Abstract
The next generation of wireless systems has benefits in terms of spectrum and energy inefficiencies by exploiting two promising techniques including Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access (NOMA) and Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces (RIS). The scenario of two legitimate users existing together with an eavesdropper is worth examining in terms of secure matter while enabling machine learning tools at the base station for expected improvement. The base station deals with a highly complicated algorithm to adjust parameters against the attack of eavesdroppers and to better improve the secure performance of mobile users. This paper suggests a better solution to allow the base station to predict performance at destinations to adjust necessary parameters such as power allocation coefficients properly. To this end, we propose a deep neural network (DNN)-based approach which also leverages the benefits of aerial RIS to achieve predictable performance and significant secure performance improvement could be enhanced. We first derive the formulations for security outage probability (SOP) in closed-form expressions and analyze the strictly positive secrecy capacity (SPSC), which are crucial performance metrics to determine how the systems are against the existence of eavesdroppers. Such eavesdroppers intend to overhear signal transmission dedicated to intended users and incur degraded system performance. The numerical simulations are expected to evaluate how the machine learning tool works with the traditional computation of system performance metrics which is able to be verified by comparing with the Monte-Carlo method. Our numerical simulations demonstrate that the design of a higher number of meta-surface elements at the RIS, as well as a higher signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) levels at the base station, are key parameters to achieving improved security performance for users. For detailed guidelines of the RIS-NOMA aided system, we provide a table of parameters samples resulting in secure performance as expected.
1. Introduction
The next generation of wireless systems employing Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces (RIS), similarly discussed as Intelligent Reflecting Surfaces (IRS) and software-controlled meta-surfaces which are the surfaces that are made of electromagnetic (EM) material which possess multiple numbers of large passive reflective surfaces that are being controlled by a microcontroller [1,2,3,4,5]. The foremost advantage of RIS is its capability of controlling the environment by manipulating electromagnetic signals or radio waves according to the user requirement [3]. The works from [6,7,8,9] have indicated that the inclusion of the NOMA method into RIS communications has enhanced the efficiency of the RIS device. In [10], the authors have studied the effect of hardware impairments (HI) in RIS-aided NOMA communications in means of outage probability and throughput, where the studied system has outperformed the traditional Orthogonal Multiple Access (OMA) technique. Correspondingly, the authors have found that the quantity of reflecting surfaces and power allocation (PA) factors play a major character in view of the performance efficacy of the system. In [11], the authors have studied the Residual-HI (RHI) effect on RIS-assisted downlink NOMA, in which Physical Layer Security (PLS) and SOP are studied by deriving closed-form expressions. It was proved that the severity effect of RHI will affect the SOP of the system. The NOMA in the considered system has outperformed the traditional OMA in view of performance.
The evolution of 5th generation (5G) and 6th generation (6G) wireless networks has created a huge requirement for massive device connectivity and efficient spectrum usage. Multiple-input-multiple-output (MIMO) antennas have played a remarkable role in assisting huge connectivity and enabling quality signal transmission among devices [12]. Though the MIMO technology has numerous advantages, the major drawback of the device is its hardware costs and deployment complexity [13]. Fortunately, RIS-aided systems have the ability to address these concerns. The implementation of RIS with single antenna devices has shown a performance that is nearly the same as MIMO equipped devices [14]. In [15], the authors considered a RIS-assisted NOMA system in PLS perspective with the presence of an eavesdropper and analyzed the SOP performance of the system in various scenarios. In [16], the authors have investigated the performance of secrecy capacity of RIS-assisted cooperative networks in the presence of two legitimate users and an eavesdropper, having a direct link with the legitimate users. In [17], the authors have investigated the SOP performance with discrete phase shifts applied at the RIS, considering two scenarios of colluding and non-colluding eavesdroppers. The simultaneous transmission and reflection RIS (STAR-RIS) model was proposed [18] in the presence of two legitimate users using a multiple-input-single-output (MISO) wiretap network. Various problem scenarios were considered and respective algorithms were suggested to enhance the performance of the system. It is comparatively shown that the RIS-aided system has a better performance compared to traditional RIS device integration. However, these traditional approaches used to evaluate secure performance could be ineffective for several users whose mobility is high.
