Abstract
Limited permeability through the stratum corneum (SC) is a major obstacle for numerous skin care products. One promising approach is to use lipid nanoparticles as they not only facilitate penetration across skin but also avoid the drawbacks of conventional skin formulations. This review focuses on solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs), nanostructured lipid nanocarriers (NLCs), and nanoemulsions (NEs) developed for topical and transdermal delivery of active compounds. A special emphasis in this review is placed on composition, preparation, modifications, structure and characterization, mechanism of penetration, and recent application of these nanoparticles. The presented data demonstrate the potential of these nanoparticles for dermal and transdermal delivery.
1. Introduction
In most civilizations, humans have used cosmetics for thousands of years. Their main purposes were to clean, protect, improve appearance, perfume, prevent odor, and resist aging. In this regard, numerous materials used as cosmetics are either derived from synthetic materials such as vitamin A derivatives (e.g., adapalene) [1] and UV filters (e.g., avobenzone) [2], while others are considered natural, including milk, honey, flowers, extracts, minerals, fruit, oils, and many others [3,4]. These cosmetics were applied to various parts of the body such as hair, nails, teeth, and skin. However, skin was (and still is) the main target for these products since it constitutes the largest organ of the human body and its appearance, in general, reflects the beauty of the person.
Active compounds in cosmetics are either hydrophilic (water-soluble compounds) or hydrophobic (lipid soluble compounds). Each type has its own shortcomings regarding use in dermal formulations, and in order to overcome such difficulties several aspects such as location of intended effect, mechanism of action, side effects, and duration of applications should be considered. For example, hydrophilic active compounds suffer from their inability to penetrate the SC due to their polarity. On the other hand, hydrophobic compounds suffer from their unpleasant oily texture that might be undesirable for users. Because of this, several approaches such as the use of emulsions, liposomes, polymer-based carriers, and lipid nanoparticles have been used to overcome the various obstacles to forming a most effective formulation for dermal and transdermal applications. Naturally, each technique has its own advantages and disadvantages. While emulsions lack thermodynamic stability [5], liposomes are expensive with difficult and complicated mass production [6]. Interestingly, lipid nanoparticles are both effective and economic with simple scale-up processes [7]. Accordingly, and owing to the wide interest of skin-related products, this review focuses on current knowledge about methods of preparation and characterization of lipid nanoparticles. In addition, the use of lipid nanoparticles in dermal and transdermal formulations will be discussed with emphasis on the last five years. For this purpose, we have obtained the most recent relevant references from known databases including Google Scholar, Science Direct, MEDLINE (PubMed), Scopus, and SciFinder. We hope this review will be a great help for researchers and a valuable addition to the field.
2. Skin
2.1. Skin Structure
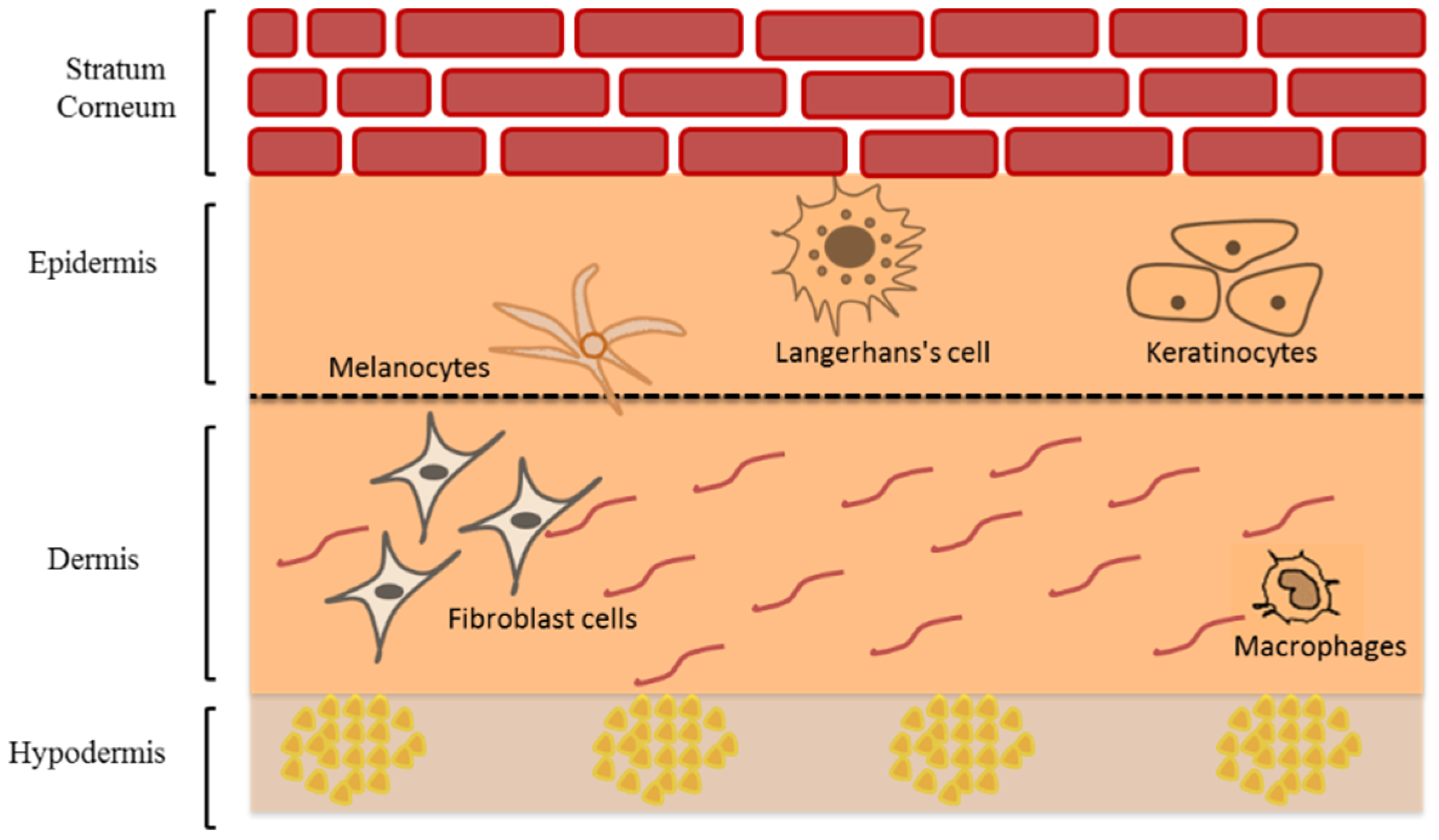
The human skin is the body’s largest multi-layers organ that acts as a formidable barrier to external factors damaging the deeper tissues and internal organs [8]. The skin consists of three main layers; epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis (or subcutis) but each with different cell composition (Figure 1). The epidermis is the upper skin layer, which is mainly composed of keratinocytes (95%) and the rest (5%) are melanocytes, Langerhans cells, and Merkel cells [9].
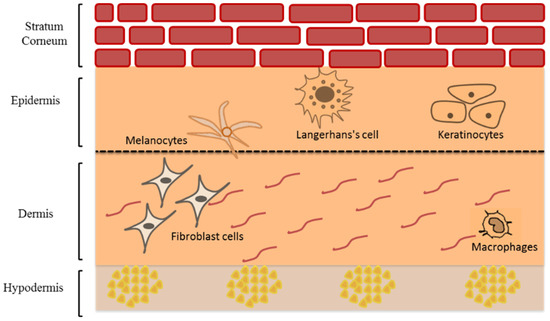
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of human skin structure modified from Saleh et al. [10] (Reprinted with permission, Copyright 2020 Elsevier B.V.).
The epidermis consists of four main layers: stratum basale, stratum spinosum, stratum granulosum, and stratum corneum (SC). The stratum basale is a single layer of the actively dividing keratinocytes as well as melanocytes, and Merkel cells [11]. These viable keratinocytes are actively dividing to give daughter cells. Some remain in the basal layer whereas the rest undergo terminal differentiation and migrate upward in a 40-day trip that ends in the formation of SC [12]. The renewal time of normal epidermal cells in adults is approximately 6 to 8 weeks [13,14], whereas the average turn over time of SC is approximately 2 weeks [15]. The activity of the enzymes involved in desquamation is affected by water level and pH. The water level depends on the presence of hygroscopic molecules known as natural moisturizing factors (NMF) [16]. The melanocytes, which produce melanin photoprotective pigments and consist of a central body and dendrite tips, are also found in the stratum basale. They include brownish to black eumelanins and the yellowish to red pheomelanins [17]. These are packed and stored in melanosomes, which then transfer via dendrites’ tips to nearby keratinocytes in the basal layer [18]. Melanin skin pigments was used mainly to determine the skin color [19] and have protective role against ultraviolet radiation (UVR) which causes damage to the skin [19]. Langerhans cells are dendritic epidermal cells characterized by the expression of Langerin (CD207) and CD1a. These cells play a vital role in antigen-presenting cells (APCs) in skin inflammation. Langerin is a type II type c lectin receptor, called Birbeck granule, which is involved in the presentation of non-peptide antigens to T cells and is expressed only in Langerhans cells in the skin. When confronted with pathogens or allergens, Langerhans cells act as APCs function triggering a series of the immune system by migrating downward through dermis to the lymph nodes and result in activation of T-regulatory cells [20,21,22]. Merkel cells are touch receptors responsible for transmitting signals to sensory neurons in the deep dermal layer [9,23].
The stratum spinosum is composed of two to six rows of keratinocytes that migrate to the skin surface changing its morphology from columnar to polygonal linked via desmosomes known as ‘prickles’ giving rigidity throughout this layer [24]. Similarly, the stratum granulosum, composed of up to three layers of granular keratinocytes, migrates and flattens upward indicating a decrease in metabolic activity. It is characterized by the presence of lamellar granules that contain intercellular lipid lamellae that will be extruded from lamellar granules in the SC [11,24]. Finally, the SC is composed of up to 15–30 rows of terminally differentiated dead keratinocytes known as corneocytes. Each corneocyte contains several natural moisturizing factors (NMF) sourced by filaggrin. Above the SC–SG interface, filaggrin is hydrolyzed to the NMF and afford several hygroscopic molecules capable of retaining a sufficient amount of water in SC. To maintain a proper hydration level in the SC, NMF should be present in the stratum corneum [25]. This horny layer is the main barrier that restrict the entry of many xenobiotics to the viable epidermis and prevent the transepidermal water loss [26], due to the densely packed corneocytes cells ‘bricks’ embedded in intercellular lipid matrix ‘mortar’. These lipids are composed mainly of ceramides, cholesterol, and long-chain free fatty acid [27,28,29]. The epidermis is structurally separated from the dermis by dermal-epidermal junction (DEJ), which is composed of glycoproteins that provide adhesion between collagen fibers in the papillary dermis and keratin filaments of keratinocytes in the basal epidermal layer [9].
The dermis mainly consists of two layers; the papillary and reticular dermis. The papillary dermis is thinner and in direct contact with DEJ, and reticular dermis is the thicker layer of the dermis in direct contact with hypodermis [12]. There are several cellular populations that are dispersed in the dermis such as mast cells, lymphocytes, dendritic cells, macrophages, and fibroblast cells, which produces collagen and elastic fibers embedded in a mucopolysaccharide gel-like matrix. This matrix also includes blood vessels, lymphatic systems, sensory neurons, as well as skin appendages such as hair follicles, sweat and sebaceous glands. The deepest layer is the subcutis containing adipocytes with large globules of fat that acts as energy storage, heat insulator, and a cushion for mechanical shock [11,12].
2.2. Skin Transport Mechanism
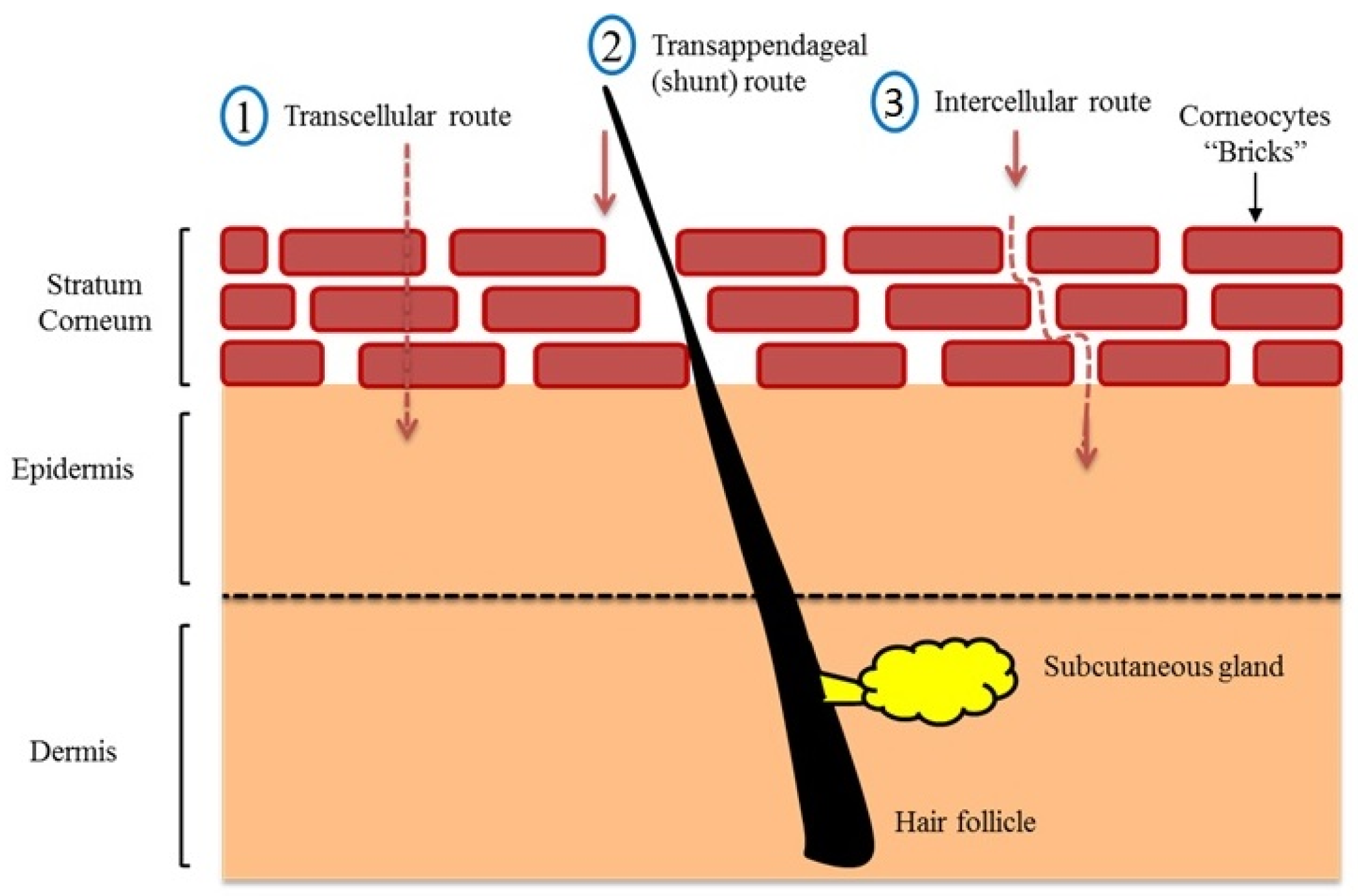
Three main passive routes were identified for drug penetration into the human skin (Figure 2). These are the transcellular (intracellular) pathway, the shunt pathway via hair follicles and sweat glands, and the intercellular pathway [30]. Although the intracellular route appears to be the shortest, it requires crossing through tightly confluent corneocytes and successive partitioning into intercellular lipid bilayers, which slows the penetration of hydrophobic actives through this route. The shunt pathway was thought to be a minor contributor to drug absorption, as the skin appendages only occupy 0.1% of the total human skin. However, it has recently been shown that this route is a potential (significant) transport for a variety of compounds ranging from charged molecules to nanomaterial [31,32,33]. In this regard, most topically applied hydrophilic and amphiphilic actives permeate across the skin via intercellular (tortuous) route, i.e., via the lipid matrix [10,26,34,35]. Changing the lipid composition of human epidermis has shown to dramatically increases water diffusion through human skin [36,37]. After the active release from the formulation and partition into SC, it diffuses via lipid matrix and reaches an interface where it passively undergoes partition from SC lipid into aqueous viable epidermis followed by diffusion through viable epidermis and hydrophilic dermis at the DEJ. Then the active compound can be absorbed into systemic circulation via a dermal capillary network [38].
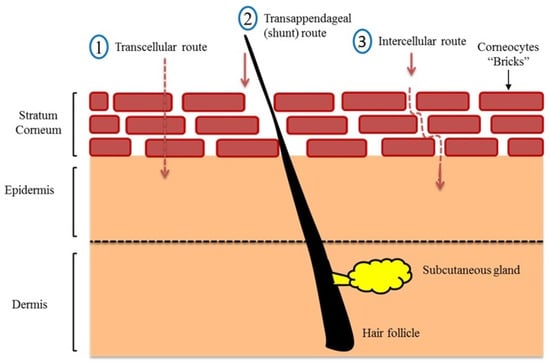
Figure 2.
Route of drug penetration into human skin modified from Saleh et al. [10] (Reprinted with permission, Copyright 2020 Elsevier B.V.).
2.3. Skin Cosmetics
A cosmetic (or toiletry), as defined by the U. S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), is a formulation that is applied to the eyes, skin, mouth, hair, or nails for cleansing, enhancing appearance, giving a pleasant smell, or protective effect. Cosmetics can also be multifunctional products that are intended to offer numerous benefits on skin health over simple cosmetics and advertised as “Cosmeceuticals”. Cosmetics comprise a growing sector of the skincare industry related to photo aging, hyperpigmentation, wrinkles, and other applications, and have widespread usage. Cosmeceuticals are formulated from either natural or synthetic bioactive ingredients include botanicals, vitamins, antioxidants, hydroxy acids, peptides, and many others [39]. Sunscreens regulations differ all around the world; the FDA and Australia recognize them as over-the-counter drugs or therapeutic goods, respectively. On the other hand, the European Union (EU), Brazil, Japan, and China consider sunscreens as cosmetic products [40,41,42].
Cosmeceuticals can be commercially available as liquids, lotion, cream, ointment, paste, gel, powders, capsules, or stick [43,44], which could have a beneficial effect within viable skin layers [45,46,47]. However, the actives must pass the skin’s outermost layer, the SC, to elicit their beneficial effects; thus, their efficacy can be limited by their physiochemical properties. It is possible that an active may remain on the skin surface, may be retained in the SC, or it may permeate into the viable skin layers without reaching the systemic circulation. In the cosmeceutical arena, nanotechnology has played an important role. Nano cosmeceuticals offer many advantages in skin products, such as increased bioavailability of active ingredients in deeper skin layers, prevent dehydration of skin due to occlusive effect, and increase the aesthetic appeal of cosmeceutical products, i.e., transparent appearance with prolonged effects [47]. Examples are nano-encapsulation vesicular delivery systems, including nanoemulsions and nanocrystals, liposomes and niosomes, micelles, polymeric nanocapsules, solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers, carbon nanotubes and fullerene, and dendrimers, nano-lipid carriers, carbon nanotubes, fullerenes, and dendrimers, which may contribute to the development of novel nanocosmeceuticals [48,49,50,51,52].
