A Novel Stilbene-Like Compound That Reduces Melanin through Inhibiting Melanocyte Differentiation and Proliferation without Inhibiting Tyrosinase
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Zebrafish Husbandry and In Vitro Fertilization
2.2. Chemical Treatment of Zebrafish Embryos
2.3. Chemicals
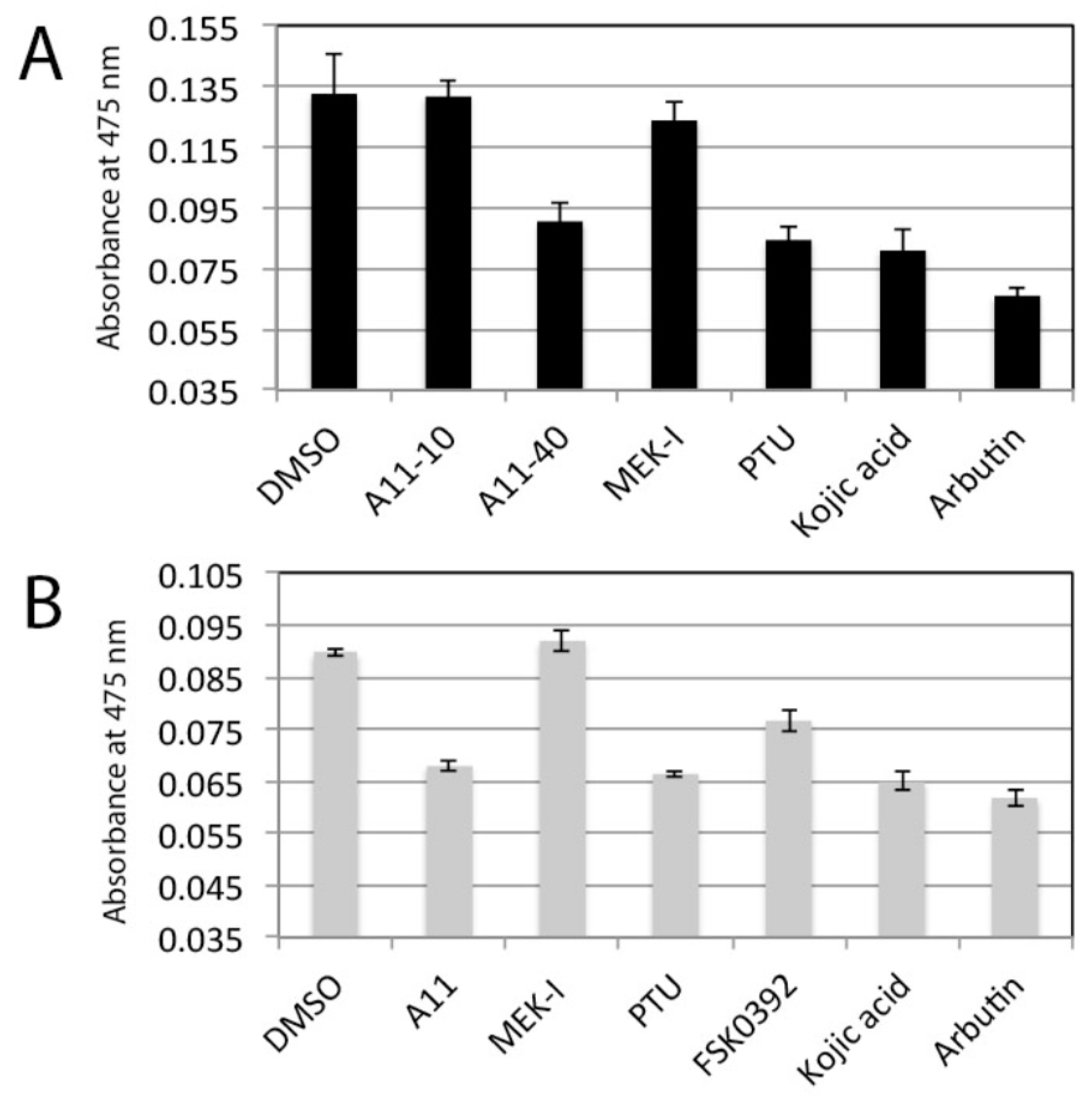
2.4. In Vitro Tyrosinase Assay
2.5. Immunohistochemistry and TUNEL Assay
2.6. In Situ Hybridization
2.7. Western Blotting
2.8. Cell Culture
3. Results
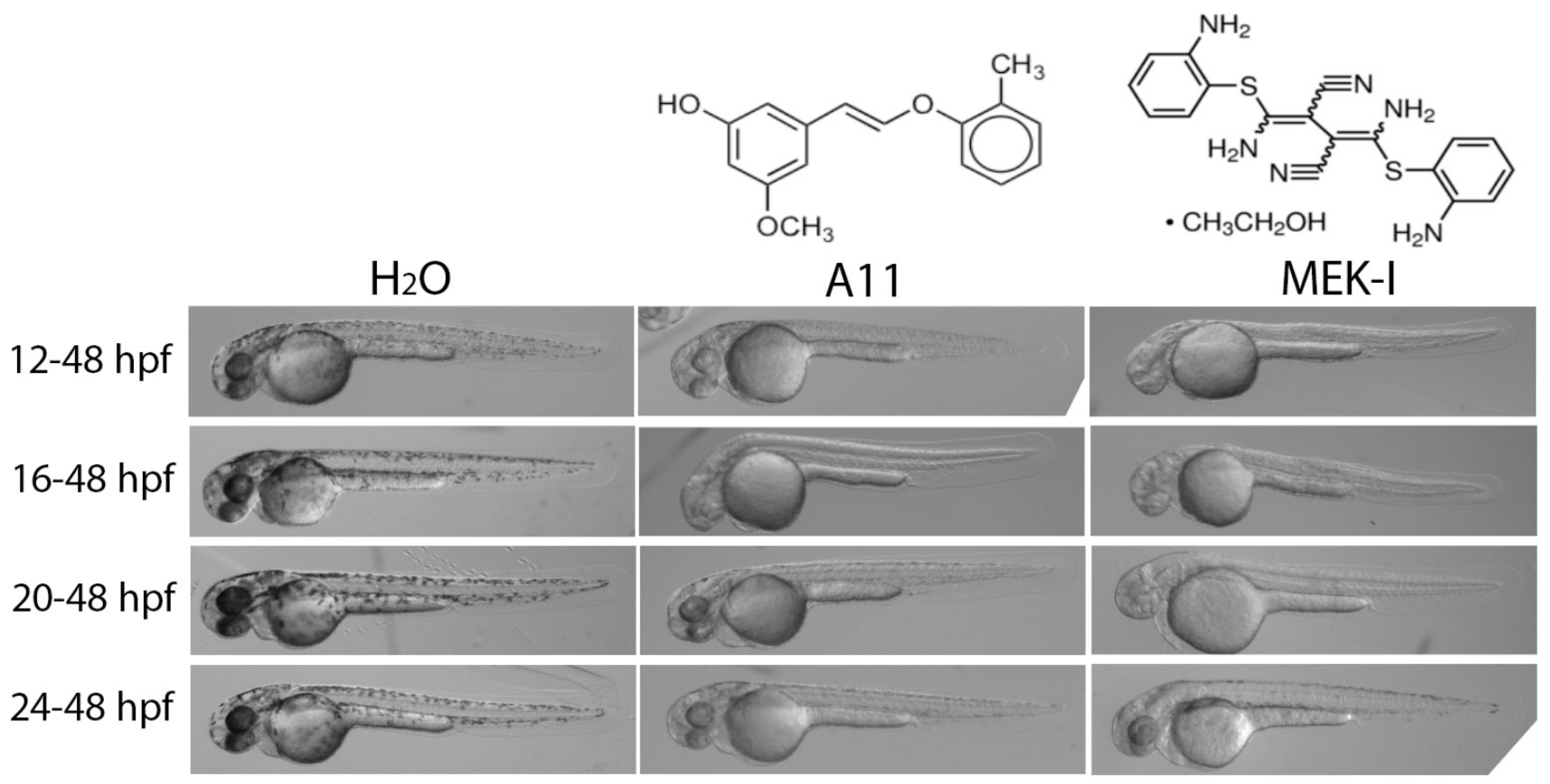
3.1. A11 and MEK-I as Skin-Lightening Compounds
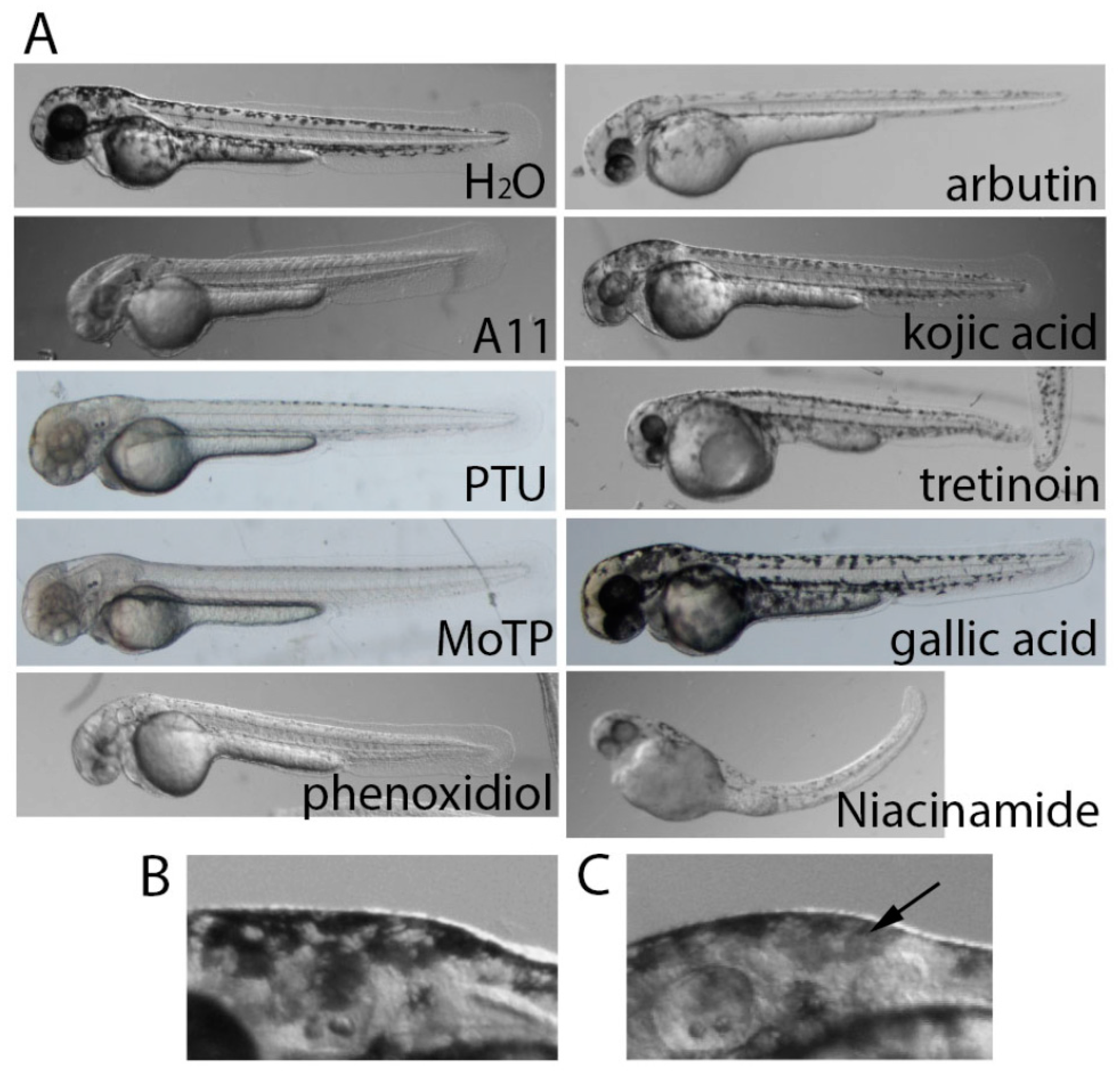
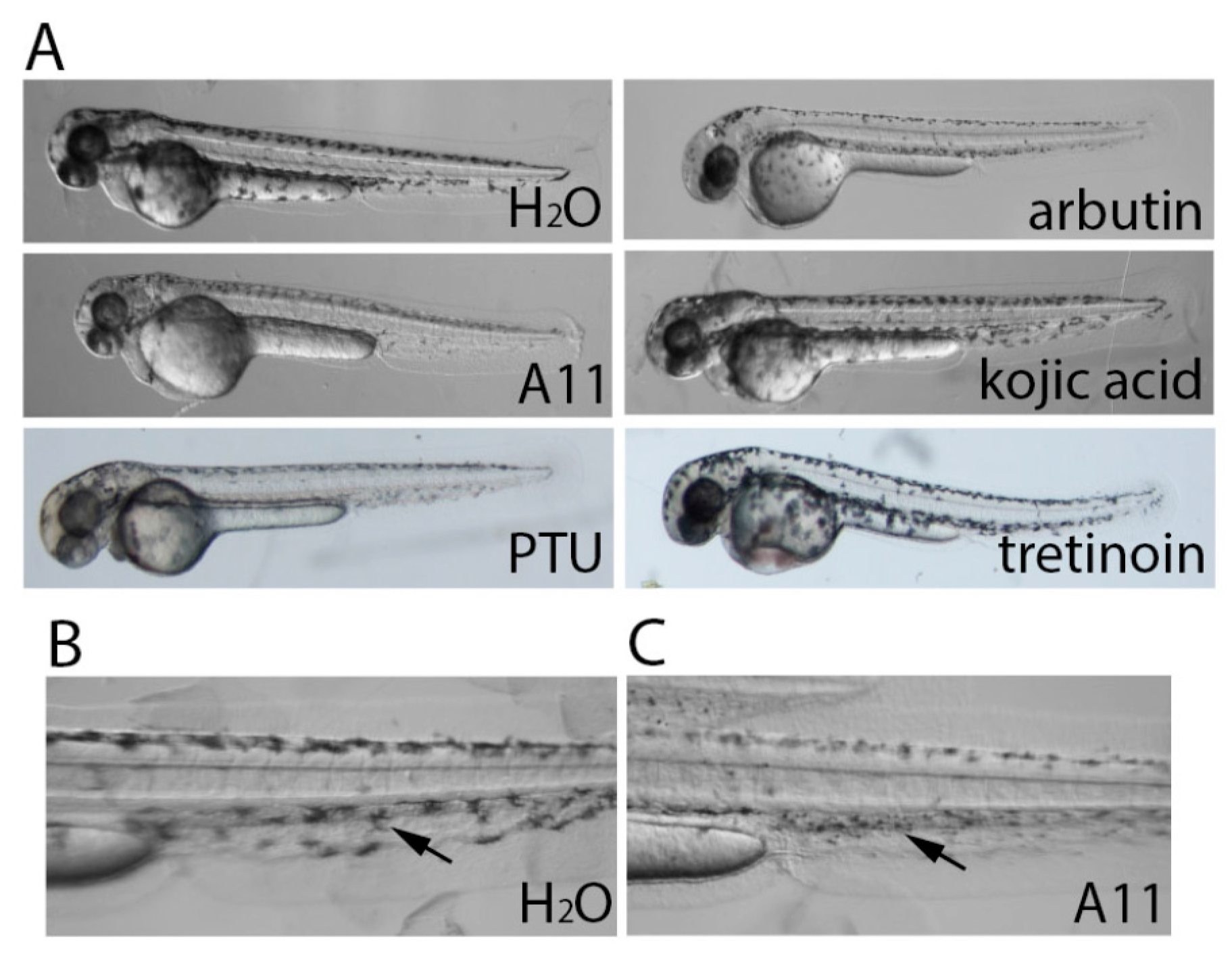
3.2. Stronger Potency of A11 over Most Skin-Lightening Compounds
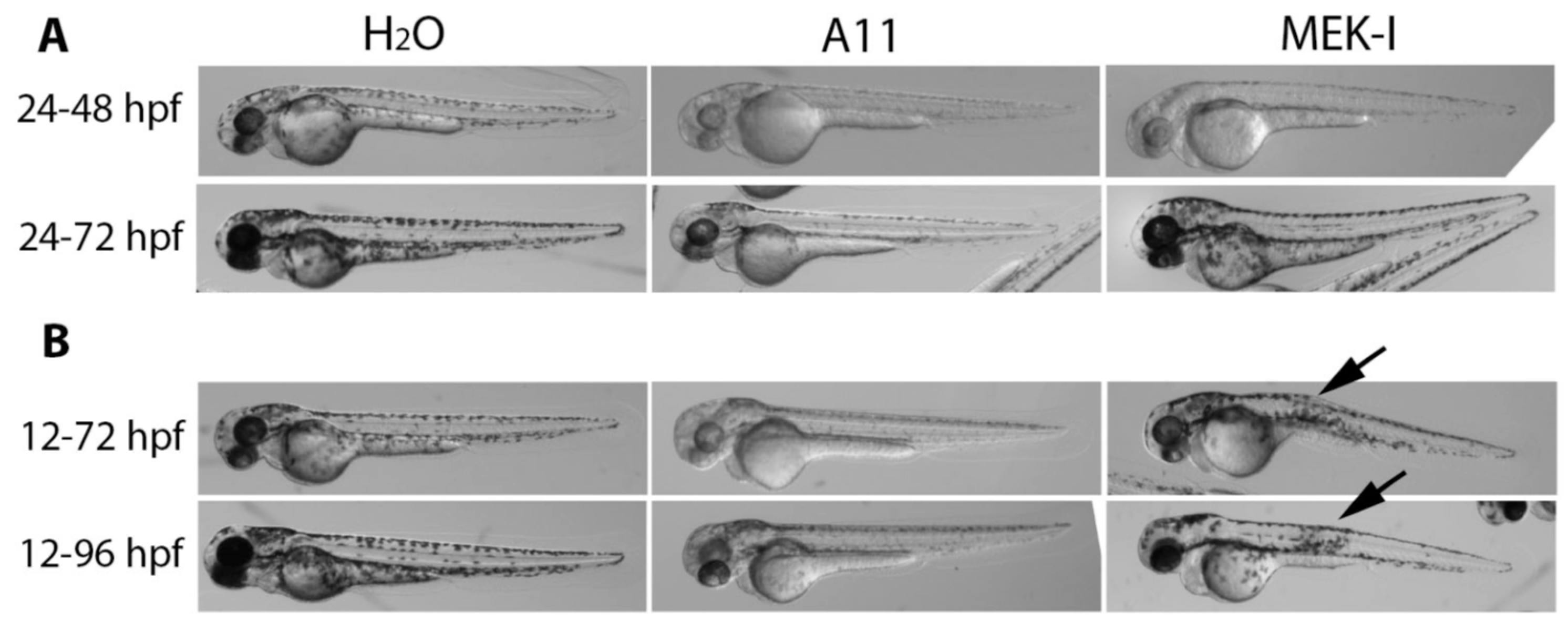
3.3. A11 Reduces Existing Pigment
3.4. Slow Pigment Recovery by A11
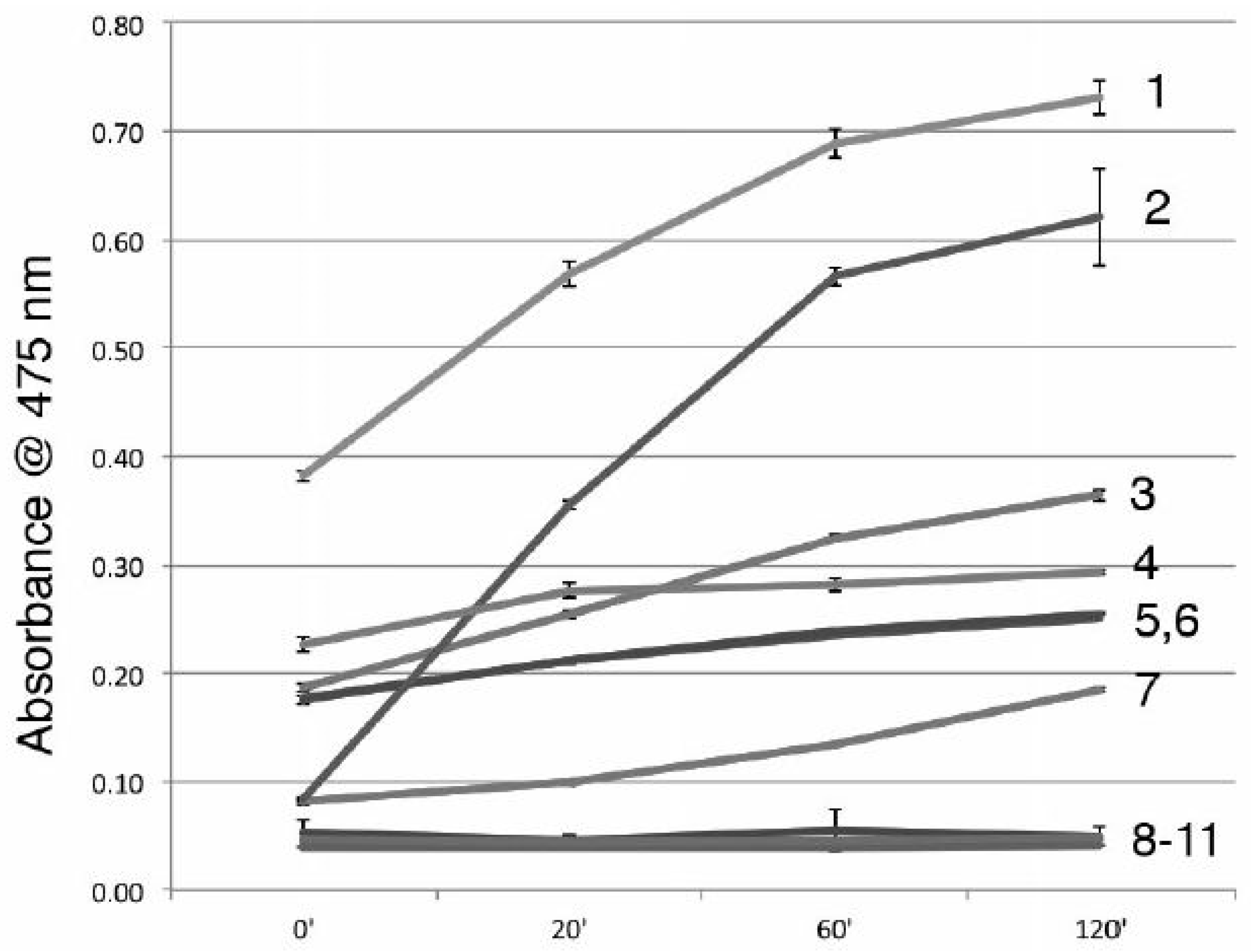
3.5. A11 is Not a Tyrosinase Inhibitor
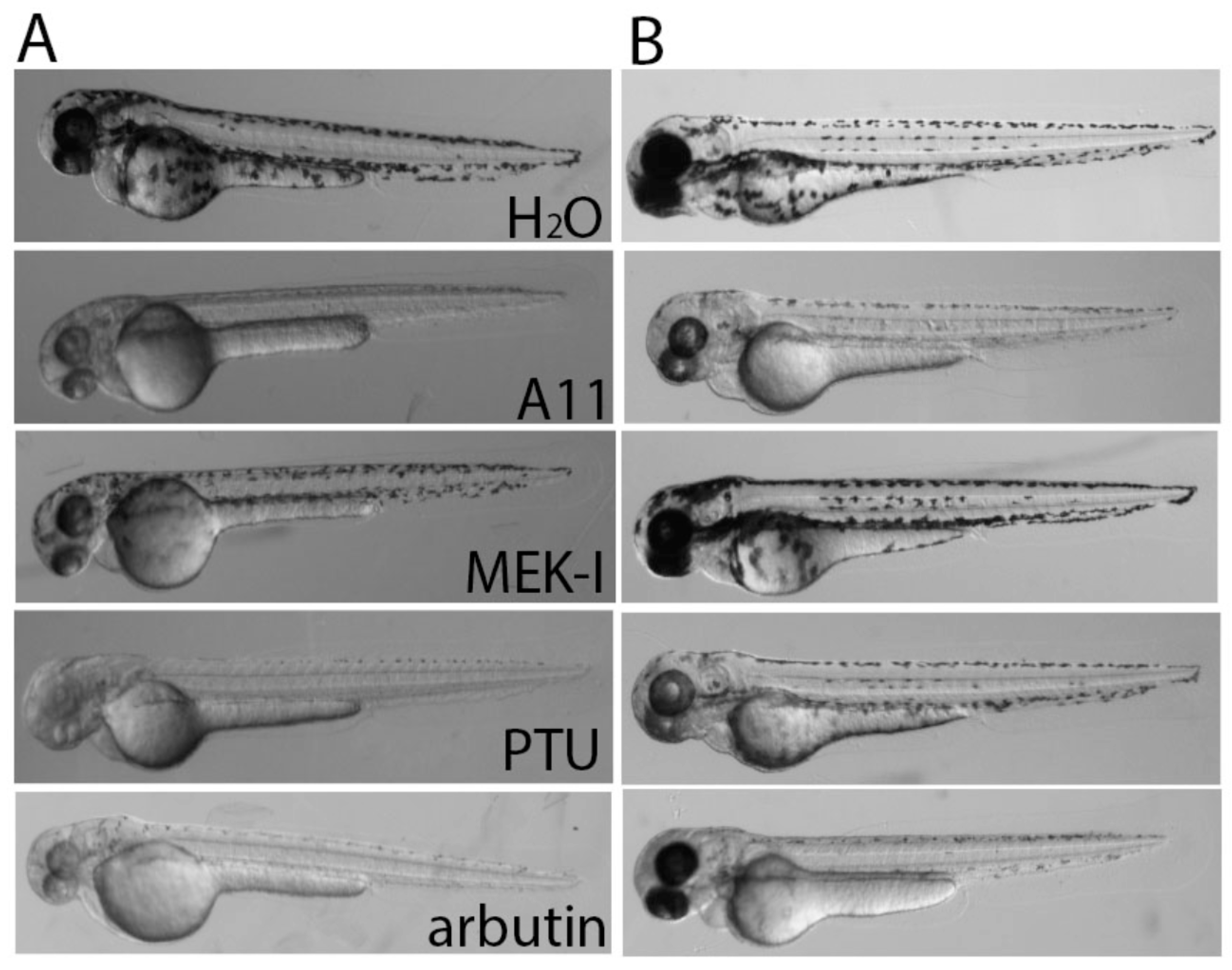
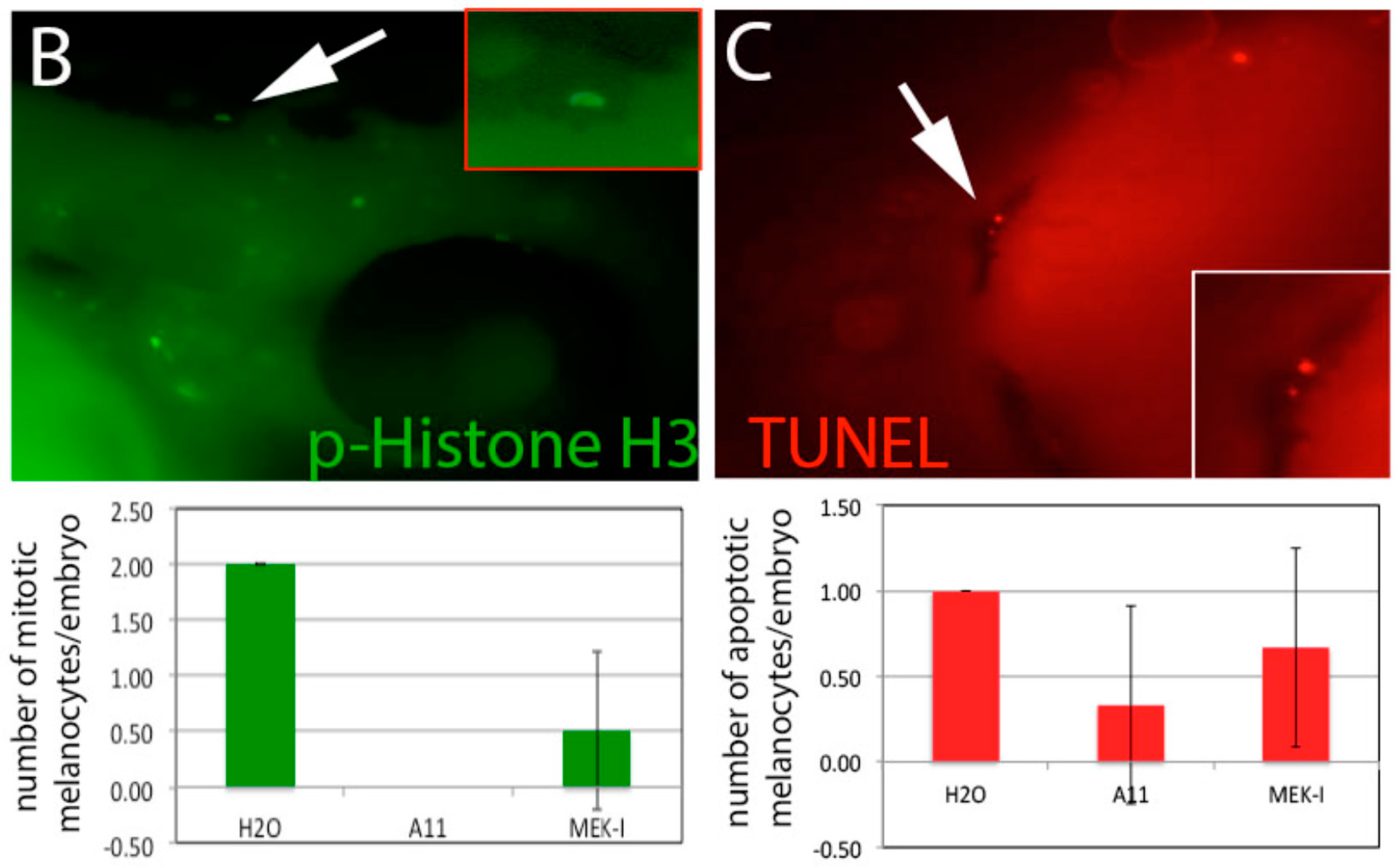
3.6. A11 Causes Defects in Melanocyte Differentiation
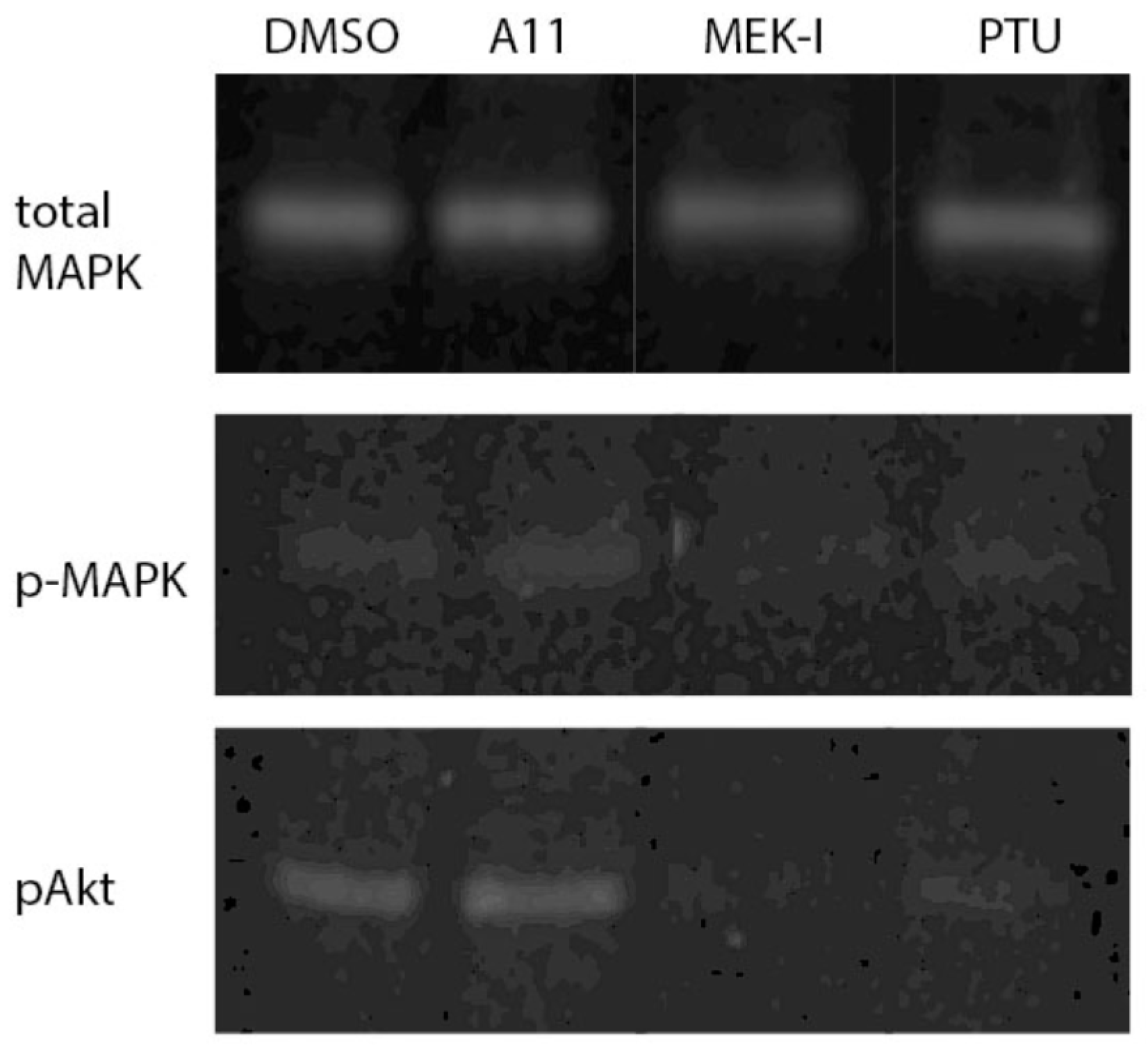
3.7. A11 Activates MAPK and Akt Pathways in Fish Embryo
3.8. A11 Also Causes Melanin Reduction in Mammalian Cells
