Abstract
This paper aims at realizing upper limb rehabilitation training by using an fNIRS-BCI system. This article mainly focuses on the analysis and research of the cerebral blood oxygen signal in the system, and gradually extends the analysis and recognition method of the movement intention in the cerebral blood oxygen signal to the actual brain-computer interface system. Fifty subjects completed four upper limb movement paradigms: Lifting-up, putting down, pulling back, and pushing forward. Then, their near-infrared data and movement trigger signals were collected. In terms of the recognition algorithm for detecting the initial intention of upper limb movements, gradient boosting tree (GBDT) and random forest (RF) were selected for classification experiments. Finally, RF classifier with better comprehensive indicators was selected as the final classification algorithm. The best offline recognition rate was 94.4% (151/160). The ReliefF algorithm based on distance measurement and the genetic algorithm proposed in the genetic theory were used to select features. In terms of upper limb motion state recognition algorithms, logistic regression (LR), support vector machine (SVM), naive Bayes (NB), and linear discriminant analysis (LDA) were selected for experiments. Kappa coefficient was used as the classification index to evaluate the performance of the classifier. Finally, SVM classification got the best performance, and the four-class recognition accuracy rate was 84.4%. The results show that RF and SVM can achieve high recognition accuracy in motion intentions and the upper limb rehabilitation system designed in this paper has great application significance.
1. Introduction
The upper extremity is an important part of the human body. Research has found that 80% of severe stroke patients have upper extremity motor dysfunction. It is a relatively feasible and efficient treatment method to perform rehabilitation training by using rehabilitation robot equipment to drive patients. However, in the traditional rehabilitation robot training scheme, the robot usually assists the patient to complete the training action after the specific training process is set [1]. The form of this program is very simple, and patients may feel negative and slack during the training process due to boredom.
Many previous studies have shown that the process of autonomous training by patients is very important. Compared with passive exercise training, the active willingness of patients to participate in training can better promote neurocortical reconstruction and motor function recovery [2]. As a new human-computer interaction method, the brain-computer interface (BCI) can bypass the function of nerve transmission channels and muscle parts, and directly establish information communication channels between the brain and the external environment, and control external devices. The application of BCI in the field of rehabilitation has helped a lot of patients with limb dysfunction to carry out rehabilitation training and accelerate their rehabilitation process. Therefore, in the field of rehabilitation medicine, the study of feasible BCI technology has very important social significance [3,4,5].
At present, many BCI researchers at home and abroad have focused on applying BCI technology to the field of upper limb motor function rehabilitation, and have obtained excellent research results. Anirban of the University of Essex and his research partners successfully developed a hybrid BCI device to control the exoskeleton of the hand in order to overcome the problem of low recognition accuracy in BCI system. The system combines EEG and EMG signals. After the grasping intention of the subject is successfully detected, the exoskeleton will perform finger flexion and extension. Finally, the recognition accuracy of the system reached (90.00 ± 4.86)%, significantly improving the performance of BCI system [6]. Zhai Wenwen hoped to improve the life independence of patients with severe motor dysfunction through BCI technology. The upper-limb movement-related instructions can control the robotic arm to complete the rehabilitation training of the shoulder, wrist and elbow. The recognition accuracy of the system is as high as 93% [7]. Yoshiyuki Suzuki studied the effects of human corticospinal excitability on motor tasks in the process of imagining or observing the upper limbs. The experiments have shown that kinesthetic MI, including visualizing and observing the virtual hand, can cause phase-dependent muscle-specific corticospinal stimulation of wrist muscles that match those in the actual hand [8]. Although they have achieved remarkable research results in the field of sports rehabilitation technology, there are still many key technologies that need to be improved. For example, the recognition accuracy of multi-classification tasks is low, real-time performance needs to be improved, and it is difficult for users to autonomously control the pace of rehabilitation training.
This paper proposes a set of upper limb rehabilitation training robot system based on user spontaneous movement fNIRS-BCI. Four upper limb movement paradigms are designed: Lifting up, putting down, pulling back, and pushing forward. The start of each task and the rest time were all controlled by the subjects autonomously without any prompts from the outside world [9]. A variety of classifiers such as RF and SVM were selected for evaluation, and a high accuracy rate was achieved. Furthermore, the most suitable multiclass recognition algorithm was selected.