1.1. Related Studies
One can leverage the advantages of deep learning (DL) to empower the smart environment in signal transmission for wireless systems [19,20,21,22,23,24,25], which inspires some attempts to address the predictable system performance at destination aiming to adjust system parameters at the base station. In [19], the authors considered the optimization problem to achieve the optimal throughput related to the entire transmission period. In particular, the optimal throughput could be conducted by jointly optimizing the power allocation of the access point and the phase shift of the RIS. The authors also leverage the benefits of a DL approach and a reinforcement learning (RL) approach to investigate the optimal phase shifts at RIS. The promising RIS-aided NOMA system is studied in [21] by conducting a deep deterministic policy gradient (DDPG) algorithm to collaboratively adjust meta-surface elements of the RIS to obtain an optimal phase shifting matrix. The expected results are a better sum data rate compared with the traditional OMA while a dynamic resource allocation policy in the long term is achieved by the DDPG algorithm. Every given state through exploration and exploitation is processed by learning the optimal action. Similar work in [22] developed the distributed machine learning (DML) technique to enable the base station and the users and then achieved a promising method of a downlink channel estimation using a neural network. To enhance the channel estimation accuracy, a hierarchical neural network architecture is explored by extracting different channel features for different channel scenarios. In the other scenario of RIS-aided unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) networks, a deep Q-network (D-DQN)-based approach is performed to deal with optimization of the energy consumption, phase shifts of the RIS and power allocation policy from the UAV to mobile users. In this perspective, the central controller relying on the D-DQN-based scheme is assigned as an agent for periodically determining the state of the UAV-aided wireless network and guaranteeing actions to fit the dynamic environment.
1.2. Motivations and Our Contributions
The authors in [23] studied the physical layer security applied in RIS-aided NOMA 6G networks. Although the optimal power allocation scheme can be achieved, but it is hard to be obtained due to its complexity. If we want to have further improvement of the system physical security concern, a more effective method is missing. Further, when deploying NOMA-assisted transmission with RIS-aided communications, previous works assumed fixed power allocation factors applied for users and secure performance for each user is unpredictable [24]. Furthermore, the behavior and data demands from mobile users cannot be measured at the base station. To overcome these aforementioned shortcomings, we propose an efficient solution relying on DNN to predict secure performance metrics at mobile users and to be known at the base station. The DNN approaches exhibit a flexible and smart control related to parameters of NOMA and RIS. With trained neural networks, the base station in the RIS-aided system can choose proper parameters at the base station to deal with the enhanced performance expected by mobile users who operate in dynamic environments. Furthermore, continuous learning with up-to-date data is a new way for base stations to face the attack of eavesdroppers. To the best of our knowledge, our work tries to provide a smart way for a base station to adjust its parameters to better serve mobile users who want to enlarge the advantages of both NOMA and RIS.
We summarize the key findings of this study as follows
- This study presents how we derive new closed-form formulas to evaluate the secure performance once legitimate users against the appearance of eavesdroppers who exist in the same group of users. In particular, the SOP and SPSC are computed mathematically. The secure performance analysis is not only crucial to the system dealing with security concerns but also provides some inputs for the machine learning algorithm.
- By enabling real-time configurations, we develop a DNN framework for the RIS-aided system, where the NOMA scheme is converted to an optimal model once the base station is able to predict secure performance thanks to enabling the DNN model. Furthermore, predicting the SOP with high accuracy and short execution time, the DNN model deduces the goodput and energy efficiency (EE).
- Lastly, the normal base station is verified to operate efficiently with the dynamic changes of the environment since the predicted and mathematical curves of SOP are matched tightly through simulation results. We deploy mean squared error (MSE) to demonstrate the effectiveness of the DNN model which is evaluated through the simulation in comparison with the existing conventional approaches. Other results were also assessed to confirm the advances of using RIS and NOMA in improving the performance of wireless communication under attack from eavesdroppers.
The remaining sections of our study can be summarized as follows. The second section develops a system description. The usual method of computing safe performance metrics is then demonstrated in Section 3. The machine learning tool for predicting secure metrics is presented in Section 4. In Section 5, the numerical simulation results are described and discussed, and in Section 6, the study is concluded.
2. System Model
Consider the downlink RIS-NOMA-aided system shown in Figure 1 where a base station (BS) intends to communicate with mobile users following the NOMA scheme with the existence of eavesdroppers. We just focus on presenting the performance of a selected group of users while other groups have similar analyses. In such a group of users, the suitable model includes a flying device mounted with a RIS and two legitimate users and . The multiple users (more than two users) in a group could be further researched although it brings worse performance for each user since there is much interference from surrounding users affecting the considered user. As a key report in [15], the two-NOMA users approach exhibits better services in the deployment of the Internet of Things (IoT) devices rather than the system dealing with groups containing multiple users. Therefore, our result in this paper could be considered a solution introducing the upper bound of SOP performance.
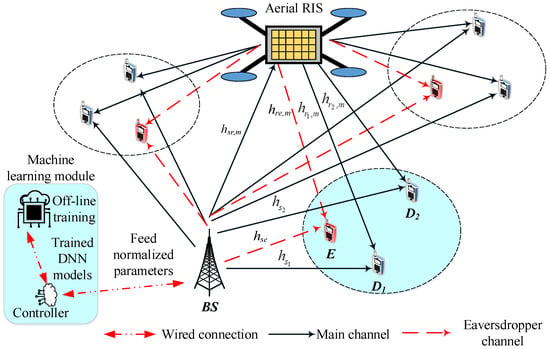
Figure 1.
A model of DNN-based RIS-NOMA system.
