4′,7-Isoflavandiol (Equol) Enhances Human Dermal Fibroblast Renewal and Has Effects Similar to 17β-Estradiol in Stimulating Collagen and Elastin Expression. Cell Cycle and RT-PCR Analysis without Phenol Red
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Material Stock Solution Preparation
2.2. Monolayer Cell Culture
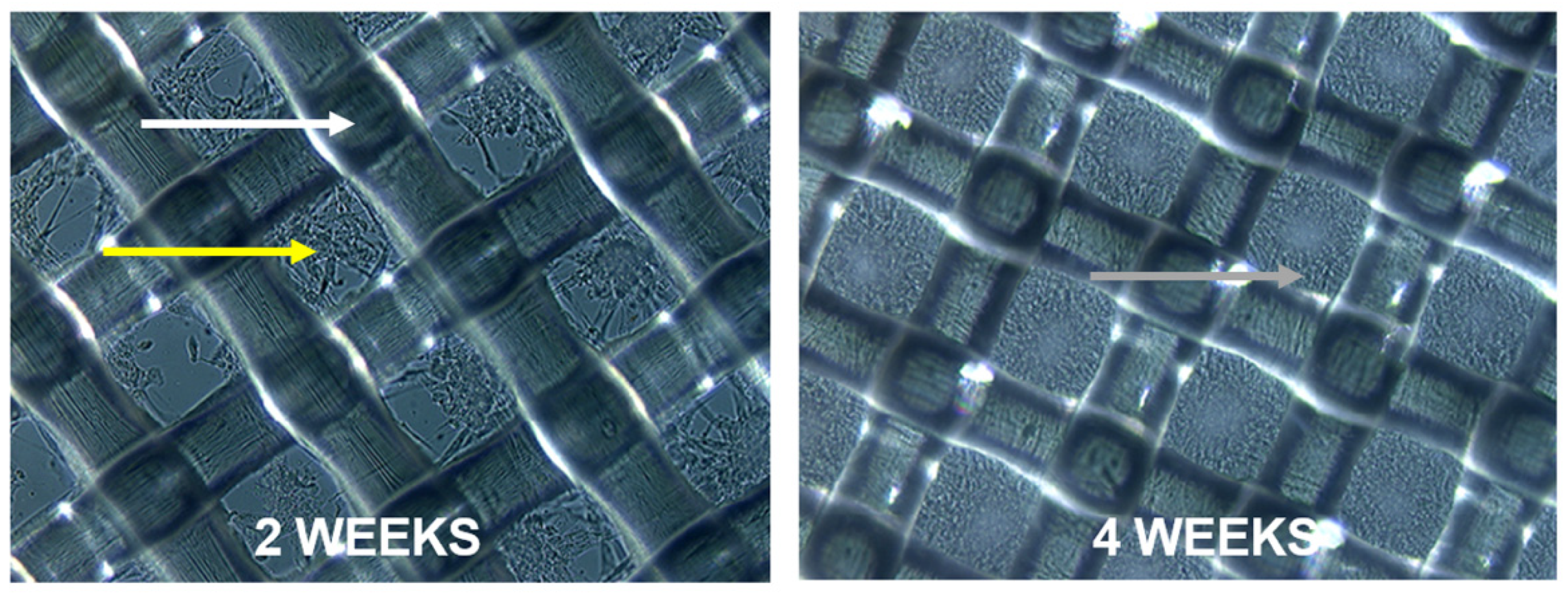
2.3. Organotypic 3D Dermal Cultures
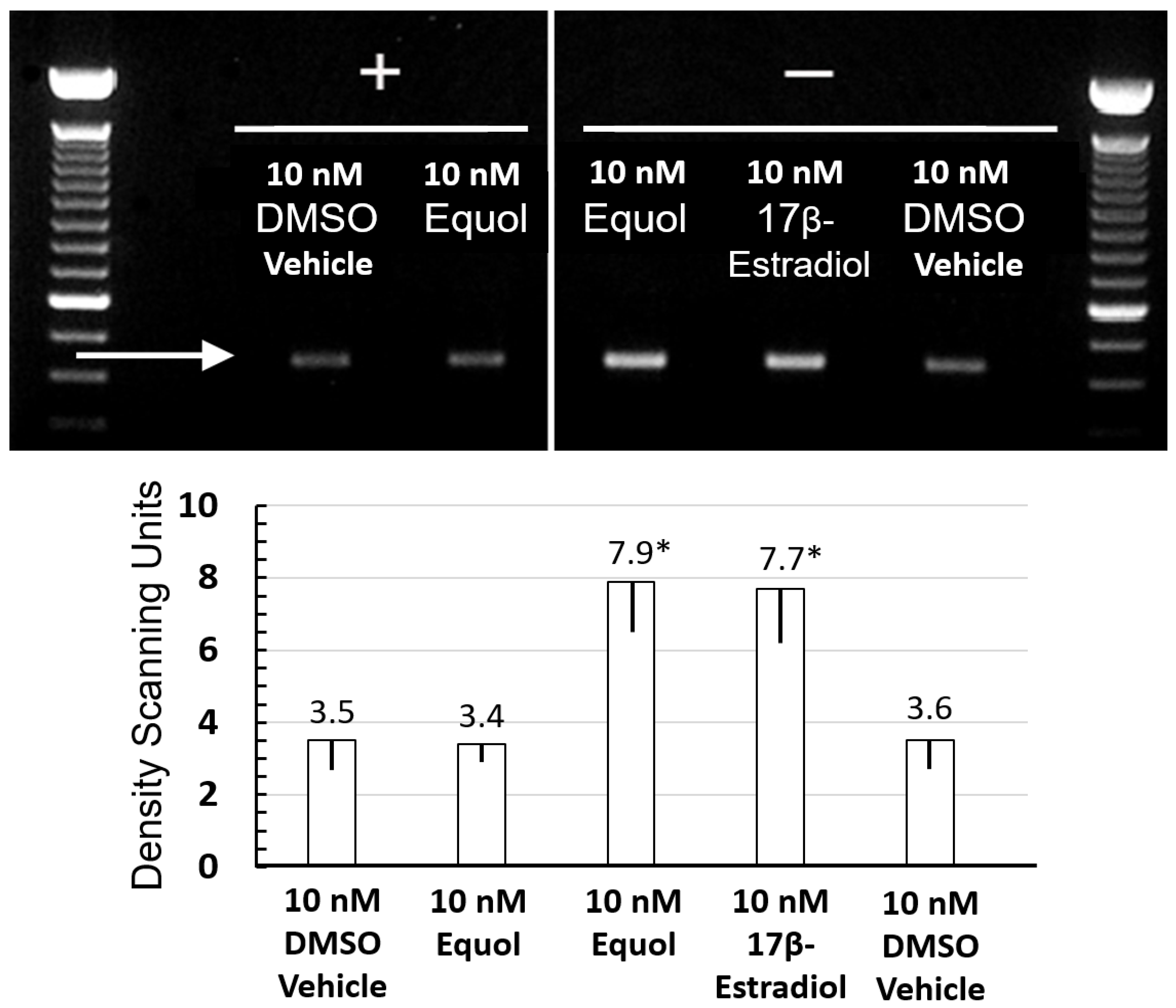
2.4. RT-PCR Analysis of Elastin Gene Expression
2.5. Intracellular FACS Analysis and Cell Cycle Determinations
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
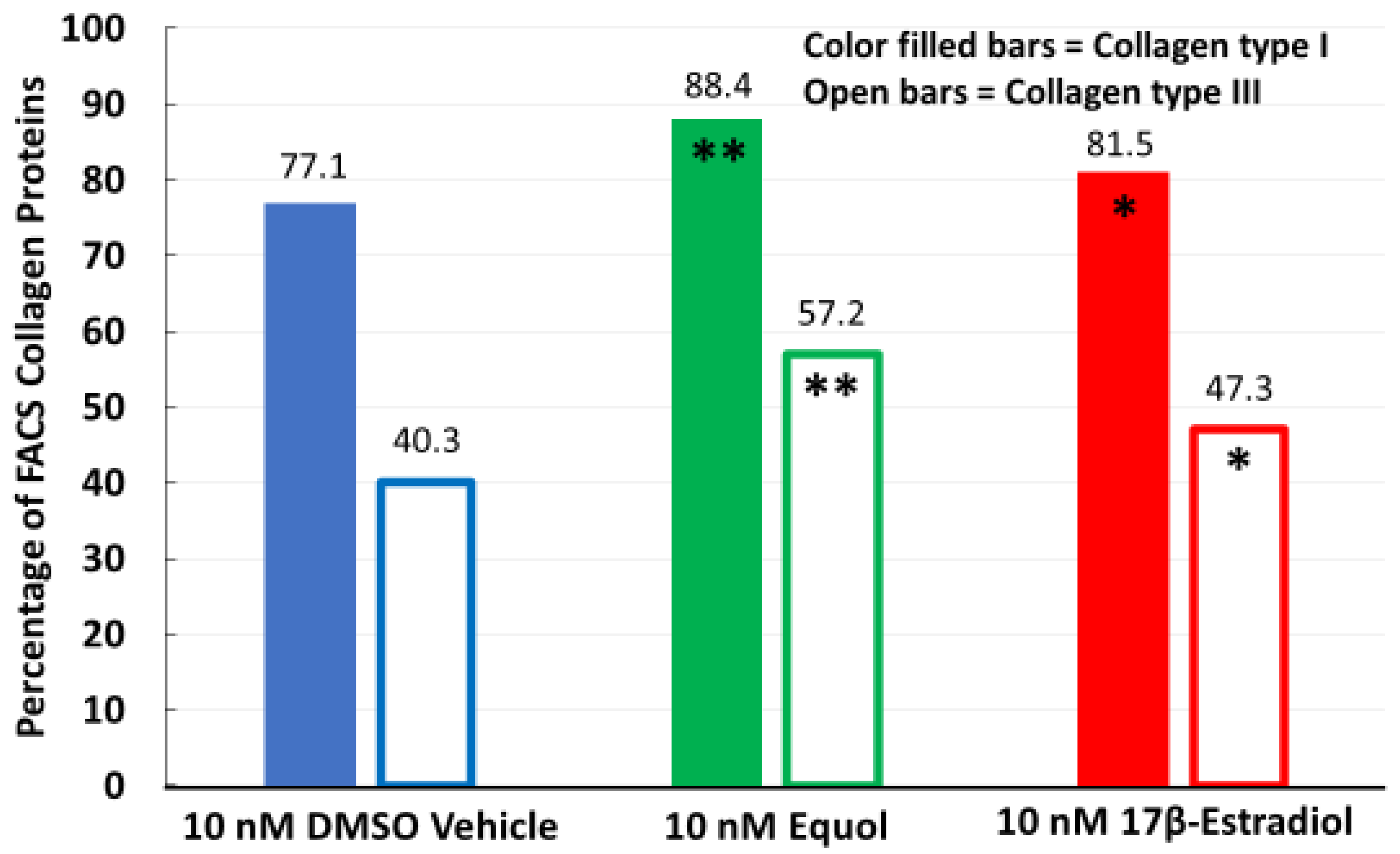
3.1. Equol and 17β-Estradiol Stimulated Collagen Types I and III Protein Expression via FACS Analysis in Long-Term 3D Human Fibroblast Cultures
3.2. Equol and 17β-Estradiol Stimulated Elastin Gene Expression via RT-PCR Analysis. Phenol Red Tissue Indicator Inhibits Gene Expression
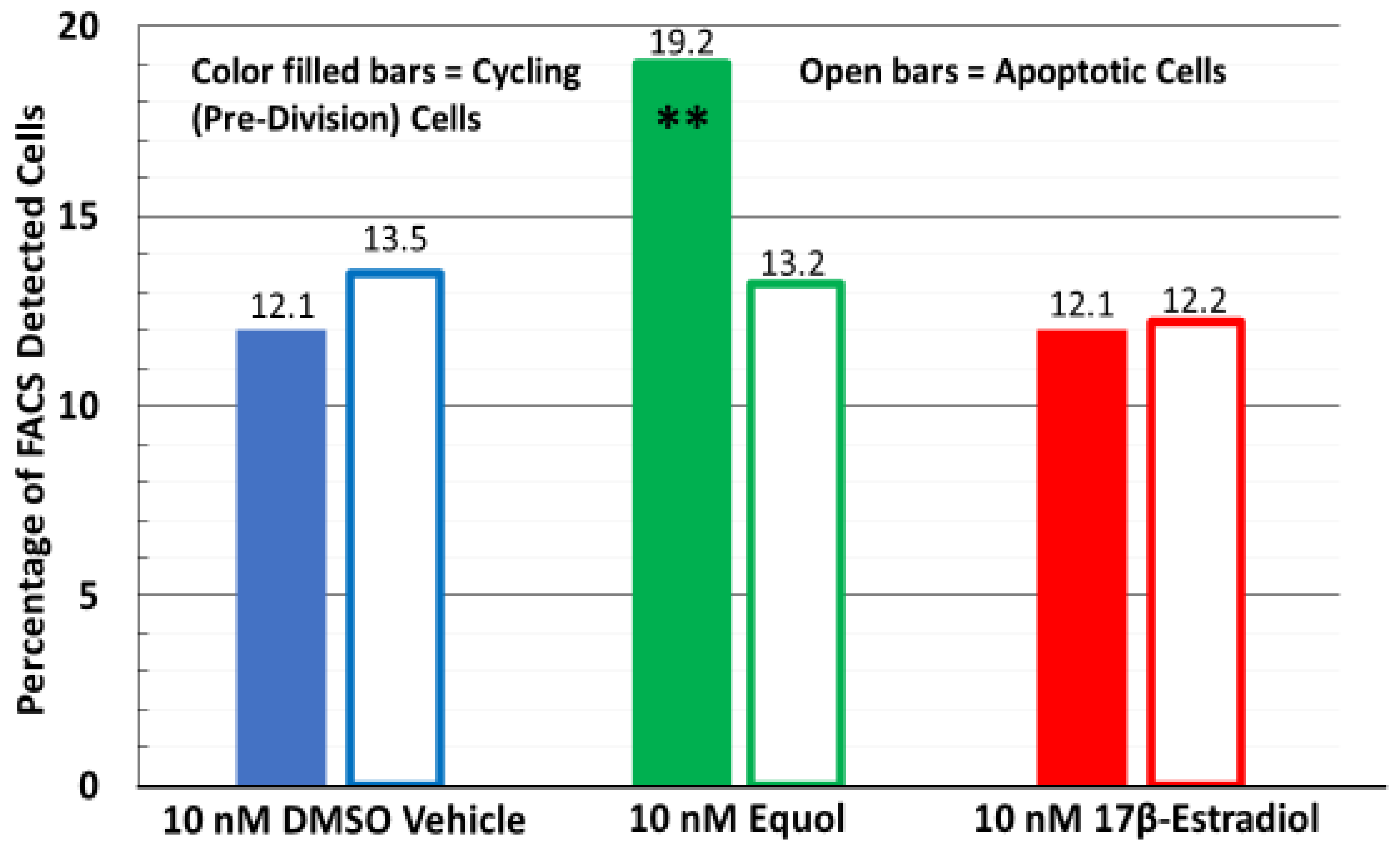
3.3. Only Equol Stimulated Human Fibroblast Cell Renewal in Long-Term Tissue Cultures via FACS Analysis While Apoptosis Was Not Altered Among Any of the Treatments
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lui, T.; Li, N.; Yan, Y.-Q.; Liu, Y.; Xiong, K.; Liu, Y.; Xia, Q.-M.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Z.-D. Recent advances in the anti-aging effects of phytoestrogens on collagen, water content, and oxidative stress. Phytother. Res. 2020, 34, 435–447. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, S.; Zhang, J.C.; Yang, B.; Elias, P.M.; Man, M.Q. Role of resveratrol in regulating cutaneous functions. Evid. Bases Compl. Alternat. Med. 2020, 2020, 2416837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronsisvalle, S.; Panarello, F.; Longhitano, G.; Siciliano, E.A.; Montenegro, L.; Panico, A. Natural Flavones and Flavonols: Relatio ships among antioxidant activity, glycation, and metalloproteinase inhibition. Cosmetics 2020, 7, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lephart, E.D. Skin aging and oxidative stress: Equol’s anti-aging effects via biochemical and molecular mechanisms. Ageing Res. Rev. 2016, 31, 36–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lephart, E.D. Resveratrol, 4′ Acetoxy Resveratrol, R-Equol, Racemic Equol or S-Equol as cosmeceuticals to Improve Dermal Health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavida, P.; Meephansan, J.; Prapapan, O.; Komine, M.; Ohtsuki, M. Role of matrix metalloproteinases in photoaging and photocarcinogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weihermann, A.C.; Lorencini, M.; Brohem, C.A.; de Cavalho, C.M. Elastin structure and its involvement in skin photoaging. Internat. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2017, 39, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uitto, J. The role of elastin and collagen in cutaneous aging: Intrinsic aging versus photoexposure. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2008, 7 (Suppl. S2), s12–s16. [Google Scholar]
