Microalgae as a Sustainable, Natural-Oriented and Vegan Dermocosmetic Bioactive Ingredient: The Case of Neochloris oleoabundans
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Inoculum Maintenance and Culture
2.2. Extracts Preparation
2.3. In Vitro Antioxidant Capacity
2.4. Dermocosmetic Prototype Formulation
2.5. Cutaneous Compatibility of N. oleoabundans Dermocosmetic
2.6. In Vivo Anti-Inflammatory Activity
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. N. oleoabundans Cultivation and Biomass Composition
3.2. Extracts Preparation and Cosmetic Formulation
3.3. In Vitro Antioxidant Activity
3.4. Cutaneous Compatibility of the N. oleoabundans Gel
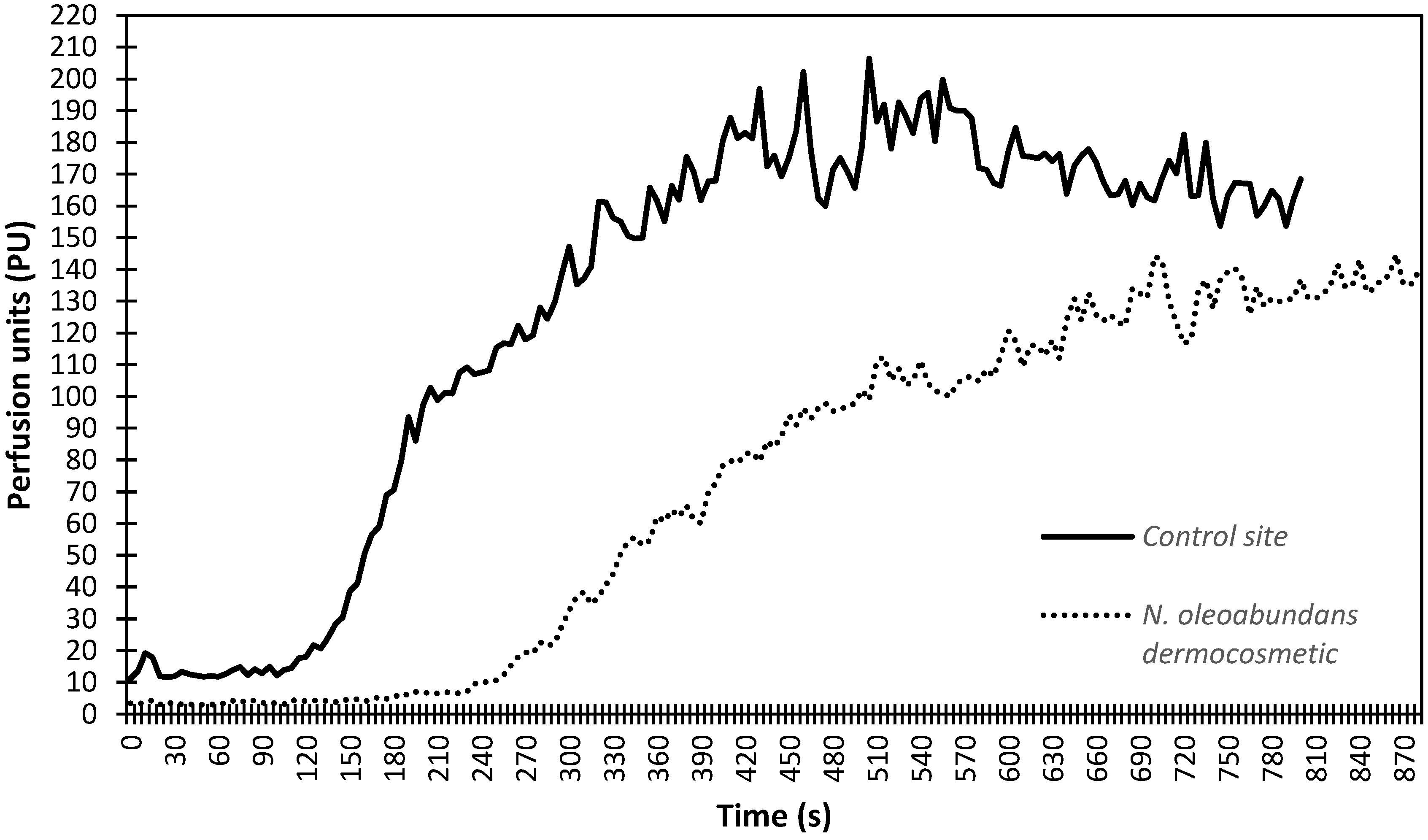
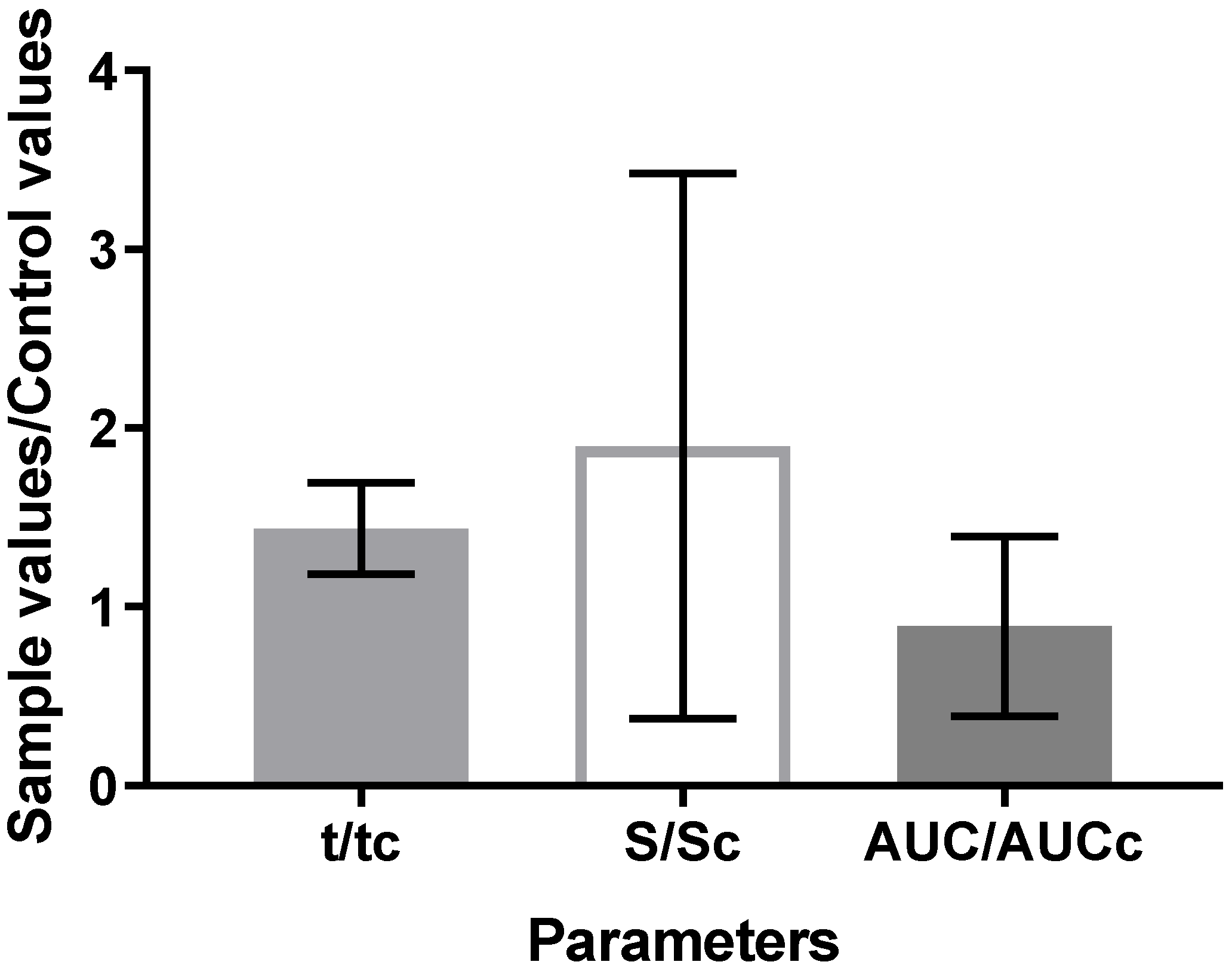
3.5. In Vivo Anti-Inflammatory Activity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hayase, M. Introduction to Cosmetic Materials. In Cosmetic Science and Technology; Sakamoto, K., Lochhead, R.Y., Maibach, H.I., Yamashita, Y., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 149–154. [Google Scholar]
- Morocho-Jácome, A.L.; Ruscinc, N.; Martinez, R.M.; Carvalho, J.C.M.; Santos de Almeida, T.; Rosado, C.; Costa, J.G.; Velasco, M.V.R.; Baby, A.R. (Bio)Technological Aspects of Microalgae Pigments for Cosmetics. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 9513–9522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, T. Psychology of Cosmetic Behavior. In Cosmetic Science and Technology; Sakamoto, K., Lochhead, R.Y., Maibach, H.I., Yamashita, Y., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 101–113. [Google Scholar]
- Giliver, L. Global Vegan Cosmetics Market to Exceed $21 Billion by 2027, Predicts New Report. Available online: https://plantbasednews.org/lifestyle/beauty/global-vegan-cosmetics-market-exceed-21-billion/ (accessed on 3 September 2021).