2.4. Skin Therapy
Numerous dermatological conditions affect the skin, such as atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, acne, skin mycosis. The continuous topical administration of certain drugs such as retinoids can cause severe toxic or irritation effects [53,54]. Moreover, Hydrophilic compounds, such as caffeine cannot permeate the lipophilic SC and reach the target site at the viable epidermis due to its polarity and solubility, leading to poor clinical efficacy [55]. In contrast, lipophilic compounds get stuck in SC without reaching a viable epidermis. Other limitations are high chemical instability and photo-degradation (seen in Vitamin E, retinoids, and sunscreens [56,57]). Within this context, bioactive compounds with balanced Log P = octanol–water partition coefficient of chemical values of 1–3 and molar mass (MW) < 500 are typically considered good candidates for dermal delivery in normal skin [58]. The effective permeation of normal skin would be a reasonable requirement for any bioactive compound considered for topical management of skin. One more problem in dermal drug penetration is related to inflammation skin pathology. The barrier is changed, and the drug resides much less on the targeted site because of fast penetration. Nanotechnology strategies seem capable to overcome the challenge due to the rational design and innovative effect in promoting penetration of drugs into the SC, prolong the effect, reduce toxicity, and prevent chemical degradation and photo-instability [53,56].
3. Lipid Drug Delivery Systems
Nanomedicine is a highly valuable field that provides advanced solutions to improve health and beauty. Cosmetics industry was among the first industries to incorporate nanoparticles in its products. Nanoparticles have distinguished properties to be used in cosmetic science and/or as nanocarriers for cosmetically active agents. Lipid nanoparticles (LNs) are the most commonly used for dermal and transdermal application [59]. LNs possess essential characteristics as biocompatibility, biodegradability, self-assembly, versatile particle size and low cost, making them an attractive tool in cosmetics formulations [60].
3.1. Dermal and Transdermal Drug Delivery
Dermal drug delivery includes topical skin application to treat local problems, whereas transdermal drug delivery represents transport through the intact skin into systemic circulation for the treatment of various chronic diseases. Dermal drug delivery is used to increase the local bioavailability of therapeutics or cosmetics at their site of action. The main objective for a dermal delivery is to bypass systemic adverse effects [61], whereas the main limitations for healing skin problems are the poor skin penetration of the drug or cosmetic that leads to low drug efficacy [62]. In this respect, SC of epidermis is the major skin barrier that should be bypassed through changing the penetration pathway from transcellular to paracellular or follicles [63]. For this purpose, novel nanocarriers have been designed to meet the skin healing requirements by enhancing skin penetration and provide superiority for dermal applications compared to free active drugs [62].
Lipid nanosystems such as liposomes, nanoemulsions (NEs), and lipid nanostructures, have become increasingly important as promising carriers for the selective delivery of cosmetic active ingredients in specific skin layers [64]. Furthermore, these nanosystems enhance the desired effects by improving their own transport effects. In this context, Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs) and nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs) represent an alternative nanocarriers system to traditional lipid colloids [65]. Muller research group first described these lipid nanocarriers in cosmetic application [66]. In addition, SLNs and NLCs are considered safe carriers since they are composed of biocompatible and biodegradable lipids, such as triglycerides, complex glyceride mixtures, or even waxes [67] that are stabilized by emulsifiers [61]. SLNs and NLCs were met with great interest in dermal application of cosmetics and pharmaceutics due to the improved stability and bioavailability of the water insoluble active ingredients, controlled release, and improved loading capacity and enhanced skin hydration and protection through film formation on the skin by close contact and strong skin adhesion [68,69]. Moreover, SLNs and NLCs enable drug targeting and showed an improvement of the benefit/risk ratio compared to other cosmetic products [70]. On the other hand, nanoemulsions (NEs) are considered a good nanodelivery system in cosmetics and dermatology application. NEs have the advantages of simple formulation, controllable particle size, and high stability with low surfactant concentration [71]. NEs are very promising nanocarriers for the treatment of various skin problems due to their fast and easy penetration through skin lipids, and their non-greasy characteristics. NEs-forming lipids are biocompatible, biodegradable, and considered safe in inflammatory skin problems [72].
3.2. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLNs)
Topical treatment of the dermatological diseases was used to provide high drug levels at the site of the disease, and systemic side effects can be reduced compared to orally or parenterally drug administration. A major challenge for the topical applications is their ability to cross the SC barrier [61]. Hydrophilic drugs, in the most conventional case, cannot easily penetrate through the lipid domain of the SC barrier. In addition, increasing drugs lipophilicity can result in improved percutaneous flux by chemical modification or using hydrophobic prodrug [70].
Several research approaches are in progress to improve the flux and enhance the delivery of either lipophilic or hydrophilic drugs, and also to determine the exact amount of drug that reaches the different skin layers [70]. SLNs technology represents a favorable new approach for delivering these moieties. These new strategies were initiated in the early 1990s [66]. SLNs are formed using solid lipids, at room temperature, instead of liquid lipid (oil) of an oil/water emulsion. SLNs are composed of 0.1% to 30% (w/w) solid lipid dispersed in an aqueous medium, which is stabilized with 0.5% to 5% (w/w) surfactant [73]. These SLNs can be easily loaded with medical bioactives and cosmetics. The mean particle size of SLNs range from 10 to 1000 nm [74].
SLNs have highly arranged crystalline structure that minimizes their drug loading efficiency due to drug expulsion phenomena during the storage conditions [75]. This phenomenon usually occurs when the drug molecules are placed between the highly ordered solid fatty acid chains or glycerides. Upon polymorphic changes in solid lipid structures, expulsion of previously dissolved drug in SLNs most likely occurs [67]. Another common disadvantage of SLNs is their gelation tendency that affects SLNs structures’ integrity [66].
3.3. Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLCs)
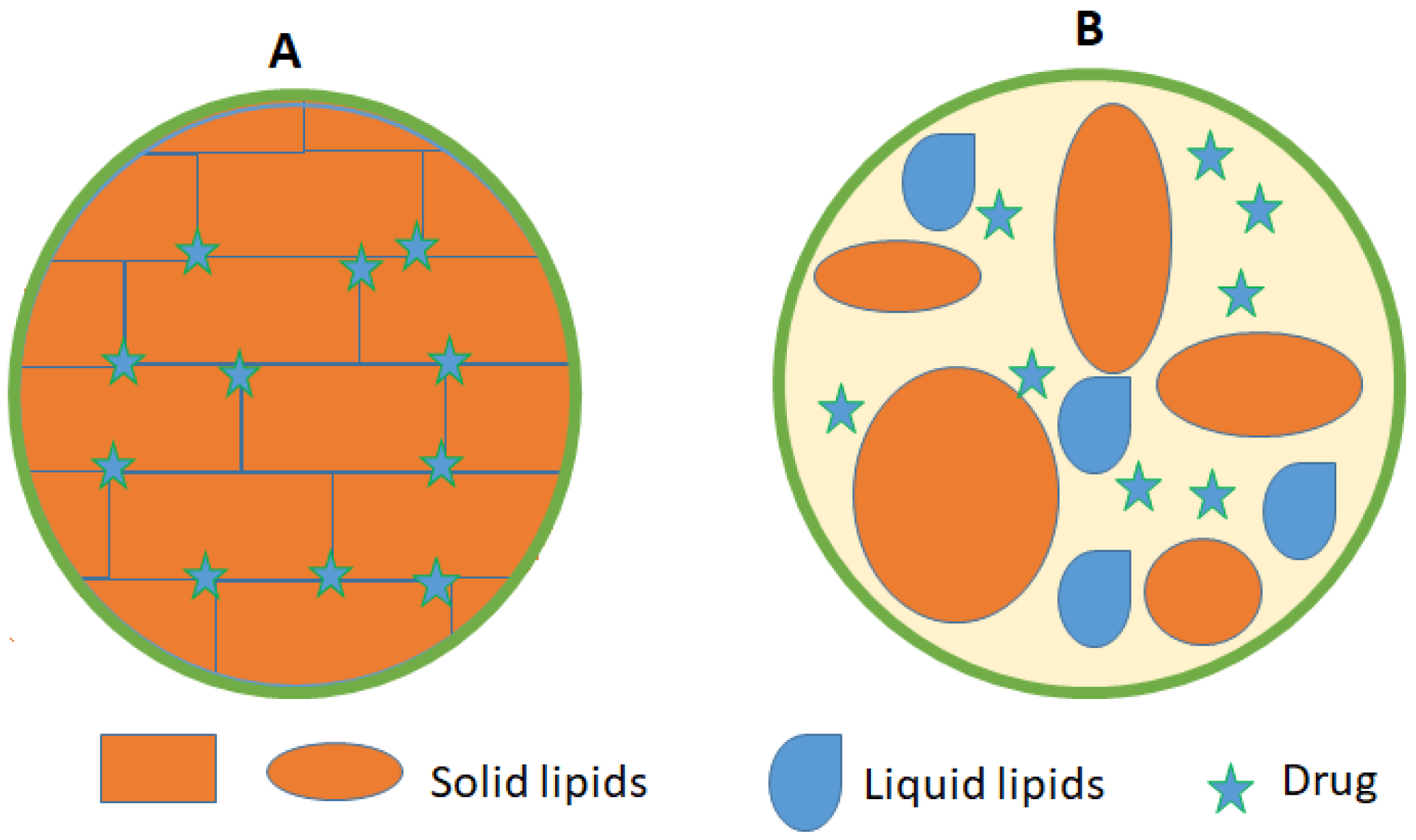
NLCs are the second generation of the lipid nanoparticle technology. NLCs are formed using a mixture of physiological and biocompatible solid lipids and liquid lipids (oils) in a ratio of 70:30 with surfactants and co-surfactants [66]. A melting point depression of the solid lipids is observed due to the presence of the liquid oil in the mixture. NLCs can also be loaded with cosmetics and medical bioactive compounds [76]. NLCs were designed to overcome SLNs drawbacks of insufficient drug loading capacity and decreased stability [61]. NLCs have a lower water content of the particle suspension and avoid/minimize potential expulsion of active compounds during storage [77]. Moreover, NLCs have a less ordered solid lipid matrix compared to SLNs that leads to higher degree of imperfections thus enable higher loading capacity [78] (Figure 3).
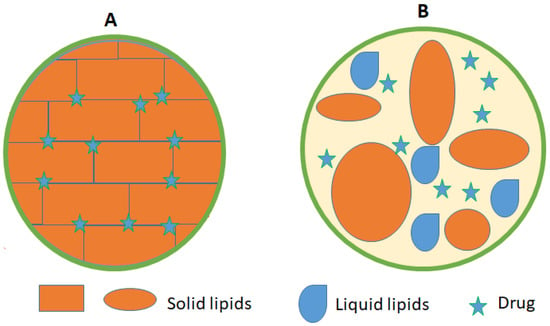
Figure 3.
Schematic view of (A) SLN) and (B) NLCs showing the drug location within the lipid matrix.
3.4. SLNs and NLCs Preparation Methods
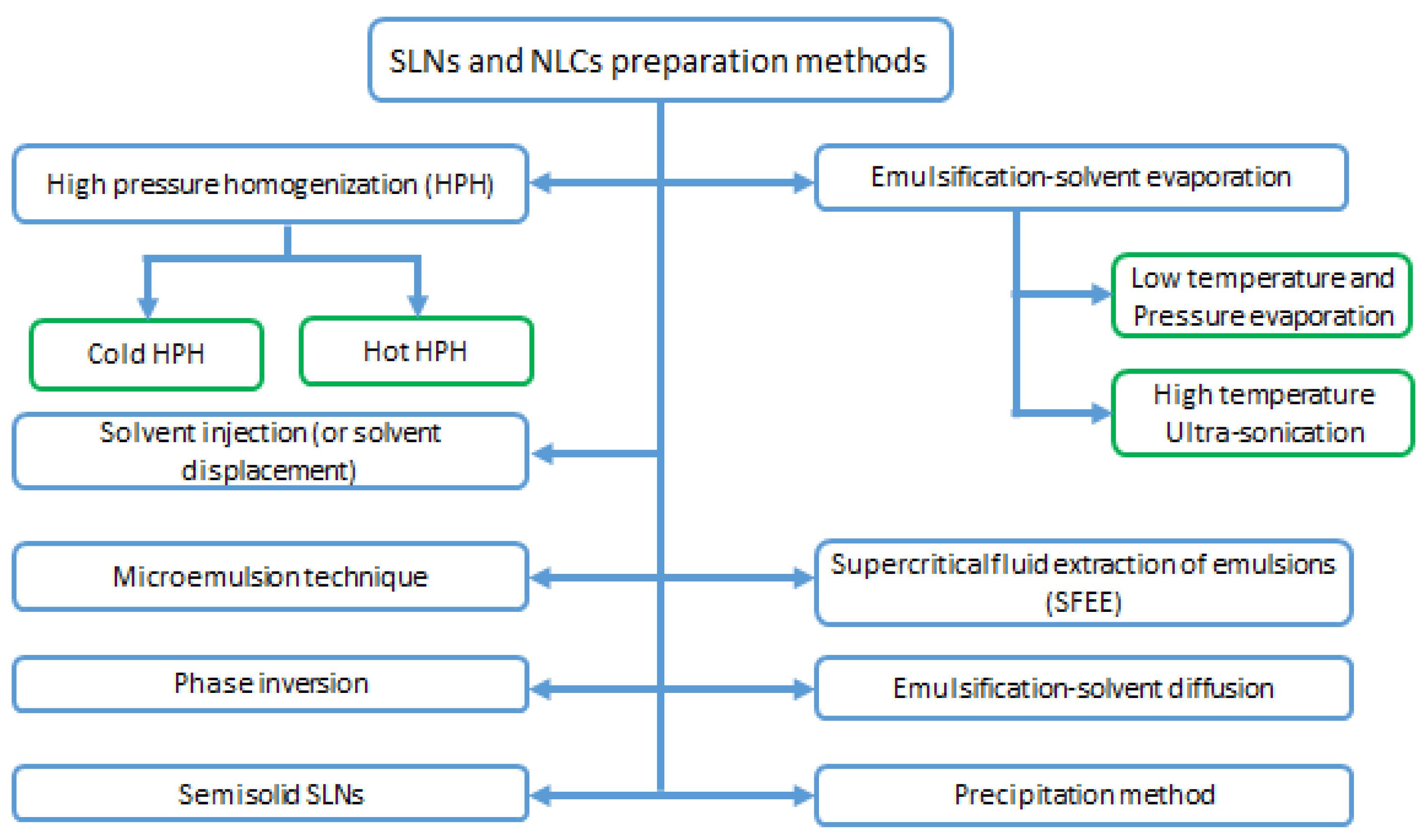
SLNs and NLCs can be prepared by different methods such as high pressure homogenization, solvent emulsification/evaporation or diffusion, microemulsion formation technique, supercritical fluid extraction of emulsions (SFEE)) [65], and ultrasonic solvent emulsification [61]. These methods are depicted in Figure 4.
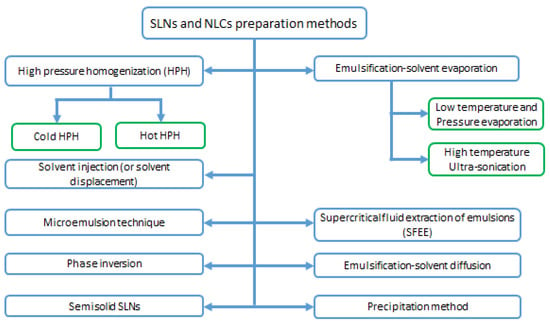
Figure 4.
Solid lipid nanoparticles and Nanostructured lipid Carriers preparation methods.
3.4.1. High Pressure Homogenization (HPH) Methods
HPH methods have several advantages over other methods. HPH is free of organic solvents, easily scaled up with short production time, and considered the most feasible for industrial synthesis [73]. In HPH methods, the active ingredient is dissolved and/or dispersed in melted solid lipid for SLNs or in a mixture of liquid lipid (oil) and melted solid lipid for NLCs [79]. A Hot surfactant, with a temperature of 5 to 10 °C above the melting point of the solid lipid or lipid mix, is used in the hot high-pressure homogenization to disperse the lipid melt containing the active ingredients using vigorous mixing [80]. The pre-emulsion is then prepared at the same temperature-high pressure homogenizer operated at three cycles at 500 bar or two cycles at 800 bars [81]. The major limitation for the hot homogenization method involves the temperature-dependent degradation of the active ingredient with a continuous movement of the drug between lipid and aqueous phase during the homogenization step [82]. On the other hand, the lipid melt loaded with the drug is solidified by cooling in the cold homogenization method. Then the solid mass is grounded to obtain lipid microparticles, then dispersed in a cold surfactant solution yielding a cold pre-suspension of micronized lipid particles [65]. This suspension is passed through a high pressure homogenizer at room temperature through a 5–10 cycles at 1500 bar [83].
3.4.2. Microemulsion Technique
Microemulsion was first exploited in lipid nanoparticle preparation by Muller and Gasco [84]. Microemulsion is usually formulated by vigorously mixing the melted fatty acids with an aqueous solution of surfactants and co-surfactants at a temperature above the melting point of the used solid lipid [78]. To achieve homogeneous microemulsion, a mild mixing in a cold water or buffer (0–4 °C) is preferred [85,86]. The LNs properties depend on the of microemulsion droplet size and temperature difference between microemulsion and cooled water. No special equipment or energy is needed for production of LNs using this method and it is simple to scale up the strategy [78].
3.4.3. Emulsification-Solvent Evaporation
This method is based on dissolving the lipids in an organic solvent such as methanol, acetone, dichloromethane, or chloroform to form the organic phase [87]. The organic phase is then mixed with an aqueous solution of a certain surfactant under vigorous stirring at nearly 80 °C and/or under reduced pressure until complete evaporation of the organic solvent [73]. The produced lipid nanoparticles are then solidified at 0 to 5 °C cooling temperature [88,89]. Ultra-sonication could be applied for the obtained emulsion at high temperatures for sufficient time before cooling the lipid nanoparticles in an ice bath [90].
3.4.4. Supercritical Fluid Extraction of Emulsions (SFEE)
This method is based on using Carbon dioxide as a supercritical fluid for solvent extraction from o/w emulsions. The major limitation for this method is that not all pharmaceuticals can be dissolved in carbon dioxide [91].
3.4.5. Emulsification-Solvent Diffusion Method
In this method, the solid lipids are dissolved in an organic solvent, and the produced organic solution is emulsified with excess water under gentle stirring. LNs are then formed as emulsion droplets due to the diffusion of the organic phase into the continuous aqueous phase. The LNs dispersion can be purified by ultra-filtration or lyophilization [60,78].
3.4.6. Solvent Injection (or Solvent Displacement) Method
This method is similar to preparation of liposomes using the injection method. A water-miscible solvent, such as ethanol, acetone, isopropyl alcohol, or ethanol, is used to dissolve the solid lipids. Using an injection needle, dissolved lipids are then injected into a stirring aqueous solution containing a surfactant [60]. The volume of the used organic solvent should not exceed 10% of the final solution. Types of the water-miscible solvent and the process of injection are the main factors that affect the produced lipid nanoparticles [92]. This easily handled method does not need technical equipment, and only safe organic solvents can be used [78].