- Rittie, L.; Fisher, G.J. Natural and sun-induced aging of human skin. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2015, 5, a015370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlsen, M.H.; Halvorsen, B.L.; Holte, K.; Bohn, S.K.; Dragland, S.; Sampson, L.; Willey, C.; Senoo, H.; Umezono, Y.; Sanada, C.; et al. The Total Antioxidant Content of More than 3100 Foods, Beverages, Spices, Herbs, and Supplements Used Worldwide. Nutr. J. 2010, 9, 3. Available online: http://www.nutritionj.com/content/9/1/3 (accessed on 28 December 2020). [CrossRef]
- Son, M.; Pinnola, A.; Gordon, S.C.; Bassi, R.; Schlau-Cohen, G.S. Observation of dissipative chlorophyll-to-carotenoid energy transfer in light-harvesting complex II in membrane nanodiscs. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lephart, E.D.; Naftolin, F. Menopause and the skin: Old favorites and new innovations in cosmeceuticals for estrogen-deficient skin. Dermatol. Ther. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischmajer, R.; Contard, P.; Schwartz, E.; MacDonald, E.D., 2nd; Jacobs, L., 2nd; Sakai, L.Y. Elastin-associated microfibrils (10 nm) in a three-dimensional fibroblast culture. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1991, 97, 638–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slivka, S.R.; Landeen, L.K.; Zeigler, F.; Zimber, M.P.; Bartel, R.L. Characterization, barrier function, and drug metabolism of an in vitro skin model. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1993, 100, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Contard, P.; Jacobs, L., II; Perlish, J.S.; Fleischmajer, R. Collagen fibrillogenesis in a three-dimensional fibroblast cell culture system. Cell Tissue Res. 1993, 273, 571–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.; Fischer, A.H.; Dyring-Andersen, B.; Rosner, B.; Okoye, G.A. Research techniques made simple: Choosing appropriate statistical methods for clinical research. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, e173–e178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Gan, R.Y.; Li, S.; Zhou, Y.; Li, A.N.; Xu, D.P.; Li, H.B. Antioxidant phytochemicals for the prevention and treatment of chronic diseases. Molecules 2015, 20, 21138–21156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnet, U.; Urbanek, C.; Gaisberger, D.; Tomeva, E.; Dunn, E.; Pointner, A.; Haslberger, A.G. Topical equol preparation improves structural and molecular skin parameters. Internat. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2017, 39, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lephart, E.D. Equol’s efficacy is greater than astaxanthin for antioxidants, extracellular matrix integrity & breakdown, growth factors and inflammatory biomarkers via human skin gene expression analysis. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 59, 380–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welshons, W.V.; Wolf, M.F.; Murphy, C.S.; Jordan, V.C. Estrogenic activity of phenol red. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 1988, 57, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Cuevas, J.E.; Sirbasku, D.A. Estrogen mitogenic action. III. Is phenol red a “red herring”? In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 2000, 36, 447–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milo, G.E.; Malarky, W.B.; Powell, J.E.; Blakeslee, J.R.; Yohn, D.S. Effects of steroid hormones in fetal bovine serum on plating and cloning of human cell in vitro. In Vitro 1976, 12, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vollmer, D.L.; West, V.A.; Lephart, E.D. Enhancing skin health: By oral administration of natural compounds and minerals with implications to the dermal microbiome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, J.H.; Karsdal, M.A. Elastin. In Biochemistry of Collagens, Laminins and Elastin (Structure, Function and Biomarkers); Karsdal, M.A., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA; Elsevier Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 197–201. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780128098479000301 (accessed on 28 December 2020).