4. Discussion
4.1. A11 as a Potent and Safer Skin-Lightening Compound
4.2. Possible Cellular Mechanism of A11
4.3. MAPK Signaling Pathway in Melanogenesis
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Battaini, G.; Monzani, E.; Casella, L.; Santagostini, L.; Pagliarin, R. Inhibition of the catecholase activity of biomimetic dinulcear copper complexes by kojic acid. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2000, 5, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, K.; Hughes, J.; Hong, M.; Jia, Q.; Orndorff, S. Modulation of melanogenesis by aloesin: A competitive inhibitor of tyrosinase. Pigment Cell Res. 2002, 15, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Choi, H.-R.; Kim, D.-S.; Park, K.-C. Topical hypopigmenting agents for pigmentary disorders and their mechanisms of action. Ann. Dermatol. 2012, 24, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenner, M.; Hearing, V.J. Modifying skin pigmentation-approaches through intrinsic biochemistry and exogenous agents. Drug Discov. Today Dis. Mech. 2008, 5, e189–e199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eastmond, D.A.; Rupa, D.S.; Hasegawa, L.S. Detection of hyperdiploidy and chromosome breakage in interphase human lymphocytes following exposure to the benzene metabolite hydroquinone using multicolor fluorescence in situ hybridization with DNA probes. Mutat. Res. 1994, 322, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takizawa, T.; Mitsumori, K.; Tamura, T.; Nasu, M.; Ueda, M.; Imai, T.; Hirose, M. Hepatocellular tumor induction in heterozygous p53-deficient CBA mice by a 26-week dietary administration of kojic acid. Toxicol. Sci. 2003, 73, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mezick, J.A.; Bhatia, M.C.; Capetola, R.M. Topical and systemic effects of retinoids on hor-filled utriculus size in the rhino mouse, A model to quantify “anti-keratinizing” effect of retinoids. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1984, 83, 110–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, M.; Kondo, M.; Sato, K.; Umeda, M.; Kawabata, K.; Takahashi, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Matsunaga, K.; Inoue, S. Rhododendrol, a depigmentation-inducing phenolic compound, exerts melanocyte cytotoxicity via a tyrosinase-dependent mechanism. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2004, 27, 754–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imokawa, G.; Ishida, K. Inhibitors of intracellular signaling pathways that lead to stimulated epidermal pigmentation: Perspective of anti-pigmenting agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 8293–8315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Baek, S.H.; Kim, D.H.; Choi, T.Y.; Yoon, T.J.; Hwang, J.S.; Kim, M.R.; Kwon, H.J.; Lee, C.H. Down regulation of melanin synthesis by haginin A and its application to in vivo lightening model. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2008, 128, 1227–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, W.-S.; Kuan, Y.-D.; Chiu, K.-H.; Wang, W.-K.; Chang, F.-H.; Liu, C.-H.; Lee, C.-H. The extract of Rhodobacter sphaeroides inhibits melanogenesis through the MEK/ERK signaling pathway. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 1899–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, T.-R.; Lin, J.-J.; Tsai, C.-C.; Huang, T.-K.; Yang, Z.-Y.; Wu, M.-O.; Zheng, Y.-Q.; Su, C.-C.; Wu, Y.-J. Inhibition of melanogenesis by gallic acid: Possible involvement of the PI3K/Akt, MEK/ERK and Wnt/b-catenin signaling pathways in B16F10 cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 20443–20458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irion, U.; Singh, A.P.; Nusslein-Volhard, C. The developmental genetics of vertebrate color pattern formation: Lessons from zebrafish. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2016, 117, 141–169. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Choi, T.-Y.; Kim, J.-H.; Ko, D.H.; Kim, C.H.; Hwang, J.-S.; Ahn, S.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, C.-D.; Lee, J.-H.; Yoon, T.-J. Zebrafish as a new model for phenotype-based screening of melanogenic regulatory compounds. Pigment Cell Res. 2007, 20, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, G.R.; Noyes, P.D.; Tanguay, R.L. Advancements in zebrafish applications for 21st century toxicology. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 161, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.-C.; Monte, A.; Cook, J.M.; Kabir, M.S.; Peterson, K.P. Zebrafish heart failure models for the evaluation of chemical probes and drugs. Assay Drug Dev. 2013, 11, 561–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stueven, N.A.; Schlaeger, N.M.; Monte, A.P.; Hwang, S.