Anti-melanogenic Activity of Auraptene via ERK-mediated MITF Downregulation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
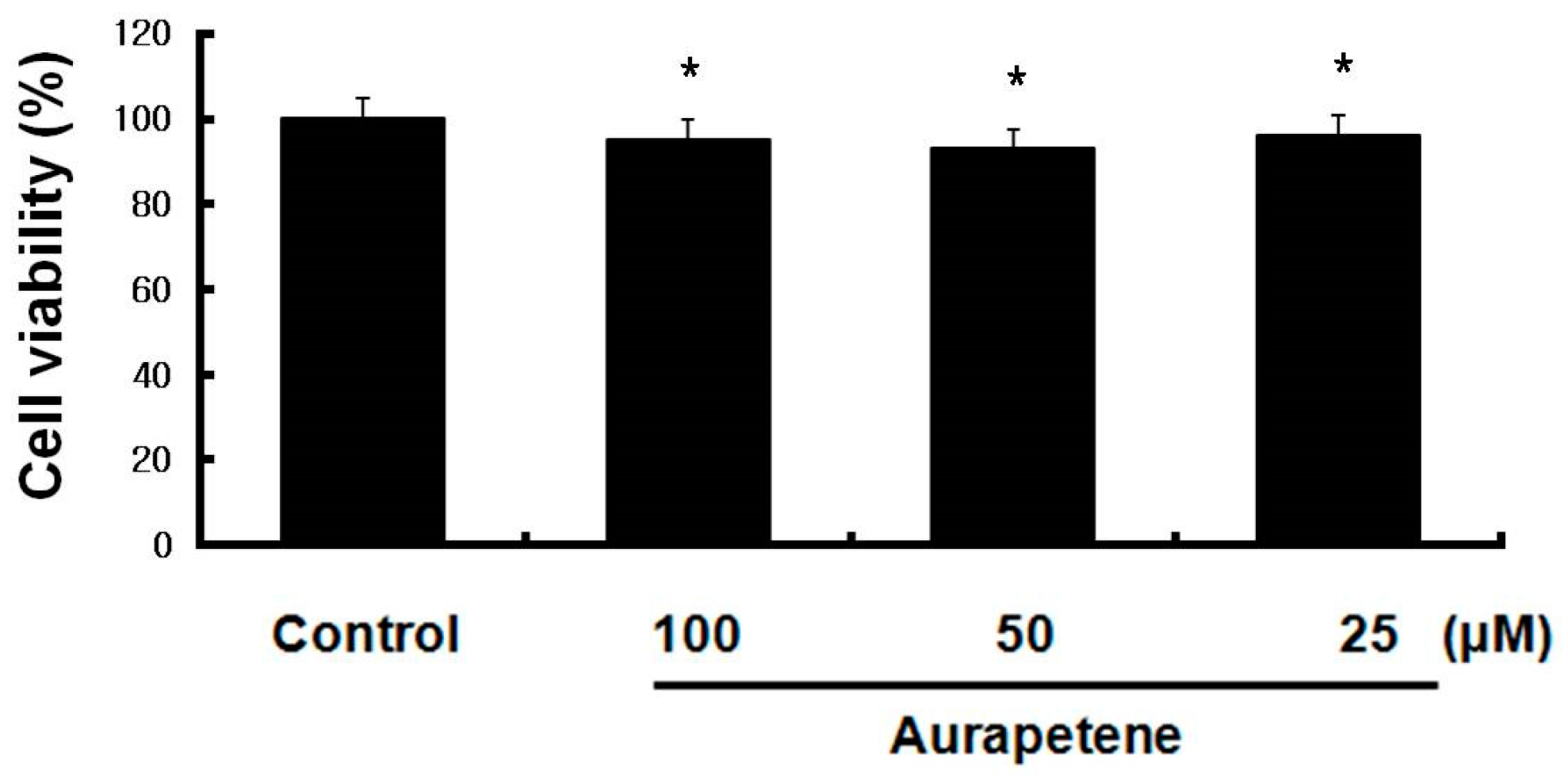
2.2. MTT Assay
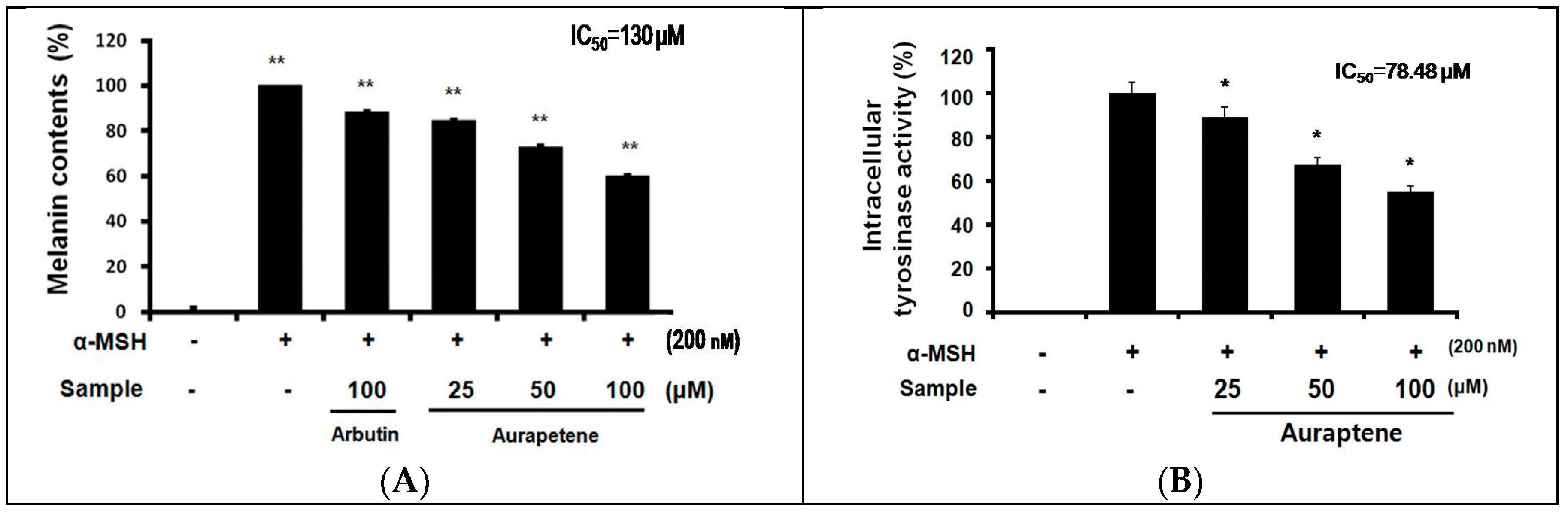
2.3. Measurement of Melanin Content
2.4. Intercellular Tyrosinase Activity
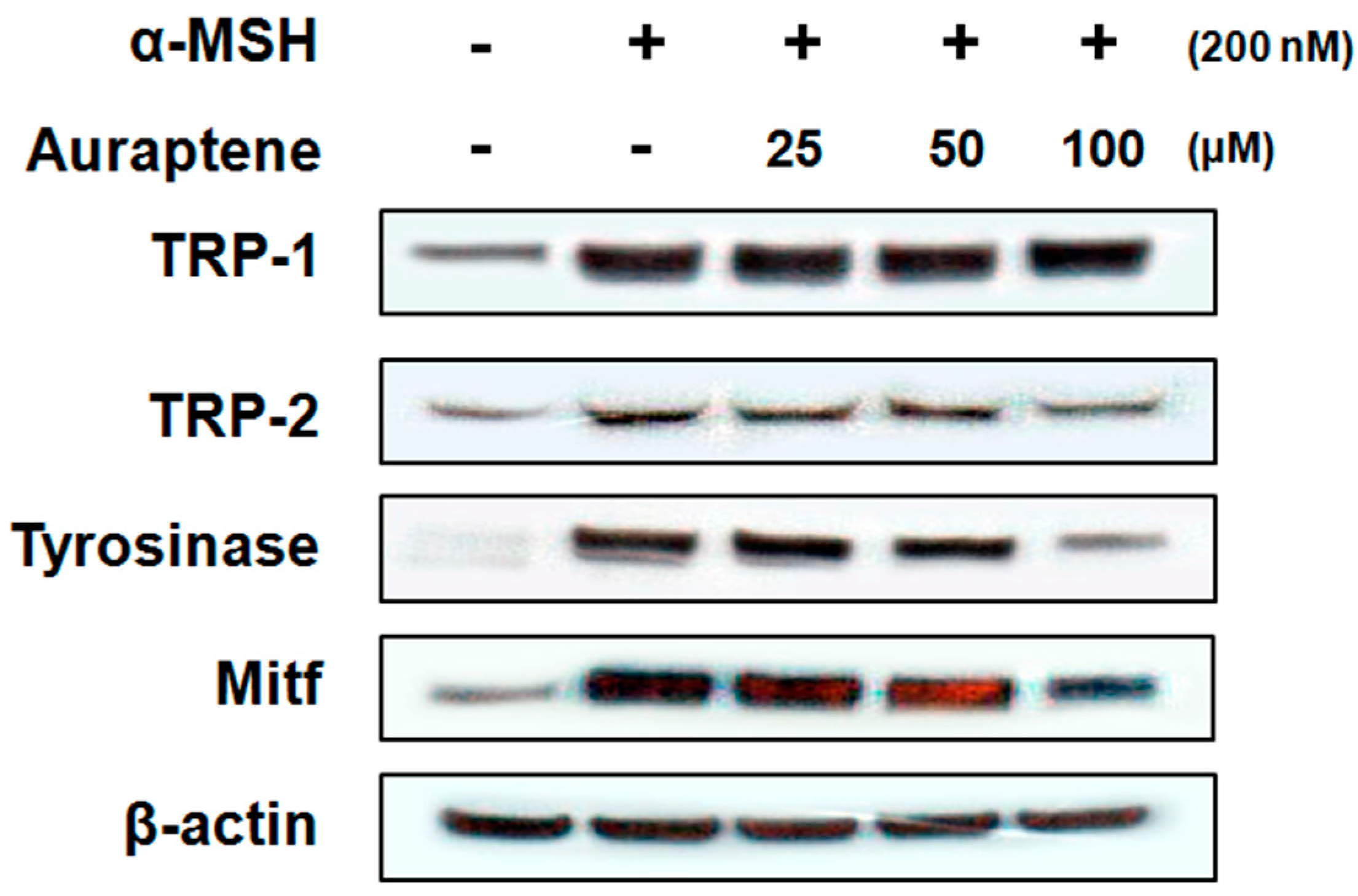
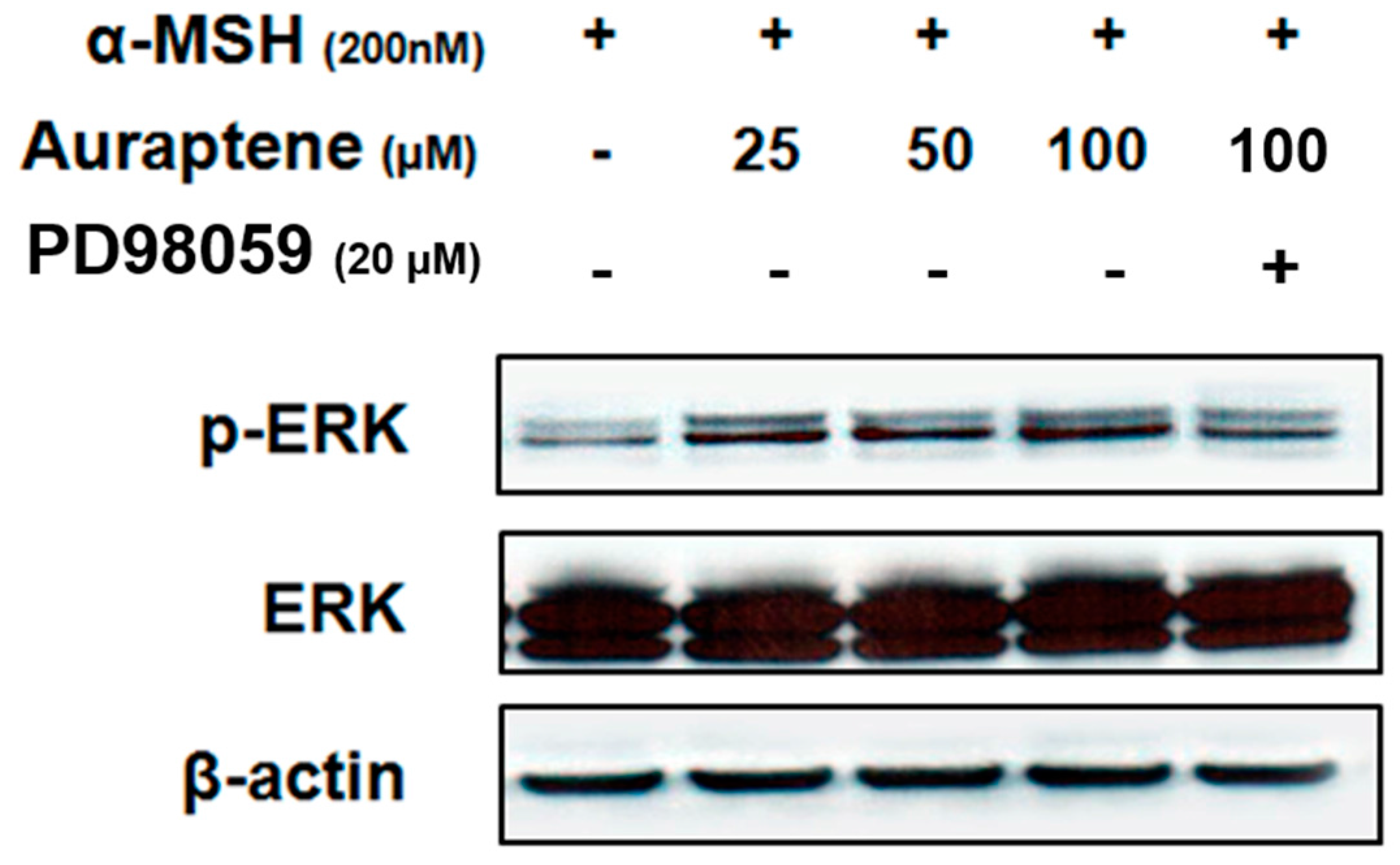
2.5. Western Blotting Analysis
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Auraptene Does Not Affect the Viability of B16F10 Murine Melanoma Cells
3.2. Auraptene Inhibits α-MSH-induced Melanin Synthesis and Intracellular Tyrosinase Activity in B16F10 Murine Melanoma Cells
3.3. Auraptene Inhibits Melanogenesis-Related Proteins in B16F10 Murine Melanoma Cells
3.4. Auraptene Stimulates ERK Phosphorylation
4. Discussion
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Edwards, D.J.; Bellevue, F.H.; Woster, P.M. Identification of 6′,7′-dihydroxybergamottin, a cytochrome P450 inhibitor, in grapefruit juice. Drug Metab. Dispos. 1996, 24, 1287–1290. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hearing, V.J. Biogenesis of pigment granules: a sensitive way to regulate melanocyte function. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2005, 37, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tucker, M.A. Melanoma epidemiology. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. North Am. 2009, 23, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slominski, A.; Tobin, D.J.; Shibahara, S.; Wortsman, J. Melanin pigmentation in mammalian skin and its hormonal regulation. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 1155–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugumaran, M.; Barek, H. Critical analysis of the melanogenic pathway in insects and higher animals. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chadwick, S.; Heath, R.; Shah, M. Abnormal pigmentation within cutaneous scars: A complication of wound healing. Indian J. Plast. Surg. 2012, 45, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, A.; Ma, J.Y. Anti-melanogenic activity of the novel herbal medicine, MA128, through inhibition of tyrosinase activity mediated by the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases and protein kinase signaling pathway in B16F10 cells. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2014, 10, S463–S471. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kondo, T.; Hearing, V.J. Update on the regulation of mammalian melanocyte function and skin pigmentation. Expert Rev. Dermatol. 2011, 6, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vachtenheim, J.; Borovanský, J. Transcription physiology of pigment formation in melanocytes: Central role of MITF. Exp. Dermatol. 2010, 19, 617–627. [Google Scholar]
- Schiaffino, M.V. Signaling pathways in melanosome biogenesis and pathology. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2010, 42, 1094–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tief, K.; Hahne, M.; Schmidt, A.; Beermann, F. Tyrosinase, the key enzyme in melanin synthesis, is expressed in murine brain. Eur. J. Biochem. 1996, 241, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuda, M.; Tejima, T.; Suzuki, T. Skin lighteners. Cosmet. Toiletries 1996, 111, 65–77. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, G.; Neda, G. Flavonoids and phenolic acids: Role and biochemical activity in plants and human. J. Med. Plant. Res. 2011, 5, 6697–6703. [Google Scholar]