3.4.7. Phase Inversion, Multiple Emulsion Technique
This method is mainly used for the preparation of LNs loaded with hydrophilic drugs and biologically active large molecules. SLNs are produced in this method from w/o/w multiple emulsions via the solvent in water emulsion diffusion technique [48]. First, the hydrophilic active molecule is dissolved in the inner aqueous phase of the w/o/w multiple emulsion, whereas solid lipids are dissolved in the water-miscible organic phase. Then LNs are formed by diluting the w/o/w emulsion in water, which enables diffusion of the organic solvent into the aqueous phase and precipitation of the LNs [73]. This method allows encapsulation of several bioactive compounds [93].
3.4.8. Precipitation Method
LNs can also be easily produced by precipitation method. In this method, the solid lipids are dissolved in an organic solvent (e.g., chloroform) and this solution is emulsified in an aqueous phase. After evaporation of the organic solvent, the lipid precipitates forming nanoparticles. A clear disadvantage is the use of organic solvents, which requires controlled evaporation on a large scale [48].
3.4.9. Semisolid Solid Lipid Nanoparticles
This fast and effective single-step process is performed by dispersing the hot surfactant in melted solid lipid solution above the melting point of the lipids under fast rotation using rota evaporator at 500 bar pressure in a one-min three cycles [60]. The hot viscous nanoparticles are then cooled at room temperature and recrystallize to form a semi-solid structure. This process is free of organic solvent, and enhances the stability of drug delivery systems [94].
3.5. Nanoemulsions (NEs)
Nanoemulsions or “ultrafine emulsions” are part of multiphase colloidal dispersions [95]. They are defined as dispersion made of oil, water, and surfactant(s) made of an isotropic and thermodynamically stable system with dispersed domain diameter and droplet sizes formed at the nano scale (within the range 20–200 nm) by means of mechanical forces [85,95,96]. NEs are divided into two categories, oil-in-water (O/W) and water-in-oil (W/O) types, in which water or oil is the continuous phase, respectively [97]. To facilitate the in situ pathway of the delivery system to the skin, nanoparticulates are used. Nanoparticulates consist of lipid nanoparticles and nanoemulsions to enhance physicochemical properties that are suitable for transdermal drug delivery [98]. Advantages of NEs include improving absorption of the drug through the skin, providing sustained release of the drug for extended periods of time, and protecting the encapsulated drug from degradation [99]. Therefore, when lipid nanoparticulates are applied to the skin, they are able to enhance adhesiveness and increase hydration. Thus, improved skin hydration is obtained because nanosized particles are capable of forming a thin layer on the surface of skin, which enhances blockage and reduces water evaporation from the skin [70].
3.6. NEs Preparation Methods
NEs preparation methods depend on the forming constituents and the scale-up requirements. NEs preparation methods are classified into high energy and low energy methods (Figure 5). High shear stirring, ultrasonic emulsification, and high pressure homogenization are examples of high energy methods [100]. In addition to the phase inversion temperature method (PIT), the Phase Inversion Composition (PIC) and spontaneous emulsification are the most common low energy methods [101].
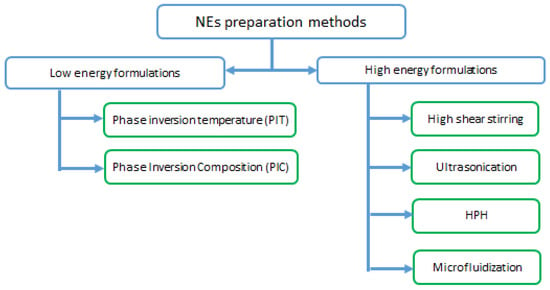
Figure 5.
Nano-emulsions preparation methods.
3.6.1. High Energy Formulations
High energy formulations are extensively used, where high mechanical energy is used to supply external energy to produce nanoemulsions with high kinetic energy by breaking up large droplets into nano-sized ones [102]. The mechanism of high energy formulations follows two-steps; reducing the size of large droplets followed by surface absorption. The droplet size is reduced by increasing the fluid compression to overcome the surface tension between the two phases, resulting in a high interfacial area [103]. High energy methods are classified into four categories:
High Shear Stirring
This method applies a hydrodynamic shear stress. The shear stress reduces droplet size, then surfactants and stabilizers are added to stabilize the smaller droplets. Disadvantage to this method, is that the average droplet size is rarely less than 200 nm, and as the viscosity of the medium increases the efficiency of this method decreases. A pre-emulsification step is always required to achieve a nanoscale droplet [104,105].
Ultrasonication
Cavitation is the principle of this method. The applied sonication power leads to an increase in the interfacial area by releasing energy and the formation of bubbles, which implode and create shock waves. High energy sonication may also lead to decomposition of surfactant molecules by thermal decomposition of water into free radicals. However, this method is not suitable for industrial expansion, it can only be used in small batches [106,107].
High Pressure Homogenization (HPH)
HPH is the most popular high energy method, and is placed under high pressure conditions (10–350 MPa) [101]. Nano-droplets are produced by subjecting the components to cavitation, shear forces, and increasing the number of cycles of operation. However, there are some limitations to this method, such as lack of efficiency with highly viscous fluids, and the big challenge is that the method is not suitable for thermos sensitive compound [100,108,109].
Microfluidization
Formulation of nanofluidic emulsions requires the use of high energy inputs and powerful equipment for a much lower surfactant-to-oil ratio (SOR < 0.1). The ratio of surfactant-to-oil (SOR) is relatively lower than other high energy methods (SOR less than 0.1). In this process, preparation of the coarse emulsion starts by homogenized oil and water phases. Then it is pumped into a chamber lined with microchannel by reciprocating pumps with pressure in the range of 1400–3500 kPa [110,111]. The fluid flow produces finer droplets compared to other methods. However, this method is not suitable for large-scale production [112].
3.6.2. Low Energy Formulations
In these methods, the oil phase emulsifies into droplets using the internal energy of the nanosystem. The chemical potential of the surfactant leads to spontaneous emulsification. These methods are suitable for scale up production [113,114]. The most common low energy methods are as follows.
Phase Inversion Temperature (PIT) Method
A specific temperature-sensitive nonionic poly-ethoxylated surfactants are used in this method [115], by using the inversion temperature of the lipid phase to form the nanodroplets by the drop of the interfacial tension. The system must be quickly cooled to a low temperature to prevent the droplets from coalescing [115].
Phase Inversion Composition (PIC) Method
In this method, a constant dilution is used at a given temperature to accelerate the shifting of the lipophilic/hydrophilic balance of the nanosystem. This described using three phase diagrams [115,116,117]. Briefly, the continuous phase (water or oil) is slowly added over the dispersed phase (oil/surfactant or water/surfactant). During the emulsification pathway, a phase inversion occurs, and PIC is induced by a change in composition at constant temperature during the emulsification process [118].
3.7. LNs Characterization
Numerous approaches were adapted to verify the physiochemical characteristics of the prepared nanoparticles. Several factors should be considered, such as particle size, surface charge, encapsulation efficiency and particle morphology, to clarify the performance and the stability of the formulated LNs. Table 1 summarizes the main used approaches for the characterization of LNs with their investigated characteristics.

Table 1.
Characterization methods for lipid nanoparticles.
3.7.1. Particle Size and Distribution
Nanoparticles average size can be determined using several methods such as photon correlation spectrometry (PCS) (also known as dynamic light scattering (DLS)), laser diffraction (LD), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) [119]. SEM and TEM are very useful in determining shape and morphology of lipid nanoparticles and allow the determination of particle size and particle size distribution [120]. DLS measures the fluctuations in scattered light arising from Brownian motion of the nanoparticles. DLS provide an average particle size (z-average) and polydispersity of the nanosystem for the particle size distribution. LD based on the diffraction pattern depicting particle shape and size using Fraunhofer theory [78,121]. On the other hand, poly dispersity index (PDI) indicates the wideness of the size distribution of a nanoparticle population. It is the measure of homogeneity between nanoparticle distribution and its value between 0 and 1. PDI measurement is essential to confirm the narrow size distribution of the nanoparticles [122]. The desirable regular PDI for LNs should be less than 0.22 [110].
3.7.2. Surface Charge
Measurement of zeta potential (ZP) predicts the long-term storage stability of the nano-dispersions. At higher ZP, particle aggregation is less likely to occur, due to electrical repulsions [123]. The measurements of ZP were performed by using the Laser Doppler electrophoresis by applying an electric field across the sample. Despite the general rule that ZP of the nano-dispersion outside the range of ±30 mV indicates a high electrostatic stabilization of nanoparticles [124]. A stable and effective SLNs and NLCs for dermal delivery of fluconazole against cutaneous candidiasis with a ZP of −25 and −29 mV, respectively, were developed [125]. In addition, Gupta et al. developed a stable SLNs with −21.2 mV for brain targeting [126]. Moreover, Argimon et al. developed a vitamin A-Loaded SLNs for topical application with slightly negatively charged mean ZP value of −17.7 ± 1.9 mV. The studied SLNs were monitored over a period of 45 days and no phase separation was observed in this period and tend to remain stable [127]. Electrical conductivity (ionic strength), pH, dilution factor and the nature of the nanoparticles components can affect the ZP [128]. LNs may also be sterically stabilized by coating the nanoparticle with a hydrophilic polymer such as polyethylene glycol (PEG, polyethylene glycol) to prevent aggregation [64].
3.7.3. Encapsulation Efficiency (EE)
EE determines the amount of drug loaded into the LNs. It is the ratio between the weight of encapsulated drug and the total weight of drug added to the nano-dispersion. EE can be determined either by direct or in direct way [129]. Indirect measurements involve quantification of the free unloaded drug, which is then subtracted from the total weight of drug added to the nano-dispersion. Direct EE measurements involve quantication of the loaded drug compared to the total amount of drug added to the nanoparticle. Free unloaded drug can be removed by various means such as ultrafiltration, centrifugation, or using dialysis membrane with the appropriate cut off [129]. Drug quantification can be achieved using calibration curves and determined by spectrophotometric tools [130].
3.7.4. Crystallinity and Polymorphism
LNs may undergo a polymorphic transitional variation leading to a possible unwanted drug leakage during long-term storage [131]. The crystallinity of LNs has an impact on the encapsulation efficiency and degree of drug release [132]. Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and X-ray diffraction (XRD) are usually used to investigate crystallinity and polymorphic status of the LNs [133]. DSC detects the heat change due to physical or chemical alteration within the nanoparticle as a function of temperature [134]. DSC provides information about the status of lipid, melting, and crystallization behavior of solid lipids in nanostructures compared to their precursors. Much information related to polymorphism, crystal structure, eutectic systems, glass transition temperature, and drug lipid interactions can be obtained through interruption and fusion of the crystal lattice of the nanoparticle by heating or cooling processes [135].
In XRD, the monochromatic beam of X-ray is diffracted at different angles according to the type and arrangement of atoms inside the planes in the crystals. Lipids inside the LNs can aggregate into different polymorphic forms [78]. Wide angle and small angle X-ray scattering techniques (WAXS and SAXS respectively) are used to discover the layer arrangements, crystal structure, phase, and polymorphic behavior of lipid and bioactive molecules. It also gives information about lipid lattice and localization of drug in it [136].
4. LNs Mechanism of Skin Penetration
Skin administration has the advantage of avoiding hepatic first-pass effect and an increased localization of bioactive via skin organelles such as hair follicles. Obtaining dermal or trans-dermal drug delivery is often challenging due to the need to overcome the skin strong barriers [130]. The main barrier that limits the drug penetration through skin layers is the SC. Other less mentioned barriers include, Langerhans cells in the epidermis layer, macrophages in the dermis layer, dendritic cells, and enzymatic systems [137]. Topical administration is limited to hydrophobic and low-molecular weight drugs. Because hydrophilic drugs have low oil/water partition coefficients, high molecular weights and ionic characters do not easily cross the SC. The bioavailability of drugs permeating the skin can be increased using lipid nanoparticles because of the small particulate size with close contact to SC [138].
SLNs and NLCs are considered to be excellent carriers for cosmetic and dermatological application. They protect the fragile active compounds from chemical degradation and enhance the water content of the skin [139]. Compared to conventional topical formulations, NEs have been also reported to improve the transdermal permeation of several drugs [138]. These lipid nanoformulations resemble skin structure and have a safe effect when used topically. Due to their high control behaviors on skin penetration of active substances, they have UV-blocking and skin hydration behavior [140].
Mechanism of nanoparticle penetration through the skin is still not fully understood [141]. Active ingredients can pass skin layers by several penetration mechanisms including trans-cellular, inter-cellular, and trans-appendages. The penetration mechanism through the skin layers depends on the physicochemical characteristics of free drugs and the drug delivery system, such as hydrophilicity/lipophilicity of the free drug and the particle size, charge, fluidity, and lipid content of the nanocarriers [140]. The main proposed mechanism of LNs skin penetration involves that LNs can make close contact with superficial junctions of SC and penetrate between corneocytes islands, allowing superficial spreading of the active ingredient. After water evaporation from the skin-applied nanosystems [142], LNs form an adhesive layer occluding the skin. In addition, hydration of SC may reduce corneocyte packing and width inter corneocytes gaps, and influence partitioning of the drug into SC. Since epidermal lipids are rich in SC, LNs on the skin surface would allow lipid exchange between SC and the nanocarriers. Lipid nanoparticles have the potential to deliver drugs via the follicles [143]. Moreover, each follicle is associated with sebaceous glands, which secrete the triglycerides, squalene, and waxes rich sebum, creating an environment enriched in lipids. This environment is beneficial for trapping of LNs. Furthermore, some glyceride lipids present in LNs may accelerate the entrance into the follicles/sebaceous glands [143].
SLNs, NLCs, and NEs have been highly recommended as dermal and transdermal drug delivery systems [144]. They have an adhesive and occlusive properties, which enable them to form a homogenous and uniform layer on the SC. This layer increases the residence time and improves skin penetration [145]. Moreover, SLNs and NLCs are capable of interacting with lipid bilayer membranes and cause lipid rearrangement, which can improve the penetration of encapsulated drug molecules [146]. On the other hand, targeting the different skin organelles including pilosebaceous gland, hair follicle, and dermis layer for the better management of different local diseases of the skin layers has been considered during recent decades. In this context, the nanoparticles average size could determine the depth of penetration through the hair follicles [147,148]. Follicluar drug delivery provides an alternative route to avoid direct contact of SC [63]. The hair follicles act as a vascular rich-reservoir for drugs and the nanocarriers [149]. Furthermore, lipid drug delivery systems can target sebaceous gland associated with hair follicles for selected treatment. Therefore, it is possible for compounds containing lipids, oils, surfactants, and alcohols such as SLNs, NLCs and NEs to facilitate transfollicular transport of both hydrophilic and lipophilic compounds [150].
5. Nanocarriers for Transdermal and Dermal Drug Delivery
In the dermal delivery system, drugs and cosmeceuticals are delivered into the skin as the primary target (local delivery) [151]. In comparison, transdermal delivery is a self-contained, specific type of dosage that delivers drugs to diffuse through the skin layers to reach the systematic circulation at a controlled rate [152]. Transdermal drug delivery is preferred due to its ability to avoid first-pass metabolism of drugs. Both dermal and transdermal systems are easily applied without pain and with reduced side effects [153].
Lipid nanocarriers play a crucial role in dermal and transdermal drug delivery for many reasons. They are produced from inexpensive, physiologically well-tolerated lipids, which give them safe interaction with skin layers [154]. Incorporation of cosmeceuticals and drugs into lipid nanocarriers does not require organic solvents at any processing stages, preventing organic waste formation and keeping the formulation safe [154]. Lipid nanocarriers facilitate dermal and transdermal delivery of both lipophilic and hydrophilic drugs [155]. The small sizes of these carriers ensures direct contact with the SC, possibly increasing the amount of drug that is absorbed into the skin [68]. Lipid nanocarriers also reduce bioactive compounds adverse side effects, protect sensitive incorporated bioactive compounds from degradation (oxidative and chemical) [156,157], and allow controlled release [158].
Moreover, Lipid nanocarriers have a unique property called the occlusive effect [159,160]. The occlusive effect tends to form a thin film on the skin surface, and this reduces transepidermal water loss [161]. The occlusive effect becomes more valuable as particle sizes decrease and surface area increases [161]. The occlusive also has an exceptional capacity to enhance bioactive molecules ability to permeate the uppermost barrier, the SC. Hence, this leads to higher cellular uptake of bioactive molecules and modified release profile [157,160]. In general, lipid nanocarriers facilitate skin permeation via adhesion, occlusion, and hydration effects on the skin [162].
5.1. Vitamins and Vitamin Derivatives Delivery
Vitamins are active agents in pharmaceuticals and cosmetics due to their antioxidant [163] and photoprotective properties [149]. However, these formulations efficacy has been limited due to their lipophilicity, chemical instability, and low skin penetration [164]. In this respect, lipid-based nanocarriers, including SLNs and NLCs, offer a solution to the conventional formulations containing vitamins, specifically for vitamins A, E, and C, and their derivatives [163,165]. Vitamin A is an active agent used in anti-aging products and helps treat numerous skin disorders such as inhibition of UV-induced extracellular matrix degradation and epidermal cell renewal [166]. Vitamin E (tocopherol) has a vital role in biological activities. It acts as an anti-tumor [167], neuroprotective [168], and photo-protective [169]. It is also considered the main physiologic barrier antioxidant [170]. Vitamin C, also known as ascorbic acid, is an essential water-soluble molecule with strong antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity. On the other hand, vitamin C is required for many important biosynthesis carnitines, collagen, and neurotransmitter molecules in the body [171]. Additionally, vitamin C is also essential in treating skin diseases that range from mild inflammation to skin cancer [172].
Within this context, Al Zahabi and coworkers developed NLCs containing vitamin A and compared them with SLNs. These formulations were prepared from Emulium® κ2 (a mixture of lipids, derived from natural waxes of Candelilla, rice bran, and Jojoba Polyglyceryl-3 Esters), Prickly Pear seed oil as lipid phase, and Brij 721 as a surfactant. The optimized NLCs exhibited a smaller particle size (215–244 nm) than SLNs (265 nm). In addition, NLCs formulations showed an enhancement in the drug release profile, higher drug loading, and better skin deposition ex vivo in rat skin [173].
Similarly, Argimón et al. [127] developed SLNs loaded with vitamin A for topical application to protect this vitamin from degradation. The formulation offered particle size around 40 nm and entrapment efficiency above 90%. Additionally, the formulation successfully protected vitamin A from degradation. Moreover, the lipids in this formulation showed a melting point so close to average body temperature making them a good option for topical application of vitamin A.
Agrawal et al. [174] developed NLC- formulations to encapsulate acitretin, a vitamin A derivative, for topical treatment of psoriasis. The formulations were prepared by the solvent diffusion technique using 32 full factorial experimental design, and contained precirol ATO 5, oleic acid, and Tween 80. The optimized acitretin-NLC formulations offered entrapment efficiency of 63.0%, average particle size of 223 nm, and zeta potential of −26.4 mV. Additionally, 1% w/w Carbopol 934 P gel base was used to incorporate acitretin-NLC formulations. In vitro release studies of acitretin -NLC revealed a biphasic drug release pattern, initial fast release, and delayed sustained release. Clinical investigations showed that the NLC gel improved the therapeutic index for acitretin and reduced local side effects compared to plain gel. Similarly, Sabouri et al. [175] introduced nanoemulsion containing tretinoin, a widely used retinoid, for topical treatment of acne vulgaris. These researchers used high pressure homogenization as a preparation method to have a stable nanoemulsion formulation with an average particle size of 150 nm and encapsulation efficiency of 99%. The formulation succeeded in enhancing the therapeutic efficacy of tretinoin and reduced its side effects.