We refer to examine how an eavesdropper affects secure performance. The number of meta-surfaces at RIS is denoted as M. Here, RIS can co-work with remaining nodes which are facilitated with a single antenna for reduced cost of design. The RIS-NOMA system experiences the Rayleigh fading model to characterize the wireless channels.
In general circumstances, these mobile users have chances to communicate with both RIS and BS. The RIS is expected to improve performance at destinations while eavesdropper attacks on transmission are dedicated to legitimate users. The system is assumed to know the information of the channel state information (CSI) at RIS with respect to the highest value of the received SNR which is computed to detect signal for dedicated user. The channel error regarding CSI estimation is beyond the scope of this study.
The BS transmits the superimposed signals to serve two users in the considered group, corresponding the signal for user while P stands for the transmit power at the BS, represents power allocation factors. To guarantee fairness when the BS treats qualified service to the users related to their QoS demands. Therefore, it is reasonable to assume that satisfying [26]. We denote the channels , , , , following complex Gaussian random variables (RV) with unit variance and zero mean. These channels experience a slowly varying and flat fading channel model. Further, the distances for the -, -RIS and RIS-, -E, RIS-E links are represented by , , , , , respectively. The two mobile users could be evaluated firstly via computing SNR at which is given by [27,28]
where parameter of RIS is the adjustable phase for the m-th reflecting element of the RIS, is the amplitude reflection coefficient while are the additive white Gaussian noise (AWGN) at and such noise follows a zero-mean complex Gaussian distribution with variance , denotes the path loss exponent.
In the perceptive of distribution of channels, all small-scale fading channel coefficients follow independent and identically distributed variables [29]. The RIS relying on a large meta-surface element M is fundamentally expected as a crucial factor to control the quality of the received signal at users. By exploiting the central limit theorem, we have and [27]. It is noted that the RIS is able to adjust its phases of reflector conditioned on known CSI [27].
The signal to interference plus noise ratio (SINR) could be calculated at the user to decode signal as
where in order to simplify the analysis, Ideal Passive Beamforming (IPB) with Perfect Channel Estimation (PCE) is assumed at the RIS, and all elements have the same reflection amplitude. We have the phase and [30]. We let , , . Due to in the case of perfect CSI [27].
Following the NOMA scheme, the successive interference cancellation (SIC) is enabled and SNR at the user for detecting signal is given by .
Similarly, the second user in this group has the received signal as [27,28]
where the parameter of RIS is the adjustable phase for the m-the reflecting element of the RIS, is the amplitude reflection coefficient.
At the user , we refer to achieve SNR for the process of signal decoding . Such SNR can be determined as
where in order to simplify the analysis, Ideal Passive Beamforming (IPB) with Perfect Channel Estimation (PCE) is assumed at the RIS, and all elements have the same reflection amplitude. We have the phase and [30]. We let , . Due to in the case of perfect CSI [27].
From the perspective of PLS, is denoted as the AWGN of E following the complex Gaussian distribution with variance . Then, the eavesdropper E has a similar opportunity to acquire the received signal as [27,28]
Similar to SIC, an eavesdropper leverages parallel interference cancellation (PIC), user E want to achieve SNR using to decode as [31], where , , , , . can be approximated with an exponential RV parameter [32].
In this step, we refer to the instantaneous secrecy rate to look at how secure performance can be evaluated by two users. Firstly, at we compute the instantaneous secrecy rate as [31,32]
The similar formula of instantaneous secrecy rate can be represented for user as
We compute these necessary values of instantaneous secrecy rates to initially determine how eavesdroppers create a degraded performance for the intended users. However, we also have other system metrics to demonstrate exact secure outage performance which is expected to examine in the next section.
3. The Mathematical Method to Achieve Secrecy Performance Metrics
3.1. SOP Analysis
In RIS-NOMA systems, the operation of an eavesdropper makes reduced performance obtained at the intended users, and which are still empowered by the smart reflection scheme from RIS. The system works well with expecting rate of . Unfortunately, a security concern needs to be verified once the corresponding transmission cannot be guaranteed for the case that the secrecy rate is less than . The two important secure metrics could be examined, i.e., SOP and SPSC are enough to show initial confirmation in terms of security problems. The SOP could be computed as the probability which tells us that the instantaneous secrecy capacity falls below a threshold target secrecy rate and which is presented as
Therefore, secure outage circumstance happens if we refer to the instantaneous secrecy rate in (6) and (7), i.e., either or falls below their own target rates. We then formulate the SOP performance as [31]
where is threshold secure rate [31].
Proposition 1.
We represent the approximate closed-form computation of the first important secure performance, i.e., is expressed by
where .
Proof.
We provide the proof in detail in Appendix A. □
Remark 1.
Although the results of (10) are quite complicated to know how the SOP performance of the proposed system can be improved by the advantages of RIS, we try to examine several key parameters such as the threshold secure rate, the setup of RIS, the transmit SNR at the BS and power allocation factors. These factors are expected to show intuitive illustrations in the numerical simulation section.