- Ueda, M.; Saito, S.; Terusasa, M.; Hirano, T.; Bise, R.; Kabashima, K.; Suzuki, S. Combined multiphoton imaging and biaxail tissue extension for quantitative analysis of geometric fiber organization in human reticular dermis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attia-Vigneau, J.; Terryn, C.; Lorimier, S.; Sandre, J.; Antonicelli, F.; Hornbeck, W. Regeneration of human dermis by a multi-headed peptide. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rippa, A.L.; Kalabusheva, E.P.; Vorotelyak, E.A. Regeneration of the dermis: Scarring and cells involved. Cells 2019, 8, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorrell, J.M.; Caplan, A.I. Fibroblasts—A diverse population at the center of it all. Internat. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2009, 276, 161–214. [Google Scholar]
- Harper, R.A.; Grove, G. Human skin fibroblasts derived from papillary and reticular dermis: Differences in growth potential in vitro. Science 1979, 204, 526–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janson, D.G.; Saintigny, G.; van Adrichem, A.; Mahé, C.; El Ghalbzouri, A. Different gene expression patterns in human papillary and reticular fibroblasts. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 2565–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, A.; Donahue, C.J.; Bauer, K.D.; Mather, J.P. Simultaneous measurement of cell cycle and apoptotic cell death. Methods Cell Biol. 1998, 57, 265–278. [Google Scholar]
- Sadowska-Bartosz, I.; Bartosz, G. Effect of antioxidants on the fibroblast replicative lifespan in vitro. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 6423783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleischer, J.G.; Schulte, R.; Tsai, H.H.; Tyagi, S.; Barra, I.A.; Shokhirev, M.V.; Navlakha, S. Predicting age from the transcriptome of human dermal fibroblasts. BMC Genome Biol. 2018, 19, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lephart, E.D. A review of the role of estrogen in dermal aging and facial attractiveness in women. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2018, 17, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, A.; Maibach, H.I. Chapter 35: Biological effects of estrogen on skin. In Textbook of Aging Skin; Farage, M.A., Miller, K.W., Maibach, H.I., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lephart, E.D. 4′,7-Isoflavandiol (Equol) Enhances Human Dermal Fibroblast Renewal and Has Effects Similar to 17β-Estradiol in Stimulating Collagen and Elastin Expression. Cell Cycle and RT-PCR Analysis without Phenol Red. Cosmetics 2021, 8, 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics8010005
Lephart ED. 4′,7-Isoflavandiol (Equol) Enhances Human Dermal Fibroblast Renewal and Has Effects Similar to 17β-Estradiol in Stimulating Collagen and Elastin Expression. Cell Cycle and RT-PCR Analysis without Phenol Red. Cosmetics. 2021; 8(1):5. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics8010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleLephart, Edwin D. 2021. "4′,7-Isoflavandiol (Equol) Enhances Human Dermal Fibroblast Renewal and Has Effects Similar to 17β-Estradiol in Stimulating Collagen and Elastin Expression. Cell Cycle and RT-PCR Analysis without Phenol Red" Cosmetics 8, no. 1: 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics8010005
APA StyleLephart, E. D. (2021). 4′,7-Isoflavandiol (Equol) Enhances Human Dermal Fibroblast Renewal and Has Effects Similar to 17β-Estradiol in Stimulating Collagen and Elastin Expression. Cell Cycle and RT-PCR Analysis without Phenol Red. Cosmetics, 8(1), 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics8010005



