Improved Active Disturbance Rejection Control Strategy for LCL-Type Grid-Connected Inverters Based on the Backstepping Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Preliminaries and Problem Description
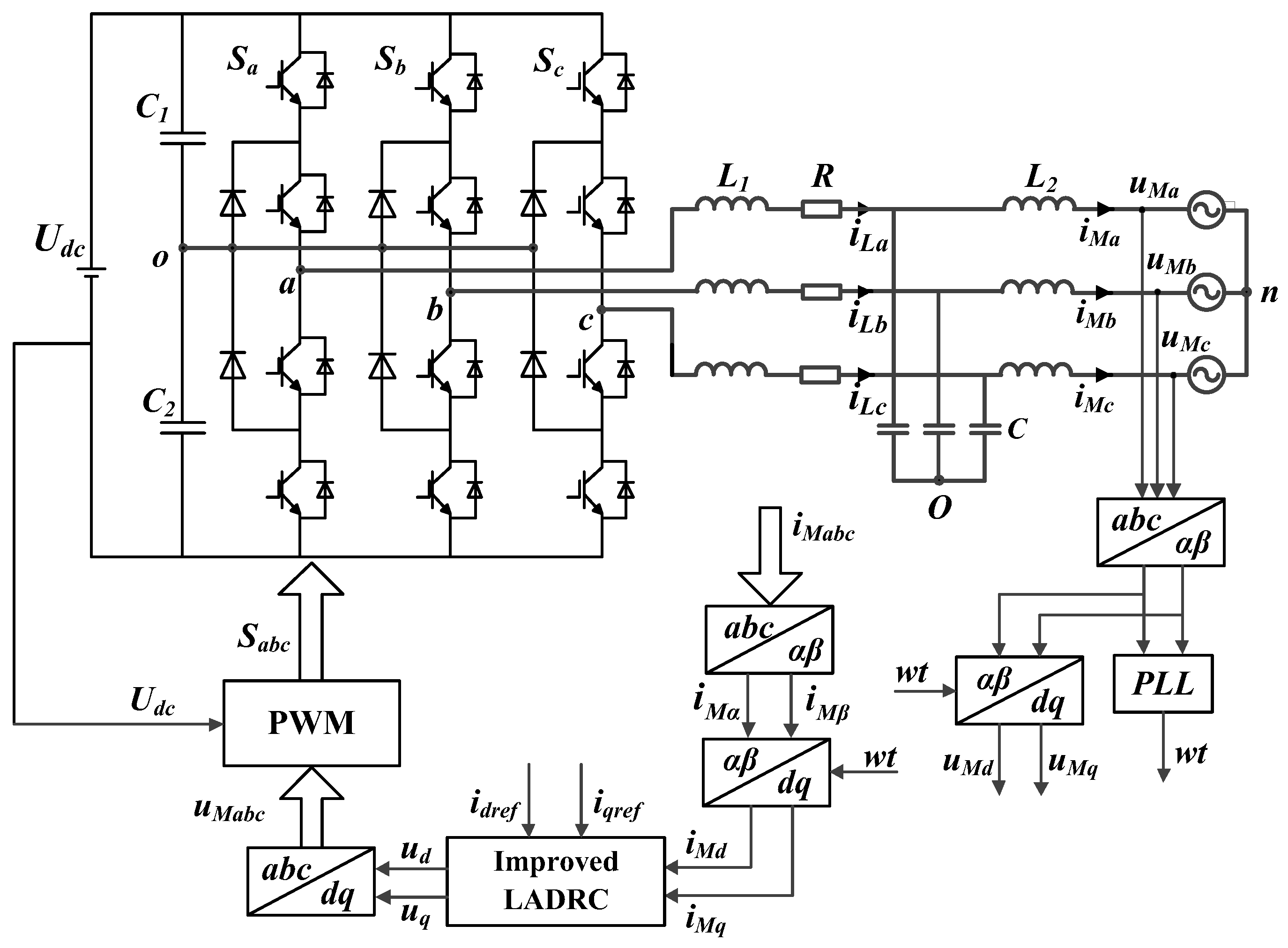
2.1. Test System Description
2.2. Constructing the LCL Inverter State Equation
2.3. Design of Second-Order LESO
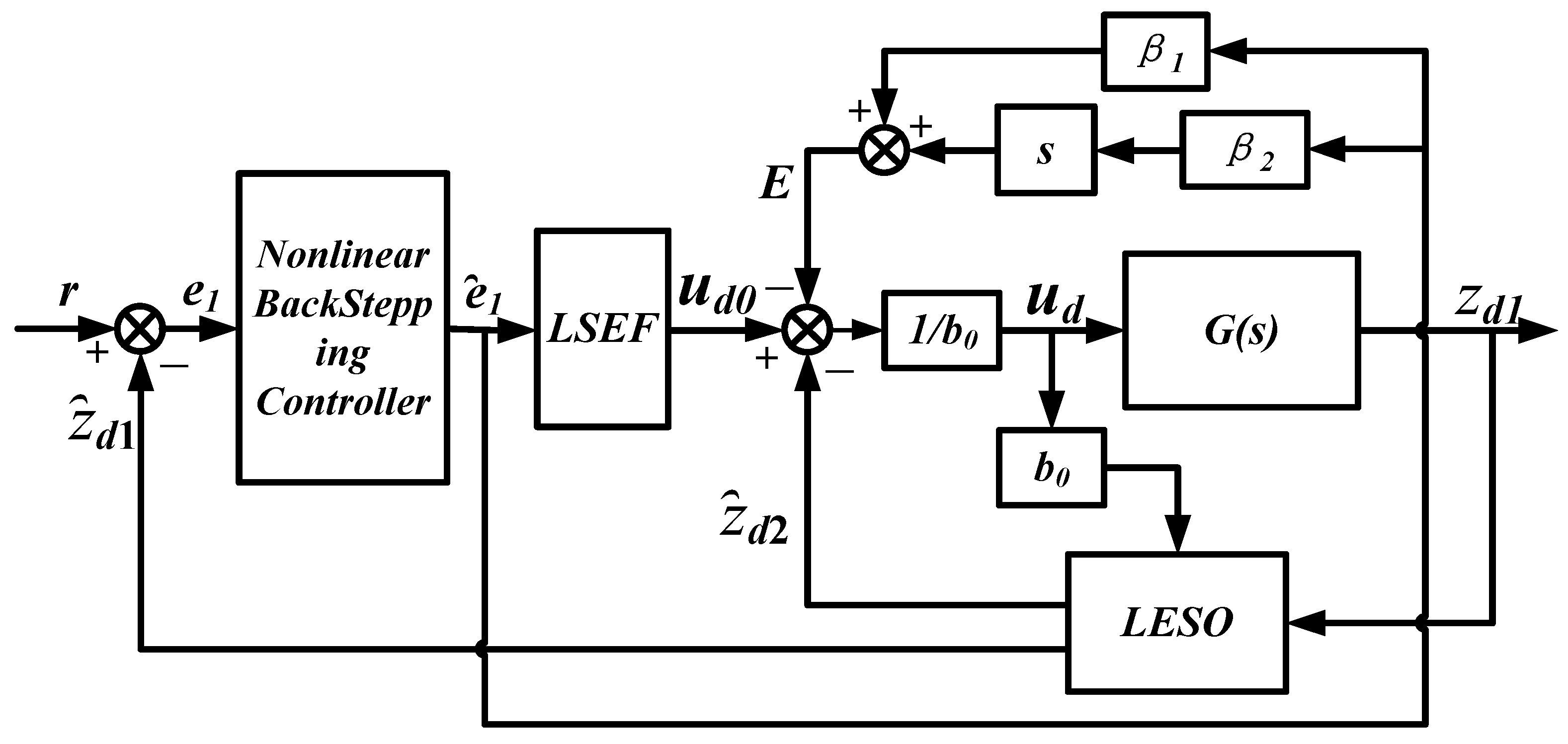
2.4. Improved Control Law Design Based on LESO Estimation Error Compensation
2.5. Backstepping Outer-Loop Control Law Design
2.6. Parameter Design
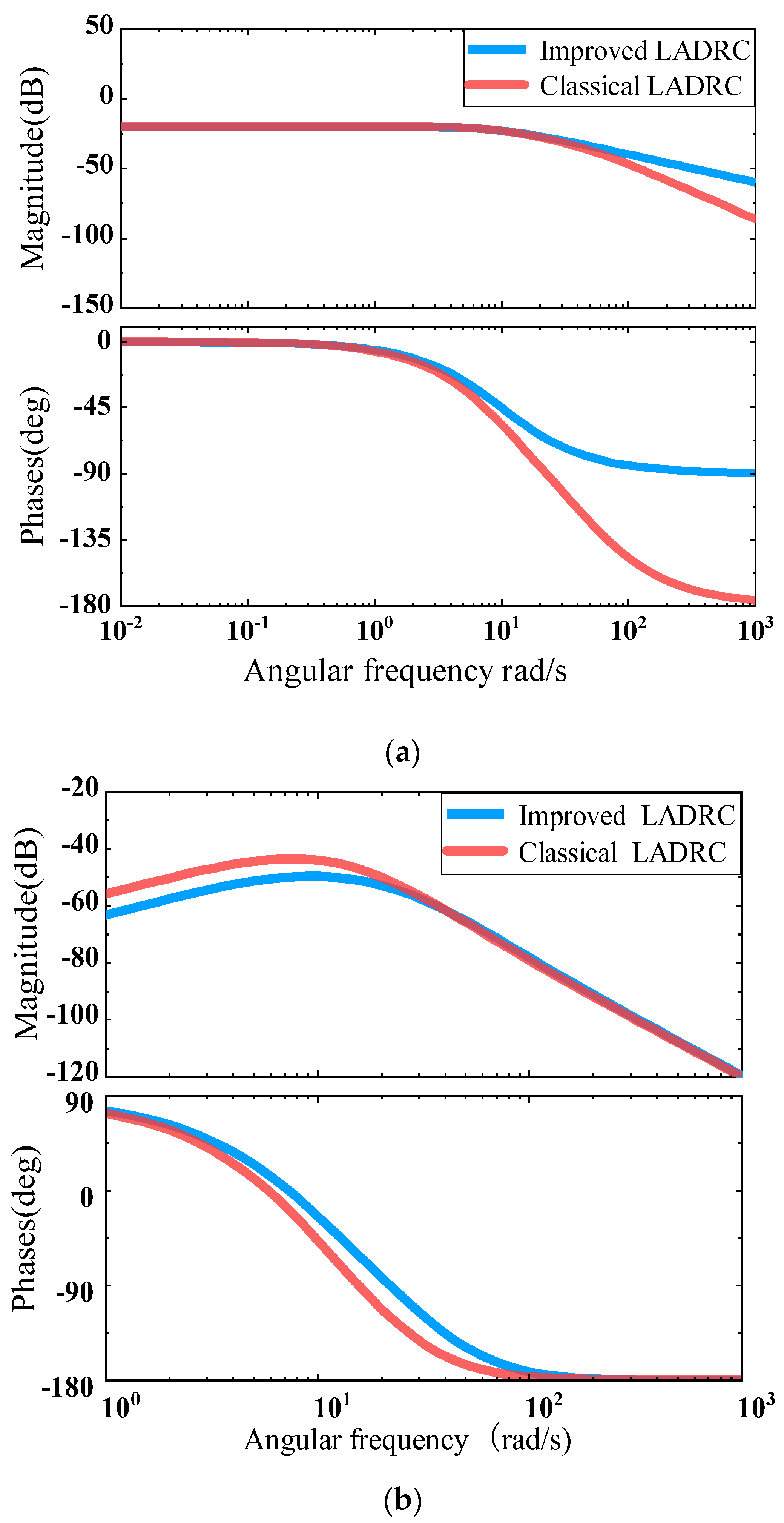
3. Performance Analysis of the BS-LADRC
4. Simulation Verification
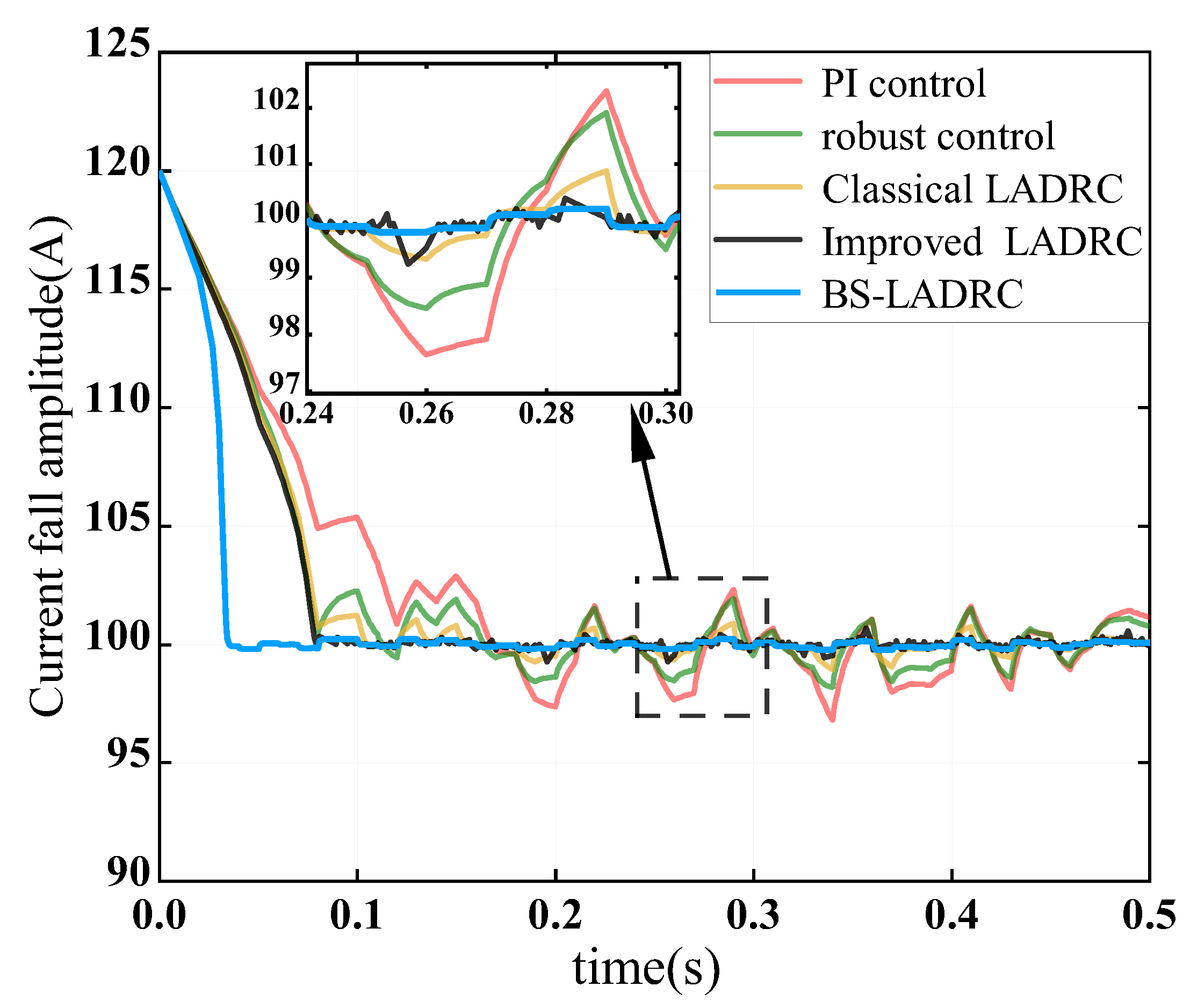
4.1. Verifying the Controlled Antidisturbance in Disturbances
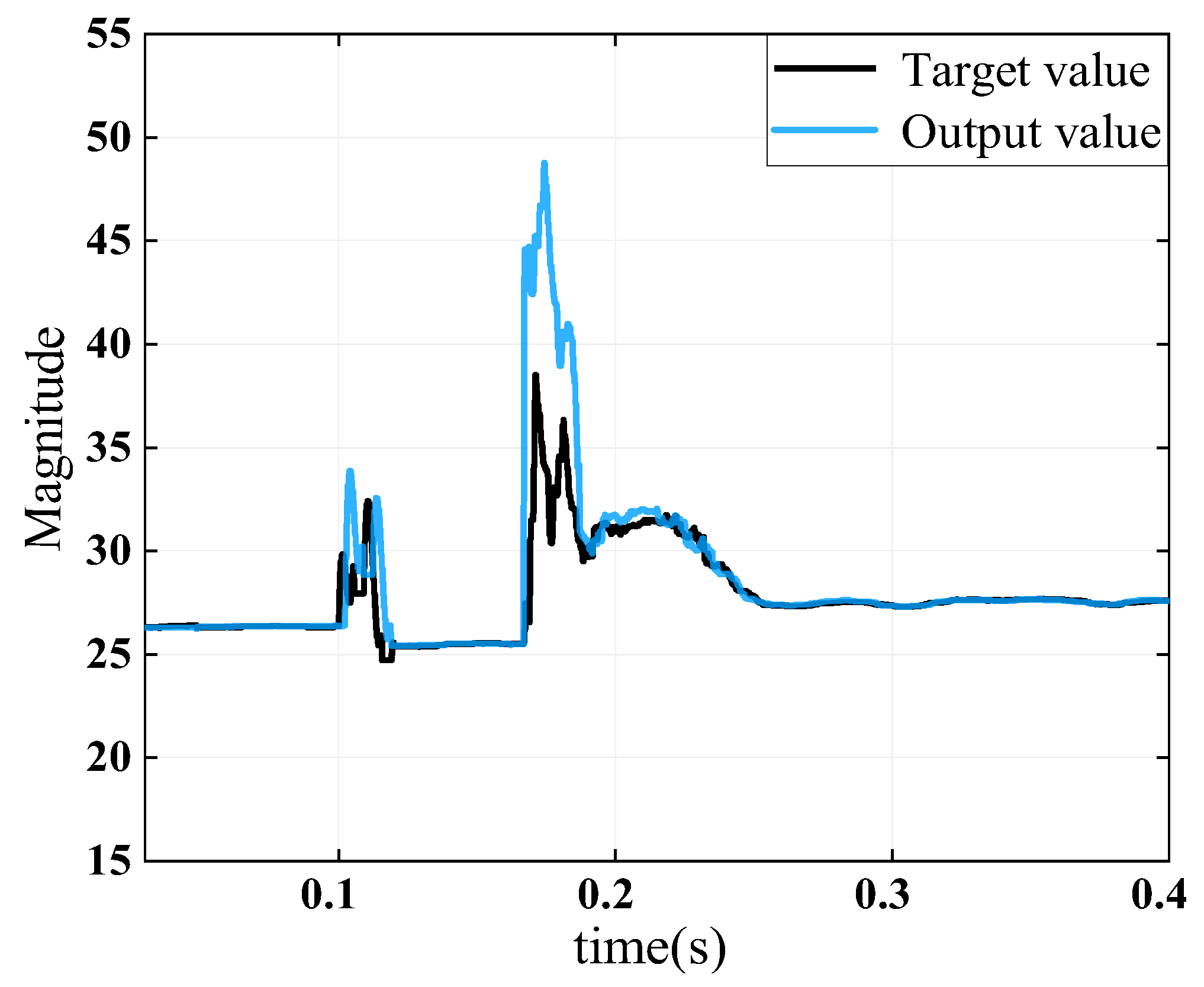
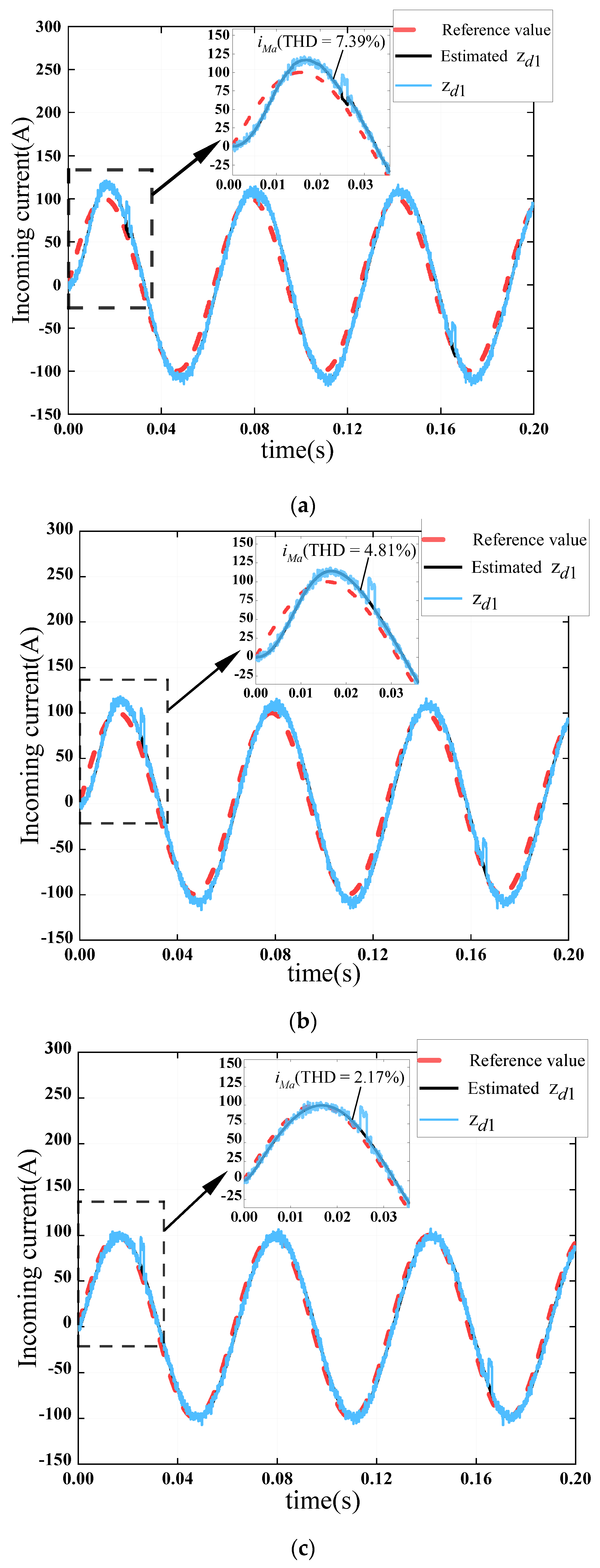
4.2. Verifying the Transient Tracking Performance of Current Disturbances
4.3. Verification of Grid-Side Power-Glitch-Suppression Harmonic Performance
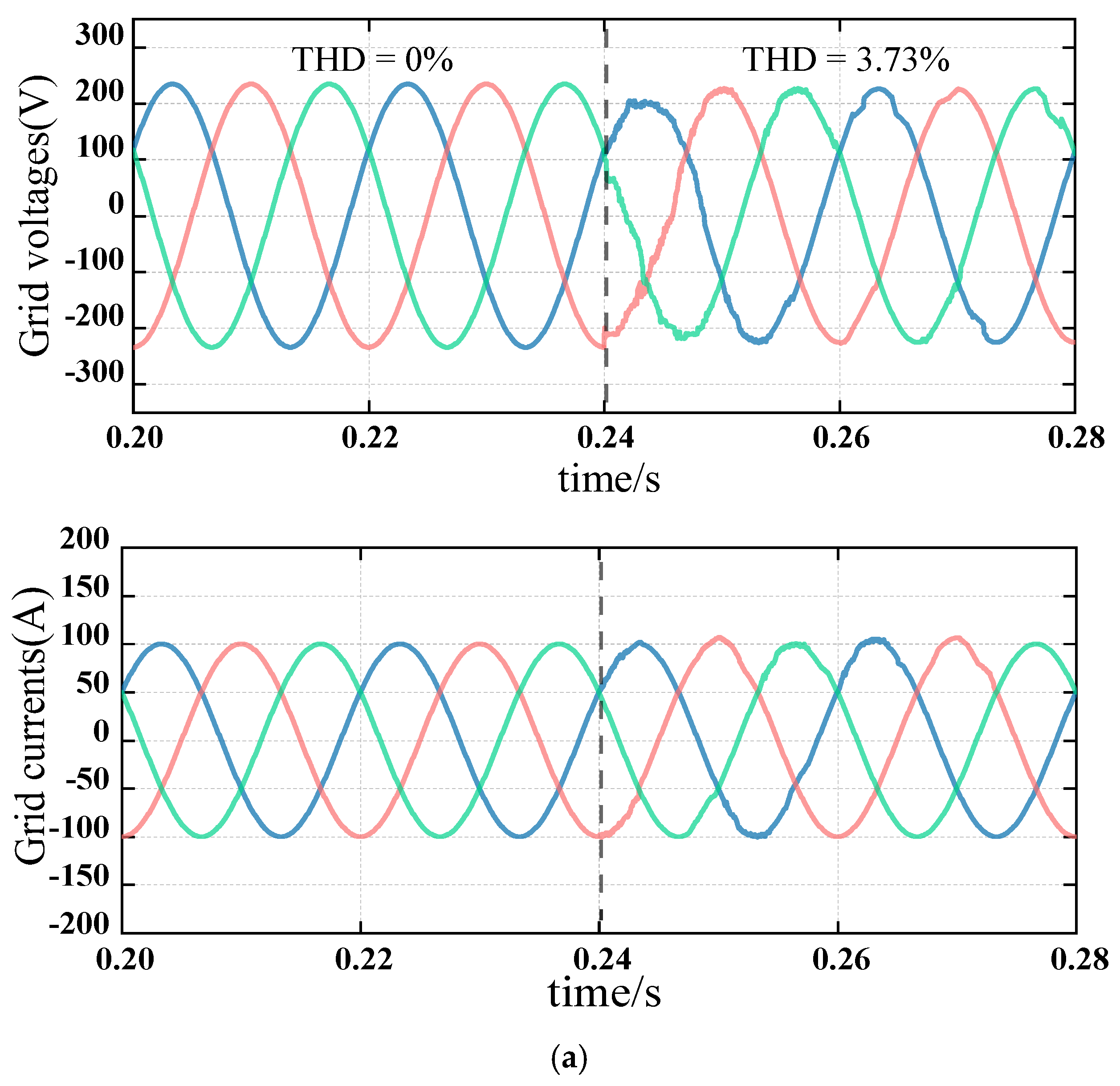
4.4. Verification of Grid-Side Voltage Harmonic Distortion Rate’s Abrupt Harmonic Suppression Performance
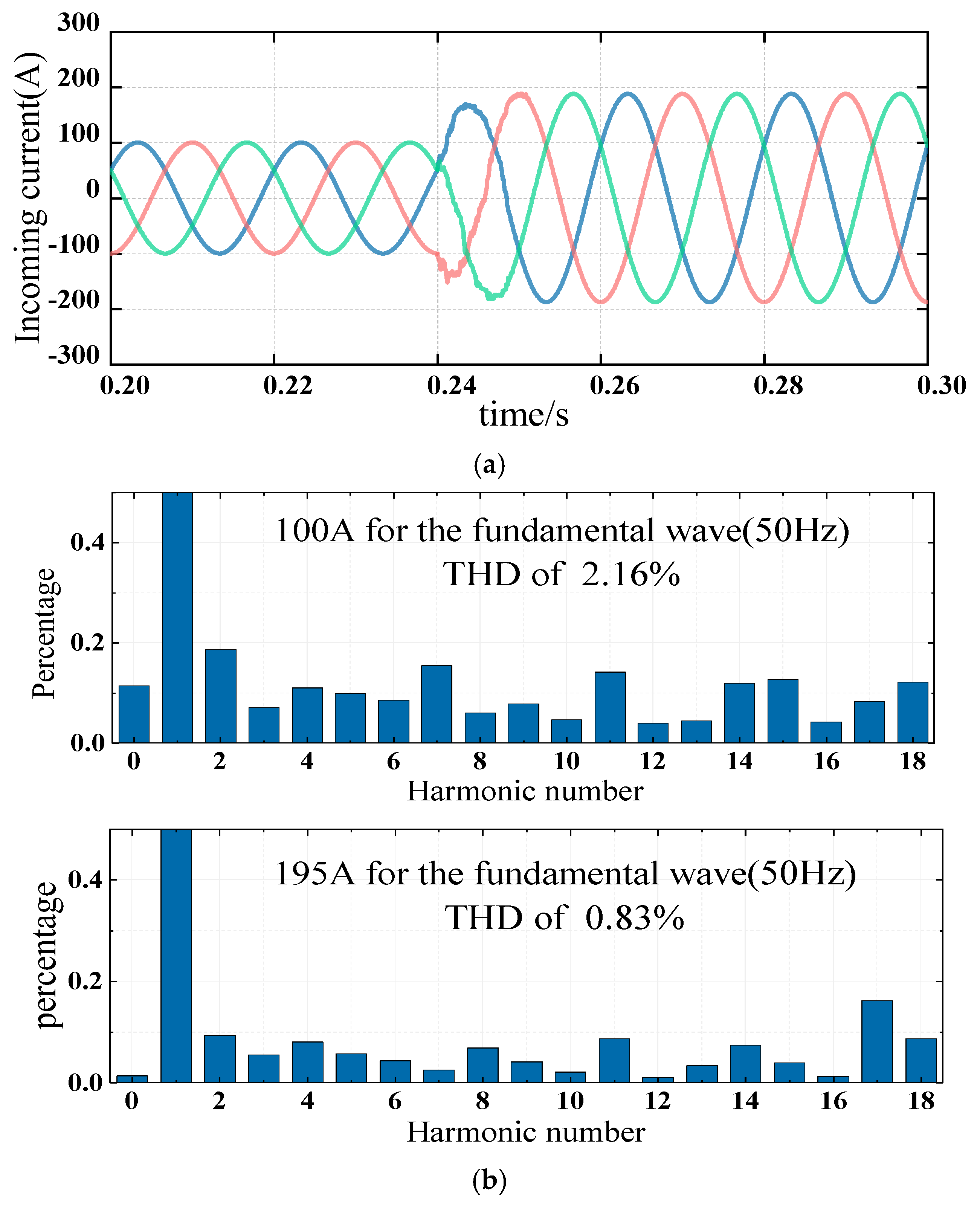
4.5. Harmonic Suppression Performance of Nonlinear Load Surges in the Power Grid
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| dw | Unknown perturbation |