3.2. Asymptotic SOP
Using the aforementioned analytical findings in (10), when the asymptotic SOP is specified by
3.3. SPSC Analysis
The SOP is not enough to demonstrate secure performance. Therefore, we intend to calculate SPSC which is considered as the further secrecy performance metric. The existence of strictly positive secrecy capacity is studied when it occurs as a special case of the SOP for the case of the target secrecy rate, . In the other way, we represent the probability of non zero secrecy capacity if we consider corresponding, respectively, as SNRs for legitimate user and eavesdropper as [31]
Then, it can be obtained the SPSC performance for the considered system as
Proposition 2.
We characterize the second performance metric through the approximate formula, i.e., is given by
Proof
We refer to the proof in detail in Appendix B. □
3.4. Asymptotic SPSC
In a similar way, considering (14), when the asymptotic SPSC could be obtained as
Remark 2.
It is hard to know the secure performance at destinations. It is worth pointing out that the BS relying on DNN can collect some parameters and trains them to predict the performance of users. The complexity of computations is seen in some derived expressions. We can reduce computation load by levering DNN. In particular, we expect to have a machine learning tool to deal with such situations in the next main section.
4. Predication of Main Secure Performance Based on DNN
The base station arranges several system parameters before transmitting signals to the RIS and destinations. The fairness and expected secure performance are only known once signals approach the dedicated users. It is assumed that if secure performance is not good enough, the user might lose the chance to detect its signal as expected. The results of secure performance is so complicated since they depend on the propagation environment and parameters of RIS and NOMA. These procedures take time to proceed and require the mathematical expression for evaluation of how the system serves secure metrics as expected, which is infeasible for real-time computing if we deploy such RIS-NOMA in several practical IoT applications. To overcome such problems, we design the DNN approach to allow the base station to learn the system variables and compute the secure metrics properly.
With regard to the model of aerial RIS, it is assumed that the motion in three-dimensional space (3D) is characterized for the aerial-RIS related to the random waypoint mobility model. It is noted that a uniform 3D Poisson process is applied to the samples of its locations and distances among nodes should be updated. It is reasonable to assume that the 3D motion morphology of Aerial-RIS resembles a 3D cylinder, as depicted in Figure 2. The distances along with important system parameters are presented in Table 1. The distributions of several values are so complicated, which makes fairness and security possible to be controlled hard. Finding optimal values in (10) to improve secure performance could be infeasible. We, fortunately, deploy DNN to indicate the system SOP by treating it as a regression technique issue in supervised machine learning. For data to be trained, we provide a data set that completely characterizes the parameters supplied in the considered system. The considered DNN approach is capable to provide accurate predication of the SOP when the training process is good enough, shown in Figure 3.
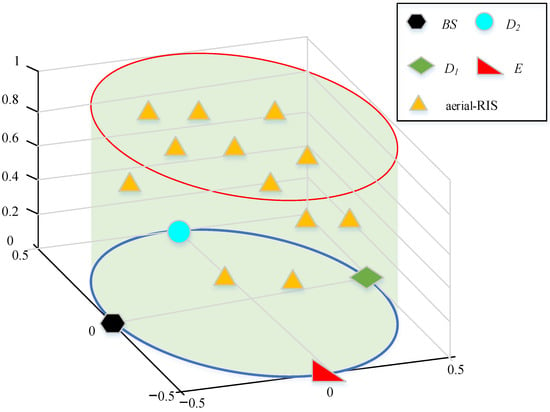
Figure 2.
Motion morphology of Aerial-RIS in such RIS-NOMA systems.

Table 1.
The system parameters using in DNN for training and testing procedures.
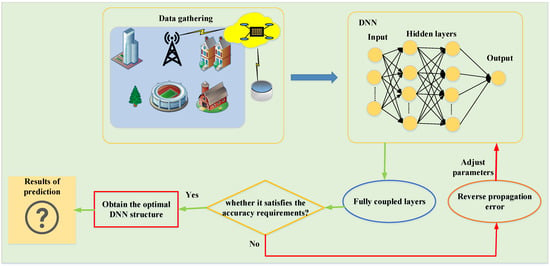
Figure 3.
The procedures of SOP prediction.
4.1. DNN Model Structure
4.1.1. The Structure of The DNN
The DNN model we use is a feed-forward neural network model. The detailed configuration of DNN can be seen in Figure 4. Such DNN has single-input layer, single-output layer, and hidden layers, and one output layer. The main key system parameters are provided to the server to add them as input values corresponding 15 neurons, shown in Table 1. We refer to the output layer with one neuron. To return the predicted SOP, the linear function along with its activation function is employed, [33,34]. There are , , neurons in every single hidden layer i. The system is equipped with the rectified linear unit (RLU) function as an activation function.
