Citrate-Coated Platinum Nanoparticles Exhibit a Primary Particle-Size Dependent Effect on Stimulating Melanogenesis in Human Melanocytes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.3. Cell Culture
2.4. Cytotoxicity Assay
2.5. Melanogenesis Assay in MNT-1 Cells
2.6. Recovery Study of Melanogenesis by PtNPs in MNT-1 Cells
2.7. Intracellular Tyrosinase Activity in MNT-1 Cells
2.8. Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) in MNT-1 Cells
2.9. Melanogenesis Assay in HEMn-MP Cells
2.10. Dendricity Measurement in HEMn-MP Cells
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
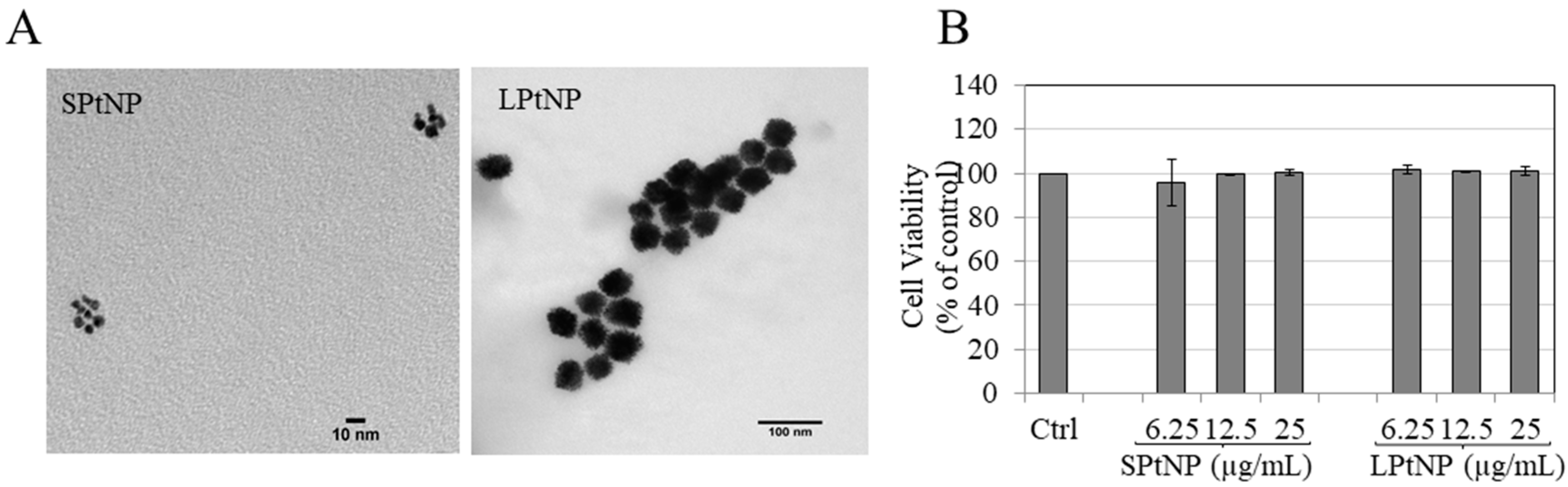
3.1. Characterization of PtNPs
3.2. Cellular Viability in MNT-1 Cells
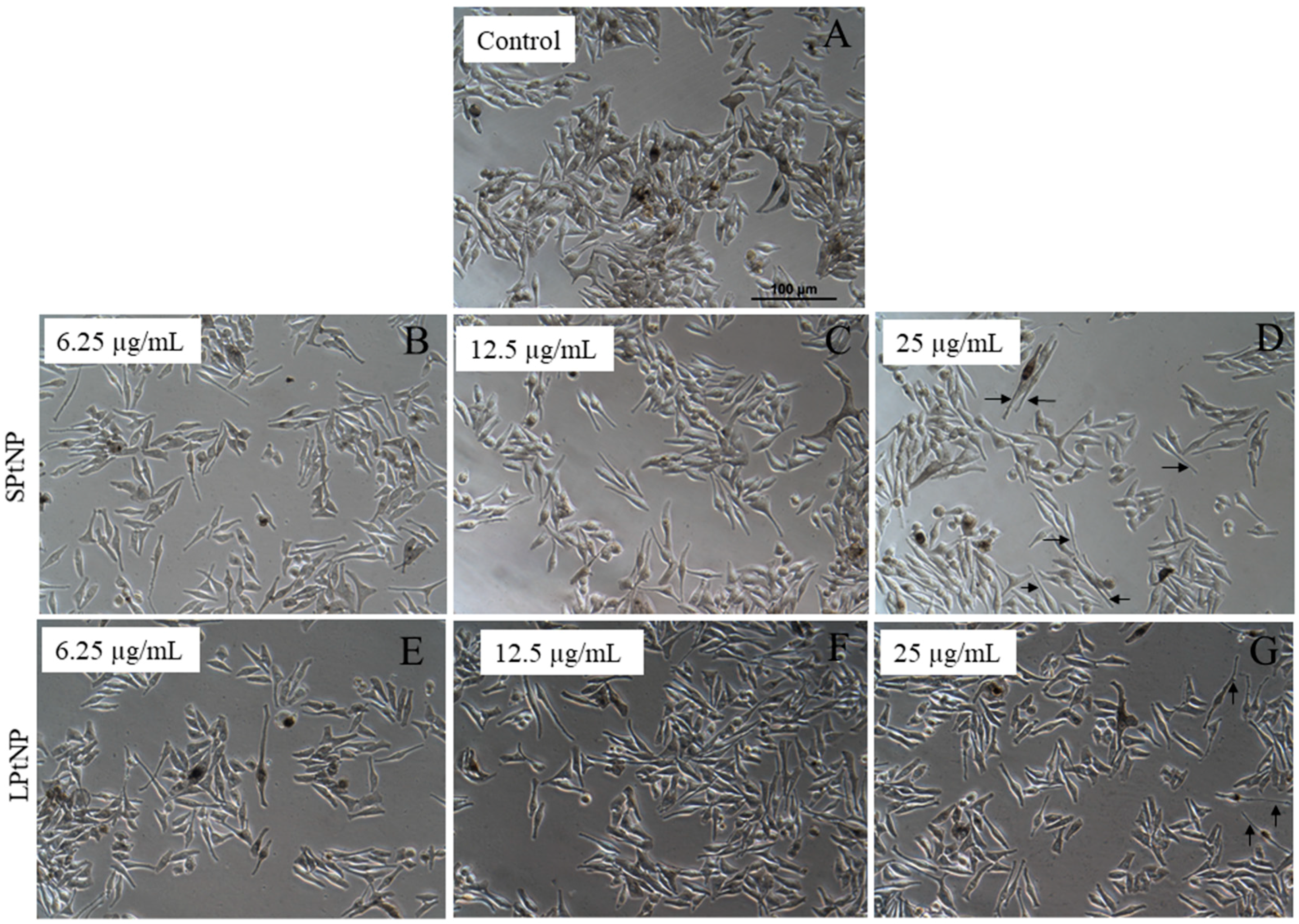
3.3. Cellular Morphology of MNT-1 Cells
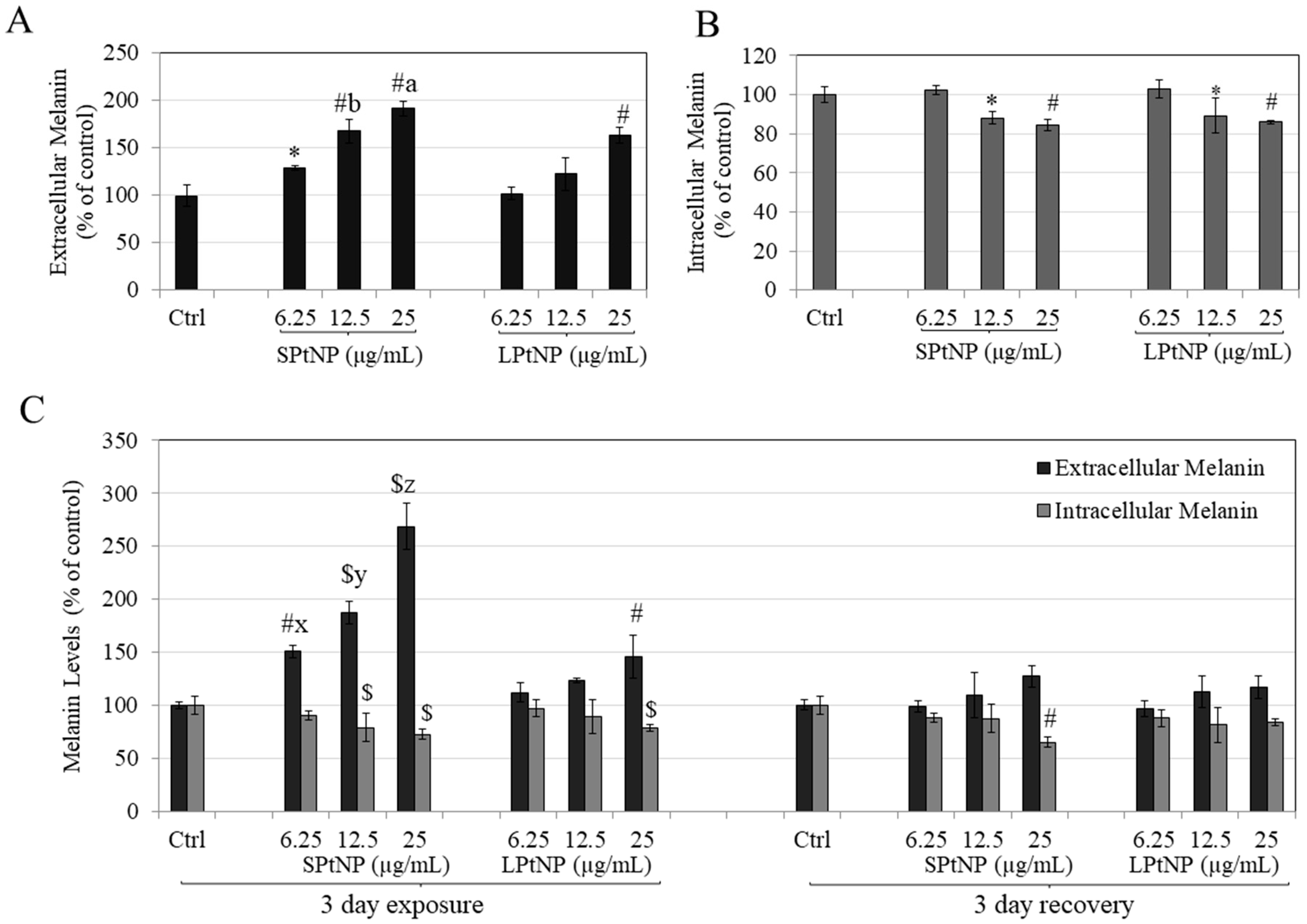
3.4. PtNPs Stimulated Extracellular Melanin in MNT-1 Human Melanoma Cells
3.5. Effects of PtNPs on Reversibility of Melanosome Export in MNT-1 Cells
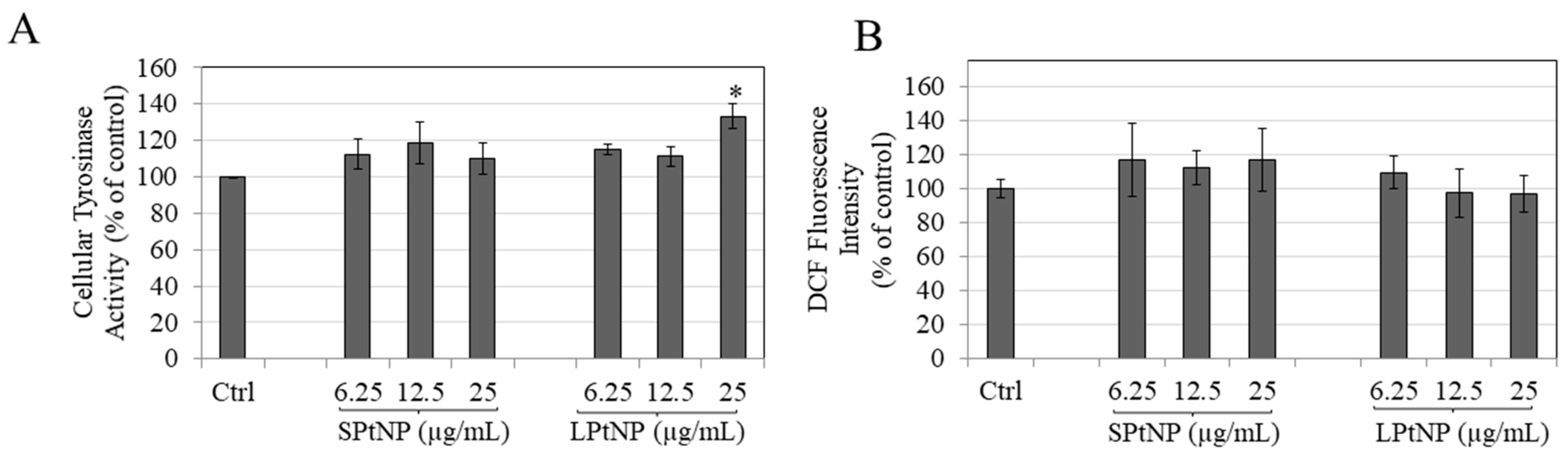
3.6. PtNPs Effects on Intracellular Tyrosinase Activity
3.7. Effects of PtNPs on Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Levels in MNT-1 Cells
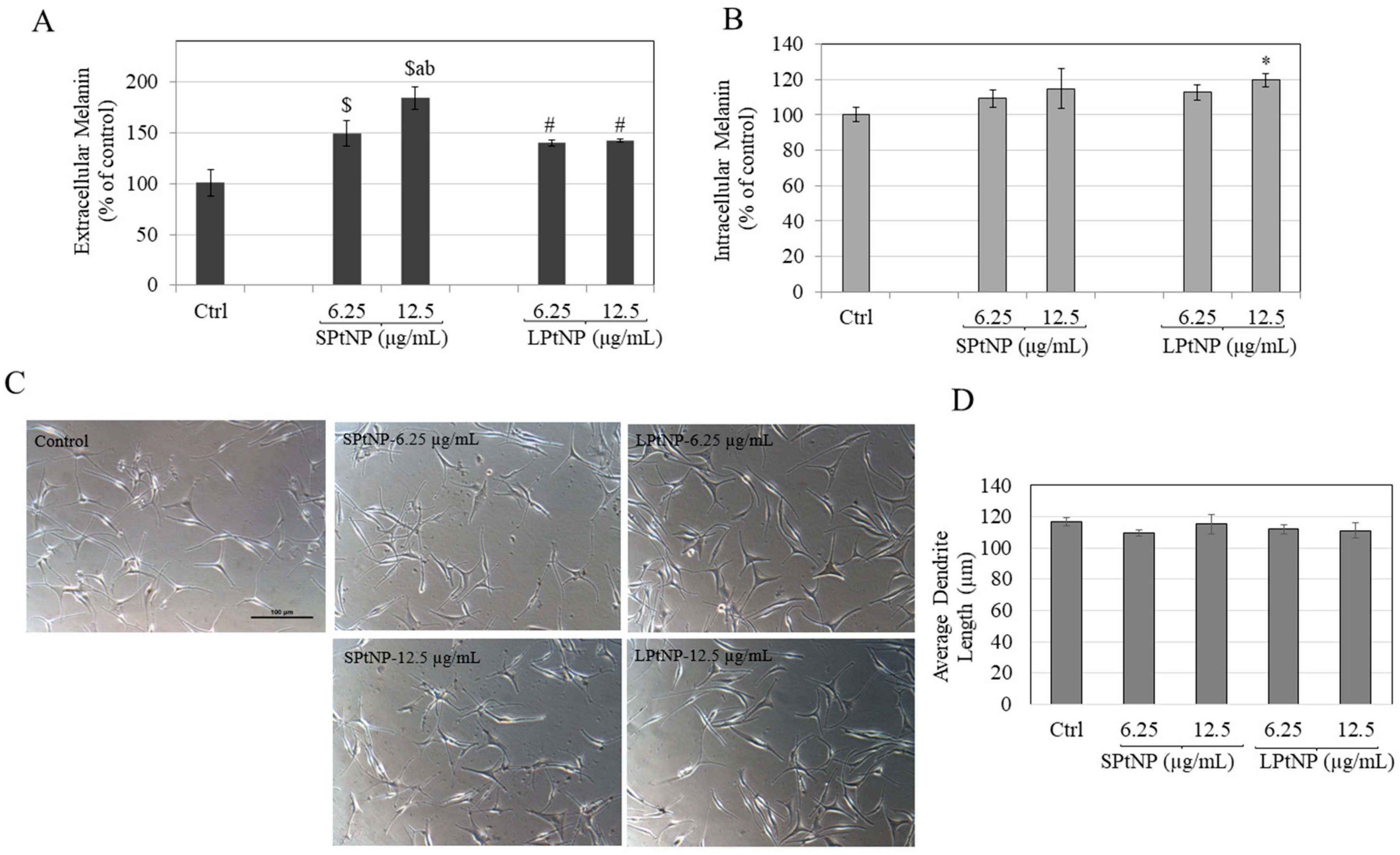
3.8. Effects of PtNPs in HEMn-MP Cells
3.9. PtNPs Did Not Alter Dendritic Morphology of HEMn-MP Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| L-DOPA | L-3,4 dihydroxyphenylalanine |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium |
| HMGS | Human Melanocyte Growth Supplement |
| HEM | Human-Epidermal Melanocytes |
| MP | Moderately Pigmented |
| TEM | Transmission Electron Microscopy |
| PtNPs | Platinum Nanoparticles |
| SPtNP | Small Platinum Nanoparticles |
| LPtNP | Large Platinum Nanoparticles |
| ANOVA | Analysis of Variance |
| HBSS | Hank’s Balanced Salt Solution |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| DCF | Dichlorofluorescein |
References
- Fernandez-Flores, A.; Saeb-Lima, M.; Cassarino, D.S. Histopathology of Aging of The Hair Follicle. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2019, 46, 508–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maranduca, M.A.; Branisteanu, D.; Serban, D.N.; Branisteanu, D.C.; Stoleriu, G.; Manolache, N.; Serban, I.L. Synthesis and Physiological Implications of Melanic Pigments. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 4183–4187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riley, P.A. Melanogenesis and Melanoma. Pigment Cell Res. 2003, 16, 548–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’orazio, J.; Jarrett, S.; Amaro-Ortiz, A.; Scott, T. Uv Radiation and the Skin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 12222–12248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hearing, V.J. Determination of Melanin Synthetic Pathways. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2011, 131, E8–E11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, T.B.; Breathnach, A. The Epidermal Melanin Unit System. Dermatol. Wochenschr. 1963, 147, 481. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hirobe, T. Structure and Function of Melanocytes: Microscopic Morphology and Cell Biology of Mouse Melanocytes in The Epidermis and Hair Follicle. Histol. Histopathol. 1995, 10, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dutta, S.; Panda, S.; Singh, P.; Tawde, S.; Mishra, M.; Andhale, V.; Athavale, A.; Keswani, S.M. Hypopigmentation in Burns Is Associated with Alterations in the Architecture of the Skin and the Dendricity of The Melanocytes. Burns 2020, 46, 906–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ando, H.; Niki, Y.; Ito, M.; Akiyama, K.; Matsui, M.S.; Yarosh, D.B.; Ichihashi, M. Melanosomes Are Transferred from Melanocytes to Keratinocytes Through the Processes of Packaging, Release, Uptake, and Dispersion. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 1222–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, A.B.; Wulf, H.C.; Gniadecki, R.; Gajkowska, B. Dihydroxyacetone, The Active Browning Ingredient in Sunless Tanning Lotions, Induces Dna Damage, Cell-Cycle Block and Apoptosis in Cultured Hacat