2. Experimental Design
2.1. Participants
A total of 50 volunteers were recruited for this experiment. Among them, 29 were male volunteers and 21 were female volunteers. The ratio of male to female was approximately 3:2. All volunteers were right-handed, in good health, and had no history of mental illness or cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. In addition, all volunteers participated in the experiment for the first time and only once. Before the experiment, all volunteers were informed of the experiment details and signed the informed consent form of the experiment.
2.2. Experiment Paradigm
In order to increase the controllability and practicability of upper-limb auxiliary equipment, four common upper-limb movement paradigms in daily life designed in daily life: Lifting up, putting down, pulling back and pushing forward. During the experiment, the near-infrared data of the subjects in different motion states were collected to provide a supervised learning data set for subsequent research on motion intention recognition. The experimental process is shown in Figure 1. Tasks 1, 2, 3, and 4 in the figure represent the four action paradigms of lifting up, putting down, pulling back, and pushing forward, respectively.
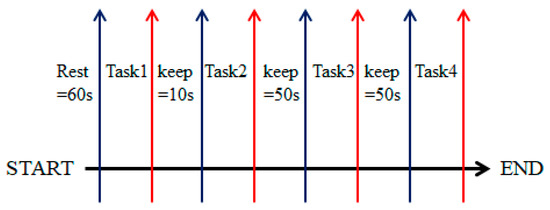
Figure 1.
The diagram of the experiment.
During the experiment, the subjects should keep their scalp clean and keep their hair dry before the experiment. It should be noted that the subjects need to rest for about 60 s before the start of the experiment. The rest time between lifting and lowering actions was 10 s, and the rest time between other actions was about 50 s. The start of each task and the rest time were all controlled by the subjects autonomously without any prompts from the outside world. The specific paradigm of the experiment is shown in Figure 2. Figure 2a–d represents the four action paradigms of lifting up, putting down, pulling back, and pushing forward, respectively.
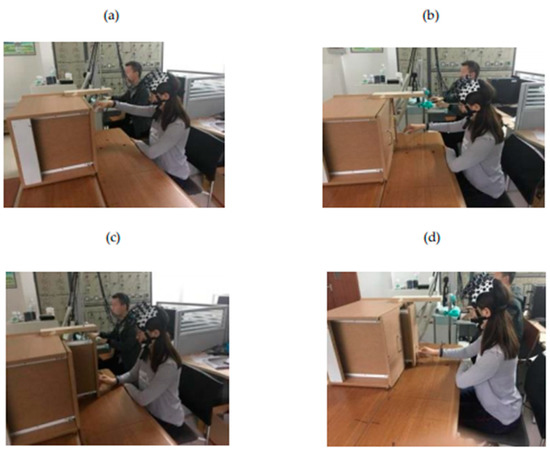
Figure 2.
The experimental diagram of upper limb movement. (a) Lifting up, (b) putting down, (c) pulling back, and (d) pushing forward.
2.3. Cortical Regions
The FOIRE-3000 near-infrared acquisition system of Shimadzu Corporation was used as a brain signal acquisition device to record the changes in the concentration of oxygen, deoxygenation, and total oxygen hemoglobin in the experiment [10]. Because this experiment emphasized the spontaneous movement intention of the subjects, task execution and rest time were controlled by the subjects spontaneously, we chose to use continuous mode to measure the cerebral hemoglobin information during the experiment. The equipment sampling time was 130 ms.
This study used the internationally recognized 10–20 system as the positioning standard to locate brain functional areas. The experiment designed a 4 × 4 headgear layout to detect the above key functional areas. There were a total of 24 effective test channels. The overall headgear layout is shown in Figure 3. In the layout, the Cz point was used as a reference point for the relative position, and the distance between Cz and the center of the 23rd channel was 1.5 cm. The entire layout can cover four brain functional areas: PFC, SMA, PMC (PMC = PMCL + PMCR), PMCR, and M1 brain area function [11].
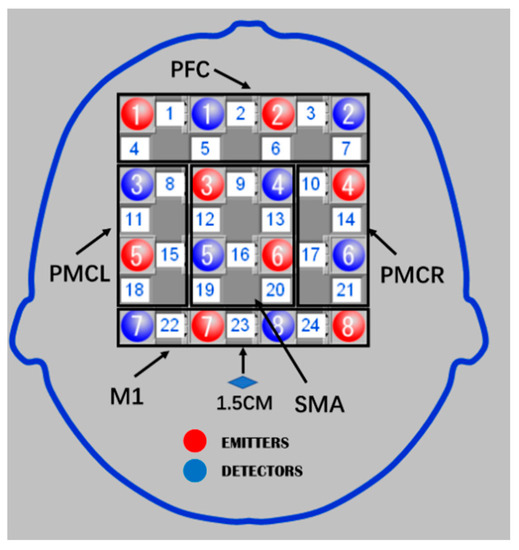
Figure 3.