A group of researchers [176] managed to design an adapalene (vitamin A derivative) loaded SLN formulated in cabopol gel as an acne treatment. The optimized formulations were prepared using the hot homogenization technique and based on Box-Behnken design (32 factorial designs). Optimized adapalene—SLN contained glyceryl monostearate as a lipid. Non-ionic surfactants including Pluronic F68, Brij 78, Tween 80, and span 20 were screened to alter the SC barrier function toward drug permeation; results indicated that Pluronic F68 is very efficient. Adapalene—SLN showed particle size of 102 nm and entrapment efficiency greater than 85%. Skin irritation study proved adapalene—SLN has had more excellent skin tolerability than conventional Gel. Moreover, skin tolerability, bioavailability and anti-acne potential were enhanced. In a similar fashion, scientists developed adapalene-loaded SLNs incorporated into carbopol hydrogel for topical application [177]. Clinical investigation showed that adapalene-loaded SLNs could resist systemic uptake of adapalene in skin layers and localize it in the epidermis. Another study [178] introduced gel loaded with NLCs and co-encapsulated with adapalene and vitamin C. This formulation was prepared by the high pressure homogenization and composed of tristearin, labrasol, phospholipid-90NG, and Tween 80. Carbopol 934 and ascorbyl-6-palmitate were fabricated to form the Gel. Co-administration of vitamin C resulted in an adjunct effect in acne therapy in physiological conditions. This combination was investigated on a testosterone-induced acne model and showed higher skin-targeting potential compared to free adapalene [178].
For topical application, a group of researchers [179] developed retinyl palmitate –SLN formulation modified by dicetyl phosphate. This formulation also contained glyceryl palmitostearate and PEG-32 glyceryl stearate, and was incorporated into a hydrogel. PEG-32 glyceryl stearate, an amphiphilic molecule with a high hydrophilic-lipophilic balance value of 13, has an essential role in preventing aggregation. The optimum ratio of glyceryl palmitostearate to PEG-32 glyceryl stearate was 60:40 to have homogenous SLN smaller than 100 nm and an encapsulation efficiency greater than 99%. Retinyl palmitate distribution in the skin was enhanced by 4.8 fold after surface modification and delivered to a greater depth than those unmodified SLNs. This formulation could be useful in the preparation of skincare and anti-wrinkle products.
On the other hand, Pinto et al. [180] succeeded in developing NLC formulations containing four bioactive vegetable oils (sunflower, sweet almond, olive, and coconut oil) enriched with α-tocopherol. The achieved entrapment efficiencies and drug loading capacity were above 79.4% and 48.4%, receptively. The particle sizes and zeta potential were between 240–315 nm and −45.6 to −55.1 mV, respectively. The antioxidant activity assessment demonstrated that all free NLCs prepared with each vegetable oil have a vigorous inherent scavenging activity. The formulations also assured controlled release of α-tocopherol and were stable for eight months. This study has contributed to the production of advanced cosmetic products focusing on natural bioactive vegetables.
Similarly, de Souza and colleagues [181] introduced NLC containing vitamin E using the emulsion-solidification technique as the preparation method. Three liquid oils, namely avocado oil, coconut oil, and medium-chain triglycerides, were mixed with stearic acid and nonionic surfactants (Tween 80, Cremophor RH40, and Pluronic F-127). Some parameters such as the proportion of liquid lipid, time, and energy of sonication were employed to compare their effects on the physical and chemical properties, including particle size and drug release profile. The NLC prepared from medium-chain triglycerides as liquid lipid at a 3:1 mass ratio of liquid lipid-to-solid lipid was the most promising nanocarrier because it exhibited the highest vitamin E release and had homogeneous particle size distribution. Moreover, Tween 80 was the most effective in producing homogeneous particle size distribution with the lowest mean particle diameters and showed the highest release rate for particles.
In addition, Chen and coworkers [182] formulated three antioxidants: resveratrol, epigallocatechin gallate, and vitamin E, into several different lipid nanoparticles to provide a long lasting antioxidant effect. These formulations were prepared from cetyl palmitate, compritol®, or phospholipon 80 as solid lipid, sesame oil as liquid oil, and Tween 80 as a surfactant. Skin penetration studies showed that the formulations improved the penetration of resveratrol through the SC. Moreover, the formulations containing vitamin E and resveratrol provided adequate protection against UV-induced degradation, while those containing epigallocatechin gallate did not show protection from UV degradation.
Recently, Haruna et al. [183] developed nanoemulsified α-tocopherol and γ-tocotrienol formulations for the treatment of atopic dermatitis, a chronic skin inflammation. These researchers designed two types of formulations, water-poor NE and water-rich NE containing Tween 80, span 80, sunflower oil, α-tocopherol, and γ-tocotrienol. The droplet size of the NE was smaller than 150 nm with negative zeta potential values. Furthermore, these researchers combined the use of this formulation on the skin with a microwave system to assist the translation of this formulation into the skin. The formulations exhibited higher skin retention and penetration than the neat vitamin E. In a similar fashion, Prasertpol and colleagues [184] developed NLCs formulation loaded with vitamin E acetate to treat hair damage using a high pressure technique. The formulations were prepared from glyceryl monostearate, stearic acid, and myristic acid as lipids and Tween 80 as surfactant. These nanocarriers were with average particle size nm of 140 nm and zeta potential values above −45 mV.
Brownlow and colleagues [185] developed a vitamin E-nanoemulsion formulation loaded with genistein for dermal photoprotection. Nanoemulsion was prepared by hybrid homogenization and composed of tocomin (red palm oil), isopropyl alcohol, and a surfactant mixture of polyethyleneglycol hydroxystearate and polyethyleneglycol succinate. These researchers investigated the effect of several polyethoxylated nonionic emulsifier blends toward the formulation. The optimized formulation offered an average particle size below 150 nm and a zeta potential of −30 mV. This formulation showed enhanced preventive and UVB-protective properties for genistein, a natural chemopreventative agent, and can be useful for topical treatment of UV-induced skin disorders.
On the other hand, Nasiri et al. [186] developed α -tocopherol acetate-loaded with SLN coated with chitosan. The optimized formulation displayed a size of 175 nm and an entrapment efficiency of 90.58% and was stable at least for three months at refrigerated temperature. Coating with chitosan caused the negative zeta potential to have a positive value (around +35 mV). In a similar fashion, Campani et al. [187] formulated nanoemulsions containing vitamin K for topical application. This formulation was prepared with low energy and contained an oil phase of α-tocopherol and Tween 80 as a surfactant. The formulation was stable for a prolonged time at different temperatures and prepared by a simple and economical method.
NLC loaded with calcipotriol, a synthetic derivative of Vitamin D3 form, and enriched with nanogel (carbopol 931 gel base) for topical treatment of psoriasis was formulated by Pradhan and coworkers [188]. The achieved entrapment efficiency for this formulation was 85.31 ± 1.18%, the mean particle size 123.60 ± 1.21 nm, and zeta potential −36.8 ± 8.85 mV. Drug release was prolonged and obeyed Higuchi mode. In vivo data showed negligible permeation of drugs into the systemic circulation, and retention of the drug from nanogel formulation was enhanced by 1.57 and 3.67 folds in the SC and viable layers, respectively, compared to pure calcipotriol containing gel formulation. Similarly, Teeranachaideekul et al. [189] designed an NLC formulation loaded with ascorbyl palmitate, a vitamin C derivative with a wide range of cosmetic applications. This formulation showed a modified release profile and enhanced therapeutic efficiency. Table 2 summarizes the studies related to lipid-based nanocarriers loaded with vitamins or vitamin derivatives for dermal and transdermal applications in recent years.

Table 2.
Lipid-based nanocarriers loaded with vitamins and vitamin derivatives.
5.2. Sunscreens Delivery
Sunscreen products are experiencing increasing demand to deal with health problems associated with exposure to solar radiation such as skin burn [51], aging of the skin, damaging of connective tissues and collagen [51], and an increased risk of developing skin cancers [51]. Lipid-based nanoparticles are gaining tremendous attention for different kinds of sunscreens (inorganic, herbal, synthetic, and combined) since they proved to have a synergistic UV scattering effect when used as a carrier for molecular sunscreens [190]. Similarly, solid lipid nanoparticles provide outstanding photo-protective action for the formulated sunscreens. They increase their UV-blocking ability and enhance sun protection factor (SPF) [191,192]. In addition, solid lipid nanoparticles help reduce the concentrations of incorporated molecular sunscreens, minimizing the undesirable side effects of sunscreens and production costs [190]. Moreover, molecular sunscreens have been reported to have a higher UV absorption effect when incorporated into particles of SLNs [192]. The increased UV absorption capacity leads to less penetration of UV radiation into the skin [7].
Nanostructured lipid carriers are an efficient entrapment system for sunscreens, with the characteristics of UV-blocking. The use and penetration of particulate scatter such as ultra-small titanium dioxide cause immune system irritation. Incorporating 10–120 nm TiO2 nanoparticles into NLCs with approximate diameters of 400 nm firmly enclose TiO2 nanoparticles and prevent them from diffusing out. Nanostructured lipid carriers also decrease potential skin irritation thus maintaining long-term stability [193]. In this regard, Puglia and coworkers [193] investigated NLCs and NE’s efficiency as carriers for the following UV filters: ethyl hexyltriazone, diethylamino hydroxybenzoyl hexyl benzoate, bemotrizinol, octyl methoxycinnamate, and avobenzone. Compritol 888 ATO and Miglyol 812 were used as lipid phase and Lutrol F68 as a surfactant in NLC formulation, whereas Miglyol 812 replaced Compritol 888 ATO in NE formulation. Findings showed that NlCs were more effective than NE; they preserved the photostability for all UV filters except for octyl methoxycinnamate and avobenzone. NlCs also lowered the skin permeability of the sun filters and maintained their location on the skin surface. In another study, researchers [56] compared SLN and NLC dispersions as possible carriers for octyl methoxycinnamate and found that NLC dispersions were more effective against UV-mediated filter photodegradation.
Nikolic et al. [194] incorporated a set of UV chemical filters (ethylhexyl triazone, bis-ethylhexyloxyphenol methoxyphenyl triazine, and ethylhexyl methoxycinnamate) into NLC formulations that were incorporated into a hydrogel. Nine solid lipids (Atowa, Compritol, Softisan, Dynasan, Phytowax, Syncrowax, Beeswax, Carnauba wax, Apifil) were investigated; results showed that NLCs, which are composed of carnauba wax were superior in UV absorbance. Results also revealed that the SPF values of UV filters increased by 45%. Miglyol® 812 was used as oil and PlantaCare® 2000 UP as a surfactant to have NLCs with particle size around 200 nm. On the other hand, Sanad and colleagues [195] designed NLCs loaded with oxybenzone to enhance its limited solubility. The formulations were produced by the solvent diffusion method and involved using monostearate as solid lipid and Miglyol 812 or oleic acid as liquid oil. In this formulation, 23 factorial design was employed to investigate the effect of oxybenzone concentration (5% and 10%), type of liquid lipid, and its concentration (15% and 30%). Results indicated that smaller particle sizes and entrapment efficiency were obtained when Miglyol 812 was used instead of oleic acid. Additionally, oxybenzone concentration affected only particle size and not entrapment efficiency, and the diameters of the particles increased as well as the oxybenzone concentration increased. Moreover, NLCs made with Miglyol 812 (10%) showed slower drug release when compared to those prepared from oleic acid (30%). The formulated sunscreen was successfully incorporated into a hydrogel without any crystallization problem, and oxybenzone irritation effect reduced and its UVA protection factor enhanced by about six-fold.
Niculae and coworkers [196] encapsulated methoxydibenzoylmethane (BMDBM), UVA protector, into NLCs formulations composed of two solid lipids (cetyl palmitate and glyceryl stearate) and two liquid lipids (medium-chain triglycerides and squalene). In a subsequent study, these workers co-encapsulated BMDBM and octocrylene into a different kind of NLC containing rice bran oil or raspberry seed oil [197]. Co-encapsulation and co-release of both types of UVA and UVB absorbers improved the photoprotection effect (EUVA-PF = 40.2 and SPF UVB = 17.3). The high content of vegetable oils led to a high capacity to scavenge the free radicals generated in a chemiluminescence system and enhanced antioxidant activity. Furthermore, the required amount of UV blockers was reduced after incorporating vegetable oils, which resulted in a safe NLC formulation with reduced undesirable side effects on biological systems. Niculae et al. [50] also co- encapsulated BMDBM and α-tocopherol, antioxidant, into SLNs and NLCs formulations to enhance the photostability. Results demonstrated that α-tocopherol was efficient in the photostabilization of the unstable BMDBM. However, it did not improve the photoprotective properties, including SPF and Erythemal UVA protection factors, as did SLNs/NLCs loaded with only BMDBM. SLNs showed better photoprotective properties than NLCs formulation.
Researchers [198] designed various NLCs formulations based on vegetable oils, namely amaranth and pumpkin, to co-encapsulate and co-deliver octocrylene and avobenzone. NLCs were prepared by selecting a mixture of glycerol monostearate and cetyl palmitate, or emulgade and carnauba wax as solid lipid, squalene, or pumpkin oil, or amaranth as liquid lipid. The formulations stabilized by a surfactant mixture composed of sodium collate, Tween 20, and Poloxamer. All formulations showed a prolonged release profile, improved antioxidant activity, and photoprotective properties (SPF of 40–45 and FP-UVA of 27–34) compared to the conventional cream. The antioxidant activity was superior in the formulations containing amaranth oil. The highest encapsulation efficiency was observed for a formulation consisting of emulgade, carnauba wax, and amaranth oil. Others [199] proposed NLCs formulation containing bocaiúva almond oil or pulp almond oil to co-encapsulate and co-deliver both octocrylene and avobenzone. Scientists investigated the effect of the oils on enhancing the photoprotective activity and their ability to replace organic filters. Nanostructured lipid carriers loaded with bocaiu’va almond oil showed average diameters between 106.9 and 188.4 nm. The entrapment efficiency for avobenzone was 2.3 times higher in NLC containing bocaiúva almond oil than NLC containing pulp oil. The entrapment efficiency for octocrylene was close in both NLC formulations. These studies confirmed that NLC containing bocaiu’va almond oil has a synergistic effect and can eliminate the ratio of organic filters in sunscreen products.
Andre´o-Filho et al. [200] introduced SLN loaded with octyl methoxycinnamate and partially substituted it (20%) with urucum oil. Glyceryl monostearate was selected as lipid matrix, sodium lauryl sulfate and hydroxyethylcellulose were used to enhance formulation stability. Solid lipid nanoparticles containing urucum oil were stable and safe for topical application. In the meantime, replacing the UV filter with urucum oil did not cause a reduction in SPF, and this makes sun protection products safer. Within the same context, Badea et al. [201] implemented numerous NLCs containing vegetable oils (pomegranate seed, wheat germ, rice bran, raspberry seed, carrot root, and blackcurrant seed) to achieve formulation with high antioxidant activity and adequate UV protection. The used solid lipid was a blend of emulgade and glycerol monostearate, and the stabilizer was a mixture of sodium collate, Tween 20, and Poloxamer. These formulations were loaded with diethylamino hydroxybenzoyl hexyl. Among the produced NLCs, the ones based on a mix of pomegranate seed oil and wheat germ oil were the most effective against UV radiation (a UVAPF of 9.5 and SPF of 5.1) and showed the highest entrapment efficiency. Recently, Badea et al. [202] introduced NLC loaded with diethylamino hydroxybenzoyl hexyl benzoate and naringenin. The addition of naringenin formulated into Carbopol 940 hydrogels with polyphenol-rich UVA filter increased the SPF and the antioxidant activity against both short- and long-lived radicals. These formulations showed no cytotoxicity concentrations below 50 g/mL.
Chu et al. [203] developed NLCs loaded with the organic filters Uvinul T150 and Uvinul A Plus Granular and containing pumpkin and kenaf seed oil as liquid oil and carnauba wax and beeswax as solid lipid. A mixture of Tween 20, soy lecithin, and poloxamer 188 worked as emulsifiers and stabilizers. NLC formulation containing a mixture of oils contributed to enhancing only antioxidant properties but not UV-absorbing properties and entrapment efficiency. The optimized formulations offered particle sizes of 238 nm and showed high entrapment efficiency (95%), antioxidant activities, and UV-absorbing properties.
Salunkhe and coworkers [204] developed idebenone-loaded NLC as a sunscreen product with antioxidant properties. Idebenone-loaded NLC was prepared by the solvent precipitation method and contained Compritol 888 ATO as solid lipid, Captex 500 P as liquid oil, and Labrasol and Transcutol surfactant and co-surfactant, respectively. The optimized formulation offered a particle size of 605 nm and an entrapment efficiency of 82.5%. Clinical studies showed enhanced antioxidant effect, high skin deposition, and SPF value of 23. In a similar fashion, Asfour and colleagues [205] created NLC formulations containing titanium dioxide (6%) to improve the photostability of all-trans retinoic acid and reduce its skin photosensitivity. Dependent variables such as particle size and viscosity were optimized by Box–Behnken. Three factors, namely, % total lipid, % liquid lipid, and % total surfactant, were selected as independent variables. The in vivo study conducted on mice proved that the optimized formulation improved all-trans retinoic acid photostability by about 1.5 and 2 times.
Pivetta et al. [206] introduced NLC that efficiently retained quercetin, an unstable flavonoid with weak skin permeability. These NLCs offered an average particle size of 130 nm, entrapment efficiency of 97.42%, and recrystallization index of 13.03%. Moreover, nanocarriers containing quercetin were not phototoxic in a reconstructed human skin model and showed antioxidant and antiallergic potential. On the other hand, Netto MPharm and colleagues [192] prepared SLNs loaded with silymarin, natural flavonoids with antioxidant activity, and incorporated this formulation into sunscreen cream. Increasing the concentration of the emulsifier (Tween 80) led to increased entrapment efficiency for silymarin. The optimized SLNs carrier enhanced the silymarin’s stability and photoprotection action. Hence, SLNs formulation can be a promising carrier for herbal products and eliminate toxic synthetic UV filters.
Abdel-Salam et al. [207] prepared NLC co-loaded with diflucortolone valerate (corticosteroid) and titanium dioxide (inorganic UV filter) to treat chronic inflammation and provide protection against UV radiation. The formulations were prepared by mixing the solid lipids of Precirol® and Tristearin with the liquid lipid of isopropyl myristate or Capryol 90 and stabilized by Labrafil (lipid-based surfactant) and an aqueous solution of Poloxamer® 407. A synergistic UV-blocking activity was observed in this combination. The SPF value increased ten folds compared with conventional gel formulation containing the same amount of TiO2. Similarly, Medeiros et al. [208] developed sunscreen formulation based on NLCs containing bemotrizinol as an organic filter. The formulation was optimized based on Box-Behnken design to have an average size of 122.4 nm during a month of storage. Table 3 summarizes the studies that involved the preparation of lipid-based nanocarriers loaded with UV- filters in recent years.

Table 3.
Lipid-based nanocarriers loaded with UV filters.