Keratinocytes. Mutat. Res. 2004, 560, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, J.A.; Sorace, M.; Spencer, J.; Siegel, D.M. The Indoor Uv Tanning Industry: A Review of Skin Cancer Risk, Health Benefit Claims, and Regulation. J. Am. Acad. Derm. 2005, 53, 1038–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawelek, J.M. Approaches to Increasing Skin Melanin with Msh Analogs and Synthetic Melanins. Pigment Cell Res. 2001, 14, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Malek, Z.; Swope, V.B.; Suzuki, I.; Akcali, C.; Harriger, M.D.; Boyce, S.T.; Urabe, K.; Hearing, V.J. Mitogenic and Melanogenic Stimulation of Normal Human Melanocytes by Melanotropic Peptides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 1789–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fytianos, G.; Rahdar, A.; Kyzas, G.Z. Nanomaterials in Cosmetics: Recent Updates. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, Z.A.A.; Mohd-Nasir, H.; Ahmad, A.; Mohd Setapar, S.H.; Peng, W.L.; Chuo, S.C.; Khatoon, A.; Umar, K.; Yaqoob, A.A.; Mohamad Ibrahim, M.N. Role of Nanotechnology for Design and Development of Cosmeceutical: Application In Makeup and Skin Care. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Iqbal, H. New Insights on Unique Features and Role of Nanostructured Materials in Cosmetics. Cosmetics 2020, 7, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigano, L.; Lionetti, N. Nanobiomaterials In Galenic Formulations and Cosmetics. In Nanobiomaterials in Galenic Formulations and Cosmetics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 121–148. [Google Scholar]
- Kockler, J.; Oelgemöller, M.; Robertson, S.; Glass, B.D. Influence of Titanium Dioxide Particle Size on the Photostability of the Chemical Uv-Filters Butyl Methoxy Dibenzoylmethane and Octocrylene in a Microemulsion. Cosmetics 2014, 1, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddada, M.B.; Gerometta, E.; Chawech, R.; Sorres, J.; Bialecki, A.; Pesnel, S.; Spadavecchia, J.; Morel, A.-L. Assessment of Antioxidant and Dermoprotective Activities of Gold Nanoparticles as Safe Cosmetic Ingredient. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 189, 110855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajbhiye, S.; Sakharwade, S. Silver Nanoparticles in Cosmetics. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. Sci. Appl. 2016, 6, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, M.; Foote, M.; Prow, T.W. Therapeutic Gold, Silver, and Platinum Nanoparticles. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2015, 7, 428–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choosing Platinum Skin Care. Available online: https://bionyxskincare.com/choosing-platinum-skincare/ (accessed on 6 September 2020).
