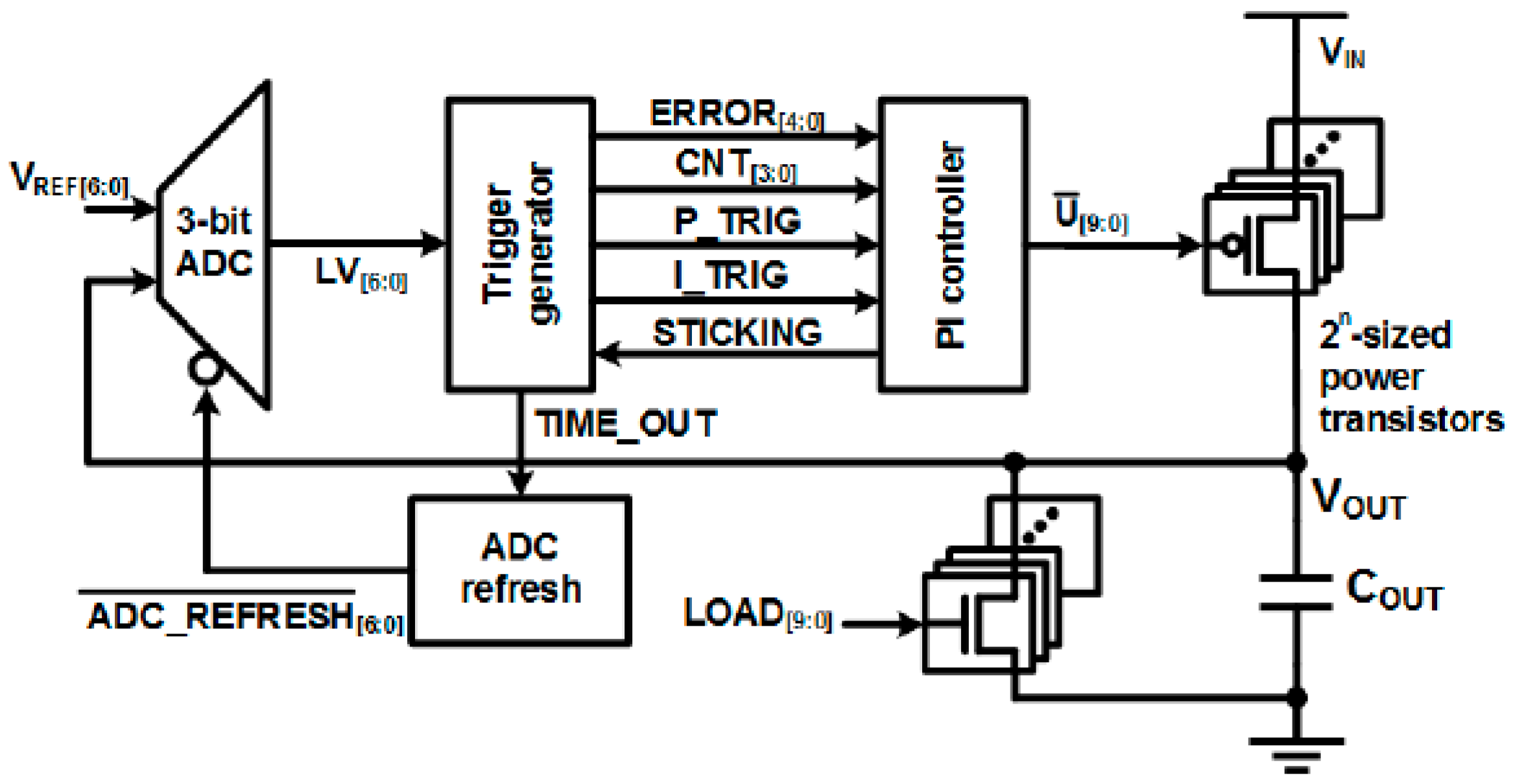
3.2.4. Event-Driven Explicit Time-Coding Architecture-Based DLDO
3.2.5. Beat-Frequency Quantizer and VCO-Based DLDO
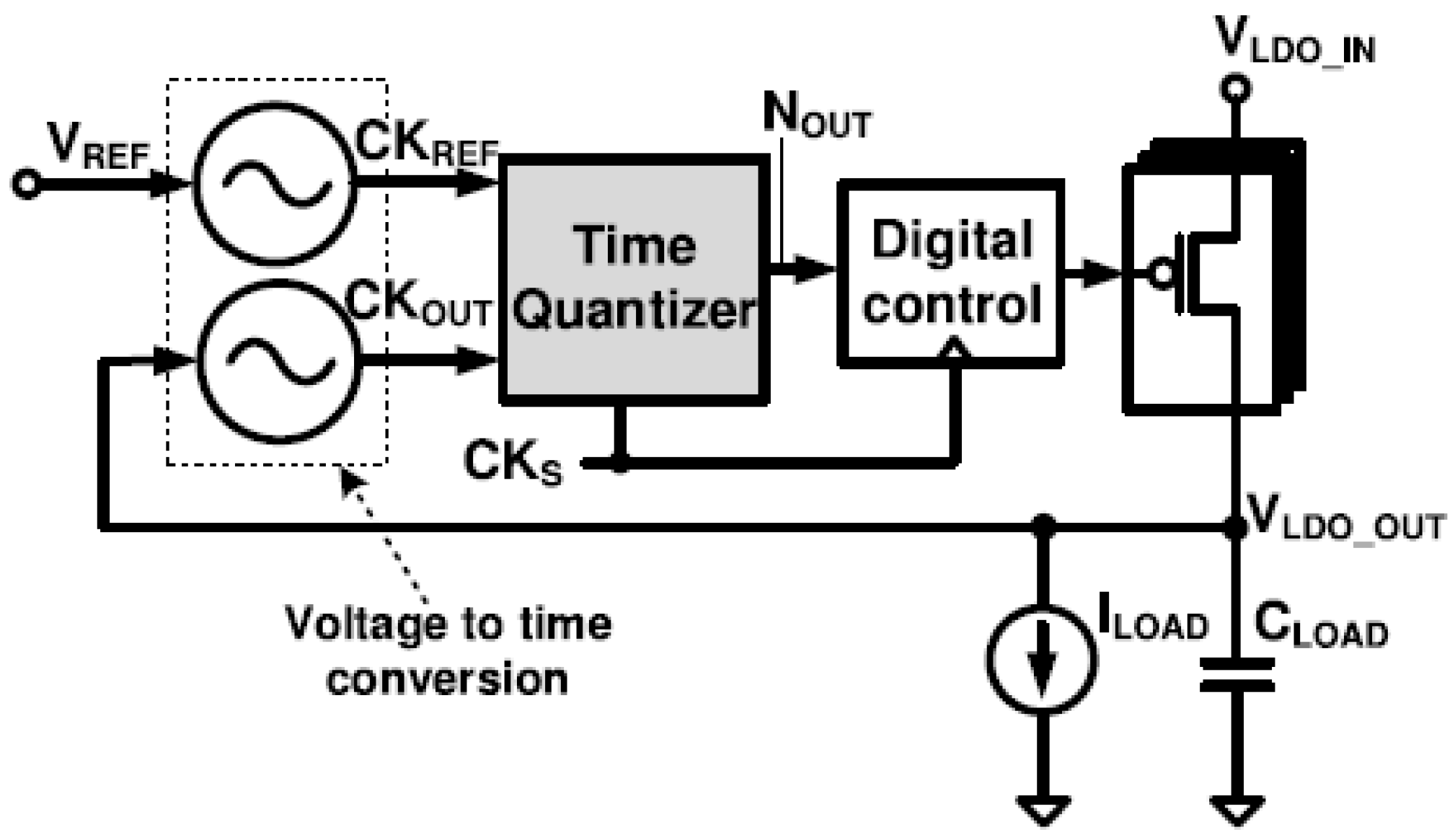
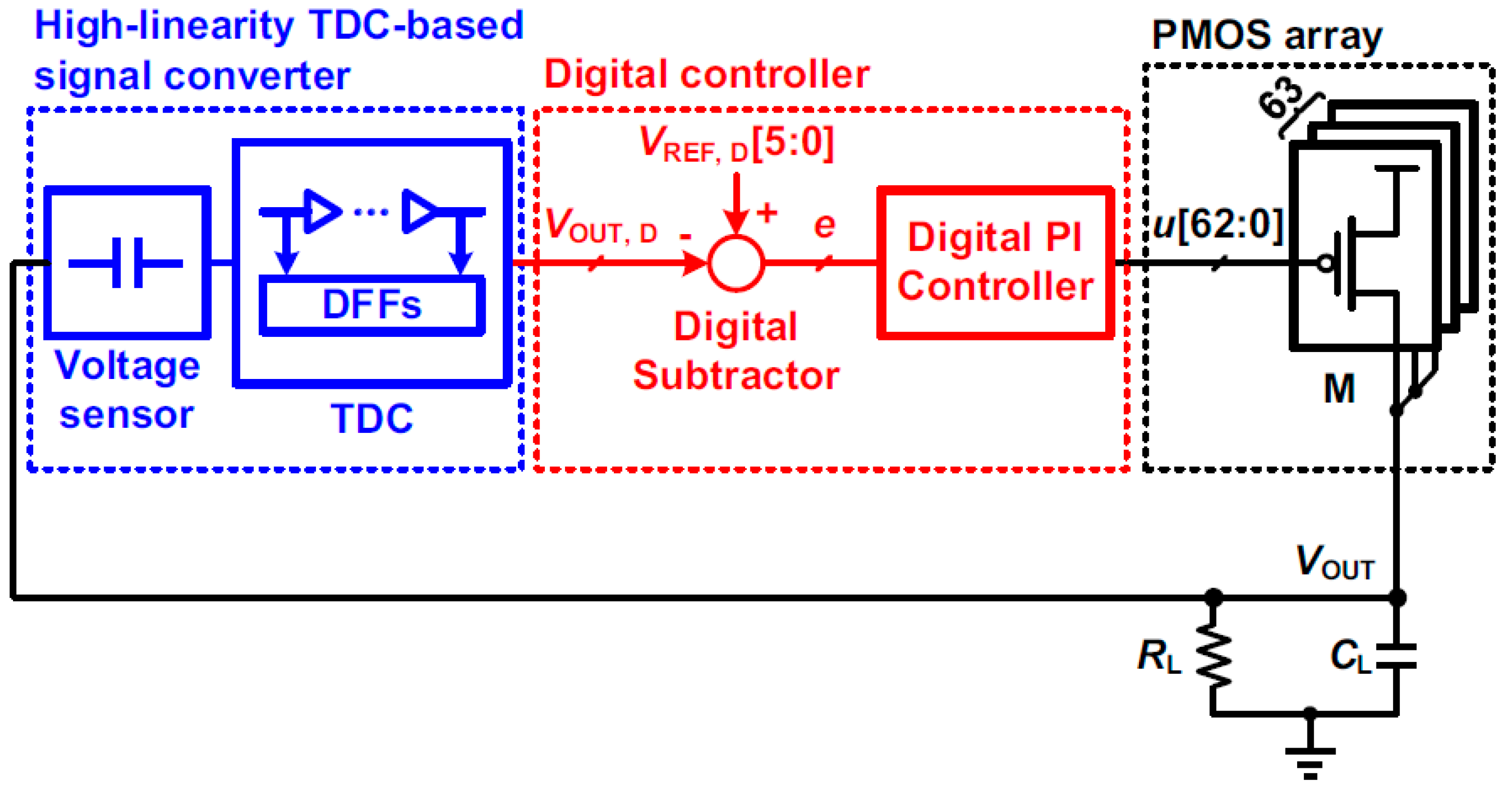
3.2.6. Time-to-Digital Converter (TDC)-Based DLDO
3.2.7. Performance Comparison of DLDO
3.3. HD-LDO Design Topologies
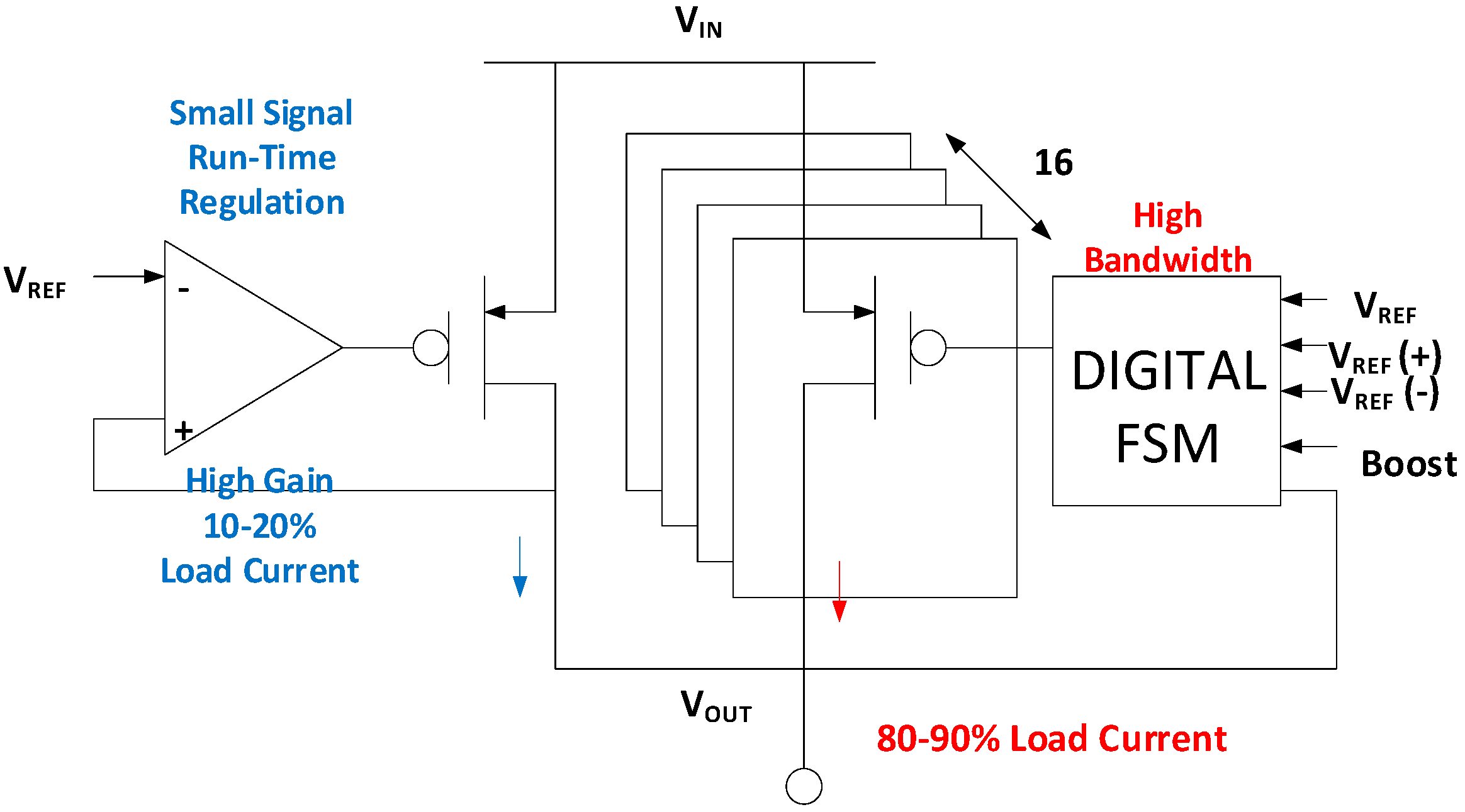
3.3.1. Scan Reconfigurable Hybrid LDO
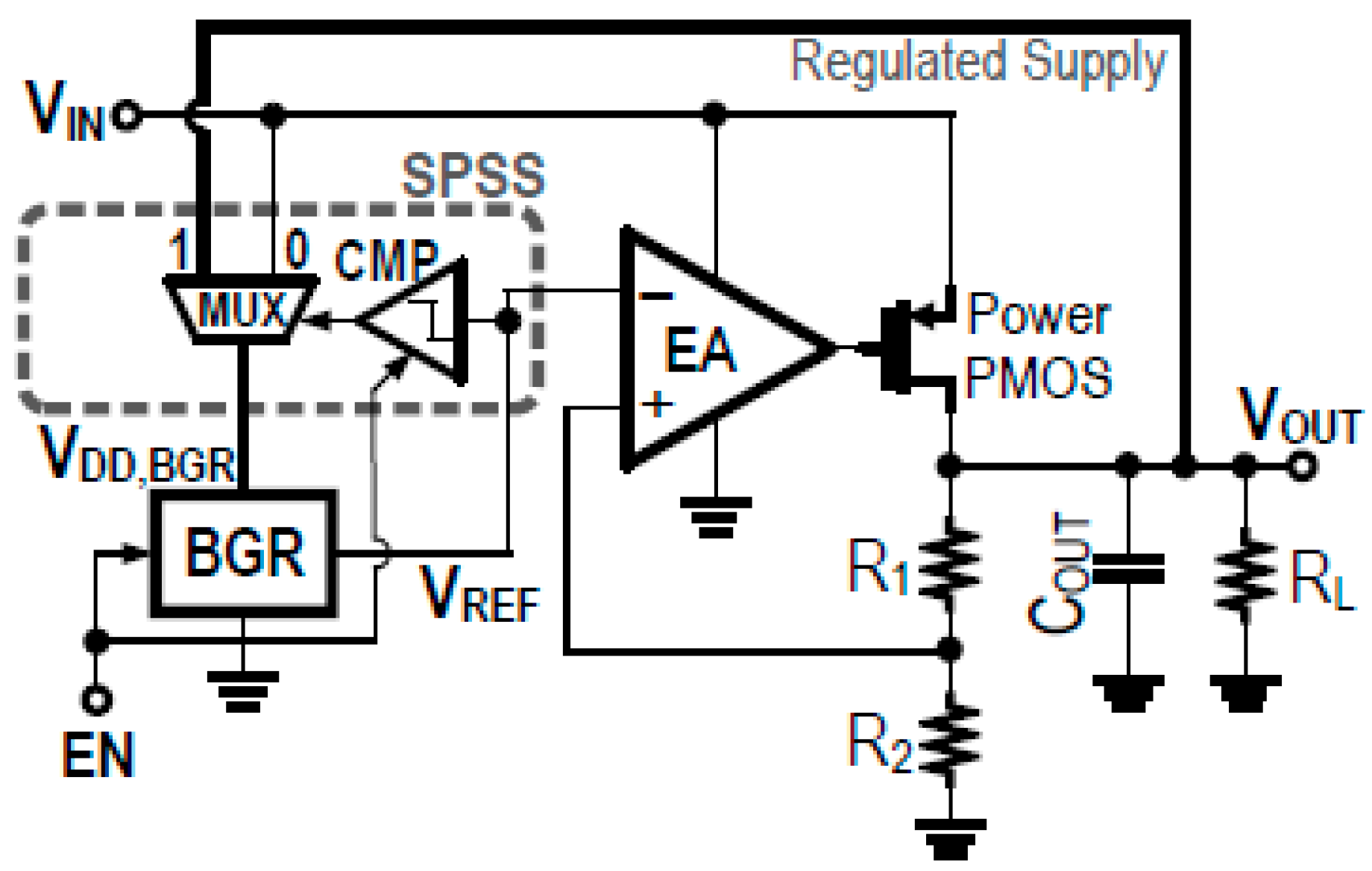
3.3.2. Bandgap Reference-Based Hybrid LDO
3.3.3. Active Ripple Suppression-Based HD-LDO
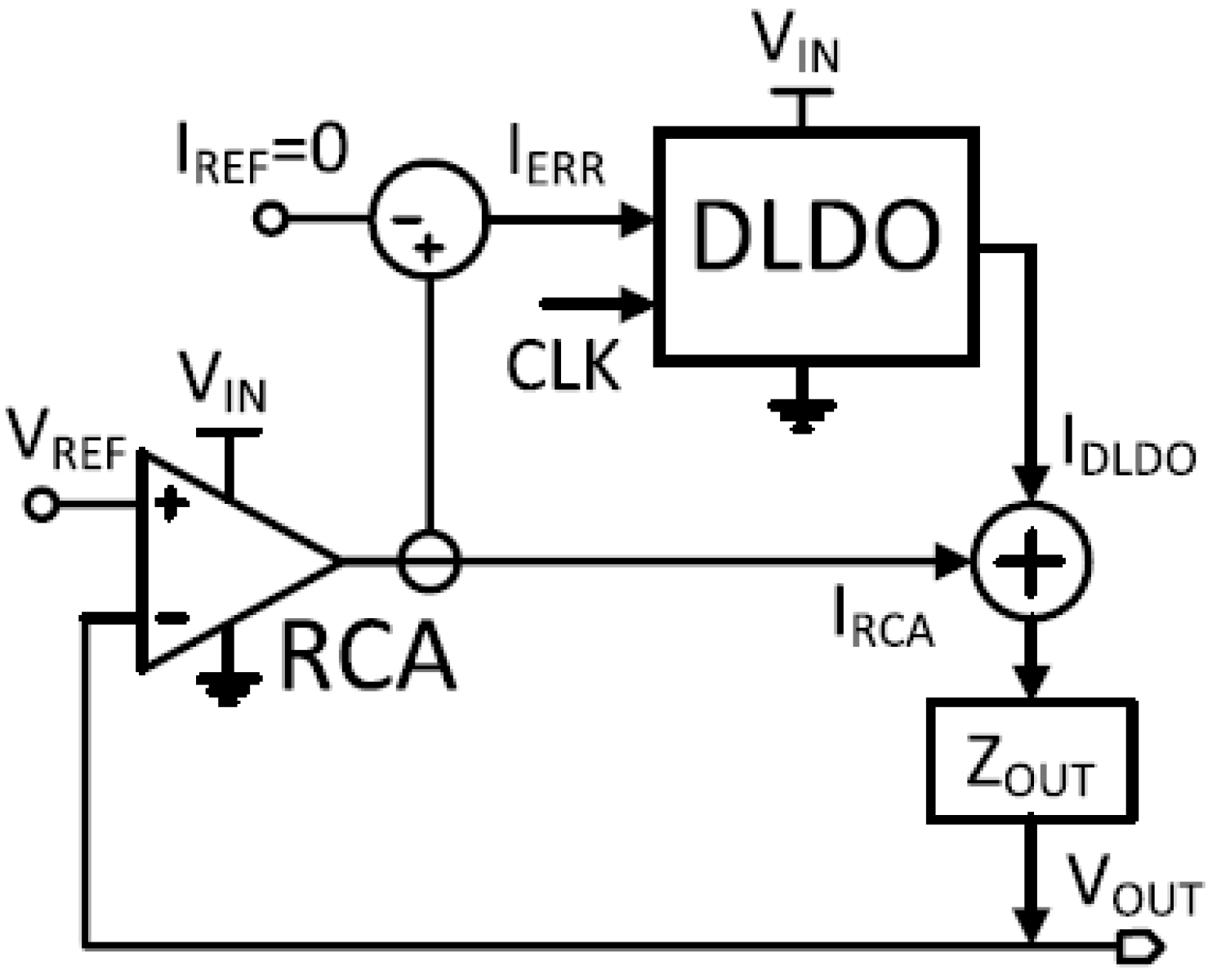
3.3.4. Switched-Mode-Control-Based Hybrid LDO
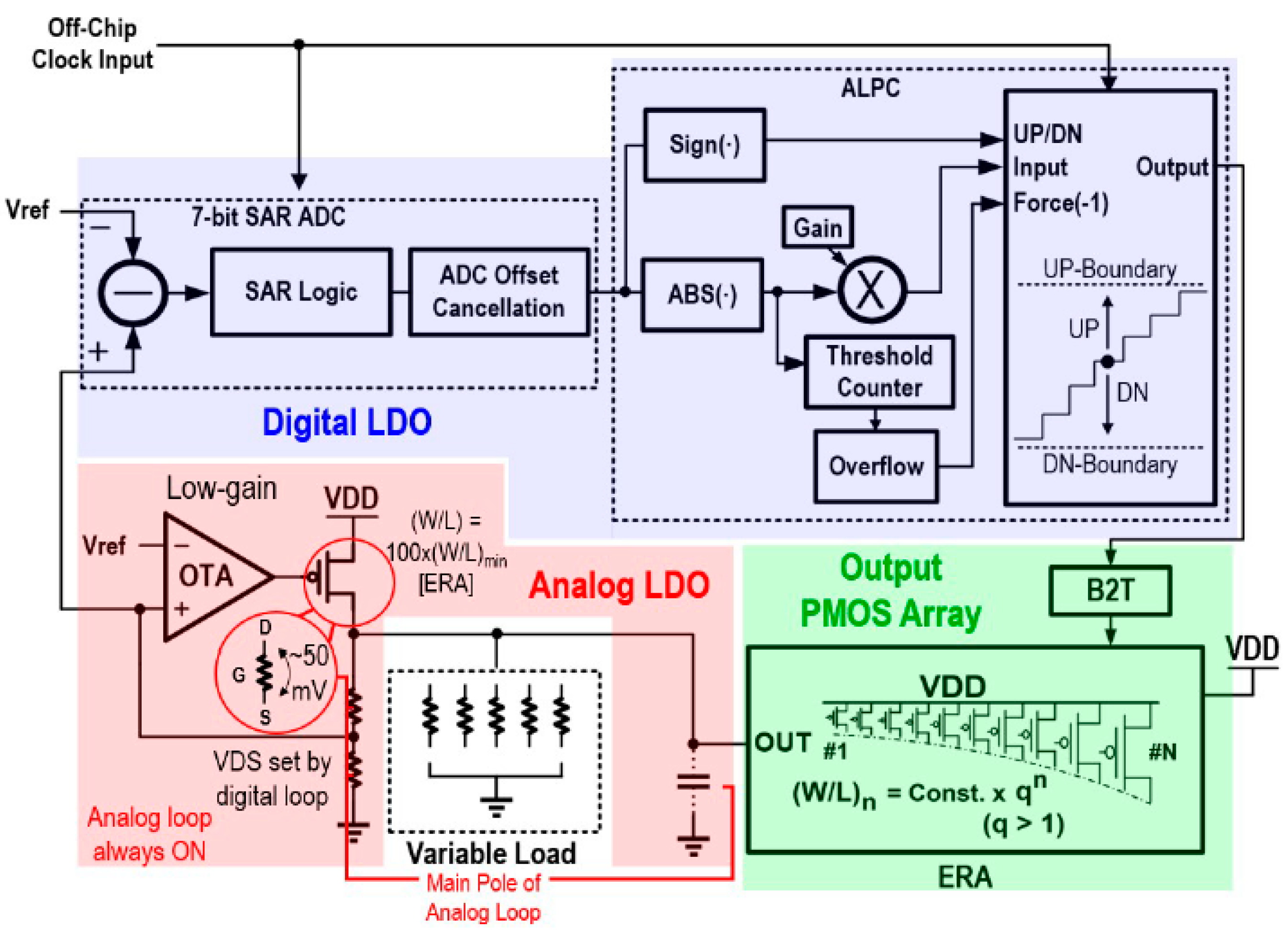
3.3.5. Exponential-Ratio Array (ERA)-Based Hybrid LDO
3.3.6. Performance Comparison of HD-LDO
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Badal, T.I.; Reaz, M.B.I.; Bhuiyan, M.A.S.; Kamal, N. CMOS Transmitters for 2.4-GHz RF Devices: Design Architectures of the 2.4-GHz CMOS Transmitter for RF Devices. IEEE Microw. Mag. 2019, 20, 38–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuiyan, M.A.S.; Badal, M.T.I.; Reaz, M.B.I.; Crespo, M.L.; Cicuttin, A. Design Architectures of the CMOS Power Amplifier for 2.4 GHz ISM Band Applications: An Overview. Electronics 2019, 8, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badal, M.T.I.; Reaz, M.B.I.; Jalil, Z.; Bhuiyan, M.A.S. Low power high-efficiency shift register using implicit pulse-triggered flip-flop in 130 nm CMOS process for a cryptographic RFID tag. Electronics 2016, 5, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folla, J.K.; Wembe, E.T.; Essimbi, B.Z.; Crespo, M.L.; Cicuttin, A.; Reaz, M.B.I.; Bhuiyan, M.A.S. An 8.72 µW low-noise and wide bandwidth FEE design for high-throughput pixel-strip (PS) sensors. Sensors 2021, 21, 1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folla, J.K.; Crespo, M.L.; Wembe, E.T.; Bhuiyan, M.A.S.; Cicuttin, A.; Essimbi, B.Z.; Reaz, M.B.I. A low-offset low-power and high-speed dynamic latch comparator with a preamplifier-enhanced stage. IET Circuits Devices Syst. 2021, 15, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuiyan, M.A.S.; Reaz, M.B.I.; Jalil, J.; Rahman, L.F.; Chang, T.G. A compact transmit/receive switch for 2.4 GHz reader-less active RFID tag transceiver. J. Cent. South Univ. 2015, 22, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, L.; Agarwal, A. A CMOS standard-cell based fully-synthesizable low-dropout regulator for ultra-low power applications. Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2021, 141, 153958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikandan, P.; Bindu, B. A transient enhanced cap-less low-dropout regulator for wide range of load currents and capacitances. Microelectron. J. 2021, 115, 105207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badal, T.I.; Reaz, M.B.I.; Yeng, L.S.; Bhuiyan, M.A.S.; Haque, F. Advancement of CMOS transimpedance amplifier for optical receiver. Trans. Electr. Electron. Mater. 