- Queiroz, M.I.; Vieira, J.G.; Maroneze, M.M. Morphophysiological, Structural, and Metabolic Aspects of Microalgae. In Handbook of Microalgae-Based Processes and Products; Jacob-Lopes, E., Maroneze, M.M., Queiroz, M.I., Zepka, L.Q., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 25–48. [Google Scholar]
- Cezare-Gomes, E.A.; Mejia-da-Silva, L.C.; Pérez-Mora, L.S.; Matsudo, M.C.; Ferreira-Camargo, L.S.; Singh, A.K.; Carvalho, J.C.M. Potential of Microalgae Carotenoids for Industrial Application. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2019, 188, 602–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro-Puyana, M.; Pérez-Sánchez, A.; Valdés, A.; Ibrahim, O.H.M.; Suarez-Álvarez, S.; Ferragut, J.A.; Micol, V.; Cifuentes, A.; Ibáñez, E.; García-Cañas, V. Pressurized Liquid Extraction of Neochloris Oleoabundans for the Recovery of Bioactive Carotenoids with Anti-Proliferative Activity against Human Colon Cancer Cells. Food Res. Int. 2017, 99, 1048–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Günerken, E.; D’Hondt, E.; Eppink, M.H.M.; Garcia-Gonzalez, L.; Elst, K.; Wijffels, R.H. Cell Disruption for Microalgae Biorefineries. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015, 33, 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ariede, M.B.; Candido, T.M.; Morocho-Jácome, A.L.; Velasco, M.V.R.; Carvalho, J.C.M.; Baby, A.R. Cosmetic Attributes of Algae—A Review. Algal Res. 2017, 25, 483–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baby, A.R.; Morocho-Jácome, A.L. Dermocosmetic Applications of Microalgal Pigments. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2021; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Gouveia, L.; Marques, A.E.; Da Silva, T.L.; Reis, A. Neochloris Oleabundans UTEX #1185: A Suitable Renewable Lipid Source for Biofuel Production. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 36, 821–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pruvost, J.; Van Vooren, G.; Cogne, G.; Legrand, J. Investigation of Biomass and Lipids Production with Neochloris Oleoabundans in Photobioreactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 5988–5995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.-B.; Cheng, K.-W.; Wong, C.-C.; Fan, K.-W.; Chen, F.; Jiang, Y. Evaluation of Antioxidant Capacity and Total Phenolic Content of Different Fractions of Selected Microalgae. Food Chem. 2007, 102, 771–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Puyana, M.; Herrero, M.; Urreta, I.; Mendiola, J.A.; Cifuentes, A.; Ibáñez, E.; Suárez-Alvarez, S. Optimization of Clean Extraction Methods to Isolate Carotenoids from the Microalga Neochloris Oleoabundans and Subsequent Chemical Characterization Using Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 4607–4616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosado, C.; Pinto, P.; Rodrigues, L.M. Assessment of Moisturizers and Barrier Function Restoration Using Dynamic Methods. Ski. Res. Technol. 2009, 15, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, B.; Kasper, M.; Surber, C.; Imanidis, G. Permeation, Metabolism and Site of Action Concentration of Nicotinic Acid Derivatives in Human Skin: Correlation with Topical Pharmacological Effect. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2003, 20, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagemaker, T.A.L.; Rijo, P.; Rodrigues, L.M.; Maia Campos, P.M.B.G.; Fernandes, A.S.; Rosado, C. Integrated Approach in the Assessment of Skin Compatibility of Cosmetic Formulations with Green Coffee Oil. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2015, 37, 506–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benyó, Z.N.; Gille, A.; Bennett, C.L.; Rn, B.; Clausen, E.; Offermanns, S. Nicotinic Acid-Induced Flushing Is Mediated by Activation of Epidermal Langerhans Cells. Mol. Pharmacol. 2006, 70, 1844–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandersee, S.; Erdmenger, U.; Patzelt, A.; Beyer, M.; Meinke, M.C.; Darvin, M.E.; Koscielny, J.; Lademann, J. Significance of the Follicular Pathway for Dermal Substance Penetration Quantified by Laser Doppler Flowmetry. J. Biophotonics 2016, 9, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, C.A.; Dario, M.F.; Sarruf, F.D.; Mariz, I.F.A.; Velasco, M.V.R.; Rosado, C.; Baby, A.R. Safety and Efficacy Evaluation of Gelatin-Based Nanoparticles Associated with UV Filters. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 140, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vertuani, S.; Ziosi, P.; Solaroli, N.; Buzzoni, V.; Carli, M.; Lucchi, E.; Valgimigli, L.; Baratto, G.; Manfredini, S. Determination of Antioxidant Efficacy of Cosmetic Formulations by Non-Invasive Measurements. Ski. Res. Technol. 2003, 9, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahlberg, J.E. Erythema-Inducing Effects of Solvents Following Epicutaneous Administration to Man—Studied by Laser Doppler Flowmetry. Scand. J. Work. Environ. Health 1984, 10, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peres, D.A.; Oliveira, C.A.; Costa, M.S.; Tokunaga, V.K.; Mota, J.P.; Rosado, C.; Consiglieri, V.O.; Kaneko, T.M.; Velasco, M.V.R.; Baby, A.R. Rutin Increases Critical Wavelength of Systems Containing a Single UV Filter and with Good Skin Compatibility. Ski. Res. Technol. 2016, 22, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UTEX Culture Collection of Algae UTEX. Available online: https://utex.org/products/modified-bold-3n-medium (accessed on 16 April 2018).
- Rijo, P.; Falé, P.L.; Serralheiro, M.L.; Simões, M.F.; Gomes, A.; Reis, C. Optimization of Medicinal Plant Extraction Methods and Their Encapsulation through Extrusion Technology. Measurement 2014, 58, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falé, P.L.; Borges, C.; Madeira, P.J.A.; Ascensão, L.; Araújo, M.E.M.; Florêncio, M.H.; Serralheiro, M.L.M. Rosmarinic Acid, Scutellarein 4′-Methyl Ether 7-O-Glucuronide and (16S)-Coleon E Are the Main Compounds Responsible for the Antiacetylcholinesterase and Antioxidant Activity in Herbal Tea of Plectranthus Barbatus (Falso Boldo). Food Chem. 2009, 114, 798–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Hajar, H.A.; Riefler, R.G.; Stuart, B.J. Cultivation of the Microalga Neochloris Oleoabundans for Biofuels Production and Other Industrial Applications (A Review). Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2017, 53, 640–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila-León, I.A.; Matsudo, M.C.; Ferreira-Camargo, L.S.; Rodrigues-Ract, J.N.; Carvalho, J.C.M. Evaluation of Neochloris Oleoabundans as Sustainable Source of Oil-Rich Biomass. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 37, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borowitzka, M.A. High-Value Products from Microalgae—Their Development and Commercialisation. J. Appl. Phycol. 2013, 25, 743–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibbetts, S.M.; Milley, J.E.; Lall, S.P. Chemical Composition and Nutritional Properties of Freshwater and Marine Microalgal Biomass Cultured in Photobioreactors. J. Appl. Phycol. 2015, 27, 1109–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oliveira, A.C.; Morocho-Jácome, A.L.; Castro Lima, C.R.; Marques, G.A.; Bispo, M.O.; Barros, A.B.; Costa, J.G.; Santos de Almeida, T.; Rosado, C.; Carvalho, J.C.M.; et al. Cosmetics Applications. In Microalgae; Galanakis, C.M., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2020; pp. 313–338. [Google Scholar]