| e1 | iMd and the error of its estimate |
| e2 | fab and the error of its estimate |
| E | Real need for compensation |
| fab | Total disturbance inside and outside the system |
| iLa, iLb, iLc | Three-phase inverter side a, b, c phase current |
| iMa, iMb, iMc | Grid-connected side a, b, c phase load current |
| iMd, iMq | Grid-side current under the d-axis and q-axis components |
| ua, ub, uc | Phase voltage of the inverter circuit from the center of the three bridge arms to the load |
| ud, uq | Inverter-side voltage under the d-axis and q-axis components |
| uMa, uMb, uMc | Grid-connected side a, b, c phase load voltage |
| uMd, uMq | Grid-side voltage under the d-axis and q-axis components |
| Udc | DC busbar voltage |
| Estimated value of iMd | |
| Estimated value of fab | |
| δ1 | Error of e1 with its estimated value |
References
- Wang, S.; Lv, Z. Research on repetitive control method in LCL grid connected inverter. Chin. J. Electr. Eng. 2010, 30, 69–75. [Google Scholar]
- Eren, S.; Pahlevaninezhad, M.; Bakhshai, A. Composite Nonlinear Feedback Control and Stability Analysis of a Grid-Connected Voltage Source Inverter with LCL Filter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 5059–5074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Xie, S.; Zhang, B. Review on current control of LCL filter grid connected inverter in distributed generation system. Chin. J. Electr. Eng. 2015, 35, 4153–4166. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, K.; Sun, P.; Wang, L.; Zhou, L.; Xue, T.; Du, X.; Li, Z. High robustness weighted average current control strategy for LCL grid connected inverter in weak current network. Chin. J. Electr. Eng. 2020, 40, 3592–3602. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Jiang, Q.; Hong, L.; Zhang, C.; Wei, Y. A novel phase-locked loop based on frequency detector and initial phase angle detector. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2013, 28, 4538–4549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Chen, Z.; Tang, W.; Zhu, J. Control strategy of LCL grid connected inverter considering the influence of phase locked loop under weak current network. Power Syst. Prot. Control 2022, 50, 178–187. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, N.; Tang, H.; Yao, C. A Systematic Method for Designing a PR Controller and Active Damping of the LCL Filter for Single-Phase Grid-Connected PV Inverters. Energies 2014, 7, 3934–3954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Loh, P.C.; Wang, P. Generalized Design of High Performance Shunt Active Power Filter with Output LCL Filter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 59, 1443–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Jin, N.; Li, Y.; Dai, L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, K. Model predictive control of grid connected inverter without AC voltage sensor based on sliding mode observer. Power Autom. Equip. 2020, 40, 108–114. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, C.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, K. Deadbeat repetitive control of three-phase four leg grid connected inverter. Power Syst. Autom. 2018, 42, 142–148. [Google Scholar]
- Young, H.A.; Marin, V.A.; Pesce, C. Simple Finite-Control-Set Model Predictive Control of Grid-Forming Inverters with LCL Filters. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 81246–81256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.; Liu, S.; Liang, G.; An, X. Research on Microgrid inverter control method based on model predictive control. Power Syst. Prot. Control 2019, 47, 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J. From PID technology to “auto disturbance rejection control” technology. Control Eng. 2002, 3, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, B.; Gao, Z. A DSP-based active disturbance rejection control design for a 1-kW H-bridge DC-DC power converter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2005, 52, 1271–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, Z. Research on the idea of active disturbance rejection control. Control Theory Appl. 2013, 30, 1498–1510. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Zeng, J.; Huang, Z. Application of linear active disturbance rejection technology in grid connected current control and active damping of LCL inverter. Power Grid Technol. 2019, 43, 1378–1386. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, D.; Ma, X.; Zeng, Q.; Qiu, X. Research on frequency band characteristics and parameter allocation of linear ADRC for second order systems. Control Theory Appl. 2013, 30, 1630–1640. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Zeng, J.; Ma, W.; Huang, Z. Voltage control of microgrid inverter based on improved second-order linear active disturbance rejection technology. Power Syst. Autom. 2019, 43, 146–153. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, R.; Han, W.; Tan, W. Applicability and tuning of linear active disturbance rejection control. Control Theory Appl. 2018, 35, 1654–1662. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.; Xu, M.; Sun, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, L.; Tao, L. Grid connection control of wind power system combining correction link and LADRC. J. Power Syst. Autom. 2020, 32, 120–127. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, C.; Tan, W. Parameter adjustment of linear ADRC based on high order controller design. Control Theory Appl. 2017, 34, 265–272. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Zeng, J.; Huang, J.; Feng, J.; Xiong, T. Time frequency voltage control strategy of microgrid inverter based on linear active disturbance rejection control. Power Syst. Autom. 2020, 44, 145–154. [Google Scholar]
- Chao, Z.; Ji, Z.; Gao, Y. Design and performance analysis of self-anti-disturbance controller based on minimum beat observer. Control Theory Appl. 2015, 32, 29–34. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, X.; Lou, G.; Chen, L.; Li, Q.; Liu, D.; Gu, W. Smooth switching control strategy of micro grid based on linear active disturbance rejection. Power Grid Technol. 2017, 41, 3824–3831. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Liu, W.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wang, D.; Qiu, Y. System analysis of three-phase four wire shunt active power filter based on LADRC. High Volt. Technol. 2016, 42, 1290–1299. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, M.; Liao, P.; Cai, Y.; Lei, E.; He, Y. First order ADRC of LCL grid connected inverter and control parameter tuning method based on particle swarm optimization. Power Autom. Equip. 2021, 41, 174–182. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Wei, Z.; Kong, W.; Pan, L.; Liu, W. Parameter tuning of linear ADRC for PMSM Servo System. Control Theory Appl. 2022, 39, 165–178. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Q.; Huang, S.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, T.; Ma, M.; Zou, Y.; Kuang, J. Variable structure self-anti-disturbance control of PWM rectifiers under asymmetric voltage. J. Electr. Mach. Control 2014, 18, 50–55. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J. Adaptive Backstepping Control of Uncertain Systems. Electron. Opt. Control 2010, 11, 1115–1119. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Q.; Richter, H.; Gao, Z. Active Disturbance Rejection Control for Piezoelectric Beam. Asian J. Control 2014, 16, 1612–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Liao, P.; Cai, Y.; Lei, E.; He, Y. Active disturbance rejection control strategy of LCL grid connected inverter. High Volt. Technol. 2021, 47, 2223–2231. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, X. Improved LADRC control of inverter stage of solid-state transformer based on fuzzy adaptive. J. Power Syst. Autom. 2022, 34, 123–131. [Google Scholar]




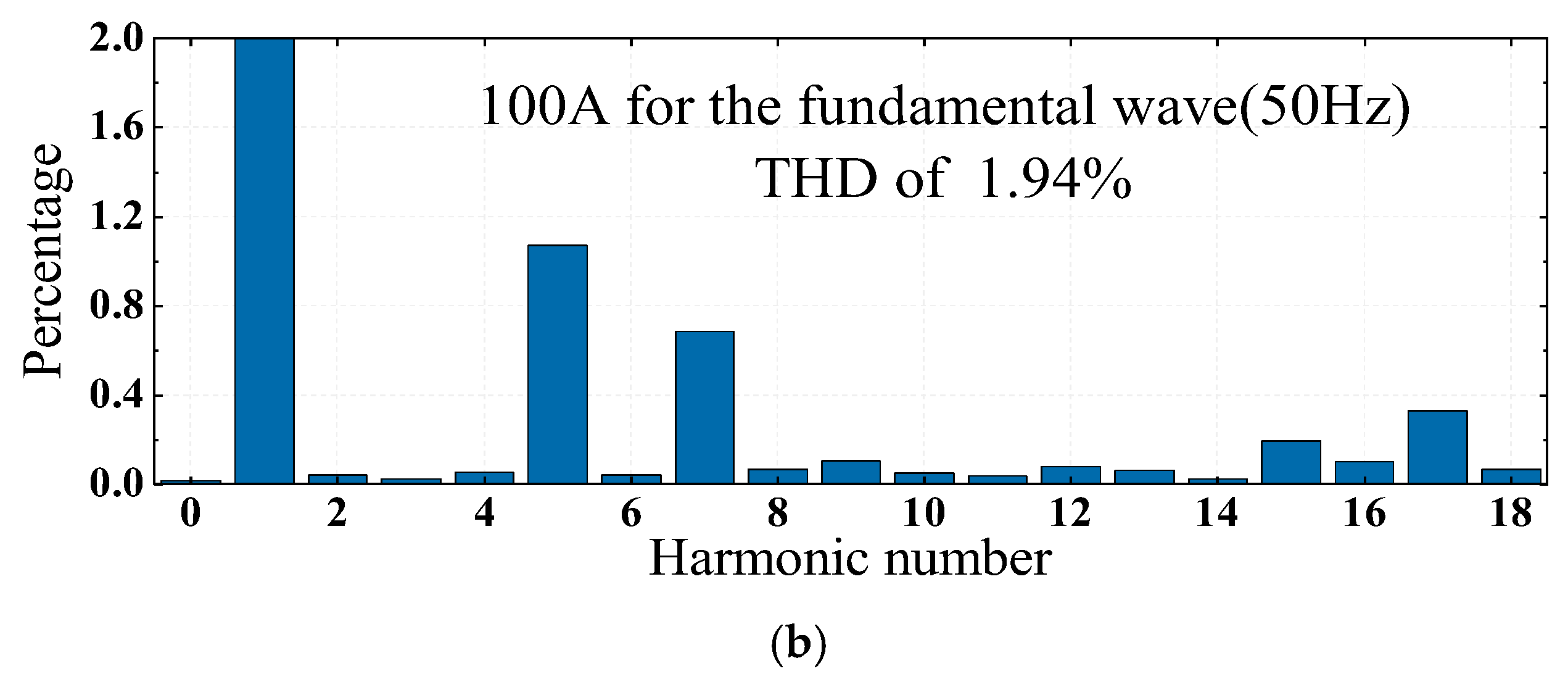
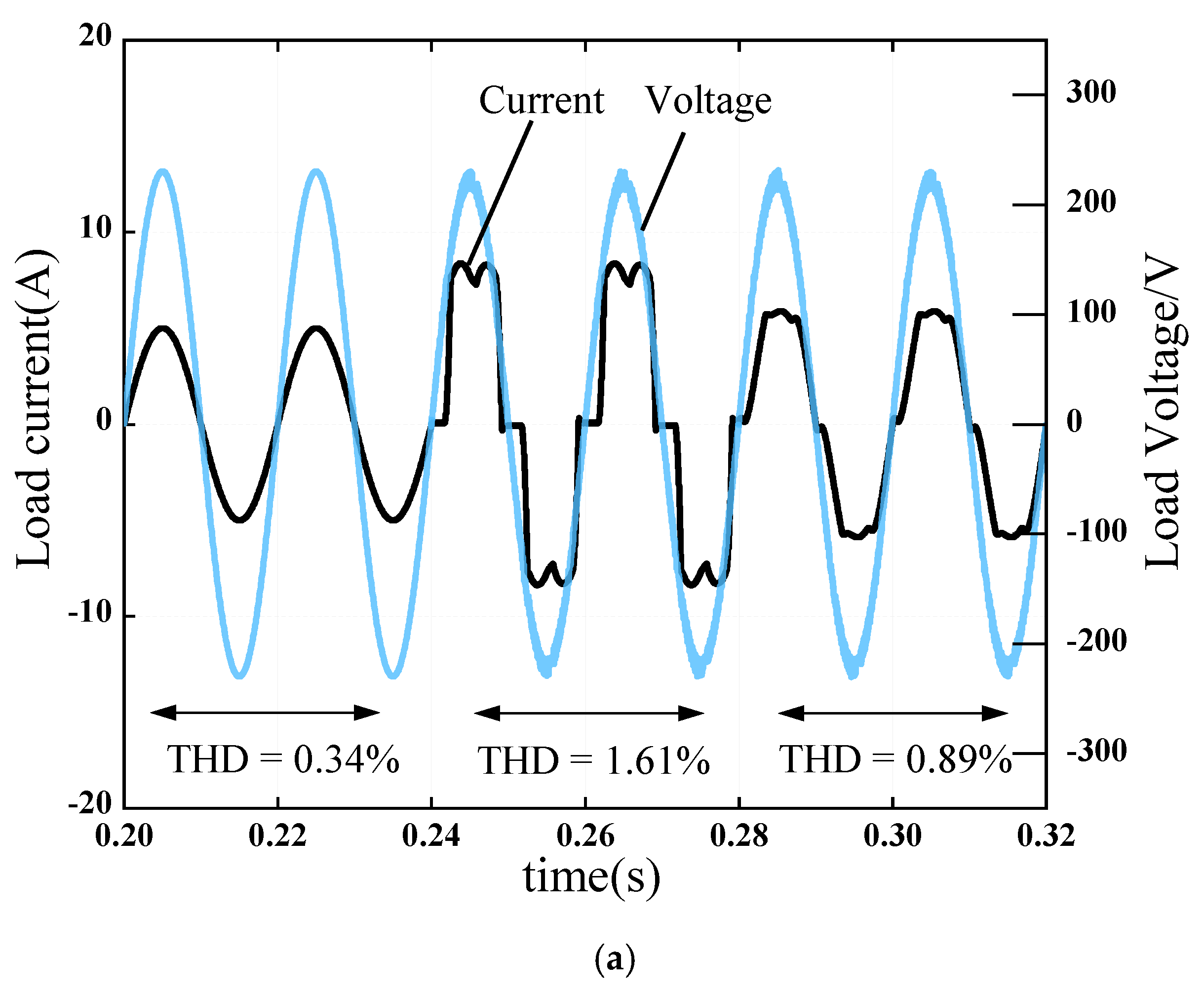
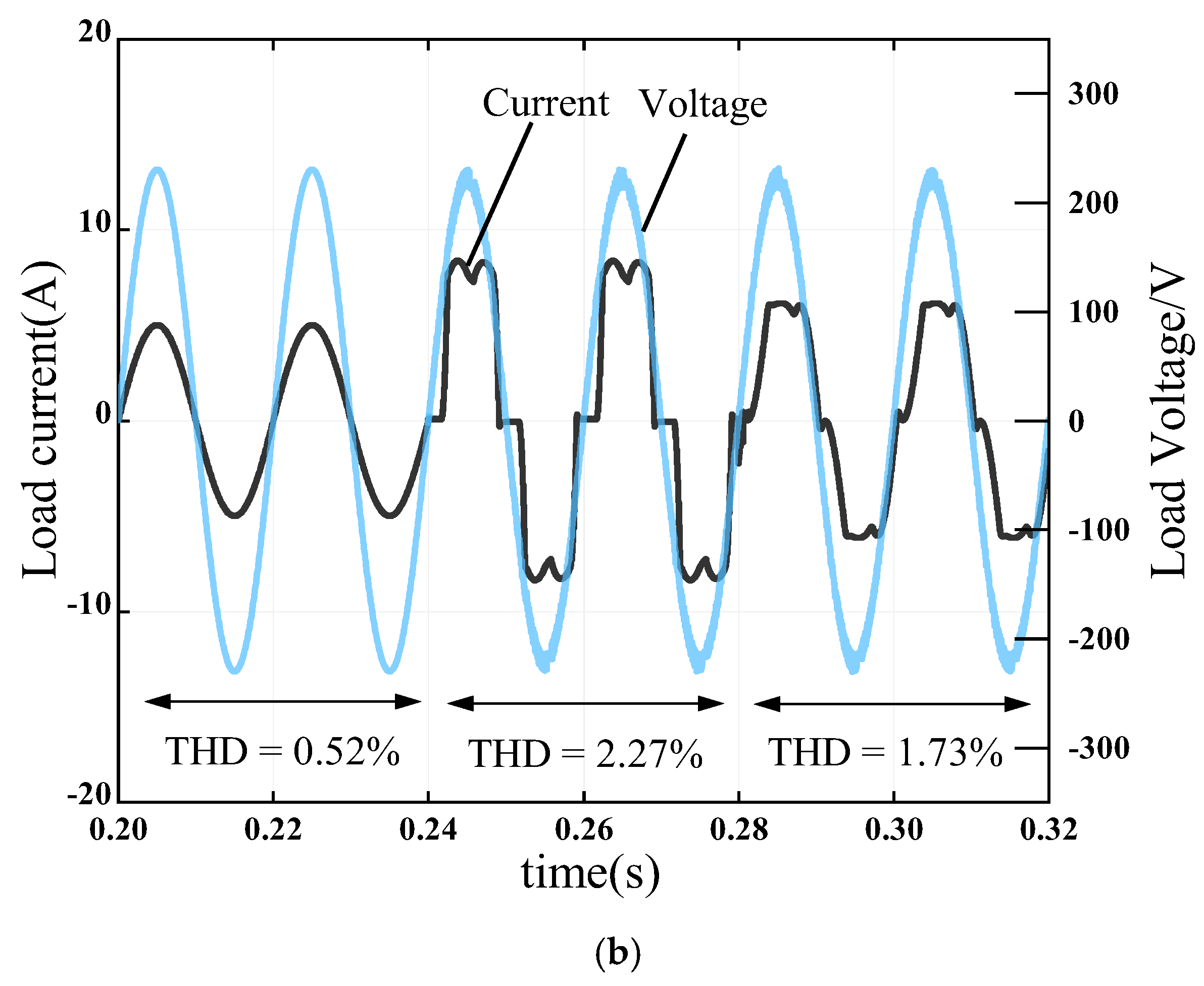
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| DC-side voltage Udc/V | 600 |
| Power P/kW | 120 |
| RMS grid voltage uM/V | 280 |
| Resonant frequency f/Hz | 900 |
| Inverter-side filter inductor L1/mH | 0.6 |
| Switching frequency fsw/kHz | 3.2 |
| Grid-side filter inductor L2/mH | 0.3 |
| Filter capacitors C/μF | 160 |
| Control gain b0 | 625 |
| Observer bandwidth ω0 | 1000 |
| Controller initial bandwidth ωc | 25 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Ding, W. Improved Active Disturbance Rejection Control Strategy for LCL-Type Grid-Connected Inverters Based on the Backstepping Method. Electronics 2022, 11, 2237. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11142237
Zhang Z, Ding W. Improved Active Disturbance Rejection Control Strategy for LCL-Type Grid-Connected Inverters Based on the Backstepping Method. Electronics. 2022; 11(14):2237. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11142237
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zhiru, and Wenfang Ding. 2022. "Improved Active Disturbance Rejection Control Strategy for LCL-Type Grid-Connected Inverters Based on the Backstepping Method" Electronics 11, no. 14: 2237. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11142237
APA StyleZhang, Z., & Ding, W. (2022). Improved Active Disturbance Rejection Control Strategy for LCL-Type Grid-Connected Inverters Based on the Backstepping Method. Electronics, 11(14), 2237. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11142237