The schematic diagram of 4 × 4 headgear layout.
3. Data Analysis
3.1. Data Preprocessing
The interference components in the near-infrared signal mainly include baseline drift, physiological interference, and high-frequency noise. Mathematical morphology has a very strict data theoretical basis, and research shows that this method achieved good results in nonlinear signal processing. Corrosion calculation and expansion calculation were the basic calculation methods of this method. Based on the corrosion expansion calculation, two different morphological calculations were used for the combination of opening and closing. Among them, the open operation used the first expansion and then the corrosion operation method to eliminate the peak of the signal to filter the peak noise above the signal, and the closed operation used the first erosion and then the expansion operation to fill the signal trough to smooth or suppress the signal valley noise. We combined the on-off filter to eliminate both positive and negative impulse noises in the signal to avoid unidirectional deviation of the filtered signal [12,13].
3.2. Data Preprocessing
3.2.1. Action Initiation Intent Feature Extraction
In order to accurately and quickly detect the time point of the subject’s transition from resting to exercise, the selected feature has the ability to detect sudden changes and singular signals. Near-infrared signals are non-stationary and nonlinear. Among a variety of feature categories based on biological information to distinguish resting/exercise status, Teager–Kaiser energy operator and slope value were used in many initial detection studies of biological signals [14,15]. By calculating the Teager–Kaiser energy operator at each time point and the blood oxygen slope characteristics at each time point, the instantaneous changes attributed to the signal at each time point were obtained, and the waveform changes of the measured signal were tracked in real time.
3.2.2. Motion State Feature Extraction
In the exercise state classification task, the goal was to recognize the exercise intention before the real action. Therefore, it was necessary to extract the data of the real pre-exercise time period for analysis. The training time period selection method is shown in Figure 4. Took the starting point of the real action as the reference point (0), took the signal from −3 s to 0 s as the training time period, and applied the sliding time window method. The length of the window was set to 20. The overlapping length of two adjacent sliding windows was three sampling points. Then, we calculated the features within the time window to obtain the feature data set.

Figure 4.
The schematic diagram of 4 × 4 headgear layout.
3.3. Feature Selection
3.3.1. Action Initiation Intention Feature Selection
During the data collection process, because the subjects were at rest time and the length of time in the task was different, there were also differences in the number of samples in the rest segment and the number of samples in the task segment in the collection of data. The construction of the action initiation intention recognition model faced the problem of sample imbalance between different categories. Compared with the traditional RF feature selection algorithm, this paper proposes an improved feature selection method based on RF. For the original feature set, the algorithm first set the final number of retained features, then used the sequential backward search method to remove the features with low importance score from the feature set, until the number of features was the specified number, the algorithm stopped, and the reserved feature subset was taken as the final feature set [14,15].
3.3.2. Movement State Feature Selection
Facing the high dimensionality of features in multi-classification tasks, this paper proposes a combined feature selection method based on ReliefF algorithm and genetic algorithm. In order to eliminate irrelevant features and redundant features in the original feature space, the ReliefF algorithm was first applied to evaluate the feature importance based on the distance measurement between sample features, and features with higher feature importance were retained as a feature subset [16,17]. On this basis, genetic algorithm was applied to find the optimal feature combination under the current feature subset. The flow of the feature selection method is shown in Figure 5.

Figure 5.
Feature selection flowchart.
4. Results
4.1. Data Preprocessing Results
In order to obtain the ideal morphological filtering effect, the signal-to-noise ratio and mean square error were used as evaluation indicators to conduct experiments on filters with different structural elements, different amplitudes, and different widths. We selected the parameter combination with the best comprehensive performance to construct the morphology learn filters. Table 1 shows the maximum signal-to-noise ratio the minimum filtering error and the corresponding combination of amplitude and width of the near-infrared signal after filtering by different structural elements.

Table 1.
The filtering effect of various structural elements on the near-infrared signal.
