Abstract
Cannabidiol is a phytocannabinoid with proven pharmacological properties that is also used in the cosmetic industry for its sebostatic and antioxidant activities, being considered a new anti-aging ally. An analytical method is proposed for the determination of CBD in cosmetic products by liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry, after leaching the CBD from the cosmetic matrix with ethanol. Low instrumental limits of detection (0.22 ng mL−1) and quantification (0.74 ng mL−1) allow the determination of CBD at trace levels without needing preconcentration, whereas the wide linearity of the method allows the determination of CBD in more concentrated samples without high dilution. The method was successfully applied to the analysis of six cosmetic products and a raw material. The proposed method is suitable for the quality control of cosmetic products containing CBD, being able to quickly and easily determine this compound, ensuring that its concentration in the finished product is the desired one.
1. Introduction
Cannabidiol (CBD) is a phytocannabinoid found in the Cannabis plant that does not have psychoactive activity, unlike tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) also present in Cannabis.
CBD has aroused a lot of interest in recent years due to its various pharmacological properties, which include analgesic, anti-inflammatory, antineoplastic, and chemopreventive activity. In addition, it has recently started to be used in the cosmetic industry for its antioxidant, skin conditioning, and sebostatic properties. CBD acts on the function of sebaceous glands, behaving like a highly effective sebostatic agent, inhibiting the proliferation of sebocytes and the production of sebum. CBD also exerts anti-inflammatory actions that, combined with its lipostatic and antiproliferative effects, make it a promising therapeutic agent for the treatment of acne vulgaris, since it counteracts the multiple pathogenic factors of acne: sebum overproduction, sebocyte overproliferation, and inflammation [1]. Moreover, CBD is a powerful antioxidant that helps counteract oxidative cell damage generated by free radicals by helping to decrease the visible signs of skin aging [2], and it is mainly for this reason that it is becoming one of the star ingredients of the cosmetic sector in recent years [3,4].
Current European legislation does not prohibit the use of synthetically obtained CBD in cosmetic products. Cannabis seeds and leaves (without the upper part of the plant, flowers, or fruits) obtained from varieties of hemp with a low THC content (less than 0.2%) can be also used, both after proper treatment (such as to obtain oils, e.g., Cannabis sativa seed oil) or after a process to obtain and purify CBD for direct use as an ingredient [5,6,7].
Many articles related to CBD and other cannabinoids determination in plants [8], oils [9], or other matrices, such as biological fluids, hair, or food products can be found in the analytical literature based on the use of different sample preparation strategies [10] and chromatographic techniques [11]. Gas chromatography coupled to simple mass spectrometry (GC-MS) was used for the analysis of hair [12,13,14,15,16], oral fluid [17,18], and hemp food [19] samples. Gas chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry (GC-MS/MS) was also used for hair sample analysis [20,21,22,23]. Liquid chromatography with ultraviolet detection (LC-UV) was used for the analysis of urine [24,25] and brain and blood mice [25]. Liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) was used for the analysis of hair [26] and oral fluid samples [27], and ultra-high performance liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry (UHPLC-MS/MS) was used for serum and urine [28,29] and oral fluid and sweat patches [28] analysis.
Only a few recent publications are related to the determination of CBD and other cannabinoids in cosmetic products. In this context, Meng et al. [30] analyzed commercial creams by LC-MS/MS after dilution of samples with methanol (MeOH) containing 0.005% of formic acid and 5% of water, sonication, and centrifugation, thus obtaining a limit of detection (LOD) of 0.048 ng mL−1 of CBD in the measurement solutions. Nemeskalová et al. [31] analyzed hydrophobic cosmetics by LC-UV and LC-MS/MS by treatment with ethyl acetate:isopropanol 1:1 by vortex, followed by heating to get a good dispersion and separation of the supernatant after cooling to −20 °C and finally dilution with a 60% aqueous acetonitrile solution, shaking by vortex, and filtering before analysis; a LOD of 0.2 µg g−1 of CBD in samples was obtained. Huber et al. [32] determined CBD in creams by LC-UV by microextraction using MeOH and an ionic liquid and sonication at 40 °C, followed by centrifugation, evaporation of the supernatant, and dilution of the remaining ionic liquid with an acetonitrile solution; a LOD of 0.01 mg g−1 of CBD in samples was obtained.