- Trabelsi, L.; Mnari, A.; Abdel-Daim, M.M.; Abid-Essafi, S.; Aleya, L. Therapeutic Properties in Tunisian Hot Springs: First Evidence of Phenolic Compounds in the Cyanobacterium Leptolyngbya Sp. Biomass, Capsular Polysaccharides and Releasing Polysaccharides. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manivannan, K.; Anantharaman, P.; Balasubramanian, T. Evaluation of Antioxidant Properties of Marine Microalga Chlorella Marina (Butcher, 1952). Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2012, 2, S342–S436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanab, S.M.M.; Mostafa, S.S.M.; Shalaby, E.A.; Mahmoud, G.I. Aqueous Extracts of Microalgae Exhibit Antioxidant and Anticancer Activities. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2012, 2, 608–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berardesca, E.; Loden, M.; Serup, J.; Masson, P.; Rodrigues, L.M. The Revised EEMCO Guidance for the in Vivo Measurement of Water in the Skin. Ski. Res. Technol. 2018, 24, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remane, Y.; Leopold, C.S. Time of Erythema Onset after Application of Methyl Nicotinate Ointments as Response Parameter: Influence of Penetration Kinetics and Enhancing Agents. Ski. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2006, 19, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauce, R.; Pinto, C.A.S.d.O.; Velasco, M.V.R.; Rosado, C.; Baby, A.R. Ex Vivo Penetration Analysis and Anti-Inflammatory Efficacy of the Association of Ferulic Acid and UV Filters. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 156, 105578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Composition * | Concentration (% w/w) | |
|---|---|---|
| Control Gel | Neochloris Oleoabundans (N. oleoabundans) Gel | |
| Ammonium acryloyldimethyltaurate/VP copolymer (Aristoflex® AVC) | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| N. oleoabundans aqueous extract | - | 1.0 |
| Derivatives of parabens | 0.8 | 0.8 |
| Aqua | qsp 100% | qsp 100% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Morocho-Jácome, A.L.; Santos, B.B.d.; Carvalho, J.C.M.d.; Almeida, T.S.d.; Rijo, P.; Velasco, M.V.R.; Rosado, C.; Baby, A.R. Microalgae as a Sustainable, Natural-Oriented and Vegan Dermocosmetic Bioactive Ingredient: The Case of Neochloris oleoabundans. Cosmetics 2022, 9, 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics9010009
Morocho-Jácome AL, Santos BBd, Carvalho JCMd, Almeida TSd, Rijo P, Velasco MVR, Rosado C, Baby AR. Microalgae as a Sustainable, Natural-Oriented and Vegan Dermocosmetic Bioactive Ingredient: The Case of Neochloris oleoabundans. Cosmetics. 2022; 9(1):9. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics9010009
Chicago/Turabian StyleMorocho-Jácome, Ana Lucía, Bruna Bertoloni dos Santos, João Carlos Monteiro de Carvalho, Tânia Santos de Almeida, Patrícia Rijo, Maria Valéria Robles Velasco, Catarina Rosado, and André Rolim Baby. 2022. "Microalgae as a Sustainable, Natural-Oriented and Vegan Dermocosmetic Bioactive Ingredient: The Case of Neochloris oleoabundans" Cosmetics 9, no. 1: 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics9010009
APA StyleMorocho-Jácome, A. L., Santos, B. B. d., Carvalho, J. C. M. d., Almeida, T. S. d., Rijo, P., Velasco, M. V. R., Rosado, C., & Baby, A. R. (2022). Microalgae as a Sustainable, Natural-Oriented and Vegan Dermocosmetic Bioactive Ingredient: The Case of Neochloris oleoabundans. Cosmetics, 9(1), 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics9010009