4.2. The Results and Analysis of Initial Intention Detection
4.2.1. The Results of Initial Intention of the Action
The initial intention detection task of this action divided the data samples of 50 subjects participating in the experiment into a data set, of which the experimental data of 40 subjects were used as the cross-validation set, the total number of samples was 65,354, and the experimental data of the remaining 10 subjects were used as a test set, the total number of samples was 16,392. Figure 6 shows the test results of the participants’ initiation of action during the experiment. The red dashed line represented the start time of the action, and the green dashed line marked the end of the task. In the example in the figure, “0” and “1” were used to indicate the rest state and task state, respectively. If it was judged as “0” in the rest period, it was regarded as correct, and when it was judged as “1”, it was regarded as a misjudgment, it was judged in the task segment. If it was “1”, it was deemed correct.
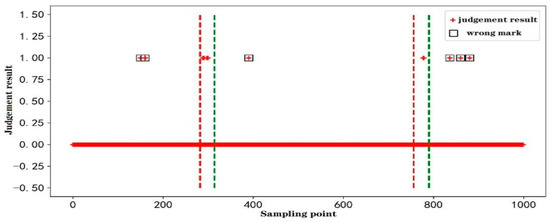
Figure 6.
Schematic diagram of the judgment result of the initial intention of the action.
In order to explore the impact of different feature dimensions and different probability thresholds on the classification results, we used 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, and 90 as the feature dimensions, and applied the “threshold shift method” with 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6, and 0.7, respectively, as probability threshold to carry out the experiment. We used RF and gradient boosting tree (GBDT) classification algorithm to detect the initial intention of the action. It can be seen that when the feature dimension was 60 and the threshold was 0.4, both classification algorithms maintain their optimal performance. The optimal recognition results of the RF and GBDT are shown in Table 2 and Table 3.

Table 2.
Optimal results of the RF algorithm.

Table 3.
Optimal results of GBDT algorithm.
By comparing the comprehensive indicators of the two classifiers of RF and GBDT, the RF is finally selected as the final classification algorithm.
4.2.2. Feature Analysis
The distribution of the brain areas of each feature and the feature weight proportion of the blood oxygen type were sorted out. The results show that among the three types of characteristics of oxygen, deoxygenation, and total oxygen, the dominant characteristic channels were channels 1, 4, and 5, and the important characteristic channels were 6, 12, 13, 19, 20 channels. The remaining channels are generally active channels, which are helpful to the recognition task.
4.3. The Results and Analysis of Exercise Status Recognition
4.3.1. Recognition Results of Motion State
In this classification task, the 50 test data samples participating in the experiment were divided into data sets. Among them, the experimental data of 40 subjects were used as the cross-validation set, the total number of samples was 160, and the experimental data of the remaining 10 subjects were used as the test set. The total number of samples was 40.
By comparing the final convergence results of the genetic algorithms of different classification algorithms, the final iterative results of the four classification algorithms are shown in Table 4. The final classification algorithm was sorted from highest to lowest score as SVM > LR > LDA > NB. Therefore, for the classification task of this data set, SVM was selected as the classifier of the final results [18]. The SVM algorithm’s recognition results for all subject samples are shown in Table 5.

Table 4.
The best evaluation indicators of different classifiers.

Table 5.
Multi-state classification and recognition results.
4.3.2. Feature Analysis
The distribution of the brain regions of each feature and the weight ratio of the blood oxygen type were classified and statistics [19]. In the characteristics of oxygen content, the dominant characteristic channels are channel 1, 4, 5, and 12, and the important characteristic channels are channel 6, 11, 13 and 15, among which channel 2, 21, 23, and 24 have no relevant characteristics, and other channels are generally active. Among the deoxygenation characteristics, the dominant characteristic channels are channel 1, 4, 5 and 6, and the important characteristic channels are channel 3, 7, 11, 12, 15, and 19. Channel 24 has no relevant characteristics, and other channels are generally active. Among the total oxygen characteristics, the dominant characteristic channels are channel 1, 4, 5, 6, 9, 12, and 13, and the important characteristic channels are channel 7, 8, 10, 17, 19, and 20. Channel 22, 23, and 24 have no relevant characteristics, while other channels are generally active.
5. Discussion
This paper proposed a set of upper limb rehabilitation training robot systems based on user spontaneous movement fNIRS-BCI. Four upper-limb movement paradigms that are highly related to daily life were designed. The combined filtering method of morphological filtering and Butterworth band-pass filtering was used to preprocess the signal. In terms of the recognition algorithm for detecting the initial intention of upper limb movements, GBDT and RF were selected for classification experiments. Finally, RF classifiers with better comprehensive indicators were selected as the final classification algorithm. The best offline recognition rate was 94.4% (151/160), the false positive rate was 1.1% (733/65354). The ReliefF algorithm based on distance measurement and the genetic algorithm proposed in the genetic theory were used to select features. In terms of upper limb motion state recognition algorithms, LR, SVM, NB, and LDA were selected for experiments, and Kappa coefficient was used as the classification index to evaluate the performance of the classifier. Finally, SVM classification got the best performance. The Kappa coefficient of the classification result was 0.792, and the four-class recognition accuracy rate was 84.4%.