- Spencer, J.P.; Schroeter, H.; Kuhnle, G.; Srai, S.K.; Tyrrell, R.M.; Hahn, U.; Rice-Evans, C. Epicatechin and its in vivo metabolite, 3′-O-methyl epicatechin, protect human fibroblasts from oxidative-stress-induced cell death involving caspase-3 activation. Biochem. J. 2001, 354, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gismondi, A.; Di Marco, G.; Canuti, L.; Canini, A. Antiradical activity of phenolic metabolites extracted from grapes of white and red Vitis vinifera L. cultivars. J. Grapevine Res. 2017, 56, 19–26. [Google Scholar]
- Curini, M.; Cravotto, G.; Epifano, F.; Giannone, G. Chemistry and biological activity of natural and synthetic prenyloxycoumarins. Curr. Med. Chem. 2006, 13, 199–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y. Understanding the biological activity of amyloid proteins in vitro: From inhibited cellular MTT reduction to altered cellular cholesterol homeostatis. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 1999, 23, 377–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, S.E.; Buffey, J.; Thody, A.J.; Oliver, I.; Bleehen, S.S.; Mac Neil, S. Investigation of the regulation of pigmentation in alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone responsive and unresponsive cultured B16 melanoma cells. Pigment Cell Res. 1989, 2, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alesiani, D.; Cicconi, R.; Mattei, M.; Bei, R.; Canini, A. Inhibition of Mek 1/2 kinase activity and stimulation of melanogenesis by 5,7-dimethoxycoumarin treatment of melanoma cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2009, 34, 1727–1735. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Kim, J.; Hahn, H.G.; Yun, J.; Jeong, H.S.; Yun, H.Y.; Baek, K.J.; Kwon, N.S.; Min, Y.S.; Park, K.C.; Kim, D.S. KHG26792 inhibits melanin synthesis in Mel-Ab cells and a skin equivalent model. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2014, 18, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimi, E.; Oskoueian, E.; Hendra, R.; Oskoueian, A.; Jaafar, H.Z. Phenolic compounds characterization and biological activities of Citrus aurantium bloom. Molecules 2012, 17, 1203–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asthana, S.; Zucca, P.; Vargiu, A.V.; Sanjust, E.; Ruggerone, P.; Rescigno, A. Structure-activity relationship Study of hydroxycoumarins and mushroom tyrosinase. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 7236–7244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wu, F.; Chen, L.; Zhao, L.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, M.; Lei, S. Biological evaluation of coumarin derivatives as mushroom tyrosinase inhibitors. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 2872–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.Y.; Koo, J.H.; Song, Y.G.; Kwon, K.B.; Lee, J.H.; Sohn, H.S.; Park, B.H.; Jhee, E.C.; Park, J.W. Stimulation of melanogenesis by scoparone in B16 melanoma cells. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2006, 27, 1467–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masamoto, Y.; Murata, Y.; Baba, K.; Shimoishi, Y.; Tada, M.; Takahata, K. Inhibitory effects of esculetin on melanin biosynthesis. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2004, 27, 422–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masamoto, Y.; Ando, H.; Murata, Y.; Shimoishi, Y.; Tada, M.; Takahata, K. Mushroom tyrosinase inhibitory activity of esculetin isolated from seeds of Euphorbia lathyris L. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2003, 67, 631–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.E.; Kim, E.H.; Choi, H.R.; Sohn, U.D.; Yun, H.Y.; Baek, K.J.; Kwon, N.S.; Park, K.C.; Kim, D.S. Dipeptides inhibit melanin synthesis in Mel-Ab cells through down-regulation of tyrosinase. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2012, 16, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buscà, R.; Ballotti, R. Cyclic AMP a key messenger in the regulation of skin pigmentation. Pigment Cell Res. 2000, 13, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, M.-J.; Kim, S.S.; Park, K.-J.; An, H.J.; Choi, Y.H.; Lee, N.H.; Hyun, C.-G. Anti-melanogenic Activity of Auraptene via ERK-mediated MITF Downregulation. Cosmetics 2017, 4, 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics4030034
Kim M-J, Kim SS, Park K-J, An HJ, Choi YH, Lee NH, Hyun C-G. Anti-melanogenic Activity of Auraptene via ERK-mediated MITF Downregulation. Cosmetics. 2017; 4(3):34. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics4030034
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Min-Jin, Sang Suk Kim, Kyung-Jin Park, Hyun Joo An, Young Hun Choi, Nam Ho Lee, and Chang-Gu Hyun. 2017. "Anti-melanogenic Activity of Auraptene via ERK-mediated MITF Downregulation" Cosmetics 4, no. 3: 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics4030034
APA StyleKim, M.-J., Kim, S. S., Park, K.-J., An, H. J., Choi, Y. H., Lee, N. H., & Hyun, C.-G. (2017). Anti-melanogenic Activity of Auraptene via ERK-mediated MITF Downregulation. Cosmetics, 4(3), 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics4030034