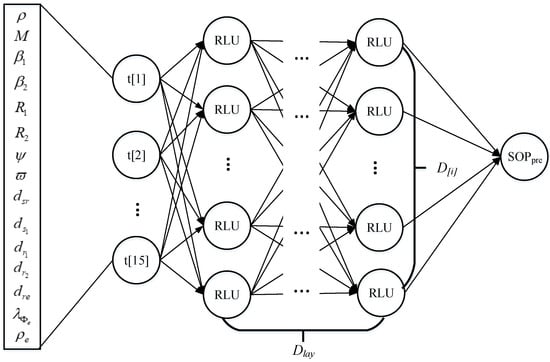
Figure 4.
The configuration of DNN for the considered regression problem.
4.1.2. Data Set
The server associated with the BS processes with i samples of our data set, the relationship between input and output is , in which stands for a feature vector corresponding to input parameters declared in Table 1. Monte-Carlo simulations provide feature vector is used and then returns an expected secure metric . In this model, we created samples, i.e., . We arranged the data set into , and corresponding to training set, , validation set, , and test set , respectively.
We measure how DNN works by considering the MSE, i.e., [33,34].
We leverage Algorithm 1 in [33,34] to refer to necessary procedures for the training and testing related to such a DNN.
Remark 3.
We aim to examine secure performance of the RIS-NOMA-aided system. In this way, the secure performance of users is evaluated in detail. If we extend the model to the general system with multiple RIS, multiple users, the method of traditional computations and DNN could be conducted in similar way.
5. Numerical Results
In this section, to verify mathematical computations, we do a simulation to demonstrate two secure performance metrics. We compare theorical results with Monte-Carlo simulation which is expected to match together. Figure 5 represents the flowchart to process input data with respect to achieving SOP as expected.
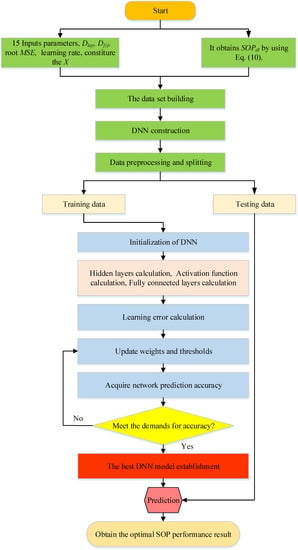
Figure 5.
SOP prediction algorithm.
Figure 6 confirms how DNN achieves the expected accuracy when we compare curves of the training set and validation set. It can be observed that two curves are matched tightly. It also means that the MSE value is able to approach the level of lowest error, and such MSE can be obtained after conducting 20 epochs.
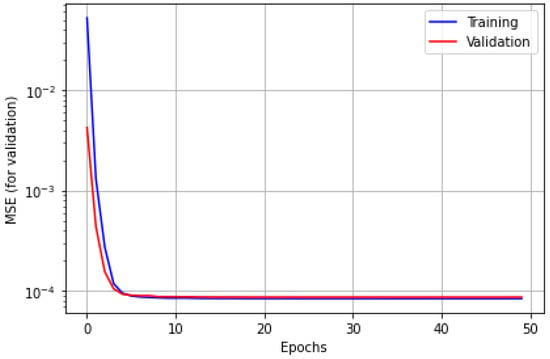
Figure 6.
The MSE convergence in DNN training and validation.
Figure 7 demonstrates SOP versus the transmit SNR at the BS. The numerical results for both Monte-Carlo and mathematical simulations can be seen as the same value which means our derived expression of SOP is exact. The SOP performance could be better when the system increase transmits SNR . It is worth noting that the power allocation factor is used to deal with improvement of SOP. However, these factors cannot be known at the BS without the assistance of DNN. The BS implement such a DNN to confirm which power factor should be assigned to each user to satisfy the fairness and data demands. Such a numerical result is confirmation for expression in (9) and (10). Further, the transmit SNR contributes significantly to achieving the expected SOP performance. By leveraging DNN, we have similar values of SOPs which are computed by mathematical method and DNN method. The SOP performance meets the saturation when the BS has the level of the transmit SNR as 15 (dB). It can be explained that SOP is based on more system parameters than which limits the expected performance, for example, channel gains and data rates . More importantly, the lower bounds of such SPSC at four values of can achieved as goes over 105 (dB). It means limitation of SOP can be seen even though the base station improves its average SNR.
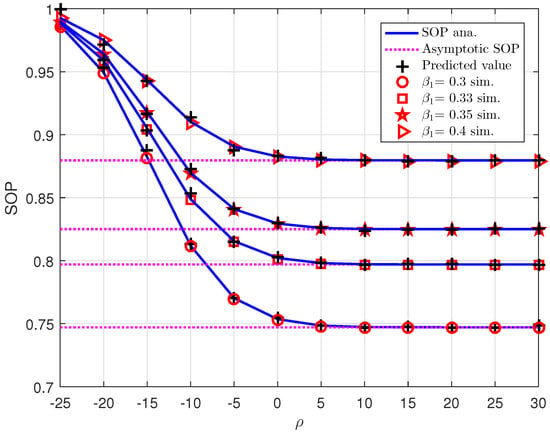
Figure 7.