The aim of this work is to develop and validate an analytical method for the determination of CBD in different types of cosmetic products, with good analytical features for use in the quality control of the cosmetic industry, such as replacement or reduction of toxic organic reagents, quickness, and simplicity, especially in the sample preparation stage. Moreover, the proposed method allows the determination of CBD both at trace level and in higher concentrations. Recommended performance parameters in single-laboratory validation of analytical methods for cosmetics given by the Joint Research Centre Guidelines [33] have been studied.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Apparatus
An Agilent Technologies 1100 Series liquid chromatography system, equipped with a degasser, a quaternary pump, an automatic injector, and an oven, was used. The chromatography system was coupled to an Agilent 6410B Triple Quad LC-MS/MS detector. Reverse-phase chromatographic separations were carried out using an Agilent Zorbax SB-C18 column (50 mm in length, 21 mm in internal diameter, and 1.8 µm in particle size). The acquisition and processing of data were carried out using a computer equipped with the Agilent Technologies MassHunter Workstation LC/QQQ software (Version B.08.02).
A ZX3 vortex mixer from VELP Scientifica (Usmate Velate, Italy) was used to facilitate the lixiviation of the analyte from the sample.
2.2. Reagents and Samples
A solution of CBD in MeOH with a concentration of 1.0 mg mL−1 from Sigma-Aldrich (Saint Louis, MO, USA) (purity 99.3%) was used as a stock standard solution.
A solution of Cannabidiol-D3 (CBD-D3) in MeOH with a concentration of 100 μg mL−1 from Sigma-Aldrich (Saint Louis, MO, USA) (purity 99.7%) was used as a stock internal standard solution.
Ethanol (EtOH) HPLC grade from Panreac (Barcelona, Spain) and deionized water obtained through a Connect water purification system from Adrona (Riga, Latvia) were used for sample and standards preparation.
A chromatographic mobile phase composed of LC-MS grade MeOH and LC-MS grade water from Panreac (Barcelona, Spain) was used, both phases containing 0.1% of formic acid prepared from formic acid provided by VWR chemicals (Fontenay-sous-Bois, France).
Six commercial cosmetic products (i.e., four creams, a shower gel, and a hair mask) and a raw material (Cannabis sativa oil standardized in 1.3% CBD) were analyzed, and their brands are not mentioned for confidentiality reasons. According to the labels, the four creams and the raw material contained CBD among the labeling ingredients, while the labels on the shower gel and the hair mask indicated that they contained the ingredient Cannabis sativa oil.
2.3. Proposed Method
2.3.1. Standards Preparation
An ethanolic CBD solution of 100 ng mL−1 was prepared by successive dilutions of the 1.0 mg mL−1 CBD stock standard solution with EtOH. Working standard solutions containing different concentrations of CBD (1 to 30 ng mL−1) were prepared by dilution of the 100 ng mL−1 ethanolic standard solution with the appropriate volumes of EtOH and water to get 1:1 EtOH:water solutions. These solutions also contained the appropriate volume of a 200 ng mL−1 ethanolic CBD-D3 solution to get a fixed internal standard concentration of 8 ng mL−1. The obtained standard solutions were transferred to injection vials for chromatographic analysis.
2.3.2. Samples Preparation
First, 1 g of sample was weighed into a volumetric flask and brought to a final volume of 10 mL with EtOH. To facilitate CBD leaching, the sample was shaken with a vortex mixer. Then, 1 mL of this initial solution was taken and transferred to a 10 mL volumetric flask and the appropriate volumes of EtOH and water were added to get a 1:1 EtOH:water solution. A lower mass of sample or a lower volume of the initial sample solution was taken if CBD concentration was relatively high. As in the standards, sample solutions contained the appropriate volume of the 200 ng mL−1 ethanolic CBD-D3 solution to get a fixed internal standard concentration of 8 ng mL−1. The obtained solutions were filtered through nylon filters with a pore size of 0.45 µm and transferred to injection vials for LC-MS/MS.
2.3.3. LC-MS/MS Analysis
Ten microliters of sample or standard solutions were injected into the chromatographic system and the ratio of the analyte (CBD) peak area to the internal standard (CBD-D3) peak area was used as an analytical signal to carry out the determination of CBD. The mobile phase consisted of MeOH:water (both with 0.1% of formic acid) by isocratic elution at a mixing ratio of 80:20% (v/v). The flow rate was 0.2 mL min−1, and the column temperature was maintained constant at 35 °C. The run time was below 4 min.