- Pedone, D.; Moglianetti, M.; De Luca, E.; Bardi, G.; Pompa, P.P. Platinum Nanoparticles in Nanobiomedicine. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 4951–4975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshihisa, Y.; Honda, A.; Zhao, Q.L.; Makino, T.; Abe, R.; Matsui, K.; Shimizu, H.; Miyamoto, Y.; Kondo, T.; Shimizu, T. Protective Effects of Platinum Nanoparticles Against Uv-Light-Induced Epidermal Inflammation. Exp. Dermatol. 2010, 19, 1000–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatto, F.; Moglianetti, M.; Pompa, P.P.; Bardi, G. Platinum Nanoparticles Decrease Reactive Oxygen Species and Modulate Gene Expression without Alteration of Immune Responses in Thp-1 Monocytes. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajita, M.; Hikosaka, K.; Iitsuka, M.; Kanayama, A.; Toshima, N.; Miyamoto, Y. Platinum Nanoparticle Is a Useful Scavenger of Superoxide Anion and Hydrogen Peroxide. Free Radic. Res. 2007, 41, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moglianetti, M.; De Luca, E.; Pedone, D.; Marotta, R.; Catelani, T.; Sartori, B.; Amenitsch, H.; Retta, S.F.; Pompa, P.P. Platinum Nanozymes Recover Cellular Ros Homeostasis in an Oxidative Stress-Mediated Disease Model. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 3739–3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusof, F.; Ismail, N.A.S. Antioxidants Effects of Platinum Nanoparticles: A Potential Alternative Treatment to Lung Diseases. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsumi, H.; Fukui, K.; Sato, K.; Maruyama, S.; Yamashita, S.; Mizumoto, E.; Kusamori, K.; Oyama, M.; Sano, M.; Sakane, T. Pharmacokinetics and Preventive Effects of Platinum Nanoparticles as Reactive Oxygen Species Scavengers on Hepatic Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury In Mice. Met. Integr. Biometal Sci. 2014, 6, 1050–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuncer, S.; Colakoglu, M.; Ulusan, S.; Ertas, G.; Karasu, C.; Banerjee, S. Evaluation of Colloidal Platinum on Cytotoxicity, Oxidative Stress and Barrier Permeability Across the Gut Epithelium. Heliyon 2019, 5, E01336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depciuch, J.; Stec, M.; Klebowski, B.; Maximenko, A.; Drzymala, E.; Baran, J.; Parlinska-Wojtan, M. Size Effect of Platinum Nanoparticles in Simulated Anticancer Photothermal Therapy. Photodiagn. Photodyn. 2020, 29, 101594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchtelova, H.; Dostalova, S.; Michalek, P.; Krizkova, S.; Strmiska, V.; Kopel, P.; Hynek, D.; Richtera, L.; Ridoskova, A.; Adam, P.; et al. Size-Related Cytotoxicological Aspects of Polyvinylpyrrolidone-Capped Platinum Nanoparticles. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 105, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konieczny, P.; Goralczyk, A.G.; Szmyd, R.; Skalniak, L.; Koziel, J.; Filon, F.L.; Crosera, M.; Cierniak, A.; Zuba-Surma, E.K.; Borowczyk, J. Effects Triggered by Platinum Nanoparticles on Primary Keratinocytes. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 3963. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.J.; Chang, S.E.; Choi, J.H.; Sung, K.J.; Moon, K.C.; Koh, J.K. Periungal Hyperpigmentation Induced by Cisplatin. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2002, 27, 118–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noori, M.; Hunter-Ellul, L.; Kelly, B. Serpentine Supravenous Hyperpigmentation Following Cisplatin and Pemetrexed Chemotherapy. Cutis 2017, 99, E20–E22. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Lamki, Z.; Pearson, P.; Jaffe, N. Localized Cisplatin Hyperpigmentation Induced by Pressure. A Case Report. Cancer 1996, 77, 1578–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibuya, S.; Ozawa, Y.; Watanabe, K.; Izuo, N.; Toda, T.; Yokote, K.; Shimizu, T. Palladium and Platinum Nanoparticles Attenuate Aging-Like Skin Atrophy Via Antioxidant Activity in Mice. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, E109288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, T.; Yoshikawa, R.; Ichihashi, M. The Novel Therapy for Vitiligo Vulgaris: Topical Use of Cosmetic Cream of Platinum Nanoparticles and Palladium Nanoparticles Which Show Strong Catalase-Like Activity. J. Pigment. Disord. 2015, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, G.; Hashimoto-Hachiya, A.; Takemura, M.; Kanemaru, T.; Ichihashi, M.; Furue, M. Palladium and Platinum Nanoparticles Activate Ahr and Nrf2 In Human Keratinocytes-Implications In Vitiligo Therapy. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 1582–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takabe, W.; Yagi, M.; Ichihashi, M.; Yonei, Y. Anti-Glycative Effect of Palladium and Platinum Nanoparticle Solution. Glycative Stress Res. 2016, 3, 222–228. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, H.; Chong, Y.; Wamer, W.G.; Xia, Q.; Cai, L.; Nie, Z.; Fu, P.P.; Yin, J.-J. Platinum Nanoparticles: Efficient and Stable Catechol Oxidase Mimetics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 19709–19717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirimahachaiyakul, P.; Sood, R.F.; Muffley, L.A.; Seaton, M.; Lin, C.-T.; Qiao, L.; Armaly, J.S.; Hocking, A.M.; Gibran, N.S. Race Does Not Predict Melanocyte Heterogeneous Responses To Dermal Fibroblast-Derived Mediators. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, E0139135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denat, L.; Kadekaro, A.L.; Marrot, L.; Leachman, S.A.; Abdel-Malek, Z.A. Melanocytes As Instigators and Victims of Oxidative Stress. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 1512–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, A.; Kajita, M.; Kim, J.; Kanayama, A.; Takahashi, K.; Mashino, T.; Miyamoto, Y. In Vitro Free Radical Scavenging Activity of Platinum Nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 455105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asharani, P.V.; Xinyi, N.; Hande, M.P.; Valiyaveettil, S. Dna Damage and P53-Mediated Growth Arrest In Human Cells Treated With Platinum Nanoparticles. Nanomedicine 2010, 5, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoshan, M.S.; Vonderach, T.; Hattendorf, B.; Wennemers, H. Peptide-Coated Platinum Nanoparticles With Selective Toxicity Against Liver Cancer Cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2019, 58, 4901–4905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monopoli, M.P.; Aberg, C.; Salvati, A.; Dawson, K.A. Biomolecular Coronas Provide the Biological Identity of Nanosized Materials. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juling, S.; Niedzwiecka, A.; Bóhmert, L.; Lichtenstein, D.; Selve, S.R.; Braeuning, A.; Thünemann, A.F.; Krause, E.; Lampen, A. Protein Corona Analysis of Silver Nanoparticles Links to Their Cellular Effects. J. Proteome Res. 2017, 16, 4020–4034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundqvist, M.; Stigler, J.; Elia, G.; Lynch, I.; Cedervall, T.; Dawson, K.A. Nanoparticle Size and Surface Properties Determine the Protein Corona with Possible Implications For Biological Impacts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 14265–14270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenzer, S.; Docter, D.; Rosfa, S.; Wlodarski, A.; Kuharev, J.R.; Rekik, A.; Knauer, S.K.; Bantz, C.; Nawroth, T.; Bier, C. Nanoparticle Size Is A Critical Physicochemical Determinant of the Human Blood Plasma Corona: A Comprehensive Quantitative Proteomic Analysis. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 7155–7167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, V.; Srirangam, A.; Abburi, R. In Vitro Modulation of Proliferation and Melanization of Melanoma Cells by Citrate. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 1998, 187, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-X.; Gu, J.-L.; Cao, J.-M. The Acute Toxic Effects of Platinum Nanoparticles on Ion Channels, Transmembrane Potentials of Cardiomyocytes In Vitro and Heart Rhythm In Vivo In Mice. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 5595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labrador-Rached, C.J.; Browning, R.T.; Braydich-Stolle, L.K.; Comfort, K.K. Toxicological Implications of Platinum Nanoparticle Exposure: Stimulation of Intracellular Stress, Inflammatory Response, and Akt Signaling In Vitro. J. Toxicol. 2018, 2018, 1367801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gollwitzer, C.; Bartczak, D.; Goenaga-Infante, H.; Kestens, V.; Krumrey, M.; Minelli, C.; Pálmai, M.; Ramaye, Y.; Roebben, G.; Sikora, A. A Comparison of Techniques for Size Measurement of Nanoparticles In Cell Culture Medium. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 5272–5282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marucco, A.; Aldieri, E.; Leinardi, R.; Bergamaschi, E.; Riganti, C.; Fenoglio, I. Applicability and Limitations in the Characterization of Poly-Dispersed Engineered Nanomaterials In Cell Media By Dynamic Light Scattering (Dls). Materials 2019, 12, 3833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, V.; Bucher, J.; Kropf, C.; Arenz, M.; Segner, H. Comparative Study of Cytotoxicity By Platinum Nanoparticles and Ions In Vitro Systems Based on Fish Cell Lines. Toxicol. In Vitro 2020, 66, 104859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehrke, H.; Pelka, J.; Hartinger, C.G.; Blank, H.; Bleimund, F.; Schneider, R.; Gerthsen, D.; Bräse, S.; Crone, M.; Türk, M. Platinum Nanoparticles and Their Cellular Uptake and Dna Platination At Non-Cytotoxic Concentrations. Arch. Toxicol. 2011, 85, 799–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiberg, M. Keratinocyte–Melanocyte Interactions During Melanosome Transfer. Pigment Cell Res. 2001, 14, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delevoye, C. Melanin Transfer: The Keratinocytes Are More Than Gluttons. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 877–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirobe, T. Keratinocytes Regulate the Function of Melanocytes. Dermatol. Sin. 2014, 32, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.N.; Marfatia, R.K.; Saikia, S.S. A Study of Noncultured Extracted Hair Follicle Outer Root Sheath Cell Suspension for Transplantation In Vitiligo. Int. J. Trichology 2016, 8, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobin, D.J.; Paus, R. Graying: Gerontobiology of the Hair Follicle Pigmentary Unit. Exp. Gerontol. 2001, 36, 29–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, K.I.; George, E.L.; Hall, L.L.; Stara, J.F. Dermal Irritancy of Metal Compounds. Studies with Palladium, Platinum, Lead, and Manganese Compounds. Arch. Environ. Health 1975, 30, 168–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czubacka, E.; Czerczak, S. Are Platinum Nanoparticles Safe To Human Health? Med. Pr. 2019, 70, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibuya, S.; Watanabe, K.; Tsuji, G.; Ichihashi, M.; Shimizu, T. Platinum and Palladium Nanoparticle-Containing Mixture, Paplal, Does Not Induce Palladium Allergy. Exp. Dermatol. 2019, 28, 1025–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aygun, A.; Gülbagca, F.; Ozer, L.Y.; Ustaoglu, B.; Altunoglu, Y.C.; Baloglu, M.C.; Atalar, M.N.; Alma, M.H.; Sen, F. Biogenic Platinum Nanoparticles Using Black Cumin Seed and Their Potential Usage as Antimicrobial and Anticancer Agent. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 179, 112961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseer, A.; Ali, A.; Ali, S.; Mahmood, A.; Kusuma, H.; Nazir, A.; Yaseen, M.; Khan, M.; Ghaffar, A.; Abbas, M. Biogenic and Eco-Benign Synthesis of Platinum Nanoparticles (Pt Nps) Using Plants Aqueous Extracts and Biological Derivatives: Environmental, Biological and Catalytic Applications. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 9093–9107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, P.G.; Nair, N.; Begum, G.; Joshi, N.B.; Sinkar, V.P.; Vora, S. Melanocyte-keratinocyte interaction induces calcium signalling and melanin transfer to keratinocytes. Pigment Cell Res. 2007, 20, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Goenka, S.; Toussaint, J. Citrate-Coated Platinum Nanoparticles Exhibit a Primary Particle-Size Dependent Effect on Stimulating Melanogenesis in Human Melanocytes. Cosmetics 2020, 7, 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics7040088
Goenka S, Toussaint J. Citrate-Coated Platinum Nanoparticles Exhibit a Primary Particle-Size Dependent Effect on Stimulating Melanogenesis in Human Melanocytes. Cosmetics. 2020; 7(4):88. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics7040088
Chicago/Turabian StyleGoenka, Shilpi, and Jimmy Toussaint. 2020. "Citrate-Coated Platinum Nanoparticles Exhibit a Primary Particle-Size Dependent Effect on Stimulating Melanogenesis in Human Melanocytes" Cosmetics 7, no. 4: 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics7040088
APA StyleGoenka, S., & Toussaint, J. (2020). Citrate-Coated Platinum Nanoparticles Exhibit a Primary Particle-Size Dependent Effect on Stimulating Melanogenesis in Human Melanocytes. Cosmetics, 7(4), 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics7040088