5.3. Psoralen Plus Ultraviolet Light A Therapy (PUVA)
Psoralen plus ultraviolet light A therapy (PUVA) is known as the administration of photoactive compounds, specifically psoralens, followed by exposure to long-wave ultraviolet radiation (320–400 nm, UVA) [209]. Numerous dermatological disorders such as vitiligo, psoriasis, and mycosis fungoides are handled with this technique [210]. In PUV A therapy, three psoralens are widely used, 5-methoxypsoralen, 8-methoxypsoralen, and 4,5,8-trimethylpsoralen. These compounds are administered either orally or through a topical route [211]. Oral administration of psoralen suffers from numerous adverse side effects such as gastrointestinal problems and ocular and liver disease. In contrast, topical PUVA therapy has several distinct advantages such as the absence of hepatic toxicity. However, topical PUVA therapy suffers from weak skin permeability of psoralen [212], and induces the development of nonmelanoma skin cancer. Hence, incorporating psoralens into lipid-based nanocarriers could overcome the disadvantages associated with topical and oral routes. Indeed, it enables close contact and adhesion to SC through their small particle sizes and large surface area. Moreover, their occlusive property promotes skin hydration [213]. Along this line, several psoralens have been successfully incorporated into SLNs and NLC formulations. For example, Lai et al. [214] introduced NE formulations for topical application of 8-methoxypsoralen. These NEs were formulated from soybean oil and different mixtures of phospholipids (soy phosphatidylcholine or hydrogenated soy phosphatidylcholine or soy lecithin). Furthermore, enhancement in the permeability of 8-methoxypsoralen occurred in different skin layers after its incorporation into the nanoemulsion.
Similarly, Oliveira and coworkers [215] developed an 8-methoxypsoralen-NE consisting of clove essential oil and poloxamer 407 for topical treatment dermatoses. Full factorial designs (25 and 32) met the optimized conditions: ultrasonication time of 60 s, the potency of 60 %, 2% v/v of the oil phase, and 10% m/v of Poloxamer 407. The mean droplet diameter of the NE was 24.98 ± 0.49 nm. The ex vivo permeation analysis showed that 8.5% of the 8-methoxypsoralen dose applied permeated through the biological membranes, with a flux of 1.35 μg cm−2 h−1. The drug retention was 1.95 ± 0.71 µg cm−2 in SC and 10.15 ± 1.36 µg cm−2 in epidermis and dermis. The NE-induced retention in viable skin was almost double that of a compounded cream (5.04 ± 0.30 μg cm−2). On the other hand, Fang and colleagues [216] developed SLN and NLC formulations for delivering psoralens (8-methoxypsoralen, 5-methoxypsoralen, and 4,5,8-trimethylpsoralen) to treat psoriasis. These formulations were made from precirol and/ or squalene as lipid phase, myverol or phosphatidylcholine as lipid emulsifier, and Pluronic F68 or Tween 80 hydrophilic emulsifiers. Only NLC formulations led to enhanced permeation and controlled release of psoralens. The optimized NLC formulation had a particle size of 172.7 nm and a zeta potential of −42.3 mv. Moreover, 8-methoxypsoralen was the most permeable, and its flux was 2.8 times greater than that of the conventional emulsion, while 4,5,8-trimethylpsoralen exhibited lowest permeability.
Recently, researchers combined transcutol and SLNs to enhance skin permeation of 8-methoxypsoralen. The formulations were prepared from Compritol® 888 ATO and Poloxamer 188, and investigated using Franz cells and newborn pig skin. In vitro penetration and permeation studies verified a more significant accumulation of 8-methoxypsoralen in each skin layer after applying SLN-Transcutol (2% and 4% Transcutol) than SLNs free of Transcutol without increasing cytotoxicity, and higher % transcutol caused higher diffusion and skin accumulation of 8-methoxypsoralen [217]. Similarly, Battaglia et al. [218] developed 8-methoxypsoralen-loaded SLNs and NEs formulation modified with α-tocopherol using hot homogenization. The optimized formulations showed enhanced entrapment efficiency, reduced skin photooxidation, and irritation. Listed in Table 4 are several psoralens incorporated into NEs, SLNs, and NLCs.

Table 4.
Psoralens incorporated into NEs, SLNs, and NLCs.
5.4. Wound Healing and Skin Burns Products
Several studies revealed that incorporating compounds used in treating topical wounds and burns into SLN and NLCs enhances their stability and healing properties. Table 5 shows some compounds used in the topical treatment of wounds or burns and incorporated into SLNS and NLCs. Within this context, Gad and coworkers [219] encapsulated chamomile oil, an essential oil with antimicrobial activity, into SLNs prepared by a hot homogenization method, to treat wounds. Other researchers [220] developed NLCs and SLNs loaded with eucalyptus or rosemary essential oil to enhance the healing of wounds. In this respect, the NLCs composed of olive and loaded with eucalyptus were superior in stability, antimicrobial activity, and biocompatibility. On the other hand, Ghaffari et al. [221] investigated the co-encapsulation of curcumin and ampicillin into SLNs to improve wound healing. These researchers observed a synergic antibacterial effect of ampicillin-curcumin-SLNs in the prepared formulation with increased healing capacity and reduced toxicity. In a similar fashion, scientists [222] encapsulated superoxide dismutase (an enzyme used to treat skin ulcers) into SLNs formulation. The optimized SlNs showed a significant enhancement in the permeability of superoxide dismutase through burned rat skin and protected the incorporated enzyme from environmental degradation.

Table 5.
Wound and burn healing products loaded into SLNs and NLCs.
5.5. Anti-Aging and Skincare Products
Skin’s absorption of anti-aging formulation and other skincare products is enhanced after being incorporated into different kinds of lipid nanocarriers [223]. As shown in Table 6, several molecules used in anti-aging and skincare are incorporated into NE, SLNs, and NLC. In this respect, researchers formulated two types of nanocarriers to encapsulate coenzyme Q10, NLC, and NE [219]. The NLC and NE were incorporated into xanthan gum hydrogels to enhance their long-term stability. Both nanocarriers were effective in improving the stability and skin penetration of coenzyme Q10 [223]. In contrast, Pardeike and coworkers [224] compared the first NLC containing cosmetic product introduced to the market, Cutanvoa Nanorepair Q10 cream, to conventional o/w cream without NLC. These researchers found that Cutanvoa Nanorepair Q10 cream is more efficient than conventional o/w cream. Cutanvoa Nanorepair Q10 cream achieved long-term stability after its incorporation into xanthan gum hydrogels, and showed higher skin hydration and did not have irritating effects on the skin. Similarly, Schwarz et al. [146] developed a Q10-ultra-small NLC and compared it to the conventional Q 10-NLC and Q10-NE. Particle sizes were around 80 nm for ultra-small NLC, 87 nm for NE, and 230 nm for NLC. Skin permeation and penetrations studies revealed that ultra-small NLC exhibits improved dermal delivery of CoQ10 compared to conventional NLC. Additionally, clinical studies proved that the ultra-small NLC was superior to identically sized 80 nm NE.

Table 6.
Compounds used in anti-aging and skincare and incorporated into NE, SLNs, and NLC.
On the other hand, Nayak and colleagues [225] co-loaded coenzyme Q10 and retinaldehyde into NLCs and investigated the efficacy of this formulation to reduce wrinkles. The formulation was incorporated into Carbopol® 934P-NF gel. Clinical studies showed enhanced cellular uptake without cytotoxicity, whereas the in vitro release profile was prolonged. Moreover, the developed NLCs exhibited high efficacy as an anti-wrinkle product. In a similar fashion, Gokce et al. [158] loaded resveratrol, a polyphenolic compound with antioxidant effect, into SLNs and NLCs. Both NLCs and SLNs showed enhanced antioxidant activity, although NLCs penetrated deeper into the skin and displayed higher entrapment efficiency than SLNs. In another study, Shrotriya et al. [226] encapsulated resveratrol into SLN incorporated into Carbopol gel to treat and prevent irritant contact dermatitis. Results indicated that resveratrol aqueous solubility and bioavailability was enhanced after its incorporation into SLNs. Along this line, Puglia and colleagues [227] introduced SLN loaded with caffeine to overcome its hydrophobicity and improve its penetration through the skin. The optimized formulation offered an average size of 182.6 nm and entrapment efficiency of 75%. In addition, researchers [228] encapsulated ellagic acid, a natural antioxidant, into NLC to enhance its solubility and stability. Results showed that the administered dose was reduced after ellagic acid incorporation, and the antioxidant capacity of ellagic acid-NLCs enhanced by 60% compared to the active solution. Other researchers [229] encapsulated neem oil into SLN as a topical application for acne, whereas Lacatusu et al. [230] introduced carotene-loaded NLCs using two liquid oils (squalen and grape seed) to enhance antioxidant activity.
5.6. Topical Glucocorticoids
Glucocorticoids are a subclass of corticosteroids, which could come from two sources, natural (e.g., cortisol) or synthetic (e.g., betamethasone). Natural glucocorticoids are produced by the adrenal cortex and are required to protect the body against inflammation, stress, and shock. Synthetic glucocorticoids are widely prescribed as anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive drugs for various diseases. Moreover, corticosteroids can be used to treat asthma, allergy, rheumatoid, and inflammatory bowel [231,232]. Unfortunately, prolonged application of glucocorticoids may lead to numerous severe side effects. It causes gastrointestinal, endocrine, cardiovascular, dermatological, immunological, and ocular problems [233]. Hence, developing lipid-based nanocarriers targeted to epidermis infected by inflammation is a promising approach. The therapeutic benefits can be improved, and dangerous side effects minimized [234].
Along this line, Beloqui and coworkers [235] designed Budesonide-loaded NLC and evaluated its efficacy in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. The particle size was approximately 200 nm and zeta potential around 42 mV. Budesonide-loaded NLC was more effective in a murine model of dextran sulfate-induced colitis than free Budesonide or unload NLC. Similarly, researchers [236] designed Betamethasone 17-valerate- loaded SLN formulation to investigate the potential of SLN formulations to improve the efficiency of corticosteroids applied on the skin. These authors examined the effect of two solid lipids, namely beeswax and monostearin, on the properties of SLN. The particle size was reduced to approximately 10 nm when monostearin was replaced by beeswax. Using monostearin in the formulation led to a lower permeation rate and more significant drug reservoir formation in the human epidermis than drug suspension and commercial lotions. In addition, the lipid concentration affected the quality of permeation of the drug. Replacing monostearin by beeswax caused failure to the controlled release properties. Moreover, beeswax formulations could not raise drug content in the upper layer of the skin and could not decrease drug permeability through the skin. The formulation composed of monostearin had the highest ratio for drug content in the epidermis to that in the dermis compared with other formulations, which confirms enhanced drug permeation through the SC to the dermis to the systemic circulation.
Kong et al. [237] developed betamethasone dipropionate-loaded NLC for the treatment of atopic dermatitis. The particle size was 169.1 nm, and a zeta potential of −23.4 mV. The optimized betamethasone dipropionate-loaded NLC showed high entrapment efficiency (85%). W/O ointment matrix and Carbopol® emulgel ointment were investigated; results revealed that the W/O ointment matrix was selected with betamethasone dipropionate –NLC because it showed lower skin penetration, higher skin retention, and better drug release profile than Carbopol® emulgel ointment. This study proved the ability to develop betamethasone dipropionate-NLC to improve skin retention and reduce side effects induced by systemic absorption such as skin irritation.
Similarly, scientists designed betamethasone dipropionate-loaded NLCs for topical application to treat eczema. Betamethasone dipropionate-loaded NLCs were prepared based on high shear homogenization and sonication, using the following excipients: Glycerylmonostearate, oleic acid, Tween 80, Span 20 phospholipon 90 G, cremophor RH 40, and sodium tauroglucocholate. They also investigated the effect of manipulating the concentration of excipients on different physical properties. Sodium tauroglucocholate was excluded from the formulations because it failed to produce particles in the nano range. Results showed that the oleic acid ratio has an essential effect on the penetration of the drug to deeper skin layers (as the oleic acid ratio increased in the formulation higher amount of betamethasone dipropionate penetrated to the deeper skin layer) [238].
In another study, Nagaich et al. [239] developed clobetasol propionate-loaded NLCs-based gel as a potential treatment for eczema. Clobetasol propionate-loaded NLCs were prepared by high pressure homogenization and composed of Compritol® ATO 888, oleic acid, Poloxamer 188, and sodium taurocholate. The optimized formulations contained particles with diameters of 137.9 nm and a zeta potential of −20.5 mV. All permeability parameters, such as steady-state flux and permeability coefficient, were higher for NLC-based gel formulation than the market gel. In this formulation, the anti-inflammatory effect extended due to the prolonged release effect. Similarly, Silva and coworkers [240,241] formulated clobetasol propionate-loaded NLCs to investigate their ability to target the skin. Some formulations were coated with chitosan and compared with those uncoated. In vitro permeation and retention studies showed that chitosan-coated NLCs cause higher permeability and retention in the SC layer than in the commercial formulation. Even one-fifth of the drug dose was required in the formulation of chitosan-coated NLCs. However, chitosan-coated NLCs were not useful for epidermal targeting purposes, and uncoated NLC enhanced permeability without showing dermal retention.
Andrade et al. [242] investigated the effect of co-encapsulation of tacrolimus and clobetasol into NLCs coated with chitosan oligosaccharide. The co-encapsulated formulations caused enhancement of numerous physical properties. The entrapment efficiency was high for the two drugs (above 90%). In this formulation, clobetasol worked as an absorption enhancer and promoted the penetration of tacrolimus into deeper skin layers. The drug release profiles were enhanced, and clobetasol was released faster than tacrolimus. Moreover, coating caused a further permeation to deeper skin layers.
Jain and coworkers [243] formulated and characterized four different kinds of lipid-based nanocarriers loaded with tacrolimus: liquid crystalline nanoparticles, liposomes, SLNs, and NLCs. All of these formulations were loaded into a gel to permit proper usage of the formulation and to improve the system’s viscosity. In this respect, different nanoformulations were optimized to show particle sizes smaller than 200 nm, zeta potential greater than −10 mV, and entrapment efficiency of more than 85%. All the formulations exhibited higher penetration of the drug into the skin than the marketed ointment of tacrolimus. Additionally, tacrolimus-SLN and tacrolimus- NLC loaded gel showed more enhanced efficacy to deliver tacrolimus. Similarly, Pradhan et al. [244] investigated the potential of NLC for delivery of triamcinolone acetonide using microemulsion method. The formulation was optimized 17-run, 3-factor (Liquid lipid concentration: Total lipid concentration, surfactant concentration, drug concentration), 3-level Box-Behnken design offered in the design expert software. The release profile was prolonged obeying Higuchi release kinetics with r2 = 0.995 while pure triamcinolone acetonide showed fast release.
On the other hand, Doktorovová and colleagues [245] fabricated two forms of fluticasone propionate-NLCs modified by PEG for topical application. One of two liquid lipids, namely labrasol and softigen 767 was mixed with precirol, tween, and soybean lecithin using the microemulsion technique. The achieved entrapment efficiency of fluticasone propionate-loaded NLC was 95%, and the mean particles size within the range of 380 and 408 nm. PEG modification was effective in enhancing physicochemical stability. Particles were stable over 60 days with a low-crystalline structure of fluticasone propionate. Different topical glucocorticoids were incorporated into SLNs, NLCs, and NEs as listed in Table 7.

Table 7.
List of topical glucocorticoids incorporated into SLNs, NLCs, and NEs.
5.7. Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatorty Drugs
The most commonly prescribed medicines worldwide are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). NSAIDs are heterogeneous organic compounds that lack a steroid core with a diverse chemical structure with anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antipyretic effects [246]. Most NSAIDs have limited aqueous solubility, specifically in acidic media, and are categorized as class-II drugs in biopharmaceutical classifications (BCS) [246]. Because most inflammatory diseases occur locally and near the body’s surface, topical application of NSAIDs on the inflamed site could be reasonable to reduce toxicity and avoid undesirable side effects associated with the oral route [247]. In this case, the skin works as a biological barrier due to the stratum corneum layer (SC) [248]. The SC hinders permeation of a considerable number of bioactive molecules through the skin. In light of this, lipid-based nanocarriers are attractive for transdermal drug delivery, where they can enhance lipophilicity and permeability through the SC [162].
Piroxicam, an oxicam NSAID, was encapsulated into SLNs composed of ATO 188 and polysorbate 80. The formulations were incorporated into a transdermal patch made from ethyl cellulose and polyvinyl pyrrolidone. Results showed enhanced bioavailability and transdermal permeation [249]. Similarly, piroxicam was incorporated into SLN composed of lecithin, glycerol monostearate, and Tween 80. Oleic acid was used as a chemical enhancer for the skin penetration of piroxicam. Characterization and clinical investigation of the formulation indicated a high drug loading efficiency (87.5%), sustained drug release, and decreased inflammatory responses. The particle size was around 102 ± 5.2 nm, and the zeta potential was 30.21 ± 2.05 mV. The combined use of SLN and oleic acid dramatically enhanced piroxicam’s skin penetration [250]. Recently, Mohammadi-Samani et al. [251] developed piroxicam loaded into SLNs and formulated in a gel as a topical delivery system. The range of particle size extended from 100 to 300 nm. The prepared formulations enhanced the permeation of piroxicam into the skin. The use of cholesterol improved loading efficiency but led to undesirable diameters.
Dasgupta and coworkers [252] investigated the potential of incorporating lornoxicam, an oxicam, into SLNs, NLCs, and NEs, and whether this would enhance the lornoxicam’s efficacy. Particle sizes were in the range of 140–193 nm for SLNs, 146–201 nm for NLCs, and 138–195 nm for NEs. The zeta potentials were in the range of −22 to −32 mV for SLNs, −23 to −30 mV for NLCs, and −26 0.123 mV for NEs. These researchers showed that drug loading and entrapment efficiency improved as the lipid ratio increased. Furthermore, the bioavailability and lornoxicam’s therapeutic potential were enhanced compared to conventional gel. In another study, lornoxicam was encapsulated into NLCs-gel modified with polyarginine, a cell-penetrating peptide. The mean particle size increased by 1.2 times, and the zeta potential decreased approximately to 0.48 due to surface modification. The drug loading and encapsulation efficiency did not affect surface modification, and they were 7.92% and 74.61%, respectively. This study showed an enhancement in cell internalization of nanoparticles, skin permeation, and anti-inflammatory effect after surface modification [253]. In a similar fashion, Elkomy and colleagues [254] explored the potential topical application of SLNs formulation containing ketoprofen. These authors investigated the incorporation of novel techniques, Artificial Neural Network, and clustered bootstrap to optimize ketoprofen-SLN formulation and demonstrated a longitudinal dose response-model. This model helped design efficient dermatological bioequivalence assessment methods.