2019, 20, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boanloo, M.M.; Yavari, M. A low-power high-gain low-dropout regulator for implantable biomedical applications. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2021, 40, 1041–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, C.H.; Jaaskelainen, K.; Hu, Y. A fully integrated CMOS voltage regulator for supply-noise-insensitive charge pump PLL design. Microelectron. J. 2010, 41, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, C.Y.; Wang, L.W.; Huang, P.C. An integrated linear regulator with fast output voltage transition for dual-supply SRAMs in DVFS systems. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2010, 45, 2239–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, A.; Patra, A. Trade-offs Aware Design Procedure for an Adaptively Biased, Capacitor-less Low Drop-out Regulator Using Nested Miller Compensation. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, N.B.; Amin, S.; Reaz, M.B.I.; Hashim, F.H.; Kamal, N. Evolution of low drop out voltage regulator in CMOS technologies. Prz. Elektrotech. 2015, 91, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Ma, D. A fast-response hybrid SIMO power converter with adaptive current compensation and minimized cross-regulation. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2014, 49, 1242–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walling, J.S.; Allstot, D.J. Linearizing CMOS switching power amplifier using supply regulator. IEEE Trans. Circuit Syst. 2010, 57, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Dower, P.M. A max-plus based fundamental solution for a class of discrete time linear regulator problems. Linear Algebra Appl. 2015, 471, 693–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.; Kim, J.; Cho, Y.; Jin, S.; Kang, D.; Kim, B. CMOS linear power amplifier with envelope tracking operation. J. Electromagn. Eng. Sci. 2014, 14, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, W.; Bakkaloglu, B. A CMOS low-dropout regulator with current-mode. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2007, 54, 922–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priewasser, R.; Agostinelli, M.; Unterrieder, C.; Marsili, S.; Hueme, M. Control and implementation of DC-DC converters for variable frequency operation. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 287–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.C.; Wu, H.H.; Chang, T.Y. An active-frequency compensation scheme for CMOS low-dropout regulators with transient-response improvement. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2008, 55, 853–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shyoukh, M.A.; Lee, H.; Perez, R. A transient-enhanced low-quiescent current low-dropout regulator with buffer impedance attenuation. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2007, 42, 1732–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saberkari, A.; Alarcón, E.; Shokouhi, S.B. Fast transient current-steering CMOS LDO regulator based on current feedback amplifier. Integration 2013, 46, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kankanamge, K.; Kularatna, N. Improving the end-to-end efficiency of DC–DC converters based on a supercapacitor-assisted low-dropout regulator technique. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Ki, W.; Yue, C.P. An NMOS-LDO regulated switched-capacitor DC-DC converter with fast-response adaptive-phase digital control. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 1294–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazucha, P.; Moon, S.T.; Schrom, G.; Paillet, F.; Gardner, D.; Rajapandian, S.; Karnik, T. High voltage tolerant linear regulator with fast digital control for biasing of integrated DC-DC converters. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2007, 42, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chun, H.; Torsten, L. Dual-stacked current recycling linear regulators with 48% power saving for biomedical implants. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2013, 60, 1946–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Leung, K.N. A 6W chip-area-efficient output-capacitorless LDO in 90-nm CMOS technology. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2010, 45, 1896–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazucha, P.; Karnik, T.; Bloechel, B.A.; Parsons, C.; Finan, D.; Borkar, S. An area-efficient, integrated, linear regulator with ultra-fast load regulation. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2005, 40, 933–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, T.Y.; Leung, K.N.; Leung, C.Y.; Mok, P.K.T.; Chan, M. Development of single-transistor-control LDO based on flipped voltage follower for SoC. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2008, 55, 1392–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, S.; Chan, P.K. A 0.9-/spl mu/A quiescent current output-capacitorless LDO regulator with adaptive power transistors in 65-nm CMOS. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2013, 60, 1072–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhao, X.; Dong, L.; Yu, L.; Wang, Y. Design of a capacitor-less adaptively biased low dropout regulator using recycling folded cascode amplifier. Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2021, 135, 153745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, M.; Ali, I.; Khan, D.; Rehman, M.R.; Pu, Y.; Yoo, S.S.; Lee, K.Y. Design of high performance hybrid type digital-feedback low drop-out regulator using SSCG technique. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 28167–28176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Q.; Qu, P.; Hu, W.; Xiao, Z. An adaptively biased LDO regulator with 11nA quiescent current and 50mA available load. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Daegu, Korea, 22–28 May 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.C.; Huang, M.H.; Chen, K.H. High-PSR-bandwidth capacitor-free LDO regulator with 50µA minimized load current requirement for achieving high efficiency at light loads. WSEAS Trans. Circuits Syst. Arch. 2008, 7, 428–437. Available online: http://www.wseas.us/e-library/transactions/circuits/2008/30-815N.pdf (accessed on 29 October 2021).
- Chen, J.; Zhang, W.; Sun, Q.; Liu, L. An 8–12.5-GHz LC PLL with dual VCO and noise-reduced LDO regulator for multilane multiprotocol SerDes in 28-nm CMOS technology. Electronics 2021, 10, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahramali, A.; Lopez-Vallejo, M. An RFID-based self-biased 40 nm low power LDO regulator for IoT applications. Micromachines 2021, 12, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Oh, J.; Cho, S.Y.; Jeong, D.K.; Park, J.E. A fast droop-recovery event-driven digital LDO with adaptive linear/binary two-step search for voltage regulation in advanced memory. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 37, 1189–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Ki, W.H. Linear Regulators for WPT. In CMOS Integrated Circuit Design for Wireless Power Transfer; Analog Circuits and Signal Processing; Springer: Singapore, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, F.I.B.A.; Mamun, M.; Bhuiyan, M.A.S.; Bakar, A.A.A. A low drop-out voltage regulator in 0.18 µm CMOS technology. Mod. Appl. Sci. 2013, 7, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crepaldi, P.C.; Pimenta, T.C.; Moreno, R.L.; Rodriguez, E.C. A low power CMOS voltage regulator for a wireless blood pressure biosensor. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2012, 61, 729–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boas, A.V.; Haddad, S.P.; Dias, J.A.S. A CMOS fast transient response low-dropout regulator with a compact NMOS output driver. Microelectron. J. 2014, 45, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakolski, O.; Poongodan, P.K.; Vanselow, F. A feedforward compensated high-voltage linear regulator with fast response, high-current sinking capability. IEEE Solid-States Circuits Lett. 2020, 3, 114–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.P.; Tang, K.T. A fully integrated high-power-supply-rejection linear regulator with an output-supplied voltage reference. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2020, 67, 3828–3838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adorni, N.; Stanzione, S.; Boni, A. A 10-mA LDO with 16-nA IQ and operating from 800-mV supply. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2020, 55, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, K.; Manandhar, S.; Bakkaloglu, B. A 5.6 µA wide bandwidth, high power supply rejection linear low-dropout regulator with 68 dB of PSR up to 2 MHz. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2020, 55, 2151–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Zhan, C.; Wang, G. A fully-on-chip analog low-dropout regulator with negative charge pump for low-voltage applications. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2018, 66, 1361–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Lee, B.; Hong, S.W. A output capacitor-less low-dropout regulator with a low-VDD inverting buffer for the mobile application. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 8931–8935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.H.; Liao, W.C. A high-performance LDO regulator enabling low-power SoC with voltage scaling approaches. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. Syst. 2020, 28, 1141–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magod, R.; Suda, N.; Ivanov, V.; Balasingam, R.; Bakkalogu, B. A low noise output capacitor-less low dropout regulator with a switched-RC bandgap reference. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 2856–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, K.; Jee, D.W.; Jeon, D. A 65nm-.6-1.2V low-dropout regulator using voltage-difference-to-time converter with direct output feedback. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2020, 68, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, M.A.; Hong, W.; Hwang, I.C. Fast transient fully standard-cell-based all digital low-dropout regulator with 99.97% current efficiency. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 8011–8019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, L.G.; Warchall, J.; Mercier, P.P. A successive approximation recursive digital low-dropout voltage regulator with PD compensation and sub-LSB duty control. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2018, 53, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.J.; Qu, W.; Singh, S.; Kim, D.Y.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, S.H.; Park, J.J.; Cho, G.H. A 200-mA digital low drop-out regulator with coarse_fine dual loop in mobile application processor. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2017, 52, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Seok, M. A fully integrated digital low-dropout regulator based on event-driven explicit time-coding architecture. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2017, 52, 3071–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, S.; Liu, M.; Wen, S.J.; Wong, R.; Kim, C.H. A fully integrated digital LDO with bulit-in adaptive sampling and active voltage positioning using a beat-frequency quantizer. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2019, 54, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wan, P.; Geng, J.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Z. a fast transient response digital LDO with a TDC-based signal converter. Electronics 2020, 9, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, S.B.; Sen, S.; Raychowdhury, A. switched-mode-control based hybrid LDO for fine-grain power management of digital load circuits. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2018, 53, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, S.B.; Sen, S.; Raychowdhury, A. A reconfigurable hybrid low dropout voltage regulator for wide-range power supply noise rejection and energy-efficiency trade-off. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2018, 65, 1864–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.K.; Shin, S.U.; Kim, H.S. A BGR-recursive low-dropout regulator achieving high PSR in the low-to mid-frequency range. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 13441–13454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheah, M.; Mandal, D.; Bakkaloglu, B.; Kiaei, S. A 100-mA, 99.11% current efficiency 2-m Vpp ripple digitally controlled LDO with active ripple suppression. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. Syst. 2017, 25, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Song, H.; Zhou, R.; Rhee, W.; Shim, I.; Wang, Z. A capacitor-less ripple-less hybrid LDO with exponential ratio array and 4000x load current range. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2019, 66, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayıhan, H.İ.; İnam, B.B.; Doğan, B.; Yelten, M.B. A wide-temperature range (77–400 K) CMOS low-dropout voltage regulator system. Analog. Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 2021, 106, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailón, J.P.; Calvo, B.; Medrano, N. A fully-integrated 180 nm CMOS 1.2 V low-dropout regulator for low-power portable applications. Electronics 2021, 10, 2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, J.J.; Liang, H.; Zhang, J.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, Z.W.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, B. A fast-transient low-dropout regulator with current-efficient super transconductance cell and dynamic reference control. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2021, 68, 2354–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| References | Process (µm) | Imax (mA) | Vin (V) | Vout (V) | Cout (µF) | IQ (µA) | (mV) | (mV) | Load reg. (mV/mA) | Line reg. (mV/V) | Current Efficiency (%) | Active Area (mm2) | PSR (dB) | Topology | FOM # (ps) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [19] | 0.25 | 50 | 2–2.5 | 1.5–1.97 | 0.05 | 100 | 0.47 | 530 | 0.08 | N/A | 99.8 | 0.23 | 43 @ 30 KHz | Current Feedback Amplifier | 940 |