-P.L.; Huang, C.-C. A novel stilbene-like compound that inhibits melanoma growth by regulating melanocyte differentiation and proliferation. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 2017, 337, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westerfield, M. The Zebrafish Book; A Guide for the Laboratory Use of Zebrafish (Danio rerio); University of Oregon Press: Eugene, OR, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Baurin, N.; Arnoult, E.; Scior, T.; Do, Q.T.; Bernard, P. Preliminary screening of some tropical plants for anti-tyrosinase activity. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2002, 82, 155–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dooley, C.M.; Schwarz, H.; Mueller, K.P.; Mongera, A.; Konantz, M.; Neuhauss, S.C.F.; Nusslein-Volhard, C.; Geisler, R. Slc45a2 and V-ATPase are regulators of melanosomal pH homeostasis in zebrafish, providing a mechanism for human pigment evolution and disease. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2013, 26, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.-T.; Johnson, S.L. Small molecule-induced ablation and subsequent regeneration of larval zebrafish melanocytes. Development 2006, 133, 3563–3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkins, T.A.; Cavodeassi, F.; Erdelyi, F.; Szabo, G.; Lele, A. The small molecule Mek1/2 inhibitor U0126 disrupts the chrodamesoderm to notochord transition in zebrafish. BMC Dev. Biol. 2008, 8, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Likhitwitayawuid, K. Stilbenes with tyrosinase inhibitory activity. Curr. Sci. 2008, 94, 44–52. [Google Scholar]
- Oka, M.; Nagai, H.; Ando, H.; Fukunaga, M.; Matsumura, M.; Araki, K.; Ogawa, W.; Miki, T.; Sakaue, M.; Tsukamoto, K.; Konishi, H.; Kikkawa, U.; Ichihashi, M. Regulation of melanogenesis through phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-Akt pathway in human G361 melanoma cells. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2000, 115, 699–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, Y.; Hasegawa, S.; Yamada, T.; Date, Y.; Mizutani, H.; Nakata, S.; Matsunaga, K.; Akamatsu, H. Analysis of the effects of hydroquinone and arbutin on the differentiation of melanocytes. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2013, 36, 1722–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martinson, K.; Stueven, N.; Monte, A.; Huang, C.-c. A Novel Stilbene-Like Compound That Reduces Melanin through Inhibiting Melanocyte Differentiation and Proliferation without Inhibiting Tyrosinase. Cosmetics 2018, 5, 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics5030045
Martinson K, Stueven N, Monte A, Huang C-c. A Novel Stilbene-Like Compound That Reduces Melanin through Inhibiting Melanocyte Differentiation and Proliferation without Inhibiting Tyrosinase. Cosmetics. 2018; 5(3):45. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics5030045
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartinson, Kristy, Noah Stueven, Aaron Monte, and Cheng-chen Huang. 2018. "A Novel Stilbene-Like Compound That Reduces Melanin through Inhibiting Melanocyte Differentiation and Proliferation without Inhibiting Tyrosinase" Cosmetics 5, no. 3: 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics5030045
APA StyleMartinson, K., Stueven, N., Monte, A., & Huang, C.-c. (2018). A Novel Stilbene-Like Compound That Reduces Melanin through Inhibiting Melanocyte Differentiation and Proliferation without Inhibiting Tyrosinase. Cosmetics, 5(3), 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics5030045