The triple quadrupole MS operated in positive electrospray ionization mode (ESI+, capillary voltage at 3 kV) by multiple reaction monitoring (MRM). The other conditions were gas temperature at 310 °C, nebulizer gas flow rate at 12 L min−1, and nebulizer gas at 50 psi.
The collision energy and the m/z precursor→product ion transitions for quantification are indicated in Table 1, together with the summary of the instrumental variables.

Table 1.
Instrumental variables of LC-MS/MS analysis.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chromatographic Conditions
The standards and samples were prepared as EtOH:water solutions (see Section 2.3), which allowed the sample preparation step to be as environmentally friendly as possible. However, commercialized EtOH does not reach the degree of purity necessary to be used as a mobile phase in LC-MS/MS, so MeOH:water was used in the chromatographic step.
The optimization and selection of MS/MS transitions were performed using Agilent MassHunter Optimizer software in multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) mode in positive polarity. The variables related to the detector were studied by injecting a CBD standard solution of 1 µg mL−1 and a CBD-D3 solution of 1 µg mL−1, both 1:1 EtOH:water. The product ions generated from the two precursor ions were studied, and then the fragmentor and the collision energy were optimized for each of the product ions. The optimized parameters are shown in Table 1. It was also determined that the quantification ion, the one that provides a higher signal, is the one that corresponds to the transition 315 > 193 for CBD and the one that corresponds to the transition 318 > 196 for CBD-D3. Finally, the capillary voltage was optimized for the product ions, being +3 kV in all of them.
Figure 1 shows the chromatogram of a standard solution containing 4 ng mL−1 of CBD and 8 ng mL−1 of CBD-D3 obtained under these conditions. The CBD peak is observed at a retention time of approximately 3.2 min with a good resolution.
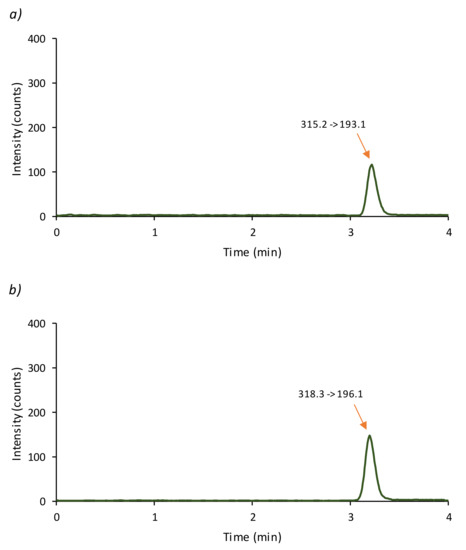
Figure 1.
Chromatogram obtained applying the proposed LC-MS/MS method to a standard solution containing 4 ng mL−1 of analyte and 8 ng mL−1 of internal standard ((a) CBD; (b) CBD-D3).
3.2. Standards Preparation
EtOH is proposed as a solvent for the stock standard solutions, since it is a harmless and relatively inexpensive solvent compared to other organic solvents in which CBD is also soluble. However, elution force differences between MeOH (used in the mobile phase) and EtOH (used as solvent) caused a split of the peak if only EtOH was used as the solvent. Then, before injection to the LC-MS/MS system, the ethanolic standard solutions were diluted with water to obtain EtOH:water 1:1 solutions that prevented splitting.
3.3. Samples Preparation
The method was tested by applying it to six commercial cosmetic products and a raw material with different types of matrix.
The sample preparation process does not require any prior preconcentration steps, only brief shaking of the samples with EtOH to achieve leaching of CBD from the cosmetic matrix. Samples were filtered through a 0.45 µm pore size nylon filter, preventing solid particles from reaching the injector or column. As for standard solutions, filtered samples were diluted with water to obtain EtOH:water 1:1 solutions.
3.4. Analytical Figures of Merit of the Proposed Method
Quality parameters such as linearity, limit of detection (LOD), limit of quantification (LOQ), repeatability, and recovery were evaluated to validate the proposed method. The results are summarized in Table 2.

Table 2.
Main analytical parameters of the proposed LC-MS/MS method.
The linearity can be defined in this case as the ability of the LC-MS/MS proposed method to induce an analytical signal whose intensity is directly proportional to CBD concentration. Analytical signals (analyte and internal standard peaks area ratio) of six standards containing CBD concentrations between 0.75 and 200 ng mL−1 and a fixed concentration of CBD-D3 (8 ng mL−1) were calculated, and linearity was estimated by the coefficient of determination (R2). An R2 value of 0.9992 was obtained, showing that it is possible to determine CBD in samples with a relatively high concentration without needing to add more dilution steps than those recommended in the proposed method.