| [22] | 0.35 | 200 | 2.0 | 1.8 | 1.0 | 20 | 0.2 | 200 | 34 | 2 | 99.8 | 0.264 | 340 @ ILM | Buffer Impedance Attenuation | 100 |
| [21] | 0.35 | 150 | 2.0 | 1.8 | 1.0 | 27 | 0.2 | 200 | 10 | 0 | 60 | 0.409 | 40 @ 20 KHz | Folded Cascade Topology | 0.01 |
| [23] | 0.35 | 100 | 3–5 | 2.8 | 1 | 59–189 | 3 | 2200 | 0.025 | 13.5 | 99.8 | N/A | >56 (0 Hz–100 Hz) | Current Steering Approach | 17.7 |
| [25] | 0.65 | 30 | 2.5 | 1 | 39 | 10 | 195 | 50 | 0.2 | 0 | 80.3 | 0.154 | 2.8 @ 100 mHz | Adaptive Phase Scheme | 0.085 and 0.08 n * |
| [50] | 0.25 | 100 | N/A | 1–3.3 | Capless | 40 | N/A | 230 | N/A | N/A | N/A | 0.21 | 50 @ 10 KHz | Sample and Hold Switched RC Filter | N/A |
| [47] | 0.065 | 45 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 10−4 | 21 | 44 | 100 | 0.047 | 1 | 99.95 | 0.045 | N/A | Negative Charge Pump | 0.1037 |
| [44] | 0.18 | 11 | 1.3 | 1.09 | N/A | 276 | 45 | 210 | 0.015 | 0.6 | N/A | 0.105 | −54 @ 10 MHz | Dual Feedback Structure with Charge Pump | 10.49 and 0.677 mV ** |
| [43] | 0.18 | 0 | 70 | 66 | 0.066 | 288 | 0.17 | 4000 | 1.7 | 90 | 99.71 | 0.15 | N/A | Feedforward Compensated Method | 0.03 |
| [45] | 0.055 | 10 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 1 | 0.016 | 70 | 200 | 1.05 | 0.5 | N/A | 0.042 | 42.7 @ 50 KHz | Differential Flipped Voltage Follower | 11.4 |
| [49] | 0.04 | 100 | 1.1–1.9 | 0.2–1.1 | 1 | 56 | 28 | 900 | 0.176 | 0.857 | 99.94 | 0.375 | −60 @ 1 MHz | Multistage Error Amplifier with TAPG | 157 |
| [48] | 0.5 | 600 | 1.5–5.0 | 1.3–4.8 | 5.1 × 10−6 | 16.5 | 514 | 200 | 0.011 | 0.156 | 99.95 | 0.082 | −26.7 @ 1 MHz | Low-VDD Inverting Buffer | 0.00012 and 1.42 ns.mV *** |
| [51] | 0.65 | 60 | 0.6–1.2 | 0.5–1.15 | 10−5 | 0.1–10 | 111 | 100 | N/A | N/A | 99.99 | 0.086 | N/A | Voltage Difference to Time Converter | 0.000202 and 0.182 fF **** |
| References | [54] | [52] | [55] | [56] | [53] | [57] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Technology (nm) | 28 | 65 | 65 | 65 | 65 | 65 |
| VIN (V) | 1.1 | 0.7–1.2 | 0.5–1 | 0.6–1.2 | 0.5–1 | 0.7–1.1 |
| VOUT (V) | 0.9 | 0.6–1.1 | 0.45–0.95 | 0.4–1.1 | 0.3–0.45 | 0.65–1.05 |
| VOUT (mV) @ ILOAD (mA) | 120@180 | 200@23.5 | 40@0.5VIN | 108@50 | 40@1.06 | 371@80 |
| ILOAD,MAX (mA) | 200 | 25 | 0.0072–3.511 | 100 | 2 | 120 |
| IQ (mA) | 0.2 | 0.006 | 0.012–0.216 | 0.1–1.07 | 0.014 | 0.495 |
| Current Peak Efficiency (%) | 99.94 | 99.97 | 96.3 | 99.5 | 99.8 | 99.6 |
| CLOAD (nF) | 23.5 | 1 | 0.4 | 0.04 | 0.4 | 0.5 |
| Load Regulation (mV/mA) | N/A | 0.04 | N/A | 0.638 | <5.6 | 0.6 |