On the other hand, scientists [255] developed ibuprofen-loaded SLN-based hydrogels to enhance skin penetration of ibuprofen. These SLNs were prepared by hot homogenization, and composed of cetostearyl alcohol and Tween 80. The xanthan gum worked as a gelling agent and created a homogeneous and stable network to incorporate ibuprofen-loaded SLNs. The particle sizes of optimized ibuprofen-loaded SLN were in the range 98–101 nm, and their zeta potential extended from –2.66 to –3.46 mV. The encapsulation efficiency was from 56.88% to 58.89%. This study showed enhanced in vitro permeation and local anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities compared to conventional gels. Similarly, researchers developed two kinds of nanocarriers loaded with oxaprozin (NLC and deformable liposomes) using a specific approach. This approach involved loading the drug as a ternary complex with randomly methylated ß-cyclodextrin and L-arginine, and incorporating this complex into NLC and liposomes that were further incorporated into carbopol gel. The mean particle size and zeta potential of complex loaded liposomes were 231.3 nm and +22.8 mV, whereas the mean particle size and zeta potential of complex loaded NLC were 180.6 nm and –13.4 mV. This study proved that cyclodextrin and liposome or NLC cause an increase in the drug permeability by 16 and 8 times, respectively. In addition to promoted permeation, these formulations were stable for three months at 4 °C with high entrapment efficiency [256].
Garg et al. [257] reported on aceclofenac-loaded NLC using a quality by design oriented approach, where a 27-factorial design was employed for the optimization of NLCs. In this respect, the formulation was prepared by a microemulsion method, and composed of cetyl alcohol, Transcutol®P, and Tween 80. The optimized NLCs were further incorporated into carbopol gel. The optimized aceclofenac-loaded NLC better showed skin permeation efficiency and better anti-inflammatory activity. Furthermore, a group of researchers formulated salicylic acid-loaded-NE against inflammation. The formulation contained lemongrass oil, labrasol, and carbitol. This investigation involved combining two approaches, hydrophilic-lipophilic balance (HLB) and response surface methodology. The mean particle size and HLB of optimized formulation were 134.7 nm and 14.8, respectively. Results of this study showed that retention of salicylic acid in the skin increases by 2.8 fold in epidermis and 4.13 fold in the dermis [258].
Khaurs et al. [259] designed meloxicam-loaded SLN-based gel formulation for dermal application using the microemulsion method. This formulation’s particle size was 239 nm, and its zeta potential was −24.53 mV. Meloxicam-loaded SLN-based gel formulation was compared with meloxicam-loaded nanoemulsion-based gel that the same authors previously developed [260]. Meloxicam-loaded SLN-based gel formulation penetrated different skin layers with controlled release. However, its flux of meloxicam was lower than meloxicam nanogel-based formulation. Additionally, nanogel-based formulation showed better skin tolerability and anti-inflammatory effect. Listed in Table 8 are several of NSAIDs incorporated into SLNs, NLCs, and NEs.

Table 8.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs incorporated into SLNs, NLCs, and NEs.
6. Conclusions and Future Prospective
Skin inherits the selective nature as a barrier and affords low permeability in the two opposite directions. Therefore, therapeutic molecules that can permeate the skin should be small and have an adequate degree of lipophilicity; however, few drugs can fit these criteria and stand-alone to provide the desired therapeutic outcomes. Overcoming these challenges can be achieved through the development of delivery systems that can pass the skin barrier. Owing to their biocompatible and versatile properties, solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN), nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC), and nanoemulsions (NE) display advantages over other organic and inorganic nanoparticles for the delivery of different types of drugs into the skin. These advantages include low toxicity, high drug loading capacity, biodegradability, large-scale production, and diverse chemical and formulations landscape. In addition, the availability of different preparation techniques and the diverse range of lipids, enable a wide range of topical, dermal, and transdermal applications, therefore providing a reason for the high interest by the academic and industrial sectors. Although lipid nanoparticles acquired a major share in developing cosmetics for the skin, the clinical applications for therapy still need more efforts and investigation. Moreover, more attention should be provided to in vivo studies to enhance the knowledge about the bio-distribution, wanted and unwanted effects in the short and long terms. Taken all together, the ultimate goal is to find simple-and-smart therapeutics and drug delivery systems that are efficient and effective to produce higher therapeutic index and high-quality products.
Author Contributions
F.O. Writing original draft Section 1; M.S. Writing original draft Section 2; H.N. and A.J. Writing original draft Section 3 and Section 4; D.K. Writing original draft Section 5 and editing; W.A. Writing original draft Section 6; F.O., A.A.B. and M.S.M. Writing-review and editing, M.S.M. and F.O. project administration. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Babamiri, K.; Nassab, R.J.A.S.J. Cosmeceuticals: The evidence behind the retinoids. Aesthetic Surg. J. 2010, 30, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- d’Agostino, S.; Azzali, A.; Casali, L.; Taddei, P.; Grepioni, F. Environmentally Friendly Sunscreens: Mechanochemical Synthesis and Characterization of β-CD Inclusion Complexes of Avobenzone and Octinoxate with Improved Photostability. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 13215–13225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Ahsan, H. Lipid-based formulations in cosmeceuticals and biopharmaceuticals. Biomed. Dermatol. 2020, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, C.; Barros, R.B.G. Natural and Organic Cosmetics: Definition and Concepts. Preprints 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodarzi, F.; Zendehboudi, S. A comprehensive review on emulsions and emulsion stability in chemical and energy industries. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 97, 281–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Tran, V.; Moon, J.-Y.; Lee, Y.-C. Liposomes for delivery of antioxidants in cosmeceuticals: Challenges and development strategies. J. Control. Release 2019, 300, 114–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, R.H.; Staufenbiel, S.; Keck, C.M. Lipid Nanoparticles (SLN, NLC) for innovative consumer care & household products. Househ. Pers. Care Today 2014, 9, 18–24. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Q.; Nash, J.F. Pathology of Aging Skin; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 277–291. [Google Scholar]
- Lai-Cheong, J.E.; McGrath, J.A. Structure and function of skin, hair and nails. Medicine 2017, 45, 347–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, M.M.; Woods, A.; Harvey, R.D.; Young, A.R.; Jones, S.A. Nanomaterials fusing with the skin: Alpha-tocopherol phosphate delivery into the viable epidermis to protect against ultraviolet radiation damage. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 594, 120000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benson, H.A.; Watkinson, A.C. Topical and Transdermal Drug Delivery: Principles and Practice; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 357–366. [Google Scholar]
- McGrath, J.A.; Uitto, J. Structure and Function of the Skin, 9th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2016; pp. 1–52. [Google Scholar]
- Koster, M.I. Making an epidermis. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1170, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergstresser, P.R.; Richard Taylor, J. Epidermal ‘turnover time’—A new examination. Br. J. Dermatol. 1977, 96, 503–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M.; Machida, Y.; Marks, R. Measurement of turnover time of stratum corneum using dansyl chloride fluorescence. J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem. 1987, 38, 321–331. [Google Scholar]
- Bouwstra, J.A.; Groenink, H.W.W.; Kempenaar, J.A.; Romeijn, S.G.; Ponec, M. Water distribution and natural moisturizer factor content in human skin equivalents are regulated by environmental relative humidity. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2008, 128, 378–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, S.; Wakamatsu, K. Quantitative analysis of eumelanin and pheomelanin in humans, mice, and other animals: A comparative review. Pigment. Cell Res. 2003, 16, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seiberg, M. Keratinocyte–melanocyte interactions during melanosome transfer. Pigment. Cell Res. 2001, 14, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.; Kosmadaki, M.; Yaar, M.; Gilchrest, B.A. Cellular mechanisms regulating human melanogenesis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2009, 66, 1493–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunger, R.E.; Sieling, P.A.; Ochoa, M.T.; Sugaya, M.; Burdick, A.E.; Rea, T.H.; Brennan, P.J.; Belisle, J.T.; Blauvelt, A.; Porcelli, S.A.; et al. Langerhans cells utilize CD1a and langerin to efficiently present nonpeptide antigens to T cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 113, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valladeau, J.; Ravel, O.; Dezutter-Dambuyant, C.; Moore, K.; Kleijmeer, M.; Liu, Y.; Duvert-Frances, V.; Vincent, C.; Schmitt, D.; Davoust, J.; et al. Langerin, a novel C-type lectin specific to Langerhans cells, is an endocytic receptor that induces the formation of Birbeck granules. Immunity 2000, 12, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Liu, N.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Zhu, W.; Kuang, Y.; Chen, X.; Peng, C. The role of Langerhans cells in epidermal homeostasis and pathogenesis of psoriasis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 11646–11655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tachibana, T.; Nawa, T. Recent progress in studies on Merkel cell biology. Anat. Sci. Int. 2002, 77, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, G.P.; Gullick, D.R.; Wilkinson, S.C. Predictive Methods in Percutaneous Absorption; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Rawlings, A.V. Trends in stratum corneum research and the management of dry skin conditions. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2003, 25, 63–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michaels, A.; Chandrasekaran, S.; Shaw, J.E. Drug permeation through human skin: Theory and in vitro experimental measurement. Am. Inst. Chem. Eng. 1975, 21, 985–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, P.M.; Cooper, E.R.; Korc, A.; Brown, B.E. Percutaneous transport in relation to stratum corneum structure and lipid composition. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1981, 76, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemes, Z.; Steinert, P.M. Bricks and mortar of the epidermal barrier. Exp. Mol. Med. 1999, 31, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weerheim, A.; Ponec, M. Determination of stratum corneum lipid profile by tape stripping in combination with high-performance thin-layer chromatography. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2001, 293, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadgraft, J.; Lane, M.E. Skin: The ultimate interface. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 5215–5222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kattou, P.; Lian, G.; Glavin, S.; Sorrell, I.; Chen, T. Development of a two-dimensional model for predicting transdermal permeation with the follicular pathway: Demonstration with a caffeine study. Pharm. Res. 2017, 34, 2036–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nastiti, C.M.; Ponto, T.; Abd, E.; Grice, J.E.; Benson, H.A.; Roberts, M.S. Topical nano and microemulsions for skin delivery. Pharmaceutics 2017, 9, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeb, A.; Arif, S.T.; Malik, M.; Shah, F.A.; Din, F.U.; Qureshi, O.S.; Lee, E.-S.; Lee, G.-Y.; Kim, J.-K. Potential of nanoparticulate carriers for improved drug delivery via skin. J. Pharm. Investig. 2019, 49, 485–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morganti, P. Use and potential of nanotechnology in cosmetic dermatology. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. CCID 2010, 3, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Förster, M.; Bolzinger, M.-A.; Fessi, H.; Briançon, S. Topical delivery of cosmetics and drugs. Molecular aspects of percutaneous absorption and delivery. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2009, 19, 309–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berenson, G.S.; Burch, G.E. Studies of diffusion of water through dead human skin: The effect of different environmental states and of chemical alterations of the Epidermis1. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1951, 1, 842–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweeney, T.M.; Downing, D.T. The role of lipids in the epidermal barrier to water diffusion. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1970, 55, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalia, Y.N.; Guy, R.H. Modeling transdermal drug release. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 48, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, K.I.; Glaser, D.A. Cosmeceuticals: The new medicine of beauty. Mo. Med. 2011, 108, 60. [Google Scholar]
- Stiefel, C.; Schwack, W. Photoprotection in changing times–UV filter efficacy and safety, sensitization processes and regulatory aspects. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2015, 37, 2–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, A.R.; Claveau, J.; Rossi, A.B. Ultraviolet radiation and the skin: Photobiology and sunscreen photoprotection. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2017, 76, S100–S109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schalka, S.; Steiner, D.; Ravelli, F.N.; Steiner, T.; Terena, A.C.; Marçon, C.R.; Ayres, E.L.; Addor, F.A.S.; Miot, H.A.; Ponzio, H.; et al. Brazilian consensus on photoprotection. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2014, 89, 1–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, C.T.; Shah, V.P.; Derdzinski, K.; Ewing, G.; Flynn, G.; Maibach, H.; Marques, M.; Rytting, H.; Shaw, S.; Thakker, K.; et al. Topical and transdermal drug products. Pharmacop. Forum 2009, 35, 750–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.K.; Soni, P.; Shrivastava, J.; Rajput, P.; Parashar, S. Cosmeceutical role of Medicinal plants/Herbs: A Review on commercially available Cosmetic ingredients. Int. J. Innov. Sci. Technol. 2018, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draelos, Z.D. Cosmeceuticals: Undefined, unclassified, and unregulated. Clin. Dermatol. 2009, 27, 431–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lintner, K.; Mas-Chamberlin, C.; Mondon, P.; Peschard, O.; Lamy, L. Cosmeceuticals and active ingredients. Clin. Dermatol. 2009, 27, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, A.; Sahu, R.K.; Matlam, M.; Deshmukh, V.K.; Dwivedi, J.; Jha, A.K. In vitro techniques to assess the proficiency of skin care cosmetic formulations. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2013, 7, 97. [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee, S.; Ray, S.; Thakur, R. Solid lipid nanoparticles: A modern formulation approach in drug delivery system. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 71, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, L.; Sprando, R.L. Application of nanotechnology in cosmetics. Pharm. Res. 2010, 27, 1746–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niculae, G.; Lacatusu, I.; Bors, A.; Stan, R. Photostability enhancement by encapsulation of α-tocopherol into lipid-based nanoparticles loaded with a UV filter. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2014, 17, 1028–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damiani, E.; Puglia, C. Nanocarriers and Microcarriers for Enhancing the UV Protection of Sunscreens: An Overview. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 108, 3769–3780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, M.M.U. Delivery of Tocopherol Phosphate Nanomaterials into the Skin to Protect against Ultraviolet Radiation. Ph.D. Thesis, King’s College London, London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Golmohammadzadeh, S.; Mortezania, S.; Jaafari, M.R. Improved photostability, reduced skin permeation and irritation of isotretinoin by solid lipid nanoparticles. Acta Pharm. 2012, 62, 547–562. [Google Scholar]
- Amer, S.S.; Nasr, M.; Mamdouh, W.; Sammour, O. Insights on the use of nanocarriers for acne alleviation. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2019, 16, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, M.; Farinha, A.; Faustino, E.; Hadgraft, J.; Pais, J.; Toscano, C. Topical delivery of caffeine from some commercial formulations. Int. J. Pharm. 1999, 182, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puglia, C.; Bonina, F.; Rizza, L.; Blasi, P.; Schoubben, A.; Perrotta, R.; Tarico, M.S.; Damiani, E. Lipid nanoparticles as carrier for octyl-methoxycinnamate: In vitro percutaneous absorption and photostability studies. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 101, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dingler, A.; Blum, R.; Niehus, H.; Muller, R.; Gohla, S. Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNTM/LipopearlsTM) a pharmaceutical and cosmetic carrier for the application of vitamin E in dermal products. J. Microencapsul. 1999, 16, 751–767. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ng, K.W. Penetration Enhancement of Topical Formulations; Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute: Basel, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Neubert, R.H. Potentials of new nanocarriers for dermal and transdermal drug delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2011, 77, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Y.; Dhar, A.; Patel, C.; Khimani, M.; Neogi, S.; Sharma, P.; Kumar, N.S.; Vekariya, R.L. A brief review on solid lipid nanoparticles: Part and parcel of contemporary drug delivery systems. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 26777–26791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemiyeh, P.; Mohammadi-Samani, S. Solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers as novel drug delivery systems: Applications, advantages and disadvantages. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 13, 288. [Google Scholar]
- Lauterbach, A.; Müller-Goymann, C.C. Applications and limitations of lipid nanoparticles in dermal and transdermal drug delivery via the follicular route. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 97, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorzelanny, C.; Mess, C.; Schneider, S.W.; Huck, V.; Brandner, J.M. Skin Barriers in Dermal Drug Delivery: Which Barriers Have to Be Overcome and How Can We Measure Them? Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, V.; Bansal, K.K.; Verma, A.; Yadav, N.; Thakur, S.; Sudhakar, K.; Rosenholm, J.M. Solid lipid nanoparticles: Emerging colloidal nano drug delivery systems. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseri, N.; Valizadeh, H.; Zakeri-Milani, P. Solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers: Structure, preparation and application. Adv. Pharmaceut. Bull. 2015, 5, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, R.H.; Mäder, K.; Gohla, S. Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) for controlled drug delivery–a review of the state of the art. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2000, 50, 160–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, J.; Singh, G.; Saini, S.; Rana, A.C. Innovative Growth in Developing New Methods for Formulating Solid Lipid Nanoparticles and Microparticles. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 2012, 2, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shende, P.; Patel, D.; Takke, A. Nanomaterial-Based Cosmeceuticals. In Handbook of Functionalized Nanomaterials for Industrial Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 775–791. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, R.; Petersen, R.; Hommoss, A.; Pardeike, J. Nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC) in cosmetic dermal products. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardeike, J.; Hommoss, A.; Müller, R.H. Lipid nanoparticles (SLN, NLC) in cosmetic and pharmaceutical dermal products. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 366, 170–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, V.S.R.; Garg, A.; Kori, M.L.; Rai, G. Nanoemulsion in Cosmetic: From Laboratory to Market. In Nanocosmetics; Nanda, A., Nanda, S., Nguyen, T.A., Rajendran, S., Slimani, Y., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 327–347. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Mottaleb, M. Nanoparticles for Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis. In Nanoscience in Dermatology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 167–175. [Google Scholar]
- Duong, V.-A.; Nguyen, T.-T.-L.; Maeng, H.-J. Preparation of Solid Lipid Nanoparticles and Nanostructured Lipid Carriers for Drug Delivery and the Effects of Preparation Parameters of Solvent Injection Method. Molecules 2020, 25, 4781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garud, A.; Singh, D.; Garud, N. Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN): Method, characterization and applications. Int. Curr. Pharm. J. 2012, 1, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayón-Cordero, L.; Alkorta, I.; Arana, L. Application of solid lipid nanoparticles to improve the efficiency of anticancer drugs. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azar, F.A.N.; Pezeshki, A.; Ghanbarzadeh, B.; Hamishehkar, H.; Mohammadi, M. Nanostructured lipid carriers: Promising delivery systems for encapsulation of food ingredients. J. Agric. Food Res. 2020, 2, 100084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poonia, N.; Kharb, R.; Lather, V.; Pandita, D. Nanostructured lipid carriers: Versatile oral delivery vehicle. Futur. Sci. OA 2016, 2, FSO135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, I.; Yasir, M.; Verma, M.; Singh, A.P. Nanostructured lipid carriers: A groundbreaking approach for transdermal drug delivery. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2020, 10, 150–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, A.; De Freitas, V.; Mateus, N.; Fernandes, I.; Oliveira, J. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles as Carriers of Natural Phenolic Compounds. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trombino, S.; Mellace, S.; Cassano, R. Solid lipid nanoparticles for antifungal drugs delivery for topical applications. Ther. Deliv. 2016, 7, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Floury, J.; Desrumaux, A.; Lardières, J. Effect of high-pressure homogenization on droplet size distributions and rheological properties of model oil-in-water emulsions. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2000, 1, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parhi, R.; Suresh, P. Preparation and characterization of solid lipid nanoparticles-a review. Curr. Drug Discov. Technol. 2012, 9, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gora, S.; Mustafa, G.; Sahni, J.K.; Ali, J.; Baboota, S. Nanosizing of valsartan by high pressure homogenization to produce dissolution enhanced nanosuspension: Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodyanamic study. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 930–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, R.H.; Radtke, M.; Wissing, S. Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) and nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC) in cosmetic and dermatological preparations. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2002, 54, S131–S155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J. Nanoemulsions versus microemulsions: Clarification of critical differences. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 1719–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.M.; Malherbe, F.; Eldridge, D.; Palombo, E.A.; Harding, I.H. Physicochemical characterization of solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs) prepared by a novel microemulsion technique. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 428, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, S.P. Nanostructured Lipid Carrier-Based Drug Delivery Systems for Tuberculosis Treatment. In Nanotechnology Based Approaches for Tuberculosis Treatment; Kesharwani, P., Ed.; Academic Press: New Delhi, India, 2020; pp. 193–205. [Google Scholar]