This study has many advantages: First of all, in the process of the experiment, the corresponding tasks were automatically controlled by the subjects, during which there was no task hint and no external stimulation. Four upper-limb movement paradigms that are highly related to daily life were designed. At present, numerous research subjects need to carry out experiments according to stimulus cues (mostly visual or auditory stimulus). Kus et al. instructed the subjects to imagine left/right/feet movements according to the prompts displayed on the screen, and tried to classify different imaginary movements [20]. Tengfei Ma et al. instructed the subjects to perform left/right hand finger tapping task guided by a voice prompt [21]. Furthermore, in this paper, the research on upper limb movement intention was based on the blood oxygen signal before the real action task. According to the brain signal before the actual action, the motor intention was judged, which provided an important practical basis for the realization of real-time control application based on brain computer interface technology. Now the majority of research on motor imagery is based on the extraction of real motion signals for experiments, but this cannot guarantee great real-time performance. For example, Trakoolwilaiwan et al. extracted the time samples of the subjects during the resting and left and right hand movement tasks for training and recognition [22,23]. Finally, in this paper, a variety of algorithms (including ensemble learning) were selected for experiments and achieved high accuracy. In the aspect of the initial intention recognition algorithm of upper limb movement, GBDT and RF are selected for classification experiments. RF classifier with better comprehensive indicators was selected as the final classification algorithm. The best offline recognition rate was 94.4%(151/160). In the aspect of upper limb motion state recognition algorithms, LR, SVM, NB, and LDA were selected for the experiment. SVM got the highest recognition accuracy in four classification recognition (84.4%). Now, the recognition accuracy of multi-classification tasks on motor imagery is relatively low in a lot of research. Keum Shik Hong et al. simultaneously obtained fNIRS signals of mental arithmetic (MA), right hand motor imagery (RI) and left hand motor imagery (LI) from prefrontal cortex and primary motor cortex. Multiclass linear discriminant analysis was utilized to classify MA vs. RI vs. LI with an average classification accuracy of 75.6% across the ten subjects, for a 2–7 s time window during the 10 s task period [22,24]. Wang Wenle et al. collected fNIRS signals of 16 subjects’ brain motor areas during the actual and imaginary movements of six types of sign language tasks. Finally, they used AdaBoost.M1, SVM, LDA, HMM, NB, and KNN algorithms to recognize the fNIRS signals. Finally, LDA achieves the highest average classification accuracy (78.70% ± 1.78%) [23,24]. The recognition accuracy in our paper is higher than 75.6% and 78.70% ± 1.78%.
Although this study has the above advantages, there are still some areas that need improvement. For example, the cascade structure adopted by the current system will cause errors to occur between different classification tasks, during which a problem in a certain recognition link will affect the final overall recognition rate. Therefore, in future research, it is expected that other real-time algorithm frameworks can be used to make up for this deficiency, such as parallel structure and hybrid structure.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, funding acquisition, project administration, supervision, methodology, C.L.; data analysis, experimental verification, writing, Y.X.; data preprocessing, methodology, L.H.; data curation, Y.Z.; investigation, S.K.; supervision, formal analysis, L.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (61673286), and National key research and development program of China (U1713218).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Li, C.; Xu, J.; Kuang, S.; Qu, W.; Hu, H.; Sun, L. To Identify Motion Pattern of Lower Limbs by Using Cerebral Hemoglobin Information during Motor Imagery. In Proceedings of the 2017 9th International Conference on Intelligent Human-Machine Systems and Cybernetics (IHMSC), Hangzhou, China, 26–27 August 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Myrden, A.; Chau, T. Effects of user mental state on EEG-BCI performance. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tung, S.W.; Guan, C.; Kai, K.A.; Kok, S.P.; Chuan, C.W.; Ling, Z.; Wei, P.T.; Effie, C. Motor imagery BCI for upper limb stroke rehabilitation: An evaluation of the EEG recordings using coherence analysis. In Proceedings of the 2013 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Osaka, Japan, 3–7 July 2013; pp. 261–264. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, S.; Yang, Q.; Wang, R.; Lin, P.; Gao, J.; Leng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, H. A Brain-Computer Interface Based on a Few-Channel EEG-fNIRS Bimodal System. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rota, G.; Handjaras, G.; Sitaram, R.; Birbaumer, N.; Dogil, G. Reorganization of functional and effective connectivity during real-time fMRI-BCI modulation of prosody processing. Brain Lang. 2011, 117, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, A.; Raza, H.; Meena, K.Y.; Dutta, A.; Prasad, G. An EEG-EMG correlation-based brain-computer interface for hand orthosis supported neuro-rehabilitation. Neurosci. Methods 2019, 15, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, W.; Yang, Y.; Lu, S.; Gao, N. Brain computer interface system research of upper limb rehabilitation training robot. Res. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 3, 269–274. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, Y.; Kaneko, N.; Sasaki, A.; Fumiya, T.; Kimitaka, N.; Taishin, N.; Matija, M. Muscle-specific movement-phase-dependent modulation of corticospinal excitability during upper-limb motor execution and motor imagery combined with virtual action observation. Neurosci. Lett. 2021, 755, 135907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glowinski, S.; Krzyzynski, T.; Bryndal, A.; Maciejewski, I. A Kinematic Model of a Humanoid Lower LimbExoskeleton with Hydraulic Actuators. Sensors 2020, 20, 6116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, K.S.; Khan, M.J.; Hong, M.J. Feature Extraction and Classification Methods for Hybrid fNIRS-EEG Brain-Computer Interfaces. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuzuki, D.; Jurcak, V.; Ksingh, A.; Okamoto, M.; Eiju, W.; Dan, I. Virtual spatial registration of stand-alone fNIRS data to MNI space. Neuroimage 2007, 34, 1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, S.; Nesterets, Y.; Rana, R.; Tahtali, M.; Gureyev, T.E. EEG source localization using a sparsity prior based on Brodmann areas. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 2014, 27, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhateja, V.; Verma, R.; Mehrotra, R.; Urooj, S. A Non-Linear Approach to ECG Signal Processing using Morphological Filters. Int. J. Meas. Technol. Instrum. Eng. (IJMTIE) 2013, 3, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Li, C.; Sun, L.; Hu, H.; Xu, J.; Qu, W. To classify two-dimensional motion state of step length and walking speed by applying cerebral hemoglobin information. In Proceedings of the 2017 10th International Conference on Human System Interactions (HIS), UIsan, Korea, 17–19 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Song, Y.; Ma, K.; Su, E.; Xie, L. A novel motor imagery EEG decoding method based on feature separation. J. Neural Eng. 2021, 18, 036022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodin, Z.; Mansor, W.; Lee, K.Y.; Mohamad, N.B. An analysis of EEG signal power spectrum density generated during writing in children with dyslexia. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 11th International Colloquium on Signal Processing & its Applications (CSPA), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 6–8 March 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, T.; Yan, G.; Yang, B.; Sun, H. EEG feature extraction based on wavelet packet decomposition for brain-computer interface. Measurement 2008, 41, 618–625. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhary, U.; Birbaumer, N.; Ramos-Murguialday, A. Brain-computer interfaces for communication and rehabilitation. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2016, 12, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durgabai, R.P.L.; Ravi, B.Y. Feature selection using ReliefF algorithm. Int. J. Adv. Res. Comput. Commun. Eng. 2014, 3, 8215–8218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kus, R.; Valbuena, D.; Zygierewicz, J.; Malechka, T.; Graeser, A.; Durka, P. Asynchronous BCI Based on Motor Imagery with Automated Calibration and Neurofeedback Training. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2012, 20, 823–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, T.; Wang, S.; Xia, Y.; Zhu, X.; Evans, J.; Sun, Y.; He, S. CNN-based classification of fNIRS signals in motor imagery BCI system. J. Neural Eng. 2021, 18, 056019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trakoolwilaiwan, T.; Behboodi, B.; Lee, J.; Kyungson, K.; Ji-Woong, C. Convolutional neural network for high-accuracy functional near-infrared spectroscopy in a brain-computer interface: Three-class classification of rest, right-, and left-hand motor execution. Neurophotonics 2018, 5, 011008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Gong, A.; Fu, Y. Identification of One—Hand Sign Language Based on fNIRS. J. Kunming Univ. Sci. Technol. (Nat. Sci.) 2020, 45, 74–81. [Google Scholar]
- Keum-Shik, H.; Noman, N.; Yun-Hee, K. Classification of prefrontal and motor cortex signals for three-class fNIRS–BCI. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 587, 87–92. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).