The instrumental LOD and LOQ, i.e., the smallest CBD concentration that can be detected or quantified with acceptable accuracy, were calculated as three and 10 times, respectively, the signal-to-noise ratio. Methods LOD and LOQ were calculated as the corresponding values in the sample, according to the preparation procedure. The LOD and LOQ were 0.22 and 0.74 ng mL−1 in the measurement solutions (i.e., 22 and 74 ng g−1 in the sample), respectively. These values allow the determination of CBD at trace levels in cosmetic formulations without needing pre-concentration steps.
The repeatability of the measurements is expressed as relative standard deviation (RSD) of several replicates of the same solution. It was evaluated by applying the proposed method to five replicates of two standard solutions containing different concentration levels of CBD (2 and 4 ng mL−1) on the same day (intra-day) and for five consecutive days (inter-day). The results revealed that good repeatability was achieved (RSD < 8.5%).
The proposed method was applied to the analysis of six commercially available cosmetics (containing cannabidiol or Cannabis sativa seed oil) and a raw material (containing Cannabis sativa oil and a known amount of CBD).
The results are shown in Table 3. It revealed that CBD was detected in the raw material and in the cosmetic samples in where CBD was indicated on the label as an ingredient, while CBD was not detected in those samples in which Cannabis sativa seed oil was indicated as an ingredient.

Table 3.
Application of the method to the analysis of commercial samples.
In order to evaluate the recovery of the method, six cosmetic samples were spiked with 1 mL of a CBD standard solution of 200 or 400 ng in the first step of the procedure (before treatment with EtOH), which results in 2 and 4 ng mL−1 in the measurement solutions. The recovery of CBD was calculated as the percentage of the CBD obtained by using the proposed method. As can be seen, the relative recovery values obtained ranged between 100% and 114%, which shows negligible matrix effects.
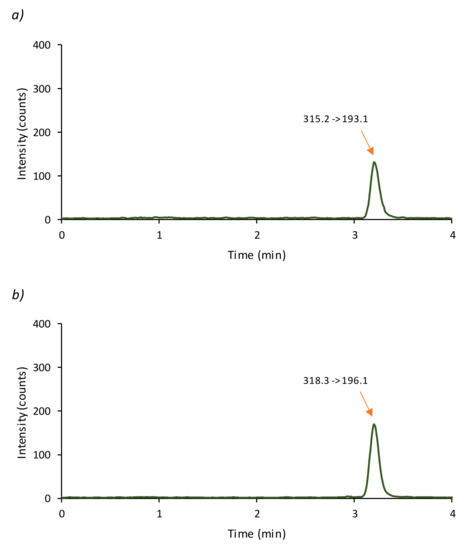
Figure 2.
Chromatogram obtained applying the proposed LC-MS/MS method to Cannabis sativa oil raw material (sample G) ((a) CBD; (b) CBD-D3).
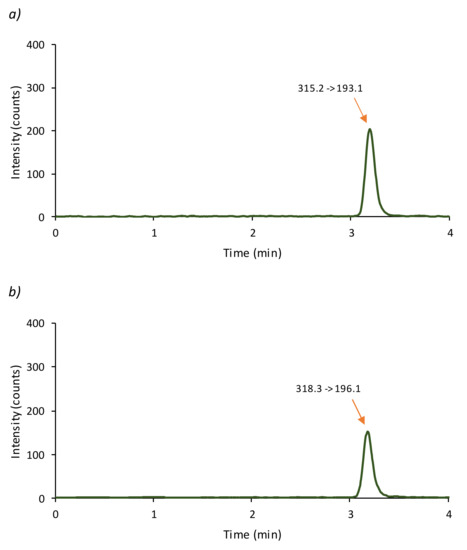
Figure 3.
Chromatogram obtained applying the proposed LC-MS/MS method to a cosmetic cream (sample C) ((a) CBD; (b) CBD-D3).
4. Conclusions
A sensitive analytical method is proposed to determine CBD in cosmetic products using LC-MS/MS.
The proposed analytical method is simple and highly sensitive, since it allows the determination of CBD at trace levels. Likewise, the wide linearity range of the method allows the determination of CBD in samples with relatively high concentrations.