- Mehnert, W.; Mäder, K. Solid lipid nanoparticles: Production, characterization and applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 83–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pooja, D.; Tunki, L.; Kulhari, H.; Reddy, B.B.; Sistla, R. Optimization of solid lipid nanoparticles prepared by a single emulsification-solvent evaporation method. Data Brief 2016, 6, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Chen, D.; Ren, L.; Zhao, X.; Qin, J. Solid lipid nanoparticles for enhancing vinpocetine’s oral bioavailability. J. Control. Release 2006, 114, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, P.; Shekunov, B.; Yim, D.; Cipolla, D.; Boyd, B.; Farr, S. Production of solid lipid nanoparticle suspensions using supercritical fluid extraction of emulsions (SFEE) for pulmonary delivery using the AERx system. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schubert, M.; Müller-Goymann, C. Solvent injection as a new approach for manufacturing lipid nanoparticles–evaluation of the method and process parameters. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2003, 55, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heurtault, B.; Saulnier, P.; Pech, B.; Proust, J.E.; Benoit, J.P. A novel phase inversion-based process for the preparation of lipid nanocarriers. Pharm. Res. 2002, 19, 875–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippacher, A.; Müller, R.H.; Mäder, K. Semisolid SLN™ dispersions for topical application: Influence of formulation and production parameters on viscoelastic properties. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2002, 53, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Eral, H.B.; Hatton, T.A.; Doyle, P.S. Nanoemulsions: Formation, properties and applications. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 2826–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attwood, D.; Mallon, C.; Ktistis, G.; Taylor, C. A study on factors influencing the droplet size in nonionic oil-in-water microemulsions. Int. J. Pharm. 1992, 88, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, Y.; Miyahara, R.; Sakamoto, K. Emulsion and emulsification technology. In Cosmetic Science and Technology: Theoretical Principles and Applications; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 489–506. [Google Scholar]
- Prow, T.W.; Grice, J.E.; Lin, L.L.; Faye, R.; Butler, M.; Becker, W.; Wurm, E.M.; Yoong, C.; Robertson, T.A.; Soyer, H.P.; et al. Nanoparticles and microparticles for skin drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 470–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, S. Lipid-based nano-delivery systems for skin delivery of drugs and bioactives. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yukuyama, M.N.; Ghisleni, D.D.M.; Pinto, T.I.A.; Bou-Chacra, N.A. Nanoemulsion: Process selection and application in cosmetics—A review. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2016, 38, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, J.; McClements, D.J. Stabilization of phase inversion temperature nanoemulsions by surfactant displacement. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 7059–7066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, A.; Nikmaram, N.; Roohinejad, S.; Estevinho, B.N.; Rocha, F.; Greiner, R.; McClements, D.J. Production, properties, and applications of solid self-emulsifying delivery systems (S-SEDS) in the food and pharmaceutical industries. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 538, 108–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Narayan, S.; Dutcher, C.S. Phase-Dependent Surfactant Transport on the Microscale: Interfacial Tension and Droplet Coalescence. Langmuir 2020, 36, 14904–14923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz, P.; Keck, C.M. Nanoemulsions produced by rotor—Stator high speed stirring. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 482, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roselan, M.A.; Ashari, S.E.; Faujan, N.H.; Mohd Faudzi, S.M.; Mohamad, R. An Improved Nanoemulsion Formulation Containing Kojic Monooleate: Optimization, Characterization and In Vitro Studies. Molecules 2020, 25, 2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leong, T.S.H.; Manickam, S.; Martin, G.J.; Li, W.; Ashokkumar, M. Ultrasonic Production of Nano-Emulsions for Bioactive Delivery in Drug and Food Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gharibzahedi, S.M.; Jafari, S.M. Fabrication of Nanoemulsions by Ultrasonication. In Nanoemulsions; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 233–285. [Google Scholar]
- Calligaris, S.; Plazzotta, S.; Valoppi, F.; Anese, M. Combined high-power ultrasound and high-pressure homogenization nanoemulsification: The effect of energy density, oil content and emulsifier type and content. Food Res. Int. 2018, 107, 700–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Montañez, G.; Ragazzo-Sanchez, J.A.; Picart-Palmade, L.; Calderón-Santoyo, M.; Chevalier-Lucia, D. Optimization of nanoemulsions processed by high-pressure homogenization to protect a bioactive extract of jackfruit (Artocarpus heterophyllus Lam). Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2017, 40, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che Marzuki, N.H.; Wahab, R.A.; Abdul Hamid, M. An overview of nanoemulsion: Concepts of development and cosmeceutical applications. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2019, 33, 779–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalobos-Castillejos, F.; Granillo-Guerrero, V.G.; Leyva-Daniel, D.E.; Alamilla-Beltrán, L.; Gutiérrez-López, G.F.; Monroy-Villagrana, A.; Jafari, S.M. Fabrication of Nanoemulsions by Microfluidization. In Nanoemulsions; Jafari, S.M., Ed.; McCl: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2018; pp. 207–232. [Google Scholar]
- Uluata, S.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J. Optimization of nanoemulsion fabrication using microfluidization: Role of surfactant concentration on formation and stability. Food Biophys. 2016, 11, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, J.; Alfaro, M.C.; Trujillo-Cayado, L.A.; Santos, J.; Martín-Piñero, M.J. Production of Food Bioactive-Loaded Nanostructures by Microfluidization. In Nanoencapsulation of Food Ingredients by Specialized Equipment; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 341–390. [Google Scholar]
- Jafari, S.M.; McClements, D.J. Nanoemulsions: Formulation, Applications, and Characterization; Academic Press: New Delhi, India, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Jasmina, H.; Džana, O.; Alisa, E.; Edina, V.; Ognjenka, R. Preparation of Nanoemulsions by High-Energy and Lowenergy Emulsification Methods. In CMBEBIH 2017; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 317–322. [Google Scholar]
- Sonneville-Aubrun, O.; Yukuyama, M.N.; Pizzino, A. Application of Nanoemulsions in Cosmetics. In Nanoemulsions; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 435–475. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, L.; Li, C.; Xu, J.; Hao, J.; Sun, D. Highly stable concentrated nanoemulsions by the phase inversion composition method at elevated temperature. Langmuir 2012, 28, 14547–14552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Rodríguez-Abreu, C.; Esquena, J.; Solans, C. A Concise Review on Nano-emulsion Formation by the Phase Inversion Composition (PIC) Method. J. Surfactants Deterg. 2020, 23, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teulon, J.-M.; Godon, C.; Chantalat, L.; Moriscot, C.; Cambedouzou, J.; Odorico, M.; Ravaux, J.; Podor, R.; Gerdil, A.; Habert, A.; et al. On the operational aspects of measuring nanoparticle sizes. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, S.B.; Chan, C.; Brown, S.C.; Eschbach, P.; Han, L.; Ensor, D.S.; Stefaniak, A.B.; Bonevich, J.; Vladár, A.E.; Walker, A.R.H.; et al. Particle size distributions by transmission electron microscopy: An interlaboratory comparison case study. Metrologia 2013, 50, 663–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loo, C.; Basri, M.; Ismail, R.; Lau, H.; Tejo, B.; Kanthimathi, M.; Hassan, H.; Choo, Y. Effect of compositions in nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC) on skin hydration and occlusion. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danaei, M.; Dehghankhold, M.; Ataei, S.; Davarani, F.H.; Javanmard, R.; Dokhani, A.; Khorasani, S.; Mozafari, M.R. Impact of particle size and polydispersity index on the clinical applications of lipidic nanocarrier systems. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midekessa, G.; Godakumara, K.; Ord, J.; Viil, J.; Lättekivi, F.; Dissanayake, K.; Kopanchuk, S.; Rinken, A.; Andronowska, A.; Bhattacharjee, S.; et al. Zeta Potential of Extracellular Vesicles: Toward Understanding the Attributes that Determine Colloidal Stability. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 16701–16710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Necula, B.; Apachitei, I.; Fratila-Apachitei, L.; Teodosiu, C.; Duszczyk, J. Stability of nano-/microsized particles in deionized water and electroless nickel solutions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 314, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahari, L.A.S.; Hamishehkar, H. The impact of variables on particle size of solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers; a comparative literature review. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2016, 6, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Kesarla, R.; Chotai, N.; Misra, A.; Omri, A. Systematic approach for the formulation and optimization of solid lipid nanoparticles of efavirenz by high pressure homogenization using design of experiments for brain targeting and enhanced bioavailability. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argimón, M.; Romero, M.; Miranda, P.; Mombrú, Á.W.; Miraballes, I.; Zimet, P.; Pardo, H. Development and characterization of vitamin a-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles for topical application. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2017, 28, 1177–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tantra, R.; Schulze, P.; Quincey, P. Effect of nanoparticle concentration on zeta-potential measurement results and reproducibility. Particuology 2010, 8, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Cheng, X.; Li, N.; Wang, H.; Chen, H. Nanocarriers and their loading strategies. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2019, 8, e1801002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doktorovova, S.; Souto, E.B. Nanostructured lipid carrier-based hydrogel formulations for drug delivery: A comprehensive review. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2009, 6, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Censi, R.; Di Martino, P. Polymorph impact on the bioavailability and stability of poorly soluble drugs. Molecules 2015, 20, 18759–18776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazila, K.; Yameen, B.; Wu, J.; Farokhzad, O.C. Nanoparticles: Mechanisms of Controlling Drug Release Nazila. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 2602–2663. [Google Scholar]
- Gil-González, E.; Perejón, A.; Sánchez-Jiménez, P.E.; Medina-Carrasco, S.; Kupčík, J.; Šubrt, J.; Criado, J.M.; Pérez-Maqueda, L.A. Crystallization kinetics of nanocrystalline materials by combined X-ray diffraction and differential scanning calorimetry experiments. Cryst. Growth Des. 2018, 18, 3107–3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, P.; Moghadam, T.T.; Ranjbar, B. Differential scanning calorimetry techniques: Applications in biology and nanoscience. J. Biomol. Tech. 2010, 21, 167. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, A.P.B.; Masuchi, M.H.; Miyasaki, E.K.; Domingues, M.A.F.; Stroppa, V.L.Z.; de Oliveira, G.M.; Kieckbusch, T.G. Crystallization modifiers in lipid systems. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 3925–3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyler, A.I.; Law, R.V.; Seddon, J.M. X-Ray Diffraction of Lipid Model Membranes. In Methods in Membrane Lipids; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 199–225. [Google Scholar]
- Baroli, B. Penetration of nanoparticles and nanomaterials in the skin: Fiction or reality? J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99, 21–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahbari, R.; Ichim, I.; Bamsey, R.; Burridge, J.; Guy, O.J.; Bolodeoku, J.; Graz, M. Characterisation of Drug Delivery Efficacy Using Microstructure-Assisted Application of a Range of APIs. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guimarães, K.L.; Ré, M.I. Lipid nanoparticles as carriers for cosmetic ingredients: The first (SLN) and the Second Generation (NLC). In Nanocosmetics and Nanomedicines; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 101–122. [Google Scholar]
- Ghasemiyeh, P.; Mohammadi-Samani, S. Potential of Nanoparticles as Permeation Enhancers and Targeted Delivery Options for Skin: Advantages and Disadvantages. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2020, 14, 3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakadia, P.G.; Conway, B.R. Lipid nanoparticles for dermal drug delivery. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2015, 21, 2823–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Ge, Z.-Q. Nanostructured lipid carriers improve skin permeation and chemical stability of idebenone. AAPS Pharmscitech 2012, 13, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto, E.B.; Baldim, I.; Oliveira, W.P.; Rao, R.; Yadav, N.; Gama, F.M.; Mahant, S. SLN and NLC for topical, dermal, and transdermal drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2020, 17, 357–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borgia, S.L.; Regehly, M.; Sivaramakrishnan, R.; Mehnert, W.; Korting, H.; Danker, K.; Röder, B.; Kramer, K.; Schäfer-Korting, M. Lipid nanoparticles for skin penetration enhancement—Correlation to drug localization within the particle matrix as determined by fluorescence and parelectric spectroscopy. J. Control. Release 2005, 110, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, R.; Katiyar, S.S.; Kushwah, V.; Jain, S. Solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carrier-based nanotherapeutics in treatment of psoriasis: A comparative study. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2017, 14, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, J.C.; Baisaeng, N.; Hoppel, M.; Löw, M.; Keck, C.M.; Valenta, C. Ultra-small NLC for improved dermal delivery of coenyzme Q10. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 447, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghasemiyeh, P.; Azadi, A.; Daneshamouz, S.; Heidari, R.; Azarpira, N.; Mohammadi-Samani, S. Cyproterone acetate-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers: Effect of particle size on skin penetration and follicular targeting. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2019, 24, 812–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patzelt, A.; Mak, W.C.; Jung, S.; Knorr, F.; Meinke, M.C.; Richter, H.; Rühl, E.; Cheung, K.Y.; Tran, N.B.N.N.; Lademann, J. Do nanoparticles have a future in dermal drug delivery? J. Control. Release 2017, 246, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blume-Peytavi, U.; Vogt, A. Human hair follicle: Reservoir function and selective targeting. Br. J. Dermatol. 2011, 165, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Jain, A.; Hurkat, P.; Jain, S.K. Transfollicular drug delivery: Current perspectives. Res. Rep. Transdermal Drug Deliv. 2016, 5, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- van der Maaden, K.; Jiskoot, W.; Bouwstra, J. Microneedle technologies for (trans) dermal drug and vaccine delivery. J. Control. Release 2012, 160, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kesarwani, A.; Yadav, A.K.; Singh, S.; Gautam, H.; Singh, H.N.; Sharma, A.; Yadav, C. Theoretical aspects of transdermal drug delivery system. Bull. Pharm. Res. 2013, 3, 78–89. [Google Scholar]
- Marchetti, J.M.; de Souza, M.C.; Marotta-Oliveira, S.S. Nanocarriers and cancer therapy: Approaches to Topical and Transdermal Delivery. In Nanocosmetics and Nanomedicines; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 269–286. [Google Scholar]
- Das, S.; Chaudhury, A. Recent advances in lipid nanoparticle formulations with solid matrix for oral drug delivery. AAPS Pharmscitech 2011, 12, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakadia, P.G.; Conway, B.R. Solid lipid nanoparticles: A potential approach for dermal drug delivery. Am. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 2, 4–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenning, V.; Gohla, S.H. Encapsulation of retinoids in solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN). J. Microencapsul. 2001, 18, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Castro, G.A.; Coelho, A.L.L.; Oliveira, C.A.; Mahecha, G.A.; Oréfice, R.L.; Ferreira, L.A. Formation of ion pairing as an alternative to improve encapsulation and stability and to reduce skin irritation of retinoic acid loaded in solid lipid nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 381, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gokce, E.H.; Korkmaz, E.; Dellera, E.; Sandri, G.; Bonferoni, M.C.; Ozer, O. Resveratrol-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles versus nanostructured lipid carriers: Evaluation of antioxidant potential for dermal applications. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wissing, S.A.; Müller, R.H. A novel sunscreen system based on tocopherol acetate incorporated into solid lipid nanoparticles. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2001, 23, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Bansal, R.; Gupta, S.; Jindal, N.; Jindal, A. Nanocarriers and nanoparticles for skin care and dermatological treatments. Indian Dermatol. Online J. 2013, 4, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalli, R.; Morel, S.; Gasco, M.R.; Chetoni, P. Preparation and evaluation in vitro of colloidal lipospheres containing pilocarpine as ion pair. Int. J. Pharm. 1995, 117, 243–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto, E.B.; Müller, R.H. 14 Lipid Nanoparticles (Solid Lipid Nanoparticles and Nanostructured Lipid Carriers) for Cosmetic, Dermal, and Transdermal Applications. Nanoparticulate Drug Deliv. Syst. 2007, 166, 213. [Google Scholar]
- Montenegro, L. Nanocarriers for skin delivery of cosmetic antioxidants. J. Pharm. Pharmacogn. Res. 2014, 2, 73–92. [Google Scholar]
- Ratnam, D.V.; Ankola, D.; Bhardwaj, V.; Sahana, D.K.; Kumar, M.R. Role of antioxidants in prophylaxis and therapy: A pharmaceutical perspective. J. Control. Release 2006, 113, 189–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, H.S. Potential involvement of free radical reactions in ultraviolet light-mediated cutaneous damage. Photochem. Photobiol. 1987, 46, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, J.O.; Valdés, K.; Morales, J.; Oyarzun-Ampuero, F. Lipid nanoparticles for the topical delivery of retinoids and derivatives. Nanomedicine 2015, 10, 253–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundram, K.; Khor, H.; Ong, A.S.; Pathmanathan, R. Effect of dietary palm oils on mammary carcinogenesis in female rats induced by 7, 12-dimethylbenz (a) anthracene. Cancer Res. 1989, 49, 1447–1451. [Google Scholar]
- Pace, A.; Savarese, A.; Picardo, M.; Maresca, V.; Pacetti, U.; Del Monte, G.; Biroccio, A.; Leonetti, C.; Jandolo, B.; Cognetti, F. Neuroprotective effect of vitamin E supplementation in patients treated with cisplatin chemotherapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 927–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werninghaus, K.; Meydani, M.; Bhawan, J.; Margolis, R.; Blumberg, J.B.; Gilchrest, B.A. Evaluation of the photoprotective effect of oral vitamin E supplementation. Arch. Dermatol. 1994, 130, 1257–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiele, J.J.; Ekanayake-Mudiyanselage, S. Vitamin E in human skin: Organ-specific physiology and considerations for its use in dermatology. Mol. Asp. Med. 2007, 28, 646–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, F.E.; May, J.M. Vitamin C function in the brain: Vital role of the ascorbate transporter SVCT2. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2009, 46, 719–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gašperlin, M.; Gosenca, M. Main approaches for delivering antioxidant vitamins through the skin to prevent skin ageing. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2011, 8, 905–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlZahabi, S.; Sakr, O.S.; Ramadan, A.A. Nanostructured lipid carriers incorporating prickly pear seed oil for the encapsulation of vitamin A. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2019, 18, 1875–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, Y.; Petkar, K.C.; Sawant, K.K. Development, evaluation and clinical studies of Acitretin loaded nanostructured lipid carriers for topical treatment of psoriasis. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 401, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabouri, M.; Samadi, A.; Nasrollahi, S.A.; Farboud, E.S.; Mirrahimi, B.; Hassanzadeh, H.; Kashani, M.N.; Dinarvand, R.; Firooz, A. Tretinoin loaded nanoemulsion for acne vulgaris: Fabrication, physicochemical and clinical efficacy assessments. Pharmaceutics 2018, 31, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harde, H.; Agrawal, A.K.; Katariya, M.; Kale, D.; Jain, S. Development of a topical adapalene-solid lipid nanoparticle loaded gel with enhanced efficacy and improved skin tolerability. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 43917–43929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.K.; Jain, A.; Garg, N.K.; Agarwal, A.; Jain, A.; Jain, S.A.; Tyagi, R.K.; Jain, R.K.; Agrawal, H.; Agrawal, G.P.; et al. Adapalene loaded solid lipid nanoparticles gel: An effective approach for acne treatment. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 121, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, A.; Garg, N.K.; Jain, A.; Kesharwani, P.; Jain, A.K.; Nirbhavane, P.; Tyagi, R.K. A synergistic approach of adapalene-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers, and vitamin C co-administration for treating acne. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2016, 42, 897–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, H.S.; Seo, J.E.; Kim, M.S.; Kang, M.H.; Oh, D.H.; Jeon, S.O.; Jeong, S.H.; Choi, Y.W.; Lee, S. A retinyl palmitate-loaded solid lipid nanoparticle system: Effect of surface modification with dicetyl phosphate on skin permeation in vitro and anti-wrinkle effect in vivo. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 452, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, F.; de Barros, D.P.; Fonseca, L.P. Design of multifunctional nanostructured lipid carriers enriched with α-tocopherol using vegetable oils. Pharmaceutics 2018, 118, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, I.D.; Saez, V.; de Campos, V.E.; Mansur, C.R. Size and Vitamin E Release of Nanostructured Lipid Carriers with Different Liquid Lipids, Surfactants and Preparation Methods. Macromol. Symp. 2019, 388, 1800011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wei, N.; Lopez-Garcia, M.; Ambrose, D.; Lee, J.; Annelin, C.; Peterson, T. Development and evaluation of resveratrol, Vitamin E, and epigallocatechin gallate loaded lipid nanoparticles for skin care applications. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 117, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harun, M.S.; Wong, T.W.; Fong, C.W. Advancing skin delivery of α-tocopherol and γ-tocotrienol for dermatitis treatment via nanotechnology and microwave technology. Biology 2021, 593, 120099. [Google Scholar]