| Line Regulation (mV/V) | N/A | 0.78 | N/A | N/A | 2.3 | 0.5 |
| PSRR (dB) | N/A | N/A | N/A | –38@1MHz | N/A | N/A |
| Active Area (mm2) | 0.021 | 0.014 | 0.029 | 0.0374 | 0.0023 | 0.017 |
| Response Time, TR (ns) | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 15.1 | 2.1 |
| FOM # | 7.75 (ps) | 2.17 (ps) | 1.11 (ps) | 1.38 (ps) | 199 (ps) | 8.7 (ps) |
| Circuit Topology | Current-mirror flash analog to digital converter (ADC) | Logic-Threshold Triggered Comparator | Event-Driven Explicit Time-Coding | Beat-Frequency Quantizer and VCO | PD Compensation and Sub-LSB Duty Control | Time-to-Digital Converter (TDC) |
| References | [61] | [58] | [59] | [63] | [60] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Technology (nm) | 180 | 130 | 130 | 65 | 500 |
| Input Voltage, VIN (V) | 1.43–2.0 | 0.6, 1.1–1.2 | N/A | 0.8–1.0 | 2.2–5 |
| Output Voltage, VOUT (V) | 1.0–1.57 | 0.5–0.55, 0.8–1.1 | N/A | 0.75–0.95 | 2–4.85 |
| VDROP (mV) | N/A | N/A | N/A | 50 | 120 (P-type) |
| Maximum ILOAD (mA) | 100 | 12 | 5 | 0.01–40 | 300 |
| Quiescent Current, IQ (mA) | 1 | N/A | 0.057 | 0.12 | 0.050 |
| Current Peak Efficiency (%) | 99.11 | 98.5 (R), 98.64 (L) | 98.86 | 99.7 | N/A |
| COUT(nF) | Cap-Free | 0.5 | 0.5 | Cap-Free | 1 |
| Load Regulation (mV/mA) | 0.01 | <2.67 | N/A | N/A | 0.003 |
| Line Regulation (mV/V) | 1 | N/A | N/A | N/A | 0.28 |
| PSR (dB) | N/A | N/A | −9 to −34 @ 100 MHz | N/A | 80 @0.1 MHz |
| Active Area (mm2) | 0.679 | 0.0818 | N/A | 0.175 | N/A |
| FOM (ps) # | N/A | 166(R), 244.8 (Linear) and 0.58 (R), 1.747(Linear) ns/mA ## | 28.06 and 28.06 @ 100 MHz ### | 0.0188 | 11 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sobhan Bhuiyan, M.A.; Hossain, M.R.; Minhad, K.N.; Haque, F.; Hemel, M.S.K.; Md Dawi, O.; Ibne Reaz, M.B.; Ooi, K.J.A. CMOS Low-Dropout Voltage Regulator Design Trends: An Overview. Electronics 2022, 11, 193. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11020193
Sobhan Bhuiyan MA, Hossain MR, Minhad KN, Haque F, Hemel MSK, Md Dawi O, Ibne Reaz MB, Ooi KJA. CMOS Low-Dropout Voltage Regulator Design Trends: An Overview. Electronics. 2022; 11(2):193. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11020193
Chicago/Turabian StyleSobhan Bhuiyan, Mohammad Arif, Md. Rownak Hossain, Khairun Nisa’ Minhad, Fahmida Haque, Mohammad Shahriar Khan Hemel, Omar Md Dawi, Mamun Bin Ibne Reaz, and Kelvin J. A. Ooi. 2022. "CMOS Low-Dropout Voltage Regulator Design Trends: An Overview" Electronics 11, no. 2: 193. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11020193
APA StyleSobhan Bhuiyan, M. A., Hossain, M. R., Minhad, K. N., Haque, F., Hemel, M. S. K., Md Dawi, O., Ibne Reaz, M. B., & Ooi, K. J. A. (2022). CMOS Low-Dropout Voltage Regulator Design Trends: An Overview. Electronics, 11(2), 193. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11020193