The characteristics of the method and the results obtained show its usefulness in carrying out this determination simply and quickly. The compound has been efficiently determined in cosmetic samples of different natures with good analytical features. For this reason, the proposed method is suitable for quality control of cosmetic products that contain this ingredient, thus assuring that its concentration in the finished product is the desired one.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: L.S., J.L.B., A.C., and A.S.; methodology: L.S., J.L.B., and A.C.; investigation: L.S. and M.P.; resources: J.L.B., A.C., and A.S.; writing—original draft preparation: L.S.; writing—review and editing: J.L.B., A.C., and A.S.; supervision: A.C. and A.S.; funding acquisition: A.C. and A.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
J.L.B. would like to thank the Generalitat Valenciana and the European Social Fund for his postdoctoral grant.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Oláh, A.; Tóth, B.I.; Borbíró, I.; Sugawara, K.; Szöllõsi, A.G.; Czifra, G.; Pál, B.; Ambrus, L.; Kloepper, J.; Camera, E. Cannabidiol exerts sebostatic and antiinflammatory effects on human sebocytes. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 3713–3724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casares, L.; García, V.; Garrido-Rodríguez, M.; Milán, E.; Collado, J.A.; García-Martín, A.; Peñarando, J.; Calzado, M.A.; De la Vega, L.; Muñoz, E. Cannabidiol induces antioxidant pathways in keratinocytes by targeting BACH1. Redox Biol. 2020, 28, 101321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahawar, N.; Schoenberg, E.; Wang, J.V.; Saedi, N. The growing trend of cannabidiol in skincare products. Clin. Derm. 2019, 37, 279–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, S.; Kim, M.S.; Lee, S.H.; Park, B.D. Epidermal endocannabinoid system (EES) and its cosmetic application. Cosmetics 2019, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations, Office on Drug and Crime. The Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs of 1961 as Amended by the 1972 Protocol. Available online: https://www.unodc.org/unodc/en/commissions/CND/conventions.html (accessed on 25 February 2021).
- CosIng Database—European Comission Database for Information on Cosmetic Substances and Ingredients. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/growth/sectors/cosmetics/cosing_en (accessed on 25 February 2021).
- Regulation (EU) No 1307/2013 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 17 December 2013 Establishing Rules for Direct Payments to Farmers under Support Schemes within the Framework of the Common Agricultural Policy and Repealing Council Regulation (EC) No 637/2008 and Council Regulation (EC) No 73/2009. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=celex%3A32013R1307 (accessed on 25 February 2021).
- Lazarjani, M.P.; Torres, S.; Hooker, T.; Fowlie, C.; Young, O.; Seyfoddin, A. Methods for quantification of cannabinoids: A narrative review. J. Cannabis Res. 2020, 2, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebling, J.P.; Clarkson, N.J.; Gibbs, B.W.; Yates, A.S.; O’Sullivan, S.E. An analysis of over-the-counter cannabidiol products in the United Kingdom. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brighenti, V.; Protti, M.; Anceschi, L.; Zanardi, C.; Mercolini, L.; Pellati, F. Emerging challenges in the extraction, analysis and bioanalysis of cannabidiol and related compounds. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 192, 113633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, K. Advances in Chromatographic Analysis of Cannabidiol (CBD). Anal. Sci. 2020, 36, 781–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, S.S.; Chiarotti, M. Solid-phase microextraction for cannabinoids analysis in hair and its possible application to other drugs. J. Anal. Toxicol. 1999, 23, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musshoff, F.; Junker, H.P.; Lachenmeier, D.W.; Kroener, L.; Madea, B. Fully automated determination of cannabinoids in hair samples using headspace solid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2002, 26, 554–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadulski, T.; Pragst, F. Simple and sensitive determination of Δ9- tetrahydrocannabinol, cannabidiol and cannabinol in hair by combined silylation, headspace solid phase microextraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2007, 846, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosmann, B.; Roth, N.; Hastedt, M.; Bauer, A.J.; Pragst, F.; Auwarter, V. Cannabinoid findings in children hair—What do they really tell us? An assessment in the light of three different analytical methods with focus on interpretation of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinolic acid. Drug Test. Anal. 2015, 7, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musshoff, F.; Lachenmeier, D.W.; Kroener, L.; Madea, B. Automated headspace solid-phase dynamic extraction for the de-termination of cannabinoids in hair samples. Forensic