- Prasertpol, T.; Tiyaboonchai, W. Nanostructured lipid carriers: A novel hair protective product preventing hair damage and discoloration from UV radiation and thermal treatment. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2020, 204, 111769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownlow, B.; Nagaraj, V.J.; Nayel, A.; Joshi, M.; Elbayoumi, T. Development and in vitro evaluation of vitamin E-enriched nanoemulsion vehicles loaded with genistein for chemoprevention against UVB-induced skin damage. Pharm. Nanotechnol. 2015, 104, 3510–3523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiri, F.; Faghfouri, L.; Hamidi, M. Preparation, optimization, and in-vitro characterization of α-tocopherol-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs). Molecules 2020, 46, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campani, V.; Biondi, M.; Mayol, L.; Cilurzo, F.; Pitaro, M.; De Rosa, G. Development of nanoemulsions for topical delivery of vitamin K1. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 511, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, M.; Singh, D.; Singh, M.R. Fabrication, optimization and characterization of Triamcinolone acetonide loaded nanostructured lipid carriers for topical treatment of psoriasis: Application of Box Behnken design, in vitro and ex vivo studies. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2017, 41, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teeranachaideekul, V.; Souto, E.B.; Müller, R.H.; Junyaprasert, V.B. Physicochemical characterization and in vitro release studies of ascorbyl palmitate-loaded semi-solid nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC gels). J. Microencapsul. 2008, 25, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wissing, S.; Müller, R. Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN)—A novel carrier for UV blockers. Pharmazie 2001, 56, 783–786. [Google Scholar]
- Nesseem, D. Formulation of sunscreens with enhancement sun protection factor response based on solid lipid nanoparticles. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2011, 33, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netto MPharm, G.; Jose, J. Development, characterization, and evaluation of sunscreen cream containing solid lipid nanoparticles of silymarin. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2018, 17, 1073–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puglia, C.; Damiani, E.; Offerta, A.; Rizza, L.; Tirendi, G.G.; Tarico, M.S.; Curreri, S.; Bonina, F.; Perrotta, R.E. Evaluation of nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC) and nanoemulsions as carriers for UV-filters: Characterization, in vitro penetration and photostability studies. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 51, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolić, S.; Keck, C.; Anselmi, C.; Müller, R. Skin photoprotection improvement: Synergistic interaction between lipid nanoparticles and organic UV filters. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 414, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanad, R.A.; AbdelMalak, N.S.; Badawi, A.A. Formulation of a novel oxybenzone-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs). AAPS PharmSciTech 2010, 11, 1684–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niculae, G.; Lacatusu, I.; Badea, N.; Meghea, A. Lipid nanoparticles based on butyl-methoxydibenzoylmethane: In vitro UVA blocking effect. Nanotechnology 2012, 23, 315704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niculae, G.; Lacatusu, I.; Badea, N.; Stan, R.; Vasile, B.S.; Meghea, A. Rice bran and raspberry seed oil-based nanocarriers with self-antioxidative properties as safe photoprotective formulations. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2014, 13, 703–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacatusu, I.; Niculae, G.; Badea, N.; Stan, R.; Popa, O.; Oprea, O.; Meghea, A. Design of soft lipid nanocarriers based on bioactive vegetable oils with multiple health benefits. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 246, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dario, M.F.; Oliveira, F.F.; Marins, D.S.; Baby, A.R.; Velasco, M.V.; Löbenberg, R.; Bou-Chacra, N.A. Synergistic photoprotective activity of nanocarrier containing oil of Acrocomia aculeata (Jacq.) Lodd. Ex. Martius—Arecaceae. Colloids Interfaces 2018, 112, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreo-Filho, N.; Bim, A.V.K.; Kaneko, T.M.; Kitice, N.A.; Haridass, I.N.; Abd, E.; Lopes, P.S.; Thakur, S.S.; Parekh, H.S.; Roberts, M.S.; et al. Development and evaluation of lipid nanoparticles containing natural botanical oil for sun protection: Characterization and in vitro and in vivo human skin permeation and toxicity. Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 2018, 31, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badea, G.; Lăcătuşu, I.; Badea, N.; Ott, C.; Meghea, A. Use of various vegetable oils in designing photoprotective nanostructured formulations for UV protection and antioxidant activity. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2015, 67, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badea, G.; Badea, N.; Brasoveanu, L.I.; Mihaila, M.; Stan, R.; Istrati, D.; Balaci, T.; Lacatusu, I. Naringenin improves the sunscreen performance of vegetable nanocarriers. NJC 2017, 41, 480–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.C.; Tan, C.P.; Nyam, K.L. Development of nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs) using pumpkin and kenaf seed oils with potential photoprotective and antioxidative properties. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2019, 121, 1900082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salunkhe, S.S.; Bhatia, N.M.; Pokharkar, V.B.; Thorat, J.D.; Bhatia, M.S. Topical delivery of Idebenone using nanostructured lipid carriers: Evaluations of sun-protection and anti-oxidant effects. Int. J. Pharm Investig. 2013, 43, 287–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asfour, M.H.; Kassem, A.A.; Salama, A. Topical nanostructured lipid carriers/inorganic sunscreen combination for alleviation of all-trans retinoic acid-induced photosensitivity: Box-Behnken design optimization, in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 134, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pivetta, T.P.; Silva, L.B.; Kawakami, C.M.; Araujo, M.M.; Del Lama, M.P.F.; Naal, R.M.Z.; Maria-Engler, S.S.; Gaspar, L.R.; Marcato, P.D. Topical formulation of quercetin encapsulated in natural lipid nanocarriers: Evaluation of biological properties and phototoxic effect. J. Drug Del. Sci. Tech. 2019, 53, 101148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Salam, F.S.; Ammar, H.O.; Elkheshen, S.A.; Mahmoud, A.A. Anti-inflammatory sunscreen nanostructured lipid carrier formulations. Colloids Interfaces 2017, 37, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, T.S.; Moreira, L.M.; Oliveira, T.M.; Melo, D.F.; Azevedo, E.P.; Gadelha, A.E.; Fook, M.V.; Oshiro-Júnior, J.A.; Damasceno, B.P. Bemotrizinol-Loaded Carnauba Wax-Based Nanostructured Lipid Carriers for Sunscreen: Optimization, Characterization, and In vitro Evaluation. AAPS PharmSciTech 2020, 21, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrish, J.A.; Fitzpatrick, T.B.; Tanenbaum, L.; Pathak, M.A. Photochemotherapy of psoriasis with oral methoxsalen and longwave ultraviolet light. Engl. J. Med. 1974, 291, 1207–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparro, F.P. The role of PUVA in the treatment of psoriasis. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2000, 1, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadet, J.; Voituriez, L.; Nardin, R.; Viari, A.; Vigny, P. A new class of psoralen photoadducts to DNA components: Isolation and characterization of 8-MOP adducts to the osidic moiety of 2′-deoxyadenosine. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 1988, 2, 321–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doppalapudi, S.; Jain, A.; Chopra, D.K.; Khan, W. Psoralen loaded liposomal nanocarriers for improved skin penetration and efficacy of topical PUVA in psoriasis. Eur. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 96, 515–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer-Korting, M.; Mehnert, W.; Korting, H.-C. Lipid nanoparticles for improved topical application of drugs for skin diseases. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 427–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, F.; Sinico, C.; Valenti, D.; Manca, M.L.; Fadda, A.M. Nanoemulsions as vehicle for topical 8-methoxypsoralen delivery. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2008, 4, 326–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, C.A.; Gouvêa, M.M.; Antunes, G.R.; de Freitas, Z.M.F.; de Carvalho Marques, F.F.; Ricci-Junior, E. Nanoemulsion containing 8-methoxypsoralen for topical treatment of dermatoses: Development, characterization and ex vivo permeation in porcine skin. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 547, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.-Y.; Fang, C.-L.; Liu, C.-H.; Su, Y.-H. Lipid nanoparticles as vehicles for topical psoralen delivery: Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) versus nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC). Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 70, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitzanti, G.; Rosa, A.; Nieddu, M.; Valenti, D.; Pireddu, R.; Lai, F.; Cardia, M.C.; Fadda, A.M.; Sinico, C. Transcutol® P Containing SLNs for Improving 8-Methoxypsoralen Skin Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battaglia, L.; Peira, E.; Sapino, S.; Gallarate, M. Lipid nanosystems in topical PUVA therapy. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2012, 33, 565–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad, H.A.; Abd El-Rahman, F.A.; Hamdy, G.M. Chamomile oil loaded solid lipid nanoparticles: A naturally formulated remedy to enhance the wound healing. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 50, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saporito, F.; Sandri, G.; Bonferoni, M.C.; Rossi, S.; Boselli, C.; Cornaglia, A.I.; Mannucci, B.; Grisoli, P.; Vigani, B.; Ferrari, F. Essential oil-loaded lipid nanoparticles for wound healing. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffari, S.; Alihosseini, F.; Sorkhabadi, S.M.R.; Bidgoli, S.A.; Mousavi, S.E.; Haghighat, S.; Nasab, A.A.; Kianvash, N. Nanotechnology in wound healing; semisolid dosage forms containing curcumin-ampicillin solid lipid nanoparticles, in-vitro, ex-vivo and in-vivo characteristics. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2018, 8, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami, M.A.; Sharif Makhmal Zadeh, B.; Koochak, M.; Moghimipur, E. Superoxide dismutase-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles prepared by cold homogenization method: Characterization and permeation study through burned rat skin. Jundishapur J. Nat. Pharm. Prod. 2016, 11, e33968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junyaprasert, V.B.; Teeranachaideekul, V.; Souto, E.B.; Boonme, P.; Müller, R.H. Q10-loaded NLC versus nanoemulsions: Stability, rheology and in vitro skin permeation. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 377, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardeike, J.; Schwabe, K.; Müller, R.H. Influence of nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC) on the physical properties of the Cutanova Nanorepair Q10 cream and the in vivo skin hydration effect. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2010, 396, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayak, K.; Katiyar, S.S.; Kushwah, V.; Jain, S. Coenzyme Q10 and retinaldehyde co-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers for efficacy evaluation in wrinkles. J. Drug Target. 2018, 26, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrotriya, S.; Ranpise, N.; Vidhate, B. Skin targeting of resveratrol utilizing solid lipid nanoparticle-engrossed gel for chemically induced irritant contact dermatitis. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2017, 7, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puglia, C.; Offerta, A.; Tirendi, G.G.; Tarico, M.S.; Curreri, S.; Bonina, F.; Perrotta, R.E. Design of solid lipid nanoparticles for caffeine topical administration. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh Hallan, S.; Sguizzato, M.; Pavoni, G.; Baldisserotto, A.; Drechsler, M.; Mariani, P.; Esposito, E.; Cortesi, R. Ellagic acid containing nanostructured lipid carriers for topical application: A preliminary study. Molecules 2020, 25, 1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayan, V.; Aafreen, S.; Sakthivel, S.; Reddy, K.R. Formulation and characterization of solid lipid nanoparticles loaded Neem oil for topical treatment of acne. J. Acute Dis. 2013, 2, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacatusu, I.; Badea, N.; Ovidiu, O.; Bojin, D.; Meghea, A. Highly antioxidant carotene-lipid nanocarriers: Synthesis and antibacterial activity. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2012, 14, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozaki, O. Steroid analysis for medical diagnosis. J. Chromatogr. A 2001, 935, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Goes, M.C.; Jacobs, J.W.; Bijlsma, J.W. The value of glucocorticoid co-therapy in different rheumatic diseases-positive and adverse effects. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2014, 16, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oray, M.; Abu Samra, K.; Ebrahimiadib, N.; Meese, H.; Foster, C.S. Long-term side effects of glucocorticoids. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2016, 15, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, M.D.; Hood, E.D.; Zern, B.; Shuvaev, V.V.; Grosser, T.; Muzykantov, V.R. Nanocarriers for vascular delivery of anti-inflammatory agents. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2014, 54, 205–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beloqui, A.; Coco, R.; Alhouayek, M.; Solinís, M.Á.; Rodríguez-Gascón, A.; Muccioli, G.G.; Préat, V. Budesonide-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers reduce inflammation in murine DSS-induced colitis. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 454, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Smith, E. Percutaneous permeation of betamethasone 17-valerate incorporated in lipid nanoparticles. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100, 896–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Zhao, Y.; Quan, P.; Fang, L. Development of a topical ointment of betamethasone dipropionate loaded nanostructured lipid carrier. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 11, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, P.A.; Ghorab, M.M.; Gad, S. Development of betamethasone dipropionate-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers for topical and transdermal delivery. Antiinflamm Antiallergy Agents Med Chem. 2019, 18, 26–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaich, U.; Gulati, N. Nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC) based controlled release topical gel of clobetasol propionate: Design and in vivo characterization. Drug Deliv. Res. 2016, 6, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.A.D.; Taveira, S.F.; Lima, E.M.; Marreto, R.N. In vitro skin penetration of clobetasol from lipid nanoparticles: Drug extraction and quantitation in different skin layers. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 48, 811–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.A.D.; Andrade, L.M.; de Sá, F.A.P.; Marreto, R.N.; Lima, E.M.; Gratieri, T.; Taveira, S.F. Clobetasol-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers for epidermal targeting. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2016, 68, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, L.M.; Silva, L.A.D.; Krawczyk-Santos, A.P.; de SM Amorim, I.C.; da Rocha, P.B.R.; Lima, E.M.; Anjos, J.L.V.; Alonso, A.; Marreto, R.N.; Taveira, S.F.; et al. Improved tacrolimus skin permeation by co-encapsulation with clobetasol in lipid nanoparticles: Study of drug effects in lipid matrix by electron paramagnetic resonance. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm 2017, 119, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, S.; Addan, R.; Kushwah, V.; Harde, H.; Mahajan, R.R. Comparative assessment of efficacy and safety potential of multifarious lipid based Tacrolimus loaded nanoformulations. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 562, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, M.; Singh, D.; Murthy, S.N.; Singh, M.R. Design, characterization and skin permeating potential of Fluocinolone acetonide loaded nanostructured lipid carriers for topical treatment of psoriasis. Steroids 2015, 101, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doktorovová, S.; Araújo, J.; Garcia, M.L.; Rakovský, E.; Souto, E.B. Formulating fluticasone propionate in novel PEG-containing nanostructured lipid carriers (PEG-NLC). Pharmaceutics 2010, 75, 538–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Siril, P.F.; Javid, F. Unusual anti-leukemia activity of nanoformulated naproxen and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2016, 69, 1335–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altman, R.D.; Barthel, H.R. Topical therapies for osteoarthritis. Drugs 2011, 71, 1259–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saino, V.; Monti, D.; Burgalassi, S.; Tampucci, S.; Palma, S.; Allemandi, D.; Chetoni, P. Optimization of skin permeation and distribution of ibuprofen by using nanostructures (coagels) based on alkyl vitamin C derivatives. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2010, 76, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhalekar, M.R. Solid lipid nanoparticles incorporated transdermal patch for improving the permeation of Piroxicam. AJP 2016, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.-H.; Wei, W.; Shan, Y.-H.; Chong, Y.-S.; Yu, L.; Gao, J.-Q. Sustained release of piroxicam from solid lipid nanoparticle as an effective anti-inflammatory therapeutics in vivo. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2017, 43, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi-Samani, S.; Zojaji, S.; Entezar-Almahdi, E. Piroxicam loaded solid lipid nanoparticles for topical delivery: Preparation, characterization and in vitro permeation assessment. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 47, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, S.; Ray, S.; Dey, S.; Pal, P.; Mazumder, B. Transdermal Lipid Nanocarriers: A Potential Delivery System for Lornoxicam. Pharm. Nanotechnol. 2017, 5, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Tian, B.; Han, J.; Zhang, J.; Shi, Y.; Lv, Q.; Li, K. Enhanced transdermal delivery of lornoxicam by nanostructured lipid carrier gels modified with polyarginine peptide for treatment of carrageenan-induced rat paw edema. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 6135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elkomy, M.H.; Elmenshawe, S.F.; Eid, H.M.; Ali, A.M. Topical ketoprofen nanogel: Artificial neural network optimization, clustered bootstrap validation, and in vivo activity evaluation based on longitudinal dose response modeling. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 3294–3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, C.V.; Van, M.C.; Thi, H.P.; Thanh, C.Đ.; Ngoc, B.T.; Van, B.N.; Le Thien, G.; Van, B.N.; Nguyen, C.N. Development of ibuprofen-loaded solid lipid nanoparticle-based hydrogels for enhanced in vitro dermal permeation and in vivo topical anti-inflammatory activity. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 101758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mennini, N.; Cirri, M.; Maestrelli, F.; Mura, P. Comparison of liposomal and NLC (nanostructured lipid carrier) formulations for improving the transdermal delivery of oxaprozin: Effect of cyclodextrin complexation. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 515, 684–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, N.K.; Sharma, G.; Singh, B.; Nirbhavane, P.; Tyagi, R.K.; Shukla, R.; Katare, O. Quality by Design (QbD)-enabled development of aceclofenac loaded-nano structured lipid carriers (NLCs): An improved dermatokinetic profile for inflammatory disorder (s). Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 517, 413–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, P.; Srivastava, N.; Rai, V.K.; Mishra, R.; Ajayakumar, P.; Yadav, N.P. A novel approach for dermal controlled release of salicylic acid for improved anti-inflammatory action: Combination of hydrophilic-lipophilic balance and response surface methodology. AAPS PharmSciTech 2019, 52, 870–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurana, S.; Bedi, P.; Jain, N. Preparation and evaluation of solid lipid nanoparticles based nanogel for dermal delivery of meloxicam. Chem. Phys. Lipids. 2013, 175, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurana, S.; Jain, N.; Bedi, P. Nanoemulsion based gel for transdermal delivery of meloxicam: Physico-chemical, mechanistic investigation. Life Sci. 2013, 92, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).