SOP versus for different .
Figure 8 confirms other parameters, data rate , could be further factor to control the quality of security at destinations. We present the numerical result for SOP when the BS increases the transmit SNR. The SOP performance shows its different curves corresponding to these values of the target rates assigned to the users. The lower value of required at user results in the better SOP performance. It can be explained that SOP performance derived in (9) and (10) are theoretically limited by such threshold target rates .
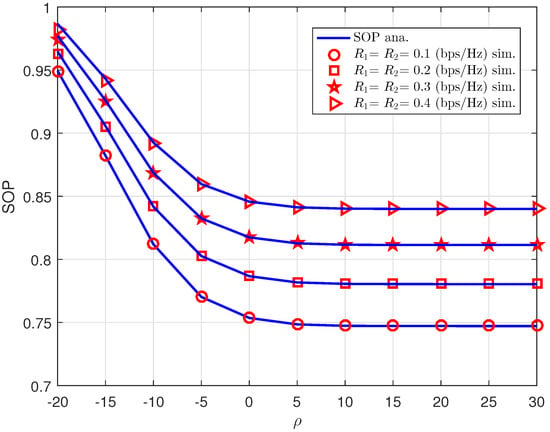
Figure 8.
SOP versus for different .
We can look at how RIS configuration makes improvement of SOP, shown in Figure 9. We can see the transmit SNR increases to contribute to enhanced SOP, but it still meets the saturation as the previous result Figure 8. The number of meta-surface at RIS could be main factor affecting the SOP performance. It can be explained that SNR at user depends on channel gains which relies on how large meta-surface of RIS is. We can confirm that saturation point happens at (dB).
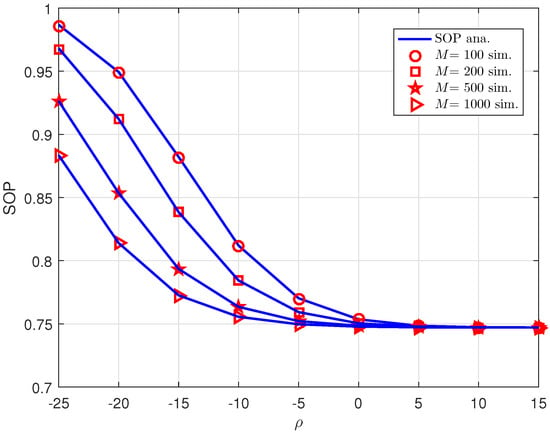
Figure 9.
SOP versus for different M.
At the eavesdropper, SOP performance Figure 10 can be seen when increases. Similar trend of SOP is observed in this case.
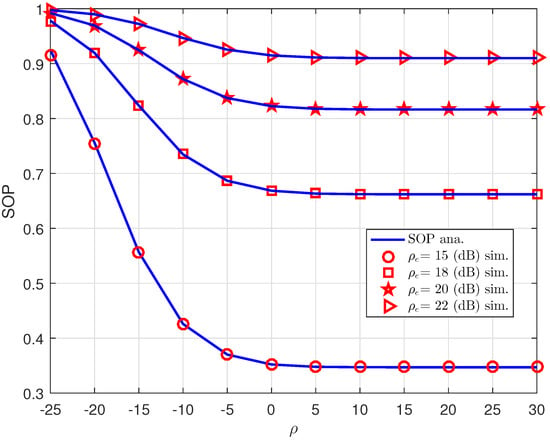
Figure 10.
SOP versus for different .
We can see SPSC performance shown in Figure 11 which confirms the transmit SNR still contributes to the improvement of SPSC. The BS changes the levels of power allocation at each user to deal with different values of SPSC. If the BS allocates to the first user which corresponds to highest value of SPSC. Similar as evaluation of SOP, SPSC can be enhanced significantly when is greater than 13 (dB). More importantly, the upper bound of such SPSC can achieved as goes over 15 (dB) which exhibits the limitation of SPSC although we improve the average SNR at the base station.
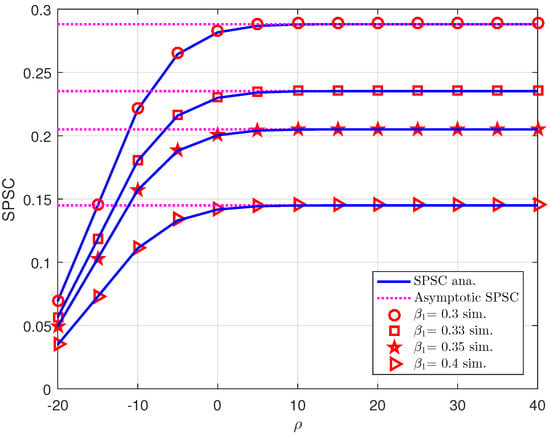
Figure 11.
The strictly positive secrecy capacity versus for various .