Sci. Int. 2003, 133, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fucci, N.; Giovanni, N.D.; Chiarotti, M. Simultaneous detection of some drugs of abuse in saliva samples by SPME tech-nique. Forensic Sci. Int. 2003, 134, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzillotti, L.; Castrignano, E.; Rossi, S.S.; Chiarotti, M. Cannabinoids determination in oral fluids by SPME-GC/MS and UHPLC-MS/MS and its application on suspected drivers. Sci. Justice 2014, 54, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachenmeier, D.W.; Kroener, L.; Musshoff, F.; Madea, B. Determination of cannabinoids in hemp food products by use of headspace solid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2004, 378, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emidio, E.S.; Prata, V.D.M.; Dorea, H.S. Validation of an analytical method for analysis of cannabinoids in hair by head-space solid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography-ion trap tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2010, 670, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeli, I.; Casati, S.; Ravelli, A.; Minoli, M.; Orioli, M. A novel single-step GC-MS/MS method for cannabinoids and 11-OH-THC metabolite analysis in hair. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 155, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachenmeier, D.W.; Kroener, L.; Musshoff, F.; Madea, B. Application of tandem mass spectrometry combined with gas chromatography and headspace solid-phase dynamic extraction for the determination of drugs of abuse in hair samples. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2003, 17, 472–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emidio, E.S.; Prata, V.D.M.; Santana, F.J.M.D.; Dorea, H.S. Hollow fiber-based liquid phase microextraction with fractional design optimization and gas chromatography- tandem mass spectrometry for determination of cannabinoids in human hair. J. Chromatogr. B 2010, 878, 2175–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, M.; Yamini, Y.; Baheri, T. Analysis of abuse drugs in urine using surfactant- assisted dispersive liquid-liquid mi-croextraction. J. Sep. Sci. 2011, 34, 1722–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.; Xie, W. Determination of cannabinoids in biological samples using a new solid phase micro-extraction membrane and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Forensic Sci. Int. 2006, 162, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Míguez-Framil, M.; Cocho, J.Á.; Tabernero, M.J.; Bermejo, A.M.; Moreda-Piñeiro, A.; Bermejo-Barrera, P. An improved method for the determination of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol, cannabinol and cannabidiol in hair by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Microchem. J. 2014, 117, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergi, M.; Montesano, C.; Odoardi, S.; Rocca, L.M.; Fabrizi, G.; Compagnone, D. Microextraction by packed sorbents coupled to liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry for the rapid and sensitive determination of cannabinoids in oral fluids. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1301, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichini, S.; Malaca, S.; Gottardi, M.; Perez-Acevedo, A.P.; Papaseit, E.; Perez-Mana, C.; Farre, M.; Pacifi, R.; Tagliabracci, A.; Mannocchi, G.; et al. UHPLC-MS/MS analysis of cannabidiol metabolites in serum and urine samples. Application to an individual treated with medical cannabis. Talanta 2021, 223, 121772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichini, S.; Mannocchi, G.; Gottardi, M.; Perez-Acevedo, A.P.; Poyatos, L.; Papaseit, E.; Perez-Mana, C.; Farre, M.; Pacifici, R.; Busardo, F.P. Fast and sensitive UHPLC-MS/MS analysis of cannabinoids and their acid precursors in pharmaceutical prep-arations of medical cannabis and their metabolites in conventional and non-conventional biological matrices of treated in-dividual. Talanta 2020, 209, 120537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Buchanan, B.; Zuccolo, J.; Pouling, M.M.; Gabriele, J.; Baranowski, D.C. A reliable and validated LC-MS/MS method for the simultaneous quantification of 4 cannabinoids in 40 consumer products. PLoS ONE 2018, 135, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemeškalová, A.; Hájková, K.; Mikulů, L.; Sýkora, D.; Kuchař, M. Combination of UV and MS/MS detection for the LC analysis of cannabidiol-rich products. Talanta 2020, 219, 121250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, S.; Harder, M.; Funck, K.; Erharter, K.; Popp, M.; Bonn, G.K.; Rainer, M. Novel Room Temperature Ionic Liquid for Liquid-Phase Microextraction of Cannabidiol from Natural Cosmetics. Separations 2020, 7, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, U. JRC Guidelines for 1—Selecting And/Or Validating Analytical Methods for Cosmetics 2—Recommending Standardization Steps of Analytical Methods for Cosmetics; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2015. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).