Figure 12 demonstrates the numerical result of SPSC when the BS adjusts the transmit SNR and RIS also modifies the different levels of amplitude reflection coefficients. It can give us the strong confirmation that the levels of do not show much effect on SPSC at high SNR region. We can see that the best performance can be obtained when we have .
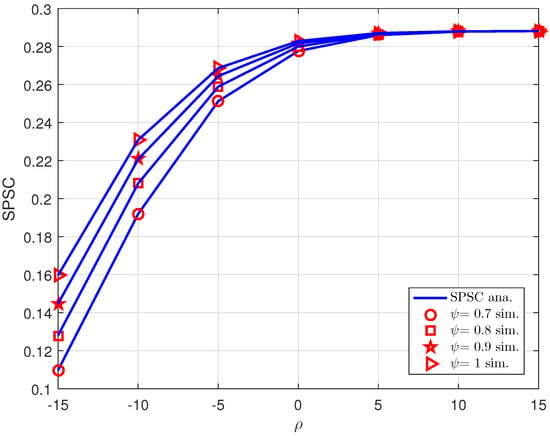
Figure 12.
SPSC versus for different = .
As expected, Table 2 is considered as the guideline of main parameters for achieving the SOP to satisfy QoS requirement from users. This result is necessary to further obtain the fairness among users.

Table 2.
The parameters of the proposed method for better performance.
6. Conclusions
In this paper, we have deployed DNN to activate smart features at the base station in the RIS-NOMA system to allow two legitimate users to have different secure performances based on their demands. We demonstrate the numerical results to look at different secure performances under the impacts of several parameters such as the transmit SNR at the base station and the configuration of RIS. The DNN approach provides perfect matching when we compare the systems between numerical results of mathematical analysis and machine learning tool. We confirmed the exact computations of expressions derived for SOP and SPSC via simulations. As the main finding, the number of meta-surfaces at the RIS and SNR level at the base station contribute mainly to the improvement of security for DNN-aided RIS-NOMA systems.
Author Contributions
H.-P.D. introduced the idea, contributed to developing some mathematical analysis; M.-S.V.N. performed the simulation experiments; D.-T.D. introduced the idea, contributed to developing some mathematical analysis; M.-H.N. and M.-T.P. provided valuable comments; A.-T.K. contributed to preparing the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was fully funded by Tra Vinh University under grant contract number 182/HD.HDKH&DT-DHTV.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A. Proof of Proposition 1
From (9) can be written as
From (A1), we can observe that the variables is correlated, which makes untractable exact analysis. Hence, we focus on the analysis for high SNR regime and adopt the following upper bounds [31]. Then, an upper bound of can be written as
where .
Then, can be formulated by
From (9), we can observe that the variables is correlated, which makes untractable exact analysis. Hence, we focus on the analysis for high SNR regime and adopt the following upper bounds [31]. Then, an upper bound of can be written as
Appendix B. Proof of Proposition 2
From (13), can be written as
We can observe that the variables is correlated, which makes untractable exact analysis. Hence, we focus on the analysis for high SNR regime and adopt the following upper bounds [31]. Then, an upper bound of can be written as
Next, can be calculated as
From (13), we can observe that the variables is correlated, which makes untractable exact analysis. Hence, we focus on the analysis for high SNR regime and adopt the following upper bounds [31]. Then, an upper bound of can be written as
References
- Basar, E.; Renzo, M.D.; Rosny, J.D.; Debbah, M.; Alouini, M.-S.; Zhang, R. Wireless communications through reconfigurable intelligent surfaces. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 116753–116773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Hu, S.; Alexandropoulos, G.C.; Zappone, A.; Yuen, C.; Zhang, R.; Renzo, M.D.; Debbah, M. Holographic MIMO surfaces for 6G wireless networks: Opportunities, challenges, and trends. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2020, 27, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Zhang, R. Towards smart and reconfigurable environment: Intelligent reflecting surface aided wireless network. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2020, 58, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaskos, C.; Nie, S.; Tsioliaridou, A.; Pitsillides, A.; Ioannidis, S.; Akyildiz, I. A new wireless communication paradigm through softwarecontrolled metasurfaces. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2018, 56, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Mo, R.; Yuen, C. Reconfigurable intelligent surface assisted multiuser MISO systems exploiting deep reinforcement learning. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2020, 38, 1839–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, D.-T.; Nguyen, M.-S.V.; Voznak, M.; Kwasinski, A.; de Souza, J.N. Performance Analysis of Clustering Car-Following V2X System with Wireless Power Transfer and Massive Connections. IEEE Int. Things J. 2022, 9, 14610–14628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, D.; Nguyen, M.-S.V. Device-to-device transmission modes in NOMA network with and without Wireless Power Transfer. Comput. Commun. 2019, 139, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, D.-T.; Nguyen, M.-S.V.; Jameel, F.; Jäntti, R.; Ansari, I.S. Performance Evaluation of Relay-Aided CR-NOMA for Beyond 5G Communications. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 134838–134855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, D.-T.; Le, C.-B.; Afghah, F. Enabling Full-Duplex and Energy Harvesting in Uplink and Downlink of Small-Cell Network Relying on Power Domain Based Multiple Access. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 142772–142784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemanth, A.; Umamaheswari, K.; Pogaku, A.C.; Do, D.-T.; Lee, B.M. Outage Performance Analysis of Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces-Aided NOMA Under Presence of Hardware Impairment. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 212156–212165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Meiling, L.; Xiaoxia, Y.; Ryan, A.; Alshehri, M.D.; Khan, F. Impact of Residual Hardware Impairment on the IoT Secrecy Performance of RIS-Assisted NOMA Networks. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 42583–42592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castanheira, D.; Silva, A.; Dinis, R.; Gameiro, A. Efficient Transmitter and Receiver Designs for SC-FDMA Based Heterogeneous Networks. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2015, 63, 2500–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldsmith, A.; Jafar, S.A.; Jindal, N.; Vishwanath, S. Capacity limits of MIMO channels. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2003, 21, 684–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, A.-T.; Ha, N.-D.X.; Do, D.; Silva, A.; Yadav, S. Enabling User Grouping and Fixed Power Allocation Scheme for Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces-Aided Wireless Systems. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 92263–92275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yuan, Y. Secrecy outage probability analysis for RIS-assisted NOMA systems. Electron. Lett. 2020, 56, 1254–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almohamad, A.; Al-Kababji, A.; Tahir, A.; Khattab, T.; Hasna, M. On Optimizing the Secrecy Performance of RIS-Assisted Cooperative Networks. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 92nd Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2020-Fall), Virtual, 18 November–16 December 2020; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Trigui, I.; Ajib, W.; Zhu, W.-P. Secrecy Outage Probability and Average Rate of RIS-Aided Communications Using Quantized Phases. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2021, 25, 1820–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Chu, Z.; Zhou, F.; Zhu, Z. Simultaneous Transmission and Reflection Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface Assisted Secrecy MISO Networks. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2021, 25, 3498–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, R.; Liu, Y.; Mu, X.; Chen, Y.; Song, L. AI Empowered RIS-Assisted NOMA Networks: Deep Learning or Reinforcement Learning? IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2022, 40, 182–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezer, A.; Altan, A. Detection of solder paste defects with an optimization based deep learning model using image processing techniques. Solder. Surf. Mt. Technol. 2021, 33, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Al-Dhahir, N. Machine Learning for User Partitioning and Phase Shifters Design in RIS-Aided NOMA Networks. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2021, 69, 7414–7428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Wei, X. Distributed Machine Learning Based Downlink Channel Estimation for RIS Assisted Wireless Communications. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2022, 70, 4900–4909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, C.; Jia, F.; Ge, J.; Gong, F. Improving Physical Layer Security for Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface Aided NOMA 6G Networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2021, 70, 4451–4463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Hou, T.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhong, C. A Novel Design of RIS for Enhancing the Physical Layer Security for RIS-Aided NOMA Networks. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2021, 10, 2398–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y. Machine Learning Empowered Trajectory and Passive Beamforming Design in UAV-RIS Wireless Networks. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2021, 39, 2042–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.; Liu, Y.; Kang, S.; Nallanathan, A.; Ding, Z. Exploiting Full/Half-Duplex User Relaying in NOMA Systems. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2018, 66, 560–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Wang, G.; Atapattu, S.; Tsiftsis, T.A.; Tellambura, C. Is Backscatter Link Stronger than Direct Link in Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface-Assisted System? IEEE Commun. Lett. 2020, 24, 1342–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Yan, S.; Zhou, X.; Chen, R.; Sun, J. Intelligent Reflecting Surface (IRS)-Aided Covert Communication With Warden’s Statistical CSI. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2021, 10, 1449–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkhelifa, F.; Tall, A.; Rezki, Z.; Alouini, M. On the low SNR capacity of MIMO fading channels with imperfect channel state information. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2014, 62, 1921–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, Z.; Chen, G.; Lambotharan, S.; Chambers, J.A. A Hybrid Relay and Intelligent Reflecting Surface Network and Its Ergodic Performance Analysis. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2020, 9, 1653–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yang, L.; Alouini, M. Physical Layer Security for Cooperative NOMA Systems. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2018, 67, 4645–4649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yang, J.; Xie, W.; Hasna, M.O.; Tsiftsis, T.; Renzo, M.D. Secrecy Performance Analysis of RIS-Aided Wireless Communication Systems. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 12296–12300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Zeng, Y.; Jin, S.; Zhang, R. Aerial intelligent reflecting surface: Joint placement and passive beamforming design with 3D beam flattening. IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun. 2021, 20, 4128–4143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, T.N.; Kaddoum, G.; Nguyen, T.L.; da Costa, D.B.; Haas, Z.J. Aerial Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface-Aided Wireless Communication Systems. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 32nd Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications (PIMRC), Helsinki, Finland, 13–16 September 2021; pp. 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).